Опыт культивирования левзеи сафлоровидной Rhaponticum carthamoides (Willd.) Iliin в качестве ресурсного источника экдистерона в условиях Архангельской области
Автор: Тимофеев Николай Петрович
Журнал: Сельскохозяйственная биология @agrobiology
Рубрика: Нетрадиционные культуры и технологии
Статья в выпуске: 1 т.58, 2023 года.
Бесплатный доступ
В настоящей работе описаны результаты впервые реализованного альтернативного способа получения экдистерон содержащей субстанции из листового материала левзеи сафлоровидной Rhaponticum carthamoides. Биосинтез и накопление экдистерона были прямо связаны с вегетативным размножением: при анализе содержания экдистерона в розеточных побегах в зависимости от величины надземной массы коэффициент детерминации содержания экдистерона близок к 80 % (R2 = 0,768). Более 90 % ежегодно синтезируемого экдистерона (22 кг/га) накапливалось в надземной части растений в оптимальный уборочный возраст (с 5-го по 32-й годы), или около 600 кг экдистерона за 27 лет эксплуатации.
Фитоэкдистероиды, 20-гидроксиэкдизон, рапонтикум сафлоровидный, левзея сафлоровидная, маралий корень, кормовые добавки, анаболические субстанции
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/142238090
IDR: 142238090 | УДК: 633.8:58.144:58.01:57.017.6:574.45:581.192 | DOI: 10.15389/agrobiology.2023.1.114rus
Текст научной статьи Опыт культивирования левзеи сафлоровидной Rhaponticum carthamoides (Willd.) Iliin в качестве ресурсного источника экдистерона в условиях Архангельской области
Левзея сафлоровидная Rhaponticum carthamoides (Willd.) Iliin, 1933 — многолетнее растение семейства Asteraceae (р. Rhaponticum , подрод Forni-cium ) (1, 2), синтезирующее биологически активное вещество экдистерон (син.: 20-гидроксиэкдизон, 20Е) из класса экдистероидов (ЭС). Это единственное экдистерон-содержащее растение-адаптоген (син.: Leuzea car-thamoides DC; Stemmacantha carthamoides , рапонтикум сафлоровидный, ма-ралова трава, маралий корень), включенное в официальную фармакопею Российской Федерации IX-XIV изданий (с 1961 года) (3), а также Республики Беларусь (4). Оно не токсично и не имеет противопоказаний при использовании (5). В фармакопее других стран Европы, Азии и Америки этот вид в настоящее время отсутствует (6, 7).
Основные фармакотерапевические эффекты R. carthamoides — адап-тогенный, анаболический, антистрессовый, антикоагулянтный, антиоксидантный, гемореологический, гипогликемический, ноотропный, эргоген-ный (5). В последние годы опубликована серия научных обзоров в связи с открывшимися возможностями и перспективами практического применения экдистерон-содержащих субстанций в различных областях: в официальной фармакологии и медицине для лечения сердечно-сосудистых, нейро-дегенеративных и метаболических заболеваний (5, 8, 9); для защиты и восстановления при осложнениях коронавирусной инфекции (COVID-19) (1012); для профилактики и адъювантной терапии злокачественных новообразований, в частности рака молочной железы (13-15); для предотвращения дегенеративных изменений в организме, связанных с длительным стрессом и старением человека (6, 16); для преодоления тяжелых физических и психических нагрузок у здорового человека, включая спорт высоких достижений, где экдистерон не относится к запрещенным средствам (17-21); как фитобиотическая и анаболическая субстанция в составе кормовых добавок для оздоровления сельскохозяйственных животных и значимого повышения их среднесуточного прироста и продуктивности (22-25). В этой связи интересен факт недавнего обнаружения в кровотоке у 20 видов птиц семейства Passeridae (Воробьиные) (Aves: Passeriformes) относительно высокого содержания экдистерона и его метаболитов, поступающих из семян дикоросов, что способствует защите от вредных факторов среды, а также высокой ско- рости метаболических процессов роста и развития (26).
Мировой рынок экдистерон-содержащих субстанций на 2021 год оценивался в 100 млрд долларов и, согласно аналитическому отчету и прогнозу глобальной исследовательской и консалтинговой компании «Quince Market Insights» (Индия), в ближайшие 5 лет потребность будет значительно возрастать (27). Рынок препаратов экдистерона из-за резкого дефицита сырьевых ресурсов в значительной степени сфальсифицирован, поскольку не контролируется надзорными органами. Заявленные в продаже через Интернет-сети продукты с экдистероном не соответствуют стандартам качества и безопасности, а также маркировкам на этикетках (28, 29), в основно это экстракт из цианотиса паутинистого ( Cyanotis arachnoidea C.B. Clarke) из стран Азии, запрещенный к продаже из-за содержания токсических веществ, в частности канцерогенной аристолохиевой кислоты (30, 31).
Высокоочищенный выделенный экдистерон слишком дорог. Стоимость 10 мг экдистерона 93 % чистоты у такой известной глобальной компании, как «Sigma-Aldritch» (США) (32), на 15 мая 2022 года составляла 40 тыс. руб., а на 8 февраля 2023 года — 52 тыс. руб., или 4-5 млрд руб. за 1 кг, поэтому на практике предлагаются суррогаты. Проведенный анализ показал, что вместо указанных на этикетке 100-500 мг экдистерона в препаратах фактически в среднем содержится в 700 раз меньше — 0,09-4,2 мг на одну капсулу (или 0,38 % чистоты), разброс среди 9 препаратов составил 0,017-0,75 %. Это абсолютно не соответствует заявленным показателям концентрации 20Е 95-99 % чистоты (30). В июле 2021 года опубликованы новые данные: из 16 изученных спортивных добавок, закупленных в США, Канаде, Великобритании, России, Китае, только 5 содержали экдистерон, притом в мизерном количестве (от 0,00005 до 0,15 %). В 11 других препаратах экдистерон не обнаружен (31). Экдистерон не синтезируется в организме млекопитающих и не может быть синтезирован искусственно в промышленных масштабах (химическим, микробиологическим способами или в культуре клеток и тканей), поэтому его получают исключительно из растений, число которых на практике сильно ограничено (9, 33).
Ценность того или иного потенциального источника 20Е определяется его уникальностью, которая складывается из таких показателей, как концентрация экдистерона в биомассе, доступность, биологическая активность, целевое предназначение, экономическая целесообразность. Очевидно, что промышленный интерес представляют те виды, которые характеризуются повышенным содержанием целевых веществ, высокой продуктивностью, отсутствием токсичных примесей, устойчивостью и способностью к интродукции, а также к долголетнему произрастанию в условиях агроценоза (33).
Ключевые требования, которые предъявляются международными экспертами и специалистами к источникам промышленного получения экдистерона (9), следующие: растение должно накапливать не менее 0,5 % 20E, иметь простой экдистероидный профиль, где не менее 95-97 % приходится на целевой высокоактивный компонент экдистерон (в идеале полное отсутствие минорных и слабоактивных компонентов), растворимый в воде и спирте, а очистка не должна требовать дорогостоящих хроматографических методов; вид должен быть не редким или не охраняемым, мало зависеть от климата и быть невосприимчивым к вредителям и болезням (то есть интродуцируемым и успешно культивироваться в агроценозе); затраты на культивирование, сбор урожая и переработку сырья должны быть минимальными, а первоначальная обработка урожая происходить недалеко от места выращивания (то есть это должны быть многолетние растения в аг- ропопуляции, у которых сырьем служит ежегодно отчуждаемая надземная фитомасса).
Экдистерон относится к низкотоксичным веществам, не аккумулируется и быстро исчезает из организма после приема внутрь. ЛД 50 для экди-стерона составляет 6,4 г/кг при внутривенном и 9,0 г/кг — при пероральном введении. Полупериод распада 20E в организме невелик и зависит от дозы, способа введения, интенсивности абсорбции в кровь, вида подопытных животных. Например, для овец полупериод распада экдистерона равен 0,2 ч при внутривенным, 0,4 ч — при пероральном и 2,0 ч — при внутримышечном введении. Выделение из организма осуществляется через печень и желчь в кишечник и мочу. У крыс с высокой скоростью обмена веществ при внутривенном введении период полувывода составлял 8 мин. У человека пик содержания экдистерона в плазме крови при разовых дозировках 350-1400 мг наступает через 2-4 ч, после чего его количество начинает резко снижаться, и через 1 сут остаются только следы 20E (9, 34).
В 2020 году безопасность очищенного до фармацевтической чистоты экдистерона (20-гидроксиэкдизон ≥ 97 %), полученного из левзеи сафлоровидной, была исследована на грызунах и домашних собаках. Применяли высокие дозировки (до 1000 мг/кг ежесуточно) в течение 180 сут для крыс и 270 сут для собак. Препарат при пероральном введении продемонстрировал хороший профиль безопасности при отсутствии наблюдаемых побочных эффектов. Исследования на генотоксичность in vitro и in vivo были отрицательными при дозах 1,0-1,5 г/кг для крыс и собак в течение 28 сут. Комплекс тестов Safety Pharmacology (поведение животных, ЦНС, функция дыхания, тест hERG и сердечная телеметрия) не выявил отклонений (10). Затем в 2021 году после завершения клинических испытаний препарат был зарегистрирован в США в качестве фармацевтического под коммерческим названием BIO101 от американо-французской компании «Biophytis» (идентификатор NCT03452488) для усиления роста мышц и ингибирования протеолиза (против ускоренного распада белка, при мышечной слабости, саркопении пожилых людей, дыхательной недостаточности грудных мышц) (9, 35).
Растения, которые в настоящее время рассматриваются в странах Европы как лучшие источники экдистерона и заслуживают внимания для масштабного производства субстанций в достаточных количествах и по разумной цене, — это виды из родов Achyranthes (соломоцвет из сем. Amar-anthaceae ), Cyanotis (цианотис из сем. Commelinaceae ), Pfaffia (сума из сем. Amaranthaceae ), Leuzea / Stemmacantha / Rhaponticum (рапонтикум, или левзея, из сем. Asteracea ), Serratula (серпуха из сем. Asteraceae ) (9). Согласно данным, представленным в ряде аналитических обзоров (6, 8, 10), среди указанных групп растений для получения экдистерон-содержащих составов фармацевтического качества в первую очередь подходят надземные и подземные части левзеи сафлоровидной ( R. carthamoides ) .
Другие представители мировой флоры с адаптогенными свойствами и относительно высоким содержанием экдистерона — Cyanotis arachnoidea C.B. Clarke , Cyanotis vaga (Lour.) Schult. & Schult. f., Achyranthes aspera L., Cyathula capitata Moq., Pfaffia paniculata (Mart.) Kuntze , Pfaffia glomerata (Spreng.) Pedersen — официально не разрешены и не могут продаваться в качестве пищевых или кормовых добавок из-за содержания запрещенных веществ, токсичности и генотоксичности (36). При сравнении эффективности биологически активных соединений из коммерчески доступных расте-ний-адаптогенов — женьшеня обыкновенного Panax ginseng C.A.Mey, маки перуанской Lepidium meyenii Walp., левзеи сафлоровидной Rhaponticum carthamoides (Willd.) Iljin, элеутерококка колючего Eleutherococcus senticosus (Rupr. & Maxim.) Maxim. наибольший потенциал для расширенного использования на практике имел R. carthamoides (6).
Некоторые другие представители рода Rhaponticum, исторически происходящие из субальпийской зоны, также синтезируют экдистерон и его аналоги. Например, Rhaponticum uniflorum DC. встречается в Сибири, Китае и Монголии, Rhaponticum scariosum (Lam.) — в Альпах в Европе (2, 38, 39). Однако подобные перспективные виды еще только изучаются на примере единичных экземпляров и не относятся к культурам, которые возделываются в полевых условиях (40, 41).
Как подземные части левзеи с корневищами, так и надземные, а именно листья вегетативных (розеточных) побегов разрешено использовать в составе фармпрепаратов и пищевых добавок для человека (42), а также фитобиотиков для животных (35). Нормируемым действующим веществом и в листьях, и в корнях служит экдистерон — 0,1 %, или 1000 мг/кг, в расчете на сухое вещество (3, 4). По результатам сравнительных испытаний экстрактов из корней и листьев (вытяжка 1:10), проведенных в Институте мозга человека им. Н.П. Бехтеревой РАН (г. Санкт-Петербург), листья розеточных побегов левзеи имели многократное преимущество перед подземными органами по комплексной активности — 66 баллов против 16 (43). Аналогичные результаты изложены в совместной работе британских и австрийских ученых (44).
Экдистерон после биосинтеза в корнях или листьях перераспределяется и концентрируется в молодых и развивающихся органах и тканях (растущие листья, апикальные части, почки и семена). Листья вегетативных побегов R. carthamoides по сравнению с корнями, как правило, значительно богаче экдистероном (содержание обычно от 0,25 до 0,5-0,7 %) (6, 36), при этом они ежегодно отрастают, представляя собой возобновляемое растительное сырье. Завершившие вегетацию многолетние корни выполняют прежде всего якорную функцию в почве, поэтому низкое содержание экди- стерона в заготавливаемых осенью корнях левзеи объяснимо. Согласно публикациям из разных стран (СССР, Чехия, Узбекистан, Франция, Австрия), реальный выход экдистерона из 30-50-65 кг сухих корней с корневищами левзеи сафлоровидной составлял 0,013 % (45); 0,0153 % (46); 0,03 % (44); 0,036 % (47); 0,05 % (48); 0,075 % (49); 0,101 % (50).
Важно подчеркнуть, что в процессе хранения и переработки растительного сырья, загрязненного микроорганизмами, в частности подземных органов R. carthamoides , экдистерон может быстро разрушаться (9, 51). Например, в порошкообразной субстанции из корней с корневищами R. carthamoides , закупленной в аптечной сети трех крупных городов России и изученной в научной лаборатории, экдистерон не обнаружили (52). Выявленный факт соответствует информации, опубликованной ранее лабораторией аналитической химии (Московский государственный университет им. М.В. Ломоносова), о том, что содержание экдистерона в таблетках Левзеи-П (порошок корневищ с корнями левзеи, ООО «Парафарм», Россия) было следовым (0,040 мг/таблетка) (53).
Кроме того, в результате использования подземных частей плантация перестает существовать, заготовленное таким образом лекарственное сырье характеризуется низким качеством и быстро теряет экдистерон в процессе хранения, а сам технологический процесс экономически невыгоден производителю из-за высокой себестоимости. Следовательно, более перспективен сбор ежегодно отрастающей надземной фитомассы R. carthamo-ides с высоким содержанием экдистерона,
Действительно, в этнографических первоисточниках по Алтайско-Саянской горной области указывается, что местные охотники и вожди известных племен (Цэцэн-хан) использовали мараловую траву в виде порошка из листьев левзеи, но не из корней с корневищами (54). Практические сведения про особенности применения R. carthamoides этническими группами из малоизвестных и неизученных областей Центральной Азии, прежде всего из Северо-Западной Монголии, были зафиксированы русским путешественником и этнографом Г.Н. Потаниным в 1876-1870 годах в ходе экспедиций, организованных Императорским Русским географическим обществом.
Утверждение, что маралы (горные олени) выкапывают из-под снега корни R. carthamoides и питаются ими в период гона, не соответствует действительности. При проведении специальных исследований учеными Сибирского отделения РАСХН было установлено, что маралы поедают холодостойкие розеточные листья, которые остаются зелеными под рано выпадающим в горах снегом (55). Все иные представители животного мира на высокогорных пастбищах (лошади, коровы, овцы, олени) также поедают листья левзеи, но не корни, и иногда обрывают соцветия.
К сожалению, общепринятые технологии и изучение R. carthamoides в России и за рубежом не связаны с качеством получаемого лекарственного сырья. В опубликованных ранее монографиях авторы не исследовали биосинтез и накопление экдистерона и его аналогов (фитоэкдистероидов) в растительной продукции и тем более в условиях агропопуляций (55-57). Еще одна проблема заключается в том, что, несмотря на почти вековую историю культивирования (первые посевы R. carthamoides в СССР датируются 1926 годом), не удается обеспечить длительную хозяйственную эксплуатацию вида. Если на субальпийских лугах онтогенез R. carthamoides длится от 50-60 до 75-120 и более лет (55, 58), то в культуре он сокращается до 5-6 лет, а длительность хозяйственного использования обычно не превышает 3-4 лет (33).
В настоящей работе впервые реализована альтернативная техноло- гия получения экдистерон-содержащей субстанции из листьев розеточных побегов левзеи сафлоровидной R. carthamoides. Предлагаемая технология проста и масштабируема в условиях агропопуляций Европейского Севера и удовлетворяет ключевым требованиям, которые предъявляются международными экспертами и специалистами к источникам промышленного получения экдистерона. В частности, вид может длительно (до 30 лет и более) и успешно культивироваться без пересева в агроценозе в условиях холодного и прохладного климата с повышенной влажностью, невосприимчив к болезням и вредителям, служит источником ежегодно возобновляемого лекарственного сырья; в растительном сырье накапливается большое количество экдистерона (0,4-0,6 %), сырье имеет простой экдистероидный профиль, где более 97 % приходится на экдистерон; субстанция удовлетворяет всем нормативным требованиям надзорных органов.
Нашей целью было проанализировать 32-летний опыт культивирования левзеи сафлоровидной в условиях промышленно эксплуатируемой плантации, расположенной на европейском северо-востоке России (Архангельская обл.), выявить потенциал долголетия и продуктивности агропопуляции Rhaponticum carthamoides по возрастным периодам, изучить закономерностей накопления экдистерона в ежегодно отчуждаемой надземной фитомассе, а также оценить качество получаемого растительного сырья по содержанию нормируемых веществ.
Методика. Исследования выполняли на юго-востоке Архангельской области, в подзоне средней тайги (Котласский р-н; 61 ° 20" с.ш., 47 ° в.д.) в агропопуляции R. carthamoides (единый участок площадью 1 га) в период с 1989 по 2022 годы. Агропопуляцию семенного происхождения заложили в 1989 году. Семена были получены из Ботанического сада Коми НЦ УрО РАН (г. Сыктывкар). Исходное происхождение семян — алтайская природная популяция; первичный сбор от 1956 года, затем там же (ИБ Коми НЦ) были выполнены 3-4 репродукции с индивидуальным отбором и пересевом.
Предшественниками в севообороте были картофель, однолетние и зерновые культуры. Предпосевная обработка почвы включала вспашку на глубину 22-25 см, дискование и 2-кратную культивацию с одновременным боронованием. Перед посевом участок прикатывали гладкими водоналивными катками. Посев подзимний, с междурядьями 70 см, в середине октября после начала осенних заморозков, четырехрядной овощной навесной сеялкой СОН-2,8А (Россия). Норма высева семян — 2,7 кг/га при полевой всхожести 58 %, ширина междурядий — 70 см, глубина заделки семян — 23 см. Минеральные удобрения (NPK 60-90 ) вносили только в первые три года после посева; далее культивирование в онтогенезе вели по типу органического земледелия: минеральные и органические удобрения, химические средства защиты и регуляторы роста растений, гербициды не применяли. Отчуждение урожая розеточных листьев из надземной части проводили ежегодно одноразово в фазу бутонизации; урожай семян собирали в фазу плодоношения.
Для определения комплекса агрохимических показателей почвы участка отбирали и исследовали образцы общепринятыми методами (ФГУ «Агрохимцентр Кировский», г. Киров).
Изучение возрастных состояний в онтогенезе растений и его периодизацию в жизненном цикле, плотность популяции (число растений на единице площади), валовую продукцию надземных и подземных органов, урожайность семян (с учетом фактической плотности аrроценоза) проводили по методикам, изложенным в публикации, посвященной исследованию других агропопуляций R. carthamoides в той же местности (59). Возрастные состояния учитывали по доминирующей группе особей. Выделяли вирги-нильный (прегенеративный), генеративный и постгенеративный периоды онтогенеза. В виргинильный период выделяли следующие возрастные состояния: проростки (p), ювенильные (j), имматурные (im) и взрослые вегетативные растения (v), в генеративном — молодые (g1), средневозрастные (g2) и старые генеративные растения (g3), а также субсенильное возрастное состояние (ss). Календарный (абсолютный) возраст популяций отсчитывался со времени появления всходов. Исходили из следующих критериев: молодое генеративное возрастное состояние — формирование репродуктивных побегов, слабое плодоношение, отсутствие процессов отмирания корневища; взрослое генеративное состояние — относительный максимум репродуктивных побегов, высокая интенсивность процессов роста и плодоношения, уравновешенность процессов новообразования и отмирания; старое генеративное состояние — резкое снижение доли репродуктивных побегов, ослабленный рост, неполноценность и периодичность плодоношения, преобладание процессов отмирания на ветвях корневища. В постгенеративный период субсенильное возрастное состояние различали по отсутствию генеративных побегов у большинства особей, резкому снижению качества плодоношения и ослабленной способности к формированию почек возобновления, партикуляции корневища (60).
В процессе фенологических наблюдений ежегодно отмечали следующие фазы: отрастание побегов, бутонизацию, начало цветения, массовое цветение, плодоношение, отмирание побегов, покой. Динамику роста учитывали, исходя из высоты наиболее развитых побегов растения, от уровня почвы до верхушки побега в выпрямленном виде. Ширину листовой пластинки измеряли в самом широком месте, распрямив лист.
Валовую продукцию популяций устанавливали с учетом надземной и подземной фитомассы в сухом виде, умноженной на фактическую плотность агроценоза в изучаемом возрасте. Плотность определяли с использованием метода учетных площадок размерами 60-80 м2, закладываемых в 6-9 точках по диагонали поля. Семенное плодоношение оценивали методом учета всех плодоносящих соцветий в пределах исследуемого сообщества, исходя из выхода выполненных семян (%) и массы 1000 шт. (г).
Изъятие образцов проводили в оптимальные фазы развития растений: надземной фитомассы — в фазу бутонизации (I и II декада июня), корневищ — осенью после завершения вегетации (октябрь) или ранней весной до начала вегетации (апрель). В надземной фитомассе выделяли морфологически разнородные органы — укороченные вегетативные (розеточные) и стеблевые генеративные (репродуктивные) побеги с соцветием. В каждой выборке исследовали 275-300 вегетативных побегов, содержащих 1100-1500 розеточных листьев, и до 30-35 генеративных побегов. Промышленный сбор растительного сырья осуществляли в конце мая—начале июня, в фазу бутонизации, которая характеризуется максимальной концентрацией действующего вещества (экдистерона) в розеточных листьях вегетативных побегов (смесь фракций молодых и взрослых листьев). Растительный материал (органы, элементы и фракции) высушивали при переменной температуре от 23-25 до 35-40 °С и относительной влажности воздуха 25-40 % в соответствии с правилами по заготовке и сушке лекарственного сырья. Остаточная влажность воздушно-сухого сырья, определенная методом ускоренной сушки при 130 °С, составляла 10-12 %. Образцы из воздушно-сухого сырья для дальнейшего определения содержания первичных и вторичных метаболитов формировали методом квартования. До анализа их хранили 35 мес в полиэтиленовых пакетах при комнатной температуре.
Количественное содержание экдистерона в сухих образцах определяли методом обращенно-фазовой высокоэффективной жидкостной хроматографии (ОФ-ВЭЖХ) с компьютерной обработкой данных по методу внутреннего стандарта (3). Анализы выполняли в лаборатории биохимии и биотехнологии растений (за 1989-2000 годы) и биохимической лаборатории Ботанического сада (2001-2021 годы) Института биологии Коми НЦ УрО РАН (ИБ ФИЦ, г. Сыктывкар). Использовали жидкостный микроколоночный хроматограф Милихром-5 (колонка 80½2 мм, сорбент Nucleosil C18 с размером частиц 5 мкм) (ООО «Медикант», Россия). Элюент — раствор ацетонитрила, этанола в воде, подкисленный уксусной кислотой в режиме градиентного элюирования компонентов при скорости 100 мкл/мин, УФ-детектор ( λ = 242 нм). Учитывали средние значения 2 биологических и 3 аналитических повторностей (% от воздушно-сухого вещества). Качественный состав определяли по соотношению долевого участия наиболее активного соединения экдистерона (20E) к слабоактивному экдизону (Е) — 20E/E. Этот показатель должен быть ≥ 20:1, что соответствует качественной чистоте ≥ 95 % (или соотношению экдистерона к иным экдистероидам 95:5) (9, 61).
Химические анализы сухих образцов на содержание потенциально опасных веществ (тяжелые металлы Hg, Cd, As, Zn, Ni, Cu, Cr, хлор- и фосфорорганические соединения, радионуклиды 90Sr и 137Cs, нитраты и нитриты) выполняли в соответствии с принятыми методами исследований в аккредитованных лабораториях ФГБУ «Агрохимцентр Кировский» (г. Киров) (см. сайт .
Безопасность R. carthamoides и выявленных действующих веществ оценивали, пользуясь сведениями о ядовитых растениях и лекарственных средствах растительного происхождения с нежелательными побочными эффектами, включая руководства по синтезируемым растениями токсическим веществам (37, 62, 63), Технический регламент Таможенного союза «О безопасности пищевой продукции» (42) и обзоры A.C. Brown (64-68) по токсичным растениям мировой флоры, обнаруженным в пищевых добавках. Названия упомянутых в статье родов и видов растений приведены по международной классификации IPNI (International Plant Names Index) (69).
Математическую обработку данных проводили стандартными методами вариационной и корреляционной статистики с помощью модуля Statistica в программе Microsoft Excel 2016. Использовали параметры генеральной (по результатам сплошного учета) и выборочной совокупности. Для исключения систематических погрешностей с краевых участков агроценоза образцы не отбирали, поверхностные слои отбираемых проб не анализировали; данные по единичным экземплярам, по виду резко отличающимся от нормальных, при обработке не учитывали; к остаточному материалу и типичным особям применяли метод случайной выборки. Вычисляли средние значения показателей и среднеквадратичные отклонения ( M ±SD), коэффициенты вариации ( Cv , %), амплитуды минимальных и максимальных значений (lim, min-max), исходя из объема выборки особей из популяции (N).
Изменчивость оценивали по шкале, выраженной коэффициентом вариации для биологических исследований: ≤ 7 % — очень низкая, 7-15 % — низкая, 15-25 % — средняя, 26-35 % — повышенная, 36-50 % — высокая, ≥ 50 % — очень высокая (70). Были проанализированы корреляционные связи между накоплением экдистерона и фитомассой растений за 32 года жизни агропопуляции. На кривых аппроксимации экспериментальных данных приведена соответствующая величина их достоверности в виде коэффициента детерминации, или коэффициента аппроксимации (R2) как показателя силы и направления взаимосвязи двух изучаемых количественных переменных при доверительном интервале 95 % (при уровне значимости p = 0,05).
Результаты. В зоне расположения участка рельеф местности слабоволнистый повышенный, почвы супесчаные, дерново-среднеподзолистые, сформированы на двучленных отложениях. Верхний горизонт (0-28 см) — частицы песка, с глубины 70-85 см преобладала среднесуглинистая фракция. По комплексу агрохимических показателей почва участка относилась к высокоокультуренным минеральным (почвенные пробы исследовали общепринятыми методами в ФГУ «Агрохимцентр Кировский», г. Киров). Содержание гумуса в пахотном слое — 3,6 %, органического вещества — 3,1 %. Кислотность корнеобитаемого слоя была оптимальной (pH KCl обменная 6,4-6,5; pH гидролитическая 0,7 мг-экв.), насыщенность основаниями высокой (12,4 мг-экв., или 93,5 %). По элементам питания обеспеченность фосфором была высокой (P 2 O 5 подвижный — 31,2 мг/100 г почвы), калием — средней (K 2 O подвижный — 9,6 мг/100 г); содержание Ca составляло 6,4, Mg — 1,0 мг-экв/100 г.
Территория выполнения исследований относится к подзоне средней тайги и входит в состав Европейско-Западно-Сибирской таежно-лесной био-климатической области с умеренно прохладным летом и умеренно прохладной зимой, коротким безморозным периодом, значительной облачностью и недостатком солнечного света в ультрафиолетовом диапазоне, избыточным увлажнением. Зональный коэффициент увлажнения (отношение количества осадков к испарению) близок к 1,5. Продолжительность светлого времени суток в начале отрастания R. carthamoides (I декада мая) — 16-17 ч, во время цветения (во II-III декаде июня) — 20 ч. Продолжительность вегетационного периода составляла 165-186 сут, безморозного — 105 сут (с амплитудой колебаний по годам 77-139 сут). Среднегодовые суммы температур выше 15 ° С составляли 911 ° С (54-57 сут), 10 ° С — 1577 ° С (107-110 сут), 5 ° С — 1936 ° С (153 сут). Средняя температура самого теплого месяца (июля) — +17,4 ° С, самого холодного (января)--14,3 ° С. Устойчивый снежный покров со средней высотой 52-58 см появлялся 11-16 ноября и сохранялся до 17-19 апреля.
Температура на глубине узла кущения многолетних трав держалась в пределах -1,5..-2,2 °С, в отдельные периоды она снижалась до -3,5...-4,0 °С. При переходе температуры воздуха через +5 °С, который наступал 29 апреля, начиналась вегетация многолетних сельскохозяйственных культур. Однако возвраты холодов с заморозками на поверхности почвы (до -5...-7 °С) и повторное выпадение снега часто тормозили рост и развитие растений до начала II декады мая. Заморозки полностью прекращались со второй декады июня и возобновлялись с начала сентября. Завершение вегетации наблюдалось в начале октября, что совпадало с осенним переходом температуры через +5 °С. За год выпадало 495-538 мм осадков, в том числе за теплый период 367-387 мм. Запасы продуктивной влаги в слое почвы 0-20 см за теплый период составляли 37-44 мм, в слое 0-50 см — 55-70 мм, что достаточно для жизнедеятельности большинства многолетних культур. Среднедекадная относительная влажность воздуха в дневное время составляла 62-74 %, наиболее низкие показатели приходились на полуденное время — 54-57 %. В отдельные засушливые периоды влажность могла опус- каться до 25-35 % и ниже.
Параметры роста и развития побегов в онтогенезе. Левзея сафлоровидная (рис. 1) — многолетнее зимостойкое и холодоустойчивое растение, взрослые особи образуют куст высотой 90-150 см (иногда 50-250 см). Вид интродуцирован из высокогорной зоны субальпийского пояса (до 3000 м над у.м.) и с начала 1960-х годов введен в производство на Европейском Севере (33).
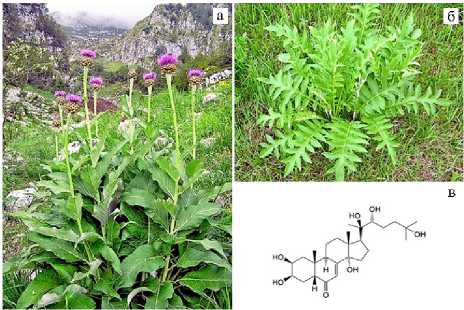
Рис. 1. Представители рода Rhapon-ticum, синтезирующие экдистерон: а — R. scariosum Lam. с генеративными побегами (фото Adriano Bruna, Альпы, 2009; ; б — R. carthamoides (Willd.) Iliin с розеточными листьями (фото Н.П. Тимофеева; Архангельская обл., Котласский р-н, май 2022 года), в — химическая структура экдистерона (71).
По жизненной форме R. carthamoides — крупное травянистое полурозе-точное поликарпическое рас- тение с ежегодно отмирающими побегами двух типов — вегетативных розеточных и генеративных стеблевых с соцветиями разной степени развитости. Имеет два типа размножения — семенной и вегетативный (клонами). Онтогенез R. carthamoides в условиях субальпийских лугов длится 50-75 лет, где средний относительный возраст особей 25-35 лет. Генеративный период продолжается с 6-9 до 30-48 лет. Сенильные особи в природных ценозах чаще всего отсутствуют (55, 72).

Рис. 2. Растения Rhaponticum car-thamoides (Willd.) Iliin из агропопуляции, культивируемой в условиях Европейского Северо-Востока: а — семена, б — растения 1-го года жизни, в — растения генеративного периода в фазу цветения (фото Н.П. Тимофеева; Архангельская обл., Котласский р-н, июль 2001 года).
Жизнедеятельность вида в условиях агропопуляции (рис. 2) по итогам 32 лет наблюдений можно было подразделить на два этапа: формирование ценопо-пуляции, с 1-го по 5-й год жизни (табл. 1); дальнейшее устойчивое продуцирование надземной массы с высоким биосинтезом экдистерона (табл. 2).
В первые 5 лет происходило интенсивное развитие особей на фоне многократного ежегодного нарастания фитомассы (см. табл. 1): проростки в 1-й год проходили имматурные и ювенильные возрастные состояния, на 2-й год достигали виргинильного состояния, которое продолжалось и на 3-й год жизни, а на 4-й год начинался переход в генеративный возраст, кото- рый закреплялся на 5-й календарный год. В дальнейшем (6-32-й годы) интенсивный прирост прекращался. Особи вступали во взрослый генеративный (6-8-й годы), старый генеративный (9-12-й годы) и субсенильный возраст (13-32-й годы), которые различались по способности к продуцированию семян, строению и целостности корневищ.
-
1. Средние показатели развития надземных органов у Rhaponticum carthamoides (Willd.) Iliin из агропопуляции, культивируемой в условиях Европейского Северо-Востока, в первые 5 лет онтогенеза (Архангельская обл.. Котласский р-н)
Показатель
Год и возраст растений
1990
1991
1992
1993
1994
N
p 1
j
im
im
1 v
v
g1
g1-g2
Число побегов, шт.:
всего
1,0
1,0
1,0
1,2
4,2
5,7
17,2
35,6
15-20
вегетативных
1,0
1,0
1,0
2,8
3,8
5,1
16,0
31,1
15-20
генеративных
0,4
0,6
1,2
4,2
15-20
плодоносящих
0,01
0,16
0,84
186-4233
Высота генеративных побегов, см
3-42
90,3
114,0
15-20
Высота вегетативных побегов, см
1,5
17,4
21,1
63,7
58,3
75,0
89,8
15-20
Ширина розеточных листьев, см
0,6
3,0
5,0
12,0
14,0
14,5
17,5
22,5
15-20
Масса надземной части:
всего, г
0,01
0,27
0,42
6,2
10,2
16,4
56,8
210,7
12-15
доля розеточных листьев, %
100
100
100
100
100
93,3
84,0
85,4
12-15
Содержание 20Е в розеточных
листьях, %
0,04
0,06
0,11
0,19
0,22
0,25
0,27
0,28
3-4
Пр им еч ан и е. 20Е — экдистерон. Возраст растений
в онтогенезе:
р — проросток,
j — ювенильный,
im — имматурный, v — виргинильный, g1, g2 —
молодой и зрелый генеративный.
-
2. Показатели развития надземных органов Rhaponticum carthamoides (Willd.) Iliin из агропопуляции, культивируемой в условиях Европейского Северо-Востока, в период устойчивого продуцирования надземной фитомассы с высоким биосинтезом экдистерона с 5-го по 32-й год жизни (Архангельской обл., Котласский р-н, 1994-1921 годы)
Показатель
1 M ±SD
Cv , %
max
1 min
1 N
Число побегов, шт.:
всего
31,00±12,40
40,1
60,4
17,9
15-20
вегетативных
28,30±10,70
37,9
54,6
14,8
15-20
генеративных
2,71±2,13
78,6
3,8
0,6
15-20
плодоносящих
0,19±0,31
167,9
1,1
0,001
20188-52
Высота генеративных побегов, см
125,0±10,1
8,1
143,1
107,9
15-20
Высота вегетативных побегов, см
87,3±11,3
13,0
119,1
65,2
15-20
Ширина розеточных листьев, см
24,5±3,8
15,6
33,0
19,4
15-20
Масса надземной части:
всего, г
223,4±74,4
33,3
354,0
95,1
6-9
доля розеточных листьев, %
84,4±5,3
6,3
93,9
73,2
6-9
Содержание 20Е в розеточных листьях, %
0,41±0,10
24,4
0,64
0,28
3-4
Сенильный период в целом по популяции не наступал: растения продолжали нормально отрастать и вегетировать на 31-33-й годы жизни. При анатомическом исследовании подземных частей в начале 33-го года жизни (29 апреля 2022 года) было обнаружено, что процессы отмирания и новообразования особей находятся в относительном динамическом равновесии (1:1). Общее число побегов (31,5 шт., Cv = 28,0 %) и многолетних почек возобновления (52,7 шт., Cv = 42,5 %) было сопоставимо с суммарным числом отмерших побегов (83,7 шт., Cv = 47,7 %).
-
3. Продуктивность агропопуляции Rhaponticum carthamoides (Willd.) Iliin, культивируемой в условиях Европейского Северо-Востока, в первые 5 лет онтогенеза (Архангельской обл., Котласский р-н)
Год и возраст растений
Показатель
1990
1991
1992
1993
1994
p j 1 im
im v
v
g1
g1-g2
Плотность, тыс. шт/га
114,3 34,6 31,5
30,8 28,3
27,5
27,3
24,0
40-48
Масса одного растения, г:
надземные части
0,013 0,27 0,42
6,2 10,2
16,4
56,8
210,7
12-15
подземные части
0,003 0,07 0,30
2,3 4,7
11,9
38,2
141,3
12-15
Развитые соцветия, шт/растение
0,01
0,16
0,84
186-4233
Продуктивность, кг/га:
надземная часть
1,5 9,3 13,2
191 289
452
1553
5046
12-15
подземная часть
0,3 2,4 9,5
71 133
328
1044
3384
12-15
семена
0,17
8,0
30,3
186-4233
Примечания. Возраст растений в онтогенезе: р —
проросток, j —
ювенильный, im — имматурный,
v — виргинильный, g1, g2 — молодой и зрелый генеративный.
Растения во время роста надземных органов и зимующие корневища не поражались болезнями и вредителями. Для листьев существовали кратковременные периоды в жизненном цикле (фаза проростков), когда они не обладали потенциалом устойчивости к листогрызущим фитофагам. Вредителями семян в фазу созревания были птицы из сем. Воробьиные (Passeridae), соцветий (единичные поражения в некоторые годы) в фазу формирования семяпочек — жуки-бронзовки Oxythyrea funesta, Potosia cu-prea ssp. metallica (Cetoniinae), восковик полосатый, или перевязанный, Trichius fasciatus (Scarabaeidae: Trichiinae) (61).
Основу лекарственного сырья R. carthamoides в надземных органах составляли розеточные листья вегетативных побегов: крупные черешковые, у взрослых растений более или менее глубоко перисто-рассеченные на 1522 долей (минимальный показатель — отсутствие рассечений, максимальный — 27 долей), по окраске светло-, желто- или темно-зеленые, образовывали розетку диаметром в среднем 55-90 см (от 37 до 112 см). В молодом возрасте поверхность листьев была паутинисто-опушенной, придающей им серебристый оттенок. Размеры взрослых листьев достигали 60-90 см, иногда до 120 см по длине и 25-33 см по ширине листовой пластинки. Появление новых листьев, их взросление и отмирание не было приурочено к определенным фазам развития, они функционировали в течение всего вегетационного периода, меняя друг друга во времени, с момента схода снежного покрова и до наступления устойчивых осенних заморозков.
Цветоносные (генеративные) побеги имели высоту 110-140 см, иногда до 180 см. Стебель нарастал за счет вставочного роста междоузлий, на котором были спиралеобразно расположены 28-55 листьев различной сложности строения. На верхушке полого неразветвленного стебля формировалось одиночное соцветие — крупная шаровидная корзинка диаметром 46 см (разброс от 3 до 8 см), с обоеполыми фиолетово-лиловыми цветками. Сроки цветения особей в агропопуляции приходились обычно на 1426 июня. В конце июня зацветали менее 1 % побегов. Даты трех самых ранних отклонений для агропопуляции — 10.06.1995, 10.06.2005, 09.06.2015; одна поздняя дата — 07.07.2017. Появление новых генеративных побегов, их цветение в июле-сентябре не наблюдалось. В целом развитие R. car-thamoides до фазы бутонизации занимало 15-23, цветения — 44-56, плодоношения — 72-77 сут. После плодоношения в середине июля репродуктивные побеги отмирали, розеточные побеги продолжали вегетировать, пока среднесуточной температуры не опускалась ниже 0 ° С во II декаде октября, постепенно уменьшаясь по числу и размерам. В надземной сфере преобладали вегетативные (розеточные) побеги: их доля в массе надземных органов в первые 3 года жизни составляла 100-93,3 %, на 4-5 годы — 84,0-85,4 %, в дальнейшем (5-32-й годы) практически не менялась — 84,4 % (при минимальном Cv = 6,3 %). Вклад генеративных побегов в величину фитомассы оказался незначителен на всем протяжении 32-летнего жизненного цикла: 6,7 % — на 3-й год, 6,0 % — на 4-й год, 4,6 % — на 5-й год, 5,6 % — в среднем за период с 5-го по 32-й годы жизни.
Общее число побегов у особей в первые 5 лет последовательно возрастало (см. табл. 1): с 1,0 до 4,2 шт. на 2-й год; 5,7 шт. — на 3-й год; 17,2 шт. — на 4-й год; 35,6 — на 5-й год жизни. Максимальное число зафиксировали во взрослый генеративный период на 6-9-й годы (60,452,1 шт.), минимальное пришлось на начало субсенильного возраста — на 13-15-й годы (17,9-20,6 шт.). В период стабильного функционирования агропопуляции с устойчивым продуцированием надземной фитомассы (с 5-го по 32-й годы; см. табл. 2) средняя численность побегов была равна 31,0 шт. ( Cv = 40,1 %), а на начало 33-го года — 31,5 шт.
Число вегетативных побегов возрастало до 5-го года жизни (с 1,0 до 31,1 шт.), и в последующие годы сохранялось среднее значение 28,3 шт. ( Cv = 37,9 %). Генеративные побеги с соцветиями начинали появляться с 3-го года, однако они отмирали, не достигая фазы плодоношения (высота 126
3-42 см). На 4-й год растение в среднем формировало 1,2 генеративных побега, из которых лишь незначительная часть (0,16 шт.) цвела и завязывала полноценные семена; на 5-й год на растении было в среднем 0,84 плодоносящих побега. В субсенильном возрасте число генеративных побегов снова оказалась незначительной (см. табл. 2) — 0,19 шт/растение, что было близко к параметрам природных популяций (55) и указывало на преимущественно вегетативный тип размножения клонами после дезинтеграции материнского растения на относительно самостоятельные дочерние особи.
Обращает на себя внимание то, что при стабильной величине затрат на формирование генеративных побегов (не более 15-16 % от фитомассы на протяжении всего онтогенеза при минимальном коэффициенте вариации 6,3 %) число плодоносящих репродуктивных побегов за 27 лет (с 5-го по 32-й годы) при средних значениях 0,19 шт/растение варьировало очень сильно — от 0,001 до 1,13 шт. ( Cv = 167,9 %). Это было связано как с возрастными особенностями индивидцальных растений в популяции, так и с поздневесенними заморозками до - 7... - 10 ° С от проникающих на территорию воздушных арктических масс, вызывающих необратимые повреждения и отмирание соцветий (розеточные листья R. carthamoides устойчивы к ним). Аналогичное влияние климатических факторов на варьирование параметров плодоношение отмечено и для природных горных популяций (55).
Фитомасса и изменчивость ее накопления в онтогенезе. Продуктивность популяции определят умножением числа растений на единице площади на величину сухой фитомассы особей. Густота всходов R. carthamoides в агроценозе в 1-й год жизни составляла 114 тыс. шт/га, с 34-го по 10-й — 27-24 тыс. шт/га, с 13-го по 15-й — 16-20 тыс. шт/га, далее колебалось по годам с 22-30 до 20-23 тыс. шт/га (рис. 3). В целом субсенильном возрасте (с 13-го по 32-й годы) среднее значение плотности равнялось 24,5 тыс. шт/га (с колебаниями от 16,4 до 30,5 тыс. шт., Cv = 16,0 %). В пересчете на норму при подзимнем посеве (с 4-5-кратным запасом на единицу площади) при квалифицированном уходе потребность семян для высева составляла около 3 кг/га (при средней массе 1000 семян 15 г и полевой всхожести около 60 %).
Иные нормы высева, рекомендованные в монографиях по культивированию R. carthamoides и составляющие до 10-15 кг/га (57) и 20-25 кг/га семян первого класса (56), следует считать завышенными. При высоких нормах высева в последующие годы происходило самоизреживание и стабилизация численности популяции. Факторами среды, вызывающими снижение численности особей в ценозе для R. carthamoides , могут быть переувлажнение, вызывающее загнивание корневой системы, конкурентное подавление со стороны быстрорастущих многолетних сорных растений в первые три года жизни, ранние сроки укоса надземной фитомассы (со 2-го года), сроки посева семян (весенний вместо подзимнего), дефицит влаги почв (засуха), старение и т.д.
В биологии R. carthamoides проявлялось характерное для высокогорных растений постепенное прорастание в течение 3 лет: весной 1-го года, во 2-3-й декаде мая, появлялось 85-88 % растений от общего их числа, на 2-й год — 10-12 %, на 3-й — 2-3 % (при условии, что почва не была переувлажнена и семена не загнили). Первые 2 мес были наиболее уязвимым периодом по причине слаборазвитости первичной корневой системы, образованной боковыми ответвлениями главного корня диаметром 0,03-0,05 мм, которые располагались в поверхностном слое почве. Была возможна массовая гибель особей из-за неоптимального режима почвы от переувлажнения и от пересыхания. Подземная сфера интенсивно развивалась после форми- рования стеблекорня (с появлением придаточных корней из зоны гипокотиля), что следовало по времени за фазой развертывания розеточного зародышевого побега в ювенильном возрасте. В имматурном возрасте доля корневой системы растений возрастала с 19-21 до 43 % от общей фитомассы, что приводило к повышению устойчивости к летней засухе и обеспечивало рост пазушных почек возобновления в многочисленные боковые вегетативные побеги.
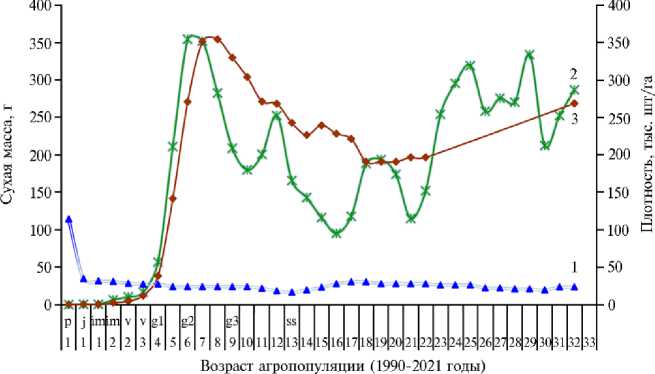
Рис. 3. Динамика плотности (1) и величина сухой фитомассы надземных (2) и подземных (3) органов у Rhaponticum carthamoides (Willd.) Iliin в агропопуляции, культивируемой в условиях Европейского Северо-Востока, в течение онтогенеза. Возраст растений в онтогенезе: р — проросток, j — ювенильный, im — имматурный, v — виргинильный, g1, g2, g3 — молодой, зрелый и старый генеративный; ss — субсенильный (Архангельской обл., Котласский р-н, 1990-2021 годы).
В первые 3 года жизни сухая надземная фитомасса ювенильных, им-матурных и виргинильных растений составляла соответственно 0,3; 6,2 и 16,4 г и не представляла интереса для отчуждения (табл. 3). С 4-го года, когда начинался переход агропопуляции в генеративный возраст, надземная масса возрастала до 56,8 г. С 5-года жизни наблюдался массовый переход популяции в генеративное состояние и выход на средние параметры развития — 210,7 г надземной массы с растения при среднем значении 223,4 г за период 5-32-й годы (табл. 4). На 6-8-й годы (зрелый генеративный возраст) были зафиксированы максимальные значения фитомассы особей — соответственно 354, 352 и 282 г. На 9-12-й годы жизни популяция находилась в старогенеративном возрасте, масса надземных органов составляла 208,7179,9 г (см. рис. 3).
При старении растений на начало субсенильного возраста (13-17-й годы), которое сопровождалось постепенным разрушением корневой системы первичного растения в зоне главного корня и ее расчленением на дочерние, приходилась минимальная величина фитомассы надземных органов — 95,1 г/растение. В последующие годы отмечалось возрастание фитомассы надземных органов во втором обновленном цикле онтогенеза, когда дочерние особи, вегетативно возникшие в форме клона, занимали место материнских растений, то есть происходило омоложение популяции. П ри этом среднее значение надземной фитомассы за период с 5-го по 32-й год жизни (223,4 г) оказалось близко к значению за 5-й год жизни (210,7 г). Повышенная изменчивость обсуждаемого показателя по годам наблюдений ( Cv = 33,3 %) (см. рис. 3) вызвана сильным влиянием влажности (интенсивные дожди) и температуры воздуха (35-38 ° С и заморозки до - 5^ - 10 ° С) на сезонное развитие.
|
Показатель |
M ±SD |
Cv , % |
max |
min |
N |
|
Плотность, тыс. шт/га |
24,1±3,5 |
14,7 |
30,5 |
16,4 |
40-48 |
|
Масса одного растения, г: |
|||||
|
надземные части |
223,4±74,4 |
33,3 |
354,0 |
95,1 |
6-9 |
|
подземные части |
246,3±58,6 |
23,8 |
354,4 |
190,6 |
6-9 |
|
Развитые соцветия, шт/растение |
0,19±0,31 |
167,9 |
1,13 |
0,0005 |
20188-52 |
|
Продуктивность: |
|||||
|
надземная часть, кг/га |
5338,4±1760,6 |
33,0 |
8483 |
2634 |
6-9 |
|
подземная часть, кг/га |
6019,3±1337,1 |
22,9 |
8548 |
3977 |
6-9 |
|
семена, кг/га |
1,31±0,65 |
49,6 |
1,98 |
0,49 |
20188-52 |
Масса подземных частей (корней с корневищами в сухом виде) возрастала вслед за надземной (см. табл. 3, 4): в первые 3 года она также была незначительна (0,3, 4,7 и 11,9 г/растение), на 4-й год составляла 38,2 г, на 5-й —141,3 г. Максимальную величину за генеративный период с возрастанием до максимума от 270,6 до 354,4 г и последующим снижением до 303,7 г отмечали на 6-10-й годы жизни. Среднее значение массы подземных органов в субсенильном возрасте (13-32-е годы) было равно 217,3 г, а на 33-й год жизни (после перезимовки на 29.04.2022 года) — 268,5 г ( Cv = 28,6 %). Усредненное значение массы корней с корневищами в период с относительно устойчивым продуцированием надземной фитомассы (с 5-го по 32-й год) составляло 246,3 г ( Cv = 23,8 %), что несколько выше среднего значения для надземных частей (223,4 г при Cv = 33,3 %) и свидетельствует об их важности в качестве запасающего органа для формирования надземной фитомассы в будущем периоде.
Таким образом, колебания величины подземной массы по годам были в целом более сглажены, поскольку она менее зависима от сезонных температур по сравнению с надземной и формируется за счет оттока органических веществ из надземных органов в процессе их постепенного отмирания.
Закономерности накопления экдистерона в надземной части растений . Процессы биосинтеза и накопления экдистерона зависимы от ростовых процессов в надземной сфере, обусловленных, в свою очередь, развитием корневой системы материнского растения и ее дезинтеграцией на дочерние особи. Розеточные листья вегетативных побегов R. carthamoides составляли 84-94 % от массы надземных органов. Содержание экдистерона в них было минимальным в 1-й год (0,06-0,11 %), затем возрастало последовательно до 0,19-0,28 % с 2-го по 5-й год жизни (см.
табл. 1, рис. 4). В генеративный период (с плодоносящими цветоносными побегами) оно составляло 0,29-0,33 % (на 6-10-й годы) и уменьшалось от 0,44 до 0,40 % при переходе с генеративного в субсенильный возраст за 1113-й годы (см. табл. 2).
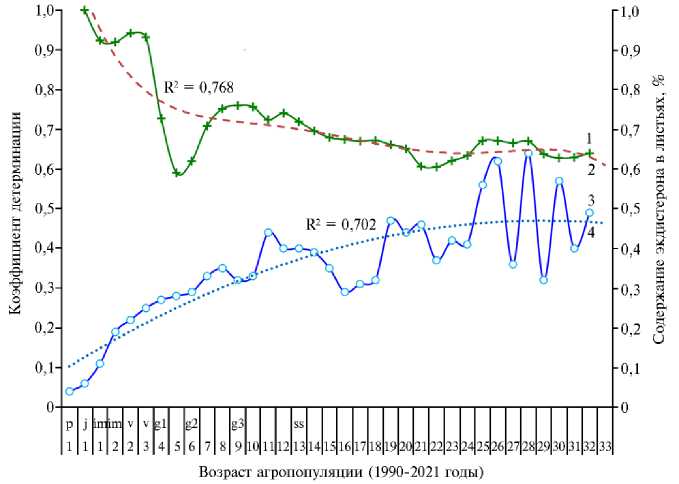
Рис. 4. Корреляционная связь между величиной надземной массы растений и содержанием экди-стерона (1) , достоверность аппроксимации (2) , накопление экдистерона 20Е (3) и тренд его накопления (4) в листьях вегетативных побегов Rhaponticum carthamoides (Willd.) Iliin из агропопуляции, культивируемой в условиях Европейского Северо-Востока, в течение онтогенеза. Возраст растений в онтогенезе: р — проросток, j — ювенильный, im — имматурный, v — виргинильный, g1, g2, g3 — молодой, зрелый и старый генеративный; ss — субсенильный (Архангельской обл., Котласский р-н, 1990-2021 годы).
За последующие годы субсенильного возраста (16-32-й годы), при минимальной репродукции (в среднем 1 плодоносящее соцветие на 5 растений) содержание экдистерона в вегетативных побегах оставалось высоким — 0,41 % (варьирование 20Е по годам от 0,28 до 0,64 % при колебании числа плодоносящих соцветий от 0,001 до 1,13 шт.). В этот период резко сокращалась семенная репродукция и синтезированный экдистерон, ранее перераспределявшийся с водным потоком ассимилятов от листьев к семяпочкам соцветий и семенам, оставался в розеточных листьях. Ранее на примере 8 популяций R. carthamoides и Serratula coronata в возрасте до 15 лет мы показали, что динамика содержания экдистероидов в их вегетативных органах обратно и сильно зависима от семенной репродукции (59). Полученную в настоящей работе модель взаимной связи (R2 = 0,768) между суммарной величиной надземной массы R. carthamoides и содержанием экдистерона в розеточных побегах с коэффициентом детерминации около 80 % (что соответствует r = 90 %) можно признать объясняющей зависимость биосинтеза и накопления экдистерона от развитости вегетативных побегов.
Мы установили комплекс коррелятивных параметров растений в онтогенезе, сочетающихся с наибольшим (0,56-0,64 %) накоплением экдисте-рона в вегетативных побегах R. carthamoides : длина розеточных листьев — 97-119 см (максимум), доля розеточных листьев в структуре фитомассы — 91-94 % (максимум), число плодоносящих соцветий — 0,016-0,021 шт/растение (минимум), суммарная величина надземной фитомассы (вместе с генеративными побегами) — 270-320 г (выше средней величины 223 г на 20-40 %).
Продуктивность агропопуляции. Валовая продукция на единице площади популяции (с учетом плотности) служит интегральным показателем, характеризующим экологический оптимум, и отражает отношение организма ко всей совокупности факторов внешней и внутренней среды. В природных условиях урожайность надземной массы дикорастущих зарослей R. carthamoides на Горно-Алтайской сельскохозяйственной опытной станции составляет 2200-4000 кг/га. Максимальная биопродуктивность отдельных фрагментов чистых зарослей может достигать 6500-7000 кг/га. Продуктивность подземных органов R. carthamoides в Алтайско-Саянской горной области колеблется в пределах 80-1500 кг/га. Наибольшие площади субальпийских лугов заняты ценозами, где средняя масса корневищ составляет около 57-75 кг/га, а 12-20 % ресурсных участков имеют продуктивность 570-640 кг/га (55). На относительно небольших участках на территории Казахстанского Алтая продукция сухих корней R. carthamoides оценивается в 1,0-1,1 т/га (73).
В культуре корневища левзеи сафлоровидной для использования в качестве фармакопейного лекарственного сырья начинают убирать с 3-го года жизни. Учитывая, что наиболее интенсивный прирост корневой массы происходит в конце вегетационного периода, уборку проводят в сентябре-октябре. Средняя урожайность сухих корней (без учета фактической плотности) в Московской области составляла 2000-2500 кг/га (56). В Финляндии ожидаемый урожай корней (в пересчете с квадратных метров на гектар) через 3 года выращивания был около 2000 кг/га, надземных частей — 10002500 кг/га (57). В условиях Пермского края урожайность надземной массы без применения удобрений в среднем за 6 лет составила 2520 кг/га (74). В Сибири на полях экспериментального хозяйства Центрального сибирского ботанического сада урожайность надземной массы R. carthamoides в возрасте 4-5 лет достигала 3600 кг/га (56). В более старых посевах отмечено снижение урожайности, например в Ленинградской области в посевах 7-8-летнего возраста она не превышала 700-800 кг/га. В Московской области на среднесуглинистой почве опытной станции Российского государственного аграрного университета — МСХА им. К.А. Тимирязева продуктивность на 6-й год составила 3740 кг/га и к 9-му году снижалась в 3,6 раза (59).
В изучаемых условиях Европейского Севера валовая продукции агропопуляции (см. табл. 3) была мизерной в первые 2 года и на 3-й год культивирования и составляла соответственно лишь 8 % и 5 % по отношению к средним значениям за 5-32-й годы жизни (или 452 кг/га надземной и 328 кг/га подземной фитомассы). На 4-й год продуктивность агропопуляции примерно соответствовала данным литературы — 1553 кг/га для надземной части и 1044 кг/га для подземной. В дальнейшем продуктивность продолжала увеличиваться, составив на 5-й год соответственно 5046 и 3384 кг/га, и вышла на пик в зрелом генеративном возрасте — около 8500 кг/га на 67-й годы для надземных и на 7-8-й годы для подземных органов. В старом генеративном и субсенильном возрасте фитомасса снижалась и варьировала в соответствии с закономерностями, описанными выше (см. рис. 4). В целом, с 5-го по 32-й годы жизни (за 27 лет хозяйственной эксплуатации) средняя расчетная продуктивность надземной части агропопуляции составила около 5338 кг/га ( Cv = 33,0 %), подземной — 6019 кг/га ( Cv = 22,9 %) (см. табл. 4).
Урожайность семян с единицы площади в первые 3 года отсутствовала. На 4-й и 5-й жизни она составила соответственно 8 и 30 кг/га, а наибольшие значения показателя пришлись на 6-й и 7-й годы — 108 и
78 кг/га, снизившись на 8-10-й годы соответственно до 50, 26 и 5 кг/га. После перехода в субсенильный возраст, когда доминировало вегетативное размножение, средний ежегодный выход семян за период с 13-го по 32-й год составил 1,3 кг/га (от 0,49 до 1,98 кг/га). Коэффициент семенного размножения особи (отношение числа полноценных семян на единице площади к плотности) в этот период был равен 3,3.
Для сравнения — в естественных условиях субальпийских лугов Алтая средний урожай семян составлял 8-30 кг/га, а в редких зарослях мог доходить до 150-200 кг/га (55). В условиях Европейского Севера урожайность семян с опытных делянок была следующей: Финляндия — до 200290 кг/га (57), Коми Республика — до 295-410 кг/га. В Пермском крае (75) на 9-10-й год жизни выход семян оценивался в 386-542 кг/га (38,654,2 г/м2). При этом обильное плодоношение в таких случаях сопровождалось крайне низким значением содержания экдистерона в листовых органах — от 0,05-0,07 до 0,14 % (43); 0,04-0,09 % (44).
Тем самым подтверждается наш тезис о том, что одним из ключевых факторов регуляции концентрации экдистерона в листовых органах становится процесс конкуренции между семенным и вегетативным размножением: обильное продуцирование семян приводит к оттоку экдистерона из вегетативных побегов и раннему завершению жизненного цикла растений вследствие массового отмирания генеративных побегов после плодоношения вместе с почками возобновления, служащих базисом для формирования в будущие годы новых розеточных листьев, синтезирующих экдистерон.
Приблизительная оценка валового синтеза и накопления экдисте-рона в оптимальном эксплуатируемом возрасте (с 5-го по 32-й годы) составляла в надземной сфере (при амплитуде содержания 20Е 2,8-6,4 г/кг) около 21,9 кг/га (14,9-34,2 кг/га) ежегодно, или около 600 кг экдистерона за 27 лет эксплуатации. В подземной сфере растений при ориентировочном содержании 20Е 0,3-0,5 г/кг аккумулировалось около 2,4 кг/га (от 1,8 до 3,0 кг/га) экдистерона, но эти части растений могут отчуждаться лишь один раз.
Таким образом, 90 % ежегодно синтезируемого экдистерона накапливается в надземной части растений из агропопуляции R. carthamoides . Если же исходить из потенциала жизненного цикла промышленно эксплуатируемой популяции с учетом возможности многократного изъятия фитомассы, то экдистерон сконцентрирован в надземных органах более чем на 99 % .
Качественные показатели лекарственного сырья из листовых органов. Важным показателем качества лекарственного сырья R. carthamoides для изготовления препаратов служит соотношение высокоактивного экдистерона (активность в биотестах 7,5*10 - 9 M) к слабоактивному экдизону (активность 1,1*10 - 6 M), поскольку менее активные экдистероиды могут полностью или частично блокировать физиологическое действие более активных соединений, содержащихся в экстрактах растений (8, 48). Желательно, чтобы чистота экдистерона была не менее 95 % ( > 20:1), лучше 97 % ( > 30:1), а в идеале — почти полное отсутствие минорных и слабоактивных компонентов ( > 1000:1) (9). В противном случае исходное сырье приходится подвергать сложной многоступенчатой хроматографической процедуре очистки от неактивных примесей (10).
Для сухого неочищенного спиртового экстракта, выделенного из 65 кг сухих корней R. carthamoides с корневищами, соотношение 20Е/Е было равно около 60:1, где экдистерона содержалось 0,37 %, экдизона — 0,006 % (46).
Согласно данным из Чехии (50), соотношение 20Е/Е для сухих корней R. carthamoides составило более 1000:1. Для надземной части R. carthamoides этот показатель качества непостоянен и зависит от интенсивности формирования и развития генеративных побегов. Ранее на 12 разновозрастных агропопуляциях R. carthamoides и S. coronаta в первые 16 лет культивирования мы показали, что у R. carthamoides до вступления в генеративный период состав фитоэкдистероидов был представлен только высокоактивным экдистероном. Экдизон в надземных репродуктивных органах синтезировался синхронно их развитию: в начале вегетации в генеративных побегах он не обнаружен, во время цветения его долевое участие достигало 9,1 %, в период налива семян и плодоношения — 17,8-18,7 %. В период обильного плодоношения долевое участие экдизона возрастало и в вегетативных побегах, хотя в меньшей степени — с 1,5 до 4,7 % в фазе бутонизации и до 13,3 % в фазе цветения (61).
Качественное соотношение экдистерона к экдизону (20E/E) в вегетативных побегах R. carthamoides за 32 года выращивания в условиях агропопуляции менялось следующим образом: у имматурных и виргинильных растений оно было выше 1000:1 (1-3-й годы), у молодых генеративных растений в фазе бутонизации составляло около 980:1. У взрослых генеративных растений при переходе в фазу цветения 20E/E уменьшалось до 20-6:1, а к началу плодоношения — до 3-4:1. В субсенильный период (13-32-й годы), когда семенное размножение было подавлено, экдизон синтезировался в следовом количестве ( ≤ 0,001 %) — соотношение 20E/E варьировало по годам от 560-900:1 до 60-80:1, что отвечало требованию относительному качеству чистоты 20Е 97 %.
Сравнение с другими промышленными источниками экдистерона показало, что R. carthamoides имеет преимущество перед ними как по количественному содержанию, так и по доброкачественности синтезируемого экдистерона. В частности, A. Hunyadi с соавт. (30) исследовали состав пищевых добавок Европейского рынка, изготовленных из экстракта цианотиса паутинистого Cyanotis arachnoidea C.B. Clarke, и показали, что соотношение экдистерона к другим (минорным) ЭС было ухудшенным — около 0,9:1 при количественном содержании 0,2-2,4 %/0,09-2,49 %. Близкий вид, цианотис длиннолистный Cyanotis longifolia Benth., выращенный в горшечной культуре во Франции, имел аналогичное качественное соотношение экдистерона: в надземной фитомассе — 1,8:1 (0,095 %/0,052 %), в корнях — 0,63:1 (0,385 %/0,607 %) (76). В целом и другие виды из сем. Commelinaceae из естественных мест обитания характеризуются относительно пониженным содержанием экдистерона в сухой фитомассе: Cyanotis hirsuta Baker — 0,140 %, Cyanotis kewensis C.B. Clarke — 0,0245 %, Cyanotis longifolia Benth. — 0,008 %, Cyanotis somaliensis C.B. Clarke — 0,111 %, Cyanotis speciosa (L.f.) Hassk. — 0,093 % (76). Кроме того, в коммерческих экстрактах Cyanotis в 2021 году обнаружены примеси полусинтетических экдистероидов нефтяного происхождения, взаимодействующих с рецепторами экдистерона в качестве конкурирующих агонистов и антагонистов, что может привести к множеству негативных фармакологических и токсикологических последствий при их употреблении (29).
Среди других показателей качества лекарственного сырья важны сведения о накоплении в нем токсических соединений естественного или антропогенного происхождения, включая тяжелые металлы, радионуклиды, хлор и фосфорорганические соединения. Результаты первых исследований начала 1970-х годов, выполненных методами цветных реакций, которые свидетельствовали о наличии алкалоидов у R. carthamoides, впоследствии не были подтверждены (77). В современной литературе нет также сведений о накоплении этим видом тритерпеновых сапонинов, других сильнодействующих, наркотических или ядовитых веществ, потенциально опасных для здоровья человека или могущих представлять опасность для животных при использовании в качестве корма и кормовых добавок (буфадиенолидов, сердечных гликозидов, аристолохиевой кислоты, фотосенсибилизирующих, кумулятивных или расщепляющих витамины веществ и т.п.) (42, 63, 65-67).
Изучение токсичности надземной части R. carthamoides , используемой в качестве кормовых добавок, уже проводилось ранее. В длительных опытах с включением измельченных листьев R. carthamoides в рационы не обнаружили неблагоприятных эффектов. Была доказана их безвредность в дозах до 0,3-0,5 кг сухого вещества надземной массы. Крысы и птицы могли питаться семенами этого вида, которые содержали до 1,5 % экди-стерона (36).
5. Химический состав экдистерон-содержащей субстанции из листовых органов Rhaponticum carthamoides, выращенных в условиях промышленно эксплуатируемой плантации (Котласский р-н Архангельской обл., 2016-2020 годы) (78)
Показатель Норма Фактически полученные значения Действующие вещества, %: экдистерон (20-гидроксиэкдизон, 20Е) ≥ 0,1 0,56-0,61 доля экдистерона от ФЭС ≥ 95,0 95,3-99,6 экстрактивные вещества ≥ 12,0 50,2 протеин сырой ≥ 16-19 19-27 клетчатка сырая ≤ 23-26 16-19 Тяжелые металлы, мг/кг: Hg 0,05 0,009-0,016 Cd 0,3 0,020-0,115 As 0,5 0,05 Ni 3,0 0,59-1,30 Pb 5,0 0,18-0,30 Cu 30,0 7,9 Zn 50,0 28,4 Хлор- и фосфорорганические соединения, мг/кг: ДДТ и его метаболиты 0,05 < 0,007 ГХЦГ и его изомеры 0,05-0,20 < 0,001 метафос 0,00-0,50 Не обнаружен карбофос 2,0-5,0 Не обнаружен Соединения азота, мг/кг: NO2- 10,0 0,3-2,0 NO3- 2000 700-1200 Радионуклиды, Бк/кг: 90Sr 100,0 5,7 137Cs 600,0 4,8 Примечани е. ФЭС — фитоэкдистероиды, ДДТ — сумма хлоорганических пестицидов (дихлордифе- нилтрихлорэтан, дихлордифенилдихлорэтан, дихлордифенилдихлорэтилен и т.д.), ГХЦГ — сумма иных инсектицидов (линдан, гексахлорциклогексан, гептахлор, кельтан, альдрин) (данные представлены в соответствии с протоколами тестирования, см. http://www,agrobiology).
В условиях промышленного возделывания при санитарно-токсикологической оценке безопасности продукции приоритетным является соответствие содержания тяжелых металлов нормативным требованиям. Актуальность контроля тяжелых металлов у высокогорных растений связана с их генетической предрасположенностью к накоплению ртути, кадмия, никеля, свинца и меди. При исследовании фармакопейных характеристик лекарственного сырья из листовых органов R. carthamoides (78) нами установлено (табл. 5), что надземные части R. carthamoides, выращенные и заготовленные в изучаемой агропопуляции, не накапливали элементы первого и второго класса опасности (Hg, Cd, As, Zn; Ni, Cu, Cr) выше фонового уровня и соответствовали ПДК для зеленой массы многолетних трав. Запрещенные по санитарно-гигиеническим стандартам хлор- и фосфорорга- нические соединения в фитомассе отсутствовали. Содержание радионуклидов 90Sr и 137Cs было ниже ПДК (68,8 и 6,2 Бк/кг в сравнении с разрешенными 100 и 600 Бк/кг). Количество нитритов находилось в пределах нормы (0,3-2,0 мг/кг) (см. табл. 5).
Первые результаты массового применения добавок на основе листового материала R. carthamoides , выращенной в рассматриваемой агропопуляции, были получены в свиноводческом комплексе АО «Котласский ЦБК» (Архангельская обл., Россия) со среднемесячным поголовьем 1,6 тыс. шт., длительность эксперимента составляла 12 мес (79). Супоросным свиноматкам, поросятам-отъемышам и откормочному поголовью в возрасте 2-4 мес ежедневно скармливали гранулированную травяную муку из надземной части R. carthamoides 4-го года жизни в расчете 20 г/т живой массы. Рацион животных был основан на пищевых отходах предприятий общественного питания с неблагополучным фитосанитарным составом, что сопровождалось диспепсией. В итоге произошло оздоровление стада и снижение падежа новорожденных поросят в 2,1-2,7 раза, а анаболический эффект выразился в увеличении выхода продукции стада в живой массе на 40,6 %.
Дальнейшие исследования выполняли в племенном свиноводческом хозяйстве АО «Заречье» (Кировская обл.) в строго контролируемых условиях. Согласно полученным данным, при введении в рацион поросят-отъ-емышей субстанции из R. carthamoides их живая масса превысила показатель в контроле на 15-22 %, интенсивность среднесуточного прироста массы тела — на 24,0-32,8 %, заболеваемость животных снизилась в 1,6-2,5 раза, сохранность составила 100 % (22). Сопоставимые результаты были получены и в экспериментах с использованием химически очищенного экдисте-рона (20-гидроксиэкдизона 96 % чистоты), выделенного из R. carthamoide . Анаболический эффект в этом случае составил 12-16 % при одновременном снижении расхода кормов на 11-1 7% на 1 кг прироста живой массы (80).
Суммируя полученные результаты, следует отметить, что биосинтез и накопление экдистерона были прямо связаны с вегетативным размножением (с интенсивностью нарастания розеточных побегов по годам и их мощностью), и обратно пропорциональны интенсивности семенного плодоношения. Взаимосвязь между суммарной величиной надземной массы и содержанием экдистерона в розеточных побегах за 32 года культивирования характеризовалась коэффициентом детерминации R2 = 0,768 (или около 80 %) и отражал зависимость биосинтеза и накопления экдистерона от развитости вегетативных побегов. Приблизительная оценка валового синтеза и накопления экдистерона в оптимальном эксплуатируемом возрасте (с 5-го по 32-й годы) составляла в надземной сфере около 21,9 кг/га ежегодно, или около 600 кг экдистерона за 27 лет эксплуатации. В подземной сфере содержалось около 2,4 кг/га экдистерона. Для фабричного производства лекарственных препаратов, пищевых добавок и фитобиотиков предпочтительно использовать розеточные листья вегетативных побегов, содержащие большие концентрации экдистерона (0,4-0,6 % при нормативе 0,1 %). Качественные характеристики лекарственного сырья, заготовленного в оптимальную фазу развития (начале бутонизации) были высокими и соответствовали требованиям для изготовления фармпрепаратов с относительной чистотой экдистерона 97 %. Подземные части (корни с корневищами) не накапливали значимых концентраций экдистерона (в среднем 0,03-0,05 %) и могли быстро терять действующие вещества вследствие инфицирования почвенной микрофлорой. Семенная продуктивность возрастала по годам (8-30 кг/га) и достигало пика на 6-й и 7-й годы (108 и 78 кг/га), снижаясь в старогенеративном возрасте (8-10-й годы) соответственно до 50, 26 и 5 кг/га. В субсенильный период (с 13-го по 32-й год жизни и далее) тип размножения менялся с семенного на вегетативный и продукция семян имела крайне низкие значения (1,3 кг/га с коэффициентом семенного размножения 3,3). Усредненное значение массы корней с корневищами с 5-го по 32-й год жизни составляло 246,3 г/растение, что несколько выше среднего значения фитомассы надземных частей — 223,4 г/растение.
Из субстанций на основе листового материала R. carthamoides экди-стерон хорошо экстрагировался в водные и спиртовые растворы и хорошо сохранялась в них без консервантов (на 93-98 % течение 1 сут). Суммарный выход экстрактивных веществ составлял 50,2 % (при норме 12,0 %). В биотестах экстракт обладал стимулирующим действием при сильном разведении (10 - 9-10 - 11 М в расчете на экдистерон) и ингибирующим — при меньшем (100-кратном) разведении (10 - 4-10-5 М) (78).
В дальнейшем следует изучить влияние кратности и периодичности укосов (величины отчуждаемой надземной массы) на формирование и соотношение вегетативных и генеративных побегов левзеи сафлоровидной, а также возможность воздействовать на процесс синтеза экдистерона через применение удобрений, фитогормонов и элиситоров.
Итак, в результате 32-летних исследований агропопуляции Rhaponti-cum carthamoides, культивируемой в Архангельской области с 1989 по 2022 год по технологии ежегодного однократного отчуждения надземной фитомассы, было установлено, что природно-климатические условия Европейского Северо-Востока, характеризующиеся прохладным климатом, промывным типом водного режима, длинным световым днем и коротким вегетационным периодом, благоприятны для промышленного выращивания левзеи сафлоровидной. Длительность онтогенеза агропопуляции была близка к параметрам природных популяций на субальпийских лугах и составляла свыше 30 лет без перехода к сенильному возрастному состоянию на 33-й год жизни. Плотность растений в агроценозе достигала оптимальных значений 2823 тыс. шт/га, начиная с 3-4-го года жизни. В условиях агропопуляции в первые 4 года шел интенсивный рост и развитие растений, на 5-й год (после перехода в генеративный период) начиналось семенное размножение особей. Среднегодовая расчетная продуктивность надземной части агропопуляции в период устойчивого продуцирования надземной фитомассы с высоким уровнем биосинтеза экдистерона (с 5-го по 32-й годы жизни) составила около 5300 кг/га, подземной — около 6100 кг/га. С накоплением наибольшего количества экдистерона в вегетативных побегах R. carthamoides (0,56-0,64 %) сочетались такие параметры, как максимальная длина розеточных листьев (97-119 см), максимальная доля розеточных листьев в структуре фитомассы (91-94 %), минимальное число плодоносящих соцветий (0,016-0,021 шт/растение), суммарная величина надземной фитомассы вместе с генеративными побегами — 270-320 г (выше средней величины 223 г на 20-40 %). Экдистерон из листовых органов хорошо экстрагировался в водные и спиртовые растворы без потери действующих веществ (при хранении водного экстракта в течение 1 сут сохранность экдистерона — 9398 %). Суммарный выход экстрактивных веществ из листьев составлял 50,2 % при нормативе 12,0 %. Полученное лекарственное сырье удовлетворяло всем нормативным требованиям надзорных органов по содержанию радионуклидов, тяжелых металлов, остатков гербицидов, инсектицидов и иных химических средств защиты растений. Применение субстанции из листового материала R. carthamoides в промышленном животноводстве сопро- вождалось оздоровлением стада и снижением смертности молодняка свиней в 2 и более раз, возрастанием интенсивности среднесуточного прироста на 24-33 %, снижением расхода кормов на 11-17 %.
Список литературы Опыт культивирования левзеи сафлоровидной Rhaponticum carthamoides (Willd.) Iliin в качестве ресурсного источника экдистерона в условиях Архангельской области
- Rhaponticum carthamoides. В кн.: Растительные ресурсы СССР. Цветковые растения, их химический состав, использование. Семейство Asteraceae (Compositae) /Отв. ред. П.Д. Соколов. СПб, 1993, вып. 7: 161-163.
- Hidalgo O., Garcia-Jacas N., Garnatje T., Susanna A. Phylogeny of Rhaponticum (Asteraceae, Cardueae-Centaureinae) and related genera inferred from nuclear and chloroplast DNA sequence data: taxonomic and biogeographic implications. Annals of Botany, 2006, 97(5): 705-714 (doi: 10.1093/aob/mcl029).
- Фармстатья 2.5.0091.18. 2018. Рапонтикума сафроловидного корневища с корнями (Rhapontici carthamoides rhizomata cum radicibus). В кн.: Государственная фармакопея Российской Федерации. XIV изд. М., 2018, т. 4: 6360-6368.
- Левзеи сафлоровидной листья: Rhapontici carthamoides folium Leuzea leaf ). В кн.: Государственная Фармакопея Республики Беларусь. 2-е изд. Молодечно, 2016 , т 2 1257-1258.
- Shikov A.N., Narkevich I.A., Flisyuk E.V., Luzhanin V.G., Pozharitskaya O.N. Medicinal plants from the 14th edition of the Russian Pharmacopoeia, recent updates. Journal of Ethnopharmacol-ogy, 2021, 268: 113685 (doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.113685).
- Todorova V., Ivanov K., Ivanova S. Comparison between the biological active compounds in plants with adaptogenic properties (Rhaponticum carthamoides, Lepidium meyenii, Eleutherococcus senticosus and Panax ginseng). Plants, 2022, 11(1): 64 (doi: 10.3390/plants11010064).
- Liu X.X., Chen C.Y., Li L., Guo M.M., He Y.F., Meng H., Dong Y.M., Xiao P.G., Yi F. Bibliometric study of adaptogens in dermatology: pharmacophylogeny, phytochemistry, and pharmacological mech-anisms, drug design. Development and Therapy, 2023, 17: 341-361 (doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S395256).
- Głazowska J., Kaminski M.M., Kamiński M. Chromatographic separation, determination and identification of ecdysteroids: focus on maral root (Rhaponticum carthamoides, Leuzea car-thamoides). Journal of Separation Science, 2018, 41(23): 4304-4314 (doi: 10.1002/jssc.201800506).
- Dinan L., Dioh W., Veillet S., Lafont R. 20-Hydroxyecdysone, from plant extracts to clinical use: therapeutic potential for the treatment of neuromuscular, cardio-metabolic and respiratory diseases. Biomedicines, 2021, 9(5): 492 (doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9050492).
- Lafont R., Dilda P., Dioh W., Dupont P., Signore S.D., Veillet S. 20 hydroxyecdysone extract of pharmaceutical quality, use and preparation thereof. Patent France FR 3065644A1. Publ 2020-02-21.
- Lafont R., Serova M., Didry-Barca B., Raynal S., Guibout L., Dinan L., Veillet S., Latil M., Dioh W., Dilda P.J. 20-Hydroxyecdysone activates the protective arm of the RAAS via the MAS receptor. Journal of Molecular Endocrinology, 2021, 68(2): 77-87 (doi: 10.1530/JME-21-0033).
- Latil M., Camelo S., Veillet S., Lafont R., Dilda P.J. Developing new drugs that activate the protective arm of the renin-angiotensin system as a potential treatment for respiratory failure in COVID-19 patients — review. Drug Discovery Today, 2021, 26(5): 1311-1318 (doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2021.02.010).
- Sláma K. Vitamin D1 versus ecdysteroids: growth effects on cell regeneration and malignant growth in insects are similar to those in humans. European Journal of Entomology, 2019, 116: 16-32 (doi: 10.14411/eje.2019.003).
- Slama K. Approaching a time we can prevent pernicious malignant tumors? Mini review. EC Pharmacology and Toxicology, 2020, 8(3): 01-09.
- Shuvalov O., Fedorova O., Tananykina E., Gnennaya Y., Daks A., Petukhov A., Barlev N.A. An arthropod hormone, ecdysterone, inhibits the growth of breast cancer cells via different mecha-nisms. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 2020, 11: 561537 (doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.561537).
- Panossian A.G., Efferth T., Shikov A.N., Pozharitskaya O.N., Kuchta K., Mukherjee P.K., Banerjee S., Heinrich M., Wu W., De-An Guo D.A., Wagner H. Evolution of the adaptogenic concept from traditional use to medical systems: pharmacology of stress‐ and aging‐related dis-eases. Medicinal Research Reviews, 2021, 41(1): 630-703 (doi: 10.1002/med.21743).
- Isenmann E., Ambrosio G., Joseph J.F., Mazzarino M., Torre X., Zimmer Ph., Kazlauskas R., Goebel C., Botre F., Diel P., Parr M.K. Ecdysteroids as non-conventional anabolic agent: per-formance enhancement by ecdysterone supplementation in humans. Archives of Toxicology, 2019, 93: 1807-1816 (doi: 10.1007/s00204-019-02490-x).
- Parr M.K., Müller-Schöll A. Pharmacology of doping agents — mechanisms promoting muscle hy-pertrophy (review). AIMS Molecular Science, 2018, 5(2): 131-159 (doi: 10.3934/molsci.2018.2.131).
- Parr M.K., Ambrosio G., Wuest B., Mazzarino M., Torre X., Sibilia F., Joseph J.F., Diel P., Botrè F. Targeting the administration of ecdysterone in doping control samples. Forensic Toxicol-ogy, 2020, 38: 172-184 (doi: 10.1007/s11419-019-00504-y).
- Marciniak A., Nemeczek S., Walczak K., Walczak P., Merkisz K., Grzybowski Ja., Grzywna N., Jaskuła K., Orłowski W. Adaptogens — use, history and future. Quality in Sport, 2023, 9(1): 19-28 (doi: 10.12775/QS.2023.09.01.002).
- World anti-doping code. International standard. Prohibited List 2023. Режим доступа: https://www.wada-ama.org/sites/default/files/2022-09/2023list_en_final_9_september_2022.pdf. Дата обращения: 10.05.2022.
- Ивановский А.А., Тимофеев Н.П., Ермолина С.А. Влияние адаптогенов растительного происхождения на поросят и свиноматок. Аграрная наука Евро-Северо-Востока, 2019, 20(4): 387-397 (doi: 10.30766/2072-9081.2019.20.4.387-397).
- Тимофеев Н.П. Фитобиотики в мировой практике: виды растений и действующие веще-ства, эффективность и ограничения, перспективы (обзор). Аграрная наука Евро-Северо-Востока, 2021, 22(6): 804-825 (doi: 10.30766/2072-9081.2021.22.6.804-825).
- Bathori M., Toth N., Hunyadi A., Marki A., Zador E. Phytoecdysteroids and anabolic-androgenic steroids – structure and effects on humans. Current Medicinal Chemistry, 2008; 15(1): 75-91 (doi: 10.2174/092986708783330674).
- Lafont R., Dinan L. Practical uses for ecdysteroids in mammals including humans: and update. Journal of Insect Science, 2003, 3(7): 1-30 (doi: 10.1673/031.003.0701).
- Hornok, S., Csorba, A., Kováts, D., Csörgő T., Hunyadi A. Ecdysteroids are present in the blood of wild passerine birds. Scientific Reports, 2019, 9: 17002 (doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-53090-9).
- Ecdysterone market, by type (0.95, 0.98, other), by application (pharma & healthcare, cosmetic & skin care, other), by region (North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Middle East & Africa, and South America) — Market Size & Forecasting To 2028. Report Code: CH2066906. Quince Market Insights. Hadapsar, Pune, India, 2021. Режим доступа: https://www.quincemarketinsights.com/industry-analysis/ecdysterone-marke. Дата обращения: 10.05.2022.
- Ambrosio G., Wirth D., Joseph J.F., Mazzarino M., Torre X., Botre F., Parr M.K. How reliable is dietary supplement labelling? Experiences from the analysis of ecdysterone supplements. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis, 2020, 177: 112877 (doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2019.112877).
- Tóth G., Herke I., Gáti T., Vágvölgyi M., Berkecz R., Parfenova L.V., Ueno M., Yokoi T., Nakagawa Y., Hunyadi A.A Commercial extract of Cyanotis arachnoidea roots as a source of un-usual ecdysteroid derivatives with insect hormone receptor binding activity. Journal of Natural Products, 2021, 84(7): 1870-1881 (doi: 10.1021/acs.jnatprod.0c01274).
- Hunyadi A., Herke I., Lengyel K., Báthori M., Kele Z., Simon A., Tóth G., Szendrei K. Ecdys-teroid-containing food supplements from Cyanotis arachnoidea on the European market: evidence for spinach product counterfeiting. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 37322 (doi: 10.1038/srep37322).
- Kraiem S., Al-Jaber M.Y., Al-Mohammed H., Al-Menhali A.S., Al-Thani N.J., Helaleh M., Samsam W., Touil S., Beotra A., Georgakopoulas C., Bouabdallah S., Mohamed-Ali V., Al Maadheed M. Analytical strategy for the detection of ecdysterone and its metabolites in vivo in uPA(+/+)-SCID mice with humanised liver, human urine samples and estimation of prevalence of its use in anti-doping samples. Drug Testing and Analysis, 2021, 13(7): 1341-1353 (doi: 10.1002/dta.3032).
- 20-Hydroxyecdysone. Product No H5142 (93 %, HPLC, powder). 2022. Режим доступа: https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/RU/en/product/sigma/h5142. Дата обращения: 10.05.2022.
- Тимофеев Н.П. Достижения и проблемы в изучении биологии лекарственных растений Rhaponticum carthamoides Willd .) Iljin и Serratula coronata L . о бзор). Сельскохозяйственная биология , 2007, 3: 3 17 (doi: 10.15389/agrobiology.2007.3.3rus).
- Dinan L., Balducci C., Guibout L., Foucault A.-S., Bakrim A., Kumpun S., Girault J.-P., Tou-rette C., Dioh W., Dilda P.J., Veillet S., Lafont R. Ecdysteroid metabolism in mammals: The fate of ingested 20-hydroxyecdysone in mice and rats. The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 2021, 212: 105896 (doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105896).
- A double-blind, placebo controlled, randomized interventional clinical trial (SARA-INT) (SARA-INT). ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT0345248. Режим доступа: https://clinicaltri-als.gov/ct2/show/NCT03452488. Дата обращения: 10.05.2022.
- Тимофеев Н.П. Потенциал экдистероид-синтезирующих растений для фитобиотиков (об-зор). International Agricultural Journal, 2021, 64(6): 46-112 (doi: 10.24412/2588-0209-2021-10384).
- Compendium of botanicals reported to contain naturally occuring substances of possible concern for human health when used in food and food supplements. EFSA Journal, 2012, 10(5): 2663 (doi: 10.2903/j.efsa.2012.2663).
- Das N., Mishra S.K., Bishayee A., Ali E.S., Bishayee A. The phytochemical, biological, and medicinal attributes of phytoecdysteroids: an updated review. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B, 2021, 11(7): 1740-1766 (doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2020.10.012).
- Zhang X.-P., Zhang J., Dong M., Zhang M.-L., Huo C.-H., Shi Q.-W., Gu Y.-C. Chemical constituents of plants from the genus Rhaponticum. Chemistry & Biodiversity, 2010, 7(3): 594-609 (doi: 10.1002/cbdv.200800275).
- Carasso V., Mucciarelli M., Dovana F., Müller J.V. Comparative germination ecology of two endemic Rhaponticum species (Asteraceae) in different climatic zones of the Ligurian and Mari-time Alps (Piedmont, Italy). Plants, 2020, 9(6): 708 (doi: 10.3390/plants9060708).
- Тимофеев Н.П., Пунегов В.В., Биндасова Т.Н. Специфика распределения 20-гидрокси-экдизона по органам крупнотравного альпийского растения Rhaponticum scariosum. В сб.: Химия и технология растительных веществ. Сыктывкар, 2022: 197-197.
- Технический регламент Таможенного союза. ТР ТС № 021/2011 «О безопасности пищевой продукции». Решение КТС от 09.12.2011 ¹ 880, в ред. от 14.07.2021. Астана, Казахстан.
- Барнаулов О.Д. Элементы стратегии фитотерапии детей, часто болеющих респираторными вирусными инфекциями. Клас сические фитоадаптогены. Традиционная медицина , 2015, 3: 52 56.
- Peschel W., Kump A., Prieto J.M. Effects of 20-hydroxyecdysone, Leuzea carthamoides extracts, dexamethasone and their combinations on the NF-κB activation in HeLa cells. Journal of Phar-macy and Pharmacology, 2011, 63(11): 1483-1495 (doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.2011.01349.x).
- Girault J.-P., Lafont R., Varga E., Hajdu Zs., Herke I., Szendrei K. Ecdysteroids from Luzea carthamoides. Phytochemistry, 1988, 27(3): 737-741 (doi: 10.1016/0031-9422(88)84085-8).
- Били А.Ш., Мейер М., Шевалье К., Лоренсон Л., Фольер Н., Роллер М., Биртик С., Фанса-Бертон П.Э.Р, Фалько Л.Д. Композиции и способы для улучшенного мышечного метаболизма . Патент RU 2730853 C 2 . НАТУРЕКС СА. Франция Заявл. 03.02.2016. Опубл. 26.08.2020. Бюл . № 24.
- PPíš J., BudBuděšínsknsky̌ M., VokVokáč K., LaudovLaudová V., Harmatha J. Ecdysteroids from the roots of Leuzea carthamoides. Phytochemistry , 1994, 37(3): 707 711 (doi: 10.1016/S0031-9422(00)90343-1).
- Маматханов А.У., Шамсутдинов М.-Р., Шакиров Т.Т. Выделение экдистерона из корней Rhaponticum carthamoides. Химия природных соединений, 1980, 5: 528-529.
- Балтаев У .А., Абубакиров Н.К. Фитоэкдистероиды из Rhaponticum carthamoides Химия природных соединений , 1987, 5: 681 684.
- V okokáč K., BudBuděšínsknsky̌ M., Harmatha J. Minor ecdysteroid components of Leuzea carthamoides. Collection of Czechoslovak Chemical Communications , 2002, 67( 1): 124 139 (doi: 10.1135/cccc20020124).
- Timofeev N.P., Lapin A.A., Zelenkov V.N. Quality assessment of Rhaponticum carthamoides (Willd.) Iljin as medicinal raw material by the bromic antioxidant capacity estimation. In: Func-tional foods for chronic diseases. The modern day cure without the side effects of traditionall treatments /D.M. Martirosyan (ed.). Richardson (Texas, USA), D&A Incorporated, 2006: 164-172. Дата обращения: 10.05.2022.
- Протокол исследования на содержание экдистероидов № 18 от 31.03.2021 г. Сыктывкар, ИБ ФИЦ Коми НЦ УрО РАН. Режим доступа: https://leuzea.ru/pdf/drug_leuzea-p_from_the_pharmacy.pdf. Без даты.
- Севко Д.А. Концентрирование и определение фитостероидов с помощью молекулярно-имприн-тированных сорбентов и тандемной масс-спектрометрии высокого разрешения. Автореф. канд. дис. М., 2016.
- Потанин Г.Н. Очерки Северо-западной Монголии: результаты путешествия, исполненные в 1876-1877 г. по поручению Имп. Рус. геогр. о-ва чл. сотр. оного Г.Н. Потаниным. Вып. 4. Материалы этнографические СПб, 1883: 188 189.
- Постников Б.А. Маралий корень и основы введения его в культуру. Ново сибирск, 1995.
- Терехин А.А., Вандышев В.В. Технология возделывания лекарственных растений. М., 2008.
- Галамбози Б., Киракосян Г.М., Лужанин В.Г., Флисюк Е.В., Макаров В.Г., Пожариц-кая О.Н., Шиков А.Н. Выращивание эфиромасличных и лекарственных растений в условиях Севера: монография. СПб, 2018.
- Кубентаев С.А., Данилова А.Н. Оценка эколого-биологических особенностей Rhaponticum carthamoides (Willd.) Iljin и его ресурсные показатели на хребте Ивановский (Восточный Казахстан). Вестник Томского государственного университета, 2017, 37: 31-46.
- Тимофеев Н.П. Продуктивность и динамика содержания фитоэкдистероидов в агропопу-ляциях Rhaponticum carthamoides и Serratula coronata (Asteraceae) на Европейском Севере. Растительные ресурсы, 2006, 42(2): 17-36.
- Timofeev N.P. Ecological relations of the agropopulаtions of ecdysteroid-containing plants Rhapon-ticum carthamoides (Willd.) Iljin and Serratula coronata L. with the insects-phytophagans. Report 1. Contemporary Problems of Ecology, 2009, 2(5):489-500 (doi: 10.1134/S1995425509050166).
- Timofeev N .P. Composition variability of phytoecdysteroids in agrocenoses and their role in the vulnerability of plants to phytophagans . Report 2. Ecological relations of the agropopul а tions of ecdysteroid containing plants Rhaponticum carthamoides (Willd.) Iljin and Serratula coronata L . with the insects phytophagans . Contemporary Problems of Ecology, 2009, 2(6): 531 541 (doi : 10.1134/S1995425509060071
- Baù A., Bottex B. EFSA's compendium of botanicals. Zenodo, 2018. (doi: 10.5281/zenodo.1212388).
- Yang J., Wang, L. Safety pharmacology and toxicity study of herbal medicines. In: Traditional herbal medicine research methods: identification, analysis, bioassay, and pharmaceutical and clinical sciences /W.J.H. Liu (ed.). Wiley, 2011 (doi: 10.1002/9780470921340.ch7).
- Brown A.C. An overview of herb and dietary supplement efficacy, safety, and government regu-lation in the United States with suggested improvements. Part 1 of 5 series. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 2017, 107(Part A): 449-471 (doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2016.11.001).
- Brown A.C. Liver toxicity related to herb and dietary supplements: online table of medical case reports. Part 2 of 5 series. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 2017, 107(Part A): 472-501 (doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2016.07.001).
- Brown A.C. Kidney toxicity related to herb and dietary supplements: online table of medical case reports. Part 3 of 5 series. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 2017, 107(Part A): 502-519 (doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2016.07.024).
- Brown A.C. Heart toxicity related to herb and dietary supplements: online table of case reports. Part 4 of 5. Journal of Dietary Supplements, 2018, 15(4): 516-555 (doi: 10.1080/19390211.2017.1356418).
- Brown A.C. Cancer related to herbs and dietary supplements: online table of case reports. Part 5 of 5. Journal of Dietary Supplements, 2018, 15(4): 556-581 (doi: 10.1080/19390211.2017.1355865).
- IPNI (International Plant Names Index). Режим доступа: https://www.ipni.org/. Дата обращения: 10.05.2022.
- Мамаев С.А. Основные принципы методики исследования внутривидовой изменчивости древесных растений. В кн.: Индивидуальная и эколого-географическая изменчивость растений. Труды Института экологии растений и животных УНЦ АН СССР. Том 94. Свердловск, 1975: 3-14.
- Ecdybase: The ecdysone handbook /R. Lafont, J. Harmatha, F. Marion-Poll, L. Dinan, I.D. Wil-son (eds.). Режим доступа: https://ecdybase.org/. Дата обращения: 10.05.2022.
- Положий А.В., Некратова Н.А. Рапонтик сафлоровидный — Rhaponticum carthamoides (Willd.) Iljin. В кн.: Биологические особенности растений Сибири, нуждающихся в охране. Новосибирск, 1986: 198-226.
- Мырзангалиева А.Б., Самарханов Т.Н. Фитоценотическая и ресурсная характеристика левзеи сафлоровидной Rhaponticum carthamoides (Willd.) Iljin в Казахстанском Алтае. Вестник Евразийского национального университета имени Л.Н. Гумилева. Серия Биологические науки, 2018, 124(3): 55-64.
- Матолинец Д.А., Волошин В.А. Формирование урожая левзеи сафлоровидной и его качество при разных сочетаниях минеральных удобрений. Сибирский вестник сельскохозяйственной науки , 2017, 47(6): 66 72 (doi: 10.26898/0370-8799-2017-6-9).
- Майсак Г.П., Матолинец Д.А. Семенная продуктивность левзеи сафлоровидной в условиях Пермского края. Кормопроизводство, 2021, 2: 32-35.
- Crouzet S., Maria A., Dinan L., Lafont R., Girault J.-P. Ecdysteroids from Cyanotis longifolia Benth. (Commelinaceae). Archives of Insect Biochemistry and Physiology, 2009, 72(4): 194-209 (doi: 10.1002/arch.20329).
- Kokoska L., Janovska D. Chemistry and pharmacology of Rhaponticum carthamoides: a review. Phytochemistry, 2009, 70(7): 842-855 (doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2009.04.008).
- Тимофеев Н.П. Фитохимическая характеристика и активность лекарственного сырья из листовой части фармакопейного растения левзеи сафлоровидной. Аграрная наука Евро-Северо-Востока, 2022, 23(4): 480-495 (doi: 10.30766/2072-9081.2022.23.4.480-495).
- Тимофеев Н.П. Результаты практического внедрения в свиноводство рапонтикума сафлоровидного в качестве экдистероидного сырья. Мат. III Межд. конф. по селекции, технологии возделывания и переработки нетрадиционных растений. Симферополь, 1994: 166-167.
- Kratky F., Opletal L., Hejhalek J., Kucharova S. Effect of 20-hydroxyecdysone on the protein synthesis of pigs. Zivocisna Vyroba, 1997, 42: 445-451.


