Оценка эффективности режима усиления ультразвуковой визуализации игл для периферической регионарной анестезии
Автор: Кулигин А.В., Панов В.А., Лахин Р.Е., Щеголев А.В., Яценко Д.В., Котикова М.Н.
Журнал: Саратовский научно-медицинский журнал @ssmj
Рубрика: Анестезиология и реаниматология
Статья в выпуске: 4 т.10, 2014 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Цель: оптимизация проведения периферической регионарной анестезии под контролем ультразвука. Материал и методы. Исследование выполняли на ультразвуковом аппарате SonoSite Edge (SonoSite, Bothell, США) линейным датчиком 38-мм (13-6 MHz) при фиксированных показателях общего усиления и глубины. В исследование были включены 2 сонографичные иглы и 2 несонографичные иглы. Ультразвуковые изображения получал и анализировал опытный анестезиолог. Результаты. В данном исследовании продемонстрировано улучшение ультразвуковой визуализации игл для периферической регионарной анестезии с помощью технологии SonoMBe по сравнению с традиционно используемым режимом сканирования. Заключение. Технология SonoMBe повышает эхогенность игл для периферической регионарной анестезии, что позволяет использовать данную технологию усиления при выполнении проводниковой и плексусной анестезии.
Регионарная анестезия, режим усиления, сонографичные иглы, ультразвуковая визуализация
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/14918018
IDR: 14918018
Текст научной статьи Оценка эффективности режима усиления ультразвуковой визуализации игл для периферической регионарной анестезии
1 Введение. Ультразвуковая навигация как метод объективного контроля выполнения периферических блокад широко применяется в повседневной практике проведения регионарной анестезии. Ультразвуковой контроль в режиме реального времени позволяет идентифицировать целевую анатомическую структуру, окружающие сосуды и ткани, а также положение иглы относительно них, способствуя снижению таких осложнений, как непреднамеренная пункция сосудов и эндоневральное введение [1–3]. Ультразвуковая навигация сокращает время выполнения блокады и позволяет снизить объем вводимого местного анестетика.
Визуализация тела и кончика иглы в данном контексте очень важна, хотя нередко труднодостижима [4–6]. Ухудшение визуализации несонографичных игл при увеличении угла вкола обусловлено физическими принципами образования ультразвукового изображения [7, 8]. С ростом угла введения иглы возрастает рассеивание ультразвуковых волн и тем самым снижается визуализация. В настоящее время для повышения сонографичности созданы специализированные иглы с нанесенными на их поверхность так называемыми насечками-рефлекторами, призванными отражать ультразвуковые волны обратно к ультразвуковому датчику [9, 10]. Это облегчает визуализацию иглы, но не решает всех проблем с визуализацией, особенно при проведении манипуляций с большим углом вкола [11].
Некоторые производители ультразвуковых сканеров реализовали в своих аппаратах технологии повышения эхогенности игл. Суть этих технологий заключается в компьютерном усилении эхо-сигналов, возвращающихся к трансдюсеру от линейных предметов [12, 13].
Осуществленное исследование посвящено сравнению эхогенности игл, применяемых в нашей стране для периферической регионарной анестезии, при ультразвуковом сканировании в стандартном двумерном режиме и с использованием технологии многолучевого сканирования SonoMBe, улучшающей визуализацию.
Цель: оптимизация проведения периферической регионарной анестезии под контролем ультразвука.
Материал и методы . Исследование выполняли на ультразвуковом аппарате SonoSite Edge (SonoSite, Bothell, США) линейным датчиком 38-мм (13–6 MHz) при фиксированных показателях общего усиления и глубины. Сканирование производилось в стандартном В-режиме с выключенной и включенной функцией SonoMBe. При включении этой функции визуализация иглы улучшается за счет рассмотрения исследуемой области под несколькими углами, объединения и усреднения полученных при сканировании данных. SonoMBe в зависимости от зоны действия и угла вкола иглы имеет три варианта: «полого», «средне» и «круто».
В исследование были включены 2 сонографичные иглы: Stimuplex D Ultra 22G (StDU) (BBraun, Melsungen, Германия), SonoPlex Stim 22G (SPS) (Pajunk Medizintechnologie, Geisingen, Германия) и 2 несонографичные иглы: Stimuplex D 22G (StD) и UniPlex NanoLine 22G с фасетным срезом (UPNL), (Pajunk Medizintechnologie, Geisingen, Германия).
Ультразвуковые изображения получал опытный анестезиолог, практикующий в регионарной анестезии и имеющий опыт ультразвуковой визуализации. Сканирование выполнялось при продольном направлении иглы относительно датчика на макете Blue Phantom (Advanced Medical Technologies, Kirkland, США) при введенной игле под углом 15°, 30°, 45°, 60° к поверхности макета. После выполнения сканирования в В-режиме исследование проводили в каждом из вариантов усиления иглы. В результате было отобрано 64 наилучших изображений исследуемых игл.
Количественную оценку эхогенности игл проводили путем анализа полученных изображений в программе Adobe Photoshop CS5 (Adobe Systems Software, Ирландия). Инструментом «Lasso» начиная от кончика выделялся участок иглы длинной 50 мм. Затем для этого участка строилась яркостная гистограмма, представляющая собой диаграмму градиента яркости от 0 (абсолютно неяркий, черный) до 255 (абсолютно яркий, белый). В окне диалога «Histo-gram» фиксировался параметры «Mean» и «Standart deviation», указывающие среднее значение яркости выделенного участка и отклонение от этого значения.
Статистический анализ полученных данных выполнен с применением программы Statistica 10 (StatSoft, США). Структуру связи между типом иглы, углом введения, вариантом усиления и эхогенностью выявляли в регрессионном анализе. Для сравнения исходной эхогенности игл и при активации технологии SonoMBe использовали непараметрический Т-критерий Вилкоксона для парных сравнений, для сравнения эхогенности игл различных типов применяли U-критерий Манна-Уитни. Различия считали значимыми при р<0,05.
Результаты. При анализе полученных ультразвуковых изображений в программе Adobe Photoshop CS5 были определены количественные значения яркости эхогенности исследуемых игл при углах введения от 15° до 60° в Blue Phantom при различных вариантах усиления и без него (табл. 1, 2). Рисунки 1–4 иллюстрируют эти данные.
Угол введения иглы 15°. При сканировании в В-режиме лучшее изображение исследуемых игл получено при их введении под углом 15°. Это обусловлено низкой степенью рассеивания эхо-сигнала из-за поверхностного расположения объектов. При введении под углом 15° определяли самые высокие показатели среднего значения яркости визуализируемых игл (см. табл. 1, 2), что обеспечивало их хорошую видимость. Статистически значимых различий эхогенности несонографичных и сонографичных игл при данном угле вкола не отмечено.
При сканировании с активированной функцией SonoMBe при введении иглы под углом в 15° значимого роста средней яркости зафиксировано не было, что во многом обусловлено максимальным значением эхогенности игл введенных под этим углом. Некоторое улучшение визуализации игл с включенной функцией SonoMBe происходит за счет усиления реверберационных эхо-сигналов. Этот артефакт в наибольшей степени проявлялся в варианте усиления «полого» (см. рис. 3).
Угол введения иглы 30°. При сканировании в В-режиме увеличение угла введения до 30° приводило к снижению яркости всех игл по сравнению с углом введения 15°. У несонографичных игл кончик визуализировался лучше тела, если срез иглы был обращен к трансдюсеру. Это связано с лучшим отражением ультразвуковых волн от неровной поверхно-
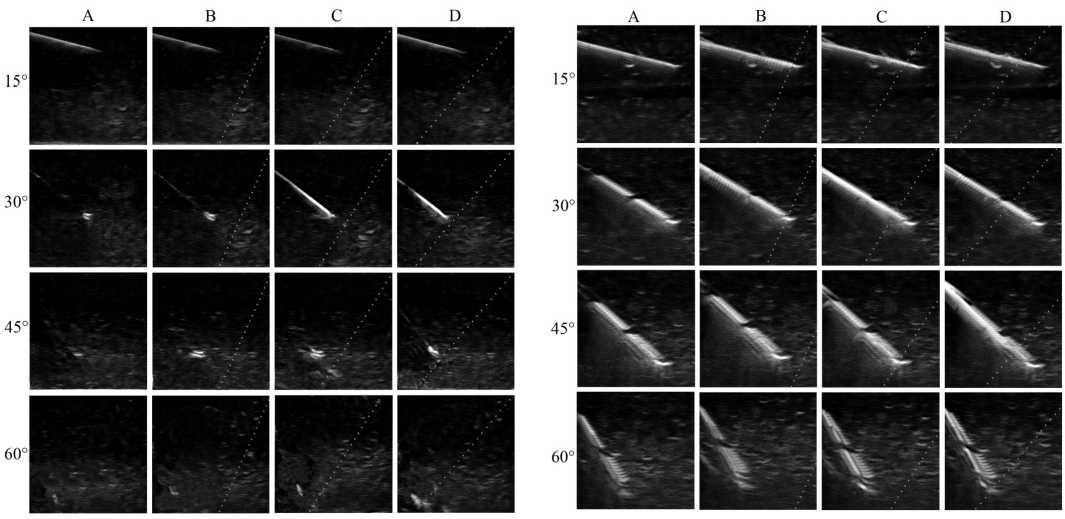
Рис. 1. Ультразвуковые изображения иглы UPNL: A — без усиления, В — вариант усиления «полого», C — вариант усиления «средне», D — вариант усиления «круто»
Рис. 2: Ультразвуковые изображения иглы SPSc: A — без усиления, В — вариант усиления «полого», C — вариант усиления «средне», D — вариант усиления «круто»
А В C D
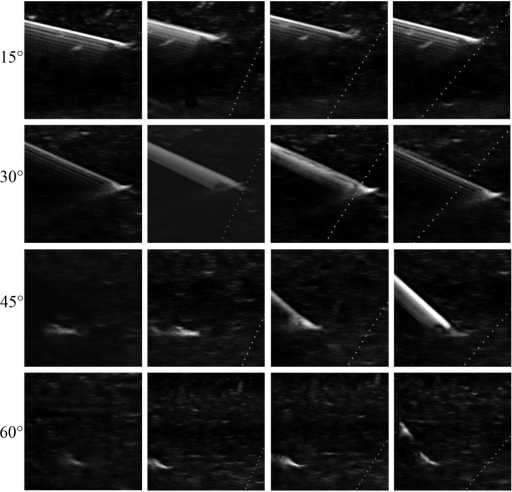
Рис. 3: Ультразвуковые изображения иглы StD: A — без усиления, В — вариант усиления «полого», C — вариант усиления «средне», D — вариант усиления «круто»
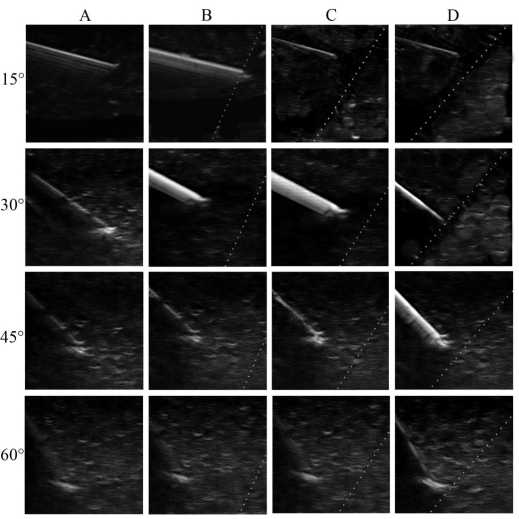
Рис. 4. Ультразвуковые изображения иглы StDU: A — без усиления, В — вариант усиления «полого», C — вариант усиления «средне», D — вариант усиления «круто»
сти кончика иглы, чем от гладкого тела. При данном угле вкола отчетливо визуализировались метки-рефлекторы сонографичных игл.
При сканировании с активированной функцией SonoMBe выявлен рост эхогенности во всех вариантах усиления. Наибольшее значение яркости получено в варианте усиления «средне». При усилении эхо-сигнала у сонографичных игл наряду с метками-рефлекторами визуализировалось и тело иглы. Игла SPSc показала максимальное в исследовании значение яркости, значимо отличающееся от других игл (см. табл. 2).
Угол введения иглы 45°. При сканировании в стандартном двумерном режиме с увеличением угла вкола эхогенность игл продолжала снижаться. Осно- вой для визуализации сонографичных игл при введении под углом 45° были метки-рефлекторы, несонографичных — кончик иглы. Тело этих игл практически не визуализировалось.
Включение функции усиления проводило к росту эхогенности в вариантах усиления «средне» и «круто» для всех типов игл, с наибольшей яркостью в позиции «круто». Игла UPNL даже при усилении визуализировалась неудовлетворительно. Для иглы SPSc рост эхогенности был несущественным, а само изображение неоднородным, такой же феномен зафиксирован и для другой сонографичной иглы StDU. Наибольший рост яркости и однородное изображение получено для иглы StD (см. рис. 3).
Таблица 1
Яркость исследуемых несонографичных игл в условных единицах на ультразвуковых изображениях при различных углах введения и вариантах усиления (M±SD)
|
Вариант усиления |
Игла UPNL |
|||
|
Угол введения |
||||
|
15° |
30° |
45° |
60° |
|
|
«без усиления» |
122,34±39,1 |
76,39±41,1 |
39,5±27,2 |
31,4±29,7 |
|
«полого» |
121,23±31,4 |
73,11±31,3 |
41,66±29,4 |
34,4±29,7 |
|
«средне» |
122,56±38,3 |
144,53±34,2 * |
70,9±28,1 |
34,7±28,9 |
|
«круто» |
121,19±36,4 |
134,2±45,2' * |
139,19±38,3* |
39,2±34,7 |
|
StD |
||||
|
«без усиления» |
131,39±36,3 |
57,95±32,9 |
36,3±29,5 |
31,1±25,9 |
|
«полого» |
140,15±34,1 |
69,11±42,8 |
11,7±40,2 |
34,3±32,1 |
|
«средне» |
139,49±39,3 |
146,18±18,2 * |
72,3±37,5 |
33,8±27,6 |
|
«круто» |
141,29±21,7 |
131,46±37,2 ' * |
145,14±19,2 * |
42,4±42,2 |
|
Примечание:*—p<0,05 при сравнении со значением в варианте «без усиления». |
||||
Таблица 2
Яркость исследуемых сонографичных игл в условных единицах на ультразвуковых изображениях при различных углах введения и вариантах усиления (M±SD)
|
Вариант усиления |
Игла SPSc |
|||
|
Угол введения |
||||
|
15° |
30° |
45° |
60° |
|
|
«без усиления» |
143,29±30,1 |
139,47±42,7 |
137,8±37,1 |
102,6±37,5 |
|
«полого» |
146,33±31,1 |
141,25±32,6 |
137,6±37,5 |
102,5±37,2 |
|
«средне» |
145,2±30,7 |
188,37±38,9 *,** |
142,12±34,1 |
107,5±36,1 |
|
«круто» |
143,1±28,4 |
150,21±42,9 * |
176,18±47,4 *,** |
108,1±41,4 |
StDU
|
без усиления |
122,75±36,3 |
64,66±30,2 |
35,18±29,8 |
30,35±28,7 |
|
«полого» |
126,14±34,3 |
140,32±21,2 |
39,8±30,6 |
30,2±28,1 |
|
«средне» |
125,71±35,1 |
143,58±26,8 * |
44,3±29,1 |
30,3±27,9 |
|
«круто» |
125,66±36,6 |
117,13±31,9 * |
145,99±30,1 * |
38,49±32,6 |
Примечание:*—p<0,05 при сравнении со значением в варианте «без усиления»; **– p<0,05 при сравнении со значением эхогенности других исследуемых игл при введении под углом 30 ° и 45 °.
Угол введения иглы 60°. Угол введения 60° оказался самым проблемным для визуализации. При стандартном сканировании выявлено наименьшее значение эхогенности всех исследуемых игл, обусловленное высокой степенью отражения и рассеивания ультразвуковых волн. При использовании функции усиления в этой позиции иглы статистически значимого роста яркости зафиксировано не было, хотя визуализация тела игл StD и StDU улучшилась (см. рис. 3, 4). Наиболее ярко визуализируемой иглой при угле введения 60° оказалась игла SPSc (см. табл. 2).
Обсуждение. Выявленные различия эхогенности исследуемых игл при активировании различных вариантов функции усиления SonoMBe вполне закономерны. Если измерить угол, который образуется между условной линией в подрежиме усиления и линией верхней горизонтальной границы полученного изображения, то для вариантов усиления «полого», «средне», «круто» он соответственно составляет 65°, 60° и 50°. Процессор ультразвукового аппарата усиливает только те эхо-сигналы от линейных объектов, которые расположены перпендикулярно определенной для варианта усиления плоскости. Соответственно, чтобы определить оптимальный угол вкола, обеспечивающий перпендикулярное расположение иглы по отношению к условной линии варианта усиления функции SonoMBe, необходимо из 90° вычесть указанное выше значение угла для конкретного варианта усиления. Таким образом, максимальная эхогенность игл будет при углах введения 25° для варианта «полого», 30° для варианта «средне» и 40° для варианта усиления «круто», что подтверждается полученными данными (см. табл. 1, 2) и результатами исследования Takatani J. и соавт. [12].
Это также согласуется с инструкций пользователя, применяемой в использовании ультразвуковой машины. Производитель для получения оптимального результата при активной функции усиления рекомендует вводить иглу под углом не более 50° к поверхности датчика.
Полученные в исследовании данные также свидетельствуют, что эхогенность зон с метками-рефлекторами выше у иглы SPSc. Это обусловлено тем, что метки-рефлекторы этой иглы представлены тремя равными по площади отражающими поверхностями, тогда как рефлекторы гиперэхогенных зон иглы StDU имеют фактически две отражающие поверхности. Еще одной причиной снижения эхогенности игл Bbraun, по мнению Guo S. и соавт. [10], может служить электроизолирующее покрытие белого цвета, рассеивающее ультразвуковые волны.
В регрессионном анализе выявлено, что наибольшее влияние на эхогенность игл при активной функции усиления оказывали угол введения (p<0,001) и вариант усиления (p<0,01). Тип иглы значимого влияния на эхогенность при активной функции усиления не показал. Схожие результаты были получены Wiesmann T. и соавт. при исследовании яркости игл на трупах [14].
Также было установлено, что эхогенность игл значимо возрастала при применении вариантов усиления в диапазоне углов введения 30°–45° (p<0,05). Значимого роста яркости при углах введения 15° и 60° не получено.
Наибольшие показатели эхогенности получены при введении иглы под углом 30° в варианте усиления «средне», а под углом 45° в варианте усиления «круто».
Заключение. Таким образом, исследование показало, что технология SonoMBe повышает эхогенность как сонографичных, так и обычных игл для периферической регионарной анестезии. Использование данной технологии усиления способно помочь при выполнении проводниковой и плексусной анестезии, однако необходимы дальнейшие исследования, чтобы оценить эти результаты в клинических условиях.
Список литературы Оценка эффективности режима усиления ультразвуковой визуализации игл для периферической регионарной анестезии
- Griffin J., Nicholls B. Ultrasound in regional Anaesthesia. Anaesthesia 2010; 65 (Suppl. 1): 1-12
- Sites B.D., Chan V.W., Neal J.M., et al. The American Society of Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine and the European Society of Regional Anaesthesia and Pain Therapy Joint Committee Recommendations for education and training in ultrasound regional anaesthesia. Reg Anest Pain Med 2009; 34 (1): 40-46
- Warman P., Nicholls B. Ultrasound-guided nerve blocks: efficacy and safety. Best Pract Res Clin Anaesthesiol 2009; 23 (3): 313-326
- Chapman G.A., Johnson D., Rodenham A.R. Visualisation of needle position using ultrasonography. Anaesthesia 2006; 61 (2): 148-158
- Hocking G., Hebard S., Mitchell C.H. A review of the benefits and pitfalls of phantoms in ultrasound-guided regional anesthesia. Reg Anest Pain Med 2011; 36 (2): 162-170
- Hebard S., Hocking G. Echogenic technology can improve needle visibility during ultrasound-guided regional anesthesia. Reg Anest Pain Med 2011; 36 (2): 185-189
- Edgombe H., Hocking G. Sonographic identification of needle tip by specialists and novices: a blinded comparison of 5 regional needles in fresh cadavers. Reg Anest Pain Med 2010; 35 (2): 207-211
- Marhofer P., Greher M., Kapral S. Br J Anaesth 2005; 94 (1): 7-17
- Deam R.K., Kluger R., Barrington C.A., et al. Investigation of a new echogenic needle for use with ultrasound peripheral nerve blocks. Anaesth Intensive Care 2007; 35 (4): 582-586
- Guo S., Schwab A., McLeod G., et al. Echogenic regional anaesthesia needles: a comparison study in thiel cadavers. Ultrasound Med Biol 2012; 38 (4): 702-707
- Phelan MP., Emerman C., Peacock WF., etal. Do echo-enhanced needles improve time to cannulate in a model of short-axis ultrasound-guided vascular access for a group of mostly inexperienced ultrasound users? Int J Emerg Med 2009; 2 (3): 167-170
- Takatani J, Takeshima N, Okuda K, et al. Enhanced Needle Visualization: advantages and indications of an ultrasound software package. Anaesth Intensive Care 2012; 40 (5): 856-860
- Viscasillas J, Benigni L, Brodbelt D, et al. Use of needle enchancing software to improve injection technique amongst inexperienced anaesthetists performing ultrasound-guided peripheral nerves blocks in dogs. Vet Anaesth Analg 2013; 40 (6): 83-90
- Wiesmann T, BorntrflgerA, Zoremba M, etal. Compound imaging technology and echogenic needle design: effects on needle visibility and tissue imaging. Reg Anest Pain Med 2013; 38 (5): 452-455.


