Novel secured biometric system procuring miniaturized prorogation
Автор: Sherin Zafar, Ayesha Hena Afzal, M. Afshar Alam
Журнал: International Journal of Computer Network and Information Security @ijcnis
Статья в выпуске: 11 vol.10, 2018 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Different organizations in today’s scenario are fully dependent on information technology for their survival, suffer from various security challenges like unauthorized access, physical damages etc. To avoid various security breaches and concerns, robust mechanism for user access need to be adopted that not only secure of valuable data but can also be utilized for developing various other security applications. “Biometric” secured technology is gaining attention for over traditional security mechanism like password, smart card etc. because information related to biometric are difficult to steal as compared to other mechanisms. In this research analysis “strong biometric approach” is proposed to overcome security apprehensions of various organizations& society through iris recognition system. Iris recognition system is a mechanism to identify a person through analyzing his or her iris pattern. This recognition system includes iris image acquisition, segmentation, normalization, encoding, matching and finally validation of iris templates. The iris recognition system developed and simulated in this research study has taken IIT database iris images as inputs and utilized hamming distance as the matching parameter. The simulated results depict an efficient and novel secured approach that will overcome various unauthorized accesses across the internet. The most novel approach of this iris based recognition system as compared to other traditional systems is that, if selected images are matched with trained iris images present in database then the resultant hamming distance as most of the iris recognition systems directly accept or reject images and causes huge congestion and execution prorogations.
Biometric, Iris Recognition System, Security Challenges, Normalization, Template Matching, Hamming Distance
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/15015645
IDR: 15015645 | DOI: 10.5815/ijcnis.2018.11.04
Текст научной статьи Novel secured biometric system procuring miniaturized prorogation
Published Online November 2018 in MECS DOI: 10.5815/ijcnis.2018.11.04
Security of information technology is one of the most serious concerns faced by the contemporary world and organizations. This increasing rate of threat and attacks has made security of data a major challenge, every organization require secure network. Security threats results into various insecure and unreliable services as they use internet or high speed wired /wireless networks. Systems used by various organizations should also be protected from unauthorized access, physical damage and operations disruption. Rise in security threat in existing computing platform and network has also raised various security concerns [1]. Therefore there is an urgent need of a secured and robust security mechanism to overcome various breaches across the network. Fig.1. depicts security challenges and solutions that are currently available.
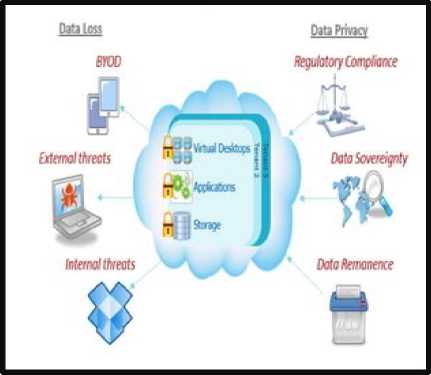
Fig.1. Current Security Challenges and Solutions across the Network
-
A. Biometric
Biometric technique is considered to be as one of the most secure and robust mechanisms for protecting valuable data. It is utilized for the verification purpose of an individual through their physical characteristics. This technique is preferred over traditional security mechanism like password, smart card etc. because information related to biometric are difficult to steal as compared to other mechanisms. Various types of strong biometric are fingerprint, facial features, voice, retinal scan, hand geometry, handwriting and the one exhibited in this paper is “iris” [14]. Types of biometric weak and strong are on the basis of various parameters are shown in Table 1. and in Fig.2. The research study of this paper utilizes strong biometric type i.e. iris because of its strong distinctive content and high rate of stability. Iris recognition techniques simulated in this research study is extremely uniqueness and is more reliable and stable validated through various simulation results depicted in section IV.
Table 1. Analysis of Biometrics on Various Features (H= High, M-Medium, L= Low)
|
Biometric |
Universality |
Uniqueness |
Permanence |
Collectability |
Performance |
Acceptability |
|
Face |
H |
L |
M |
H |
L |
H |
|
Fingerprint |
M |
H |
H |
M |
H |
M |
|
Hand Geometry |
M |
M |
M |
H |
M |
M |
|
Keystroke Dynamics |
L |
L |
L |
M |
L |
M |
|
Hand Vein |
M |
M |
M |
M |
M |
M |
|
Iris |
H |
H |
H |
M |
H |
L |
|
Retina |
H |
H |
M |
L |
H |
L |
|
Signature |
L |
L |
L |
H |
L |
H |
|
Voice |
M |
L |
L |
M |
L |
H |
|
DNA |
H |
H |
H |
L |
H |
L |
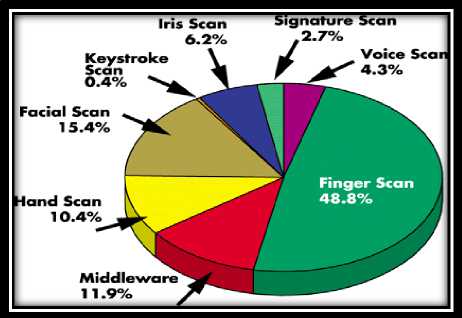
Fig.2. Percentage Utilization of Biometrics in Security
SS3/handout/
-
• Image Acquisition
-
• Iris Segmentation
-
• Iris Normalization
-
• Iris Encoding
-
• Matching
These stages will be discussed in later section of this research analysis. Rest of the paper is organized as follows: Section II lists about the literature survey which includes related work regarding biometric and iris recognition. Different security breaches and shortcomings are discussed in Section III. Methodology adopted for iris recognition system is mentioned in Section IV. Section V includes results and analysis. Conclusion and future scope is included in Section VI.
-
B. Neotric Iris based Recognition System
Iris is an organ which has unique design and stay same throughout lifetime. These quality of iris make highly unique, reliable and stable. Various countries are using iris reconition techniques in air terminals for entry and exit of pessangers.Iris recognition system is composed of stages mentioned below:
-
II. Literature Review
An extensive literature survey about biometric mechanism and iris recognition system is provided in this section depicted through Table 2.
Table 2. Literature Survey
|
S No. |
Author Name |
Outcome of research |
|
1 |
J. Daugman [2] |
In this paper author has developed an algorithm which helps in recognition of person through their iris. Iris pattern which are developed are tested and examine in various laboratory. It will provide result with high accuracy. |
|
2 |
B. Sarika[3] |
This research discusses about how iris recognition are using as biometric mechanisms. Iris mechanisms are very much in demand due to its reliability and perfection towards recognition rates. There are various areas where user needs to be authenticated like. Communication network and mobile commerce. Various processes of iris recognitions are discussed in this paper. |
|
3 |
S.Barkathunishaan, R.Meenakumari[4] |
This research has analyzed about the importance of medical information and how important it is to maintain the security and privacy of medical sensitive data. This paper decomposes above problem into two parts: (1) To secure the link between patient and devices. (2) To secure the link between the device and the network. |
|
4 |
S. Zafar, M. K. Soni [5] |
This paper focuses on extracting the features of the iris which is one of the strong biometric features. This paper has discussed that template formation or encoding is performed through the normalizing iris pattern with bi-orthogonal wavelength 3.5. Research analysis has concluded the major advantage of this scheme over classical construction method is that it doesn’t rely on the Fourier transform and the result is faster implementation of wavelength transform. |
|
5 |
R.P. Wildes[6] |
This paper mainly discusses about security mechanism and how identifications based on biometric is gaining attention all over world. As iris recognition approach is becoming very active topic in fields of research as well as practical applications the research analyzes, how iris detection work and what are various steps involved in iris detections. |
|
6 |
Y. Ping Huang et al [7] |
Through this research work various advantages of iris recognition are discussed, such as variability, stability and security which result into most promising features for security mechanism. A new algorithm is proposed in this paper for iris recognition. Algorithm includes Independent component Analysis (ICA) to extract iris features. The experimental results show that the algorithm is efficient and adaptive to environment. |
-
III. Research Motivation
After performing an intensive literature survey the following research motivations have been highlighted that will lead to the problem formulation of the novel biometric approach discussed, analyzed, implemented and simulated in this research study.
-
A. Security Challenges: Security of biometric devices is really turned into a serious security concern in today’s era. Hacking of such devices is one of the security concerns.
-
B. Privacy Challenges: Biometric collects tons of data for its various applications. These data may be very sensitive and private which need not to be made public. Necessary precautions are missing while storing and sharing of data with other service provider.
-
C. Inter-Operability Standard Issues: Information exchange needs to be done between various interconnected biometric devices, but this requires an investment of large amounts of money.
-
D. Legal Regulatory and Right Issues: There is no stronger law available which cover all the different biometric throughout the globe, so this may result into security breaches.
So the proposed research study motivates in building a secured novel approach utilizing strong biometrics iris to avoid various security breaches and enhance network performance.
-
IV. Methodology Adopted
As above sections discuses about the extensive litreture survey and gaps of study, now this section highlights on the methodology of the proposed approach, iris based recognization system explanations and what different methods are used for obtaining the desired results.
At a situation when an individual is required or wishes to recognize by iris framework, for this first eye is captured of that particular individual and then the layout made for their iris district. Then the matching process is done, for this layout is put away in database until the coordinating layout is not found and subject is distinguished or either no match is found and subject is unidentified.
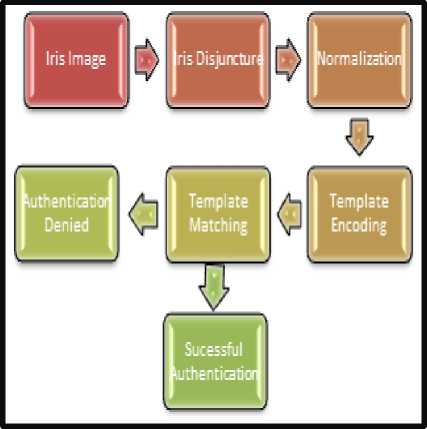
Fig.3. Steps Involved in the Proposed Iris Recognition System.
In the above flow diagram in Fig.3., iris recognition working is shown in detailed step by step. Firstly Iris image is taken, and then there are four steps to follow in the iris recognition process. First step is segmentation method followed by normalization. After normalization, iris template is encoded and then the encoded template is matched with the template from database. If template is matched then authentication mechanism is successful otherwise authentication is denied. This system consists of different sub-framework, which includes different phases of iris recognition mechanism. These steps are as follows:
-
A. Image Acquisition
Very first requirement for executing iris recognition technique framework is iris images gathering database for which best image acquisition mechanism is required. Quality of iris image plays very important role in this technique [9]. This paper hasn’t acquired images through CCD camera but has taken authentic IIT Delhi, databases to acquire iris images.
-
B. Iris Segmentation
The first step of iris recognition is to determine actual iris region from digital eye image. These images basically consist of two circles. The iris/sclera boundary is defined by outer circle and the iris/pupil boundary is defined by inner circle. The segmentation technique basically depends on the quality of eye images through image acquisition mechanism [8]. Iris segmentation can be performed by various mechanisms like, Daugman’s Integro-differential Operator, Active Contour Models, Eyelash and Noise Detection etc., among all these mechanism Hough Transform is utilized in this novel approach for iris segmentation because Hough transform mechanism is relatively unaffected by eye image error and noise. In starting of Hough transform, generation of edge map takes place by calculation of the first derivatives of intensity values in an eye image and then thresh-holding of the result is done. In Hough space votes are casted from the edge map for the parameters (centre coordinates x c and y c and the radius r) of circles passing through each edge point, which are able to define any circle according to the equation:
x2 c +y2 c -r2=0 (1)
For locating the iris boundary only the vertical gradients are taken that will reduce influence of the eyelids for performing circular Hough transform as for successful localisation, not all of the edge pixels defining the circle are required. Hence, making circle localisation more accurate and more efficient as there are less edge points to cast votes in the Hough space.
-
C. Iris Normalization
In the previous step as the segmentation is performed successfully on eye image. The very next step is to convert the obtained iris region into fix dimensions, so that it can be compared. The normalization mechanism will provide iris region with same constant dimensions [9]. Iris normalization can be performed by various mechanisms like Daugmann Rubber Sheet Model, Image
Registration, Histogram equalization etc. Among all these mechanism of normalization, Daugman’s Rubber Sheet Model is utilized in this research study for performing normalization. In Daugmann rubber sheet model, Iris region’s remapping of the (x, y) Cartesian coordinates to the normalized non-concentric polar representation is modelled as;
I(x(r,θ),y(r,θ))→I(r,θ)(2)
With:
x(r,θ)=(1-r)xp(θ)+rxl(θ)(3)
y(r,θ)=(1-r)yp(θ)+ryl(θ)(4)
where:
I(x, y) = iris region image.
(x, y) = original Cartesian coordinates.
(r, θ) = corresponding normalized polar coordinates.
x p y p and x l ,y l = coordinates of the pupil and iris boundaries along the θ direction.
Pupil dilation and size inconsistencies are taken into account by the rubber sheet model to produce a normalized representation with constant dimensions. Hence, modelling the iris region as a flexible rubber sheet is anchored at the boundary with the reference point specified as the pupil centre. This model considers for dilation of pupil, imaging distance and non-concentric pupil displacement.
-
D. Iris Encoding
In order to provide accurate recognition of individuals only the selective section of iris region need to be extracted. This selective part of iris image is encoded by using different mechanism so that comparison of template can be performed [10]. Iris encoding can be performed by various different methods like wavelet encoding, Gabor filters, Log-Gabor Filters etc. Among all these encoding mechanism Bi-orthogonal wavelet based comer template encoding methodology is utilized in this research study as it does not rely on Fourier transform and result is faster implementation of wavelet transform.
-
E. Iris Matching
In Iris matching method is comparison of two iris templates is done by passing their corresponding binary features to the function [11-16].
HD= 1\N N j=1 C a (j) + C b (j) (5)
Where C a and C b are the coefficient of two iris images and N is the size of feature vector. This formula consist of Boolean operator which when provide result as binary 1 which mean C a and C b are different and if 0 then C a and C b are same.
There are various mechanisms for iris matching. Hamming Distance is selected metric for Iris matching mechanism. It provides how many bits are not matched between two Iris templates which are compared. If the hamming distance between two templates is less than the threshold value then it validates that the two iris images are of same person otherwise different.
-
V. Results and Analysis
As in previous section methodology has been discussed. This section focuses on simulation analysis of proposed approach through MATLAB depicted and analyzed from Fig.4-14.
STEP 1: This step involves training of iris images of IITD database
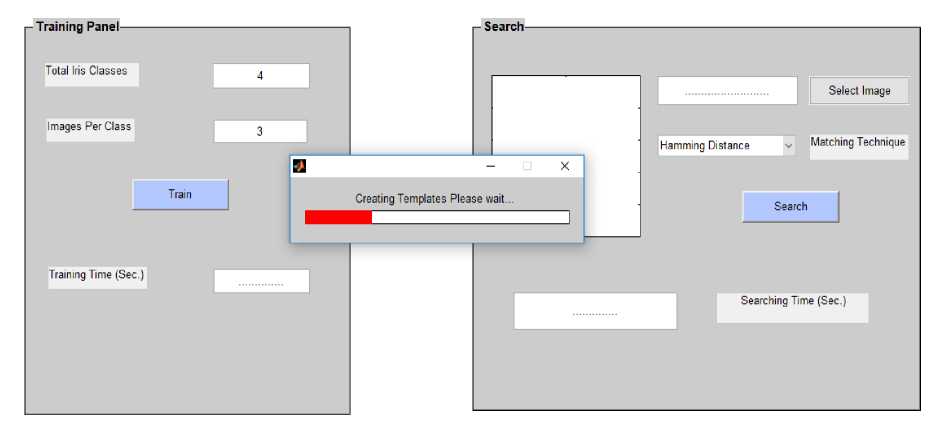
Fig.4. Training of Iris Images
STEP 2: This step involves selection of any iris image from one of the database available or from other sources.
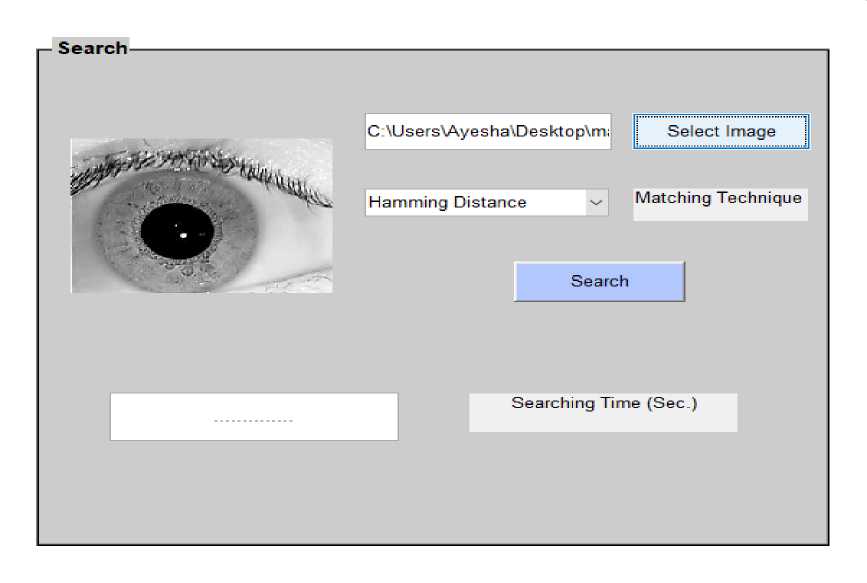
Fig.5. Iris Image which belongs to IITD Database (class 1 first image)
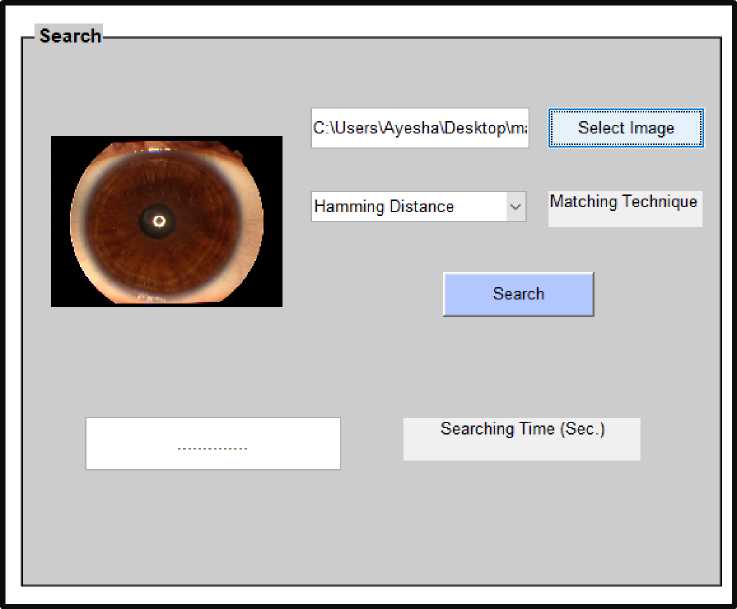
Fig.6. Iris Image Not belonging to IIT Database
Fig.6. is an iris image belongs to another database, iris images present in database which is trained.
which is not trained. Step 2 is compared with the entire Hamming distance is calculated for the images
STEP 3: Third step involves searching process and also calculating the total time taken for the searching mechanism.
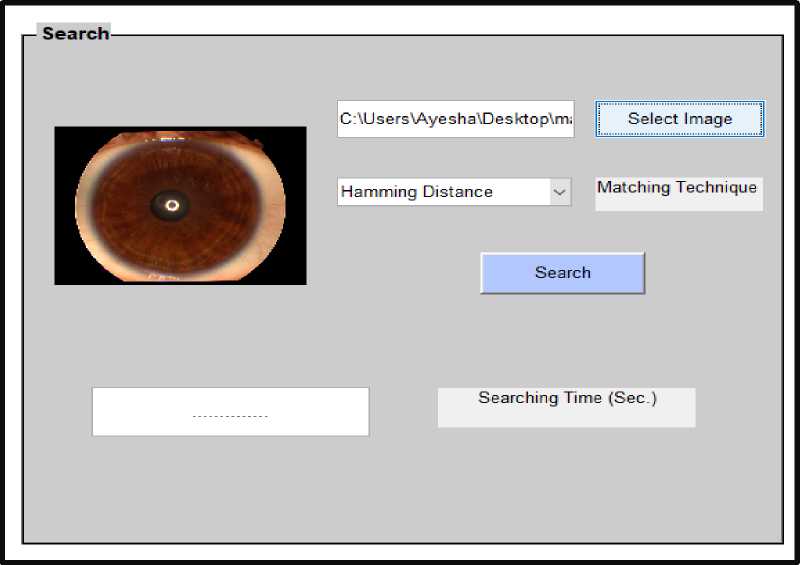
Fig.7. Iris Image belonging to IITD Database (class 1 first image)
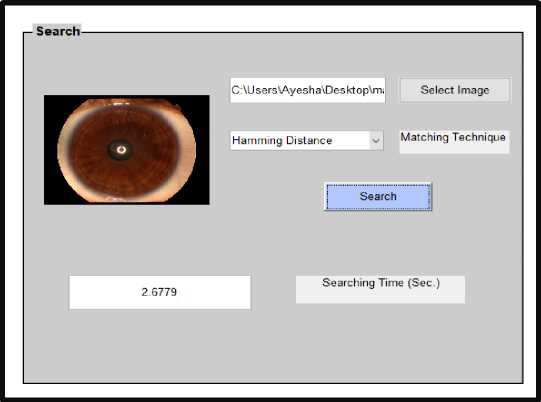
Fig.8. Iris Image that doesn’t belong to IIT Database.
STEP 4: This step performs Segmentation through Hough Transform
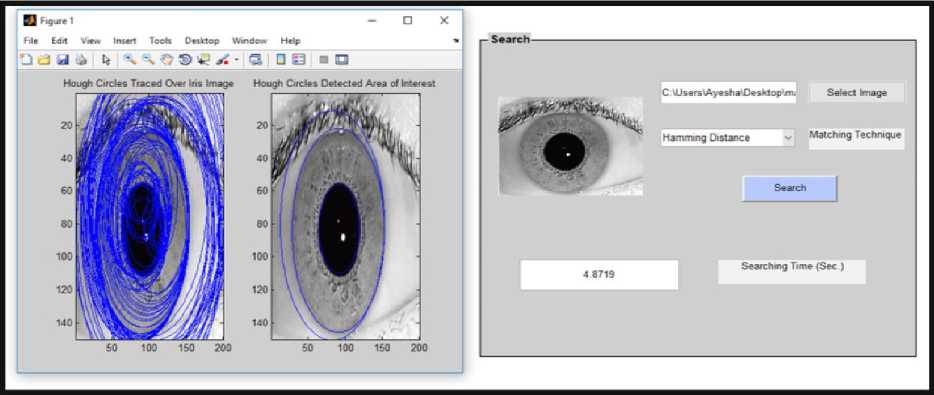
Fig.9. Hough Transform Generation of Iris Image of IIT Database
Fig.9. depicts the Hough Transform of iris image that belongs to IITD database (class one first image).
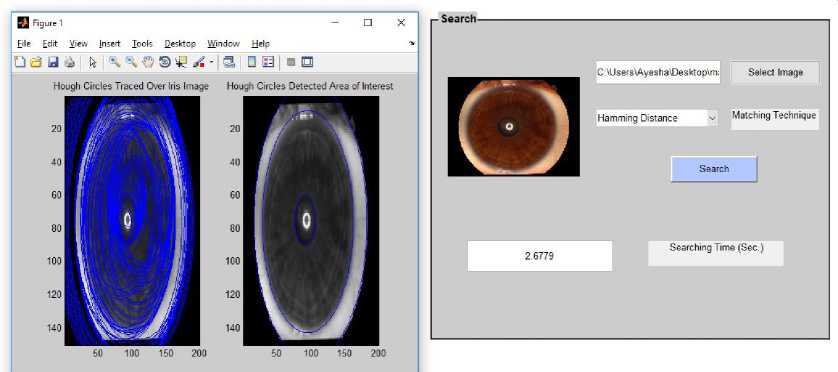
Fig.10. Hough Transform Generation of Iris Image not belonging to IIT Database
Fig. 10 depicts the Hough Transform of iris image that belongs to another database, which is not trained.
STEP 5: Involves the normalization mechanism of the iris image. It converts iris region into fix dimensions.
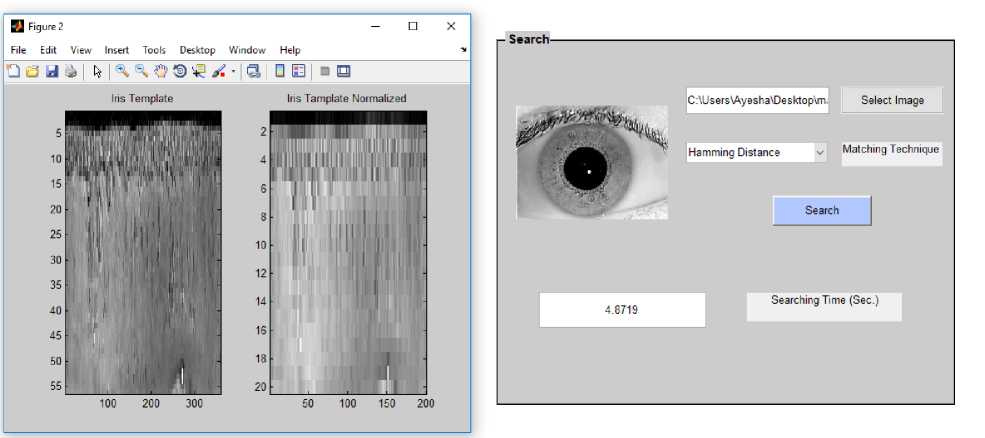
Fig.11. Iris Image Normalization of Image belonging to IIT Database
-
Fig.11. shows the normalization of iris image that belongs to IITD database (class one first image).
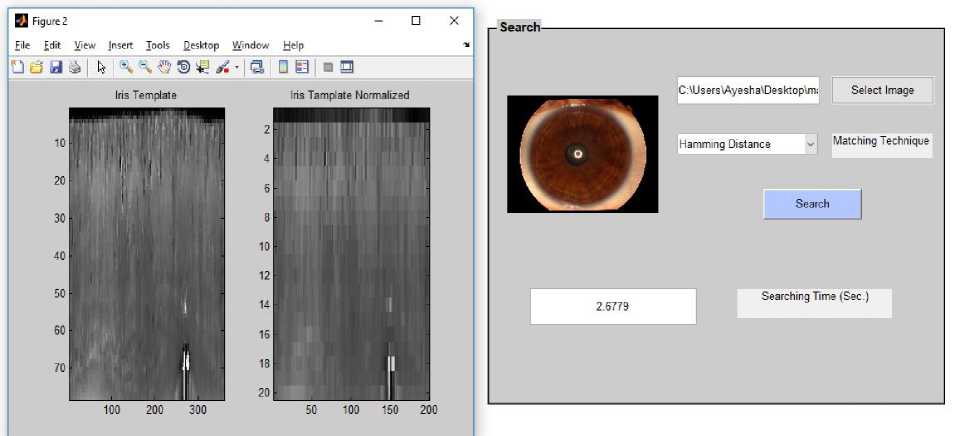
Fig.12. Iris Image Normalization of Image not belonging to IIT Database
-
Fig.12. depicts the normalization of iris image belong to another database, which is not trained.
STEP 6: This is final step it performs matching through Hamming distance method. If image selected in step II belong to database which is trained then the hamming distance will be 0 otherwise not.
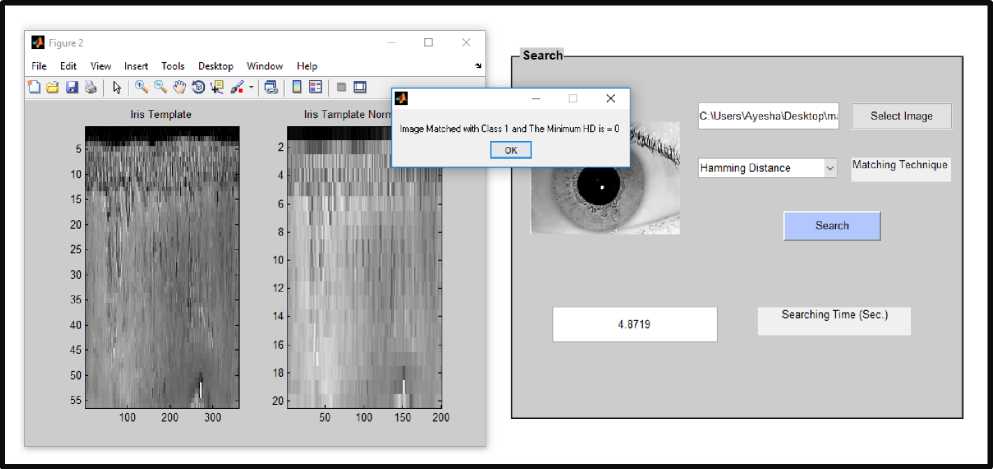
Fig.13. Hamming Distance Matching of Iris Image belonging to IIT Database
Fig.13. shows hamming distance matching. Here database (class one first image) which is trained. hamming distance is 0 because iris image belongs to IITD
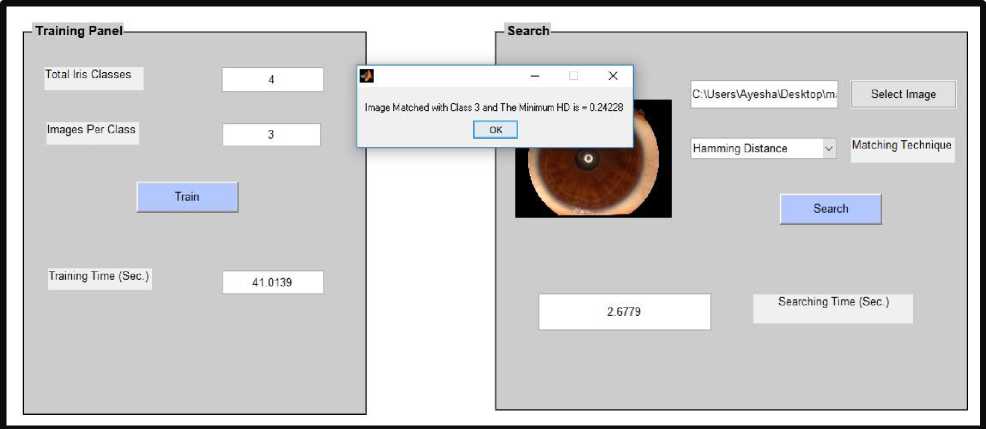
Fig.14. Hamming Distance Matching of Iris Image not belonging to IIT Database
Fig.14. shows hamming distance calculation. Here hamming distance is not 0 (HD=0.24) because iris image belongs to another database which is not trained, so this
Table 3. represents the result of iris images matching. Selected images are matched with database which
consists of trained iris images. If selected images are matched with trained iris images present in database then the resultant hamming distance will be 0 otherwise not, which is the most novel feature of this iris based recognition system as most of the iris recognition systems directly accept or reject images and causes huge congestion prorogations.
Table 3. Tabular Representation of Iris Images Matching through Hamming Distance
|
S No. |
Query Image |
Trained |
Database Class |
Hamming Distance |
|
1 |
1_1 |
Yes |
1 |
0 |
|
2 |
1_4 |
No |
1 |
0.05 |
|
3 |
1_3 |
Yes |
1 |
0 |
|
4 |
2_5 |
No |
4 |
0.02 |
|
5 |
2_1 |
Yes |
2 |
0 |
|
6 |
5_1 |
No |
1 |
0.106 |
|
7 |
5_6 |
No |
1 |
0.249 |
|
8 |
6_2 |
No |
3 |
0.111 |
|
9 |
4-1 |
Yes |
4 |
0 |
|
10 |
1_2 |
Yes |
1 |
0 |
|
11 |
2_2 |
Yes |
2 |
0 |
|
12 |
2_3 |
Yes |
2 |
0 |
|
13 |
3_1 |
Yes |
3 |
0 |
|
14 |
2_10 |
No |
1 |
0.038 |
|
15 |
7_1 |
No |
3 |
0.12 |
|
16 |
4_2 |
Yes |
4 |
0 |
|
17 |
4_3 |
Yes |
4 |
0 |
|
18 |
3_2 |
Yes |
3 |
0 |
|
19 |
1_8 |
No |
1 |
0.02 |
|
20 |
2_8 |
No |
2 |
0.07 |
-
[11] P. Khaw “Iris Recognition Technology for Improved Authentication” SANS Security Essential (GSEC) Practical Assignment , version 1.3, SANS Institute, 5–8 (2002).
-
[12] L. Masek, “Recognition of Human Eye Iris Patterns for Biometric Identification” University of West California , 2003.
-
[13] J. Daugmann, “High Confidence Visual Recognition of Persons by a test of Statistical Independence” IEEE Trans. on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence , 15(11), 1993.
-
[14] S. Zafar, M. K. Soni "A Novel Crypt-Biometric
Perception Algorithm to Protract Security in MANET” I.J. Computer Network and Information Security , 2014, pp. 64-71.
-
[15] S. Zafar, M.K. Soni, “Biometric Stationed Authentication Protocol (BSAP) Inculcating MetaHeuristic Genetic Algorithm” I.J. Modern Education and Computer Science , 2014, pp. 28-35.
-
[16] T. Bazaz, S. Zafar, “A Neoteric Optimization Methodology for Cloud Networks”, I.J. Modern Education and Computer Science , 2018, 6, 27-34.
in July 2017, Faculty of Computer Science Engineering at Jamia Hamdard, New Delhi. Her main interest is in optimization in MANET, using Biometric Approach. She has published around
30 papers in SCOPUS listed journals and reviewed around 80 papers

Ayesha Hena Afzal has pursued her M.Tech from Jamia Hamdard, India in Computer Science Engineering and B.Tech in Computer Science Engineering from Nagpur University, Nagpur, Maharashtra in 2011 and 2018 respectively. She is a Gold Medalist of
Engineering department at Jamia Hamdard. Her main interest is in security services provided by various biometric techniques especially iris recognition she has pursued.

Prof M. Afshar Alam is Professor and Head in Department of CSE, SEST Jamia Hamdard. He has around 30+ years of experience of teaching and research and published around 50+ research papers. His main interests are Wireless Networks, Sustainable
Development, Soft Computing and many more.
Список литературы Novel secured biometric system procuring miniaturized prorogation
- S. Zafar et al., “An optimized genetic stowed biometric approach to potent QOS in MANET” International Conference on Soft computing and Software Engineering (SCSE) 2015.
- J. Daugman, “How Iris Recognition Works”. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, Vol. 14, No. 1, 2004.
- B. Sarika, “Biometrics — Iris Recognition System- A Study Of Promising Approaches For Secured Authentication”, IEEE Transactions On Circuits And Systems For Video Technology, Vol. 14, No. 1, 2004.
- S.Barkathunishaan and R.Meenakumari, “Secure transmission of Medical Information using Iris Recognition” International conference on ICCPEIC, 2003 Chennai, India).
- S. Zafar, M. K. Soni, “Secure Routing in MANET through Crypt-Biometric Technique” Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Frontiers of Intelligent Computing: Theory and Applications (FICTA), 2014.
- R.P. Wildes et al., “Automated, non-invasive iris recognition system and method” U.S Patent 5, 572–596, 1996.
- Y. Ping Huang et al., “An Efficient Iris Recognition System” First International Conference on Machine Learning and Cybernetics, Beijing, China, 2002.
- R.P. Wildes, “Iris Recognition: An emerging biometric technology” Proceedings of the IEEE, 85(9), 1348–1363 CrossRef, 1997, http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/5.628669.
- M. Misiti et al., “A Biometric Authentication Approach for High Security Ad hoc Networks” Proceedings of IEEE Workshop on Information Assistance, pp. 250–256, 2004.
- J. Liu, et al., “Optimal Biometric Based Continuous Authentication in Mobile Ad hoc Networks” Third IEEE International Conference on Wireless and Mobile Computing, Networking and Communications, pp. 76–81, 2007.
- P. Khaw “Iris Recognition Technology for Improved Authentication” SANS Security Essential (GSEC) Practical Assignment, version 1.3, SANS Institute, 5–8 (2002).
- L. Masek, “Recognition of Human Eye Iris Patterns for Biometric Identification” University of West California, 2003.
- J. Daugmann, “High Confidence Visual Recognition of Persons by a test of Statistical Independence” IEEE Trans. on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 15(11) , 1993.
- S. Zafar, M. K. Soni "A Novel Crypt-Biometric Perception Algorithm to Protract Security in MANET” I.J. Computer Network and Information Security, 2014, pp. 64-71.
- S. Zafar, M.K. Soni, “Biometric Stationed Authentication Protocol (BSAP) Inculcating MetaHeuristic Genetic Algorithm” I.J. Modern Education and Computer Science, 2014, pp. 28-35.
- T. Bazaz, S. Zafar, “A Neoteric Optimization Methodology for Cloud Networks”, I.J. Modern Education and Computer Science, 2018, 6, 27-34.


