Numerical simulation research on cavitation flow of different fuels in diesel engine injectors
Автор: Shan Jingwei, Li Jun, Guo Zhengyang, Yang W.
Журнал: Бюллетень науки и практики @bulletennauki
Рубрика: Технические науки
Статья в выпуске: 1 т.7, 2021 года.
Бесплатный доступ
With the increasingly stringent requirements of diesel engine fuel consumption and pollutant emission, higher requirements are put forward for the performance of diesel engine fuel injection systems. Cavitation flow in diesel fuel injectors is an extremely important factor affecting spray characteristics. In this study, the occurrence of cavitation in the fuel injector nozzle and its impact on mass flow rate and vapor fraction at the outlet of the fuel injection hole are studied numerically for various fuels such as diesel, gasoline, ethanol and methanol. The results show that the mass flow rate of diesel is the highest and that of gasoline is the lowest. Methanol and gasoline have the highest vapor content, followed by ethanol, and then diesel with the lowest vapor phase. For mass flow, the mass flow is inversely proportional to the viscosity of the fuel, and for cavitation, the amount cavitation is inversely related to the viscosity of the fuel. This agrees with many researchers’ findings.
Cfd, diesel engine, nozzle holes, cavitation, atomization
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/14117931
IDR: 14117931 | УДК: 662.7 | DOI: 10.33619/2414-2948/62/25
Текст научной статьи Numerical simulation research on cavitation flow of different fuels in diesel engine injectors
Бюллетень науки и практики / Bulletin of Science and Practice
Nowadays, the total amount of global automobile are showing an increasing trend. Emissions such as and have caused pollution problems, while inefficient automobiles have generated more and. With the shortage of energy and the environmental deterioration, countries all over the world are strengthening the control of vehicle emissions. People have put forward higher requirements for the overall performance of diesel engines to improve efficient of vehicle fuel.
Diesel engine as a power source is widely used into our daily life, the fuel injection system plays a key role in the performance of engine. The nozzle is an important part of fuel injection system, the internal flow of fuel in the nozzle directly affects the atomization of fuel. The main factors that affect fuel cavitation include injection pressure, ambient pressure, temperature, combustor configuration, nozzle structure [1–5].
For a long time, increasing the injection pressure has been an important method to improve the atomization. Higher injection pressure will not only improve the atomization effect of fuel, but also reduce the emission of poisonous gas. Cavitation can improve the atomization effect of the fuel, but it will also erode the needle valve, thereby reducing the use time of the fuel injector. Therefore, it is necessary to study the cavitation in the nozzle.
Cavitation is one of the most important parameters affecting fuel atomization, it will directly affect the process of combustion [6]. Cavitation must have three elements: low pressure, acting time of low pressure and cavitation core. Nowadays, the physical properties of nozzle cavitation in diesel engines are not fully understood, many researchers have used experiments and computer simulations to better understand the phenomenon. At present, the experiments for cavitation in nozzle can be divided into visual tests based on actual size nozzle and enlarged size nozzle. The visualization of nozzle was carried out based on the actual size of the nozzle (about 0.2 mm) and injection pressure (about 10 ~ 100 MPa), these are very similar to the fuel injection engines used in real internal combustion engines, so the experimental results can better reflect the cavitation in nozzle. However, if the nozzle diameter is too small and the injection pressure is too high, it will significantly increase the difficulty of visual testing [7]. The theoretical basis of the visual test based on the enlarged size nozzle is that under the condition that the Reynolds number and cavitation number are consistent, the distribution of the gas phase region in the orifice with different sizes has a high degree of similarity. However, there is a certain degree of difference between the experimental results obtained by this method and the cavitation in the actual nozzle [8]. CFD is also widely used in the study of cavitation in nozzle. It is not limited by the nozzle shape, nozzle size, injection pressure and other conditions, and can provide the flow situation in the nozzle [9]. In this study, the effects of injection pressure on cavitation will be investigated. A comparison on the amount of cavitation between diesel, gasoline, ethanol and methanol will hopefully give a better understanding of how the various properties of the fuels affect cavitation. This study seeks to understand the how the injection pressure affects cavitation of various fuels.
Бюллетень науки и практики / Bulletin of Science and Practice Т. 7. №1. 2021
Methodology and diesel nozzle geometry
In this study, the commercial computational fluid dynamics (CFD) software ANSYS FLUENT was used for the numerical study. The models used are RNG turbulence model and Schnerr and Sauer cavitation model to predict onset of cavitation. The fuels tested are diesel, gasoline, methanol and ethanol. The mesh of the nozzle created above will be used. For this study, the outlet pressure is kept constant at 40 bar. The inlet pressure tested are of 50, 100, 200, 400, 600, 1000, 1500 and 2000 bar.
The mass flow rate is also calculated in the study [10]. The mass flow rate m ̇ is calculated as:
m = AC a ^PP j P (1)
where ρ is the density of the liquid-vapor fuel mixture at the nozzle outlet, A is the cross-P sectional area of the nozzle outlet orifice, inj and Pv are the injection pressure and vapor pressure of the fuel respectively. Ca is the coefficient of contraction as follows:
a
= C D
P - P injv
∆ P
where C is the coefficient of discharge and Δ P is the difference between the injection pressure and ambient pressure. C is given as:
CD
1 pV2 2
∆ P
where V is the velocity of the liquid-vapor fuel mixture.
Reynolds number is a dimensionless number that is an indicator if a flow is laminar or turbulent. It is given as:
R e = ρ VD H µ
where D H is the hydraulic diameter of the flow and µ is the dynamic viscosity of the fluid.
The fuel injector used in this project was scanned by X-ray and 3D model and mesh has been created by using ANSYS, as shown in Figure 1. Important dimensions include the nozzle outlet orifice diameter of 138µm and the fully raised needle lift height of 200µm. The injector is a multihole injector whereby fuel is injected into the combustion chamber through multiple nozzles. For the following studies, only one orifice hole will be modelled. As such, it is assumed that flow is symmetric across all the orifices. The studies will be exploring two-dimensional flows which is adequate for cavitation modelling [11].
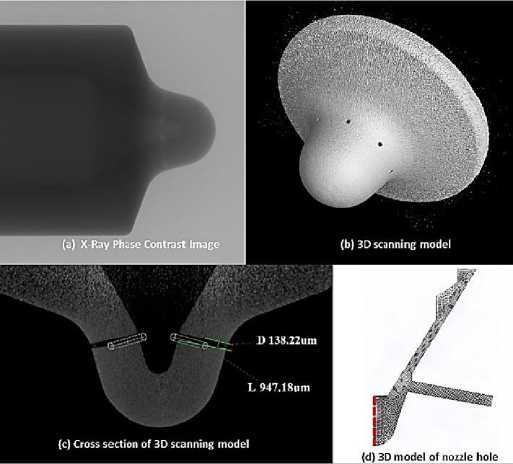
Figure 1. 3D model of the fuel injection hole and mesh.
Results and discussion
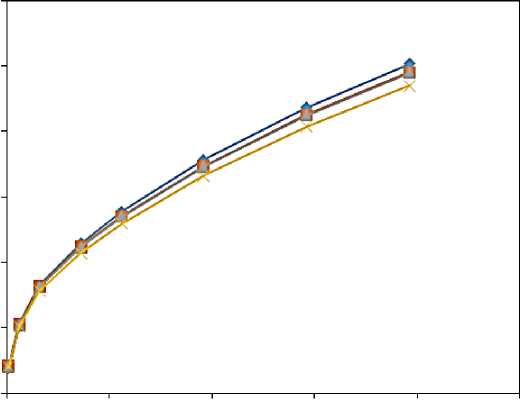
A graph of mass flow rate in Figure 2, vapor fraction in Figure 3 and turbulent kinetic energy in figure 4 at outlet against pressure difference is plotted.
Diesel has the highest mass flow rate followed by the alcohols which have similar mass flow rate and lastly is gasoline. This is because diesel has the highest density; methanol and ethanol have similar densities and gasoline has the lowest density. Up to about pressure difference of 160 bar, the mass flow rate of all the fuels are about the same. This is because cavitation does not occur before that.
6.00
5.00
5 4.00
£ 3.00 о —I UI
5 2.00
1.00
0.00
—♦—DIESEL —П—METHANOL —S—ETHANOL —^GASOLINE
0 500 1000 15 00 2000 25 00
DP (BAR)
Figure 2. Mass flow rate against difference in pressure.
For vapor fraction at outlet, a key trend has been noticed that inversely correlates to the viscosity of each fuel. Reynolds number is inversely proportional to dynamic viscosity. With higher Reynolds number, cavitation will be stronger [12]. This shows in the results as seen in figure 3 as gasoline and methanol, which have similar and lowest dynamic viscosity, has the highest vapor fraction with similar results. This is followed by ethanol which has almost twice the viscosity of ethanol and gasoline. Diesel which has twice the dynamic viscosity of methanol has the lowest vapor fraction at outlet.
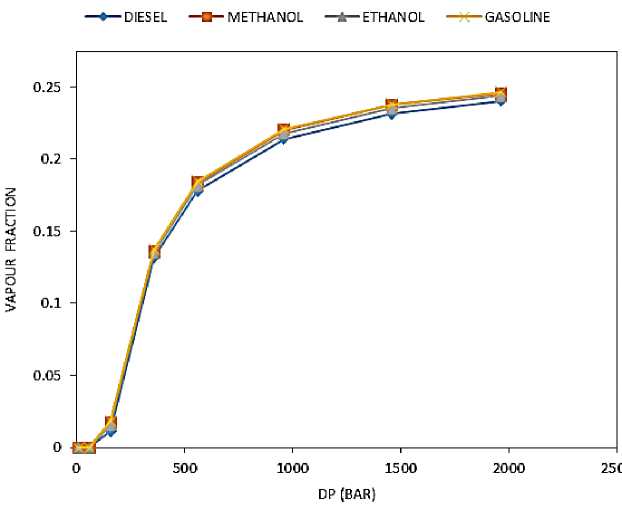
Figure 3. Vapor fraction at outlet against difference in pressure.
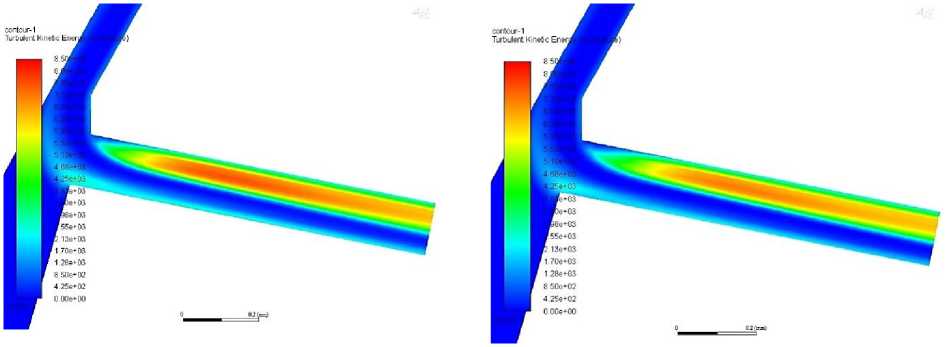
Looking at the graph of turbulent kinetic energy (TKE) in figure x at outlet, gasoline has the highest TKE and has the highest vapor fraction. Ethanol has lower TKE and vapor fraction that gasoline. Diesel has the lowest vapor fraction but the second lowest TKE. Methanol on the other hand, which has similar viscosity to gasoline, has the highest vapor fraction together with gasoline but the lowest TKE. Contours drawn as seen in figure 5 on ANSYS Fluent comparing the turbulence in the nozzle at an injection pressure of 1500 bar of the different fuels show that methanol has a later onset and less intense turbulence further from the nozzle orifice entrance.
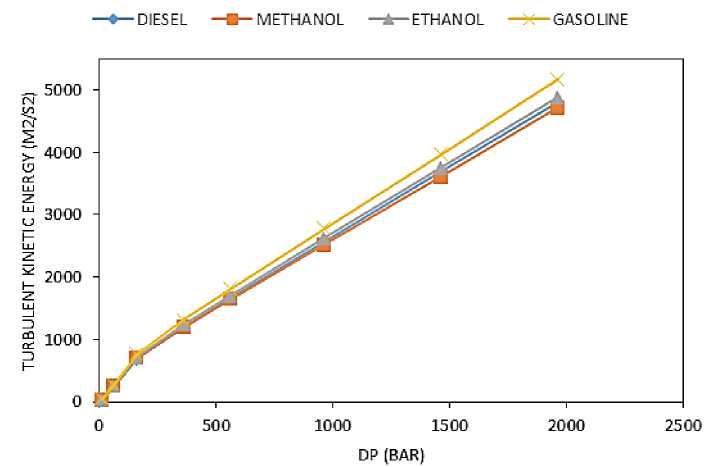
Figure 4. Turbulent kinetic energy at outlet against difference in pressure.
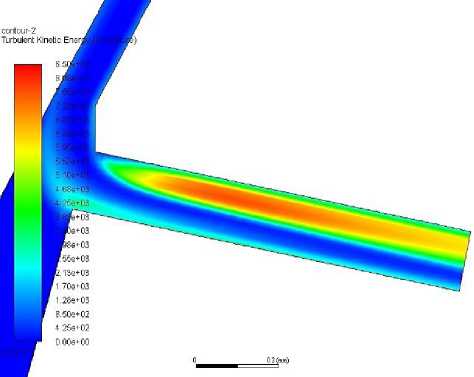
Diesel
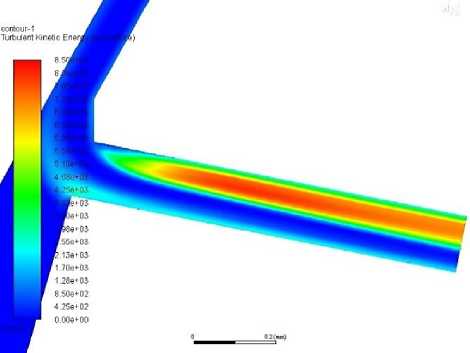
Ethanol
Methanol
Figure 5. TKE for various fuels at 1500bar injection pressure.
Conclusion
A numerical study was performed to investigate the effect of different fuels and injection pressure on the cavitation in the nozzle. The following observations were made based on the results from the numerical simulations performed.
-
1) Gasoline had the lowest mass flow rate as it has the lowest density. Ethanol and methanol have similar densities and as such have a higher mass flow rate than gasoline. Diesel has the highest density which caused it to have the highest mass flow rate.
-
2) For cavitation, the amount cavitation is inversely related to the viscosity of the fuel. This agrees with many researchers’ findings. Methanol and gasoline have the lowest viscosities and thus has the largest vapor fraction at the nozzle outlet. This is then followed by ethanol and then diesel which has the least amount of vapor fraction.
The research results show that the model can better predict the cavitation phenomenon in the diesel injector. In the future, the model will be extended to 3D to gain a deeper understanding of the flow phenomena in the injector and reconstruct it with the injection process to accurately capture spray development and fragmentation.
Список литературы Numerical simulation research on cavitation flow of different fuels in diesel engine injectors
- He Z., Zhuang Sh., Wang Q., Zhong W., Tao X. Experimental study of cavitating flow inside vertical multi-hole nozzles with different length-diameter ratios using diesel and biodiesel // Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science. 2015. V. 60 P. 252-262. DOI: 10.1016/J.EXPTHERMFLUSCI.2014.09.015
- John P. A., Neeft M. M., Jacob A. Diesel particulate emission control // Moulijn. Fuel Processing Technology. 1996. V. 1.
- Reitz R. D. Directions in internal combustion engine research // Combustion and Flame. 2013. V. 1.
- Delacourt E., Desmet B., Besson B. Characterisation of very high pressure diesel sprays using digital imaging techniques // Fuel. 2005. V. 7.
- Thombare D. G., Verma S. K. Technological development in the Stirling cycle engines // Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews. 2008. V. 12. №1.
- Tamaki N., Shimizu M., Hiroyasu H. Enhancement of the Atomization of a Liquid Jet by Cavitation in a Nozzle Hole // Atomization and Sprays. 2001. V. 11. P. 125-137.
- Arcoumanis C., Badami M., Flora H., Gavaises M. Cavitation in Real Size Multi-Hole Diesel Injector Nozzles. SAE Paper, 2000.
- Reid B. A., Hargrave G. K., Garner C. P., Wigley G. An investigation of string cavitation in a true-scale fuel injector flow geometry at high pressure // The Physics of Fluids. 2010.
- Bastawissi E. D., Elkelawy M. Computational evaluation of nozzle flow and cavitation characteristics in a diesel injector // Journal of Applied Research in Intellectual Disabilities Jarid. 2012.
- Mohan B. Performance and emission optimization of CIDI engine through various fuel injection strategies // National University of Singapore. 2015.
- Los Alamos Nation Laboratory. KIVA - Hydrodynamics Model for Chemically Reacting Flow with Spray. P. 5315.
- Mohan B., Yang W., Chou S. Cavitation in injector nozzle holes - A parametric study // Eng Appl Comput Fluid Mech. 2014. V. 8. №1. P. 70-81.


