О моделировании изменения смачиваемости металлической поверхности при лазерном текстурировании рельефа
Автор: Рыженков Артем Вячеславович, Дасаев Марат Равилевич, Григорьев Сергей Владимирович, Трушин Евгений Сергеевич
Журнал: Вестник Южно-Уральского государственного университета. Серия: Энергетика @vestnik-susu-power
Рубрика: Теплоэнергетика
Статья в выпуске: 4 т.21, 2021 года.
Бесплатный доступ
В последние годы со стороны исследователей возрос интерес к управлению смачиваемостью металлических поверхностей различными жидкостями в связи с широким спектром областей применения. В частности, применение гидрофобных функциональных поверхностей в теплоэнергетических установках и системах способствует повышению их эффективности и надежности. Несмотря на огромное количество существующих способов гидрофобизации металлических поверхностей, мировым научным сообществом был предложен и интенсивно развивается способ, основанный на текстурировании микро-/ наномасштабного рельефа с использованием лазерного оборудования (лазерная абляция). В данной работе было проведено исследование по определению влияния модификации латунных поверхностей с использованием лазерного оборудования на геометрические параметры текстурируемого рельефа и свойства смачиваемости, на основе результатов которого была предложена математическая модель прогнозирования смачиваемости.
Энергоэффективность, гидрофобность, угол смачивания, лазерное излучение, рельеф
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/147236645
IDR: 147236645 | УДК: 62-45 | DOI: 10.14529/power210402
Текст научной статьи О моделировании изменения смачиваемости металлической поверхности при лазерном текстурировании рельефа
В течени е п ос лед н и х н е ск о л ь к и х д е с ятил е ти й м и ро в ым н аучны м с оо бщ е ств о м акт и вн о ра зв ив ал о с ь на п равл ен и е , с в я з ан н о е с и с сл е д ова н и ями с в о йств с ма чив ае м о с т и твердо й по в ерх н ос ти и влия н ия с т е пе н и см ач и ва ем ости н а фу нк цио на л ьн ые сво й ст ва п овер хно ст е й ра зл ичных м ат е риа лов.
А нали з н ау ч ных п у б ли ка ци й в да н ной области по ка за л , ч т о инт е рес вызва н тем , ч то г и др оф о бны е п ове рх но с т и об л ада ют ря до м уника ль н ы х х ара к терист и к, и м еющи х ш и р ок ий сп е к т р обла ст е й п ри м е не ния . Т а к , на пр име р , и с пол ь зование гидр оф об ных п о верх но ст е й с по с об с твует с ниж е н и ю г и дравлического сопроти в лен и я п р и тр а нс по р т и ро вк е ж идк и х сред , с н и жен и ю с коро сти л ь до об р а зо ва ния, инт е нс ифи к а ци и те п ло об м е н н ы х пр оц ессов и др уг им по л ож ите ль н ым э ф фе кта м, в част н ости, г идр оф об ные ф унк цио на ль н ые п ове рх но с ти облад а ют п овы ш ен ной к о рр озио н н ой с то й к остью [ 1–10].
Для р а з р а бо тк и т е хн олог и чес ких ос н ов форм и ро в а н и я т е к ст у р ир ова н н ог о м и кр о -/наномас-шт а б н ог о р е лье ф а н а фу нк ц ио наль н ых по в е рх нос тя х эл ем ен то в те пл о энерг ети че ског о об ор удо в ания треб у е тс я п ро в е д ен ие и с сле до в а ний, включа ю щ и х чи сл е нн ое м о де л и р ова ни е значе ний у г л а с ма чи в а ния н а при м ере л а з е р но й пове р хно с т ной обработки латунных поверхностей.
Основные принципы и способы создания гидрофобных поверхностей
Согласно современной классификации по степени смачиваемости поверхностей принято различать гидрофильные и гидрофобные поверхности. В качестве количественной меры степени смачиваемости поверхности принято использовать значение угла смачивания 60 (рис. 1). Так, если значение угла смачивания твердой поверхности находится в диапазоне от 0 до 90°, то для нее свойственно смачивание жидкостью, а сама поверхность называется гидрофильной. В противном случае, когда твердая поверхность не смачивается жидкостью, а значение угла смачивания определяется диапазоном от 90 до 180°, поверхность будет являться гидрофобной.
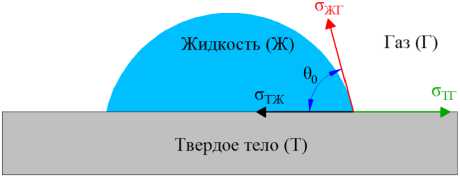
Рис. 1. Угол смачивания и силы поверхностного натяжения на границах раздела фаз:
σтг – удельная свободная поверхностная энергия твердого тела; σжг – поверхностное натяжение жидкости; σтж – межфазное натяжение на границе «твердая поверхность – жидкость»; 6 0 - угол смачивания
Величина угла смачивания может быть оценена исходя из термодинамического положения о том, что в состоянии равновесия свободная энергия системы минимальна. Впервые такая система была рассмотрена Т. Юнгом в работе [11]. В ре- зультате описания сил, действующих на каплю жидкости (см. рис. 1), было получено соотношение, именуемое уравнением Т. Юнга, использование которого позволяет рассчитать значение равновесного угла смачивания 90 твердой поверхности:
cos 90 = —Z-^ж, (1) где σ тг , σ тж и σ жжгг – соответственно поверхностные энергии на границе раздела фаз «твердое тело – газ», «твердое тело – жидкость» и «жидкость – газ».
Анализ соотношения (1) показывает, что увеличение значения угла смачивания может быть достигнуто посредством уменьшения значения поверхностной энергии σтг на границе раздела фаз «твердое тело – газ». При этом достижение гидрофобного состояния поверхности возможно только в том случае, если значение поверхностной энергии σтг будет меньшим по сравнению со значением σтж на границе «твердое тело – жидкость». Следовательно, выполнение данного условия является ключевым для получения гидрофобной поверхности.
В результате проведения экспериментальных исследований, представленных в работах [12–14], было показано, что выполнение условия, выявленного ранее из уравнения Т. Юнга, не гарантирует получение высоких значений угла смачивания. Так, для гидрофобных поверхностей, созданных на основе изменения химического состава поверхностного слоя, максимальные значения угла смачивания принимали значения 118–120°. Это связано с тем, что уравнение Т. Юнга было получено при описании сил, действующих на каплю жидкости, в условиях идеальной поверхности (однородная, гладкая и химически инертная по отношению к жидкости), вследствие чего применение полученного соотношения затруднительно к неидеальной (реальной) поверхности.
В реальных условиях применяются материалы, поверхности которых обладают шероховатостью и являются неоднородными. Согласно результатам исследований, представленных в работах [15–17], было показано, что шероховатость поверхности оказывает существенное влияние на значение угла смачивания.
В настоящее время для достижения гидрофобных свойств поверхности используют множество методов, в том числе: электроосаждение наночастиц с последующей обработкой гидрофобными материалами [18], текстурирование поверхности с целью получения упорядоченного разномасштабного рельефа [19, 20], плазмохимическое осаждение из паровой фазы [21] и другие.
Наиболее перспективным методом формирования рельефа на металлической поверхности является текстурирование с применением лазерного оборудования, то есть лазерная абляция. Такой метод за счет гибкого варьирования параметров лазерного излучения позволяет с достаточной точностью контролировать геометрические характеристики формируемого рельефа.
Лазерная абляция – оптико-термический процесс воздействия лазерного излучения на поверхность, применимый к любому материалу, поглощающему свет. Процесс лазерной абляции с использованием ультракороткого импульсного лазера при определенной частоте импульсов позволяет достигнуть высокой точности обработки поверхностей. Вместе с тем применение короткоимпульсного лазера с нано- или микросекундной частотой пульсации обеспечивает высокую скорость процесса [22, 23].
Так, анализ исследований [24–27] показал, что с целью достижения гидрофобного состояния путем модификации металлических поверхностей за счет воздействия лазерного излучения угол смачивания на поверхностях достигал значений от 120 до 171°.
Изготовление и модификация поверхности экспериментальных образцов с использованием лазерного оборудования
В качестве исследуемого материала в настоящей работе использовалась латунь марки Л63 в виде плоских пластин размерами 20×35 и толщиной 1 мм. Перед лазерной обработкой поверхности всех экспериментальных образцов очищали с использованием ультразвуковой ванны в деионизированной воде и ацетоне в течение 30 мин.
Текстурирование различных структур рельефа на поверхности латуни производилось с использованием лазерного комплекса FMark-20 NS-FB. Данный лазерный комплекс основан на инфракрасном иттербиевом волоконном лазере с длиной волны 1064 нм. Мощность лазерного излучения при обработке поверхностей образцов варьировалась в диапазоне от 10 до 20 Вт с шагом 5 Вт, а скорость сканирования – в диапазоне от 100 до 500 мм/с с шагом 100 мм/с. Частота импульсов для всех образцов была постоянна и составляла 20 кГц. Все экспериментальные исследования проводились в помещении при комнатной температуре.
С целью достижения гидрофобного состояния латунных поверхностей была произведена их модификация с использованием лазерного оборудования путем текстурирования рельефа в виде равноудаленных на 100 мкм канавок (рис. 2).
В работах [25, 26] исследовали смачиваемость медных поверхностей, текстурированных с помощью лазерного оборудования. Модифицированные образцы в первый день проявляют гидрофильность, однако со временем угол смачивания увеличивается и через 10–15 дней достигает максимального значения. Такая конверсия смачиваемости объясняется сорбцией на обработанную поверхность органических соединений, вследствие чего происходит снижение поверхностной энергии.
В связи с этим в данной работе после модификации с использованием лазерного оборудования все образцы хранились на воздухе в течение 14 дней при стандартных атмосферных условиях.
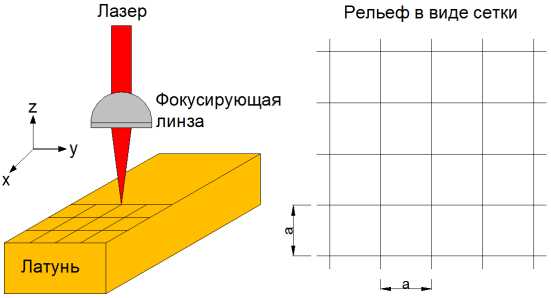
Рис. 2. Схематичное изображение траектории движения лазерного луча по поверхности
Влияние лазерной обработки на геометрические параметры формируемого рельефа и степень смачиваемости поверхности
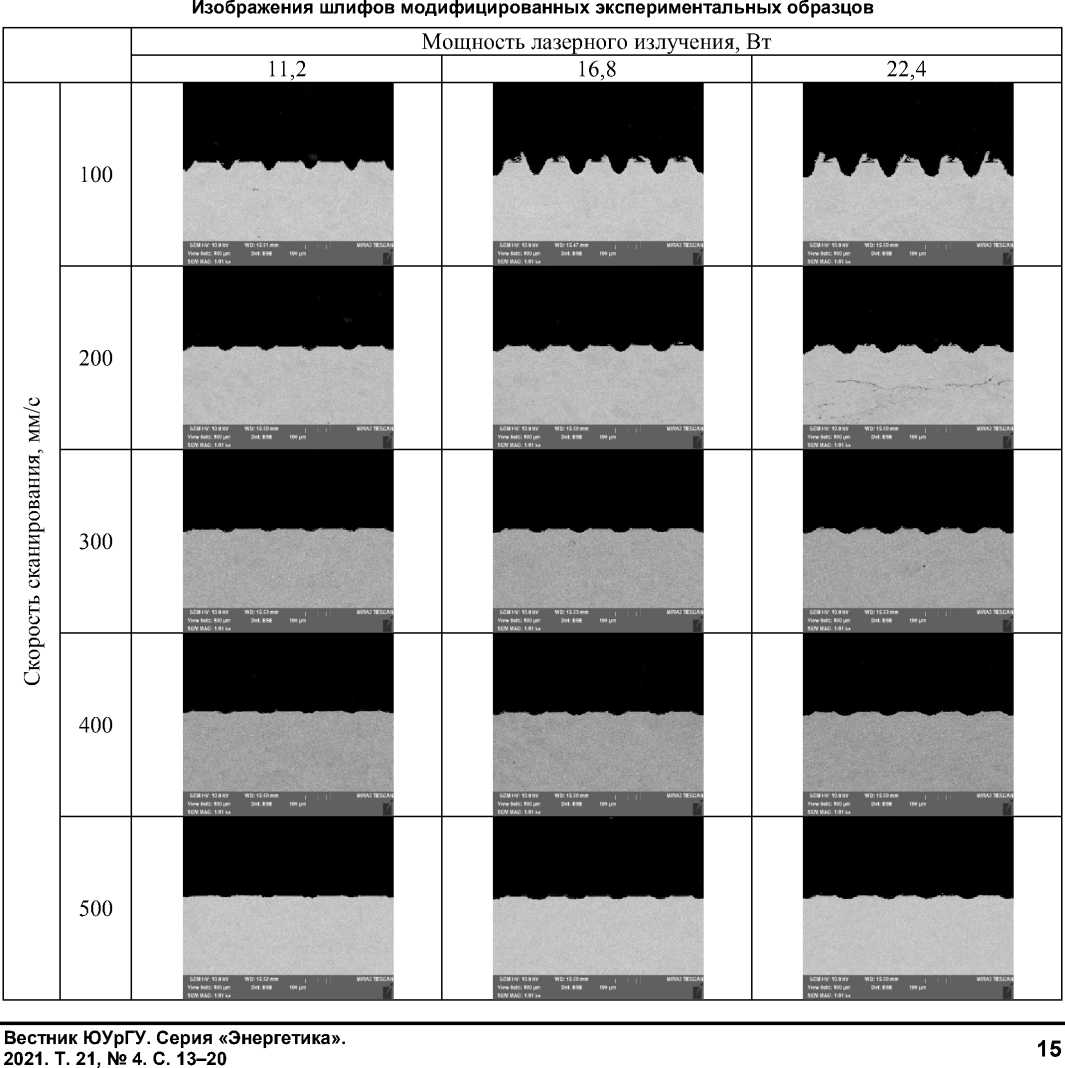
Топографию поверхности и шлифы экспериментальных образцов исследовали с использованием сканирующего электронного микроскопа Tescan MIRA 3. В табл. 1 представлены изображения шлифов, из анализа которых следует, что варьирование параметров лазерного излучения оказывает влияние на геометрические параметры текстурируемого рельефа и, как следствие, на смачиваемость поверхности.
Таблица 1
З н а чен ия уг л а с м а чив ани я л а т у н ны х п оверхностей, модифицирова н ны х с ис пол ьз ов ан ие м л азе рного об орудов ан ия, бы ли из м е ре ны с и с п ол ь зованием при бора O CA 20, п ри этом на м од ифи цир ован н у ю п ов е рх н ос ть б ыл и п оме ще ны капли дис т и л лиров а н ной в оды об ъ е мом 5 м кл . С це л ью пов ышен и я точнос т и ре зу л ьта тов з на чени я у гл а смачиван и я б ыл и из м е ре н ы на тре х ра з л ич ны х мод ифи циров а н ны х уча с тках пов е рхнос т и каж д ого экс пе рим ентал ьного обр а з ца , пр и этом опре дел ял ос ь с ре дне е з на че н ие у гла с м а чив а н ия.
Б а з ов а я пов е рх нос ть, в ка че с тв е которой и спол ьзов а л а с ь л ат у н на я пове рх нос ть в ис х о дном сос тояни и , проявл яет г ид р оф и л ь н ые с в о йс тв а , а значе ни е уг л а с м а чив а н ия с ос та в л яет 81, 8° . В рез ул ь та те л а з е рного те кст ур иров а н ия л а т у н ны х о б ра зц ов в се пов е рхнос т и с та ли ги дрофобным и, а з на че н ие у гл а с м а ч ив ани я дл я в с ех м одиф иц иров ан н ы х п ов ерхн осте й с ос тавл я л о бол е е 140° .
П ри этом м а кс им а л ьное з наче ние уг л а смачив ан и я, п олуче н н ого при те кс т уриров ани и ре л ье фа в в и де ра в но у д а л е н ны х на 100 м км ка на в ок, соста в ляе т 149, 2° при с корос ти прох ожде н ия л а з ерного луча по пов е рхнос ти 100 мм / с и м ощнос ти лазерного излучения 16,8 Вт.
Построение математической модели прогнозирования смачиваемости после лазерного текстурирования латунной поверхности
С ц ел ь ю изучени я в лия ни я ре л ье фа , с фо рм ир ован ного на ме та лличе с к и х пов е рхнос тя х констр укци он ны х м а те риа л о в с ис пол ьз ов ан ие м л а з ерного обор удов ани я, на с в ой ст в а с м а ч ив а е м ос ти б ыл а с оз да на м оде л ь в в и де ра в но уда л ен ных канав ок с боков ым и в ыс т у па ми на д исх од ной пов е рхностью (рис. 3).
На рис. 3 отображены основные геометрические параметры рельефа разработанной модели, где а и h1 – ширина и высота выступа, полученного вследствие наплыва расплавленного металла, b и h2 – ширина и высота канавки, образованной в результате воздействия лазерного излучения, с – ширина канала, образованного между боковыми выступами двух ближайших канавок.
В действительности на шероховатых поверхностях возможно становление следующих режимов смачивания:
-
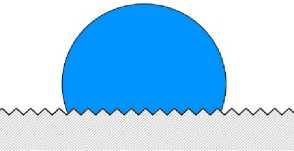
– гомогенное смачивание (рис. 4а), при котором жидкость имеет контакт со всей поверхностью, в том числе заполняя все шероховатости на ней;
-
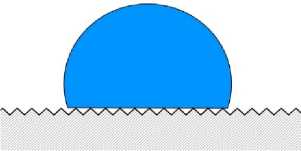
– гетерогенное смачивание (рис. 4б), когда жидкость контактирует только с выступами на поверхности, а в шероховатостях в виде пор и впадин остается воздух и нет контакта с жидкостью.
С целью определения количественной меры степени смачиваемости шероховатых поверхностей при гомогенном режиме применяется значение эффективного угла смачивания, для определения которого используется соотношение Венцеля, описанное в работе [17]:
S cos 9 = —cos 90 = rcos 90, (2)
- o
S где r =--коэффициент шероховатости, равный So отношению истинной площади поверхности 5 к кажущейся 50.
В противном случае, когда на поверхности реализуется гетерогенный режим смачивания, эффективный угол определяется из соотношения Касси – Бакстера, описанного в работе [16]:
cos 9 = / cos 90+/-1, (3)
где / = - ж - доля смачиваемых участков поверхности, определяемая отношением смоченной 5тж к фактической 5 площади поверхности.
Применение соотношений (2) и (3) для твердых поверхностей при различных режимах смачивания с целью определения значений углов воз-
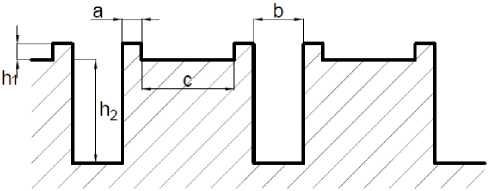
Рис. 3. Схематичное изображение модели текстурированного рельефа
а)
Рис. 4. Схематичное изображение гомогенного (а) и гетерогенного (б) режима смачивания на гидрофобной шероховатой поверхности
б)
можно лишь в том случае, если характерные геометрические параметры шероховатости значительно меньше диаметра контакта капли с поверхностью.
В соответствии с фактическим смачиванием модифицированной латунной поверхности в данной работе была создана модель смачивания, приведенная на рис. 5. Угол между линией раздела фаз «твердое тело – жидкость» и линией раздела фаз «жидкость – газ» является углом смачивания θ. Вместе с тем в модели отображены радиус r поверхности контакта капли с твердым телом и радиус R сферы капли, помещенной на поверхность.
ние поверхностной свободной энергии капли, γтж, γжг и γтг являются межфазной свободной энергией границ раздела «твердое тело – жидкость», «жид-
кость – газ» и «твердое тело – газ», соответственно. 5тж, 5жг и 5тг являются контактными площадями указанных трех фаз.
Анализ соотношений (1) и (5) показывает, что значения поверхностного напряжения и свободной
энергии одинаковы:
а = Y.
Как было указано ранее, когда капля распола-
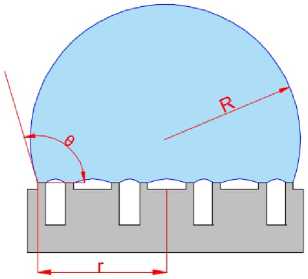
Рис. 5. Модель смачивания на текстурированном рельефе
гается на поверхности материала, она находится в равновесии. Тогда в соответствии с рис. 5 и параметрами текстуры рельефа на рис. 3 площадь по-
верхности контакта капли жидкости с твердым
телом 5тж составляет:
с _ пг2 2г 5 тж = (2г)2 ^ 7
•
2^2г 9 2а п г2
--а2 =------. 2а+Ь+ с 2а+Ь+ с
Фактическая площадь текстурированной по-
верхности определяется следующим выражением:
5 =
2а п г2
2а+Ь+ с
, 2^2 пг2
+ —2—
2а+Ь+ с
+
Ь п г2
2а+Ь+ с
+
с п г2
2а+Ь+ с
+
4^т п г2 +
2а+Ь+ с
п г2^(2а+Ь+с+4к1+2к 2 )
2а+Ь+с "
Очевидно, что объем капли, помещенной на модифицированную латунную поверхность, остается неизменным и капля будет находиться в равновесии. Тогда состояние капли на поверхности можно описать следующими уравнениями:
Тогда, подставив выражения (7) и (8), определяющие смоченную и фактическую площадь текстурированной с использованием лазерного оборудования поверхности, в уравнение Касси – Бакстера (3), получим следующее соотношение:
cos 9 =------—------(cos 90 + 1) - 1. (9)
2а+Ь+с+4к1+2к2v и
Таким образом, использование уравнения (9)
dV = 0, (4)
dG = Yтжd5тж + Yжгd5жг + YmrdS mr = 0, (5)
где dV - изменение объема капли, dG - измене-
позволяет вычислить значение угла смачивания для разработанной модели текстурированного лазерным излучением рельефа.
Как было указано ранее, варьирование параметров лазерного излучения при модификации латунной поверхности оказывает влияние на раз-
Таблица 2
Геометрические параметры текстурированного рельефа
|
№ п/п |
Мощность лазерного излучения, Вт |
Частота лазерного излучения, Гц |
Скорость сканирования, мм/с |
Геометрический параметр, мкм |
||||
|
а |
b |
с |
h i |
h2 |
||||
|
1 |
11,2 |
20000 |
100 |
13,6 |
31,2 |
37,6 |
6,5 |
18,7 |
|
2 |
200 |
7,2 |
37,7 |
50,9 |
2,0 |
9,2 |
||
|
3 |
300 |
4,6 |
39,5 |
48,7 |
2,4 |
6,6 |
||
|
4 |
400 |
5,7 |
42,3 |
49,4 |
2,4 |
5,8 |
||
|
5 |
500 |
5,6 |
31,3 |
56,5 |
2,9 |
5,4 |
||
|
6 |
16,8 |
20000 |
100 |
21,2 |
43,8 |
16,4 |
10,9 |
30,0 |
|
7 |
200 |
8,1 |
46,0 |
36,5 |
2,9 |
14,8 |
||
|
8 |
300 |
9,7 |
45,4 |
30,7 |
2,6 |
9,6 |
||
|
9 |
400 |
9,2 |
46,7 |
34,6 |
2,9 |
7,2 |
||
|
10 |
500 |
11,3 |
42,6 |
38,8 |
2,0 |
6,8 |
||
|
11 |
22,4 |
20000 |
100 |
27,8 |
44,7 |
8,4 |
10,6 |
35,9 |
|
12 |
200 |
13,6 |
52,0 |
19,9 |
4,7 |
17,7 |
||
|
13 |
300 |
11,8 |
54,2 |
21,1 |
3,1 |
13,8 |
||
|
14 |
400 |
8,4 |
56,9 |
33,6 |
2,0 |
10,0 |
||
|
15 |
500 |
7,5 |
52,5 |
27,1 |
2,3 |
8,0 |
||
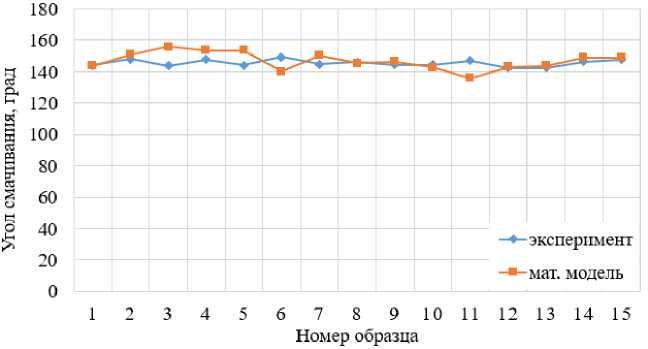
Рис. 6. Кривые значений угла смачивания, полученные путем измерений на экспериментальных образцах и расчета математической модели
ме р ге ом е триче с ких па рам е тров форм ируе м ого р ель еф а и, к ак сл е д ст в ие, на ст е п е н ь смачиваемости . С ц е ль ю вери фик ации разр аб о т а нн ой мо д е л и , с и с п о льзо ва ни ем к от о р о й по я в ля е т с я во змо ж н о с т ь п р о гн о зи р о в ат ь з н ач е ни е угла смачи в ания ил и , н ао б о р о т , о пр е д ел ят ь н еобход и мые г ео мет ри ч ес ки е п ар аме т р ы д л я д о стиже ни я мак с и ма льн о г о з н ач ения угла смачиван и я п о верх н о сти , б ыл и и зм ер ен ы о сн о в н ы е г ео мет ри ч ес ки е п ар аме т р ы т е к с ту ри р ованн о г о р ел ь еф а н а п о верх но ст ях эк с п ери мент а льных образцов, представленных в т аб л. 1 ( т а б л. 2 ) .
С и сп о л ь з ов а н ие м ура в нен ия (9) был произв ед ен рас че т з на че н и й уг л а с м а чив а н ия по ге ом етр и че ски м п ара м е тра м , пре дста в л ен ным в та б л . 2.
На рис. 6 пре дс тавл е н гра ф ик с те оре т иче с кой и экспериментальн о й кри вым и, пос трое н ным и по зн аче н иям , полу че н ным в ре зул ь та те ра с че та разр а б отан но й м а тем а тиче ской м оде л и, и з на че н иям , из ме ре нным на м одиф иц иров а н ны х с ис пол ьз ование м л аз е рного обор уд ов ан ия л ату н н ы х п ов ер х н остях, соответственно.
Таким образом, из рис. 6 в ид но , что разработан н ая м а те м а тиче ска я м оде л ь прогноз иров ани я см а чив а е м ос ти л ат у н ных п ов е рх нос тей с те кс т ур и ров а нным л а з е рным излучение м рел ье фом в в иде ра в но у дал е н ных на 100 м км ка нав ок с дос таточной точнос тью с ов пада е т с о зна че н иям и, полученными в резуль тате из м ере ний на м одифи ц ированных поверхностях.
Выводы
Определены параметры лазерного излучения, при которых на латунной поверхности достигается максимальное значение угла смачивания 149,2°, получаемого при текстурировании рельефа в виде равноудаленных на 100 мкм канавок: мощность лазерного излучения – 16,8 Вт, скорость прохождения лазерного луча по поверхности – 100 мм/с и частота импульсов – 20 кГц.
Разработана модель изменения смачиваемости поверхности на основе текстурирования разномасштабного рельефа в виде сетки с равноудаленными на 100 мкм канавками с использованием лазерного излучения, которая позволяет прогнозировать значения угла смачивания при известных значениях основных геометрических параметров рельефа или, наоборот, определять значения геометрических параметров с целью достижения требуемого значения угла смачиваемости.
Результаты были получены в рамках выполнения государственного задания Минобрнауки России по Заданию № FSWF-2020-0021 «Разработка научнотехнических основ интенсификации теплообмена при конденсации и повышения термогидродинамических характеристик и износостойкости энергетического оборудования на основе модификации функциональных поверхностей».
Список литературы О моделировании изменения смачиваемости металлической поверхности при лазерном текстурировании рельефа
- Rizhenkov A.V. About reducing the hydraulic resistance of pipeline during the oil flow. Neftyanoe Khozyaystvo - Oil Industry, 2015, vol. 11, pp. 136-139.
- Pakzad H., Liravi M., Moosavi A., Nouri-Borujerdi A., Najafkhani H. Fabrication of durable super-hydrophobic surfaces using PDMS and beeswax for drag reduction of internal turbulent flow. Applied Surface Science, 2020, vol. 513, p. 145754. DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2020.145754
- Piccolo A., Jaworski A.J. Experimental study of heat transfer characteristics of finned-tube and circular-pore heat exchangers in oscillatory flow. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2020, p. 116022. DOI: 10.1016/j .applthermaleng.2020.116022
- Ryzhenkov O.V., Kurshakov A.V., Ryzhenkov A.V., Dasaev M.R., Grigoriev S.V. On intensification of heat exchange in steam condensers made of stainless steel and brass. International Journal of Innovative Technology and Exploring Engineering, 2019, vol. 8, pp. 2290-2294.
- Bertsche D., Knipper P., Kapfer K., Wetzel T. Experimental investigation on heat transfer in laminar, transitional and turbulent circular pipe flow with respect to flow regime boundaries. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2019, vol. 145, p. 118746. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2019.118746
- Peng Q., Jia L., Ding Y., Dang C., Yin L., Yan X. Influence of groove orientation on dropwise condensation on hydrophobic and hierarchical superhydrophobic surfaces with microgroove arrays. International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer, 2020, vol. 112, p. 104492. DOI: 10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2020.104492
- Misyura S.Y. Heat Transfer and Convection of Evaporating Sessile Droplets in Transition from Super-hydrophilic to Superhydrophobic Structured Wall: Optimization of Functional Properties. International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer, 2020, vol. 112, p. 104474.
- Samanta A., Wang Q., Shaw Scott K., Ding H. Roles of chemistry modification for laser textured metal alloys to achieve extreme surface wetting behaviors. Materials and Design, 2020, p. 108744. DOI: 10.1016/j.matdes.2020.108744
- Boinovich L.B., Emelyanenko A.M., Modestov A.D., Domantovsky A.G., Shiryaev A.A., Emelyanenko K.A., Dvoretskaya O.V., Ganne A.A. Corrosion Behavior of Superhydrophobic Aluminum Alloy in Concentrated Potassium Halide Solutions: When the Specific Anion Effect Is Manifested. Corrosion Science, 2016, vol. 112, pp. 517-527. DOI: 10.1016/j.corsci.2016.08.019
- Kotenko M., Oskarsson H., Bojesen C., Nielsen M.P. An experimental study of the drag reducing surfactant for district heating and cooling. Energy, 2019, vol. 178, pp. 72-78. DOI: 10.1016/j.energy.2019.03.134
- Young T. An Essay on the Cohesion of Fluids. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London, 1805, vol. 95, pp. 65-87. DOI: 10.1098/rstl.1805.0005
- Chen W., Fadeev A., Hsieh M., Oner D., Youngblood J., McCarthy T.J. Ultrahydrophobic and ultralyophobic surfaces: some comments and examples. Langmuir, 1999, vol. 15, pp. 3395-3399.
- Woodward I., Schofield W.C.E., Roucoules V., Badyal J.P.S. Super-hydrophobic Surfaces Produced by Plasma Fluorination of Polybutadiene Films. Langmuir, 2003, vol. 19, pp. 3432-3438.
- Tserepi A., Gogolides E., Tsougeni K., Constantoudis V., Valamontes E. Tailoring the surface topography and wetting properties of oxygen-plasma treated polydimethylsiloxane. J. Appl. Phys, 2005, vol. 98, p. 113502. DOI: /10.1063/1.2136421
- Cassie A.B.D. Contact angle. Discussions of the Faraday Society, 1948, vol. 3, p. 11.
- Cassie A.B.D., Baxter S. Wettability of porous surfaces. Trans. Faraday Soc., 1944, vol. 40, pp. 546-551.
- Wenzel R. Resistance of Solid Surfaces To Wetting By Water. Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 1936, vol. 28, pp. 988-994.
- Li S., Liu Y., Tian Z., Liu X., Han Z., Ren L. Biomimetic superhydrophobic and antibacterial stainless-steel mesh via double-potentiostatic electrodeposition and modification. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2020, p. 126355. DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2020.126355
- Liu B., Wang W., Jiang G., Mei X., Wang Z., Wang K., Cui J. Study on hierarchical structured PDMS for surface super-hydrophobicity using imprinting with ultrafast laser structured models. Applied Surface Science, 2016, vol. 364, pp. 528-538. DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.12.190
- Ryzhenkov A.V., Dasaev M.R., Grigoriev S.V., Kurshakov A.V., Ryzhenkov O.V., Lukin M.V. Hydro-phobic brass surfaces created by means of multi-scale relief. International Journal of Mechanical Engineering and Technology, 2018, vol. 9, pp. 58-70.
- Kuzminova A., Shelemin A., Kylian O., Petr M., Kratochvil J., Solar P., Biederman H. From super-hydrophilic to super-hydrophobic surfaces using plasma polymerization combined with gas aggregation source of nanoparticles. Vacuum, 2014, vol. 110, pp. 58-61. DOI: 10.1016/j.vacuum.2014.08.014
- Rafieazad M., Jaffer J.A., Cui C., Duan X., Nasiri A. Nanosecond Laser Fabrication of Hydrophobic Stainless Steel Surfaces: The Impact on Microstructure and Corrosion Resistance. Materials (Basel, Switzerland), Sep. 2018, vol. 11, pp. 1577-1591.
- Yang Z., Liu X., Tian Y. Novel Metal-organic Super-hydrophobic Surface Fabricated by Nanosecond Laser Irradiation in Solution. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2020, vol. 587, p. 124343. DOI: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2019.124343
- Yang Z., Liu X., Tian Y. Novel metal-organic superhydrophobic surface fabricated by nanosecond laser irradiation in solution. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2020, vol. 587. DOI: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2019.124343
- Won S.J., Kim H.S. Effects of laser parameters on morphological change and surface properties of aluminum alloy in masked laser surface texturing. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 2019, vol. 48, pp. 260-269.
- Shirsath G.B., Muralidhar K., Pala R.G.S., Ramkumar J. Condensation of water vapor underneath an inclined hydrophobic textured surface machined by laser and electric discharge. Applied Surface Science, 2019, vol. 484, pp. 999-1009.
- Ngo C.-V., Chun D.-M. Fast wettability transition from hydrophobic to superhydrophobic laser-textured stainless steel surfaces under low-temperature annealing. Applied Surface Science, 2017, vol. 409, pp. 232-240. DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.03.038


