Нефармакологические нефропротективные стратегии в сочетании с доставкой оксида азота у кардиохирургических пациентов с хронической болезнью почек: рандомизированное контролируемое исследование
Автор: Тё М.А., Подоксенов Ю.К., Кравченко И.В., Чурилина Е.А., Свирко Ю.С., Козлов Б.Н., Каменщиков Н.О.
Журнал: Патология кровообращения и кардиохирургия @journal-meshalkin
Рубрика: Анестезиология и реаниматология
Статья в выпуске: 4 т.28, 2024 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Актуальность. Перспективным направлением нефропротекции в кардиохирургии является периоперационная доставка оксида азота. Совместное использование стратегии цель-ориентированной доставки кислорода (англ. Goal-Directed Perfusion, GDP), комплекса мер Инициативы по улучшению глобальных исходов заболеваний почек (англ. Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes, KDIGO) и доставки оксида азота за счет воздействия на разные звенья патогенеза повреждения почек может снижать частоту острого повреждения почек. Цель. Оценить нефропротективные свойства доставки оксида азота в сочетании со стратегиями KDIGO и GDP при кардиохирургических операциях с искусственным кровообращением у пациентов с хронической болезнью почек. Методы. В исследование включили 136 кардиохирургических пациентов с хронической болезнью почек. Пациентов рандомизировали в 2 группы по 68 человек в каждой. В контрольной группе выполняли комплекс нефармакологических методов нефропротекции KDIGO и GDP. В основной группе вместе с комплексом мер KDIGO и GDP проводили периоперационную доставку оксида азота. Результаты. В основной группе частота острого повреждения почек была статистически значимо ниже по сравнению с контрольной группой: 23,5 и 39,7 % соответственно (р = 0,043). Группы не различались по концентрации биомаркеров повреждения почек. В контрольной группе концентрация выдыхаемого оксида азота значимо снизилась через 2 ч после операции (р < 0,001) без изменения в основной группе (р = 0,966). Заключение. Доставка оксида азота в сочетании с комплексом мер KDIGO и GDP при кардиохирургических операциях у пациентов с хронической болезнью почек снижает частоту острого повреждения почек по сравнению с изолированным применением нефармакологических нефропротективных методик за счет нивелирования периоперационного дефицита эндогенного оксида азота, однако не влияет на экспрессию биомаркеров повреждения почек.
Искусственное кровообращение, оксид азота, острое повреждение почек, хроническая болезнь почек
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/142242707
IDR: 142242707 | DOI: 10.21688/1681-3472-2024-4-46-58
Текст научной статьи Нефармакологические нефропротективные стратегии в сочетании с доставкой оксида азота у кардиохирургических пациентов с хронической болезнью почек: рандомизированное контролируемое исследование
Цитировать: Тё М.А., Подоксенов Ю.К., Кравченко И.В., Чурилина Е.А., Свирко Ю.С., Козлов Б.Н., Каменщиков Н.О. Нефармакологические нефропротективные стратегии в сочетании с доставкой оксида азота у кардиохирургических пациентов с хронической болезнью почек: рандомизированное контролируемое исследование. Патология кровообращения и кардиохирургия. 2024;28(4):46-58. https://doi.
How to cite: Tyo M.A., Podoksenov Yu.K., Kravchenko I.V., Churilina E.A., Svirko Yu.S., Kozlov B.N., Kamenshchikov N.O. Non-pharmacologic nephroprotective strategies combined with nitric oxide delivery in cardiac surgical patients with chronic kidney disease: a randomized controlled trial. Patologiya krovoobrashcheniya i kardiokhirurgiya = Circulation Pathology and Cardiac Surgery. 2024;28(4):46-58. (In Russ.)
M.A. Tyo,
Yu.K. Podoksenov, I.V. Kravchenko, E.A. Churilina, Yu.S. Svirko, B.N. Kozlov, N.O. Kamenshchikov, https://orcid.
Острое повреждение почек (ОПП) — частое осложнение кардиохирургических операций с использованием искусственного кровообращения (ИК), которое возникает в раннем послеоперационном периоде с частотой до 42 % [1]. Наибольший риск развития этого состояния в раннем послеоперационном периоде имеют пациенты с хронической болезнью почек (ХБП) [2]. Количество кардиохирургических больных, страдающих ХБП, прогрессивно растет. По данным S.S. Waikar и соавт., число случаев манифестированного послеоперационного ОПП у пациентов с ХБП может быть в несколько раз выше по сравнению с больными с сохранной функцией почек и увеличиваться пропорционально стадии хронической болезни почек [3].
В ряде исследований и метаанализов показана эффективность стратегии цель-ориентированной доставки кислорода (англ. Goal-Directed Perfusion — GDP) и комплекса мер Инициативы по улучшению глобальных исходов заболеваний почек (англ. Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes — KDIGO) для пациентов высокого риска. Это послужило поводом для включения данных тактик в рекомендации Общества кардиоваскулярных анестезиологов (англ. Society of Cardiovascular Anesthesiologists) в качестве методов периоперационной нефропро-текции [4].
Перспективным направлением адъювантной фармакологической нефропротекции в кардиохирургии является периоперационная донация оксида азота (NO). В единичных рандомизированных клинических исследованиях показано, что в общей когорте кардиохирургических пациентов доставка NO в контур экстракорпоральной циркуляции оказывала нефропротективное действие и снижала количество эпизодов ОПП [5; 6]. В экспериментальных работах продемонстрированы системные органопротективные свойства NO [7–10]. По данным M. Blum и соавт., при ХБП снижается образование, формируется дефицит и ухудшается биодоступность эндогенного NO, в том числе в паренхиме почек [11]. Также отмечены формирование дефицита NO и снижение его биодоступности при кардиохирургических операциях с использованием ИК [12]. Таким образом, у пациентов с ХБП во время кардиохирургического вмешательства в условиях ИК имеется уникальный патофизиологический субстрат ОПП, обусловленный сочетанием локального и системного дефицита оксида азота.
Совместное использование стратегий GDP, KDIGO и доставки NO за счет воздействия на разные зве- нья патогенеза повреждения почек может снижать частоту ОПП у пациентов с ХБП при кардиохирургических операциях с искусственным кровообращением.
Цель исследования — оценить нефропротектив-ные свойства доставки NO в сочетании со стратегиями KDIGO и GDP при кардиохирургических операциях в условиях ИК у пациентов с хронической болезнью почек.
Методы
Одноцентровое двойное слепое проспективное рандомизированное контролируемое исследование выполнили в НИИ кардиологии Томского НИМЦ в соответствии с действующими нормами и правилами проведения клинических исследований, в том числе действующей редакцией (2013) Хельсинкской декларации Всемирной медицинской ассоциации, международным стандартом ICH E6 Good Clinical Practice, федеральным законом от 21 ноября 2011 г. № 323-ФЗ «Об основах охраны здоровья граждан в Российской Федерации», приказом Министерства здравоохранения РФ от 1 апреля 2016 г. № 200н «Об утверждении правил надлежащей клинической практики». Проведение исследования одобрено комитетом по биомедицинской этике НИИ кардиологии № 237 от 20 декабря 2022 г. Работа зарегистрирована в международной базе ClinicalTrials.gov, идентификатор NCT05757557.
Критерии включения:
– ХБП стадии 3а–4;
– кардиохирургическая операция в условиях искусственного кровообращения.
Наличие ХБП и ее стадию перед кардиохирургическим вмешательством оценивали с помощью клинических практических рекомендаций KDIGO 2012 г. по диагностике и лечению хронической болезни почек [13].
Критерии невключения:
– критическое состояние до операции;
– введение потенциально нефротоксичных препаратов в течение 24 ч до вмешательства (рентгеноконтрастные препараты, антимикробная терапия аминогликозидами и/или амфотерицином);
-
– легочная гипертензия более II ст.;
-
– текущее ОПП;
-
– кардиохирургическая операция в условиях гипотермического циркуляторного ареста;
-
– фракция выброса левого желудочка < 30 %.
Пациентов рандомизировали с помощью сгенерированной компьютером последовательности в 2 равные группы по 68 человек в каждой. В основной группе вместе с комплексом мер KDIGO и GDP проводили доставку NO в контуры наркозно-дыхательного аппарата (НДА), аппаратов искусственной вентиляции легких (ИВЛ) и ИК в концентрации 80 ppm во время операции и в течение 6 ч после нее. В контрольной группе выполняли комплекс мер KDIGO и GDP без доставки NO. Пациенты, лечащие врачи и другие специалисты, участвующие в лечении, не знали о результатах рандомизации до завершения исследования.
В качестве первичной конечной точки рассматривали частоту ОПП по критериям KDIGO [14]. Для этого после операции на протяжении первых 7 дней осуществляли забор и анализ крови на сывороточный креатинин с помощью биохимического анализатора Konelab 20 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Уолтем, США).
В качестве вторичных конечных точек рассматривали тяжесть и продолжительность ОПП по критериям KDIGO, скорость клубочковой фильтрации (СКФ), концентрацию выдыхаемого NO, биомаркеры повреждения почек: молекула повреждения почек 1 (KIM-1), интерлейкин 18 (IL-18), липокаин, ассоциированный с желатиназой нейтрофилов (NGAL), в моче, цистатин С в сыворотке крови.
Для мониторинга показателей состояния гомеостаза NO использовали портативный монитор для измерения NO в выдыхаемом воздухе Circassia NIOX VERO (NIOX Group plc, Оксфорд, Великобритания). Мониторинг показателей выдыхаемого NO проводили исходно, через 2 и 24 ч после операции у 40 пациентов в каждой группе.
Концентрации биомаркеров повреждения почек исследовали у 40 пациентов в каждой группе. Взятие мочи для анализа на KIM-1, IL-18, NGAL осуществляли непосредственно из мочевого катетера в вакутейнеры Vacuette TUBE (Greiner AG, Кремсмюн-стер, Австрия) без наполнителя с коническим дном для сбора мочи исходно и через 6 ч после операции. Взятие крови для анализа на цистатин С осуществляли из центрального венозного катетера в ваку-тейнеры Vacuette TUBE с активатором свертывания исходно и через 6 ч после операции. Исследование KIM-1, IL-18, NGAL и цистатина С выполняли согласно инструкции производителя.
Нефармакологические нефропротективные стратегии
Согласно стратегии GDP доставку кислорода (DO2) поддерживали на уровне ≥ 280 мл/мин/м2, регулируя объемную скорость перфузии в соответствии с уровнем гемоглобина. В случае низкого зна- чения гемоглобина и невозможности поддержания DO2 выше порога путем увеличения объемной скорости перфузии и проведения ультрафильтрации переливали 1 дозу эритроцитарной взвеси. DO2 рассчитывали по формуле:
DO2 = [ОСП × (1,34 × Hb × SaO2) / 100 + + (PaO2 × 0,003)] / ППТ, где DO2 — доставка кислорода, мл/мин/м2; ОСП — объемная скорость перфузии, л/мин; Hb — уровень гемоглобина, г/л; SaO2 — сатурация артериальной крови, %; PaO2 — парциальное давление кислорода в артериальной крови, мм рт. ст.; ППТ — площадь поверхности тела, м².
Комплекс мер KDIGO включал в себя оптимизацию гемодинамического профиля и волемического статуса путем тщательного мониторинга (по данным эхокардиографии), исключение или снижение использования нефротоксичных препаратов (рентгеноконтрастных препаратов, аминогликозидов, апротинина и других), контроль гликемии и предотвращение гипергликемии в течение первых 72 ч после операции, прекращение приема ингибиторов ангиотензинпревращающего фермента и блокаторов рецепторов ангиотензина II в течение 48 ч после операции, тщательный мониторинг уровня креатинина в сыворотке крови и темпа диуреза [15].
Методика доставки оксида азота
Донацию NO в контуры НДА, аппаратов ИВЛ и ИК, а также мониторинг уровней NO и диоксида азота (NO2) на линии вдоха выполняли с помощью аппарата «Тианокс» (ФГУП «РФЯЦ-ВНИИЭФ», Саров, Россия). Для доставки NO в НДА и аппарат ИВЛ на линию вдоха встраивали 2 переходника с разъемом Льюер: через проксимальный производили подачу NO, через дистальный осуществляли мониторинг концентрации NO и NO2. После проксимального переходника для удаления NO2 встраивали емкость с абсорбентом. Схема модифицированных контуров НДА и аппарата ИВЛ представлена на рис. 1.
Для доставки NO в аппарат ИК на линию подачи газовоздушной смеси встраивали 2 переходника 1/4 с разъемом Льюер: через проксимальный производили подачу NO, через дистальный осуществляли мониторинг уровня NO и NO2. Схема модифицированного контура ИК представлена на рис. 2.
В контрольной группе на всех этапах операции подавали кислородно-воздушную смесь, не содержащую NO. В обеих группах аппарат плазмохимического синтеза, доставки и мониторинга NO врач-
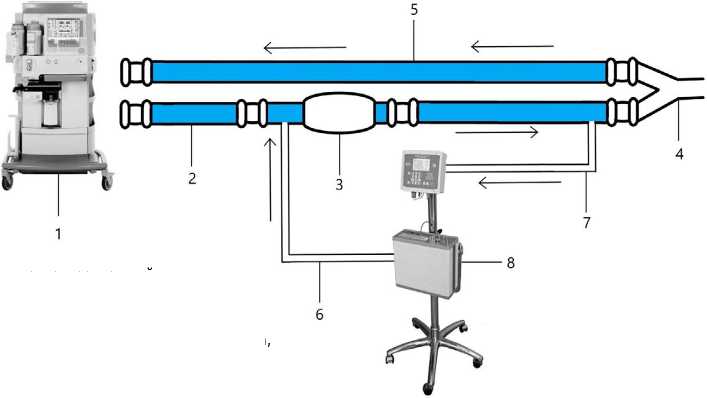
Рис. 1. Модифицированный контур искусственной вентиляции легких и наркозно-дыхательного аппарата Примечание. 1 — наркозно-дыхательный аппарат, 2 — линия вдоха, 3 — емкость с абсорбентом, 4 — У-образный тройник, 5 — линия выдоха, 6 — линия подачи оксида азота, 7 — линия забора газа на анализ, 8 — аппарат «Тианокс».
исследователь подключал к НДА, аппаратам ИК и ИВЛ, однако включал его с генерацией заданной концентрации NO только в основной группе.
Статистический анализ
Расчет размера выборки основан на данных предыдущих исследований риска ОПП при кардиохирургических вмешательствах и его снижения с использованием различных методов периоперационной защиты почек. Частота ОПП у пациентов с ХБП при операциях на сердце в условиях ИК составляет 66 % [16]. По данным одноцентрового рандомизированного контролируемого исследования PrevAKI, использование рекомендаций KDIGO в качестве стратегии периоперационной защиты почек снизило частоту ОПП у больных, перенесших операцию на сердце, на 16,6 % [15]. Мы ожидаем, что периоперационная стратегия KDIGO снизит частоту ОПП в среднем на 16 %. Прогнозируемая частота ОПП в контрольной группе составила 50 %.
Существуют единичные публикации о нефропро-тективном эффекте периоперационной доставки NO у кардиохирургических пациентов. В метаанализе 5 клинических испытаний доставки NO при кардиохирургических операциях с ИК J. Hu и соавт. продемонстрировали снижение риска ОПП на 24 % [17]. Однако этот результат получен в общей группе кардиохирургических пациентов, в то время как в настоящее исследование включены только больные с высоким риском ОПП, обусловленным наличием ХБП, что предполагает более выраженное его снижение под влиянием доставки NO. Таким образом, в нашем исследовании консервативная оценка ожидаемого снижения частоты ОПП в основной группе в среднем 25 %, соответственно, ожидаемая абсолютная частота ОПП в основной группе составила 25 %.
Размер выборки рассчитывали с использованием формулы Лера для средних величин. Таким образом, для обеспечения 80% статистической мощности заключения о превосходстве (англ. superiority) доставки NO при двустороннем уровне статистической значимости α = 0,05 в каждую группу должно быть рандомизировано не менее 61 человека. Для
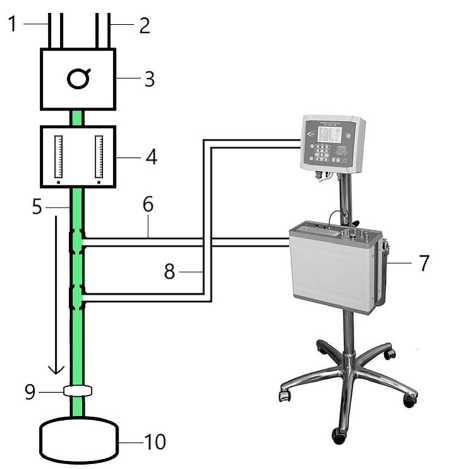
Рис. 2. Модифицированный контур искусственного кровообращения
Примечание. 1 — подача кислорода, 2 — подача воздуха, 3 — газовый смеситель, 4 — ротаметр, 5 — линия подачи газовоздушной смеси, 6 — линия подачи оксида азота, 7 — аппарат «Тианокс», 8 — линия забора газа на анализ, 9 — фильтр, 10 — оксигенатор.
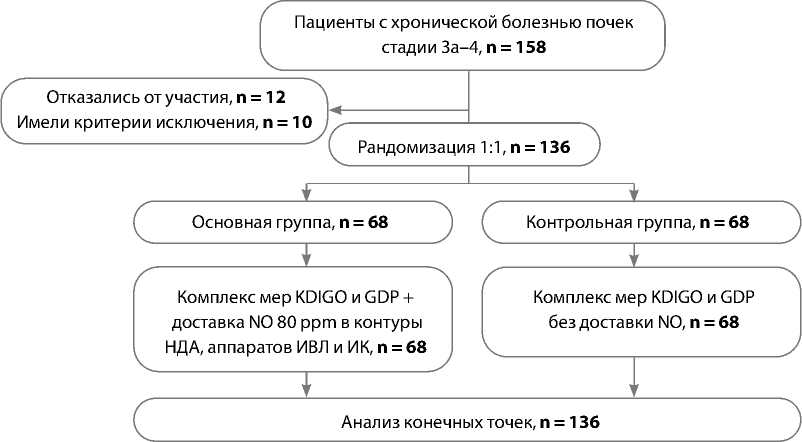
Рис. 3. Отбор пациентов
Примечание. KDIGO (англ. Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes) — Инициатива по улучшению глобальных исходов заболеваний почек; GDP (англ. Goal-Directed Perfusion) — цель-ориентированная доставка кислорода; NO — оксид азота; НДА — наркозно-дыхательный аппарат; ИВЛ — искусственная вентиляция легких; ИК — искусственное кровообращение.
увеличения мощности исследования размер выборки увеличили на 10 %, до 68 человек в каждой группе.
Статистический анализ результатов проводили с использованием пакета программ SPSS Statistics версии 26 (IBM Corporation, Армонк, США).
Количественные показатели оценивали на предмет соответствия нормальному распределению с помощью критерия Шапиро – Уилка (при числе исследуемых менее 50) или критерия Колмогорова – Смирнова (при числе исследуемых более 50), а также показателей асимметрии и эксцесса. При описании количественных показателей использовали среднее значение (M) и стандартное отклонение (SD) для показателей, имеющих нормальное распределение, или медиану (Me) и первый и третий квартили [Q1; Q3] при распределении показателя, отличном от нормального. Для выявления статистически значимых различий количественных показателей в двух независимых группах применяли критерий Стьюдента при нормальном распределении показателя или критерий Манна – Уитни при распределении показателя, отличном от нормального. Анализ качественных признаков/показателей в двух независимых группах проводили с помощью χ²-критерия Пирсона. Если число ожидаемых наблюдений в любой из ячеек четырехпольной таблицы было менее пяти, для оценки уровня значимости различий использовали точный критерий Фишера.
В качестве количественной меры эффекта при сравнении относительных показателей задействовали показатель отношения рисков (ОР). Для сравнения значений при отсутствии нормального распределения в связанных выборках применяли W-критерий Уилкоксона. При сравнении более двух зависимых выборок количественных показателей, распределение которых отличалось от нормального, использовали непараметрический критерий Фридмана. Для коррекции на множественные сравнения применили поправку Бонферрони. Критический уровень статистической значимости при проверке гипотез составлял 0,05.
Результаты
В исследование включили 136 пациентов (рис. 3). Не выявили различий между группами по клинико-демографическим характеристикам. Данные о предоперационном состоянии больных представлены в табл. 1.
Не обнаружили различий между группами по модальности оперативных вмешательств, продолжительности ИК и времени пережатия аорты. Характеристика интраоперационного периода отражена в табл. 2.
В основной группе частота развития ОПП была статистически значимо ниже по сравнению с контрольной: 16 (23,5 %) против 27 (39,7 %) (р = 0,043). В основной группе риск ОПП был на 41 %
Табл. 1. Клинико-демографические характеристики
|
Показатель |
Основная группа, n = 68 |
Контрольная группа, n = 68 |
p |
|
Возраст, лет, Me [Q1; Q3] |
68 [63,5; 72,0] |
69 [64,5; 74,5] |
0,374 |
|
Женский пол, n (%) |
17 (25) |
23 (33,8) |
0,259 |
|
Индекс массы тела, кг/м2, M ± SD |
30,10 ± 4,47 |
28,80 ± 4,94 |
0,120 |
|
ФВ ЛЖ, %, Me [Q1; Q3] |
58 [50,0; 63,5] |
59,5 [46; 67] |
0,580 |
|
Стадия хронической болезни почек |
|||
|
3а, n (%) |
54 (79,4) |
54 (79,4) |
|
|
3б, n (%) |
11 (16,2) |
14 (20,6) |
|
|
4, n (%) |
3 (4,4) |
0 (0) |
|
|
СКФ, мл/мин/1,73 м2, Me [Q1; Q3] |
53 [46,0; 56,5] |
53 [47,0; 56,5] |
0,408 |
|
Креатинин, мкмоль/л, Me [Q1; Q3] |
119 [106,5; 134,0] |
115 [102,5; 126,0] |
0,208 |
|
Тромбоциты, ×109, M ± SD |
207,0 ± 54,2 |
208,0 ± 49,7 |
0,978 |
|
ФК ХСН по NYHA |
|||
|
I, n (%) |
4 (5,9) |
5 (7,4) |
|
|
II, n (%) |
36 (52,9) |
32 (47,1) |
0,169 |
|
III, n (%) |
27 (39,7) |
31 (45,6) |
|
|
IV, n (%) |
1 (1,5) |
0 (0) |
|
|
Ишемическая болезнь сердца, n (%) |
60 (88,2) |
60 (88,2) |
1 |
|
Постинфарктный кардиосклероз, n (%) |
38 (55,9) |
32 (47,1) |
0,303 |
|
Сахарный диабет, n (%) |
19 (27,9) |
19 (27,9) |
1 |
|
Хроническая обструктивная болезнь легких, n (%) |
14 (20,6) |
9 (13,2) |
0,253 |
|
Бронхиальная астма, n (%) |
2 (2,9) |
1 (1,5) |
1 |
|
EuroSCORE II, %, Me [Q1; Q3] |
2,17 [1,51; 2,86] |
2,38 [1,55; 3,69] |
0,234 |
Примечание . ФВ ЛЖ — фракция выброса левого желудочка; СКФ — скорость клубочковой фильтрации; ФК ХСН по NYHA — функциональный класс хронической сердечной недостаточности по классификации Нью-Йоркской ассоциации кардиологов (англ. New York Heart Association); EuroSCORE II — европейская система оценки риска неблагоприятного исхода при кардиохирургических вмешательствах.
меньше по сравнению с контрольной (ОР 0,59; 95% доверительный интервал 0,35–0,99). Диаграмма представлена на рис. 4.
Группы значимо не различались по стадиям ОПП (р = 0,144). ОПП 1-й стадии в основной группе развилось в 13 (81,3 %) случаях, в контрольной группе в 22 (81,5 %) случаях. ОПП 2-й стадии в основной группе наблюдалось в 1 (6,3 %) случае, в контрольной группе в 5 (18,5 %) случаях. ОПП 3-й стадии развилось только в основной группе в 2 (12,5 %) случаях. По длительности ОПП межгрупповой разницы нет (р = 0,513). В основной группе медиана продолжительности ОПП составила 1 сут., в контрольной группе 2 сут.
Основная и контрольная группы не различались по темпу диуреза в первые сутки послеоперационного периода (р = 0,663). В основной группе в первые сутки диурез составил 2 250 (1 790; 2 985) мл, в контрольной группе 2 400 (1 825; 3 150) мл. Также не было межгрупповых различий по объему инфузионной терапии (р = 0,264). В основной группе в первые сутки после операции объем инфузионной терапии составил 3 443 (2 675; 4 193) мл, в контрольной группе 3 200 (2 565; 3 900) мл.
Группы значимо не различались по уровню креатинина в сыворотке крови в первые 7 сут. после операции и при выписке (табл. 3).
Медианы показателя концентрации NO в выдыхаемом воздухе исходно были сопоставимы в обеих группах (р = 0,137). В основной группе концентрация оставалась сопоставимой с исходными значениями через 2 и 24 ч после операции. В контрольной группе отметили значительное снижение концентрации NO в выдыхаемом воздухе относительно исходных значений через 2 ч после вмешательства (р < 0,001). Через 2 и 24 ч после операции данный показатель был значимо ниже в контрольной группе по сравнению с основной (р < 0,001; р = 0,035 соответственно). Данные о динамике концентрации выдыхаемого NO представлены в табл. 4.
Группы не различались по концентрации биомаркеров повреждения почек (табл. 5).
Табл. 2. Характеристика интраоперационного периода
|
Показатель |
Основная группа, n = 68 |
Контрольная группа, n = 68 |
p |
|
Модальность оперативных вмешательств |
|||
|
Изолированное коронарное шунтирование, n (%) |
48 (70,6) |
42 (61,8) |
|
|
Одна процедура (не коронарное шунтирование), n (%) |
11 (16,2) |
6 (8,8) |
0,108 |
|
Две процедуры, n (%) |
6 (8,8) |
12 (17,6) |
|
|
Три процедуры и более, n (%) |
3 (4,4) |
8 (11,8) |
|
|
Продолжительность искусственного кровообращения, мин, Me [Q1; Q3] |
95 [85; 111] |
96,5 [85; 115] |
0,429 |
|
Время пережатия аорты, мин, Me [Q1; Q3] |
56 [43,5; 71,0] |
55 [46,5; 77,5] |
0,471 |
|
Длительность оперативного вмешательства, мин, Me [Q1; Q3] |
300 [275; 340] |
312 [295,0; 347,5] |
0,184 |
Табл. 3. Динамика креатинина в сыворотке крови
|
Показатель |
Основная группа, n = 68 |
Контрольная группа, n = 68 |
p |
|
Креатинин на 1-е сут., мкмоль/л, Me [Q1; Q3] |
119 [103; 139] |
119 [94,5; 143,0] |
0,518 |
|
Креатинин на 2-е сут., мкмоль/л, Me [Q1; Q3] |
116 [98; 135] |
115 [92,5; 148,0] |
0,879 |
|
Креатинин на 3-е сут., мкмоль/л, Me [Q1; Q3] |
110 [94,5; 127,0] |
118 [95; 138] |
0,483 |
|
Креатинин на 4-е сут., мкмоль/л, Me [Q1; Q3] |
107 [93; 125] |
111 [94; 133] |
0,660 |
|
Креатинин на 5-е сут., мкмоль/л, Me [Q1; Q3] |
108 [93; 123] |
106 [89; 122] |
0,344 |
|
Креатинин на 6-е сут., мкмоль/л, Me [Q1; Q3] |
111 [94,5; 126,0] |
105 [94; 126] |
0,384 |
|
Креатинин на 7-е сут., мкмоль/л, Me [Q1; Q3] |
106 [91; 128] |
106 [94,5; 128,0] |
0,900 |
|
Креатинин при выписке, мкмоль/л, Me [Q1; Q3] |
107 [95; 127] |
110 [95; 131] |
0,719 |
Табл. 4. Динамика концентрации выдыхаемого оксида азота
|
Показатель |
Основная группа, n = 40 |
Контрольная группа, n = 40 |
p |
|
Выдыхаемый оксид азота до операции, ppb, Me [Q1; Q3] |
18 [14; 32] |
16 [14; 21] |
0,137 |
|
Выдыхаемый оксид азота через 2 ч после операции, ppb, Me [Q1; Q3] |
19 [14; 32] |
4 [2; 10] |
< 0,001 |
|
Выдыхаемый оксид азота через 24 ч после операции, ppb, Me [Q1; Q3] |
21 [12; 28] |
15 [12; 20] |
0,035 |
|
p |
0,966 |
< 0,001 p1–2< 0,001 p12 = 0,006 |
Табл. 5. Биомаркеры повреждения почек
|
Показатель |
Основная группа, n = 40 |
Контрольная группа, n = 40 |
p |
|
KIM-1 исходно, мкг/г креатинина, Me [Q1; Q3] |
1,26 [0,76; 2,56] |
1,44 [0,95; 2,15] |
0,780 |
|
KIM-1 через 6 ч после операции, мкг/г креатинина, Me [Q1; Q3] |
0,257 [0,08; 0,66] |
0,246 [0,10; 1,17] |
0,780 |
|
p |
< 0,001 |
< 0,001 |
|
|
NGAL исходно, нг/мг, Me [Q1; Q3] |
1,74 [1,32; 2,48] |
1,76 [1,18; 2,83] |
0,985 |
|
NGAL через 6 ч после операции, нг/мг, Me [Q1; Q3] |
3,59 [2,86; 4,87] |
3,81 [2,47; 4,75] |
0,467 |
|
p |
< 0,001 |
< 0,001 |
|
|
IL-18 исходно, пг/мл, Me [Q1; Q3] |
24,0 [13,6; 32,8] |
24,0 [8,95; 33,40] |
0,570 |
|
IL-18 через 6 ч после операции, пг/мл, Me [Q1; Q3] |
44,9 [31,6; 61,3] |
42,2 [27,8; 57,7] |
0,634 |
|
p |
< 0,001 |
< 0,001 |
|
|
Цистатин С исходно, мг/л, Me [Q1; Q3] |
1,08 [0,94; 1,20] |
1,14 [0,99; 1,28] |
0,275 |
|
Цистатин С через 6 ч после операции, мг/л, Me [Q1; Q3] |
0,85 [0,75; 1,10] |
0,95 [0,80; 1,07] |
0,444 |
|
p |
< 0,001 |
< 0,001 |
Примечание. KIM-1 — молекула повреждения почек 1; NGAL — липокаин, ассоциированный с желатиназой нейтрофилов; IL-18 — интерлейкин 18.
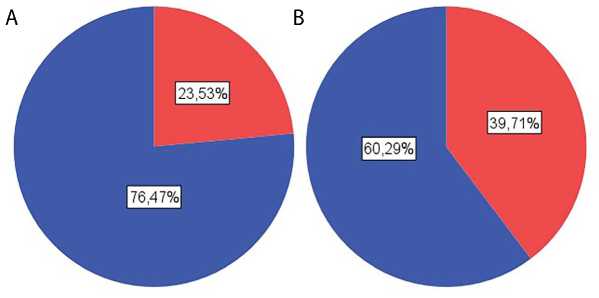
Рис. 4. Частота острого повреждения почек: в основной группе (A); в контрольной группе (B)

Острое повреждение почек
Нет острого повреждения почек
Обсуждение
Поиск способов нефропротекции у пациентов высокого риска — важное направление кардиохирургии и кардиоанестезиологии. В исследованиях и метаанализах показана эффективность стратегии GDP для всех пациентов и комплекса мер KDIGO для больных высокого риска [4].
О связи между низкими значениями гематокрита во время ИК и частотой ОПП впервые сообщалось еще в 1994 г. M. Ranucci и соавт. предположили, что в основе возникновения ОПП может лежать недостаточная DO2 вследствие гемодилюции и недостаточной объемной перфузии во время ИК [18]. Гипотеза подтверждена в многочисленных ретроспективных исследованиях [19; 20]. Таким образом была сформулирована концепция целенаправленной перфузии, которая заключается в поддержании индекса DO2 при ИК выше критического значения, которое находится в диапазоне от 260 до 272 мл/мин/м2. Был проведен ряд рандомизированных контролируемых исследований для проверки нефропротективной эффективности целенаправленной DO2 во время ИК. В работе M. Ranucci и соавт. в основной группе индекс DO2 во время ИК поддерживали на уровне ≥ 280 мл/мин/м2 путем регулировки скорости артериального насоса и оптимизации гематокрита. У пациентов контрольной группы поддерживали перфузионный индекс на уровне 2,4 л/мин/м2 без оптимизации уровня DO2. Частоту развития ОПП оценивали с помощью кри- териев AKIN (англ. Acute Kidney Injury Network). Целенаправленная DO2 при ИК значимо снизила частоту ОПП, особенно ОПП 1-й стадии [21]. H. Mukaida и соавт. в рандомизированном контролируемом исследовании выявили, что поддержание индекса DO2 > 300 мл/мин/м2 во время ИК ассоциировано со снижением частоты ОПП [22]. На основании этих и других исследований, а также относительной простоты реализации стратегии и небольшого количества побочных эффектов использование целенаправленной DO2 при ИК для предотвращения ОПП представляется разумным (умеренный уровень доказательств GRADE) [4].
Сложная патофизиология кардиохирургически ассоциированного ОПП делает маловероятным, что использование только одного фармакологического агента или одной немедикаментозной тактики способно оказывать достаточное нефропротективное действие для предотвращения ОПП. У пациентов с высоким риском ОПП, выявленным по маркерам повреждения почек, стратегия KDIGO значительно снизила частоту возникновения ОПП после операции на сердце. В многоцентровом рандомизированном исследовании с участием 278 пациентов применение стратегии KDIGO значимо снизило частоту ОПП средней и тяжелой степени. Однако частота ОПП легкой степени тяжести между группами не различалась [15]. Общество кардиоваскулярных анестезиологов рекомендует рассмотреть возможность использования у пациентов с высоким риском комплекса терапии KDIGO для профилактики ОПП (умеренный уровень доказательности GRADE) [4].
Несмотря на сочетанное использование стратегий KDIGO и GDP, частота ОПП в контрольной группе оставалась высокой и составляла 39,7 %. Не существует медикаментозных препаратов с доказанной эффективностью для нефропротекции при операциях с ИК [23]. В большинстве исследований имеются ограничения по количеству включенных пациентов, значительная вариация применяемых доз препаратов, оценка по разным клиническим исходам и разные критерии для установления наличия или отсутствия острого повреждения почек [24].
Доставка NO в сочетании с использованием технологий KDIGO и GDP продемонстрировала эффективность для нефропротекции у кардиохирургических пациентов с ХБП. Однако процедура не влияла на степень тяжести, длительность ОПП и скорость клубочковой фильтрации.
Нефропротективные свойства NO продемонстрированы в ряде фундаментальных исследований. N.O. Kamenshchikov и соавт. выявили в эксперименте, что доставка NO снижает повреждение, уменьшает степень митохондриальной дисфункции, предотвращает регулируемую клеточную гибель ткани почек [10].
Наши результаты частично воспроизводят результаты других рандомизированных контролируемых исследований, проведенных в популяции пациентов с умеренным риском развития ОПП. С. Lei и соавт. провели оценку влияния доставки NO на частоту послеоперационного ОПП у 244 больных после протезирования нескольких клапанов в условиях продленного ИК. Доставка NO ассоциировалась со снижением частоты послеоперационного ОПП с 64 до 50 % (р = 0,014) и уменьшением перехода в 3-ю стадию ХБП. Кроме того, пациенты группы NO имели меньший индекс MAKE (англ. Major Adverse Kidney Events index) через 30, 90 дней и 1 год по сравнению с контрольной группой [5].
Н.О. Каменщиков и соавт. выполнили рандомизированное контролируемое исследование, в которое включили 96 пациентов с умеренным риском развития ОПП. Доставка NO ассоциировалась со снижением частоты ОПП с 41,6 до 20,8 % (р = 0,023), более высоким темпом диуреза во время ИК и снижением концентрации биомаркера повреждения почек NGAL [6].
J. Hu и соавт. в объединенном метаанализе продемонстрировали, что доставка NO снижает риск развития послеоперационного ОПП и не влияет на продолжительность госпитализации и время на- хождения в отделении реанимации и интенсивной терапии [17]. В другом метаанализе Y. Yan и соавт. показали, что доставка NO может сократить продолжительность ИВЛ, однако значительного влияния на снижение летальности, продолжительности госпитализации и пребывания в реанимационном отделении также не выявили [25].
У пациентов с ХБП снижается выработка и нарушается биодоступность эндогенного NO, что приводит к дальнейшему усугублению повреждения и дисфункции почек. Эндотелиальная дисфункция развивается уже на ранних стадиях заболевания и характеризуется снижением синтеза NO вследствие уменьшения активности фермента NO-синтазы (NOS), ответственного за его продукцию. Повышенная выработка эндогенных ингибиторов NOS, таких как асимметричный диметиларгинин, усиливает формируемый дефицит [26]. Помимо снижения активности ферментативных систем снижается выработка главного субстрата для синтеза NO L-аргинина. Эта аминокислота синтезируется в проксимальных канальцах почек, и при значительной утрате функциональной массы почечной ткани ее образование нарушается [27]. Кроме того, высокий уровень мочевины и других субстратов в плазме ингибирует транспорт L-аргинина к эндотелиальным клеткам и дополнительно снижает активность эндотелиальной NOS. При прогрессирующем заболевании почек уменьшается доступ NO к тканям-мишеням, что усиливает абсолютный и относительный дефицит NO [28]. Формируемый таким образом кумулятивный дефицит субстрата и снижение активности NOS приводят к снижению продукции и нарушению биодоступности оксида азота [29].
В интраоперационном периоде кардиохирургические пациенты подвергаются комплексному воздействию патологических факторов, включающих хирургическую травму, анестезию и экстракорпоральное кровообращение. Воздействие роликовых насосов, контакт крови с контуром экстракорпоральной перфузии и с воздухом приводят к гемолизу, повышению уровня свободного гемоглобина, которые связывают эндогенно продуцируемый NO, снижая его биодоступность, что усугубляет исходный дефицит NO и приводит к васкулопатиям, эндотелиальной дисфункции, мультифокальной вазоконстрикции и ишемическому полиорганному повреждению [12]. Пиковые концентрации свободного гемоглобина в плазме крови и максимальное нарушение биодоступности NO приходятся на период ИК [30]. Таким образом, ИК приводит к снижению биодоступности NO как за счет связывания NO при развитии гемолиза, так и за счет снижения синтеза NO при ишемически-реперфузи-онном повреждении, окислительном стрессе и эндотелиальной дисфункции [31]. Дефицит эндогенного NO приводит к нарушению ауторегуляции сосудистого тонуса и аберрациям тканевой перфузии, что наиболее пагубно сказывается на почечной ткани, поскольку даже в физиологических условиях почки имеют низкий уровень тканевой оксигенации — парциальное давление кислорода в клубочках составляет около 40 мм рт. ст. и снижается в мозговом слое до 10 мм рт. ст. [32].
В исследованиях показано, что концентрация NO в выдыхаемом воздухе коррелирует с системным уровнем NO во время кардиохирургических операций с искусственным кровообращением [33; 34].
В контрольной группе концентрация выдыхаемого NO снижалась через 2 ч после операции относительно исходных значений, что указывает на периоперационные расстройства гомеостаза эндогенного NO с формированием его дефицита в раннем послеоперационном периоде. Через 24 ч после операции концентрация выдыхаемого NO в контрольной группе была сопоставима с исходными значениями, профиль эндогенного NO нормализовался.
В основной группе концентрация NO в выдыхаемом воздухе значимо не изменялась. При межгрупповом сравнении показателя в основной группе концентрация NO в выдыхаемом воздухе была значимо выше через 2 и 24 ч после операции по сравнению с контрольной группой.
Таким образом, доставка NO приводит к оптимизации гомеостаза эндогенного NO при кардиохирургических вмешательствах у пациентов с ХБП, что является одним из механизмов нефропротек-тивного действия оксида азота.
Несмотря на значимое уменьшение частоты ОПП в основной группе, мы не получили достоверных межгрупповых различий по биомаркерам повреждения почек. В исследованиях выявлена высокая прогностическая способность биомаркеров повреждения почек при кардиохирургических операциях у пациентов с нормальной функцией почек [35; 36]. Биомаркеры повреждения канальцев имеют решающее значение для предоставления информации в тех случаях, когда сывороточный креатинин не изменяется существенно. Например, в рандомизированном контролируемом исследовании по оценке нефропротективной эффективности предоперационного приема статинов группы не различались по частоте ОПП после перенесенного кардиохирургического вмешательства, но использование био- маркеров повреждения почек позволило выявить субклиническое повреждение почек [37].
Однако у пациентов с ХБП биомаркеры повреждения почек изучены недостаточно. При ХБП из-за протекания в почках патологических процессов и снижения массы функционирующих нефронов экспрессия биомаркеров повреждения почек может нарушаться. В случаях, когда резерв почечной фильтрации утрачен, повреждающие воздействия на почки будут соответствовать дополнительному снижению клубочковой фильтрации и, таким образом, сывороточный креатинин может предоставить больше информации, чем биомаркеры повреждения канальцев. C.-Y. Hsu и соавт. в исследовании пациентов с ХБП продемонстрировали, что уровни KIM-1, NGAL и белка, связывающего жирные кислоты (англ. Liver Fatty Acid Binding Protein, L-FABP), в моче были значительно связаны с прогрессированием ХБП в нескорректированных анализах, однако после контроля СКФ на основе сывороточного креатинина и соотношения альбумин/креатинин в моче — двух традиционных биомаркеров функции почек — эти биомаркеры больше не были независимо ассоциированы с прогрессированием ХБП. Кроме того, ни один из биомаркеров не улучшил стратификацию риска в клинической модели прогрессирования ХБП, что позволяет предположить, что биомаркеры повреждения канальцев могут иметь ограниченную полезность у пациентов со сниженным почечным резервом [38].
Таким образом, при выполнении кардиохирургических операций у пациентов с высоким риском почечных осложнений представляется оправданным сочетание стратегий нефармакологической не-фропротекции и адъювантных фармакологических агентов, в том числе оксида азота, доставка которого может расширить показания к проведению кардиохирургических вмешательств.
Ограничения
Исследование выполнено на относительно небольшой популяции пациентов в одном центре. Время наблюдения за больными ограничивалось периодом госпитализации.
Заключение
Доставка NO в сочетании с комплексом мер KDIGO и GDP снижает частоту ОПП по сравнению с изолированным применением нефармакологических нефропротективных методик за счет нивелирования периоперационного дефицита эндогенного NO, однако не влияет на экспрессию биомаркеров повреждения почек.
Список литературы Нефармакологические нефропротективные стратегии в сочетании с доставкой оксида азота у кардиохирургических пациентов с хронической болезнью почек: рандомизированное контролируемое исследование
- Kertai M.D., Zhou S., Karhausen J.A., Cooter M., Jooste E., Li Y.-J., White W.D., Aronson S., Podgoreanu M.V., Gaca J., Welsby I.J., Levy J.H., Stafford-Smith M., Mathew J.P., Fontes M.L. Platelet counts, acute kidney injury, and mortality after coronary artery bypass grafting surgery. Anesthesiology. 2016;124(2):339-352. PMID: 26599400; PMCID: PMC5040517. https://doi.org/10.1097/ALN.0000000000000959
- Grams M.E., Sang Y., Coresh J., Ballew S., Matsushita K., Molnar M.Z., Szabo Z., Kalantar-Zadeh K., Kovesdy C.P. Acute kidney injury after major surgery: a retrospective analysis of veterans health administration data. Am J Kidney Dis. 2016;67(6):872-880. PMID: 26337133; PMCID: PMC4775458. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.ajkd.2015.07.022
- Waikar S.S., Curhan G.C., Wald R., McCarthy E.P., Chertow G.M. Declining mortality in patients with acute renal failure, 1988 to 2002. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2006;17(4):1143-1150. PMID: 16495376. https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2005091017
- Peng K., McIlroy D.R., Bollen B.A., Billings F.T. 4th, Zarbock A., Popescu W.M., Fox A.A., Shore-Lesserson L., Zhou S., Geube M.A., Ji F., Bhatia M., Schwann N.M., Shaw A.D., Liu H. Society of Cardiovascular Anesthesiologists clinical practice update for management of acute kidney injury associated with cardiac surgery. Anesth Analg. 2022;135(4):744-756. PMID: 35544772. https://doi.org/10.1213/ANE.0000000000006068
- Lei C., Berra L., Rezoagli E., Yu B., Dong H., Yu S., Hou L., Chen M., Chen W., Wang H., Zheng Q., Shen J., Jin Z., Chen T., Zhao R., Christie E., Sabbisetti V.S., Nordio F., Bonventre J.V., Xiong L., Zapol W.M. Nitric oxide decreases acute kidney injury and stage 3 chronic kidney disease after cardiac surgery. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2018;198(10):1279-1287. PMID: 29932345; PMCID: PMC6290943. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.201710-2150OC
- Kamenshchikov N.O., Anfinogenova Y.J., Kozlov B.N., Svirko Y.S., Pekarskiy S.E., Evtushenko V.V., Lugovsky V.A., Shipulin V.M., Lomivorotov V.V., Podoksenov Y.K. Nitric oxide delivery during cardiopulmonary bypass reduces acute kidney injury: a randomized trial. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2022;163(4):1393-1403.e9. PMID: 32718702. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtcvs.2020.03.182
- Тё М.А., Каменщиков Н.О., Подоксенов Ю.К., Мухомедзянов А.В., Маслов Л.Н., Козлов Б.Н. Влияние доставки оксида азота на энергетическое обеспечение почечной ткани при проведении искусственного кровообращения: экспериментальное исследование. Сибирский журнал клинической и экспериментальной медицины. 2024;39(1):163-170. https://doi.org/10.29001/2073-8552-2022-592 Tyo M.A., Kamenshchikov N.O., Podoksenov Yu.K., Mukhomedzyanov A.V., Maslov L.N., Kozlov B.N. Effect of nitric oxide delivery on energy supply of renal tissue in cardiopulmonary bypass: an experimental study. Siberian Journal of Clinical and Experimental Medicine. 2024;39(1):163-170. (In Russ.) https://doi.org/10.29001/2073-8552-2022-592
- Те М.А., Каменщиков Н.О., Подоксенов Ю.К., Мухомедзянов А.В., Маслов Л.Н., Кравченко И.В., Чурилина Е.А., Козлов Б.Н. Влияние доставки оксида азота на процессы апоптоза, некроптоза и пироптоза в почечной паренхиме при моделировании искусственного кровообращения: экспериментальное исследование. Вестник анестезиологии и реаниматологии. 2024;21(3):26-33. https://doi.org/10.24884/2078-5658-2024-21-3-26-33 Tyo M.A., Kamenshchikov N.O., Podoksenov Yu.K., Mukhomedzyanov A.V., Maslov L.N., Kravchenko I.V., Churilina E.A., Kozlov B.N. The influence of nitric oxide delivery on the processes of apoptosis, necroptosis and pyroptosis in the renal parenchyma after simulating cardiopulmonary bypass: an experimental study. Messenger of Anesthesiology and Resuscitation. 2024;21(3):26-33. (In Russ.) https://doi.org/10.24884/2078-5658-2024-21-3-26-33
- Кравченко И.В., Геренг Е.А., Подоксенов Ю.К., Тё М.А., Серебрякова О.Н., Бянкина М.А., Горохова А.В., Козлов Б.Н., Мильто И.В., Каменщиков Н.О. Влияние доставки оксида азота на морфофункциональное состояние легких при моделировании искусственного кровообращения: экспериментальное исследование. Пульмонология. 2024;34(3):385-394. https://doi.org/10.18093/0869-0189-2024-34-3-385-394 Kravchenko I.V., Gereng E.A., Podoksenov Yu.K., Tyo M.A., Serebryakova O.N., Byankina M.A., Gorokhova A.V., Kozlov B.N., Milto I.V., Kamenshchikov N.O. Effect of nitric oxide supply on the morphofunctional state of the lungs during cardiopulmonary bypass modelling: an experimental study. Pulmonologiya = Pulmonology. 2024;34(3):385-394. (In Russ.) https://doi.org/10.18093/0869-0189-2024-34-3-385-394
- Kamenshchikov N.O., Podoksenov Y.K., Kozlov B.N., Maslov L.N., Mukhomedzyanov A.V., Tyo M.A., Boiko A.M., Margolis N.Y., Boshchenko A.A., Serebryakova O.N., Dzyuman A.N., Shirshin A.S., Buranov S.N., Selemir V.D. The nephroprotective effect of nitric oxide during extracorporeal circulation: an experimental study. Biomedicines. 2024;12(6):1298. PMID: 38927505; PMCID: PMC11201384. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12061298
- Blum M., Yachnin T., Wollman Y., Chernihovsky T., Peer G., Grosskopf I., Kaplan E., Silverberg D., Cabili S., Iaina A. Low nitric oxide production in patients with chronic renal failure. Nephron. 1998;79(3):265-268. PMID: 9678424. https://doi.org/10.1159/000045047
- Vermeulen Windsant I.C., de Wit N.C.J., Sertorio J.T.C., van Bijnen A.A., Ganushchak Y.M., Heijmans J.H., Tanus-Santos J.E., Jacobs M.J., Maessen J.G., Buurman W.A. Hemolysis during cardiac surgery is associated with increased intravascular nitric oxide consumption and perioperative kidney and intestinal tissue damage. Front Physiol. 2014;5:340. PMID: 25249983; PMCID: PMC4157603. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2014.00340
- KDIGO Board Members. KDIGO 2012 clinical practice guideline for the evaluation and management of chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int Suppl. 2012;3(1):1-163. Available from: https://kdigo.org/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/KDIGO_2012_CKD_GL.pdf
- Khwaja A.; KDIGO Acute Kidney Injury Work Group. KDIGO clinical practice guideline for acute kidney injury. Nephron Clin Pract. 2012;120(4):c179-c184. PMID: 22890468. https://doi.org/10.1159/000339789
- Meersch M., Schmidt C., Hoffmeier A., Van Aken H., Wempe C., Gerss J., Zarbock A. Prevention of cardiac surgery-associated AKI by implementing the KDIGO guidelines in high risk patients identified by biomarkers: the PrevAKI randomized controlled trial. Intensive Care Med. 2017;43(11):1551-1561. PMID: 28110412; PMCID: PMC5633630. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-016-4670-3
- Cho J.S., Shim J.-K., Lee S., Song J.-W., Choi N., Lee S., Kwak Y.-L. Chronic progression of cardiac surgery associated acute kidney injury: Intermediary role of acute kidney disease. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2021;161(2):681-688.e3. PMID: 31959433. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtcvs.2019.10.101
- Hu J., Spina S., Zadek F., Kamenshchikov N.O., Bittner E.A., Pedemonte J., Berra L. Effect of nitric oxide on postoperative acute kidney injury in patients who underwent cardiopulmonary bypass: a systematic review and meta-analysis with trial sequential analysis. Ann Intensive Care. 2019;9(1):129. PMID: 31754841; PMCID: PMC6872705. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13613-019-0605-9
- Ranucci M., Pavesi M., Mazza E., Bertucci C., Frigiola A., Menicanti L., Ditta A., Boncilli A., Conti D. Risk factors for renal dysfunction after coronary surgery: the role of cardiopulmo¬nary bypass technique. Perfusion. 1994;9(5):319-326. PMID: 7833539. https://doi.org/10.1177/026765919400900503
- Ranucci M., Romitti F., Isgrò G., Cotza M., Brozzi S., Boncilli A., Ditta A. Oxygen delivery during cardiopulmonary bypass and acute renal failure after coronary operations. Ann Thorac Surg. 2005;80(6):2213-2220. PMID: 16305874. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.athoracsur.2005.05.069
- de Somer F., Mulholland J.W., Bryan M.R., Aloisio T., Van Nooten G.J., Ranucci M. O2 delivery and CO2 production during cardiopulmonary bypass as determinants of acute kidney injury: time for a goal-directed perfusion management? Crit Care. 2011;15(4):R192. PMID: 21831302; PMCID: PMC3387634. https://doi.org/10.1186/cc10349
- Ranucci M., Johnson I., Willcox T., Baker R.A., Boer C., Baumann A., Justison G.A., de Somer F., Exton P., Agarwal S., Parke R., Newland R.F., Haumann R.G., Buchwald D., Weitzel N., Venkateswaran R., Ambrogi F., Pistuddi V. Goal-directed perfusion to reduce acute kidney injury: a randomized trial. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2018;156(5):1918-1927.e2. PMID: 29778331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtcvs.2018.04.045
- Mukaida H., Matsushita S., Yamamoto T., Minami Y., Sato G., Asai T., Amano A. Oxygen delivery-guided perfusion for the prevention of acute kidney injury: a randomized controlled trial. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2023;165(2):750-760.e5. PMID: 33840474. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtcvs.2021.03.032
- Joannidis M., Druml W., Forni L.G., Groeneveld A.B.J., Honore P.M., Hoste E., Ostermann M., Oudemans-van Straaten H.M., Schetz M. Prevention of acute kidney injury and protection of renal function in the intensive care unit: update 2017: Expert opinion of the Working Group on Prevention, AKI section, European Society of Intensive Care Medicine. Intensive Care Med. 2017;43(6):730-749. PMID: 28577069; PMCID: PMC5487598. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-017-4832-y
- Ostermann M., Cennamo A., Meersch M., Kunst G. A narrative review of the impact of surgery and anaesthesia on acute kidney injury. Anaesthesia. 2020;75 Suppl 1:e121-e133. PMID: 31903567. https://doi.org/10.1111/anae.14932
- Yan Y., Kamenshchikov N., Zheng Z., Lei C. Inhaled nitric oxide and postoperative outcomes in cardiac surgery with cardiopulmonary bypass: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Nitric Oxide. 2024;146:64-74. PMID: 38556145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.niox.2024.03.004
- Kielstein J.T., Böger R.H., Bode-Böger S.M., Schäffer J., Barbey M., Koch K.M., Frölich J.C. Asymmetric dimethylarginine plasma concentrations differ in patients with end-stage renal disease: relationship to treatment method and atherosclerotic disease. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1999;10(3):594-600. PMID: 10073610. https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.V103594
- Tizianello A., De Ferrari G., Garibotto G., Gurreri G., Robaudo C. Renal metabolism of amino acids and ammonia in subjects with normal renal function and in patients with chronic renal insufficiency. J Clin Invest. 1980;65(5):1162-1173. PMID: 7364943; PMCID: PMC371450. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI109771
- Peppa M., Uribarri J., Cai W., Lu M., Vlassara H. Glycoxidation and inflammation in renal failure patients. Am J Kidney Dis. 2004;43(4):690-695. PMID: 15042546. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.ajkd.2003.11.022
- Xiao S., Wagner L., Mahaney J., Baylis C. Uremic levels of urea inhibit L-arginine transport in cultured endothelial cells. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2001;280(6):F989-F995. PMID: 11352838; PMCID: PMC2756804. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajprenal.2001.280.6.F989
- Billings F.T. 4th, Ball S.K., Roberts L.J. 2nd, Pretorius M. Postoperative acute kidney injury is associated with hemoglobinemia and an enhanced oxidative stress response. Free Radic Biol Med. 2011;50(11):1480-1487. PMID: 21334433; PMCID: PMC3090463. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2011.02.011
- Reddy Y.S., Kiranmayi V.S., Bitla A.R., Krishna G.S., Srinivasa Rao P.V.L.N., Sivakumar V. Nitric oxide status in patients with chronic kidney disease. Indian J Nephrol. 2015;25(5):287-291. PMID: 26628794; PMCID: PMC4588324. https://doi.org/10.4103/0971-4065.147376
- Lübbers D.W., Baumgärtl H. Heterogeneities and profiles of oxygen pressure in brain and kidney as examples of the pO2 distribution in the living tissue. Kidney Int. 1997;51(2):372-380. PMID: 9027709. https://doi.org/10.1038/ki.1997.49
- Ishibe Y., Liu R., Hirosawa J., Kawamura K., Yamasaki K., Saito N. Exhaled nitric oxide level decreases after cardiopulmonary bypass in adult patients. Crit Care Med. 2000;28(12):3823-3827. PMID: 11153620. https://doi.org/10.1097/00003246-200012000-00012
- Marczin N., Kövesi T., Royston D. Exhaled nitric oxide as a marker of lung injury in coronary artery bypass surgery. Br J Anaesth. 2003;90(1):101-105. PMID: 12488391.
- Корабельников Д.И., Магомедалиев М.О. Современные биомаркеры острого повреждения почек. Фармакоэкономика. Современная фармакоэкономика и фармакоэпидемиология. 2023;16(1):87-104. https://doi.org/10.17749/2070-4909/farmakoekonomika.2023.171 Korabelnikov D.I., Magomedaliev M.O. Modern biomarkers of acute kidney injury. Farmakoekonomika. Modern Pharmacoeconomics and Pharmacoepidemiology. 2023;16(1):87-104. (In Russ.) https://doi.org/10.17749/2070-4909/farmakoekonomika.2023.171
- Греков И.С. Биомаркеры кардиохирургически-ассоциированного острого повреждения почек. Вестник СурГУ. Медицина. 2021;3(49):61-70. https://doi.org/10.34822/2304-9448-2021-3-61-70 Grekov I.S. Biomarkers of cardiac surgery-associated acute kidney injury. Vestnik SurGU. Meditsina = Bulletin of SurGU. Medicine. 2021;3(49):61-70. (In Russ.) https://doi.org/10.34822/2304-9448-2021-3-61-70
- Molnar A.O., Parikh C.R., Coca S.G., Thiessen-Philbrook H., Koyner J.L., Shlipak M.G., Lee Myers M., Garg A.X., TRIBE-AKI Consortium. Association between preoperative statin use and acute kidney injury biomarkers in cardiac surgical procedures. Ann Thorac Surg. 2014;97(6):2081-2087. PMID: 24725831; PMCID: PMC4068122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.athoracsur.2014.02.033
- Hsu C.-Y., Xie D., Waikar S.S., Bonventre J.V., Zhang X., Sabbisetti V., Mifflin T.E., Coresh J., Diamantidis C.J., He J., Lora C.M., Miller E.R., Nelson R.G., Ojo A.O., Rahman M., Schelling J.R., Wilson F.P., Kimmel P.L., Feldman H.I., Vasan R.S., Liu K.D.; CRIC Study Investigators; CKD Biomarkers Consortium. Urine biomarkers of tubular injury do not improve on the clinical model predicting chronic kidney disease progression. Kidney Int. 2017;91(1):196-203. PMID: 28029431; PMCID: PMC5362331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.kint.2016.09.003


