Новые возможности патогенетической терапии легочной артериальной гипертензии
Автор: Мартынюк Тамила Витальевна, Наконечников Сергей Николаевич, Чазова Ирина Евгеньевна
Журнал: Евразийский кардиологический журнал @eurasian-cardiology-journal
Рубрика: Оригинальные статьи
Статья в выпуске: 1, 2013 года.
Бесплатный доступ
В обзоре представлены новые данные о возможностях лекарственной терапии легочной артериальной гипертензии (ЛАГ). Известно, что основной характеристикой патологического процесса является легочное сосудистое ремоделирование - комплексный процесс, включающий клеточную пролиферацию, гипертрофию, миграцию клеток, нарушение апоптоза, продукции и деградации межклеточного матрикса. Это определяет интерес к лекарственным препаратам, которые являются не только мощными вазодилататорами, но и имеют антипролиферативный и антиремоделирующий эффекты. Следует выделить два основных подхода для дальнейшего улучшения терапии ЛАГ: 1) новые, более эффективные или более удобные для применения лекарственные препараты, которые воздействуют на вышеуказанные установленные мишени; 2) лекарственные препараты, которые воздействуют на новые патогенетические мишени, выявленные в результате последних научных исследований в области ЛАГ. Они показали потенциальную эффективность в экспериментальных моделях, а также в ранних фазах клинических исследований и являются перспективными с точки зрения дальнейшего совершенствования патогенетической терапии ЛАГ.
Легочная артериальная гипертензия, эндотелин-1, антагонисты рецепторов эндотелина, оксид азота, ингибиторы фосфодиэстеразы типа 5, простациклин
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/14342730
IDR: 14342730
Текст обзорной статьи Новые возможности патогенетической терапии легочной артериальной гипертензии
|
Чазова Ирина Евгеньевна |
Профессор, член-корр. РАМН, директор Института клинической кардиологии им. А. Л. Мясникова ФГБУ РКНПК МЗ РФ, тел.: 8-495-415-52-05 |
|
Наконечников Сергей Николаевич |
Д.м.н., профессор кафедры скорой медицинской помощи ФПДО МГМСУ МЗ РФ, Ученый секретарь ФГБУ РКНПК МЗ РФ, тел.: 8-495-414-61-18, snn_cardio@mail.ru |
|
Мартынюк Тамила Витальевна |
К. м. н., ведущий научный сотрудник отдела системных гипертензий Института клинической кардиологии им. А. Л. Мясникова ФГБУ РКНПК МЗ РФ, тел.: 8-495-414-64-50, trukhiniv@mail.ru |
За последние 10-15 лет в области легочной артериальной гипертензии (ЛАГ) произошли уникальные перемены. Они связаны с разработкой новых подходов к лекарственной терапии, основанных на результатах более 30 рандомизированных клинических исследований (РКИ) [1]. В клиническую практику внедрены лекарственные препараты (бозентан, амбризентан, эпопросте-нол, трепростинил, илопрост, силденафил, тада-лафил), которые воздействуют на три патогенетические мишени ЛАГ (антагонисты рецепторов эндотелина, ингибиторы фосфодиэстеразы типа 5, простаноиды) и имеют различные пути назначения (пероральный, ингаляционный, подкожный, внутривенный) (рис. 1).
Патогенетическая терапия является важным достижением в современной стратегии лечения больных с ИЛГ. Она направлена на улучшение и/или стабилизацию клинического состояния, переносимость физических нагрузок и гемодинамических показателей, позитивную динамику качества жизни больных, замедление темпов прогрессирования заболевания, снижение потребности в госпитализациях, а также улучшение прогноза больных [2]. Вышеуказанные препараты, относящиеся к трем классам специфической терапии ЛАГ, одобрены Администрацией по контролю продуктов питания и лекарственных препаратов (the Food and Drug Administration (FDA)) и/или Европейским Медицинским Агентством (the European Medicines Agency (EMA)). В России официально для лечения больных с ЛАГ одобрены бозентан, амбризентан, силденафил и ило-прост. Однако, несмотря на очевидные успехи в
Рисунок 1. Мишени патогенетической терапии ЛАГ
Эндотелин
NO
Простациклин
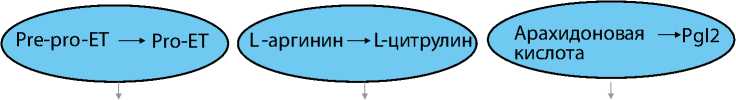
Эндотелин 1 Вазоконстрикция Пролиферация
Оксид азота
Вазодилатация
Антипролиферация
Простациклин (PgI2)
Вазодилатация
Антипролиферация
ЭТв

Антагонисты рецепторов эндотелина
Ингибиторы фосфодиэстеразы типа 5

Простаноиды
Адаптировано: M. Humbert et al. N Engl J Med 2004; 351: 1425-36
лечении больных, страдающих ЛАГ, улучшение клинических исходов, заболевание остается жизнеугрожающим, а прогноз – неблагоприятным. Согласно данным регистра ЛАГ, выполненного во Франции, 1-, 2-, 3-х годичная выживаемость больных достигает 83% (95% ДИ 72–95%), 67% (95% ДИ 57–79%) и 58% (95% ДИ 49–69%) [3].
Если ранее ЛАГ считали следствием нарушенного сосудистого тонуса в результате дисбаланса вазоконстриктивных и вазодилатирующих медиаторов, то в последние годы стало очевидным, что основной характеристикой патологического процесса является ремоделирование мелких легочных сосудов и артериол [4]. Легочное сосудистое ремоделирование – это комплексный процесс, включающий клеточную пролиферацию, гипертрофию, миграцию клеток, нарушение апоптоза, продукции и деградации межклеточного матрикса. Это определяет интерес к лекарственным препаратам, которые являются не только мощными вазодилататорами, но и имеют антипролифера-тивный и антиремоделирующий эффекты [5].
Вероятно, дальнейший прогресс патогенетической терапии может быть связан с применением внедренных в клиническую практику препаратов в виде комбинированной терапии. Вместе с тем, существует настоятельная потребность в разработке лекарственных средств, воздействующих на новые мишени заболевания. Следует выделить два основных подхода для дальнейшего улучшения терапии ЛАГ:
-
1) новые, более эффективные или более удобные для применения лекарственные препараты, которые воздействуют на вышеуказанные установленные мишени;
-
2) лекарственные препараты, которые воздействуют на новые патогенетические мишени, выявленные в результате последних научных исследований в области ЛАГ. Они показали потенциальную эффективность в экспериментальных моделях, а также в ранних фазах клинических исследованиях и являются перспективными с точки зрения дальнейшего совершенствования патогенетической терапии ЛАГ.
Новые лекарственные препараты, воздействующие на ранее установленные патогенетические мишени ЛАГ
Эндотелин-1
На роль эндотелина-1 (ЭТ-1) в патогенезе ЛАГ различной этиологии указывают значительно повышенные его уровни в плазме крови больных, а также повышенная экспрессия самого пептида и его предшественников в ткани легких [2,5]. Повы- шенная продукция ЭТ-1 показана как у больных с идиопатической (первичной) ЛАГ (ИЛГ), так и ассоциированными формами ЛАГ. При анализе соотношения уровней ЭТ-1 в крови, взятой из желудочков сердца у больных с ИЛГ, был выявлен существенный градиент его концентрации по сравнению с контролем, что указывает на нарушенный клиренс и/ или повышенную легочную продукцию ЭТ-1 [6].
Активация системы ЭТ-1 у больных с ЛАГ является обоснованием для использования АРЭ, блокирующих оба типа рецепторов – ЭТА и ЭТВ или исключительно ЭТА-рецепторы. Антагонисты рецепторов эндотелина (АРЭ) доказали способность улучшить гемодинамические параметры, толерантность к физическим нагрузкам, функциональный статус и клинические исходы в целом ряде плацебоконтролируемых РКИ [2]. Помимо мощного вазодилатирующего эффекта АРЭ воздействуют на ремоделирование легочных сосудов вследствие способности подавлять фиброз, пролиферацию клеток и воспаление [7-9].
ЭТ-1 имеет паракринный эффект, воздействуя локально. Почти 80% ЭТ-1, продуцируемого эндотелиальными клетками, секретируется базола-терально в направлении базальной мембраны, поэтому в кровотоке обнаруживается в меньших концентрациях, чем в тканях [10]. Современные АРЭ показали весьма ограниченную тканевую пенетрацию из-за наличия высокой пропорции ионизированных форм (99% у бозентана и 99,9% у амбризентана [11]. Это означает, что только незначительная доля препарата может проникнуть через липофильные клеточные мембраны и достигнуть тканевых ЭТ-рецепторов. Увеличение тканевой пенетрации для улучшения взаимодействия с ЭТ-рецепторами может повысить не только вазодилатирующий эффект АРЭ, но и их влияние на сосудистое ремоделирование.
Маситентан
Маситентан – мощный пероральный АРЭ двойного действия (ЭТA и ЭТB), специально созданный с целью улучшения тканевой пенетрации за счет увеличения доли неионизированных форм молекулы, что позволяет препарату проникать через липофильные клеточные мембраны [10]. В моно-кроталиновой модели ЛАГ маситентан вызывал снижение давления в легочной артерии (ДЛА) и предотвращал развитие гипертрофии правого желудочка более эффективно, чем бозентан в 10 раз меньшей дозе [11]. Клинические исследования фазы I и II продемонстрировали, что маси-тентан имеет дозозависимую фармакокинетику, отличается хорошей переносимостью у здоровых добровольцев и больных с артериальной гипертонией [10,11].
Недавно завершилось исследование SERAPHIN (Study of ACT-064992 on Morbidity and Mortality in Patients With Symptomatic Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension) (фаза III). Целью этого рандомизированного многоцентрового, двойного слепого, плацебоконтролируемого клинического исследования явилась оценка влияния мисатентана на заболеваемость и смертность больных с ЛАГ [12]. SERAPHIN – длительное исследование с оценкой клинических событий явилось наиболее крупным из проведенных в последние годы РКИ у больных с ЛАГ. В 150 центрах-участниках из более чем 40 стран было включено 742 пациента. Больные рандомизировались в соотношении 1:1:1 для получения маситентана 3 и 10мг или плацебо один раз в сутки. При этом они могли продолжить предшествующую специфическую терапию ЛАГ, за исключением АРЭ. Первичной конечной точкой явилось время до развития первого эпизода заболеваемости и смертности. Клинические события были выбраны в качестве конечных точек в соответствии с рекомендациями IV Мирового симпозиума по ЛГ [1,13] (рис. 2).
Включение больных в исследование SERAPHIN завершилось в декабре 2009г. Первые результаты были получены совсем недавно – в середине 2012г. Период наблюдения составлял не менее 1 года для последнего включенного в исследова- ние больного и до 4,5 лет – для первого рандомизированного больного.
Предварительные результаты исследования оказались воодушевляющими: применение маси-тентана в дозах 3 и 10 мг способствовало снижению риска заболеваемости и смертности при ЛАГ на 30% и 45% соответственно. Терапия характеризовалась благоприятным профилем переносимости: частота более чем 3-х кратного повышения трансаминаз была незначительной: 3,6% и 3,8% при применении маситентана в дозах 3 и 10 мг, 4,5% – в группе плацебо. Полученные данные по оценке заболеваемости и смертности больных с ЛАГ при длительном наблюдении в рамках рандомизированного клинического исследования имеют значение не только для установления клинических исходов при активной терапии, но и для изучения естественного течения ЛАГ.
При ЛАГ данные о выживаемости могут быть получены при длительном открытом наблюдении за больными, наблюдаемыми в краткосрочных, рандомизированных, плацебоконтролиру-емых клинических исследованиях [13]. Вместе с тем существуют определенные противоречия, связанные с переоценкой выживаемости за счет больных с положительным ответом на вазодилататоры, которые продолжают наблюдение в фазе длительного наблюдения, а также пациентов с давно установленным диагнозом [14]. Поэтому для адекватной оценки прогноза больных с ЛАГ очевидные преимущества имеют длительные,
Рисунок 2. Клиническое ухудшение в исследовании SERAPHIN
(Study with
Endothelin Receptor Antagonist in Pulmonary
Аrterial Hypertension to Improve cliNical outcome),
Рандомизация: 1:1:1
Маситентан 3мг:
Маситентан 10мг:
Плацебо
1 прием в сутки
Время до развития первого события-заболеваемость и смертность
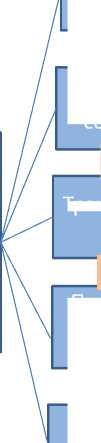
или или или или
Предсердная септостомия
Потребность в простаноидах в. / в или п/к
ФАТАЛЬНЫЙ ИСХОД
Трансплантация легких
Клиническое ухудшение
Ухудшение клинической симптоматики в виде увеличения ФК или появления / прогрессирования ПЖ декомпенсации
+
дистанции в Т 6 МХ > 15% в 2- х последоватальных тестах
+
Потребность в присоединении :
-
• Простаноидов per os или инг .
-
• ИФДЭ 5
-
• Др . АРЭ
-
• в ./ в диуретиков
рандомизированные, плацебоконтролируемые клинические исследования.
Простациклин
Роль нарушенной продукции простациклина у больных с ЛАГ доказывается как снижением экспрессии простациклинсинтазы в легочных артериях, так и уменьшением экскреции его метаболитов с мочой [1,5]. Простациклин, продуцируемый преимущественно эндотелиальными клетками, оказывает мощное вазодилатирующее действие во всех сосудистых бассейнах; цитопротективный и антипролиферативный эффекты; обладает анти-тромботической активностью, ингибируя агрегацию тромбоцитов. Это является обоснованием для использования его аналогов – простаноидов для лечения ЛАГ[15].
Первым в клиническую практику в середине 90-х годов прошлого столетия был внедрен стабильный аналог простациклина эпопростенол. Длительная терапия приводит к улучшению клинической симптоматики и гемодинамических параметров, а также выживаемости больных с ЛАГ [1–15]. Однако фармакокинетические характеристики препарата, а именно короткий период полужизни (5 минут), инактивация в кислой желудочной среде требуют проведения постоянной внутривенной инфузии. Необходимыми условиями для проведения постоянной внутривенной инфузии являются: катетеризация легочной артерии при помощи центрального венозного катетера и наличие портативной инфузионной помпы, в которую лекарственное вещество поступает из специальной охладительной установки. Это определяет возможные осложнения терапии – тромботические, инфекционные, связанные с потенциальной опасностью прекращения инфузии при нарушении работы помпы.
В последующие годы были созданы стабильные аналоги простациклина с целью улучшения возможностей терапии простаноидами – это тре-простинил для подкожной инфузии, ингаляционный илопрост, пероральный берапрост [1,15]. Терапия простаноидами сопряжена с потенциальными осложнениями. Так при подкожном введении трепростинила часто возникают местные реакции. Илопрост требует частого применения (до 9 раз в сутки). Первый простаноид для перорального применения берапрост у больных с ЛАГ улучшал переносимость физических нагрузок и ряд клинических показателей при краткосрочном применении (12 недель), однако, не оказывал влияние на функциональный класс больных и гемодинамические параметры при длительном применении [1].
Селексипаг
Селексипаг – первый представитель нового класса лекарственных препаратов для лечения ЛАГ, селективный агонист рецепторов простациклина (типа IP) для перорального применения. Этот дериват дифенилпиразина по химической структуре отличается от простациклина или его стабильных аналогов. В результате ферментативного гидролиза селексипаг превращается в активный, длительно действующий метаболит (ACT-333679 или MRE-269) с периодом полувыведения около 8 часов [16]. В отличие от аналогов простациклина метаболит селексипага обладает высокой селективностью в отношении рецепторов простациклина (IP). Селексипаг оказывает более выраженный вазодилатирующий эффект по сравнению с берапростом или илопростом, что, по-видимому, связано со структурными различиями, отсутствием тропности к рецепторам типа EP3, с активацией которых связана вазоконстрикция [17].
На монокроталиновой модели ЛАГ было показано, что селексипаг благоприятно воздействовал на функцию эндотелия, уменьшал гипертрофию сосудистой стенки легочных артерий и правого желудочка, улучшал выживаемость крыс (45-дневная выживаемость составляла 73% у крыс, получавших селексипаг по сравнению с 33% – в группе плацебо, p<0,03) [17]. В исследовании фаза II у больных с ЛАГ селексипаг в дозах 800 мг 2 раза в сутки к 17 неделе лечения приводил к существенному снижению легочного сосудистого сопротивления (–33% по сравнению с плацебо, p<0,0022) и некоторому приросту дистанции в тесте 6-минутной ходьбы (Т6МХ) (+24,7м по сравнению с исходным). Терапия отличалась хорошей переносимостью [18].
В настоящее время селексипаг исследуется в исследовании GRIPHON (ACT-293987 in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension) фазы III – рандомизированном, двойном слепом, плацебоконтролируемом клиническом исследовании. Первичной конечной точкой, также как в исследовании SERAPHIN, является время до развития первого клинического события [19]. Предварительные результаты ожидаются совсем скоро, во 2-й половине 2013г.
Пероральная форма трепростинила
Трепростинила диэтаноламин – это новая форма трепростинила с замедленным освобождением для приема 2 раза в сутки. В исследовании FREEDOM-C (Efficacy and Safety of Oral UT-15C Tablets to Treat Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension) фазы II у больных с тяжелой ЛАГ не удалось достигнуть первичной конечной точки. На фоне предшествующей терапии бозентаном и/ или силденафилом пероральный трепростинил не приводил к достоверному увеличению дистанции в Т6МХ к неделе 16, что, по-видимому, было связано с начальной титрацией дозы препарата. Вместе с тем при анализе вторичных конечных точек были обнаружены достоверные данные [20].
В международном, многоцентровом, рандомизированном, двойном слепом, плацебокон-тролируемом исследовании III фазы FREEDOM-M у больных ЛАГ к 12 неделе лечения у больных, получавших исключительно трепростинил, медиана прироста дистанции в Т6МХ составила +25 м по сравнению с –5 м в группе плацебо (первичная конечная точка) (р=0,0125, n=228) [21]. При этом трепростинил per os не оказывал влияния на индекс одышки по Боргу, функциональный класс, время до развития клинического ухудшения (вторичные конечные точки). В исследовании FREEDOM-C(2) с пероральным трепростинилом у больных с ЛАГ, получавших АРЭ и/или ингибиторы фосфодиэстеразы типа 5, первичная конечная точка не была достигнута [22].
Донаторы NO
Обоснованием для применения NO у больных с ЛАГ является сниженная экспрессия NO-синтазы и уменьшение продукции эндогенного NO [1,5,23,24]. Ингаляционный NO широко используется для проведения острых фармакологических тестов для выявления пациентов ЛАГ с потенциальным ответом на антагонисты кальция [25]. Вместе с тем терапия NO в виде ингаляций ограничивается техническими сложностями, а также потенциальным риском развития феномена отмены при внезапном прекращении терапии [1].
Альтернативой ингаляционному NO для повышения содержания эндогенного NO является использование субстрата для синтеза – L-аргинина, а также ИФДЭ5. Последние усиливают вазодилатирующие свойства эндогенного NO, предотвращая деградацию циклического гуанозинмонофосфата (цГМФ), что способствует релаксации ГМК и повышению легочного кровотока. При ЛАГ ИФДЭ5 показали эффективность при краткосрочном и длительном применении [1].
NO связывается с растворимой гуанилатци-клазой, что способствует превращению гуанозин-59-трифосфата в цГМФ. В результате происходит вазодилатация, подавление агрегации тромбоцитов, а также пролиферации гладкомышечных клеток [26,27].
Риосигуат
Риосигуат – первый препарат из класса акти- ваторов гуанилатциклазы, действие которого не зависит от исходной концентрации NO. Кроме того, препарат повышает чувствительность фермента к эндогенному NO. С теоретической точки зрения это должно приводить к более мощному терапевтическому действию риосигуата по сравнению с ИФДЭ5, эффект которых зависит от исходной экспрессии NO [4]. На экспериментальных моделях ЛАГ у животных было показано, что ри-осигуат улучшает легочную гемодинамику, предотвращает и способствует частичной реверсии ремоделирования мелких легочных артерий и гипертрофии правого желудочка [28].
Риосигуат вызывал снижение ДЛА, легочного сосудистого сопротивления и общего периферического сопротивления, а также повышал сердечный индекс (p<0,02 по сравнению с исходным для всех указанных показателей) [29]. В исследовании фазы II больные с умеренной и тяжелой ЛАГ или хронической тромбоэмболической легочной гипертензией (ФК II-III) риосигуат к 12 неделе приводил к достоверному снижению легочного сосудистого сопротивления (–215 дин/сек/см-5 по сравнению с исходным; p< 0,0001) и увеличению дистанции в Т6МХ (+55 м и +57 м по сравнению с исходным у больных с хронической тромбоэмболической легочной гипертензией и ЛАГ, соответственно, p<0,0001) при хорошей переносимости [30,31].
В ближайшее время ожидаются результаты недавно завершившегося рандомизированного, плацебоконтролируемого исследования фазы III у больных с ЛАГ [32] и хронической тромбоэмболической легочной гипертензией [33]. Первичной конечной точкой в этих исследованиях явилась динамика дистанции в Т6МХ к 12 и 16 неделе лечения соответственно.
Лекарственные препараты, воздействующие на новые мишени ЛАГ
Ингибиторы тирозинкиназы
Современные представления о патогенезе ЛАГ указывают на роль вазоконстрикции и структурного ремоделирования легочных сосудов. В то время как вазодилатирующий эффект является основой действия большинства препаратов для специфической терапии ЛАГ, их влияние непосредственно на перестройку сосудистой стенки ограничено [1,4].
Ремоделирование легочных артерий при ЛАГ имеет общие черты с формированием опухолевого процесса. Это повышенная клеточная пролиферация и воспаление, подавление апоптоза, изменения метаболизма клеток [34]. Показано, что множество факторов роста вовлечены в аномальный клеточный ответ при ремоделировании легочных артерий, в частности, тромбоцитарный фактор роста (PDGF), фактор роста фибробластов, эпидермальный фактор роста, фактор роста сосудистого эндотелия. Большинство из них реализуют свое действие за счет связывания с трансмембранными рецепторами тирозинкиназы [35].
Ряд ингибиторов тирозинкиназы создавались для лечения онкологических заболеваний, некоторые из них исследовались при ЛАГ [36]. Особого внимания заслуживают вопросы безопасности этой терапии, в особенности при ЛАГ важен аспект потенциальной кардиотоксичности [37].
Иматиниб
Тромбоцитарный фактор роста при ЛАГ способствует повышенной пролиферации и миграции гладкомышечных клеток в стенке мелких легочных артерий [64]. При морфологическом исследовании легочной ткани больных с ЛАГ была показана повышенная экспрессия рецепторов PDGF [38]. Иматиниб – пероральный ингибитор РDGF, одобренный для лечения хронического миелолейкоза и ряда опухолей желудочно-кишечного тракта. Ингибирование PDGF с помощью иматиниба приводит к реверсии легочного сосудистого ремоделирования в экспериментальной модели ЛАГ у крыс [39]. In vitro в культуре гладкомышечных клеток легочных артерий больных с ЛАГ иматиниб показал способность оказывать антипролиферативный эффект и способствовать апоптозу [40].
В клинических условиях, как показали небольшие исследования и серии случаев ЛАГ, иматиниб подавлял повышенную экспрессию PDGF, улучшал гемодинамические параметры [41]. Однако выраженные побочные эффекты, выявленные у ряда больных с ЛАГ, в частности почечная недостаточность и гепатотоксичность, потребовали особого внимания к аспекту безопасности лечения [42]. При 24-недельном исследовании фазы II у 59 больных с ЛАГ (ФК II–IV) достоверных различий по первичной конечной точке между группами лечения отмечено не было: прирост дистанции в Т6МХ составил +22 м в группе иматиниба по сравнению с плацебо (-1 м). В группе с величиной легочного сосудистого сопротивления, превышавшей 800 дин/сек/см-5, эффект лечения был более выраженным, чем у больных с величиной <800 дин/сек/см-5. Существенное улучшение было выявлено по вторичным конечным точкам, включая динамику легочного сосудистого сопротивления (–300 дин/сек/см-5; по сравнению -78 дин/сек/см-5 в группе плацебо, p<0,01) и сердеч- ного выброса (+0,6 л/мин-1 по сравнению с –0,1 л/мин-1; в группе плацебо, p<0,02). Серьезные побочные явления (сердечный арест, синкопе и пресинкопе, печеночная недостаточность и прогрессирование ЛАГ) отмечались у 39% больных в группе иматиниба [43].
В исследовании фазы III, IMPRES (Imatinib Improves Exercise Capacity and Hemodynamics at 24 Weeks as Add-on Therapy in Symptomatic Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Patients) у 202 пациентов (группа иматиниба n=103, группа плацебо n=99) в возрасте 18-77лет иматиниб в стартовой дозе 200 мг с титрацией через 2 нед. до 400 мг однократно в сутки сравнивается с плацебо. В исследование включались пациенты ЛАГ с величиной легочного сосудистого сопротивления, превышавшей 800 дин/сек/см-5, несмотря на прием 2-х препаратов специфической терапии ЛАГ. Первичной конечной точкой является динамика дистанции в Т6МХ к 24 неделе. Вторичные конечные точки включают динамику гемодинамических параметров, уровни NT-pro-BNP, а также время до развития клинического ухудшения, безопасность и переносимость лечения. 24-недельное наблюдение в исследовании завершили 67% больных в группе иматиниба и 82% больных в группе плацебо. 67,7% больных имели исходно функциональный класс III и среднюю дистанцию в Т6МХ 344 м (337 и 351 м в группах иматиниба и плацебо, соответственно). В результате терапии прирост дистанции в Т6МХ составил +32 м; p=0,002). Легочное сосудистое сопротивление снизилось на –379 дин/сек/см-5, p<0,001), сердечный индекс повысился на +0,88 л/мин/ м2, p<0,001). Уровень NT-pro-BNP уменьшился, в среднем, на –45,10 пмоль/л, p=0,04). Время до развития клинического ухудшения достоверно не изменилось. Частота нежелательных явлений оказалась сопоставимой в группах иматиниба и плацебо – 97% и 96%, соответственно. Серьезные нежелательные явления отмечались у 44% и 30% больных в группах иматиниба и плацебо [45]. Результаты 4-х летнего наблюдения в продолжении исследования IMPRES ожидаются в ближайшее время [46].
Нилотиниб
Нилотиниб – ингибитор тирозинкиназы второго поколения, созданный специально для преодоления резистентности иматиниба, что отмечалось при хроническом миелолейкозе. Этот препарат имеет более благоприятный профиль переносимости по сравнению с иматинибом, хотя имеется риск кардиальных осложнений, включая удлинение QT и внезапную смерть [47]. В монокрота линовой модели ЛАГ у крыс нилотиниб вызывал большее снижение давления в правом желудочке и индекса Fulton (показателя гипертрофии правого желудочка), а также значительные позитивные изменения морфологической картины по сравнению с иматинибом [48]. 24-недельное, плацебоконтролируемое исследование фазы II проходит для оценки эффективности, безопасности, переносимости и фармакокинетики нило-тиниба у больных с недостаточным ответом на предшествующую специфическую терапию ЛАГ [76]. В качестве первичной конечной точки будет оцениваться динамика легочного сосудистого сопротивления [49].
Антагонисты рецепторов серотонина
На роль серотонина (5-HT) в развитии ЛАГ указывает связь случаев заболевания с приемом серотонинергических аноректиков (аминорекс и дексфенфлюрамин) [50]. Серотонин способствует формированию и прогрессированию ЛАГ вследствие вазоконстрикции и ремоделирования легочных сосудов за счет пролиферации фибробластов и гладкомышечных клеток [51]. При ЛАГ выявлено повышение плазменных концентраций серотонина и повышение экспрессии переносчиков серотонина [52, 53]. В экспериментальных работах было показано, что эндогенный серотонин потенцирует развитие гипоксической ЛАГ у крыс [541], а блокада рецепторов серотонина предотвращает развитие заболевания [55]. В клинических условиях при применении ингибиторов обратного захвата серотонина наблюдалось снижение смертности у больных с ЛАГ, хотя доказательная база в пользу их применения недостаточна, что требует дальнейшего изучения [56].
Тергурид
Тергурид взаимодействует с целым рядом нейротрансмиттерных рецепторов, включая допаминовые, серотониновые и α2-адренорецепторы [57]. Препарат блокирует рецепторы 5-HT2, что определяет его потенциальную роль в лечении ЛАГ [4,57]. In vitro тергурид блокирует пролиферацию и миграцию гладкомышечных клеток в культуре клеток легочных артерий, в дозозависимой манере ингибирует пролиферацию гладкомышечных клеток, нивелирует индуцированную 5-HT вазоконстрикцию легочных артерий у крыс в монокроталиновой модели. При длительном назначении предотвращает развитие и прогрессирование ЛАГ. Исследования фазы II с тергуридом у больных с ЛАГ, получающих стабильную поддерживающую терапию, проводятся в странах Евросоюза. Первичной конечной точкой является динамика легочного сосудистого сопротивления к 12 неделе лечения [58].
Таким образом, в результате углубленного изучения патогенетических механизмов ЛАГ появляются новые лекарственные препараты, с которыми связываются перспективы клинической практики. Современная специфическая терапия позволила достигнуть значительных успехов в лечении этой категории больных, однако, проблема долгосрочного прогноза пациентов, страдающих этим тяжелым недугом, остается актуальной. Дальнейшее развитие стратегии лекарственной терапии ЛАГ связано с совершенствованием внедрённых в клиническую практику препаратов, а также созданием принципиально новых лекарственных средств. В ближайшем будущем ожидаются результаты длительных исследований по изучению влияния терапии на клинические исходы, в частности, с маситентаном и селексипагом. С новыми лекарственными препаратами, возможностями генотерапии и/ или регенеративной клеточной терапии, воздействующими на альтернативные патобиологические мишени, связываются надежды на то, что результаты лечения ЛАГ возможно значительно улучшить.
Список литературы Новые возможности патогенетической терапии легочной артериальной гипертензии
- Galie N., Manes A., Negro L. et al. A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials pulmonary arterial hypertension. Eur Heart J 2009; 30: 394-403.
- Galie N., Hoeper M.M., Humbert M., et al. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension: the Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Pulmonary Hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology and the European Respiratory Society, endorsed by the International Society of Heart and Lung Transplantation. Eur Heart J 2009; 30 (20): 2 493-537.
- Humbert M., Sitbon O., Chaouat A., et al. Survival in patients with idiopathic, familial, and anorexigen-associated pulmonary arterial hypertension in the modern management era. Circulation2010; 122: 156-163.
- Rubin L.J. Therapy of pulmonary hypertension: the evolution from vasodilators to antiproliferative agents. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2002; 166: 13081309.
- Мартынюк Т.В., Чазова И.Е., Масенко В.П. и соавт. Эндотелиальная дисфункция у больных с легочной гипертензией.//Кардиология. 1997. № 10. С. 25-29.
- Stewart D.J., Levy R.D., Cernacek P. Increased plasma endothelin-1 in primary pulmonary hypertension: marker or mediator of disease? Ann Intern Med 1991; 114: 464-469.
- Shi-Wen X., Denton C.P., Dashwood M.R., et al. Fibroblast matrix gene expression and connective tissue remodeling: role of endothelin-1. J Invest Dermatol 2001; 116: 417-425.
- Yang Z., Krasnici N., Lüscher T.F. Endothelin-1 potentiates human smooth muscle cell growth to PDGF: effects of ETA and ETB receptor blockade. Circulation 1999; 100: 5-8.
- Wagner O.F., Christ G., Wojta J., et al. Polar secretion of endothelin-1 by cultured endothelial cells. J Biol Chem 1992; 267: 16066-16068.
- Iglarz M., Binkert C., Morrison K., et al. Pharmacology of macitentan, an orally active tissue-targeting dual endothelin receptor antagonist. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2008; 327: 736-745.
- Raja S.G. Macitentan: a tissue-targeting endothelin receptor antagonist for the potential oral treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Curr Opin Investig Drugs 2010; 11: 1066-1073.
- Souza R. SERAPHIN: results from a landmark study. Abstracts from ERS Congress 2012. www. clinicaltrials.gov.NCT00660179.
- McLaughlin V.V., Badesch D.B., Delcroix M., et al. End points and clinical trial design in pulmonary arterial hypertension. J Am CollCardiol 2009; 54: Suppl. 1, S97-S107.
- Humbert M., Sitbon O., Yaici A., et al. Survival in incident and prevalent cohorts of patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension. Eur Respir J 2010; 36: 549-555.
- Mubarak K.K. A review of prostaglandin analogs in the management of patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension. Respir Med 2010; 104: 9-21.
- Kuwano K., Hashino A., Asaki T., et al. 2-[4-[(5,6-diphenylpyrazin-2-yl)(isopropyl)amino] butoxy]-N-(methylsulfonyl) acetamide (NS-304), an orally available and long-acting prostacyclin receptor agonist prodrug. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2007; 322: 1181-1188.
- Kuwano K., Hashino A., Noda K., et al. A long-acting and highly selective prostacyclin receptor agonist prodrug, 2-[4-[(5,6-diphenyl pyrazin-2-yl) (isopropyl) amino] butoxy]-N-(methylsulfonyl) acetamide (NS-304), ameliorates rat pulmonary hypertension with unique relaxant responses of its active form, [4-[(5,6-diphenylpyrazin-2-yl) (isopropyl) amino] butoxy ]acetic acid (MRE-269), on rat pulmonary artery. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2008; 326: 691-699.
- Simonneau G., Lang I., Torbicki A., et al. Efficacy, safety and tolerability of ACT-293987, a novel oral, nonprostanoid, prostaglandin I2 (IP) receptor agonist: results from a phase IIa study in pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH). Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2010; 181: A2515.
- ClinicalTrials.gov. ACT-293987in pulmonary arterial hypertension.NCT01106014. http://clinicaltrials.gov/NCT01106014. July 27, 2011.
- Tapson V.F., Torres F., Kermeen F., et al. Results of the FREEDOM-C Study: a pivotal study of oral treprostinil used adjunctively with an ERA and/or PDE5-inhibitor for the treatment of PAH. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2009; 179: A1040.
- United Therapeutics. FREEDOM-M Trial of oral treprostinil in pulmonary arterial hypertension meets primary endpoint. http://ir.unither.com/releasedetail.cfm. ReleaseID5582786. May 5, 2011.
- ClinicalTrials.gov. A 16-week, international, multicenter, double blind, randomized, placebocontrolled study of the efficacy and safety of oral UT-15C sustained release tablets in subjects with pulmonary arterial hypertension (FREEDOM-C2). NCT00887978. http://clinicaltrials.gov.NCT00887978 August 9, 2011.
- Crosswhite P., Sun Z. Nitric oxide, oxidative stress and inflammation in pulmonary arterial hypertension. J Hypertens 2010; 28: 201-212.
- Giaid A., Saleh D. Reduced expression of endothelial nitric oxide synthase in the lungs of patients with pulmonary hypertension. N Engl J Med 1995; 333: 214-221.
- Sitbon O., Brenot F., Denjean A., et al. Inhaled nitric oxide as a screening vasodilator agent in primary pulmonary hypertension.A dose-response study and comparison with prostacyclin. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1995; 151: 384-389.
- Schermuly R.T., Stasch J.P., Pullamsetti S.S., et al. Expression and function of soluble guanylate cyclase in pulmonary arterial hypertension. Eur Respir J 2008; 32: 881-891.
- Mittendorf J., Weigand S., Alonso-Alija C., et al. Discovery of riociguat (BAY 63-2521): a potent, oral stimulator of soluble guanylate cyclase for the treatment of pulmonary hypertension. ChemMedChem 2009; 4: 853-865.
- Evgenov O.V., Kohane D.S., Bloch K.D., et al. Inhaled agonists of soluble guanylate cyclase induce selective pulmonary vasodilation. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2007; 176: 1138-1145.
- Grimminger F., Weimann G., Frey R., et al. First acute haemodynamic study of soluble guanylate cyclase stimulator riociguat in pulmonary hypertension. Eur Respir J 2009; 33: 785-792.
- Ghofrani H.A., Voswinckel R., Gall H., et al. Riociguat for pulmonary hypertension. Future Cardiol 2010; 6: 155-166.
- Ghofrani H.A., Hoeper M.M., Halank M., et al. Riociguat for chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension and pulmonary arterial hypertension: a phase II study. Eur Respir J 2010; 36: 792-799.
- ClinicalTrials.gov. A study to evaluate efficacy and safety of oral BAY63-2521 in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) (PATENT-1). NCT00810693. http://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00810693 Date last updated: August 4, 2011. Date last accessed: August 4,2011.
- ClinicalTrials.gov. A study to evaluate efficacy and safety of oral BAY63-2521 in patients with CTEPH (CHEST-1). NCT00855465. http://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00855465. July 27,2011.
- Sakao S., Tatsumi K. Vascular remodeling in pulmonary arterial hypertension: multiple cancerlike pathways and possible treatment modalities. Int J Cardiol 2011; 147: 4-12.
- Grimminger F., Schermuly R.T. PDGF receptor and its antagonists: role in treatment of PAH. Adv Exp Med Biol 2010; 661: 435-446.
- Steeghs N., Nortier J.W., Gelderblom H. Small molecule tyrosine kinase inhibitors in the treatment of solid tumors: an update of recent developments. Ann Surg Oncol 2007; 14: 942-953.
- Kerkela R., Grazette L., Yacobi R., et al. Cardiotoxicity of the cancer therapeutic agent imatinib mesylate. Nature Med 2006; 12: 908-916.
- Barst R.J. PDGF signaling in pulmonary arterial hypertension. J Clin Invest 2005; 115: 2691-264.
- Klein M., Schermuly R.T., Ellinghaus P., et al. Combined tyrosine and serine/threonine kinase inhibition by sorafenib prevents progression of experimental pulmonary hypertension and myocardial remodeling. Circulation 2008; 118: 2081-2090.
- Schermuly R.T., Dony E., Ghofrani H.A., et al. Reversal of experimental pulmonary hypertension by PDGF inhibition. J Clin Invest 2005; 115: 2811-2821.
- Hatano M., Yao A., Shiga T., et al. Imatinib mesylate has the potential to exert its efficacy by down-regulating the plasma concentration of platelet-derived growth factor in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension. Int Heart J 2010; 51: 272-276.
- Ghofrani H.A., Seeger W., Grimminger F. Imatinib for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension. N Engl J Med 2005; 353: 1412-1413.
- Ghofrani HA., Morrell NW., Hoeper MM., et al. Imatinib in pulmonary arterial hypertension patients with inadequate response to established therapy. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2010; 182: 1171-1177.
- Souza R., Sitbon O., Parent F., et al. Long term imatinib treatment in pulmonary arterial hypertension. Thorax 2006; 61: 736.
- ClinicalTrials.gov. Imatinib in pulmonary arterial hypertension (IMPRES). NCT00902174. http://clinicaltrials.gov/NCT00902174 December 1,2010.
- ClinicalTrials.gov. Extension to QTI571A2301 to evaluate the long-term safety, tolerability and efficacy of imatinib in severe pulmonary arterial hypertension (IMPRES Extn). NCT01117987. http://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01117987. October 22,2011.
- Kantarjian H., Giles F., Wunderle L., et al. Nilotinib in imatinibresistant CML and Philadelphia chromosome-positive ALL. N Engl J Med 2006; 354: 2542-2551.
- Duggan N., Bonneau O., Hussey M., et al. Comparison of effects of imatinib and nilotinib in a rodent model of pulmonary arterial hypertension. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2010; 181: A6304.
- ClinicalTrials.gov. Efficacy, safety, tolerability and pharmacokinetics (PK) of nilotinib (AMN107) in pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH). NCT01179737. http://clinicaltrials.gov//NCT01179737. August 10,2010.
- Abenhaim L., Moride Y., Brenot F., et al. Appetite-suppressant drugs and the risk of primary pulmonary hypertension. International Primary Pulmonary Hypertension Study Group.N Engl J Med 1996; 335: 609-616.
- Dempsie Y., MacLean M.R. Pulmonary hypertension: therapeutic targets within the serotonin system. Br J Pharmacol 2008; 155: 455-462.
- Herve' P., Launay J.-M., Scrobohaci M.-L., et al. Increased plasma serotonin in primary pulmonary hypertension. Am J Med 1995; 99: 249-254.
- Eddahibi S., Humbert M., Fadel E., et al. Serotonin transporter overexpression is responsible for pulmonary artery smooth muscle hyperplasia in primary pulmonary hypertension. J Clin Invest 2001; 108: 1141-1150.
- Eddahibi S., Raffestin B., Pham I., et al. Treatment with 5-HT potentiates development of pulmonary hypertension in chronically hypoxic rats. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 1997; 41: H1173-H1181.
- Hironaka E., Hongo M., Sakai A., et al. Serotonin receptor antagonist inhibits monocrotaline-induced pulmonary hypertension and prolongs survival in rats. Cardiovasc Res 2003; 60: 692-699.
- Shah S.J., Gomberg-Maitland M., Thenappan T., et al. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors and the incidence and outcome of pulmonary hypertension. Chest 2009; 136: 694-700.
- Dumitrascu R., Kulcke C., Konigshoff M., et al. Terguride ameliorates monocrotaline induced pulmonary hypertension inrats. Eur Respir J 2011; 37: 1104-1118.
- Ergonex. Ergonex Pharma initiates Phase II clinical trial of terguride in pulmonary arterial hypertension. www.ergonex.om/attachments/news/: January 29, 2008. 92