Оценка устойчивости к базальному пучению подпорных конструкций в стесненных условиях строительства: метод расчета
Автор: Того И., Фролова И.Е., Данг Т.Т., Сабри М.М.С.
Журнал: Строительство уникальных зданий и сооружений @unistroy
Статья в выпуске: 1 (106), 2023 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Статья посвящена разработке расчетного метода оценки устойчивости к базальному пучению подпорных конструкций, учитывающего граничные условия в крайних точках профиля поверхности сдвига и удовлетворяющего всем трем уравнениям равновесия. Объект исследования – двухрядная шпунтовая подпорная стена в условиях фильтрации воды в ограждающий фундамент. Глубина погружения шпунтовых свай определяется условием устойчивости перемычки по схеме глубокого сдвига, а также условием суффузионной прочности грунта основания. Форма функции поверхности разрушения и функция напряжения на поверхности разрушения описываются степенными зависимостями для учета граничных условий в крайних точках поверхности сдвига для удовлетворения теории прочности Мора. Коэффициент устойчивости получается путем решения системы трех уравнений равновесия с учетом граничных условий в точках пересечения профиля поверхности сдвига с профилем основного грунтового массива. Расчет с различными вариантами проницаемости замков верхней шпунтовой стенки показывает, что герметизация замков повышает устойчивость подпорных конструкций.
Подпорные конструкции, шпунтовая стена, давление на грунт, оценка устойчивости, пучение основания, условия равновесия, граничные условия
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/143180492
IDR: 143180492 | УДК: 69 | DOI: 10.4123/CUBS.106.3
Текст научной статьи Оценка устойчивости к базальному пучению подпорных конструкций в стесненных условиях строительства: метод расчета
-
1 Introduction/ Введение
Строительство сухих доков при реконструкции действующих судостроительных предприятий осуществляется в стесненных условиях, обусловленных близким расположением эксплуатируемых объектов. В этих условиях в качестве ограждающих строительных котлованов широко применяются шпунтовые стены.
При устройстве котлованов, особенно в слабых слоях грунта, часто случаются случаи поднятия и разрушения грунта основания [1]–[4]. Потери устойчивости котлованов имеют катастрофические последствия на строительной площадке. В худшем случае они подвергают опасности рабочих и соседних сооружений. Их влияние обычно велико: может возникнуть значительная осадка грунта, а соседние объекты в пределах зоны влияния осадки могут быть значительно повреждены. Предотвращение потери устойчивость котлованов и обрушений грунта основания имеет первостепенное значение. При проектировании ограждающих конструкций должны быть предусмотрены технические решения, обеспечивающие надежность, долговечность и экономичность конструкций.
Процесс проектирования котлованов включает оценка устойчивости против опрокидывания и общего сдвига. На практике были предложены различные анализы для выполнения расчетов устойчивости ограждающих конструкций [5]-[15]. Наиболее часто применяются методы, Togo, I.; Frolova, I.; Dang, T.; Sabri M.M.S.
Basal heave stability assessment of retaining structures in cramped construction conditions;
основанные либо на схеме предельного равновесия: метод несущей способности, метод отрицательной несущей способности и метод круга скольжения [16]–[21], либо анализ методом конечных элементов [22]–[24].
Что касается метода несущей способности, Терцаги представил формулу для оценки устойчивости против сдвига на основе теории несущей способности [16]. В этом методе вес слоя грунта над уровнем поверхности выемки котлована рассматривается как нагрузка, вызывающая разрушение выемки. Предполагается, что испытательная поверхность разрушения, вызванная весом грунта в пределах первой приведенной ширины, действует на плоскость выемки, можно найти предельную нагрузку для этой ширины, следуя методу несущей способности Терцаги. Отношение предельной нагрузки к весу грунта в пределах рассматриваемой ширины является коэффициентом запаса устойчивости первой испытательной поверхности разрушения. Затем увеличивая значение ширины участки грунта и, соответственно, находят соответствующий коэффициент запаса до тех пор, пока испытательная поверхность не перекроет всю выемку. Коэффициент запаса устойчивости против общего сдвига для котлована является наименьшим среди коэффициентов запаса устойчивости, соответствующих пробным поверхностям обрушений. Для большинства котлованов коэффициент устойчивости рассчитан по формуле Терцаги должен быть больше или равен 1,5.
Метод несущей способности подходит для неглубоких котлованов, для глубоких котлованов метод может не дать разумных результатов, поскольку он предполагает, что поверхность разрушения простирается до поверхности земли и что касательные напряжения грунта основания полностью развиваются на всем протяжении к поверхности земли. Эти предположения не обязательно верны для глубоких котлованов.
Метод отрицательной несущей способности или метод Бьеррума и Эйде предполагает, что поведение разгрузки, вызванное при устройстве котлованов, аналогично тому, как фундамент здания подвергается восходящей нагрузке, а форма поверхности обрушения аналогична режиму разрушения глубокого фундамента. Тогда, используя уравнение несущей способности фундамента глубокого заложения, можно получить предельное разгрузочное давление. Коэффициент запаса устойчивости представляет собой отношение предельного давления разгрузки к давлению разгрузки. Если глубина погружения ограждающей стенки достаточно глубокая, метод отрицательной несущей способности рассчитывает коэффициент запаса устойчивости аналогично методу Терцаги. Этот метод учитывает влияние формы очертания, ширины и глубины котлована. Таким образом, методы применимы к различным типам котлованов, как к мелким, так и к глубоким. Для большинства случаев котлованов коэффициент запаса, полученный по этому методу, должен быть больше или равен 1,2.
Метод круга скольжения предполагается, что испытательная поверхности обрушения общего сдвига котлована представляет собой дуги окружности. Потом, отдельно рассчитывается отношения моментов сопротивления к разрушающим моментам для данной испытательных поверхностей обрушения. Тогда наименьший коэффициент запаса устойчивости среди полученных коэффициентов является тогда коэффициентом запаса против общего сдвига котлованов. Метод пропуска круга без установки центра в определенном положении заключается в том, чтобы опробовать круги для различных положений и размеров и найти соответствующие коэффициенты запаса устойчивости. Круг с наименьшим запасом устойчивости является критическим кругом.
В большинствах методах расчета устойчивости, использующихся в современной практике поверхность сдвигов предполагается круглоцилиндрической или плоской, а в некоторых – произвольной. В этих методах условия равновесия в предельном состоянии не полностью соблюдаются. Много из них даже интегрально не соблюдаются условия равновесия и не учитываются граничные условия по напряжениям и углам наклона площадок сдвигов. Обусловленными несовершенством расчетных предпосылок во многих случаях расчеты по этим методам дают скрытые запасы устойчивости и погрешность в сторону риска.
В данной работе предлагается расчетный метод, в котором полностью выполняются законы механики. Это выражается в соблюдении условий равновесия, а также выполнении граничных условий в крайних точках профиля поверхности сдвигов, как по напряжениям, так и по направлению площадок сдвигов в соответствии с теорией прочности Мора.
Объектом исследования является двухрядная шпунтовая подпорная стенка в условиях фильтрации воды в ограждающий котлован. Методы: Глубина погружения шпунтовых свай определяется условием устойчивости перемычки по схеме глубокого сдвига, а также условием Togo, I.; Frolova, I.; Dang, T.; Sabri M.M.S.
Basal heave stability assessment of retaining structures in cramped construction conditions;
суффозионной прочности грунта основания. Для рассмотрения граничных условий в крайних точках поверхности сдвига в соответствии с теорией прочности Мора форма функции поверхности разрушения и функция напряжения на поверхности разрушения описываются степенными зависимостями. Результаты: коэффициент устойчивости получен по результатам решения систему трех уравнений равновесия с учетом граничных условий в точках пересечения профиля поверхности сдвига с профилем поверхности основного грунтового массива. Расчет при различных вариантах замковой проницаемости верхнего шпунта стены показывает, что герметизация замков повышает устойчивость подпорных конструкций.
-
2 Materials and Methods/ Материалы и методы
Перемычка рассматривается как массивное сооружение, заглубленное в основание. Нарушение устойчивости перемычки может происходить в виде глубинного сдвига с захватом грунта основания и выпором его за пределами подошвы, ограниченной шпунтовыми рядами. Для оценки устойчивости перемычки используется схема предельного равновесия. На Рис. 1 представлена расчетная схема проекта перемычки для реконструкции одного из судостроительных заводов.
Для оценки влияния фильтрующейся воды на устойчивость перемычки можно использовать методом Дюпюи. Положение кривой депрессии внутри перемычки определяется граничными условиями: проницаемостью шпунтовых стен и положением дренажных отверстий в шпунтовой стенке со стороны котлована. Предполагается, что положение уровня грунтовых вод в пределах котлована поддерживается системой водопонижения, постоянно откачивающей воду из котлована.
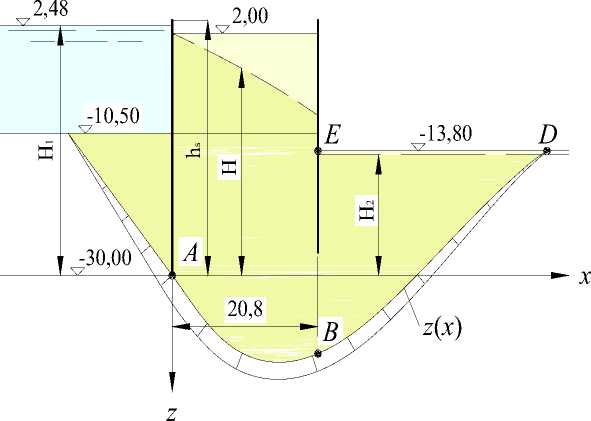
Рис. 1 - Расчетная схема к оценке устойчивости перемычки
Fig. 1 - Design scheme for assessing the stability of the cofferdam
Со стороны акватории на перемычку в пределах заглубления в основание, помимо давления воды и гравитационных сил, действует активное давление грунта. Со стороны котлована действует реактивное давление грунта призмы выпора BDE, сопротивляющееся сдвигу.
Расчетный метод основывается на решении дифференциальных уравнений равновесия сил и их моментов, действующих на произвольный элемент гипотетического тела обрушения, шириной dx, высотой h и единичным размером в третьем измерении (Рис. 2):
^ X = 0: q _ dx - dE + z'adx - tkdx = 0 (1)
^ Z = 0: qzdx - dT - a dx - z'tkdx = 0
^ M = 0: mdx - dM + z'Edx - Tdx = 0
где q x dx, q z dx – компоненты равнодействующей поверхностных и объемных сил; m=q x b – момент горизонтальной нагрузки интенсивностью q x относительно середины подошвы элемента; E, T – компоненты сил взаимодействия между элементами, являющиеся равнодействующими соответственно нормальных и касательных напряжений, действующих на вертикальных гранях элемента; М = Ea - момент силы Е относительно подошвы элемента; T k = f k a + C k , а -компоненты напряжения на поверхности обрушения, соответствующие предельному равновесию; f k , c k – параметры механической прочности грунта, соответствующие предельному равновесию; z = z (x) – функция, описывающая профиль поверхности обрушения; z' – производная от z(x) по x на интервале [ x 0 ; x n ].
dx
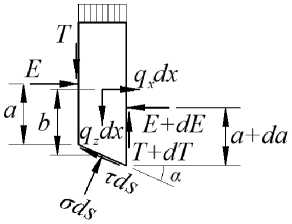
Рис. 2 - Схема сил, действующих на элемент тела обрушения
Fig. 2 - Scheme of forces acting on an element of the collapse body
После интегрирования уравнений (1), (2), (3) в пределах от х 0 до х n и соответствующего преобразования получим систему интегральных уравнений равновесия тела обрушения в целом
X n
J (Tk - z'o) dx = Qx + Eo - En
X o
X n
J (ikz' + o) dx = Qz + To - T
X o
X n
J [(Tkz' + o)(x - xo) - (ik - z'o)(z - Zo)] dx = Mq + Mg(6)
Xo где,
Q x
XE
J q x dx ; Q z
XA
X n
J q z dx; M q
X o
X n
J [ m - ( z - z o )q x + ( x - x o )q z ] dx;
X o
M g = (z - zo‘)E n - (x - xo‘)T n - (M n - Mo)
Индексы при E, T, М означают принадлежность к начальному или концевому сечению, которые проходят через точки A и D (Рис. 1). Значения: E 0 = E ( x 0) , T0 = T ( x 0) = 0 , M 0 = M ( x 0) , E n = E ( xn ) = 0 , Tn = T ( xn ) = 0 , Mn = M ( xn ) = 0 определяются граничными условиями. Для рассматриваемой задачи:
Ео = yH H1* +—1— [у» hs( J1 + f2 -A- 2cl
0 7 2 2у» base s y.^ j к j к j J'
(H12-H12*)(H1 + H1J hs |У^(Л'
^ = У--------------+ T-b--7
8 6y base L z 0
где y b ase - удельный вес взвешенного грунта основания, H 1* = H 1 - Д 1 - напор с тыльной стороны верховой шпунтовой стены, Д 1 - напор с тыльной стороны верховой шпунтовой стены.
Для проницаемых замковых соединений трубошпунта ШТС-1420×14 эти потери напора на вход в область фильтрации составляют 0,016H 1 . Для непроницаемых швов можно принять A i = H i - H 2* , где H 2* = H 2 + А 2 , А 2 - участок высачивания фильтрующейся воды в створе низовой шпунтовой стены. Участок А 2 при непроницаемых замковых соединениях определяется возвышением дренажных отверстий над уровнем грунтовых вод в котловане. При проницаемых замковых соединениях для оценки влияния фильтрующейся воды на устойчивость перемычки можно воспользоваться методом, в котором фильтрационный удельный расход определяется по Дюпюи, а положение кривой депрессии – граничными условиями с использованием вариационного принципа. Этот метод позволяет учесть высоту участка высачивания А 2 , равную разности уровней воды перед и за шпунтовой стенкой. В обоих случаях в створе шпунтовой стенки со стороны котлована действует сила давления воды E B = У( н2* - H 2 У2 , обусловленная наличием участка высачивания.
В правых частях уравнений (4), (5), (6) стоят величины, характеризующие активные силовые воздействия на грунтовый массив, в левых частях – величины, характеризующие реакции на эти воздействия в состоянии предельного равновесия.
В эту систему уравнений предельного равновесия входят в рассматриваемом случае пять неизвестных функций: E, T, М, ° , z , поэтому задача является дважды статически неопределимой. Для снятия статической неопределимости задачи необходимо ввести два дополнительных условия, определяющие «лишние» функции. Поэтому приходится задаваться видом функций о , z . Эти функции проще описать степенными зависимостями:
о = A o + A 1 ( x - Х о ) + A 2 ( x - Х о )2 + А з (х - Х о )3 (11)
z = S o + В 1 ( х - Х о ) + В 2 ( х - Х о )2 + В з ( х - Х о )3
где A 0 , A 1 , A 2 , A 3 , B 0 , B 1 , B 2 , and B 3 – числовые коэффициенты, значения которых определяются граничными условиями и условиями равновесия.
Исследованиями установлено, что такое представление функций дает относительно малую погрешность в сторону риска при соблюдении условий равновесия и граничных условий. Влияние этой погрешности можно компенсировать введением коэффициента условий работы у с = 0,95 .
Ранг статической неопределенности задачи можно понизить, используя вариационный принцип поиска функции z . В представленном варианте расчета вариационная задача не рассматривается.
Для полной постановки задачи система уравнений равновесия дополняется граничными условиями для всех перечисленных функций . Граничные условия определяются геометрическими очертаниями профиля призмы выпора и условиями равновесия в точках пересечения профиля поверхности сдвигов с профилем поверхности грунтового массива основания.
Граничные условия для функции z и ее производной по x :
-
- при х = х0 = хд ; z = z0 = zA :
z' = z 0 = z A = tern (^ + ^) = J 1 + f + f k
-
при х — Хп — xD ; z — zK — zD :
z' — z ^ — z D —
tan (4 “?) — f x 1 ' ^ 2
Граничные условия для функции а :
-
При X — Хо — Х д :
4 zA^ 1 + f k + f k^ - C k a — q a — a o — --------, ,-------
7 1+Tk2
-
при х — Хп — xD :
C k a — q d — o , — /'■/ .'
Где:
YbackfiU Ybackfill (1 'backfill)Y(18)
Ybase — Ybase - (1 - 'base )y(19)
Y backfiu — удельный вес грунта засыпки естественной влажности, Y backfiu , Ybase — удельный (объемный) вес сухого грунта засыпки и основания, nback f ill , hback f ill - пористость и глубина засыпки грунта между шпунтовыми стенами, nbase - пористость грунта основания, , hs - глубина погружения шпунта в основание.
С учетом граничных условий выражения (11) и (12) принимают вид:
ao(xn-хо)+ (Оц- ао)(х - хо) , ,, .г. , „ , „,
----------------------(х - хо)(х„ - х)[Л2 + Аз(х — 2хо + xJ]
- z — zo + z0(x - Хо) + B2(x - Хо)2 + Вз(х - Хо)3
Где:
В — 3 ( zn-Z o )-(z n +2z ‘ ) ( x-Z o )
-
2 (X n -X o )2
( z k + z 0 )( x - X o ) - 2 ( zn - z o )
( Xn - X o )3
z ' — z 0 + 2B 2 ( x - Х о ) + ЗВ 3 ( x - X o )2 (24)
Коэффициенты А 2 и А 3 определяются двумя интегральными уравнениями равновесия. Третье интегральное уравнение используется, в зависимости от постановки задачи, либо для вычисления коэффициента запаса устойчивости, либо, при заданном нормативном значении коэффициента запаса, – для вычисления соответствующего ему заглубления шпунтовых стен.
Неизвестное значение x n определяется также либо условием минимума коэффициента запаса k z , либо минимумом глубины погружения шпунтовых свай в основание hs . Поскольку величины k z и hs в уравнении равновесия явно не выражаются через Х п , вычисление их значений выполняется итерациями.
Некоторую неопределенность в расчет вносит фильтрация воды через замковые соединения шпунтовых свай. Фильтрационный расход и положение депрессионной поверхности зависят от степени заполнения зазоров замковых соединений грунтом, который попадает в эти зазоры при погружении на глубину hs или при засыпке пространства между шпунтовыми стенами выше поверхности основания. При этом часть напора тратится на вход фильтрационного потока в область фильтрации.
Можно указать лишь границы диапазонов для величин k z и hs , соответствующие абсолютной непроницаемости шпунтовой стенки и ее максимальной проницаемости, соответствующей совершенно незаполненным зазорам.
При полной непроницаемости шпунтовой стены перемычки со стороны акватории уровень воды между шпунтовыми стенами определяется участком высачивания в шпунтовой стене со стороны котлована.
При проницаемых замковых соединениях в шпунтовой стене гидравлическую задачу о фильтрации можно приближенно решить, если приравнять расход воды, протекающей через зазоры замковых соединений, расходу фильтрующейся воды, приходящемуся на ширину шпунтовой сваи. Ширина шпунтовой сваи определяется расстоянием между замками.
Для области фильтрации, ограниченной шпунтовыми стенами и условным водоупором на уровне низа верховой шпунтовой стены, удельный фильтрационный расход qf и положение депрессионной поверхности H ( x ) можно определить по Дюпюи:
О / _ Н 2 - Н 2
kf 2L а — х
H _ H i l \ а
, dH H i,
_dx_ 2vavo—x где к/ - коэффициент фильтрации грунта засыпки, H - возвышение депрессионной поверхности над плоскостью сравнения, совпадающей с условным водоупором, L – расстояние между осями шпунтовых стен, H1* = H1 -Д1 и H2* = H2 + Д2 - напоры в крайних сечениях области фильтрации, J- градиент напора в области фильтрации a = UHy*/(H* - H2*).
С учетом фильтрационных сил компоненты удельной нагрузки определяются выражениями:
| —уН ' ( Н + z — z A ) , хе [ х о , хЕ ]
-
10, хе [ хЕ,хп ]
( У backfill ^ backfill \ / backfill У backfill ) ( Н ^ s ) + у backfill ( ^ s + Z Z A ) хе [х 0 , х Е ]
Iy backfill ( h s - Д + Z — Z A ) + y base A ' хе [х Е - х п ]
где Δ – заглубление поверхности грунтовых вод под отметку дна котлована.
После подстановки выражений (20), (21), (25)-(27) и (28) в уравнения (4), (5) и (6) и соответствующего преобразования получаются алгебраические выражения:
« 2 ^ 2 + « з А з _ qx
P 2 A 2 + Р з А 3 _ q z
^ ^" [С 1 + ^’)(х — х о ) + (z ' — f k )( Z — Z o )] О"^ — M q — М о + ск [( х — хо )( Z — Z o ) — 2 J^(z — Z о )dx] _0
Где:
« 2 _ 10 ( z 0 — f) + [ 10В2 + 9В з (хл — х о ) ] (хп — х о ) (33)
« з _ [ 15 ( z 0 —f ) + 16В 2 ( хп —х о ) + 15В з ( хп —х о )2]( хп —х о ) (34)
0 2 — 9f k ^ 3 (x n - X 0 ) 2 + 10f k B 2 (x n - % o ) + 10(1 + fkz 0 )
0 3 — 10 ( 1 + fkz 0 )( xn - Xo ) + f k [I6S 2 + 15В з ( % п - X o )]( xn - % 0 )2
xn
Qx — Q x + Е 0 + Е в + J ( z - f k ) po + ^ ° n — ^ O X — Xo )] Xx - C k( x n — X 0 )
X o n
4 z — C k( z n - z0) +
fXn 1
J ( 1 + f k z )
^ 0
O o ( x n — X0 ) + (o n - O o )(x - X o ) ( x n — X 0 )
dx - Qz
Использование зависимостей (30), (31) позволяет явно выразить коэффициенты А 2 , А 3 через неизвестные пока x n и k z (или h s ):
_ qxP3 - Q z a 3 2 = «203 - « 3 0 2
_ qz« 2 - Я х Р2 A 3 = « 2 0 3 - « 3 0 2
Используя эти выражения, можно из уравнения (32) численно установить зависимость k z (или h s ) on x n . Варьируя значение x n , можно установить значение этой величины, соответствующее минимуму значению коэффициента запаса k z (или h s ).
-
3 Results and Discussion/ Результаты и обсуждение
На Рис. 3 представлен график зависимости коэффициента запаса устойчивости от глубины погружения верховой шпунтовой стены в основание при максимальном уровне воды в акватории. Вычисления выполнены для двух вариантов проницаемости замковых соединений верховой шпунтовой стены перемычки. При проницаемых замковых соединениях положение депрессионной поверхности определяется выражением (25)-(27). Положение профиля поверхности сдвигов и распределение нормальных напряжений по этой поверхности представлено на рисунке 1 для заглубления стены в основание на 19,5 метров.
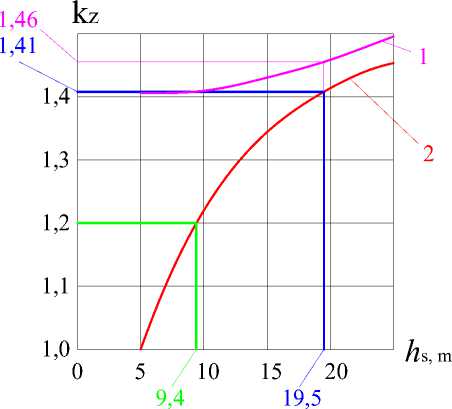
Рис. 3 - График зависимости коэффициента запаса устойчивости к з от заглубления шпунтовой стены в основание h s : 1 – для непроницаемых замковых соединений, 2 – для проницаемых замковых соединений
Fig. 3 - The dependency graph of the safety factor k z on the depth of the sheet pile wall h s : 1 - for impermeable interlocks, 2 - for permeable interlocks
Средний градиент напора фильтрационного потока в пределах основания в обоих случаях можно определить методом коэффициентов сопротивления Н.Н. Павловского, изложенного также в учебниках Р.Р. Чугаева. Расчетная схема такого расчета применительно к рассматриваемой перемычке представлена на Рис. 4.
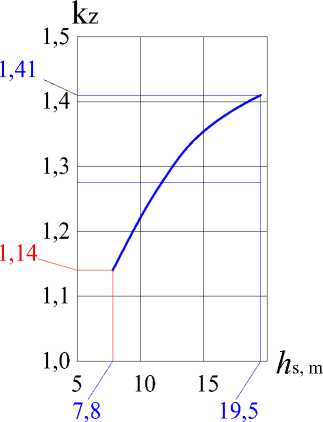
Рис. 4 - Расчетная схема к оценке суффозионной прочности основания
Fig. 4 - Design scheme for assessing the suffusion strength of the base
Оценка суффозионной прочности выполнена в соответствии с требованиями СП 23.13330.2018 «Основания гидротехнических сооружений» (Russian Federation applicable Code Design SP 23.13330.2018 “Foundations of hydraulic structures”). Коэффициент запаса суффозионной прочности определился в обозначениях упомянутого СП 23.13330.2018 зависимостью:
kz
Ip- < [t , ]
* est,m
допустимое значение коэффициента запаса, соответствующее нормативному запасу, Y n Y lc = 1,14 . Результаты расчета представлены на Рис. 5.
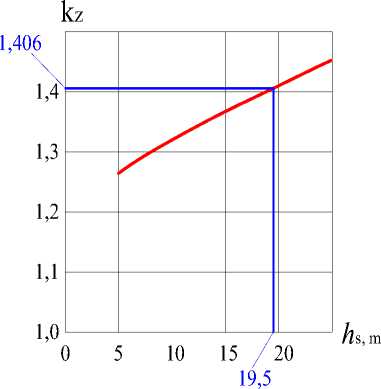
Рис. 5 - График зависимости коэффициента запаса суффозионной прочности к з от заглубления шпунтовой стены в основание
Fig. 5 - The dependency graph of the suffusion strength safety factor k z on the depth of the sheet pile wall
Для сейсмоактивных регионов требуется оценить сейсмостойкость сооружений. В России интенсивность нормативного сейсмического воздействия определяется методикой действующего СП 14.13330.2018 «Строительство в сейсмических районах» (Russian Federation applicable Code Design SP 14.13330.2018 “Construction in seismic areas”) которой в соответствии с районированием и дополнительными местными условиями устанавливается значение обобщенного сейсмического ускорения ~ p = k f k 2 k ^ Ag (обозначения СП 14.13330.2018).
Учет сейсмического воздействия применительно к рассматриваемому объекту выражается во включении сейсмических сил и их моментов в уравнения равновесия (28), (29), (30). При этом, в силу специфики конструкции перемычки, при оценке ее устойчивости допустимо принять сейсмическое ускорение одинаковым во всех точках гипотетического тела обрушения. При учете сейсмичности выражения для Е 0 , Е B , М 0 и (26), (27) надо заменить выражениями:
Н 2 - Н ^ 1 ^ hs V [
Е о = У + 71“ Р^ —2с ) + k c l 0.15y ( H 1 — h s ) 2
2 MaseX Z0 ) [
+
2Уь base
У Ь hs
I ' base s f -о
2с ) 2 |
Мо
Ев = y ( 1 + k c )( H 2 t-H 2 )/ 2
(Н 1 - Н 1 2 , )( Н 1 - Н1Л + h s f ybase h s
8 6y base z 0
2с)
+ kc [o.O6y(H
-h s ) 2 ( H1 + L5h s )+ т-^-Р^* 2y base \ z 0
—
Г к с \У^ е (Н — h s ) + y b>ase (h s + z — z A ) + y base { h backfiH + h s — Н )] cos 9 — уН ' (Н + z — ^^
Q x = j xe [% o , xB ] (4 5)
L k c [y base (z z D △ ) + y base ^ ] cos 9 , x e [x B , x n ]
y base ( h' backfill + h s н)(1 + k c sin 9) + ( y base + y base k c sin 9)(Н h s ) +
+ ( y base + y base k c sin 9)(h s + z z A )> x e [x o , x E ]
. (y base + y s ase k c sin 9 ) ( z — zd — △ ) + y^se ( 1 + k c sin 9) Д, x e [x e , x „ ]
где θ – угол между направлением равнодействующей сейсмического воздействия и горизонтальным направлением, Y ba se - удельный вес естественной влажного грунта, Y s ase - удельный вес грунта основания естественной влажности.
Исследованиями для массивных подпорных стен установлено, что наиболее неблагоприятное направление сейсмического толчка составляет приблизительно 300 к горизонтальному направлению. Для рассматриваемой перемычки при среднем уровне воды в акватории наиболее неблагоприятное направление сейсмического толчка находится в диапазоне 380 – 430. Конкретное значение этого направления зависит от соотношения высоты перемычки и глубины погружения шпунтовых стен. График зависимости коэффициента запаса устойчивости от глубины погружения верховой шпунтовой стены в основание для наиболее неблагоприятного направления сейсмического толчка представлен на рисунке 6.
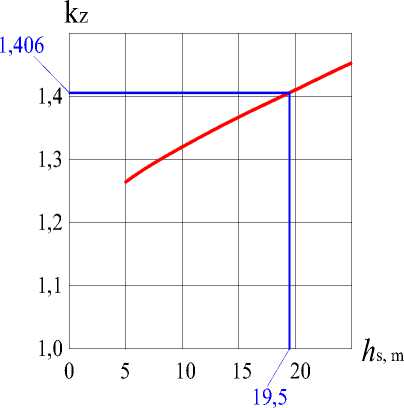
Рис. 6 - График зависимости коэффициента запаса устойчивости k z от заглубления в основание h s при учете сейсмического воздействия 7 баллов
Fig. 6 - The dependency graph of the safety factor of stability k z on the depth of the sheet pile wall h s with consideration of the seismic impact of 7 points
-
4 Conclusions/ Заключение
Разработан метод расчета базовой устойчивости подпорных конструкций, учитывающий граничные условия в крайних точках профиля поверхности сдвига и удовлетворяющий уравнениям равновесия. Полученные результаты позволяют сделать следующие выводы:
-
1. В большинствах методах расчета устойчивости, использующихся в современной практике поверхность сдвигов предполагается кругло цилиндрической или плоской, а в некоторых – произвольной. В этих методах условия равновесия в предельном состоянии не полностью соблюдаются. Много из них даже интегрально не соблюдаются условия равновесия и не учитываются граничные условия по напряжениям и углам наклона площадок сдвигов. Обусловленными несовершенством расчетных предпосылок во многих случаях расчеты по этим методам дают скрытые запасы устойчивости и погрешность в сторону риска.
-
2. Следует отметить, что использование строго обоснованного метода оценки устойчивости подобного рода конструкций позволяет повысить надежность принимаемых технических решений и, следовательно, повысить надежность работы сооружения и его безопасность.
-
3. Установлено, что при оценке устойчивости массивных сооружений по схеме глубинного сдвига с захватом грунта основания с учетом землетрясения определение наиболее неблагоприятного направления сейсмических толчков играет решающую роль.
-
4. Герметизация замковых соединений в шпунтовых стенах перемычек повышает их запас устойчивости в районе нормативных значений коэффициента запаса.
-
5 Acknowledgments/ Благодарности
Авторы выражают искреннюю благодарность профессору Владимиру Николаевичу Бухарцеву за большой вклад в исследование. Он был тем, кто придумал идею, провел большую часть исследования и дал ценные предложения, чтобы помочь авторам завершить эту статью.
Список литературы Оценка устойчивости к базальному пучению подпорных конструкций в стесненных условиях строительства: метод расчета
- Endicott, J. Case Histories of Failure of Deep Excavation Examination of Where Things Went Wrong: Nicoll Highway Collapse, Singapore. 7th International Conference on Case Histories in Geotechnical Engineering. 2013. (3).
- Endicott, L.J. Design and Construction of Excavations in an Urban Setting-Lessons Learnt from Failures. International Conference on Geotechnical Engineering. 2015.
- Chen, R.P., Li, Z.C., Chen, Y.M., Ou, C.Y., Hu, Q., Rao, M. Failure Investigation at a Collapsed Deep Excavation in Very Sensitive Organic Soft Clay. Journal of Performance of Constructed Facilities. 2015. 29(3). DOI:10.1061/(asce)cf.1943-5509.0000557.
- Lim, A. Lesson learned from retaining wall failures: A geotechnical disaster. MATEC Web of Conferences. 2292018.
- Shukla, R.P., Jakka, R.S. Failure mechanism and slope factors for a footing resting on slopes. Magazine of Civil Engineering. 2021. 104(4). DOI:10.34910/MCE.104.1.
- Chao, G., Lu, Z. Frost heaving of foundation pit for seasonal permafrost areas. Magazine of Civil Engineering. 2019. 86(2). DOI:10.18720/MCE.86.6.
- Borges, J.L., Santos, R.M. Bottom Reinforcement in Braced Excavations: Coupled Analysis and New Method for Basal-Heave Stability Study. Soils and Rocks. 2020. 43(2). DOI:10.28927/SR.432199.
- Aleksandrovich, A. Frequency-Dependent Dynamic Characteristics of the Soil Foundation. 2021. 94(9406). DOI:10.4123/CUBS.94.6.
- Goh, A.T.C., Zhang, W.G., Wong, K.S. Deterministic and reliability analysis of basal heave stability for excavation in spatial variable soils. Computers and Geotechnics. 2019. 108. DOI:10.1016/j.compgeo.2018.12.015.
- Wu, S.-H., Ou, C.-Y., Ching, J. Reliability Based Design of Base Heave Stability in Wide Excavations2011.
- Karlsrud, K., Andresen, L. Design and performance of deep excavations in soft clays. Proceedings of the 14th European Conference on Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering. 2007. I.
- Zhang, M., Zhang, Z., Li, Z., Li, P. Axisymmetric arc sliding method of basal heave stability analysis for braced circular excavations. Symmetry. 2018. 10(5). DOI:10.3390/sym10050179.
- Zhou, A., Shen, H., Sun, J. Effects of inserted depth of wall penetration on basal stability of foundation pits. AIP Conference Proceedings. 18392017.
- Ouzaid, I., Benmebarek, N., Benmebarek, S. FEM optimisation of seepage control system used for base stability of excavation. Civil Engineering Journal (Iran). 2020. 6(9). DOI:10.28991/cej-2020-03091579.
- Luo, Z., Atamturktur, S., Cai, Y., Juang, C.H. Simplified Approach for Reliability-Based Design against Basal-Heave Failure in Braced Excavations Considering Spatial Effect. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering. 2012. 138(4). DOI:10.1061/(asce)gt.1943-5606.0000621.
- Terzaghi, K. Theoretical Soil Mechanics1943.
- Bjerrum, L., Eide, O. Stability of strutted excavations in clay. Geotechnique. 1956. 6(1). DOI:10.1680/geot.1956.6.1.32.
- Clough, G.W., Hansen, L.A. CLAY ANISOTROPY AND BRACED WALL BEHAVIOR. Journal of the Geotechnical Engineering Division. 1981. 107(7). DOI:10.1061/ajgeb6.0001168.
- O'Rourke, T.D. Base stability and ground movement prediction for excavations in soft clay. Retaining structures. Proc. conference, Cambridge, 1992. 1993.
- Whittle, A.J., Ukritchon, B., Su, S.F., Liao, H.J., Lin, Y.H. Base Stability of Deep Excavation in Anisotropic Soft Clay. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering. 2000. 126(8). DOI:10.1061/(asce)1090-0241(2000)126:8(757).
- Ukritchon, B., Whittle, A.J., Sloan, S.W. Undrained Stability of Braced Excavations in Clay. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering. 2003. 129(8). DOI:10.1061/(asce)1090-0241(2003)129:8(738).
- Faheem, H., Cai, F., Ugai, K. Three-dimensional base stability of rectangular excavations in soft soils using FEM. Computers and Geotechnics. 2004. 31(2). DOI:10.1016/j.compgeo.2004.02.005.
- Faheem, H., Cai, F., Ugai, K., Hagiwara, T. Two-dimensional base stability of excavations in soft soils using FEM. Computers and Geotechnics. 2003. 30(2). DOI:10.1016/S0266-352X(02)00061-7.
- Fenton, G.A., Griffiths, D. V., Williams, M.B. Reliability of traditional retaining wall design. Risk and Variability in Geotechnical Engineering: The Institution of Civil Engineers2006.


