Обучение долговременной памяти через предсказание событий высокой неопределенности
Автор: Сорокин А. Ю., Пугачев Л. П., Бурцев М. С.
Журнал: Труды Московского физико-технического института @trudy-mipt
Рубрика: Информатика и управление
Статья в выпуске: 4 (52) т.13, 2021 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Во многих задачах обучения с подкреплением агенту требуется запоминать информацию из прошлого, необходимую для принятия эффективных решений. Причем момент наблюдения полезной информации может быть удален от момента использования этой информации на тысячи или миллионы временных шагов. К сожалению, применение методов обратного распространения ошибки для обнаружения и выучивания подобных временных зависимостей потребует хранения в оперативной памяти всех промежуточных вычислений нейросети для каждого из временных шагов. Однако, как мы покажем в данной работе, эти вычислительные ограничения можно обойти, если заранее найти критические моменты, когда агенту будет полезно обращение к своей рабочей памяти. Мы добавим в архитектуру агента подсеть памяти, которая будет обучаться предсказывать исходы событий, характеризующихся высокой степенью неопределенности исхода. Данную архитектуру памяти мы протестируем на классической задаче T-лабиринта и в трехмерной среде ViZDoom. Эксперименты демонстрируют, что предложенный нами метод обучается быстрее и стабильнее, чем альтернативные подходы.
Обучение с подкреплением, глубокое обучение, искусственные нейронные сети, рабочая память, частично обозреваемые среды
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/142231497
IDR: 142231497 | УДК: 004.852 | DOI: 10.53815/20726759_2021_13_4_39
Текст научной статьи Обучение долговременной памяти через предсказание событий высокой неопределенности
Память - важный механизм интеллектуального поведения, позволяющий быстро адаптироваться к изменениям [1, 2] и принимать решения в частично наблюдаемых средах [3-5]. Однако большинство успехов в области обучения с подкреплением были продемонстрированы в МППР средах [6, 7]. Несмотря на это, задачи, в которых мы не в состоянии предоставить агенту всю информацию о текущем состоянии среды, гораздо шире и возникают значительно чаще в реальном мире. Один из способов решения подобных задач - наделить агента механизмом рабочей памяти, чтобы он мог использовать историю предыдущих наблюдений, чтобы отличать состояния среды, порождающие одинаковые наблюдения.
Современные подходы реализации памяти сводятся к двум основных архитектурным решениям: использовать рекуррентные сети [8, 9], включая более сложные надстройки над ними (MANN [10, И], NeuralMap [12]), или использовать архитектуру трансформера [13, 14]. Исторически рекуррентные сети и трансформеры получили наибольшее развитие в применении к области обработки естественного языка, где существует множество зависимостей между близко стоящими в последовательности элементами, которые быстро ослабляются с увеличением расстояния между ними. Это не обязательно относится к задачам обучения с подкреплением, где агенту может понадобиться запомнить всего несколько битов информации на очень длительное время [15]. Например, имя человека или кодовый замок от двери, которую необходимо открыть.
Исследования, направленные на улучшение работы нейросетей с длинными временными зависимостями, преимущественно идут по усложнению архитектуры, наращивая размер и сложность моделей [8, 10, 16]. Например, трансформер [14] или дифференциальный нейронный компьютер [11] продемонстрировали себя значительно лучше, чем классический LSTM [17] в задачах, где временные зависимости удалены друг от друга на несколько сотен шагов. Но эти архитектуры значительно более требовательны к объемам оперативной памяти и вычислительной мощности, необходимой для обучения.
При этом рекуррентные сети и трансформеро-подобные архитектуры полагаются на то, что для выучивания длинной временной зависимости между далеким наблюдением в прошлом и действиями агента в настоящем необходимо хранить в памяти и проводить градиенты на последовательности, которая вмещает в себя представленную временную зависимость вместе со всеми промежуточными шагами. Таким образом, размер оперативной памяти, требующейся для обработки таких последовательностей, для LSTM будет расти линейно с длиной последовательности и квадратично для стабилизированного трансформера [14].
Учитывая, что минимальное расстояние между полезной информацией в прошлом и моментом её наблюдения может измеряться тысячами или даже сотнями миллионов временных шагов, подобные решения кажутся нереалистичными. В данной работе мы предлагаем подход, который позволит обучать память агента, способную находить зависимости между удаленными во времени событиями без необходимости проводить градиенты через всю последовательность наблюдений разом.
Вклад нашей работы заключается в следующем:
• мы разработали новый метод обучения долговременной памяти агента;
• мы реализовали конкретное архитектурное решение, позволяющее обучать рекуррентную нейросеть вместе с нашим методом обучения памяти;
• мы экспериментально продемонстрируем, что наше решение превосходит стандартные методы обучения памяти при условии, что все сравниваемые алгоритмы работают с подпоследовательностями наблюдений короче, чем целевая временная зависимость.
2. Обучение памяти через предсказание событий высокой неопределенности
2.1. Память как механизм минимизации неопределенности
Первая часть этой секции посвящена описанию и обоснованию нашей основной идеи. Во второй части описывается конкретная реализация для обучения памяти на основе LSTM-слоя, которую мы использовали в наших экспериментах по обучению с подкреплением.
Когда агент действует в POMDP, он не в состоянии определить оптимальный курс действий, основываясь исключительно на локальных налблюдениях. Невозможность выбрать правильное действие в случае глубокого обучения с подкреплением на практике сводится к невозможности сделать верное предсказание о последствии рассматриваемых действий. В model-based RL это может быть предсказание следующего наблюдения и награды, для model-free агентов, таких как DQN [6] и актор-критик [4], в основе обучения лежит предсказание ожидаемой дисконтированной будущей награды.
Память в этом случае способна помочь, если среди прошлых наблюдений агента находится информация, позволяющая ему принять оптимальное решение. То есть информация, которая способна помочь сделать нам верное предсказание относительно последствий доступных действий.
Например, если агент предсказывает будущие последствия ft для действия at и наблюдения ot. Тогда наше прошлое наблюдение ot-k может иметь полезную для нас информацию, если Р(ft, ot-k |at, ot) = P(ft\at, ot)P(ot-k \at, ot). Можно сказать что наблюдение ot-k и предсказываемая переменная ft являются началом и концом временной зависимости длины к.
Силу зависимости между прошлым наблюдением ot-k и будущим исходом ft, при наличии информации о текущем наблюдении и действии, будет передавать условная взаимная информация:
I (ft; ot-k\ot, at) = EOt,o.t~p П ) D K l [ P (ft, ot-k\at, ot)\\P (ft\at, ot)p(ot-k\at, ot)] .
Задачу обучения памяти, которая хранит наибольшее количество информации о последствиях действий агента на каждом шаге, можно формализовать как максимизацию следующей суммы относительно состояний памяти mt:
т т
^ I(ft;mt\ot,at) = ^ [Н(ft\ot,at) -Н(ft\mt,ot,at)] = (1) t=0 t=0
т т
= ^ Н(ft\ot, at) - ^ Н(ft\mt, ot, at ) . (2) t=0 t=0
Если учесть, что энтропия случайной переменной является оценкой неопределенности или неуверенности модели относительно своих предсказаний, то обучение памяти сводится к минимизации неопределенности предсказаний. В соответствии с уравнением (1) оптимальное обновление памяти на шаге t будет максимизировать количество взаимной информации между новым состоянием памяти и всеми будущими шагами в эпизоде. Таким образом, mt должно обновляться минимизируя ^T=tH(fk\mt,ok,ak) К сожалению, обучение mt в лоб потребует обработки всего эпизода целиком на каждом градиентом шаге. Вычислительная сложность такого обучения будет квадратичной О(Т 2) относительно длины эпизода.
Мы предлагаем эвристику, которая позволяет уменьшить необходимые для обучения памяти вычислительные затраты, когда среда удовлетворяет следующему ограничению. Предположим, у агента есть доступ к оптимальной памяти на каждом шаге. Тогда рассмотрим среду, в которой, при наличии оптимальной памяти, значения энтропии Н(ft\mt, ot, at)
равны (или хотя бы близки друг к другу) для всех шагов t. Эта ситуация может быть результатом стохастичности стратегии агента, погрешности в работе сенсоров робота или когда среда близка к детерминированной при оптимальной памяти. Если это условие выполняется, тогда вклад каждого временного шага в полную сумму в правой части уравнения (1) пропорционален значению Н (/t\ot,at). Другими словами, ценная информация из прошлого может внести наибольший вклад в моменты времени, когда Н(ft\ot,at~) принимает наибольшие значения.
Таким образом, вместо оптимизации памяти относительно всех будущих шагов в эпизоде можно оптимизировать память, акцентируясь лишь на шагах, когда потенциальный вклад от её использования максимален. При этом для нахождения таких шагов нет нужды обрабатывать всю последовательность разом, так как значение Н(ft\ot,at) можно оценить локально.
В данном случае высокоуровневая схема обучения памяти выглядит следующим образом:
1) генерация эпизода с оценкой неопределенности для каждого шага;
2) выбор шагов с наибольшей неопределенностью и составление из них пар (локальное наблюдение, верное значение предсказываемой переменной);
3) второй проход по эпизоду моделью памяти и обучение памяти хранить информацию для верных предсказаний наиболее неопределенных моментов в эпизоде.
2.2. Рекуррентная архитектура памяти для предсказания будущих наград
Предлагаемая выше процедура обучения требует наличия трех обучаемых компонент:
-
• Детектор Неопределенности D обучается предсказывать будущие переменные на следующем шаге на основе локальных наблюдений агента. Главное требование к данному модулю: он должен быть в состоянии оценить неуверенность модуля (uncertainty estimate) в своем следующем предсказании.
-
• Память М учится сохранять важную информацию из прошлых наблюдений.
-
• Предиктор Р учится давать точные предсказания для выбранных детектором неопределенности событий. Предиктор использует состояния памяти вместе с локальной информацией, соответствующей выбранным событиям.
Описанные выше рассуждения практически не ограничивают нас в выборе архитектур для всех трех модулей. Для того чтобы проверить работоспособность нашей идеи, мы взяли наиболее простые для реализации варианты архитектур. Ниже описана конкретная реализованная версия системы для экспериментов в обучении с подкреплением.
Целью агента в задаче обучения с подкреплением является максимизация награды в среде, поэтому в качестве целевой переменной на каждом шаге эпизода будем предсказывать дисконтированную будущую награду Rt = ^|=t 7 l-t г^. Дополнительно изменяя коэффициент дисконтирования 7, мы можем манипулировать тем, насколько далекое будущее хотим предсказывать на каждом шаге. В наших экспериментах мы в основном использовали значения 70т 0 до 0.8, таким образом акцентируя внимание на ближайших нескольких шагах.
В качестве предиктора D мы взяли алгоритм QR-DQN [18]. QR-DQN агент по умолчанию учится аппроксимировать Z^ (ot,at ) — распределение будущих дисконтированных наград для пары из наблюдения и действия. Аппроксимация распределения дает нам возможность определить неуверенность агента в своих предсказаниях. В данном случае мы предпологаем, что целевая переменная 2^ (ot, at ) имеет нормальное распределение. Это позволяет сделать два упрощения:
-
• оценить энтропию через стандартное квадратичное отклонение: Н = ln(a V 2тге);
-
• минимизировать энтропию через минимизацию средней квадратичной ошибки.
Наши эксперименты показывают, что этот метод продолжает работать, даже если распределение Ztt (ot,at ) не является гауссовым.
Используя предиктор D, мы сэплировали эпизод, одновременно оценивая дисперсию Ztt для каждого шага. Затем для каждого шага эпизода выбирались N будущих переходов с максимальной неопределенностью. Из каждого выбранного шага г с высоким значением неопределенности формировалась пара вопрос-ответ: qi = [одщ], у = Ri. Таким образом, каждому шагу t соответствовал набор из N вопросов Qt = {qt1, ..,qtN } и ответов ^t {yti , .., y-N }’
В качестве памяти М мы выбрали нейросеть с одним LSTM-слоем как самую простую и быструю для реализации архитектуру. В качестве предиктора Р использовалась простая нейросеть, которая получала на вход набор вопросов Qt и состояние памяти ht, обучаясь предсказывать yt. В качестве функции потерь мы использовали среднюю квадратичную ошибку (MSE Loss). В этой архитектуре градиенты от предиктора напрямую проходят к модулю памяти.
Совместное обучение памяти и предиктора. Схема, поясняющая принцип совместного обучения предиктора и рекуррентной памяти, представлена на рис. 1. Мы проходим рекуррентным модулем памяти по сэмплированному ранее эпизоду и каждые р шагов запускаем предиктор, который использует текущее состояние памяти hp*i, вопросы Qp*i для предсказания значений yp*i- Таким образом, на каждом шаге память М учится хранить в своем скрытом состоянии информацию, которая позволит ему сделать наиболее точные предсказания в моменты, когда он был наиболее не уверен в последствиях своих действий.
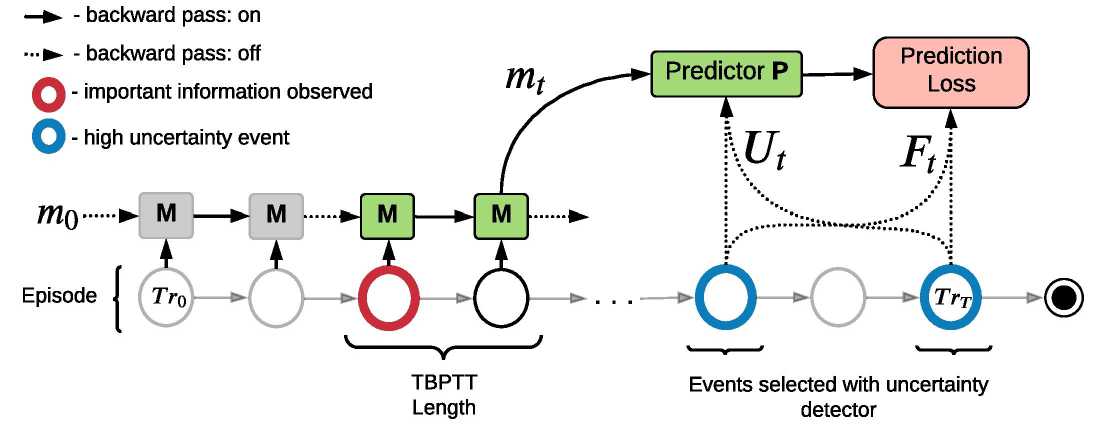
Рис. 1. Обучение памяти в алгоритме MemUP. Рекуррентный модуль памяти М последовательно обрабатывает эпизод и каждые р = 2 шагов посылает свое скрытое состояние mt (шаг t будет кратен р) предиктору Р. Синим подсвечены переходы с наибольшей оценкой неопределенности выбранные ранее при помощи детектора D. Обучающая выборка (Ut, Ft ) создается из синих переходов. Красным подсвечен переход, содержащий информацию, которая полезна для предсказания Ft в моменты времени, обозначенные синим. Р предсказывает Ft, получая на вход mt и Ut. Красные и синие переходы могут быть разделены во времени сотнями шагов, но градиенты текут от ошибок предсказаний на синих переходах до шага, на котором модуль памяти обрабатывал красный переход не более чем через р временных шагов
Соответственно, если шаги с высокой неопределенностью действительно характерезуют недостаток локальной информации, свойственной для конца длинной временной зависимости, то такая процедура позволяет нам фактически схлопнуть все промежуточные шаги для этой длинной временной зависимости и проводить градиенты от её конца до начала не более чем за р шагов. Так же нам совершенно необязательно раскручивать рекурретную нейросеть на длину всей изначальной последовательности. Достаточно длины, не мень- шей чем р шагов, что позволяет нам учить длинные временные зависимости и при этом единовременно обрабатывать только малые куски рассматриваемой последовательности.
Предобученный модуль М может быть легко скомбинирован с любым алгоритмом глубокого обучения с подкреплением. В экспериментах мы учили алгоритим РРО, который на каждом шаге получал наблюдение о- из среды, и состояние памяти mt, призведённое предобученным модулем М.
2.3. Неявная минимизация энтропии предсказаний через минимизацию средней квадратичной ошибки
В этом разделе мы используем разложение средней квадратичной ошибки для того, чтобы продемонстрировать, что при выполнении определенных ограничений на семейство распределений целевой переменной мы действительно будем обучать модуль памяти М минимизировать энтропию предсказаний при минимизации средней квадратичной ошибки предиктора Р.
Разложение ошибки, предсказывающей модели на смешение и дисперсию, является широко известным теоретическим результатом, который имеет много различных форм и вариаций [19]. В данном случае нам нужно разложить функцию потерь средней квадратичной ошибки на условную дисперсию и условное математическое ожидание. В дальнейших рассуждениях мы будем обозначать предиктор Р через выражение дд, где переменная Ө — веса нейросети предиктора, a ct — все входные данные, которые получает предиктор для вычисления предсказаний целевой переменной ft. Таким образом, получаем
Е [(ft - дд (ct))2] =Е [(ft - ЕШсН Е(ft lct) - дд (ct))2] = (За)
=е[е [((ft - Е (ft let)) + (E(ft let) - дд (ct )))2 |ct ]] =(3b)
=е[е[(ft - Е(ft|ct))2|ct] + ^(ft|ct) - дд(ct))2 +(3c)
+ 2(Еаlct) - Еаlct))(Е(ftlct) - дд(ct))] =(3d)
=E[Var(ft lct)] + Е [(Е (ft lct) - дд (ct ))2] .(3e)
Для вывода второй формулы 3b используется «law of iterated expectations». Последние два слагаемых в строке Зс получаются за счет линейности математического ожидания и того факта, что Е(ftlct ) 11 дд(ct ) являются константами. если известен ct.
В классическом случае ft и ct сэмплируются из датасета и обучаемая модель не может контролировать контекст ct, который получает в качестве входных данных. Лучшее решение, к которому может сойтись модель, будет минимизировать только второе слагаемое дд(ct ) = Е(ftlct ). Тогда как первое слагаемое останется неизменным из-за того, что совершенно не зависит от весов модели. Таким образом, минимальное достижимое значением средней квадратичной ошибки равно Е[Var(ft\а )].
Однако в случае обучения предиктора в архитектуре MemUP ct представляет собой кортеж из трех элементов [mt,ot,at ], один из которых контролируется модулем памяти. Переменные ot, at образуют локальный контекст, выбранный вместе с целевой переменной ft из траектории т детектором D. С другой стороны, mt = д^(т) — это вектор памяти, производимый модулем памяти д^ (в предыдущем разделе мы обозначали его как модуль М) в процессе обработки траектории т. На самом деле большинство предсказаний происходит, когда модуль памяти д^ обработал не всю траекторию, а только какой-то её префикс. Так же ft, ot, at взяты из более позднего перехода в траектории, чем mt, и правильнее было бы обозначать их с разными индексами. Однако для простоты нотации мы опускаем здесь эти детали. Подставив вместо контекста ct его более подробное представление в виде кортежа в итоговую формулу, из уравнения Зе мы получим
Е [(Д - дө (d))2] =Е^ог(Уч\[д1р(т ),Оі,Оі])] +
+ е ^E(/i\[g^(т), о», Оі]) - дө([gv(T),од о»]))2] .
Из полученного уравнения видно, что пока предиктор дө может влиять только на слагаемое, отвечающее за смешение предсказаний (bias), модуль памяти дф влияет и на условную дисперсию во втором слагаемом. Таким образом, минимизируя среднюю квадратичную ошибку, мы неявно учим модуль памяти д^ находить и сохранять информацию, которая поможет минимизировать условную дисперсию Vor(fi\g^p(т), о» ,Oi)
Таким образом, мы доказали, что предложенный алгоритм обучения минимизирует Vor(fi\mt, о», Oi). Однако минимизация дисперсии так же будет означать минимизацию условной энтропии того же распределения Н(fi\mt,oi,oi), если распределение принадлежит к семейству распределений, для которых энтропия является монотонной функцией от дисперсии. Примером таких распределений будут нормальное или экспоненциальное распределения (см. предположение о нормальности распределения целевой переменной в разделе 2.2).
3. Обзор работ, рассматривающих обучение долговременной памяти
Обучение долговременной памяти - это известная и давно исследуемая проблема как в обучении с учителем (SL) [20], так и обучении с подкреплением (RL) [5]. Большая часть исследований, использующих рекуррентные сети в качестве памяти, направлена на решение проблемы взрывающихся и затухающих градиентов [П, 17]. Существующий на данный момент тренд заключается в том, что предложенные решения борьбы с затухающими градиентами одновременно увеличивают количество вычислений и требуемой оперативной памяти, связанной с обучением [11]. Например, архитектура трансформер [13], доминирующая на данный момент в задачах обработки естественного языка [21, 22], требует хранения и вычисления O(N2) промежуточных результатов для обучения на последовательности длины N. Недавно предложенные модификации трансформера Linformer [23] и BigBird [24] позволяют обучать трансформеры с амортизированной сложностью в O(N ), таким образом сравниваясь по сложности с большинством архитектур на основе RNN. Стоит отметить, что большинство архитектурных решений на основе трансформера до сих пор не нашли своего применения в обучении с подкреплением.
В области обучения с подкреплением основной подход на данный момент заключается в прямом использовании рекуррентных сетей в комбинации с алгоритмами обучения с подкреплением [3, 4, 25]. Однако есть множество работ, посвященных адаптации архитектур памяти под конкретные особенности обучения с подкреплением [8, 9]. Парисотто и Салахутдинов предложили Neural Мар [12] модифицированную версию архитектуры DNC [11] для применения в задачах, связанных с ориентированием в пространстве. В работе была продемонстрирована способность агента выучить временные зависимости длиной в несколько сотен шагов в сложной трехмерной среде. Однако для применения Neural Мар необходимо хорошо знать абсолютное или относительное местоположение агента. Не совсем ясно, позволяет ли это решение сократить ресурсы, требуемые для обучения длинных временных зависимостей.
В другой статье Ха и Шмидтхубер [26] использовали сложную структуру с предобуче-нием памяти и эмбеддингов состояний. Их общий процесс обучения похож на наш, но их память обучается делать предсказания на один или несколько шагов в ближайшее будущее, тогда как мы обучаем память предсказывать произвольно удаленные в будущее события. Вейн и др. [16] предложили новый алгоритм MERLIN, который показал одни из лучших результатов на данный момент. Память MERLIN’а хранит эмбеддинги состояний в массиве, подобном тому, что используется в архитектуре DNC [11]. Сами эмбеддинги обучаются при помощи сложного вариационного автоэнкодера независимо от политики агента. Агент обучается отдельно и использует механизм мягкого внимания, чтобы получать нужную ему информацию из всех хранимых эмбеддингов.
Ханг и др. [27] развили успех архитектуры MERLIN и использовали механизм внимания по всем прошлым эмбеддингам для поощрения исследовательских действий в РОМИР среде. Фактически их решение поощряло агента при помощи внутренних наград за получение наблюдений, на которых позже акцентируется механизм внимания. В этой статье авторы рассматривали временные зависимости в пределах длины в 500-600 шагов. В отличие от нашего метода, оба решения [16, 27] обучают память предсказывать ближайшие наблюдения, а обращение к ней требует обработки всей последовательности из эмбеддингов для каждого предыдущего шага в эпизоде.
Первые попытки применения архитектуры трансформера в обучении с подкреплением продемонстрировали, что трансформеры слишком не стабильны, чтобы качественно обучаться в RL сеттинге [28]. В 2019 году Парисотто и др. [14] смогли модифицировать архитектуру трансформера и обошли проблему нестабильности трансформеров в RL. Стабилизированная версия архитектуры Transformer-XL показала лучшие на данный момент времени результаты в сложных POMDP задачах, связанных с ориентированием в ЗВ-среде.
Возвращаясь к исследованию рекуррентных сетей, Бэк и др. [15] обратили внимание, что одна из главных проблем адаптации архитектур памяти из области NLP (рекуррентные сети и трансформеры) в том, что RL задачи характеризует куда большее количество случайного шума и вариабельности наблюдений (за счет использования стохастической политики), чем задачи NLP. Для борьбы со случайным шумом в наблюдениях авторы предложили архитектуру AMRL, которая является модификацией для LSTM и добавляет специальный агрегатор по прошлым состояниям рекуррентной сети. В целом с точки вычислительных затрат AMRL практически не отличается от LSTM, но показывает куда более качественные результаты в POMDP задачах с длительными временными зависимостями.
4. Эксперименты
Мы экспериментально продемонстрируем эффективность нашего алгоритма в классической среде T-maze, главная сложность которой заключается в длинной временной зависимости. А также покажем, что предложенный алгоритм способен эффективно обобщаться на среды, требующие использования памяти в комбинации с более сложной реактивной стратегией поведения и богатым пространством наблюдений, на примере среды, реализованной на базе движка игры Doom [29].
В проведенных экспериментах мы использовали следующие бейзлайны:
• PPO-LSTM — простая комбинация алгоритма РРО [30] с использованием рекуррентной архитектуры LSTM [17]. Несмотря на простоту решения, большинство недавних успехов RL агентов в сложных частично обозреваемых средах, таких как StartCraft II [31], использовали архитектуру LSTM, а не более сложные надстройки на основе рекуррентных сетей [11, 12]. В экспериментах мы использовали имплементацию PPO-LSTM из библиотеки RLPyt [32].
• IMPALA-ST — агент на основе алгоритма IMPALA [33], использующий архитектуру трансформер [13] в качестве памяти. Данное решение было представлено в статье [14]. Мы использовали единственную доступную открытую имплементацию этого алгоритма из кода авторов статьи [34].
• AMRL — агент, предложенный в статье Бека и др. [15]. В своей работе авторы сравнили AMRL со множеством различных архитектур памяти, включая DNC [11] и многослойный LSTM. В их экспериментах AMRL показал лучшие результаты. Основное отличие AMRL от PPO-LSTM - это AMRL-слой вместо LSTM-слоя. В дополнение к
4.1. Зашумленный Т-лабиринт
классической схеме LSTM-слоя, AMRL на каждом шаге конкатенирует к скрытому рекуррентному состоянию ht вектор, который является агрегацией предыдущих скрытых состояний за последние К шагов: АССН ( { Н і^^ = - - К ). Авторы работы не указали длину раскрутки Truncated ВРТТ, поэтому мы предполагаем, что они раскручивали ВРТТ на всю длину эпизода и агрегировали по всем предыдущим шагам. Однако мв1 исследуем отношение между длиной подпоследовательности, которую на каждом шаге градиентного спуска обрабатывает архитектура памяти, и способностью этой архитектуры выучивать длинные временные зависимости. Поэтому в наших экспериментах мы будем обучать AMRL с различными фиксированными длинами роллаута, а параметр К установим равным длине роллаута. В оригинальной статье версия AMRL с МАХ агрегатором и использованием straight-through оценки градиентов показала наилучшие результаты, поэтому в экспериментах мы будем использовать именно её.
Хотя существует еще множество статей, предоставляющих различные алгоритмы обучения памяти агента, большинство из них не имеют доступных реализаций, поэтому мы ограничились проверенными методами с уже имеющейся работающей реализацией.
Для всех тестируемых алгоритмов и версий MemUP мы используем одинаковые архитектуры для получения эмбеддингов наблюдений, однако некоторые части нейросетей могут отличаться: архитектура трансформера совершенно не похожа на архитектуру рекуррентных сетей. В дополнение, LSTM-слои в PPO-LSTM и MemUP имеют одинаковую ширину.
Среда T-maze представляет собой Т-образный лабиринт, состоящий из коридора и двух рукавов (см. рис. 2). Агент размещается в центральном коридоре. Цель агента - дойти до перекрестка и выбрать правильный поворот. В лабиринте также присутствует подсказка, указывающая, какой поворот выбрать.
Задача T-maze появляется уже в ранних работах, посвященных исследованию памяти агента в обучении с подкреплением [5]. Для правильного её решения агенту нужно обнаружить временную зависимость между значением подсказки, встреченной ранее, и направлением поворота на перекрестке. Основное достоинство этой задачи заключается в том, что она позволяет изолированно протестировать механизмы памяти агента, при этом не представляя практически никаких сложностей с точки зрения всех остальных аспектов работы алгоритмов обучения с подкреплением: примитивная стратегия поведения и пространство наблюдений, отсутствие проблемы исследования-использования.
T-maze-LNR. В наших экспериментах мы использовали версию задачи, почти идентичную задаче T-maze-LN, что была представлена в статье, предложившей архитектуру AMRL [15] . Агент располагается в самом начале центрального коридора рядом с подсказкой, которую видит на первом шаге эпизода. Агент может двигаться по коридору только вперед. На каждом шаге наблюдения агента представлены вектором длины 3: на первой позиции значение подсказки (+1 ил и — 1 на первом шаге, 0 после), на второй позиции индикатор достижения перекрестка, который равен 1, если агент достиг места поворота. Последний элемент не несет информации и представляет собой случайны шум. Он равен +1 ил и —1 с равной вероятностью. Агент получает награду только в финале эпизода. Она равна +4, если был выбран верный поворот, и —3 в противном случае.
Длиной лабиринта мы будем называть число шагов между моментом, когда агент видит подсказку, и моментом, когда агент должен будет сделать выбор на основе значения подсказки. Реальная длина лабиринта в наших экспериментах будет колебаться в пределах 10 шагов от эпизода к эпизоду, но в проведенных экспериментах мы будет обозначать среду по минимальной возможной длине лабиринта. Другими словами, если мы обучаем агентов на среде T-maze-LNR-100, это значит, что длина лабиринта в каждом эпизоде может быть от 100 до 109 шагов включительно. Это позволяет декоррелировать наблюдения агентов, если модель учится, играя параллельно на нескольких экземплярах среды (см. алгоритмы РРО [30], АЗС [4], IMPALA [33]).
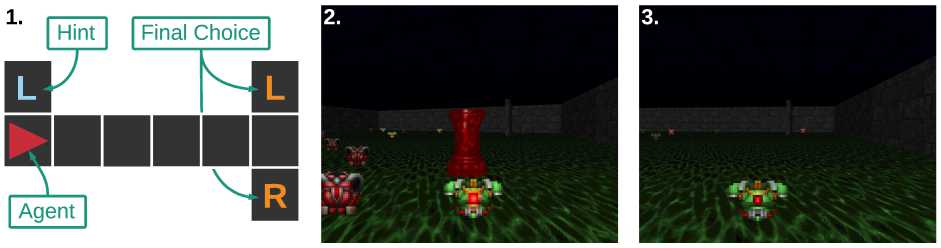
Рис. 2. Среды для тестирования долгосрочных временных зависимостей. 1) T-maze лабиринт, в котором агент должен дойти до Т-образного перекрестка и выбрать один из поворотов (L или R). Подсказка о том, какой поворот верный, предоставляется в самом начале. На каждом шаге агент может видеть только ту колонну клеток, в которой находится сам. 2,3) Задача ViZDoom-Two-Colors. Агент находится в комнате и постоянно теряет здоровье, чтобы пополнять здоровье, агенту нужно собирать жилеты такого же цвета, что и колонна. Эпизод длится 1050 шагов, но после 45 шага колонна пропадает
4.2. Трёхмерная среда ViZDoom
Несмотря на то, что среда T-maze позволяет моделировать очень длинные временные зависимости, алгоритм должен быть в состоянии действовать в более сложных задачах, где проблема запоминания важной информации является не единственным испытанием. Для соответствующего эксперимента мы выбрали среду ViZDoom-two-colors из статьи [35].
В данной задаче агент помещается в комнату, заполненную кислотой (см. рис. 2.2) и постоянно теряет здоровье. В среде по всей территории разбросаны предметы двух цветов: зеленые и красные. Предметы одного из цветов восполняют здоровье агента и дают награду +1, в то время как другие отнимают здоровье и дают награду —1. Соответствие между эффектами и цветами предметов определяется случайным образом в начале каждого эпизода. Кроме того, на карте присутствует колонна, цвет которой соответствует цвету предметов, восполняющих здоровье. Эпизод заканчивается, когда здоровье агента опускается до нуля, а за каждый шаг до этого момента агент получает небольшую награду, равную +0.02. Соответственно целью агента является как можно дольше поддерживать свое здоровье, собирая предметы нужного цвета и избегая других.
Для решения этой задачи, по идее, необходимо удерживать в памяти цвет колонны для того, чтобы иметь возможность выбирать предметы правильного цвета, даже когда колонна находится вне зоны видимости. В ходе предварительных экспериментов выяснилось, что реактивный агент без памяти способен выучить стратегию, при которой он всегда будет удерживать колонну в области видимости, даже если комната заполнена стенами, закрывающими обзор со многих углов. Следовательно, в нашей версии среды колонна исчезает после 45 шага, а число стен в комнате значительно уменьшено. Таким образом, мы усложнили задачу запоминания, но упростили задачу навигации в среде относительно оригинального варианта. Стоит отметить, что мы не подаем на вход агенту информацию относительно его текущего здоровья или получаемых наград, так как эти наблюдения фактически предоставляют ту же информацию, что и цвет колонны, но при этом не исчезают после 45 хода.
5. Результаты и обсуждение
Результаты экспериментов в среде T-maze для минимальной длины в 100 и 1000 шагов (T-Maze-LNR-100 и T-Maze-LNR-1000) приведены на рис. За и б соответственно. В этих экспериментах мы ограничиваем возможности агентов в обработке всей последовательности единовременно. Это ограничение эмулирует условия, когда приходится обучать агента на последовательностях, которые не входят в оперативную память карты из-за своего размера и вынуждают обучать модели на более коротких последовательностях, чем длины потенциальных временных зависимостей в эпизоде. Все кривые, приведенные на графиках, являются усреднением по трем отдельным запускам с одинаковыми гипперпараметрами и разным значениям зерна генератора псевдослучайных чисел.
5.1. Noizy T-Maze
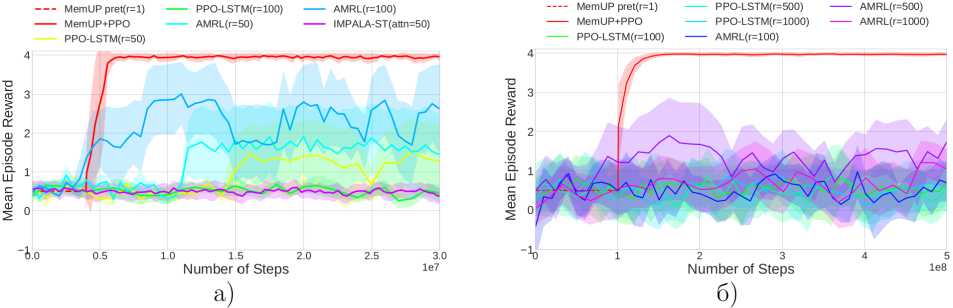
Рис. 3. а) Кривые обучения для алгоритма. MemUp и всех альтернатив в среде T-Maze-LNR-100. Все кривые являются усреднением по трем запускам с различным зерном генератора, псевдослучайных чисел. Фаза, предобучепия памяти агента. MemUP обозначена, пунктирной линией, б) Кривые обучения для среды T-Maze-LNR-1000 так же усреднены по трем запускам
Основные агенты для сравнения в этом эксперименте - это PPO-LSTM и AMRL с различными длинами раскрутки ТВРТТ. Для экспериментов в T-Maze-LNR-100 мы так же обучали агента IMPALA-ST. При этом длина окна внимания в агенте IMPALA-ST была ограничена 50 шагами. Как видно на зеленом графике (рис. За), IMPALA-ST не может выучить временную зависимость, которая длиннее, чем окно внимания агента. Это закономерный результат, так как трансформер не имеет механизма для передачи информации, лежащией вне его окна внимания. Эксперимент с агентом IMPALA-ST был проведен скорее для дополнительной проверки правильности реализации среды и метода эвалюации алгоритмов.
По графикам на рис. За видно, что PPO-LSTM с раскруткой на 50 шагов ( г = 50) показал результаты несколько лучше, чем случайная политика. Тем не менее обе версии агента для г = 50 и г = 100 оказались не в состоянии решить задачу за 30 миллионов шагов взаимодействия со средой. С другой стороны, AMRL-MAX агент показал себя значительно лучше: версия с раскруткой на 100 шагов ( г = 100) полностью решила задачу на некоторых из запусков, тогда как AMRL-MAX( г = 50) выучилась хуже, но также показала заметное улучшение средних наград по сравнению со случайной политикой. В более сложной среде T-Maze-LNR-1000 (рис. 36), где временная зависимость длиннее в 10 раз, мы учили все агенты в течение одного миллиарда шагов взаимодействия между агентами и средой. Тем не менее нам не удалось успешно обучить ни одного агента, на. основе PPO-LSTM или AMRL-MAX для всех длин раскрутки ТВРТТ, которые мы протестировали: г = 100, г = 500, г = 1000. Хотя рекуррентные сети потенциально способны обучиться находить временные зависимости, которые длиннее, чем число шагов раскрутки ТВРТТ, представленные результаты показывают, что такое обучение нестабильно, и работает только в тех случаях, когда, длина, временной зависимости невелика.
При обучении MemUP агента мы сначала тренировали детектор неопределенности D и модуль памяти М. В течение этой фазы мы использовали случайную политику, чтобы генерировать эпизоды. В качестве цели для предсказания ft использовалась дисконтированная будущая награда с коэффициентом у = 0. Обучение стратегии агента начинается во второй фазе, после того как предобучение памяти завершено. Период, соответствующий фазе предобучения памяти, отмечен на всех графиках пунктирной линией. Как видно на рис. За и б, агент обучается практически мгновенно при наличии предобученной нашим методом памяти. Для проведенных экспериментов мы с нуля учим модули D и М для каждого нового запуска.
5.2. ViZDoom- Two-Colors
Результаты в среде ViZDoom-Two-Colors продемонстрированы на рис. 4. Все графики усреднены по двум независимым запускам для каждой из конфигураций. Агент IMPALA-ST, использующий архитектуру Stabilized Transformer [14], обучался в двух разных конфигурациях с длиной окна внимания в 100 и 8 шагов.
IMPALA-ST(attn=8) с коротким окном внимания не смог выучить стратегию решения задачи, так как информации из последних 8 шагов агента недостаточно, чтобы определить, предметы какого цвета будут восстанавливать здоровье агента. С другой стороны, агент IMPALA-ST(attn=100) выучился решить задачу и стабильно выживал в среде на протяжении всех 1050 шагов.
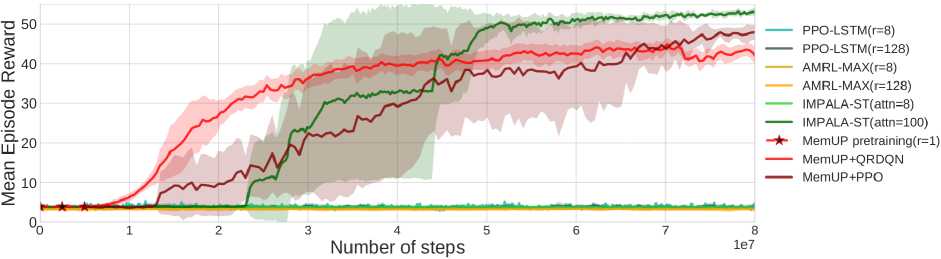
Рис. 4. Кривые обучения агентов в среде ViZDoom-Two-Colors. Все результаты усреднены по двум независимым запускам. Фаза предобучения памяти MemUP отмечена, пунктирной линией
Результаты IMPALA-ST(attn=100) продемонстрировали, что в задаче ViZDoom-Two-Colors агенту нет необходимости помнить цвет подсказки на протяжении всего эпизода. Для этого достаточно научиться выбирать правильные предметы, пока, подсказка, присутствует, и затем помнить только цвет предыдущего собранного предмета. Оказалось, что в задаче достаточно удерживать в памяти события, произошедшие не более чем 100 шагов назад, которые необходимы, чтобы добраться от одного предмета, до другого. Ни одна, из конфигураций алгоритма. PPO-LSTM и AMRL-MAX (с раскруткой на. 128 и 8 шагов) не смогла, выучиться выживать в среде дольше, чем случайный агент. Несмотря на. то, что более длинной раскрутки ТВРТТ на. 128 шагов потенциально должно хватить на. то, чтобы помнить цвет подсказки или предыдущего собранного предмета, агенты PPO-LSTM и AMRL-MAX выучились только собирать любые предметы на. пути без учета, прошлой информации о подсказке.
Для первой фазы обучения MemUP в качестве детектора. D мы использовали QR-DQN агента с е-жадной стратегией (е = 0.1). В качестве цели для предсказания ft мы использовали дисконтированную будущую награду с коэффициентом дисконтирования у = 0.8. Производилось обучение модуля памяти М с разными длинами раскрутки ТВРТТ, но оказалось, что в этой задаче мы так же в состоянии обучить модуль памяти с раскруткой всего в один шаг (фактически без использования ВРТТ). На каждом шаге предсказания t предиктор Р получал на вход N = 3 наиболее неопределенных будущих переходов Ut и состояние памяти mt- Таким образом, при обучении памяти М использовались только четыре отдельных наблюдения из последовательности на каждом градиентном шаге. Фаза предобучения памяти MemUP длилась в течение пяти миллионов шагов взаимодействия со средой. Дополнительно отметим, что параметр у = 0.8, случайное появление предметов на карте и Е-жадная стратегия значительно увеличивают уровень неопределенности целевой переменной ft- В данном случае это алеоторная неопределенность, которую нельзя уменьшить при помощи информации из прошлых наблюдений. Тем не менее это усложнение не мешает детектору неопределеноости D находить момент в эпизоде, где агенту не хватает информации, которая может быть связана с длинной временной зависимостью. Для этой среды мы обучили две версии MemUP агента. Первый агент MemUP-PPO использовал алгоритм РРО вместе с переобученной памятью. Второй агент MemUP+QRDQN использовал алгоритм QR-DQN, аналогичный тому, который мы использовали для обучения детектора. Как видно из графика, обе версии независимо от алгоритма, используемого в стратегии, обучаются несколько быстрее, чем агент IMPALA-ST(attn=100). Через 50 миллионов шагов обе версии выучиваются выживать в среде на протяжении всего эпизода. Финальный результат агентов на основе нашей памяти MemUP несколько хуже, чем у агента IMPALA-ST(attn=100). Вероятнее всего, это связано с тем, что MemUP выучился хранить исключительно информацию о долговременной зависимости между цветом колонны и наградами за сбор предметов, в то время как IMPALA-ST(attn=100) демонстрирует более эффективное пространственное ориентирование в среде. Иными словами, информация из последних 100 шагов, находящихся в окне внимания агента IMPALA-STM(attn=100), позволяет ему не только установить цвет летящих предметов, но и запоминать их взаимное расположение, чтобы потом быстрее добираться от одного собранного предмета к другому. Возможно, более сложная предсказательная цель ft в виде будущих наблюдений (а не только наград) или сложная политика сэмплирования моментов для предсказания может помочь обучать память не только для запоминания основной временной зависимости, связанной с наградами, но и для запоминания дополнительной информации, помогающей в ориентировании на местности. В целом, это направление для будущих исследований.
Мы хотим отметить, что при обучении памяти MemUP требуется значительно меньше ресурсов с точки зрения размеров обрабатываемых подпоследовательностей (4 временных шага против 100) при обучении и применении агента, чем для агента IMPALA-ST(attn=100). Если сравнивать MemUP с агентами, которые использовали сравнимое количество ресурсов (IMPALA-ST(attn=8), PPO-LSTM(r=8) и AMRL-MAX(r=8)), то наш метод обучения значительно превосходит все другие альтернативные подходы.
6. Выводы
Был разработан новый метод для обучения долговременной памяти. Суть метода сводится к идеи предсказания исходов высокой неопределенности у событий, которые могут находиться произвольно далеко в будущем. В разделе 2 мы обосновываем эту идею демонстрируя, что высокая неопределенность при предсказании исходов с использованием локальных наблюдений свидетельствует о недостатке локальной информации. Из проведенных экспериментов видно, что предложенный метод в сочетании с архитектурой рекуррентной сети способен выучивать временные зависимости, даже в 1000 раз превышающие длину, на которую мы раскручиваем метод обратного распространения ошибки через время (Truncated ВРТТ). Этим свойством не обладают ни рекуррентные сети, обучаемые классическим алгоритмом ТВРТТ, как видно из экспериментов в Noisy T-maze, ни архитектуры на основе трансформеров ввиду отсутствия механизмов передачи информации, не входящей в окно внимания трансформера. Более того, как видно из экспериментов на ViZDoom-two-colors, даже если альтернативные архитектуры способны выучить длинную временную зависимость, то используют для этого в разы больше ресурсов и делают это медленнее, чем предложенный алгоритм MemUP.
Стоит отметить, что конкретные архитектурные решения в нашей имплементации алгоритма MemUP были выбраны по причине быстроты своей реализации для тестирования работоспособности нашей идеи. Например, одним из недостатков предложенной реализации MemUp является раздельное обучение памяти и агента. Это может быть проблемой для online RL задач, когда улучшение стратегии агента может привести его в новые состояния к новым временным зависимостям, которые предобученная на другой стратегии память не умеет запоминать. С другой стороны, эта проблема не будет возникать в других видах задач, таких как обучение с учителем или imitation learning/offline reinforcement learning.
Даже учитывая этот недостаток нашей реализации, мы полагаем, что предложенный метод показал многообещающие результаты, которые оставляют множество возможностей для будущих направлений исследования. В частности, решение проблемы отдельного обучения памяти для RL задач и совмещение архитектуры памяти на основе трансформера с предложенным нами методом обучения.
Список литературы Обучение долговременной памяти через предсказание событий высокой неопределенности
- Duan Y. [et al.\. RL2: Fast Reinforcement Learning via Slow Reinforcement Learning // arXiv preprint arXiv:1611.02779. 2016.
- Peng X.B. [et al.\. Sim-to-real transfer of robotic control with dynamics randomization // IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). 2018. P. 1-8.
- Hausknecht M., Stone P. Deep recurrent q-learning for partially observable mdps // arXiv preprint arXiv: 1507.06527. 2015.
- Mnih V. [et al.\. Asynchronous methods for deep reinforcement learning // International conference on machine learning. 2016. P. 1928-1937.
- Bakker B. Reinforcement Learning with Long Short-Term Memory // Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. 2001. P. 1475-1482.
- Mnih V. [et al.\. Human-level control through deep reinforcement learning // Nature. 2015. V. 518. P. 529-533.
- Silver D. [et al.\. Mastering chess and shogi by self-plav with a general reinforcement learning algorithm // arXiv preprint arXiv: 1712.01815. 2017.
- Santoro A. [et al.\. Relational recurrent neural networks // Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. 2018. P. 7310-7321.
- Kapturowski S. [et al.\. Recurrent Experience Replay in Distributed Reinforcement Learning // 7th International Conference on LearningRepresentations, ICLR. 2019.
- Oh J. [et al.}. Control of Memory, Active Perception, and Action in Minecraft // Proceedings of the 33nd International Conference on Machine Learning, ICML. 2016. V. 48. P. 27902799.
- Graves A. [et al.}. Hybrid computing using a neural network with dynamic external memory 11 Nature. 2016. V.*538. P. 471.
- Parisotto E., Salakhutdinov R. Neural Map: Structured Memory for Deep Reinforcement Learning // 6th International Conference on Learning Representations, ICLR. 2018.
- Vaswani A. [et al.}. Attention is All you Need // Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. 2017. P. 5998-6008.
- Parisotto E. [et al.}. Stabilizing Transformers for Reinforcement Learning // arXiv preprint arXiv:1910.06764. 2019.
- Beck J. [et al.}. AMRL: Aggregated Memory For Reinforcement Learning // 8th International Conference on Learning Representations, ICLR. 2020.
- Wayne G. [et al.}. Unsupervised Predictive Memory in a Goal-Directed Agent // arXiv preprint arXiv:1803.10760. 2018.
- Hochreiter S., Schmidhuber J. Long short-term memory // Neural computation. 1997. V. 9. P. 1735-1780.
- Dabney W. [et al.}. Distributional reinforcement learning with quantile regression // Thirty-Second AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. 2018.
- Geman S., Bienenstock E., Doursat R. Neural networks and the bias/variance dilemma // Neural computation. 1992. V. 4. P. 1-58.
- Jaeger H. Tutorial on training recurrent neural networks, covering BPPT, RTRL, EKF and the «echo state network» approach. Bonn : GMD-Forschungszentrum Informationstechnik. 2002. V. 5.
- Devlin J. [et al.}. BERT: Pre-training of Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Language Understanding // Proceedings of the 2019 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, NAACL-HLT. 2019. P. 4171-4186.
- Brown T.B. [et al.}. Language models are few-shot learners // arXiv preprint arXiv:2005.14165. 2020.
- Wang S. [et al.}. Linformer: Self-Attention with Linear Complexity // arXiv preprint arXiv:2006.04768. 2020.
- Zaheer M. [et al.}. Big Bird: Transformers for Longer Sequences // Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. 2020.
- Baker B. [et al.}. Emergent Tool Use From Multi-Agent Autocurricula // 8th International Conference on Learning Representations, ICLR. 2020.
- Ha D., Schmidhuber J. Recurrent World Models Facilitate Policy Evolution // Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. 2018. P. 2455-2467.
- Hung C.C. [et al.}. Optimizing agent behavior over long time scales by transporting value // Nature communications. 2019. V. 10. P. 1-12.
- Mishra N. [et al.}. A Simple Neural Attentive Meta-Learner // 6th International Conference on Learning Representations, ICLR. 2018.
- Kempka M. [et al.}. Vizdoom: A doom-based ai research platform for visual reinforcement learning // IEEE Conference on Computational Intelligence and Games. 2016. P. 1-8.
- Schulman J. [et al.}. Proximal policy optimization algorithms // arXiv preprint arXiv:1707.06347. 2017.
- Vinyals O. [et al.}. Grandmaster level in StarCraft II using multi-agent reinforcement learning 11 Nature. 2019. V. 575. P. 350-354.
- Stooke A., Abbeel P. rlpvt: A research code base for deep reinforcement learning in pvtorch 11 arXiv preprint arXiv:1909.01500. 2019.
- Espeholt L. [et al.}. IMPALA: Scalable Distributed Deep-RL with Importance Weighted Actor Learner Architectures // Proceedings of the 35th International Conference on Machine Learning, ICML. 2018. P. 1406-1415.
- Kumar S., Parker J., Naderian P. Adaptive Transformers in RL // arXiv preprint arXiv:2004.03761. 2020.
- Beeching E. [et al.}. Deep Reinforcement Learning on a Budget: 3D Control and Reasoning Without a Supercomputer // arXiv preprint arXiv:1904.01806. 2019.


