Оценка направления роста трещины в условиях смешанного нагружения (нормальный отрыв и поперечный сдвиг): обобщенные критерии классической механики разрушения и атомистическое моделирование смешанного нагружения (метод молекулярной динамики)
Автор: Степанова Л.В., Бронников С.А., Белова О.Н.
Статья в выпуске: 4, 2017 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Работа посвящена оценке направления роста трещины в условиях смешанно-го нагружения (нормальный отрыв и поперечный сдвиг) в изотропном линейно-упругом материале с использованием двух подходов: с помощью обобщенных критериев классической континуальной механики разрушения и атомистического моделирования, выполненного с помощью метода молекулярной динамики в паке-те LAMMPS (Large-scale Molecular Massively Parallel Simulator). В рамках контину-альной классической линейной механики разрушения использовались два крите-рия: 1) критерий максимального тангенциального напряжения; 2) критерий мини-мума плотности упругой энергии деформации на примере пластины с одной центральной трещиной. В каждом критерии разрушения использовалось многопа-раметрическое представление поля напряжений у вершины трещины - полное асимптотическое разложение М. Уильямса, в котором удерживались высшие при-ближения. Получены углы направления роста трещины для параметра смешанно-сти нагружения, задающего вид нагружения в полном диапазоне смешанных форм деформирования. Выполнено компьютерное атомистическое моделирование про-цесса роста трещины в пакете LAMMPS для различных видов смешанного нагру-жения. Получены углы направления распространения трещины на примере пла-стины с центральной трещиной для различных значений параметра смешанности нагружения в широком диапазоне температур. Проведено сравнение углов распро-странения трещины, полученных с помощью двух подходов: подхода континуаль-ной механики разрушения и атомистического моделирования, базирующегося на
Направление роста трещины, смешанное нагружение, критерий максимального тангенциального напряжения, критерий минимума плотности энергии упругой деформации, атомистическое моделирование, метод молекулярной динамики
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/146211701
IDR: 146211701 | УДК: 539.42 | DOI: 10.15593/perm.mech/2017.4.13
Текст научной статьи Оценка направления роста трещины в условиях смешанного нагружения (нормальный отрыв и поперечный сдвиг): обобщенные критерии классической механики разрушения и атомистическое моделирование смешанного нагружения (метод молекулярной динамики)
PNRPU MECHANICS BULLETIN
Analytical solutions are obtained to determine the critical plane orientation for multiaxial stress state. This critical plane is the plane of development of fatigue damage under cyclic loading. The cases of in-phase and antiphase cyclic loadings are considered for the classical fatigue range (low-cycle and high-cycle fatigue).
Generalizations of the Findley fatigue criterion are proposed taking into account the orientation of the critical plane for modes of very-high-cycle fatigue under in-phase and antiphase cyclic multiaxial loadings. These generalizations are based on the similarity of the left and right branches of the bimodal fatigue curve. The procedure aimed at determining the parameters of the generalized criterion is described according to the data of two uniaxial fatigue tests for tension-compression at various coefficients of the cycle asymmetry.
The stressed state of the compressor disk of the gas turbine engine are calculated by the finite element method for a low-cycle fatigue (take off-flight-landing cycles) and for very-high-cycle fatigue (vibrations of blades). For low-cycle fatigue the effect of aerodynamic, centrifugal and contact loads for the contact system of disk, blades, fixing pins and shroud are taken into account. For very-high-cycle fatigue the additional stresses due to high-frequency torsional vibrations of blades and shroud are calculated. In both cases, a stress concentration zone was defined in the vicinity of the contact between the disc and the blades, in which the fatigue damage originates.
The distribution of stresses and the proposed generalizations of the fatigue fracture criteria were used to obtain estimates of disk durability for both low-cycle fatigue and very-high-cycle fatigue modes. Numerical analysis showed that real time durability for the considered fatigue modes can be very close taking into account the characteristic cycle period. Therefore, in predictions of a safe operation life both mechanisms of fatigue must be taken into account.
1. Определение критической плоскости для многоосного напряженного состояния в режимах МЦУ и МНЦУ
Для оценки усталостной долговечности различных элементов конструкций в реальных условиях эксплуатации существуют различные модели и критерии усталостного разрушения с учетом многоосного напряженного состояния [1–5].
В современных подходах к построению многоосных критериев усталостного разрушения часто используется понятие критической плоскости [6–14]. Один из первых критериев с определением критической плоскости для классических режимов малоцикловой (МЦУ, число циклов до разрушения 103 < N < 105) и многоцикловой (МНЦУ, число циклов до разрушения 105 < N < 107) усталости был предложен Финдли [15]. Согласно этому критерию, развитие усталостных повреждений в циклическом процессе нагружения происходит по плоскости с нормалью n (с компонентами nk, k = 1, 2, 3), на которой максимум комбинации (Δτn/2+ αFσn) достигает определенного критического значения. Такая плоскость называется критической.
В этой комбинации Δτ n – размах касательного напряжения в цикле, σ n – нормальное напряжение на этой плоскости, σ – тензор напряжений, который определяет напряженное состояние в материальной частице деформируемого тела, и
σ n = n ⋅ σ ⋅ n , τ n = σ ⋅ n - ( n ⋅ σ ⋅ n ) n .
Для определения долговечности одноосного циклического нагружения образца вплоть до его усталостного разрушения существует соотношение Баскина [16], которое аналитически представляет усталостную кривую при различных коэффициентах асимметрии цикла (левая ветвь бимодальной усталостной кривой [17] (рис. 1):
σ=σu+σcNβ, где σu – предел усталости; σc – коэффициент усталостной прочности; β – показатель усталостной прочности; N – число циклов до разрушения. На рис. 1 по оси ординат схематически показаны значения амплитуд σa циклического процесса нагружения при различных коэффициентах асимметрии цикла в зависимости от N.
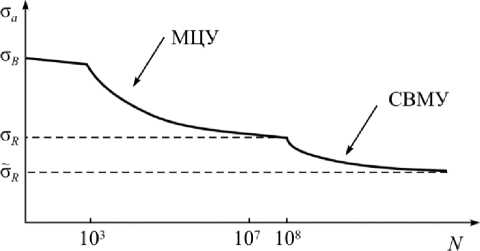
Рис. 1. Бимодальная усталостная кривая для режимов МЦУ и СВМУ Fig. 1. Bimodal fatigue curve for LCF and VHCF modes
Обобщение соотношения Баскина на многоосный случай для критерия Финдли имеет вид [1]
(Δτn/2+ αFσn)MAXn = SF+ AFNF , где βF < 0, αF , SF , AF – параметры, определяемые по данным эксперимента.
Расчет усталостной долговечности по критерию Финдли требует определения ориентации плоскости, проходящей через заданную материальную точку, на которой внутри цикла t∈ [0,T] достигается максимальное выражение функции Финдли F = Δτ +2α maxσ . Для n Ft∈[0,T] n многоосного напряженного состояния это непростая задача, которая при необходимости решается численно. Построим ее аналитическое решение для синфазного и противофазного циклического нагружения.
-
1.1. Синфазное многоосное циклическое нагружение
Рассмотрим трехосное циклическое нагружение в системе координат, связанной с главными осями тензора напряжений. Предполагаем, что эти оси не изменяются в тече- ние цикла, а главные значения тензора напряжений меняются по гармоническому закону без сдвига фаз относительно друг друга:
σ1(t)=σ1m+σ1asinωt, σ2(t)=σ2m+σ2asinωt, σ3(t)=σ3m+σ3asinωt, σ1,2,3a ≥0, где дополнительным индексом m помечены средние за цикл значения напряжений, а индексом a их амплитуды.
Размах главных напряжений в цикле
Δσ 1 = 2σ 1 a ≥0, Δσ 2 =2σ 2 a ≥0, Δσ 3 =2σ 3 a ≥0.
Выберем главные оси так, чтобы максимумы главных напряжений удовлетворяли неравенствам Σ 1 ≥Σ 2 ≥Σ 3 , где Σ 1 =σ 1 m +σ 1 a , Σ 2 =σ 2 m +σ 2 a , Σ 3 =σ 3 m +σ 3 a .
Введем следующие обозначения: Σ 12 =Σ 1 -Σ 2 , Σ 13 =Σ 1 -Σ 3 , Σ 23 =Σ 2 -Σ 3 ,
Δσ 12 = Δσ 1 -Δσ 2 , Δσ 13 = Δσ 1 -Δσ 3 , Δσ 23 =Δσ 2 -Δσ 3 .
В главных осях тензора напряжений можно получить формулы (см. Приложение)
Δτ n = -\j (Δσ 12 ) 2 n 12 n 22 + (Δσ 13 ) 2 n 12 n 32 + (Δσ 23 ) 2 n 22 n 32 , t m ∈ [0 a T x ] σ n = Σ 1 n 12 + Σ 2 n 22 + Σ 3 n 32 .
С учетом этих формул определим ориентацию критической плоскости с компонента ми нормали: x1=n12 ≥0, x2=n22 ≥0, x3= n32 ≥ 0 , x1+ x2+x3=1 .
Можно показать, что задача определения критической плоскости для трехосного напряженного состояния сводится к определению максимума функции (см. Приложение):
F ( x 2 , x 3 ) =Δσ 122 x 2 +Δσ 123 x 3 - ( Δσ 12 x 2 +Δσ 13 x 3 ) 2 + 2 α F Σ 1 - 2 α F ( Σ 12 x 2 +Σ 13 x 3 )
при ограничениях 0≤ x 2 + x 3 ≤1, x 2 ≥ 0 , x 3 ≥ 0 .
Приведем результаты решения этой задачи для всевозможных значений максимумов и размахов главных напряжений.
Вначале ищем экстремум функции F(x2,x3) внутри зоны ограничений 0
При этом возникают следующие возможные случаи соотношений между главными значениями напряжений.
-
I. Случай ∑ 12 /Δσ 12 ≠∑ 13 /Δσ 13 , Δσ 12 ≠0, Δσ 12 ≠0.
Примем обозначения
β 12 =4α F ∑ 12 /Δσ 12 , β 13 =4α F ∑ 13 /Δσ 13 , Δ = 2 ( β 13 -β 12 ) ≠ 0, Δ s = Δσ 12 β 13 - Δσ 12 β 13 ,
Δ = 2 ( Δσ -Δσ ) , Δ=ΔσΔ / Δ-Δ 2 +Δ 2 / Δ 2 , Δ =Δ 2 +Δ 2 / Δ 2 -ΔσΔ / Δ . T 13 12 213 SST 3 ST 12 S
I-а. Если Δσ12 ≠ Δσ13 , условия экстремума F(x2,x3) имеют вид x2 =Δ2 /(Δσ12Δσ23), x3 = Δ3 /(Δσ13Δσ23).
I-б. Если Δσ 12 = Δσ 13 ≠ 0, условия экстремума F ( x 2 , x 3 ) имеют вид x 2 + x 3 =Δ S / (Δσ 12 Δ).
-
II. Если ∑ 12 /Δσ 12 =∑ 13 /Δσ 13 , необходимо Δσ 12 = Δσ 13 ≠0, Σ 12 =Σ 13 .
Условия экстремума F ( x 2 , x 3 ) : x 2 + x 3 =
( 1 -£„ /^4 -p 2 ) /2.
Найденные значения x 2 , x 3 должны удовлетворять условиям x 2 > 0, x 3 > 0, x 2 + x 3 < 1 и условиям максимума F ( x 2 , x 3 ), которые имеют вид
AG 22 + 4 Ag 13 Ag 23 x 3 > 0, AG 23 - 4 Ag 12 Ag 23 x 2 > 0.
Эти неравенства следуют из условия отрицательности квадратичной формы d2 F dx2
( dx 2 ) 2 + 2
d2 F dx2dx3
0 F z. v' dx 2 dx 3 +-- 2"" ( dx 3 ) < 0.
d x 3
Если таких значений не существует, то необходимо искать максимум F ( x 2 , x 3 ) на границах зоны ограничений: либо x 2 = 0, либо x3 = 0, либо x 2 + x 3 = 1.
-
III. В этом случае максимум F ( x 2 , x 3 ) достигается при значениях
x2 = 0, x3 = (1 -P13/74 + Р132)/2, x3 = 0, x2 = (1 -Р12/74 + Р122 )/2, x2 + x3 = 1, x2 =(1 + P23/74 + P232 )/2, x3 = (1 -P23/74 + p232 )/ 2.
Из этих трех пар x 2 , x 3 следует выбрать ту, где функция F ( x 2 , x 3 ) принимает наибольшее значение. Таким образом, для режима синфазного многоосного циклического нагружения получено аналитическое решение задачи определения ориентации критической плоскости. Определив компоненты нормали к этой плоскости, можно вычислить значение функции Финдли и соответствующее ему число N , т.е. усталостную долговечность элемента конструкции, находящегося в многоосном напряженном состоянии [18].
-
1.2. Противофазное многоосное циклическое нагружение
Важным практическим примером противофазного циклического многоосного нагружения являются усталостные испытания на чистое кручение или изгиб с кручением.
Нетрудно видеть, что в системе координат, связанной с главными осями тензора напряжений, противофазное циклическое нагружение с гармоническим законом изменения по времени всегда можно представить в виде
G 1 ( t ) = G 1 m + G 1 a sin ® t , G 2 ( t ) = G 2 m + G 2 a sin “ t ,
G 3 ( t ) = G 3 m + G 3 a s in( to t + П ) = G 3 m — G 3 a sin “ t , G 1,2,3 a ^ 0
В этом случае AG 1 = 2 g , a > 0, Ag 2 = 2 g 2 a > 0, Ag 3 = - 2 g 3 a < 0.
Выражение для At n по сравнению с синфазным циклическим режимом не меняется:
222 222 222
At n = ^(AG i 2) n , n 2 + ( Agb ) n , n 3 + ( Ag 23 ) n 2 n 3 .
Нормальное напряжение на площадке с нормалью n в противофазном режиме зависит от времени по закону
σ n ( t )=(σ 1 m n 1 2 +σ 2 m n 2 2 +σ 3 m n 3 2 )+(σ 1 a n 1 2 +σ 2 a n 2 2 -σ 3 a n 3 2 )sinω t .
Поэтому для определения max σ , входящего в функцию Финдли, рассмотрим два t∈[0,T] n случая.
-
I. Если σ n 2 +σ n 2 -σ n 2 ≥0, то max σ =Σ n 2 +Σ n 2 +Σ n 2 при sin ω t =1, где aaa t ∈ [0, T ] n 11 22 3 3
Σ=σ +σ Σ=σ +σ Σ=σ -σ .
11 m 1 a , 22 m 2 a , 33 m 3 a .
Перенумеруем значения Σ k , k = 1, 2, 3 так, чтобы они удовлетворяли неравенствам Σ 1 ≥Σ 2 ≥Σ 3 . После этого проводится такой же анализ и расчет ориентации критической плоскости для перенумерованных значений Σ k , Δσ k , k = 1, 2, 3, как и для синфазного режима.
Полученные значения компонент нормали проверяются на выполнение условия σ 1 a n 12 +σ 2 a n 22 -σ 3 a n 32 ≥0 . Если это условие не выполняется, то рассматриваем следующий альтернативный случай.
-
II. Если σ n +σ n -σ n ≤0 , то max σ =Σ n 2 +Σ n 2 +Σ n 2 при sin ω t = –1, где aaa t ∈ [0, T ] n 11 22 33
S, = G, —G, . = Gt — Gt . St = On СУт .
11 m 1 a , 22 m 2 a , 33 m 3 a .
И в этом случае перенумеруем значения Σ k , k = 1, 2, 3 так, чтобы они удовлетворяли неравенствам Σ 1 ≥Σ 2 ≥Σ 3 . После этого проводится такой же анализ и расчет ориентации критической плоскости для перенумерованных значений Σ k , Δσ k , k = 1, 2, 3, как и для синфазного режима. Полученные значения компонент нормали проверяются на выполне- 222 ние условия σ 1 a n 1 +σ 2 a n 2 -σ 3 a n 3 ≤0.
Если выполняются оба условия, то следует выбрать такую ориентацию нормали, при которой значение функции Финдли имеет б о льшее значение.
-
1.3. Определение параметров многоосного критерия усталостного разрушения
Ранее в [18] была предложена процедура определения параметров классических многоосных критериев (Сайнса [19], Кроссланда [20]) в диапазоне МЦУ и МНЦУ по результатам одноосных испытаний с двумя разными коэффициентами асимметрии цикла (левая ветвь бимодальной одноосной усталостной кривой [17] (рис. 1). Приведем результаты этой процедуры для определения параметров многоосного критерия Финдли.
Многоосный критерий Финдли для одноосного нагружения с коэффициентом асимметрии цикла R = σ min / σ max будет выглядеть так:
σmax(α F +(1- R ) 2 +4α F 2 /2)/2= SF + AFN β F при n 1 =1/2+α F / (1- R ) 2 +4α F 2 .
Сравнивая с представлением Баскина одноосной усталостной кривой σ max (1- R ) /2 =σ R +σ CR N β F и имея данные испытаний при R = -1 и R 0 , получаем
SF =σ-1(αF+1+αF2)/2, AF=(σB-σ-1)(αF+1+αF2)10-3βF /2, aF = (д/(2к/(1 -R0)-1)2 + к2 -1 -2k/(1 -R0) + к2)/к/(4/(1 -R0)-к), где о , и оR - классические пределы усталости по усталостным кривым при коэффициентах асимметрии цикла -1 и R0 соответственно; оB - статический предел прочности; К = О-1/ ° R0 -
Анализ критерия Финдли для реверсного режима чистого кручения дает формулы
Т -1 = ° -1 ( 1 + a F / 71 + a F 2 ) /2 , Т c =(° B -° -1 ) ( 1 + a F / V1 + a F2 ) 10 в F /2 "
После вычисления этих параметров по результатам двух одноосных испытаний с разными коэффициентами асимметрии цикла задача вычисления ориентации критической плоскости и долговечности для многоосного напряженного состояния решается с помощью полученных выше формул для компонент нормали и уравнения для числа циклов до разрушения N.
2. Обобщение многоосного критерия усталостного разрушения в режиме СВМУ
В настоящее время установлено, что относительно небольшие циклические напряжения (меньшие классического предела усталости материала), действующие с высокой частотой (порядка 1 кГц и выше), могут приводить к разрушению конструкций [21-25]. Высокочастотное нагружение приводит к значительным наработкам ( N ~ 109 - 1010 циклов) за время расчетного срока службы изделия. Указанный диапазон долговечностей N > 108 известен в литературе как сверхмногоцикловая усталость (СВМУ).
В последние годы разработаны и реализованы методики СВМУ испытаний [25-27] для весьма ограниченного набора циклических нагружений, в первую очередь для реверсивного и пульсирующего растяжения-сжатия [26, 27], а также кручения образцов [2830]. Однако для оценок долговечности различных элементов конструкций, подверженных высокочастотным длительным воздействиям в условиях сложного нагружения, необходимы критерии многоосного СВМУ-разрушения. В данной работе предлагается простая и естественная форма такого рода критериев, основанная на обобщении известных многоосных моделей для классических усталостных режимов.
Опишем предлагаемую схему обобщения многоосного критерия разрушения на режим СВМУ (см. рис. 1, правая ветвь одноосной бимодальной усталостной кривой при N > 108).
В основе обобщенного многоосного критерия типа Финдли лежит подобие поведения левой и правой ветвей бимодальной усталостной кривой. Это обобщение заключается в замене параметров левой ветви бимодальной усталостной кривой на параметры правой ветви: о B ^ о _ 1 , о _ 1 ^ о - 1 , о R ^6 R , 3 р F ^ 8 в F , где <5 - 1 и о R - «новые» пределы усталости на правой ветви усталостной кривой для коэффициентов асимметрии R = -1 и R = R 0.
Для режима СВМУ имеем (все параметры отмечены знаком ~)
SF = о-1 (aF + 71 + aF2) / 2, AF = (о-1 - о-1) (aF + 71 + aF2) 10-8вF / 2 , К = о-J о., a F =( 7 (2K/(1 - R0)-1)2 + K2-1 - 2K/(1 - R0) + K2) / К / (4/(1 - R 0)-K).
Для реверсного режима чистого кручения Тa = т-1 + тCNвF получаем т-1 =6-, (1 + aF /ф +аF1)/2, т. = (а-,-6„ )(1 + а„ / ^ 1 + а„ 1 )10-8вF / 2.
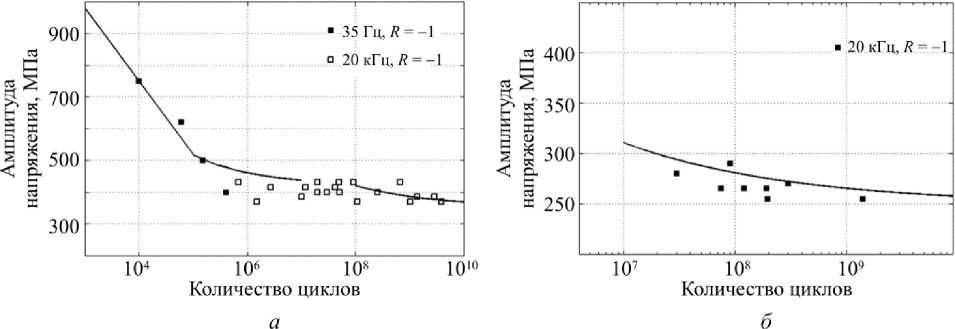
Рис. 2. СВМУ экспериментальные данные для сплава ВТ3-1: а – растяжение-сжатие; б – кручение Fig. 2. VHCF experimental data for the alloy VT3-1: а – tension-compression; b – torsion
Были определены параметры обобщенного критерия СВМУ разрушения по результатам испытаний титановых образцов: а B = 1100 МПа, а — , = 400 МПа, <5 - , = 365 МПа, 6 01 = 215 МПа, в = -0,24. На рис. 2, а приведены экспериментальные данные для R = -1 (растяжение-сжатие).
Полученные значения параметров были использованы для расчетной оценки долговечности образцов при СВМУ-испытаниях на реверсное кручение. Сравнение показало близость расчетных и экспериментальных результатов (см. рис. 2, б , где сплошной линией проведена расчетная ветвь усталостной кривой).
Таким образом, подтверждена возможность использования обобщенного критерия многоосного усталостного разрушения в режиме СВМУ и предложенной схемы определения его параметров для приближенной оценки долговечности элементов конструкций. Формулы для параметров обобщенного СВМУ-критерия и его формулировка на основе подобия левой и правой ветвей усталостной кривой позволяют определить ориентацию критической плоскости и для этого режима циклического нагружения.
3. Примеры расчета долговечности в МЦУ и СВМУ-режиме
Рассмотрим задачу усталостного разрушения диска компрессора газотурбинного двигателя в полетных циклах нагружения в условиях малоцикловой усталости. Аналитическим и численным методам расчета напряженно-деформированного состояния дисков и лопаток ГТД на различные воздействия посвящена обширная литература [31–35].
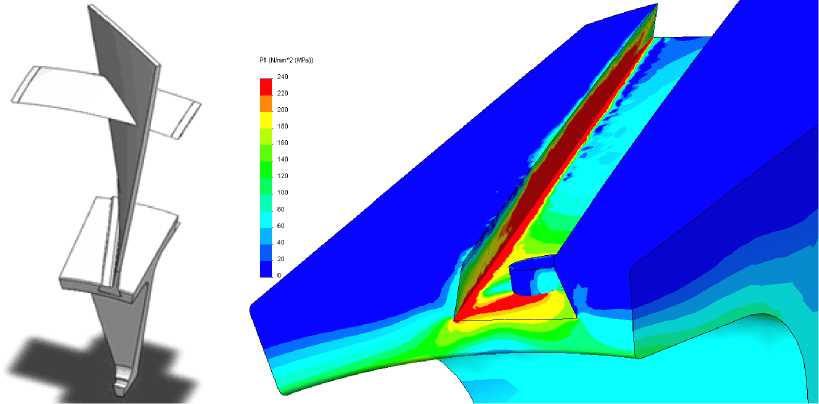
В нашем случае предполагается, что циклом многоосного нагружения системы диск– лопатка является полетный цикл нагружения (ПЦН, взлет–полет–посадка). В качестве границ цикла примем нагрузки на крейсерской скорости полета воздушного судна и соответствующие угловые скорости вращения диска компрессора. Задача состоит в определении долговечности диска N (число ПЦН до разрушения) из многоосного критерия Финдли для режима МЦУ. Для этого был проведен конечно-элементный расчет напряженно- деформированного состояния (НДС) системы диск–лопатка при учете центробежных нагрузок, распределенного аэродинамического давления на лопатку, а также сил нелинейного контактного взаимодействия диска, лопаток и иных дополнительных учитываемых элементов конструкции (рис. 3, а). Численные методы решения контактных задач описаны в работах [36, 37]. Параметры расчета принимались такими: угловая скорость вращения ω = 314 рад/с (3000 об/мин), скоростной напор на бесконечности ρv∞2 /2 = 26000 Н/м2, что соответствует скорости потока 200 м/с при плотности 1,3 кг/м3. Свойства материалов принимались следующими: диск (титановый сплав): E = 116 ГПа, ν = 0,32, ρ = 4370 кг/м3; лопатки (алюминиевый сплав): E = 69 ГПа, ν = 0,33, ρ = 2700 кг/м3; фиксирующие штифты (сталь): E = 207 ГПа, ν = 0,27, ρ = 7860 кг/м3. Расчеты показали, что наиболее опасными с точки зрения зарождения усталостных трещин являются окрестности зон контакта диска и лопаток, имеющих вид соединения типа «ласточкин хвост». На рис. 3, б представлена зона концентрации максимальных растягивающих напряжений в левом (скругленном) углу паза в диске, в который вставляется лопатка.
а
б
Рис. 3. Сектор диска с лопаткой, нагружаемый центробежными силами ( а ); максимальное главное напряжение в соединении диска и лопатки ( б )
Fig. 3. Is the sector of the disk with the blade which is loaded with centrifugal forces ( a ), is the maximum main stress in the connections of the disk and the blade ( b )
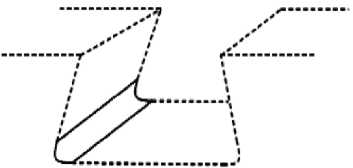
Наименьшая долговечность получилась для окрестности левого угла контактного соединения диска и лопатки, которая выделена на рис. 4, а сплошными линиями.
На рис. 4, б показаны рассчитанные величины числа полетных циклов до разрушения N для выбранного критерия многоосного усталостного разрушения. По горизонтальной оси отложена безразмерная координата закругления левого угла паза соединения, по вертикальной оси отложена безразмерная координата по глубине паза. Наименьшее значение N составило величину ~30 000 циклов. Если принять среднюю протяженность цикла за 2 ч, то в реальном времени долговечность элемента конструкции составит 60 000 ч.
Дополнительно исследовался альтернативный механизм циклического нагружения, связанный с наблюдаемыми высокочастотными осевыми колебаниями бандажных полок. Амплитуды этих колебаний и вызываемые ими возмущения напряженного состояния в окрестности концентратора напряжений относительно невелики, однако число циклов при высокой частоте колебаний за время эксплуатации может достичь величин 109–1010, что приводит к необходимости исследования режима сверхмногоцикловой усталости (СВМУ) и возможности усталостного разрушения при уровне напряжений, меньшем классического предела усталости материала. На рис. 5, а показана схема приложения низкоамплитудных
а
Рис. 4. Выделенная зона максимальной концентрации напряжений ( а ); уровни долговечности в выделенной зоне ( б )
Fig. 4. Is the maximum stress concentration zone ( a );
is the durability levels in the allocated zone ( b )
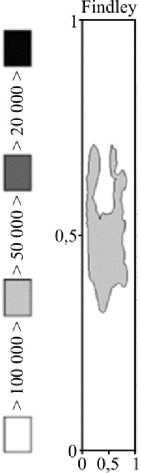
б
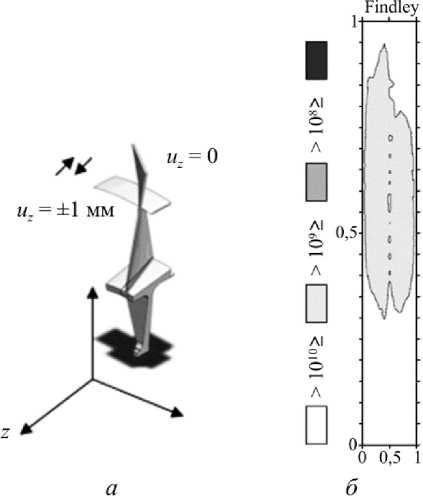
Рис. 5. Схема высокочастотных воздействий на диск и лопатку ( а ); уровни долговечности в выделенной зоне ( б )
Fig. 5. Is the scheme of high-frequency loading on the disk and blade ( a ), is the levels of durability in the allocated zone ( b )
осевых смещений. Таким образом, рассматриваются случаи, когда на левую границу приходится максимум или минимум амплитуды колебаний, равной ± 1 мм, при частоте 3000 об/мин. Как и в случае режима МЦУ, зона концентрации напряжений сосредоточена в левом углу паза. Несмотря на относительно невысокий уровень амплитуд напряжений в цикле, и в этом случае возникают зоны возможного усталостного разрушения, расположенные в тыльной зоне левого угла паза диска, примерно там же, где и в случае полетных циклов нагружения. Величина N , при которой они появляются, имеет порядок 109–1010 (см. рис. 5, б ), что в пересчете на реальное время процесса с периодом цикла 0,02 с (при выбранной частоте колебаний) дает величину 50 000 ч, вполне достижимую в процессе эксплуатации.
Таким образом, значения долговечностей в реальном времени для двух различных режимов усталостного разрушения получились достаточно близкими. Хотя эти оценки весьма приблизительны, они указывают на принципиальную возможность развития усталостного разрушения в указанных зонах диска компрессора как по механизму МЦУ (полетный цикл нагружения), так и по механизму СВМУ (высокочастотные, низкоамплитудные вибрации элементов конструкции).
Заключение
Получено аналитическое решение задачи определения ориентации критической плоскости для многоосного напряженного состояния при синфазном и противофазном циклическом нагружении для классического диапазона МЦУ-МНЦУ (левая ветвь бимодальной усталостной кривой).
Построено обобщение многоосного критерия усталостного разрушения на случай сверхмногоцикловой усталости, предложена процедура определения параметров этого обобщенного критерия по результатам одноосных экспериментов для двух коэффициентов асимметрии цикла, определена критическая плоскость развития усталостных повреждений для многоосного напряженного состояния (правая ветвь бимодальной усталостной кривой).
Проведены расчеты напряженного состояния, и на этой основе даны сравнительные оценки усталостной долговечности ответственного элемента конструкции – диска компрессора газотурбинного двигателя для режимов нагружения МЦУ и СВМУ. Анализ показал, что с учетом характерных частот рассматриваемых циклических процессов значения долговечностей в реальном времени могут быть достаточно близки и, следовательно, при определении условий безопасной эксплуатации должны учитываться оба механизма усталостного разрушения.
Работа частично выполнена по проекту РНФ № 16-19-10376.
Acknowledgments
The work has been carried out with the financial support from the Russian Science Foundation, RSF (Grant Nr. 16-19-10376).
Приложение
Выведем полезные формулы для касательного напряжения и его размаха на произвольно ориентированной площадке с нормалью n ( n 1 , n 2 , n 3 ). В системе координат, связанной с главными осями тензора напряжений, имеем для нормального напряжения a n на выбранной площадке и компонент касательного напряжения т i следующие формулы (по повторяющимся индексам k и l производится суммирование):
c n = c ki n k n i = c k n , т = a ik n k -c n n = (a -c n ) n -
Для размаха компонент касательного напряжения и его модуля имеем
AT = (Ac t -Ac n ) n , Ат = J£( Ac k -Ac n )k n k , Ac n = Ac k n 2 .
k =1
Раскрывая скобки, получаем
At =
Ac k n 2
- 2Acn Acknk +Acn E nk
k =1
= ^Ac 2 nk : -Ac k , kk n
так как Ac k n k =Ac n , ^ n k = 1.
k = 1
Окончательно
-
At = 7Ac knk - ( Ac kn^2 .
Раскрывая скобки, эту формулу можно преобразовать к виду
At = J Ac 2 n 2 - (Ac, n 2)k = ЛI (Ac, - Ac, )k n 2 n^2 + (Ac, - Ac. )k n 2 nA2 + (Ac, - Ac. )k n^2 nA2. kk kk 1212 1 313 2323
Введя обозначения Ac 1k = Ac 1 - Ac k , Ac 13 = Ac 1 - Ac 3 , Ac k3 = Ac k - Ac 3 , получим компактное выражение для размаха касательных напряжений
222 222222
At n = ^(Ac jk ) n 1 n k + (Ac 13 ) n 1 n 3 + (Ac 2з ) n k n 3 .
Исключая n 1 2 , получим формулу, используемую для вычисления максимума функции F :
22 22 22
At = JAc 12 n k +Ac 13 n 3 - I Ac 12 n k +Ac 13 n 3
Список литературы Оценка направления роста трещины в условиях смешанного нагружения (нормальный отрыв и поперечный сдвиг): обобщенные критерии классической механики разрушения и атомистическое моделирование смешанного нагружения (метод молекулярной динамики)
- Кулиев В.Д., Морозов Е.М. Градиентный деформационный критерий хрупкого разруше-ния//Живучесть и конструкционное материаловедение (ЖИВКОМ-2016): тр. конф./Институт машиноведения им. А.А. Благонравова. -М., 2016. -С. 24-27.
- Матвиенко Ю.Г. Моделирование кинетики развития трещин в поверхностных слоях мате-риала//Заводская лаборатория. -2017. -Т. 83, № 1. -С. 65-71.
- Berto F., Ayatollahi M.R. A review of the local strain energy density approach to V-nothces//Physical mesomechanics. -2017. -Vol. 20. -No. 2. -P. 14-27.
- Matvienko Y.G., Morozov E.M. Two basic approaches in a search of the crack propagation angle//Fatigue & Fracture of Engineering Materials & Structures, 2017 DOI: 10.1111/ffe.12583
- Rashidi Moghaddam M., Ayatollahi M., Berto F. The application of strain energy density criterion to fatigue crack growth behavior of cracked components//Theoretical and Applied Fracture Mechanics. -2017. -No. 1. -С. 33-56.
- Rashidi Moghaddam M., Ayatollahi M., Berto F. Mixed mode fracture analysis using generalized averaged strain energy density criterion for linear elastic materials//International Journal of Solids and Structures. -2017. -Vol. 120. -P. 137-145.
- Razavi M.J., Aliha M.R.M., Berto F. Application of an average strain energy density criterion to obtain the mixed mode fracture load of granite rock tested with the cracked asymmetric four-point bend specimen//Theoretical and Applied Fracture Mechanics. -2017. -No. 33. -P. 25-33.
- Malikova L., Vesely V. Estimation of the crack propagation direction in a mixed-mode geometry via multi-parameter fracture criteria//Frattura ed Integrita Strutturalle. -2015. -No. 33. -P. 25-32.
- Malikova L. Multi-parameter fracture criteria for the estimation of crack propagation direction applied to a mixed-mode geometry//Engineering fracture mechanics. -2015. -No. 143. -P. 32-46.
- Malikova L., Vesely V. Influence of the elastic mismatch on crack propagation in a silicate-based composite//Theoretical and Applied Fracture Mechanics. -2017. -Vol. 91. -P. 25-30.
- Crack propagation in non-homogenous materials: Evaluation of mixed-mode SIFs, T-stress and kinking angle using a variant of EFG Method/N. Muthu, S.K. Maiti, B.G. Falzon, W. Yan//Engineering Analysis With Boundary Elements. -2016. -Vol. 72. -P. 11-26.
- Berto F., Lazzarin P. Recent developments in brittle and quasi-brittle failure assessment of engineering materials by means of local approaches//Materials Science and Engineering. -2014. -R. 75. -P. 1-48.
- Sih G.C. Application of Strain -Energy -Density Theory to Fundamental Fracture Problem. -Institute of Fracture and Solid Mechanical Technical Report, Lehigh University, AFOSR-RT-73-1, 1973.
- Sih G.C. Strain-energy factor applied to mixed mode crack problems//Int. J. Fracture. -1974. -Vol. 10. -P. 305-321.
- Li Q.M. Strain energy density failure criterion//International Journal of Solids and Structures. -2001. -Vol. 38. -P. 6997-7013.
- Mirsayar M.M., Razmi A., Berto F. Tangential strain-based criteria for mixed-mode I/II fracture toughness of cement concrete//Fatigue Fracture Engineering Material and Structures. -2017. -P. 1-9 DOI: 10.1111.ffe.12665
- Wulfinghoff S., Fassin M., Reese S. A damage growth criterion for anisotropic damage models motivated from micromechanics//International Journal of Solids and Structures. -2017. -Vol. 121. -P. 21-32.
- Ayatollahi M.R., Rashidi Moghaddam M., Berto F. A generalized strain energy density criterion for mixed mode fracture analysis in brittle and quasi-brittle materials//Theoretical and Applied Fracture Mechanics. -2015. -Vol. 79. -P. 70-76.
- Local strain energy density to predict size-dependent brittle fracture of cracked specimens under mixed mode loading/F. Berto, M.R. Ayatollahi, T. Borsato, P. Ferro//Theoretical and Applied Fracture Mechanics. -2016. -Vol. 86. -P. 217-224.
- Mirsayar M.M. Mixed mode fracture analysis using extended maximum tangential strain criterion//Materials and Design. -2015. -Vol. 86. -P. 941-947.
- Seitl S., Malikova L. Williams expansion-based approximation of the stress field in an Al 2024 body with a crack from optical measurements//Frattura ed Integrita Strutturalle. -2017. -No. 41. -P. 323-331.
- Stepanova L.V., Roslyakov P.S., Multi-parameter description of the crack-tip stress field: analytic determination of coefficients of crack-tip stress expansions in the vicinity of the crack tips of two finite cracks in an infinite plane medium//International Journal of Solids and Structures. -2016. -Vol. 100-101. -P. 11-28.
- Stepanova L., Roslyakov P. Complete Williams asymptotic expansion of the stress field near the crack tip: Analytical solutions, interference-optic methods and numerical experiments//AIP Conference Proceedings. -2016. -Vol. 1785. -030029.
- Степанова Л.В., Росляков П.С. Полное асимптотическое разложение М. Уильямса у вер-шин двух коллинеарных трещин конечной длины в бесконечной пластине//Вестник Пермского национального исследовательского политехнического универистета. Механика. -2015. -№ 4. -P. 188-225.
- Hello G., Tahar M.B., Roelandt J.-M. Analytical determination of coefficients in crack-tip stress expansions for a finite crack in an infinite plane medium//International Journal of Solids and Structures. -2012. -Vol. 49. -P. 556-566.
- Stepanova L.V., Igonin S.A. Asymptotics of the near-crack-tip stress field of a growing fatigue crack in damaged materials: Numerical experiment and analytical solution//Numerical Analysis and Applications. -2015. -Vol. 8. -No. 2. -P. 168-181.
- Stepanova L.V., Adylina E.M. Stress-strain state in the vicinity of a crack tip under mixed loading//Journal of Applied Mechanics and Technical Physics. -2014. -Vol. 55(5). -P. 885-895.
- Krepl O., Klusak J. The influence of non-singular terms on the precision of stress description near a sharp material inclusion tip//Theoretical and Applied Fracture Mechanics. -2017. -Vol. 90. -P. 85-99.
- Stepanova L.V. Eigenspectra and orders of stress singularity at a mode I crack tip for a power-law medium//Comptes Rendus -Mecanique. -2008. -Vol. 336. -No. 1-2. -P. 232-237.
- Stepanova L.V. Eigenvalue of the antiplane shear crack problem for a power-law material//Journal of Applied Mechanics and Technical Physics. -2008. -Vol. 49. -No. 1. -P. 142-147.
- Ayatollahi M.R., Moazzami M. Digital image correlation method for calculating coefficients of Williams expansion in compact tension specimen//Optics and Lasers in Engineering. -2017. -Vol. 90. -P. 26-33.
- Stepanova L.V., Fedina M.Ye. Self-similar solution of a tensile crack problem in a coupled formulation//Journal of Applied Mathematics and Mechanics. -2008. -Vol. 72. -No. 3. -P. 360-368.
- Stepanova L.V. Eigenvalue analysis for a crack in power-law material//Computational Mathematics and Mathematical Physics. -2009. -Vol. 49. -No. 8. -P. 1332-1347.
- Malikova L., Klusak J., Kersner Z. Assessment of Crack Stability in a Quasi-brittle Particle Composite//Procedia Engineering. -2017. -Vol. 190. -P. 49-53.
- Stepanova L.V., Yakovleva E.M. Mixed-mode loading of the cracked plate under plane stress conditions//PNRPU Mechanics Bulletin. -2014. -No. 3. -P. 129-162 DOI: 10.15593/perm.mech/2014.3.08
- Foiles S.M., Baskes M.I., Daw M.S. Embedded-atom-method functions for the fcc metals Cu, Ag, Au, Ni, Pd, Pt, and their alloys//Physical Review B. -1986. -Vol. 33. -P. 7983-7991.
- Cui C.B., Beom H.G. Molecular dynamics simulation of edge cracks in copper and aluminium single crystals//Materials Science and Engineering A. -2014. -Vol. 609. -P. 102-109 DOI: 10.1016/j.msea.2014.04.101
- Tsai J.-L., Tzeng S.-H., Tzou Y.-J. Characterizing the fracture parameters of a graphene sheet using atomistic simulation and continuum mechanics//International Journal of Solids and Structures. -2010. -Vol. 47. -P. 503-509.
- Atomistic modeling for mechanism of crack cleavage extension on nano-scale/Y.-J. Gao, Q.-Q. Deng, L.Ye. Huang, Z.C. Wen, Zhi-R. Luo//Computational Materials Science. -2017. -Vol. 130. -P. 64-75.
- Cui C.B., Lee G.H., Beom H.G. Mixed-mode fracture toughness evaluation of a copper single crystal using atomistic simulations//Computational Materials Science. -2017. -Vol. 136. -P. 216-222.
- Andric P., Curtin W.A. New theory for Mode I crack-tip dislocation emission//Journal of Mechanics and Physics of Solids. -2017. -Vol. 106. -P. 315-337.
- Hardy R.J. Formulas for determining local properties in molecular-dynamics simulations: shock waves//Journal Chemical Physics. -1982. -Vol. 76. -P. 622-628.
- Calculation of stress in atomistic simulation. Calculation of stress in atomistic simulation/J.A. Zimmerman, E.B. Webb III, J.J. Hoyt, R.E. Jones, P.A. Klein, D.J. Bammann//Modelling and Simulation in Materials Science and Engineering. -2004. -Vol. 12. -Iss. 4. -P. S319-S332.
- Tadmor E.B., Miller R.E. Modeling Materials. Continuum, Atomistic and Multiscaling Techniques. -Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2011. -789 p.
- Structural stability and lattice defects in copper: Ab initio, tight-binding, and embedded-atom calculations/Y. Mishin, M.J. Mehl, D.A. Papaconstantopoulos, A.F. Voter, J.D. Kress//Physical Review B. -2001. -Vol. 63. -224106-1-224106-16.
- Mishin Y., Farkas D., Mehl M.J., Papaconstantopoulos D.A. Interatomic potentials for monoatomic metals from experimental data and ab initio calculations//Physical Review B. -1999. -Vol. 59. -No. 5. -P. 3393-3407.
- Molecular Dynamics Simulation of Crack Propagation in Single-Crystal Aluminum Plate with Central Cracks/J. Ding, L.-S. Wang, K. Song, B. Liu, X. Huang//Journal of Nanomaterials. -2017. -5181206 DOI: 10.1155/2017/5181206
- Molecular dynamics simulation of crack growth behavior in Al in the presence of vacancies/S. Chandra, N.N. Kumar, M.K. Samal, V.M. Chavan, R.J. Patel//Computational Materials Science. -2016. -Vol. 117. -P. 518-526.
- Curtin W.A. What can atomistic modeling contribute to the understanding of fracture//14th International Conference on Fracture (ICF 14), June 18-23, 2017. -Rhodes, Greece, 2017.
- Daw M.S., Baskes M.I. Semiempirical, quantum mechanical calculation of hydrogen embrittlement in metals//Physical Review. Letters. -1983. -Vol. 50. -P. 1285-1288.
- Hoover W.G., Holian B.L. Kinetic moments method for the canonical ensemble distribution//Physics Letters A. -1996. -Vol. 211. -No. 5. -P. 253-257 DOI: 10.1016/0375-9601(95)00973-6
- Stukowski A. Visualization and analysis of atomistic simulation data with OVITO -the Open Visualization Tool//Modelling and Simulation in Materials Science and Engineering. -2009. -Vol. 18 (1). -015012.
- Stukowski A. Visualisation and Analysis Strategies for Atomic Simulations//Introduction to Atomistic Simulation Methods. Eds. C.R. Weinberger, G.J. Tucker-Berlin: Springer, 2016. -P. 317-336.
- Mesh refinement schemes for the concurrent atomistic-continuum method/S. Xu, L. Xiong, Q. Deng, D.L. McDowell//International Journal of Solids and Structure. -2016. -Vol. 90. -P. 144-152.
- Li S., Urat S. An atomistic-to-continuum molecular dynamics: Theory, algorithm, and applications//Computational Methods of Applied Mechanical Engineering. -2016. -Vol. 306. -P. 452-478.
- Liew K.M., Yan J.-W., Zhang L.-W. Atomistic Finite Element Method and Coupling With Atomistic-Continuum Method//Mechanical Behaviors of Carbon Nanotubes. Theoretical and Numerical Approaches. Elsevier. -2017. -P. 249-259.
- Volegov P.S., Gribov D.S., Trusov P.V. Damage and fracture: Review of Experimental Studies//Physical Mesomechanics Journal. -2016. -No. 3. -P. 319-331.
- Volegov P.S., Gribov D.S., Trusov P.V. Damage and Fracture: Classical continuum Theories//Physical Mesomechanics Journal. -2017. -No. 2. -P. 157-173.
- Volegov P.S., Gribov D.S., Trusov P.V. Damage and Fracture: Crystal Plasticity Models//Physical Mesomechanics Journal. -2017. -No. 2. -P. 174-184.


