Оценка диссипативных свойств колебательной системы серийного образца расходомера кориолиса
Автор: Романов В.А., Тараненко П.А.
Статья в выпуске: 2, 2020 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Количественные оценки расхода и плотности текущей жидкости, получаемые измерениями с помощью промышленных расходомеров Кориолиса, делаются на основании предварительно выполняемых на образцовом датчике лабораторных экспериментов. Это ограничивает достоверность практических измерений рамками использованных планов лабораторных экспериментов и сдерживает совершенствование конструкции колебательной системы датчика. Альтернативой подходам описательного характера в перспективе должны стать подходы виртуального прототипирования. Одной из принципиальных задач создания виртуального прототипа расходомера Кориолиса является разделение вклада в основной измеряемый расходомером параметр (фазовый сдвиг) составляющих от гироскопических и диссипативных сил. Решение этой задачи связано с необходимостью идентификации модели диссипативных сил колебательной системы расходомера. В статье обсуждаются результаты обработки экспериментов по определению диссипативных свойств механической колебательной системы одного из серийно выпускаемых образцов расходомера Кориолиса. В основу решения задачи идентификации модели диссипативных свойств колебательной системы расходомера положено исследование степени нелинейности огибающей виброграммы свободных затухающих колебаний. Эксперименты выполнены на проливочном стенде Центра экспериментальной механики Южно-Уральского государственного университета, позволяющем управлять расходом и фазовым составом протекающего по расходомеру флюида. В статье описаны результаты обработки виброграмм затухающих колебаний, позволяющей выделить в рассеиваемой энергии вклад сухого (модель Кулона), линейного вязкого (модель Релея) и квадратичного вязкого трения. Экспериментально установлена выраженная зависимость диссипации колебательной системы расходомера Кориолиса от особенностей течения флюида (скорости, фазового состава, режима: непрерывный, слаговый), приведены полученные результаты решения задачи идентификации модели диссипативных сил. В качестве текучей среды выступает вода, в качестве дисперсной фазы - воздух. В приведенных результатах решения задачи идентификации модели диссипативных сил выделены случаи свободных затухающих колебаний расходомера с трубками, заполненными жидкостью, но без течения, режим однородного однофазного и двухфазного течения и режим неоднородного двухфазного течения.
Расходомер кориолиса, поток двухфазного флюида, свободные затухающие колебания, модели диссипативных сил
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/146281987
IDR: 146281987 | УДК: 534.12, | DOI: 10.15593/perm.mech/2020.2.11
Текст научной статьи Оценка диссипативных свойств колебательной системы серийного образца расходомера кориолиса
ВЕСТНИК ПНИПУ. МЕХАНИКА № 2, 2020PNRPU MECHANICS BULLETIN
Стоимость добываемых в мире нефти и газа огромна – около $3 трлн в год для нефти (2014 г.) и $0,5 трлн в год для газа (2013) [1]. Поступающая из скважин нефть обычно является одним из компонентов многофазного флюида, содержащего также воду и газ. Измерение расхода каждого компонента на скважине является главной метрологической задачей нефтедобычи, ставшей особенно актуальной в последние 30 лет из-за изменения условий добычи (эксплуатации все более бедных и мелких месторождений, роста доли подводной добычи, необходимости во все более точном управлении процессом добычи), а также вследствие ужесточающихся требований к составу и количеству нефтепродуктов при их учете и продаже. Технологии многофазных измерений стали развиваться относительно недавно и касаются объектов, в которых измеряемые параметры формируются в результате сложных для количественного описания процессов. В результате неоп- ределенность при оценках расхода компонентов многофазного потока для современных измерительных систем в полевых условиях достигает 20 % и более [2]. Связанные с этим финансовые риски трудно определить количественно, но считается, что они составляют порядка десятков миллиардов долларов в год. В настоящее время не найдено эффективной технической возможности резко решить эту неопределенность, идет процесс непрерывного и постепенного ее уменьшения.
В обзорах [3, 4] отмечается необходимость повышения точности многофазных расходомеров и оценки их применимости в диктуемом диапазоне условий. Важная роль в снижении той составляющей неопределенности в результатах обмера многофазных потоков, которая связана с выбором метода измерений и соответствующего прибора, принадлежит семейству кориолисовых расходомеров (КР), обладающих рядом признанных достоинств. Составной частью этого процесса является разработка экспериментальных и теоретических методов, которые позволили бы лучше понять фи- зические причины неопределенностей в результатах измерений и, следовательно, интерпретировать их наиболее адекватным способом.
Кориолисовы расходомеры за три десятилетия, прошедших с момента их массового появления на рынке, получили широкое распространение в самых разных отраслях промышленности и заслужили признание благодаря точности и надежности измерений массовых расходов и плотностей однородных, однофазных флюидов. История создания этих устройств и основные этапы в развитии их теории и практического применения подробно описаны в обзорах [5–8], краткий обзор современных исследований приведен в работе [9]. Для однофазных потоков теория измерений разработана достаточно глубоко для того, чтобы предсказывать рабочие характеристики КР данной конструкции или проектировать приборы с заданными характеристиками [10].
В связи с прикладным значением этих задач литература по данному вопросу весьма обширна. Созданные к настоящему времени модели разнообразны и могут быть классифицированы с различных точек зрения, например: распределены или сосредоточены их параметры, допускают они аналитическое или только численное решение, система «труба – жидкость» рассматривается как одно- или трехмерная и пр.
Наиболее популярны 1D-модели, в которых труба рассматривается как балка Эйлера – Бернулли [11–14] или балка Тимошенко [15–18], а жидкость моделируют однородной нерастяжимой массивной нитью, протягиваемой вдоль оси трубы с постоянной скоростью [19]. С помощью 1D-моделей получено много результатов, оправдывающихся на опыте и полезных для проектирования КР. Например, на балочной модели [19] показана основная особенность резонансных колебаний трубки при наличии в ней потока жидкости, выражающаяся в перекрестном влиянии потока на возбуждаемые собственные формы. Первая мода влияет через поток на вторую моду (но не влияет на себя), вторая мода влияет на первую и не влияет на себя. Полученный результат свидетельствует о том, что присущее традиционным консервативным колебательным системам фундаментальное свойство ортогональности собственных форм при появлении непотенциальных (гироскопических и диссипативных) сил взаимодействия упругой трубки с протекающей по ней жидкостью перестает быть справедливым, что является принципиальным положением при моделировании КР.
Из анализа литературных данных и логики развития теории видно, что следующие шаги в совершенствовании методов описания динамики КР будут сделаны в направлении более детального описания потока флюида, чем это возможно в рамках 1D-модели. Известны попытки анализа поведения КР с применением заслуженно зарекомендовавших себя при решении задач механики деформируемого твердого тела (SA – Structural Analysis) и задач гидродинамики (FF – Fluid Flow) конечно-элементных подходов (FEA – Finite Element
Analysis), для которых в случае решения задачи о взаимодействии деформируемого тела с жидкостью при параллельной работе решателей SA и FF используется специальный термин Fluid Structure Interaction (FSI). Первая попытка такого рода была сделана в работе [20], где был рассмотрен простейший вариант геометрии КР – с прямой трубкой – и один из вариантов сцепления SA-FF, известный как секционированный
На сегодняшний день основанные на использовании FSI-технологий конечно-элементные расчеты позволяют с высокой степенью достоверности моделировать поведение механической колебательной системы расходомера Кориолиса при работе с невязкой однофазной жидкостью в режиме установившихся резонансных колебаний [27]. FSI-расчеты требуют значительных вычислительных ресурсов. По этой причине реализованные на их основе алгоритмы пока не могут быть интегрированы в конструкцию промышленного датчика для использования в режиме реального времени. Основной целью создания таких моделей является возможность сравнительного анализа поведения вариантов исполнения механической колебательной системы датчика с изменениями в геометрии трубки.
Успехи в применении КР к однофазным потокам постоянно стимулируют попытки распространить метод и на многофазные потоки. Возникающие в этом случае задачи весьма разнообразны и сильно различаются по сложности в зависимости от количества фаз, их физических свойств и списка характеристик потока, подлежащих измерению. Очевидно, что не все из этих задач могут быть решены «неинвазивно», так, как это делается в однофазном случае – по наблюдениям за движениями трубопровода, возбуждаемыми потоком флюида. Наиболее простым является случай двухфазного потока, в котором одна из фаз является мелкодисперсной и равномерно распределенной по объему трубопровода. В этом случае флюид можно рассматривать как гомогенную жидкость с некоторым эффективным набором свойств [28] и для измерения его массового расхода использовать те же средства, что и для однофазных потоков. Примером являются потоки «жидкость – газ» при достаточно большой приведенной скорости жидкости, когда газ присутствует в потоке в виде мелких пузырьков (режим дисперсных пузырьков [29]). Как показывает практика, «однофазный» подход остается достаточно точным, если объемная доля газа не превышает нескольких процентов. Дальнейшее ее увеличение приводит к неприемлемой потере точности и надежности измерений. Причиной является образование крупных газовых пузырей с размерами, сопоставимыми с диаметром трубы, – переход от пузырькового режима течения к так называемому снарядному (пробковому) режиму, в котором модель гомогенного флюида перестает работать. Качественно понятно, почему в этом режиме нарушается работоспособность КРМ: распределение массы флюида вдоль измерительной трубки становится существенно неоднородным и изменяющимся во времени случайным образом, что ведет к случайным же изменениям наблюдаемых параметров колебаний – основной частоты колебаний трубки и фазового сдвига между колебаниями ее плеч. В настоящее время предложен эмпирический метод решения этой задачи, позволяющий получать надежные результаты для потоков, где объемная доля газовой фазы достигает 80 % [30–32]. В то же время отмечается, что дальнейшее совершенствование метода требует более глубокого понимания механизмов взаимодействия двухфазного флюида с измерительной трубкой КРМ и разработки соответствующих физических моделей, позволяющих предсказывать отклик прибора на двухфазный поток.
Разность фаз механических колебаний, используемая в КР в качестве параметра оценки расхода протекающей жидкости, в околорезонансной зоне любой колебательной системы оказывается крайне чувствительна к самым незначительным изменениям параметров динамической системы. Определяющим фактором, формирующим (совместно с гироскопическими кориолисовыми силами) степень чувствительности разности фаз синхронных гармонических перемещений двух разных сечений упругой трубки расходомера на установившемся режиме резонансных колебаний, является уровень и характер диссипативных сил в колебательной системе. Ключевая роль диссипативных характеристик колебательной системы в достижении точности работы расходомеров Кориолиса отмечается в работе [33]. Здесь же приводятся результаты экспериментального определения диссипации образца расходомера при разных расходах однофазной жидкости. Ошибки измерения расходомерами Кориолиса, связанные с особенностями диссипативных свойств одно- и двухфазного потока, обсуждаются в работе [34]. Указывается, что для двухфазного потока при определенной доле дисперсной фазы может происходить многократное возрастание демпфирования, что может приводить к (временной) потере работоспособности прибора. Доминирующая часть затухания обусловлена возрастанием взаимных перемещений (decoupling) между сплошной и дисперсной фазами потока. На простой модели предпринята попытка создать теорию затухания из-за возникновения заметной разницы в скоростях движения фаз (развязки, decoupling) в двухфазном потоке. Приводятся примеры смесей с водой в качестве непрерывной фазы. Дисперсная фаза представляет собой либо воздух, либо масло или песок. В работе [34] приводятся результаты экспериментов по определению диссипативных свойств двухфазных жидкостей, выполненные на специально разработанной экспериментальной установке.
Первоочередными задачами виртуального прототипирования расходомера Кориолиса являются две. Необходимость их решения заложена в концепции установления соответствия между массовым расходом протекающей жидкости и появляющимся при возникновении течения фазовым сдвигом колебаний двух геометрически симметричных половин упругой трубки расходомера. Во-первых, существует проблема выбора альтернативного фазовому сдвигу параметра для работы расходомера на переходных колебательных режимах, поскольку понятие фазового сдвига актуально только для установившихся режимов вынужденных колебаний. Однако и на режиме установившихся колебаний замеряемый фазовый сдвиг находится в зависимости не только от сил инерции Кориолиса (гироскопических сил, пропорциональных массовому расходу флюида), но и от диссипативных сил. Величина диссипативных сил (уровень необратимых потерь энергии в колебательной системе) может различаться в десятки раз при одном и том же массовом расходе жидкостной фазы, но разных объемных долях воздуха в текущем по трубке флюиде [33]. Выделение составляющих фазового сдвига, обусловливаемых отдельно гироскопическими и отдельно диссипативными силами, составляет вторую задачу, решение которой необходимо при виртуальном прототипировании расходомера Кориолиса. Исследование влияния диссипативных свойств механической части колебательной системы расходомера Кориолиса на его показания является составной частью выхода процесса его прототипирования на следующий, более высокий уровень достоверности.
В статье обсуждаются эксперименты по определению диссипативных свойств механической колебательной системы серийного образца расходомера Кориолиса, результаты обработки экспериментов и попытки обобщения (группировки) полученных результатов. В качестве текучей среды выступает вода, в качестве дисперсной фазы – воздух.
1. Влияние диссипации на показания расходомера
Принцип работы расходомера Кориолиса предполагает возбуждение установившихся резонансных колебаний трубки с протекающей по ней жидкостью. В колебательной системе без гироскопических сил резонирующей форме колебаний балки (рамы) при слабом демпфировании соответствует практически синфазное движение всех поперечных сечений, а фаза их колеба- ний при пренебрежении диссипативными силами отстает от фазы вынуждающей силы на –π/2. В этом случае амплитуды колебаний всех поперечных сечений при комплексной форме представления результатов решения дифференциальных уравнений вынужденных колебаний будут иметь чисто мнимую отрицательную величину. Амплитуды A+ и A– установившихся вынужденных колебаний двух датчиков перемещений, расположенных симметрично по отношению к перпендикулярной оси трубки плоскости её геометрической симметрии, будут одинаковыми и чисто мнимыми A+ = A - = - ia.
Возникающий при колебаниях поворот поперечных сечений трубки при появлении в ней течения жидкости сопровождается действием на трубку дополнительных сил, которые могут быть классифицированы как гироскопические (силы инерции Кориолиса). Распределение этих сил в случае симметричной формы колебаний трубки будет кососимметрично (ортогонально) к резонирующей форме колебаний и, таким образом, не может изменить её амплитуду. Кососимметричный характер распределения кориолисовых сил инерции, изменяющихся во времени с частотой резонансных колебаний, инициирует возбуждение кососимметричных форм колебаний. Поскольку кососимметричным формам соответствуют собственные частоты более высокого порядка, деформирование на кососимметричных формах (с оговоркой на достаточную разнесённость соответствующих собственных частот) носит квазиста-тический (дорезонансный) характер и соответствующие этим формам перемещения можно считать совпадающими по фазе с вынуждающей силой. Пренебрегая вкладом в амплитуду вынужденных колебаний от кососимметричных форм, число узлов в которых больше числа узлов в форме кориолисовых сил инерции, для амплитуд колебаний сечений установки датчиков перемещений получаем
A += c - ia и A - =- c - ia , (1)
где c – амплитуда квазистатических перемещений, вызванных деформированием трубки кориолисовыми силами. В соответствии с фазы амплитуд сечений установки датчиков перемещений равны по величине и противоположны по знаку. Поскольку амплитуда резонирующей формы существенно выше амплитуды квазистатических деформаций a » c , разность фаз амплитуд перемещений датчиков можно (в силу упругого характера деформаций от Кориолисовых сил инерции) считать пропорциональной амплитуде c и, соответственно, массовому расходу жидкости.
Теперь рассмотрим случай, когда диссипативными силами пренебречь нельзя. Для наглядности ограничимся наиболее простым для анализа случаем линейного вязкого сопротивления (модель Релея). Из условия динамического равновесия резонирующей механиче- ской системы с одной степенью свободы следует, что в каждый момент времени силы инерции компенсируются упругими силами, а внешняя вынуждающая сила уравновешивается диссипативной силой. Таким образом, наличие диссипативных сил отразится на вещественной составляющей амплитуд колебаний, причем одинаково для обоих сечений трубки, в которых установлены датчики перемещений
A += ( b + c ) - ia и A -= ( b - c ) - ia , (2) где b – перемещения сечений установки датчиков перемещений, возникающие в диссипативной системе в момент времени с максимальным значением вынуждающей силы при отсутствии гироскопических сил.
На рис. 1 показана зависимость разности фаз комплексных амплитуд A + и A – от отношения амплитуд ква-зистатических перемещений ξ = b/c (величины a и c были подобраны так, чтобы при b = 0 разность фаз составляла 2–3 град – примерно так, как это соответствует реальному датчику).
Из графика на рис. 1 видно, что пока величина b перемещений от вынуждающего воздействия мала (или соизмерима) с величиной перемещений от сил со стороны текущей жидкости (т.е. b ≤ c ) фазовый сдвиг между амплитудами колебаний A + и A – слабо зависит от ξ. По мере увеличения b (увеличения доли квазистатиче-ских деформаций от вынуждающего воздействия, поддерживающего режим установившихся вынужденных колебаний) такая зависимость становится заметной и отражается на величине основного измеряемого параметра (разности фаз Δφ), который в этом случае может заметно уменьшиться.
Приведенный пример дает представление о том, что замеряемый расходомером кориолиса фазовый сдвиг определяется не только силами инерции Кориолиса. Чтобы на основании фазового сдвига корректно судить о массовом расходе жидкости, необходимо иметь достаточную информацию о диссипации в колебательной системе и уметь разделять вклады в фазовый сдвиг от движения жидкости и от вынуждающей силы (которая на резонансе уравновешивает диссипативные силы). Чем выше диссипация в колебательной системе, тем большей оказывается амплитуда вынуждающей силы, необходимая для поддержания заданного уровня установившихся вынужденных колебаний, и, соответственно, больше оказывается поправка в зависимость между фазовым сдвигом и массовым расходом жидкости. Учет этого обстоятельства особенно актуален в расходомерах многофазных сред, где необратимые потери на колебания возрастают многократно. Можно предположить, что очередным шагом на пути решения задачи виртуального прототипирования расходомера Кориолиса будет моделирование установившегося режима колебаний с применением продвинутой модели диссипативных свойств.

а б
Рис. 1. Зависимость разности фаз комплексных амплитуд КР: a – внешний вид колебательной системы датчика D15, использованного при проведении экспериментов по идентификации модели диссипативных сил (толщина стенки трубок 1 мм); б – зависимость разности фаз между амплитудами A + и A – от отношения между квазистатическими составляющими перемещений ξ = b / c , обусловленными диссипативными и гироскопическими силами
Fig. 1. The dependence of the phase difference of the complex amplitudes of the Coriolis flowmeter, ( a ) the oscillating system of the D15 sensor used in the experiments to identify the dissipative forces (model (the tube wall thickness is 1 mm), ( b ) – the dependency of the phase difference between the amplitudes A + и A – on the ratio of the quasi-static displacement components ξ= b / c due to dissipative and gyroscopic forces
2. Экспериментальное определение диссипативных свойств расходомера Кориолиса
Для проведения экспериментов по определению динамических характеристик образцов датчиков Кориолиса создан специальный лабораторный стенд [35], позволяющий поддерживать заданный уровень расхода континуальной и дисперсной составляющих измеряемого потока. В обсуждаемых экспериментах в качестве жидкости использовалась водопроводная вода, в качестве дисперсной фазы – воздух.
В колебательной системе расходомера возбуждались установившиеся резонансные колебания с амплитудами, близкими к эксплуатационным. Затем возбуждение отключалось, и регистрировались показания комплектных датчиков смещений. Частота записи показаний датчиков превышала частоту колебаний примерно в 200 раз.
Обработка каждой из виброграмм затухающих колебаний сводилась к определению зависимости логарифмического декремента колебаний от амплитуд колебаний (степени нелинейности демпфирования).
-
2.1. Определение логарифмического декремента колебаний
Декремент колебаний определялся по значениям соседних максимальных отклонений основной гармоники сигнала с комплектных датчиков. Для выделения основной гармоники вектор дискретных значений показаний датчика перемещений делился на периоды колебаний и для каждого периода вычислялись коэффициенты разложения ряда Фурье по известным формулам
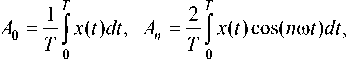
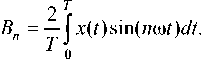
Вычислению декремента предшествовала процедура симметричного линейного сглаживания огибающей максимальных отклонений методом наименьших квадратов по правилу k -ближайших соседей, чтобы выполнить локальную линейную аппроксимацию исходных данных.
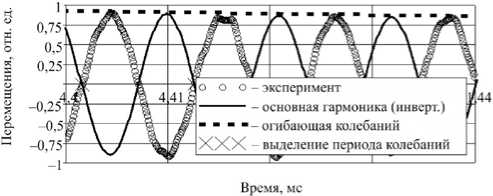
Рис. 2. Иллюстрация выделения основной гармоники регистрируемого в эксперименте перемещения для формирования огибающей затухающих колебаний
Fig. 2. The illustration of the fundamental harmonic allocation of the movement recorded in the experiment for the formation of the damped oscillations envelope
-
2.2. Анализ нелинейности демпфирования
Характер демпфирования в колебательной системе датчика Кориолиса выполнялся разложением зависимости цикловых потерь энергии от амплитуд в степенной ряд
W ^ = WC + WL + W Q + ... = П 0 A + П 1 A 2 + n2 A 3 + ... . (4)
Принимая обобщенную силу трения пропорциональной n -й степени скорости [36]
Q * = - b -I q n - 1 •
можно показать, что при справедливости допущения о медленном затухании свободных колебаний зависимость цикловых потерь энергии от амплитуд колебаний может быть представлена в виде
W ( A) = 3( A) ■ CA 2, (6)
где δ( A ) – логарифмический декремент колебаний; C – приведенная жесткость механической системы.
В случае диссипативных сил, соответствующих показателю степени n = 0 (модель Кулона), также получивших название сил сухого трения, цикловые потери энергии оказываются пропорциональны первой степени амплитуд. Для линейного вязкого трения ( n = 1) цикловые потери энергии пропорциональны второй степени амплитуд колебаний. Для квадратичного трения ( n = 2), соответственно, потери пропорциональны третьей степени амплитуд. Перечисленные степенные функции амплитуд могут быть использованы в качестве базисных при разложении экспериментально полученных виброграмм затухающих колебаний. Такое разложение в ряд по степеням малого параметра A позволяет идентифицировать характер демпфирования в колебательной системе и дать количественные оценки для ответа на вопрос, какая часть необратимых потерь в исследуемой колебательной системе рассеивается по каждой из моделей трения – сухого, линейного, квадратичного и т.д. Таким образом, η 0 , η 1 , η 2 в (4) приобретают смысл долей соответственно сухого, линейного, квадратичного трения в необратимых потерях энергии.
3. Результаты обработки виброграмм затухающих колебаний
Обработке подвергалась часть виброграммы затухающих колебаний, соответствующая уменьшению амплитуд колебаний от соответствующего этому датчику рабочего значения. Обработка результатов записи виброграмм затухающих колебаний, выполненных на одном образце серийного расходомера, показала существенную зависимость диссипативных свойств механической колебательной системы датчика от состояния заполняющей трубку среды. Демонстрируемые колебательной системой диссипативные свойства условно могут быть объединены в три группы колебательных режимов.
-
3.1. Режим без течения жидкой среды по трубке
Экспериментам этой группы соответствуют исключительно низкие значения вибропоглощающих свойств колебательной системы (продолжительность записи виброграммы затухающих колебаний с уменьшением амплитуд в 10 раз превышает 1 минуту). Обработка виброграмм свободных затухающих колебаний образца датчика Кориолиса показала, что логарифмический декремент колебаний не зависел от амплитуд колебаний только для случая сухих трубок. При заполнении трубок жидкостью (даже без движения жидкости через входное и выходное отверстия) убывание амплитуд не следует закону геометрической прогрессии (рис. 3, а ), что служит признаком нелинейного характера демпфирования.
Типичным результатом идентификации характера демпфирования в экспериментах этой группы оказался вывод о том, что на максимальной амплитуде колебаний основной вклад в рассеяние вносит составляющая сил вязкого сопротивления, пропорциональная второй степени скорости (рис. 3, б ). Количественная оценка столь низких диссипативных сил в экспериментах этой группы затруднена тем, что при необходимости продолжительной записи присутствующие в регистрируемом сигнале низкочастотные составляющие, не связанные с процессом диссипации, могут существенно повлиять на получаемый вид анализируемой огибающей затухающих колебаний, следствием чего оказывается перераспределение долей необратимо рассеиваемой энергии.
Составляющие рассеиваемой энергии
Оценка уровня демпфирования
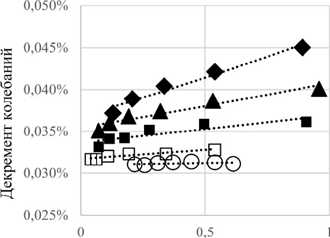
Амплитуда колебаний, отн.ед.
О - незаполненные трубки
□ - заполнение водой без протока
■ - расход воды 0,087 кг/с
А — расход воды 0,279 кг/с
♦ - расход воды 0,544 кг/с
вклад «сухого» трения вклад линейного вязкого трения вклад квадратичного вязкого трения
а
б
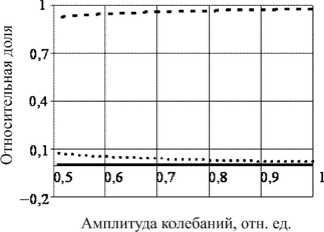
Рис. 3. Результаты экспериментальных исследований демпфирующих свойств: а – зависимость декремента колебаний от амплитуд; б – распределение потерь энергии между моделями сухого, линейного и квадратичного демпфирования в случае отсутствия течения воды
Fig. 3. The experimental results of the damping properties: a is the dependence of the decrement of oscillations on the amplitudes, b is the distribution of energy losses between the models of dry, linear and quadratic damping without the water flow
Оценка уровня демпфирования
а
Составляющие рассеиваемой энергии
вклад «сухого» трения вклад линейного вязкого трения вклад квадратичного вязкого трения
б
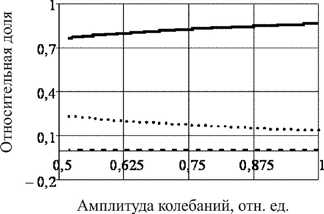
Рис. 4. Результаты экспериментальных исследований демпфирующих свойств в случае течения однофазной жидкости: а – зависимость декремента колебаний от амплитуд, б – распределение потерь энергии между моделями сухого, линейного и квадратичного демпфирования
-
Fig. 4. The experimental results of the damping properties in the case of a single-phase fluid flow: a is the dependence of the decrement of oscillations on the amplitudes; b is the distribution of energy losses between the models of dry, linear and quadratic damping
Составляющие рассеиваемой энергии
Оценка уровня демпфирования
О -расход воды 0,124 кг/с □ - расход воды 0,146 кг/с ■ расход воды 0,235 кг/с
Амплитуда колебаний, опт. ед.
• - вклад «сухого» трения
■ ■ вклад линейного вязкого трения
■ — вклад квадратичною вязкого трения
а
б
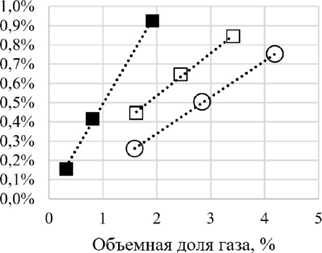
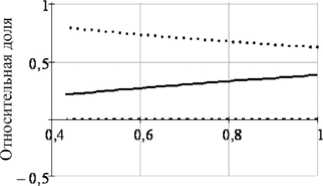
Рис. 5. Результаты экспериментальных исследований демпфирующих свойств в случае неоднородного течения жидкости: а – зависимость декремента колебаний от амплитуд; б – распределение потерь энергии между моделями сухого, линейного и квадратичного демпфирования
-
Fig. 5. The experimental results of the damping properties in the case of a single-phase fluid flow: a is the dependence of the decrement of oscillations on the amplitudes; b is the distribution of energy losses between the models of dry, linear and quadratic damping
-
3.2. Режимы однородного однофазного и двухфазного течений
-
3.3. Режим неоднородного двухфазного течения
Достаточно большим значениям массового расхода жидкости соответствует гладкая монотонная огибающая затухающих колебаний. В экспериментах этой группы зафиксированы наиболее высокие уровни демпфирования. При самом высоком из зарегистрированных уровне демпфирования (1,6 %) уменьшение амплитуд колебаний в 10 раз происходит примерно за 1,5 с. Основной вклад в рассеяние энергии в экспериментах этой группы вносит сила сопротивления, пропорциональная первой степени скорости (рис. 4, б ), и, как следствие, в этом случае декременты колебаний слабо зависят от амплитуд колебаний.
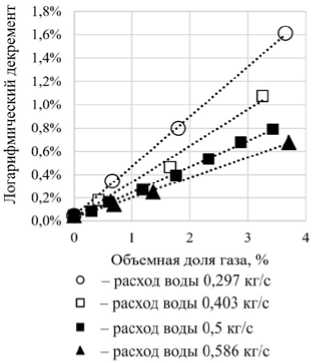
Дать определенную количественную оценку того, какую часть необратимых потерь энергии следует отнести к той иной модели демпфирования, затруднительно и для этой группы экспериментов, поскольку числовые значения долей могут заметно перераспределяться даже для одной виброграммы затухающих колебаний в зависимости от начальной амплитуды и привлекаемой к анализу продолжительности затухающих колебаний. Из устойчиво воспроизводимых особенностей диссипативного поведения колебательной системы в экспериментах этой группы можно указать следующие качественные зависимости. Обработка затухающих колебаний для двухфазных потоков демонстрирует, что для колебательных режимов этой группы диссипация растет с увеличением объемной доли газовой фазы потока, а бόльшим массовым расходам флюида соответствуют меньшие декременты колебаний (рис. 4, а).
Снижение массового расхода воды и увеличение объемной доли воздуха в прокачиваемой через трубку смеси провоцирует разрывы сплошности заполняющей трубку среды, движение которых по трубке проявляется колебаниями скорости изменения амплитуд на огибающей затухающих колебаний. Взаимное соотношение долей необратимо рассеиваемой энергии разными моделями трения еще в большей степени зависит от выбранного фрагмента виброграммы затухающих колебаний, чем в случае однородного потока. Из тенденций качественного характера обращает на себя внимание увеличение декрементов колебаний с ростом объемной доли газовой фазы, но при этом увеличение массового расхода флюида сопровождается не снижением диссипации, как в рассмотренном выше случае, а наоборот – увеличением (рис. 5, а ). Также для режимов этой группы заметно увеличение доли энергии, рассеянной силами «сухого» трения (рис. 5, б ).
Заключение
Происходящее в процессе работы датчика изменение диссипативных свойств колебательной системы расходомера может изменить соотношение между регистрируемым датчиком фазовым сдвигом и массовым расходом протекающей через трубку среды. На основании обработки экспериментов, выполненных по предложенному в рамках настоящей работы решению задачи идентификации диссипативных характеристик колебательной системы, показано, что изменение дис- сипации колебательной системы расходомера Кориолиса может быть связано как с изменением массового расхода, так и с изменением фазового состава протекающего через трубку флюида. В выполненных в рамках настоящей работы экспериментах диапазон изменения диссипативных свойств при фиксированном массовом расходе воды характеризовался изменением логарифмического декремента колебаний более чем в 50 раз. Предложенный вариант анализа степени нелинейности демонстрируемых колебательной системой расходомера Кориолиса диссипативных свойств показал возможность возникновения в колебательной системе сил сопротивления, соответствующих разным моделям трения (сухого, линейного вязкого, квадратичного вязкого). Показано, что величины вклада каждого вида трения в полную энергию, рассеиваемую колебательной системой, зависят от фазового состава и режима течения флюида. Полученные в работе результаты ориентированы на использование в качестве исходных данных при решении задачи о разделении вклада диссипативных и гироскопических сил в основной регистрируемый расходомером Кориолиса параметр – разность фаз синхронных гармонических колебаний двух разных сечений упругой трубки расходомера.
Список литературы Оценка диссипативных свойств колебательной системы серийного образца расходомера кориолиса
- Dudley B. BP Statistical Review of World Energy Statisti-cal Review of World // bp.com. – 2019. (https://www.bp.com/ content/dam/bp/business-sites/en/global/corporate/pdfs/energy-econo-mics/statistical-review/bp-stats-review-2019-full-report.pdf) (дата обращения: 01.03.2020).
- Multiphase flow metrology in oil and gas production / S. Knotek [et al.] // EURAMET Project ENG58. Final publishable JPR report. – 2017.
- Multiphase flow modelling based on experimental testing: A comprehensive overview of research facilities worldwide and the need for future developments / G. Falcone [et al.] // SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition. – Anaheim, 2007. – Р. 1–10.
- Falcone G., Harrison B. Forecast expects continued multi-phase flowmeter growth // Oil and Gas Journal. – 2011. – Vol. 109, № 10. – Р. 68–73.
- Baker R.C. Coriolis flowmeters: industrial practice and published information // Flow Measurement and Instrumentation. – 1994. – Vol. 5, № 4. – Р. 229–246.
- Wang T., Baker R. Coriolis flowmeters: a review of devel-opments over the past 20 years, and an assessment of the state of
- the art and likely future directions // Flow Measurement and In-strumentation. – 2014. – Vol. 40. – Р. 99–123.
- Binulal B.R., Kochupillai J. Coriolis flow meter: a review from 1989 to 2014 // International Journal of Scientific & Engi-neering Research. – 2014. – Vol. 5, № 7. – Р. 718–723.
- Anklin M., Drahm W., Rieder A. Coriolis mass flowmeters: Overview of the current state of the art and latest re-search // Flow Measurement and Instrumentation. – 2006. – Vol. 17, № 6. – Р. 317–323.
- Kolhe V.A., Edlabadkar R.L. An overview of Coriolis mass flowmeter as a direct mass flow measurement device // Int. J. on Emerging Trends in Technology. – 2016. – Vol. 3, iss. 2. – P. 2112–2119.
- Modeling a Coriolis mass flow meter for shape optimiza-tion / W. Hakvoort [et al.] // Proceedings of the 1st Joint Interna-tional Conference on Multibody System Dynamics. – Lappeenran-ta, 2010. – P. 1–10.
- Kutin J., Bajsić I. An analytical estimation of the Coriolis me-ter's characteristics based on modal superposition // Flow Measurement and Instrumentation. – 2002. – Vol. 12, iss. 5. – P. 345–351.
- Sultan G., Hemp J. Modelling of the Coriolis mass flowmeter // Journal of Sound and Vibration. – 1989. – Vol. 132, iss. 3. – P. 473–489.
- Effect of detector masses on calibration of Coriolis flowmeters / U. Lange [et al.] // Flow Measurement and Instru-mentation. – 1994. – Vol. 5, iss. 4. – P. 255–262.
- Raszillier H., Alleborn N., Durst F. Effect of a concen-trated mass on Coriolis flow metering // Archive of Applied Me-chanics. – 1994. – Vol. 64, iss. 6. – P. 373–382.
- Wang T., Baker R.C. An advanced numerical model for single straight tube Coriolis flowmeters // Journal of Fluids Engi-neering. – 2006. – Vol. 128, iss. 6. – P. 1346–1350.
- Ruoff J., Hodapp M., Kück H. Finite element modelling of Coriolis mass flowmeters with arbitrary pipe geometry and unsteady flow conditions // Flow Measurement and Instrumenta-tion. – 2014. – Vol. 37. – P. 119–126.
- Belhadj A., Cheesewright R., Clark C. The simulation of Coriolis meter response to pulsating flow using a general purpose f.e. code // Journal of Fluids and Structures – 2000. – Vol. 14, iss. 5. – P. 613–634.
- Stack C., Garnett G., Pawlas G. A finite element for the vibration analysis of a fluid-conveying Timoshenko beam // 34th Structures, Structural Dynamics and Materials Conference. – La Jolla, 1993. – P. 2120–2129.
- Миронов М.А., Пятаков П.А., Андреев А.А. Вынужденные изгибные колебания трубы с потоком жидкости // Акустический журнал. – 2010. – Т. 56, № 5. – С. 684–692.
- Coupled finite-volume/finite-element modelling of the straight-tube Coriolis flowmeter / G. Bobovnik [et al.] // Journal of Fluids and Structures. – 2005. – Vol. 20, iss. 6. – P. 785–800.
- An improved three-dimensional coupled fluid–structure model for Coriolis flowmeters / N. Mole [et al.] // Journal of Flu-ids and Structures. – 2008. – Vol. 24, iss. 4. – P. 559–575.
- Kumar V., Anklin M., Schwenter B. Fluid-structure in-teraction (FSI) simulations on the sensitivity of Coriolis flow me-ter under low Reynolds number flows // 15th Flow Measurement Conference (FLOMEKO 2010). – Taipei, 2010. – P. 1–10.
- Kumar V., Anklin M. Numerical simulations of Coriolis flow meters for low Reynolds number flows // Mapan – Journal of Metrology Society of India – 2011. – Vol. 26, № 3. – P. 225–235.
- Luo R., Wu J., Wan S. Numerical study on the effect of low Reynolds number flows in straight tube Coriolis flowmeters // XX IMEKO World Congress Metrology for Green Growth. – Busan, 2012. – P. 1–4.
- Luo R., Wu J. Fluid-structure coupling analysis and simula-tion of viscosity effect on Coriolis mass flowmeter // 5th Asia Pacific Congress On Computational Mechanics & 4th International Symposi-um On Computational Mechanics. – Singapore, 2013. – P. 1–8.
- Huber C., Nuber M., Anklin M. Effect of Reynolds number in Coriolis flow measurement // European Flow Measure-ment Workshop. – Lisbon, 2014. – P. 1–9.
- Romanov V.A., Beskachko V.P. The simulation of Coriolis flow meter tube movements excited by fluid flow and exte-rior harmonic force // Advanced Mathematical and Computational Tools in Metrology and Testing XI. – Glasgow, 2017. – P. 294–306.
- Brennen C.E. Fundamentals of Multiphase Flows. – Cambridge University Press, 2005. – P. 220–245.
- Dukler A.E., Taitel Y. Flow Pattern Transitions in Gas–liquid Systems: Measurement and Modeling // Multiphase science and technology. – 1986. – Vol. 2. – P. 1–94.
- Two-phase flow metering of viscous oil using a Coriolis mass flow meter: a case study / M. P. Henry [et al.] // Flow Measurement and Instrumentation. – 2006. – Vol. 17, iss. 6. – P. 399–413.
- New applications for Coriolis meter-based multiphase flow metering in the oil and gas industries / M.P. Henry [et al.] // The 10th International symposium of measurement technology and intelligent instruments. – Daejeon, 2011. – P. 1–6.
- Coriolis mass flow metering for three-phase flow: A case study / M.P. Henry [et al.] // Flow Measurement and Instrumenta-tion. – 2013. – Vol. 30. – P. 112–122.
- Basse N. Coriolis flowmeter damping for two-phase flow due to decoupling // Flow Measurement and Instrumentation. – 2016. – Vol. 52. – P. 40–52.
- Two-phase damping for internal flow: physical mecha-nism and effect of excitation parameters / C. Charreton [et al.] // Journal of Fluids and Structures. – 2015. – № 56. – P. 56–74.
- Лех И.А., Тараненко П.А., Бескачко В.П. Влияние пузырьков газа на вибрационные параметры измерительных трубок кориолисового расходомера // Вестник ЮУрГУ. Серия «Математика. Механика. Физика». – 2019. – Т. 11, № 3. – С. 47–55.
- Пановко Я.Г. Введение в теорию механических колебаний. – М.: Наука, 1980. – 272 с.


