Особенности экспрессии PD-l1 в клетках стромы опухоли, перитуморальных микрососудах и изолированных кластерах опухолевых клеток в ткани рака молочной железы и их корреляции с клинико-морфологическими характеристиками рака молочной железы
Автор: Зубарева Е.Ю., Сеньчукова М.А., Кармакова Т.А., Зайцев Н.В.
Журнал: Сибирский онкологический журнал @siboncoj
Рубрика: Лабораторные и экспериментальные исследования
Статья в выпуске: 5 т.22, 2023 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Цель исследования - изучить особенности экспрессии PD-L1 в клетках стромы опухоли, перитуморальных микрососудах и изолированных кластерах опухолевых клеток в ткани рака молочной железы (РМЖ) и их корреляции с клинико-морфологическими характеристиками РМЖ. материал и методы. В исследование включено 158 пациенток с впервые выявленным инвазивным РМЖ. Экспрессию PD-L1 изучали методом иммуногистохимии. Статистическую обработку результатов выполняли с использованием программы Statistica 12.0.
Рак молочной железы, опухолевая прогрессия, лиганд рецептора программируемой клеточный гибели 1 (pd-l1), ядерная экспрессия pd-l1, изолированные кластеры опухолевых клеток, перитуморальные микрососуды
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/140303544
IDR: 140303544 | УДК: 618.19-006.6-091.8 | DOI: 10.21294/1814-4861-2023-22-5-71-83
Текст научной статьи Особенности экспрессии PD-l1 в клетках стромы опухоли, перитуморальных микрососудах и изолированных кластерах опухолевых клеток в ткани рака молочной железы и их корреляции с клинико-морфологическими характеристиками рака молочной железы
Рак молочной железы (РМЖ) является наиболее распространенным видом злокачественных новообразований у женщин. В 2020 г. зарегистрировано свыше 2,2 млн первичных случаев РМЖ [1]. Основной причиной смерти как от РМЖ, так и от других злокачественных новообразований являются опухолевая прогрессия, связанная с метастазированием, и развитие резистентности к лекарственной терапии. Установлено, что метастазирование злокачественных новообразований (ЗНО), в том числе РМЖ, связано с активацией ангиогенеза, эпителиально-мезенхимальным переходом и развитием иммунологической толерантности [2, 3]. В ряде исследований отмечен более высокий метастатический потенциал кластеров опухолевых клеток в отличие от одиночных опухолевых клеток [4]. В то же время остается много вопросов, связанных с механизмами метастазирования, поэтому поиск новых прогностических маркеров не утратил своей актуальности.
Одним из перспективных маркеров, ассоциированных с опухолевой прогрессией, является лиганд рецептора программируемой клеточной гибели 1 (PD-L1). Известно, что PD1 и его лиганды PDL1 и PDL2 являются представителями системы «иммунологических контрольных точек», играющих важную роль в регуляции и модуляции иммунного ответа. Подавляя активность иммунных клеток, этот рецептор и его лиганды способствуют уменьшению повреждения в органах и тканях при воспалительных процессах и предупреждают запуск аутоиммунных реакций. Однако при ЗНО гиперэкспрессия этих маркеров связана с уклонением опухоли от иммунного надзора и опухолевой прогрессией.
Большое количество клинических и экспериментальных исследований посвящено изучению экспрессии PD-L1 при РМЖ. Экспериментальные данные подтвердили роль данного маркера в поддержании стволового фенотипа, химиорезисте-ности и диссеминации РМЖ [3, 5, 6], тогда как результаты клинических исследований довольно неоднозначны [7–15]. Так, по данным одних авторов, PD-L1-позитивные опухоли (>1 %) достоверно чаще встречались при наличии метастазов в регионарные лимфоузлы [10], при HER2-позитивном РМЖ [7, 13], при высоком индексе Ki67 [8, 11, 12, 15]. В то же время другие авторы отметили, что, напротив, PD-L1-позитивные опухоли встречались достоверно чаще при отсутствии метастазов в регионарные лимфоузлы [15] и при HER2-негативном РМЖ [14, 15]. Ряд исследований не выявил связи экспрессии маркера со статусом регионарных лимфоузлов [11], с HER2-статусом РМЖ [12] и с выраженностью пролиферативной активности [7, 14]. Следует отметить, что частота PD-L1 позитивных опухолей в этих исследованиях варьировала от 19,7 до 77,6 % [14].
В ранее опубликованном исследовании мы также изучали экспрессию PD-L1 в паренхиме опухоли и иммунных клетках стромы при РМЖ [16]. В отличие от вышеперечисленных авторов, мы оценивали не частоту экспрессии PD-L1, а ее выраженность, которая учитывала долю экспрессирующих клеток и интенсивность окраски маркера. Согласно полученным результатам, экспрессия PD-L1 связана с наличием регионарных (р=0,0002) и отдаленных метастазов (р=0,0004), а также периневральной инвазии (р=0,00005), что указывает на связь маркера с прогрессированием РМЖ.
Следует отметить, что принято различать мембранный PD-L1, цитоплазматический PD-L1, ядерный PD-L1 и сывороточный PD-L1 [17–19]. Полагают, что внутриклеточное распределение маркера имеет ключевое значение как для прогноза заболевания, так и для оценки эффективности лекарственной терапии [19].
Учитывая, что при изучении экспрессии PD-L1 при РМЖ цитоплазматическая экспрессия маркера выявлена в перитуморальных микрососудах и изолированных кластерах опухолевых клеток в ткани РМЖ, а также в ряде наблюдений отмечена ядерная экспрессия маркера в иммунных клетках, целью исследования явилось изучение особенностей экспрессии PD-L1 в описанных структурах и их корреляции с клинико-морфологическими характеристиками РМЖ.
Материал и методы
В проспективное когортное исследование включены 158 женщин в возрасте от 30 до 75 лет (средний возраст – 55,2 ± 12 лет) с впервые выявленным диагнозом РМЖ (табл. 1). Исследование одобрено Комитетом по этике Оренбургского государственного медицинского университета (протокол № 311 от 13 января 2023 г.). Все пациентки подписали информированное согласие на участие в клиническом исследовании.
Клинические данные о пациентках, проведенном лечении, гистологическом и иммуногистохи- мическом заключении получали из амбулаторных карт. До начала лечения всем пациенткам выполнено стандартное клинико-инструментальное обследование. Стадия заболевания установлена по результатам обследования и гистологического исследования операционного материала в соответствии с критериями TNM [20].
В исследование не включались пациентки с тяжелой сопутствующей патологией, выраженными аллергическими процессами, аутоиммунными заболеваниями; имеющие вторую опухоль другой локализации; получавшие глюкокортикоиды, нестероидные противовоспалительные препараты.
Экспрессию PD-L1 в паренхиме и строме опухоли изучали иммуногистохимическим методом на инвазивном компоненте пункционных биопта-тов с использованием поликлональных антител против PD-L1 (производитель Cloud-Clone Corp., Китай; разведение 30 мкг/мл). Процедуру окрашивания проводили в соответствии с протоколом производителя с использованием полностью автоматизированной системы окрашивания IHC и ISH BOND-MAX (компания-производитель Leica Biosystems Melboume Pty Ltd, Австралия). Система визуализации включала контрастное окрашивание DAB и гематоксилином. Для срезов отрицательного контроля первичные антитела заменяли фосфатно-солевым буфером и обрабатывали таким же образом.
Гистологические препараты исследовали методом световой микроскопии (цифровой микроскоп Levenhuk D740T, подключенный к камере 5,1 Мп, Россия). В гистопрепаратах оценивали наличие или отсутствие ядерной экспрессии PD-L1 в клетках стромы опухоли, а также цитоплазматической экспрессии маркера в перитуморальных микрососудах и изолированных кластерах опухолевых клеток (рис. 1–3).
Статистический анализ проводили с использованием программного обеспечения Statistica 12.0. Корреляции между различными данными оценивались с использованием непараметрической ранговой корреляции Спирмена или γ-корреляции. Тесты χ2 проведены для анализа различий в распределении между категоризированными данными. Значение p<0,05 считалось статистически значимым.
Результаты
Цитоплазматическая экспрессия маркера выявлена в 54 (34,2 %) образцах в перитуморальных микрососудах и в 75 (47,5 %) образцах в изолированных кластерах опухолевых клеток. Ядерная экспрессия PD-L1 в клетках стромы выявлена в 56 (35,4 %) образцах.
Установлено, что наличие экспрессии PD-L1 в перитуморальных микрососудах коррелировало с клинической формой РМЖ (γ=0,383; р=0,0009), гистологическим типом опухоли (γ=0,370; р=0,0003), категорией N (γ=0,505; р=0,000001), стадией забо-
Таблица 1/Table 1
Клинико-морфологическая характеристика больных раком молочной железыClinical and morphological characteristics of patients with breast cancer
|
Характеристики/Characteristics |
Количество больных/Number of patients |
|
Стадия заболевания/Stage of the disease |
|
|
Ia–IIb |
85 (53,8 %) |
|
IIIa–IIIc |
61 (38,6 %) |
|
IV |
12 (7,6 %) |
|
Категория Т/Category Т |
|
|
Т1 |
33 (20,9 %) |
|
Т2 |
80 (50,6 %) |
|
Т3 |
5 (3,2 %) |
|
Т4 |
40 (25,3 %) |
|
Категория N/Category N |
|
|
N0 |
69 (43,7 %) |
|
N1 |
34 (21,5 %) |
|
N2 |
35 (22,1 %) |
|
N3 |
20 (12,7 %) |
|
Категория М/Category М |
|
|
М0 |
146 (92,4 %) |
|
М1 |
12 (7,6 %) |
|
Гистологическая форма/Histology |
|
|
Протоковый (неспецифический)/Ductal (non-specific) |
112 (70,9 %) |
|
Дольковый/Lobular |
41 (25,9 %) |
|
Прочие/Others |
5 (3,2 %) |
|
Степень дифференцировки опухоли/Grade |
|
|
G1 |
8 (5,1 %) |
|
G2 |
89 (56,3 %) |
|
G3 |
61 (38,6 %) |
|
Молекулярно-биологический подтип опухоли/Molecular biological subtype |
|
|
Люминальный А/Luminal А |
23 (14,6 %) |
|
Люминальный В HER2-негативный/Luminal В HER2-negative |
79 (50,0 %) |
|
Люминальный В HER2-позитивный/Luminal В HER2-positive |
27 (17,1 %) |
|
HER2-позитивный/HER2-positive |
10 (6,3 %) |
|
Тройной негативный/Triple negative |
19 (12,0 %) |
|
Статус экспрессии ЭР/ER status |
|
|
Негативный (0 %)/Negative (0 %) |
28 (17,7 %) |
|
Позитивный (≥1 %)/Positive (≥1 %) |
130 (82,3 %) |
|
Статус экспрессии ПР/PR status |
|
|
Негативный (0 %)/Negative (0 %) |
51 (32,3 %) |
|
Позитивный (≥1 %)/Positive (≥1 %) |
107 (67,7 %) |
|
Индекс Ki67/Index Ki67 |
|
|
<20 % (низкий)/<20 % (low) |
29 (18,4 %) |
|
>20 % (высокий)/>20 % (high) |
129 (81,6 %) |
|
HER2-статус/HER2-status |
|
|
Негативный/Negative |
122 (77,2 %) |
|
Позитивный/Positive |
36 (22,8 %) |
|
Примечание: таблица составлена авторами. |
Note: created by the authors.
левания (γ=0,366; р=0,0001) (табл. 3). Экспрессия PD-L1 в перитуморальных микрососудах наблюдалась при Т1–2 и Т3–4 – в 46 (41,4 %) и 29 (61,7 %) (р=0,020) наблюдениях; при N0–1 и N2–3 – в 41 (39,8 %) и 34 (51,7 %) (р=0,008); при негативном и позитивном статусе ПР – в 30 (58,8 %) и 45 (42,1 %) случаях (р=0,048) соответственно.
В свою очередь, наличие экспрессии PD-L1 в изолированных кластерах опухолевых клеток коррелировало с клинической формой РМЖ (γ=0,518; р=0,000003), категорией Т (γ=0,339; р=0,0003), категорией N (γ=0,438; р=0,00004), категорией М (γ=0,640; р=0,00004), стадией заболевания (γ=0,451; р=0,000003), наличием ПНИ (γ=0,334;
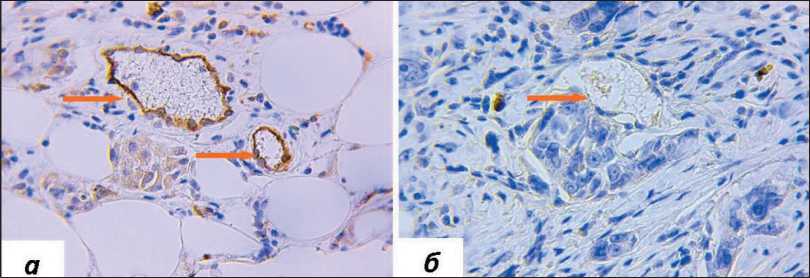
Рис. 1. Микрофото. Экспрессия PD-L1 в перитуморальных микрососудах, окраска ИГХ антителами против PD-L1, ×400: а) наличие экспрессии PD-L1; б) отсутствие экспрессии PD-L1 в перитуморальных микрососудах. Примечание: микрофото выполнены авторами
Fig. 1. Microphoto. PD-L1 expression in peritumoral microvessels, IHC staining with antibodies against PD-L1, ×400: a) presence of PD-L1 expression; b) lack of PD-L1 expression in peritumoral microvessels. Note: created by the authors
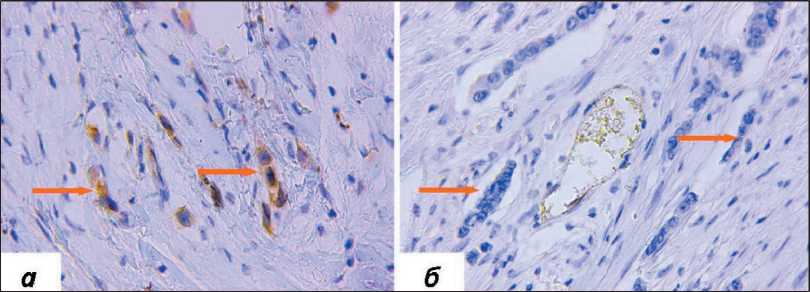
Рис. 2. Микрофото. Экспрессия PD-L1 в изолированных кластерах опухолевых клеток, окраска ИГХ антителами против PD-L1, ×400: а) наличие экспрессии PD-L1; б) отсутствие экспрессии PD-L1 в изолированных кластерах опухолевых клеток.
Примечание: микрофото выполнены авторами
Fig. 2. Microphoto. PD-L1 in isolated clusters of tumor cells, IHC staining with antibodies against PD-L1, ×400: a) presence of PD-L1 expression; b) lack of PD-L1 expression in isolated clusters of tumor cells. Note: created by the authors
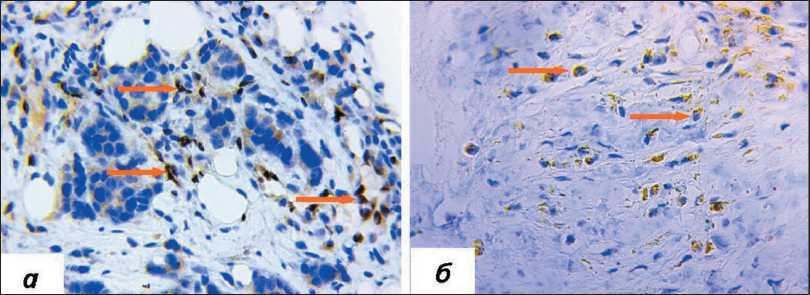
Рис. 3. Микрофото. Ядерная экспрессия PD-L1 в стромальных клетках, окраска ИГХ антителами против PD-L1, ×400: а) наличие ядерной экспрессии PD-L1; б) отсутствие ядерной экспрессии PD-L1 в стромальных клетках (наличие цитоплазматической экспрессии). Примечание: микрофото выполнены авторами
Fig. 3. Microphoto. Nuclear and cytoplasmic expressions of PD-L1 in stromal cells, IHC staining with antibodies against PD-L1, ×400: a) nuclear expression of PD-L1; b) cytoplasmic expression of PD-L1. Note: created by the authors
р=0,004). Согласно полученным данным, экспрессия маркера в изолированных кластерах опухолевых клеток (табл. 3) наблюдалась при узловой и диффузной форме РМЖ – в 33 (28,0 %) и 21 (52,5 %) случаях (р=0,005); при I–IIb, IIIa–IIIc и IV стадии РМЖ – в 22 (25,9 %), 24 (39,3 %) и в 8 (66,7 %) (р=0,011); при Т1, Т2, Т3 и Т4 – в 10 (30,3 %), 21 (26,2 %), 2 (40,0 %) и 21 (52,5 %) (р=0,040); при
N0–1 и N2–3 – в 29 (28,2 %) и 25 (45,5 %) случаях (р=0,030); при М0 и М1 – в 45 (31,0 %) и 8 (66,7 %) (р=0,007); при отсутствии и наличии периневральной инвазии – в 34 (29,6 %) и 20 (46,5 %) наблюдениях (р=0,048) соответственно.
Наличие ядерной экспрессии PD-L1 в строме опухоли коррелировало с клинической формой РМЖ (γ=0,502; р=0,000009), степенью злока-
Таблица 2/Table 2
Экспрессия Pd-L1 в перитуморальных микрососудах в зависимости от клинико-морфологических особенностей рака молочной железы
Pd-L1 expression in peritumoral microvessels depending on breast cancer clinical and morphological features
|
Характеристики/Characteristics |
Перитуморальные микрососуды с экспрессией PD-L1/ Peritumoral microvessels expressing PD-L1 |
||
|
Нет/No |
Есть/Yes |
р |
|
|
Клиническая форма/Clinical form |
|||
|
Узловая/Nodal |
67 (56,8 %) |
51 (43,2 %) |
0,061 |
|
Диффузная/Diffuse |
16 (40,0 %) |
24 (60,0 %) |
|
|
Стадия заболевания/Stage of the disease |
|||
|
I–IIb |
51 (60,0 %) |
34 (40,0 %) |
|
|
IIIa–IIIc |
27 (44,3 %) |
34 (55,7 %) |
>0,05 |
|
IV |
5 (41,7 %) |
7 (58,3 %) |
|
|
Категория Т/Category Т |
|||
|
Т1–2 |
65 (58,6 %) |
46 (41,4 %) |
0,020 |
|
Т3–4 |
18 (38,3 %) |
29 (61,7 %) |
|
|
Категория N(1)/Category N(1) |
|||
|
N0 |
40 (58,0 %) |
29 (42,0 %) |
|
|
N1 |
22 (64,7 %) |
12 (35,3 %) |
0,020 |
|
N2 |
16 (45,7 %) |
19 (54,3 %) |
|
|
N3 |
5 (25,0 %) |
15 (75,0 %) |
|
|
Категория N(2)/Category N(2) |
|||
|
N- |
40 (58,0 %) |
29 (42,0 %) |
>0,05 |
|
N+ |
43 (48,3 %) |
46 (51,7 %) |
|
|
Категория N(3)/Category N(3) |
|||
|
N0–1 |
62 (60,2 %) |
41 (39,8 %) |
0,008 |
|
N2–3 |
21 (38,2 %) |
34 (61,8 %) |
|
|
Категория М/Category M |
|||
|
М0 |
78 (53,4 %) |
68 (46,6 %) |
>0,05 |
|
М1 |
5 (41,7 %) |
7 (58,3 %) |
|
|
Гистологическая форма/Histology |
|||
|
Протоковый/Ductal |
68 (60,7 %) |
44 (39,3 %) |
|
|
Дольковый/Lobular |
13 (31,7 %) |
28 (68,3 %) |
>0,05 |
|
Прочие/Others |
2 (40,0 %) |
3 (60,0 %) |
|
|
Степень злокачественности/Grade |
|||
|
G1 |
4 (50,0 %) |
4 (50,0 %) |
|
|
G2 |
45 (50,6 %) |
44 (49,4 %) |
>0,05 |
|
G3 |
34 (55,7 %) |
27 (44,3 %) |
|
|
Внутрипротоковый компонент/Intraductal component |
|||
|
Нет/No |
61 (52,6 %) |
55 (47,4 %) |
>0,05 |
|
Есть/Yes |
22 (52,4 %) |
20 (47,6 %) |
|
|
Лимфоваскулярная инвазия/Lymphovascular invasion |
|||
|
Нет/No |
46 (52,3 %) |
42 (47,7 %) |
>0,05 |
|
Есть/Yes |
37 (52,9 %) |
33 (47,1 %) |
|
|
Периневральная инвазия/Perineural invasion |
|||
|
Нет/No |
65 (56,5 %) |
50 (43,5 %) |
>0,05 |
|
Есть/Yes |
18 (41,9 %) |
25 (58,1 %) |
|
|
Статус экспрессии ЭР/ER status |
|||
|
Негативный (0 %)/Negative (0 %) |
16 (57,1 %) |
12 (42,9 %) |
>0,05 |
|
Позитивный (≥1 %)/Positive (≥1 %) |
67 (51,5 %) |
63 (48,5 %) |
|
|
Статус экспрессии ПР/PR status |
|||
|
Негативный (0 %)/Negative (0 %) |
21 (41,2 %) |
30 (58,8 %) |
|
|
Позитивный (≥1 %)/Positive (≥1 %) |
62 (57,9 %) |
45 (42,1 %) |
0,048 |
|
Индекс Ki67/Index Ki67 |
|||
|
<20 % (низкий)/<20 % (low) |
16 (55,2 %) |
13 (44,8 %) |
>0,05 |
|
>20 % (высокий)/>20 % (high) |
67 (51,9 %) |
62 (48,1 %) |
|
|
HER2-статус/HER2- status |
Окончание аблицы 2/End of Table 2 |
||
|
Негативный Negative |
65 (53,3 %) |
57 (46,7 %) |
>0,05 |
|
Позитивный/Positive |
18 (50,0 %) |
18 (50,0 %) |
|
|
Молекулярно-биологический подтип опухоли/Molecular biological subtype |
|||
|
Люминальный А/Luminal А |
12 (52,2 %) |
11 (47,8 %) |
|
|
Люминальный В HER2-негативный/ Luminal В HER2-negative |
40 (50,6 %) |
39 (49,4 %) |
|
|
Люминальный В HER2-позитивный/ Luminal В HER2-positive |
14 (51,9 %) |
13 (48,1 %) |
>0,05 |
|
HER2-позитивный/HER2-positive |
4 (40,0 %) |
6 (60,0 %) |
|
|
Тройной негативный/Triple negative |
13 (68,4 %) |
6 (31,6 %) |
|
Примечание: р – уровень значимости отличий по критерию χ2; таблица составлена авторами.
Note: p – the level of significance according to the χ2 criterion; created by the authors.
Таблица 3/Table 3
Экспрессия Pd-L1 в изолированных кластерах опухолевых клеток в зависимости от клинико-морфологических особенностей РМЖ
Pd-L1 expression in isolated clusters of tumor cells depending on the breast cancer clinical and morphological features
|
Характеристики/Characteristics |
Кластеры с экспрес Нет/No |
сией PD-L1/Clusters wit Есть/Yes |
h PD-L1 expression р |
|
Клиническая форма/Clinical form |
|||
|
Узловая/Nodal |
85 (72,0 %) |
33 (28,0 %) |
|
|
Диффузная/Diffuse |
19 (47,5 %) |
21 (52,5 %) |
0,005 |
|
Стадия заболевания/Stage of the disease |
|||
|
I–IIb |
63 (74,1 %) |
22 (25,9 %) |
|
|
IIIa–IIIc |
37 (60,7 %) |
24 (39,3 %) |
0,011 |
|
IV |
4 (33,3 %) |
8 (66,7 %) |
|
|
Категория Т/Category Т |
|||
|
Т1 |
23 (69,7 %) |
10 (30,3 %) |
|
|
Т2 |
59 (73,8 %) |
21 (26,2 %) |
|
|
Т3 |
3 (60,0 %) |
2 (40,0 %) |
0,040 |
|
Т4 |
19 (47,5 %) |
21 (52,5 %) |
|
|
Категория N(1)/Category N(1) |
|||
|
N0 |
50 (72,5 %) |
19 (27,5 %) |
|
|
N1 |
24 (70,6 %) |
10 (29,4 %) |
|
|
N2 |
21 (60,0 %) |
14 (40,0 %) |
|
|
N3 |
9 (45,0 %) |
11 (55,0 %) |
|
|
Категория N(2)/Category N(2) |
|||
|
N- |
50 (72,5 %) |
19 (27,5 %) |
|
|
N+ |
54 (60,7 %) |
35 (39,3 %) |
>0,05 |
|
Категория N(3)/Category N(3) |
|||
|
N0–1 |
74 (71,8 %) |
29 (28,2 %) |
л иди |
|
N2–3 |
30 (54,5 %) |
25 (45,5 %) |
|
|
Категория М/Category M |
|||
|
М0 |
100 (69,0 %) |
45 (31,0 %) |
|
|
М1 |
4 (33,3 %) |
8 (66,7 %) |
|
|
Гистологическая форма/Histology |
|||
|
Протоковый/Ductal |
77 (64,3 %) |
40 (35,7 %) |
|
|
Дольковый/Lobular |
28 (68,3 %) |
13 (31,7 %) |
>0,05 |
|
Прочие/Others |
4 (80,0 %) |
1 (20,0 %) |
|
|
Степень злокачественности/Grade |
|||
|
G1 |
6 (75,0 %) |
2 (25,0 %) |
|
|
G2 |
53 (59,6 %) |
36 (40,4 %) |
>0,05 |
|
G3 |
45 (73,8 %) |
16 (26,2 %) |
|
|
Внутрипротоковый компонент/Intraductal component |
|||
|
Нет/No |
76 (65,5 %) |
40 (34,5 %) |
|
|
Есть/Yes |
28 (66,7 %) |
14 (33,3 %) |
>0,05 |
Окончание аблицы 3/End of Table 3
|
Лимфоваскулярная инвазия/Lymphovascular invasion |
>0,05 |
||
|
Нет/No |
61 (69,3 %) |
27 (30,7 %) |
|
|
Есть/Yes |
43 (61,4 %) |
27 (38,6 %) |
|
|
Периневральная инвазия/Perineural invasion |
|||
|
Нет/No |
81 (70,4 %) |
34 (29,6 %) |
0,048 |
|
Есть/Yes |
23 (53,5 %) |
20 (46,5 %) |
|
|
Статус экспрессии ЭР/ER status |
|||
|
Негативный (0 %)/Negative (0 %) |
18 (64,3 %) |
10 (35,7 %) |
>0,05 |
|
Позитивный (≥1 %)/Positive (≥1 %) |
86 (66,2 %) |
44 (33,8 %) |
|
|
Статус экспрессии ПР/PR status |
|||
|
Негативный (0 %)/Negative (0 %) |
32 (62,8 %) |
19 (37,2 %) |
>0,05 |
|
Позитивный (≥1 %)/Positive (≥1 %) |
72 (67,3 %) |
35 (32,7 %) |
|
|
Индекс Ki67/Index Ki67 |
|||
|
<20 % (низкий)/<20 % (low) |
18 (62,1 %) |
11 (37,9 %) |
>0,05 |
|
>20 % (высокий)/>20 % (high) |
86 (66,7 %) |
43 (33,3 %) |
|
|
HER2-статус/HER2- status |
|||
|
Негативный/Negative |
81 (66,4 %) |
41 (33,6 %) |
>0,05 |
|
Позитивный/Positive |
23 (63,9 %) |
13 (36,1 %) |
|
|
Молекулярно-биологический подтип опухоли/Molecular biological subtype |
|||
|
Люминальный А/Luminal А |
17 (73,9 %) |
6 (26,1 %) |
|
|
Люминальный В HER2-негативный/ Luminal В HER2-negative |
50 (63,3 %) |
29 (36,7 %) |
|
|
Люминальный В HER2-позитивный/ Luminal В HER2-positive |
18 (66,7 %) |
9 (33,3 %) |
>0,05 |
|
HER2-позитивный/HER2-positive |
6 (60,0 %) |
4 (40,0 %) |
|
|
Тройной негативный/Triple negative |
13 (68,4 %) |
6 (31,6 %) |
|
Примечание: р – уровень значимости отличий по критерию χ2; таблица составлена авторами.
Note : p – the level of significance according to the χ2 criterion; created by the authors.
Таблица 4/Table 4.
Ядерная экспрессия Pd-L1 в строме опухоли в зависимости от клинико-морфологических особенностей рака молочной железы
Pd-L1 expression in the cells of the tumor stroma depending on the breast cancer clinical and morphological features
|
Характеристики/Characteristics |
Ядерная экспрессия PD-L1 Нет/No |
в строме/Nuclear expression of PD-L1 in the stroma Есть/Yes р |
|
|
Клиническая форма/Clinical form |
|||
|
Узловая/Nodal |
84 (71,2 %) |
34 (28,8 %) |
0,003 |
|
Диффузная/Diffuse |
18 (45,0 %) |
22 (55,0 %) |
|
|
Стадия заболевания/Stage of the disease |
|||
|
I–IIb |
70 (82,4 %) |
15 (17,6 %) |
|
|
IIIa–IIIc |
29 (47,5 %) |
32 (52,5 %) |
<0,001 |
|
IV |
3 (25,0 %) |
9 (75,0 %) |
|
|
Категория Т/Category Т |
|||
|
Т1 |
26 (78,8 %) |
7 (21,2 %) |
|
|
Т2 |
57 (71,3 %) |
23 (28,7 %) |
0,002 |
|
Т3 |
1 (20,0 %) |
4 (80,0 %) |
|
|
Т4 |
18 (45,0 %) |
22 (55,0 %) |
|
|
Категория N/Category N |
|||
|
N0 |
54 (78,3 %) |
15 (21,7 %) |
|
|
N1 |
22 (64,7 %) |
12 (35,3 %) |
0,005 |
|
N2 |
17 (48,6 %) |
18 (51,4 %) |
|
|
N3 |
9 (45,0 %) |
11 (55,0 %) |
|
|
Категория М/Category M |
|||
|
М0 |
99 (67,8 %) |
47 (32,2 %) |
0,004 |
|
М1 |
3 (25,0 %) |
9 (75,0 %) |
|
Окончание аблицы 4/End of Table 4
|
Гистологическая форма/Histology |
>0,05 |
||
|
Протоковый/Ductal |
74 (66,1 %) |
38 (33,9 %) |
|
|
Дольковый/Lobular |
24 (58,5 %) |
17 (41,5 %) |
|
|
Прочие/Others |
4 (80,0 %) |
1 (20,0 %) |
|
|
Степень злокачественности/Grade |
|||
|
G1 |
6 (75,0 %) |
2 (25,0 %) |
|
|
G2 |
63 (70,8 %) |
26 (46,4 %) |
0,090 |
|
G3 |
33 (54,1 %) |
28 (45,9 %) |
|
|
Внутрипротоковый компонент/Intraductal component |
|||
|
Нет/No |
76 (65,5 %) |
40 (34,5 %) |
>0,05 |
|
Есть/Yes |
26 (61,9 %) |
16 (38,1 %) |
|
|
Лимфоваскулярная инвазия/Lymphovascular invasion |
|||
|
Нет/No |
57 (64,8 %) |
31 (35,2 %) |
>0,05 |
|
Есть/Yes |
45 (64,3 %) |
25 (35,7 %) |
|
|
Периневральная инвазия/Perineural invasion |
|||
|
Нет/No |
77 (67,0 %) |
38 (33,0 %) |
>0,05 |
|
Есть/Yes |
25 (58,1 %) |
18 (41,9 %) |
|
Статус экспрессии ЭР/ER status
|
Негативный (0 %)/Negative (0 %) |
16 (57,1 %) |
12 (42,9 %) |
>0,05 |
|
Позитивный (≥1 %)/Positive (≥1 %) |
86 (66,2 %) |
44 (33,8 %) |
|
|
Статус экспрессии ПР/PR status |
|||
|
Негативный (0 %)/Negative (0 %) |
26 (51,0 %) |
25 (49,0 %) |
0,014 |
|
Позитивный (≥1 %)/Positive (≥1 %) |
76 (71,0 %) |
31 (29,0 %) |
|
|
Индекс Ki67/Index Ki67 |
|||
|
<20 % (низкий)/<20 % (low) |
19 (65,5 %) |
10 (34,5 %) |
>0,05 |
|
>20 % (высокий)/>20 % (high) |
83 (64,3 %) |
46 (35,7 %) |
|
|
HER2-статус/HER2- status |
|||
|
Негативный/Negative |
85 (69,7 %) |
37 (30,3 %) |
0,014 |
|
Позитивный/Positive |
17 (47,2 %) |
19 (52,8 %) |
|
|
Молекулярно-биологический подтип опухоли/Molecular biological subtype |
|||
|
Люминальный А/Luminal А |
17 (73,9 %) |
6 (26,1 %) |
|
|
Люминальный В HER2-негативный/ Luminal В HER2-negative |
54 (68,4 %) |
25 (31,6 %) |
|
|
Люминальный В HER2-позитивный/ Luminal В HER2-positive |
14 (51,9 %) |
13 (48,1 %) |
>0,05 |
|
HER2-позитивный/HER2-positive |
4 (40,0 %) |
6 (60,0 %) |
|
|
Тройной негативный/Triple negative |
13 (68,4 %) |
6 (31,6 %) |
|
Примечание: р – уровень значимости отличий по критерию χ2; таблица составлена авторами.
Note: p – the level of significance according to the χ2 criterion; created by the authors.
чественности (γ=0,331; р=0,002), категорией Т (γ=0,455; р=0,000001), категорией N (γ=0,509; р=0,000003), категорией М (γ=0,727; р=0,00001), стадией заболевания (γ=0,689; р<0,000001), статусом ПР (γ=-0,404; р=0,0003), HER2-статусом РМЖ (γ=0,439; р=0,0002). Ядерная экспрессия в стромальных клетках (табл. 4) наблюдалась при узловой и диффузной форме – в 34 (28,8 %) и 22 (55,0 %) случаях (р=0,003); при раннем, местнораспространенном и метастатическом РМЖ – в 15 (17,6 %), 32 (52,5 %) и 9 (75,0 %) (р<0,001); при T1, Т2, Т3 и Т4 – в 7 (21,2 %), 23 (28,7 %), 4 (80,0 %) и 22 (55,0 %) (р=0,002); при N0, N1, N2 и N3 – в 15 (21,7 %), 12 (35,3 %), 18 (51,4 %) и 11 (55,0 %) (р=0,005); при М0 и М1 – в 47 (32,2 %) и 9 (75,0 %) (р=0,004), при негативном и позитивном статусе ПР – в 25 (49,0 %) и 31 (29,0 %) (р=0,014);
при HER2-негативном и HER2-позитивном статусе РМЖ – в 37 (30,3 %) и 19 (52,8 %) наблюдениях (р=0,014) соответственно.
Обсуждение
Ранее мы установили связь выраженности цитоплазматической экспрессии PD-L1 с рядом факторов неблагоприятного прогноза РМЖ: наличием регионарных и отдаленных метастазов, а также периневральной инвазии (ПНИ). Целью данного исследования явилось изучение особенностей экспрессии маркера в перитуморальных микрососудах, изолированных кластерах опухолевых клеток и клетках стромы.
Известно, что ангиогенез играет ключевую роль в опухолевой прогрессии и непосредственно ассоциирован с метастазированием [21]. Установлено, что экспрессия PD-L1 в эндотелиальных клетках наблюдается как в норме, так и при различных заболеваниях [3, 22–24]. Его экспрессия может быть связана с активацией и экстравазацией Т-клеток без чрезмерного повреждения сосудов, что приводит к подавлению иммунных ответов, опосредованных CD8+ Т-клетками [22]. Роль эндотелиальной экспрессии PD-L1 в развитии иммунологической толерантности подтверждена экспериментально на модели аллогенной трансплантации сердца мыши: трансплантаты, лишенные PD-L1 в эндотелиальных клетках, отторгались значительно быстрее, чем контрольные [24]. При раке легкого эндотелиальная экспрессия PD-L1 связана со снижением инфильтрации CD8 + T-клеток и повышением агрегации FoxP3 + T-клеток в опухолевых тканях, а также с прогнозом заболевания [25]. Полагают, что терапия, нацеленная на подавление экспрессии PD-L1 в эндотелиальных клетках, может ингибировать рост опухоли за счет улучшения иммунной микросреды.
В нашем исследовании экспрессия PD-L1 в перитуморальных микрососудах коррелировала с наличием регионарных метастазов и с диффузной формой РМЖ. Эти данные предполагают, что экспрессия маркера в сосудах опухоли может играть роль не только в развитии иммунной супрессии, но и в метастазировании опухоли. Однако для подтверждения этой гипотезы необходимы дальнейшие исследования.
Известно, что большинство опухолевых клеток, попадающих в кровоток, погибают и не превращаются в клинически обнаруживаемые метастазы [26]. Для эффективного метастазирования опухолевые клетки используют различные механизмы, в том числе приобретение стволового фенотипа, эпителиально-мезенхимальный переход, изменение опухолевого микроокружения и др. [27, 28]. Описан новый механизм, способствующий более эффективному метастазированию опухоли [4]. Предполагают, что метастазирование в виде связанных между собой опухолевых клеток (кластеров) способствует выживанию опухолевых клеток в метастатических сайтах. Кластеры опухолевых клеток более устойчивы к ферроптозу [29], успешнее избегают атаки иммунной системы [30], отличаются более высокой пролиферативной активностью и сходством со стволовыми клетками [31].
В доступной литературе мы не обнаружили работ, в которых бы изучалась экспрессия PD-L1 в изолированных кластерах опухолевых клеток. Под термином «изолированные кластеры опухолевых клеток» мы предполагали наличие в пери-туморальной строме отдельных (изолированных) групп опухолевых клеток, не связанных с основной массой опухоли. Согласно данным литературы, инвазия отдельных групп опухолевых клеток («cohesive clusters of the tumor cells» или «isolated small clusters tumor cells») в окружающую строму
(«collective invasion» или «collective metastasis») ассоциируется с более агрессивными подтипами рака и отдаленными метастазами [31, 32]. В нашем исследовании экспрессия PD-L1 в изолированных кластерах опухолевых клеток встречалась значимо чаще при таких неблагоприятных факторах прогноза, как диффузная форма РМЖ (р=0,005), наличие регионарных (р=0,03) и отдаленных метастазов (р=0,007), и несколько чаще при наличии периневральной инвазии (р=0,048). Полагают, что миграция опухолевых клеток в виде кластеров может быть связана с гибридными эпителиальномезенхимальными состояниями, при которых они, сохраняя адгезивные свойства с соседними клетками, характеризуются потерей апикальнобазальной полярности и лучшей подвижностью клеток [33]. Таким образом, можно предположить, что экспрессия PD-L1 в кластерах опухолевых клеток, с одной стороны, может являться одним из факторов, позволяющим им уклоняться от иммунного надзора, а с другой – способствовать метастазированию за счет активации механизмов эпителиально-мезенхимального перехода. О связи между иммунологической толерантностью и эпителиально-мезенхимальным переходом свидетельствует ряд экспериментальных исследований [3, 34, 35].
Интересным результатом нашей работы было выявление ядерной экспрессии PD-L1. Ядерная экспрессия PD-L1 оказалась значимым маркером, связанным с агрессивными характеристиками РМЖ, такими как диффузная форма РМЖ, N3, наличие отдаленных метастазов, негативный статус ПР, HER2-позитивный статус. При анализе литературы мы не обнаружили клинических исследований, в которых бы описывалось наличие ядерной экспрессии маркера в строме опухоли при РМЖ. В эксперименте ядерная экспрессия PD-L1 описана в клеточных линиях РМЖ, колоректального рака и рака легкого [36–39]. Ее наличие связано с более агрессивными опухолями и образованием отдаленных метастазов на мышиных моделях [38]. В ряде исследований показано, что PD-L1 может секретироваться во внеклеточное пространство или транслоцироваться в ядро, играя решающую роль в регуляции иммунологической толерантности, онкогенеза и иммунотерапии [40]. Полагают, что внутриклеточное распределение PD-L1 имеет огромное значение как для прогноза заболевания, так и для эффективности лекарственной и иммунотерапии. При этом существующие схемы лечения в основном сосредоточены на PD-L1, экспрессируемом на клеточной мембране. Однако они могут быть неэффективны в отношении цитоплазматического и ядерного PD-L1, которые изучены недостаточно [19]. В связи с этим полагаем, что дальнейшие исследования, направленные на изучение роли внутриклеточного распределения PD-L1 в прогрессировании РМЖ и развитии лекарственной устойчивости, представляют несомненный интерес.
Заключение
В результате проведенного исследования установлено, что экспрессия PD-L1 в перитуморальных микрососудах и в изолированных кластерах опухолевых клеток, а также ядерная экспрессия маркера связаны с рядом ключевых факторов прогрессирования РМЖ, а именно с наличием регионарных и отдаленных метастазов. Полагаем, что определение экспрессии маркера в описанных структурах может способствовать улучшению прогноза заболевания. Необходимы дальнейшие экспериментальные и клинические исследования, направленные на изучение роли PD-L1 в прогрессировании РМЖ, а также возможности использования таргетных препаратов, нацеленных на ингибирование экспрессии маркера в перитуморальных микрососудах и в изолированных кластерах опухолевых клеток.
Список литературы Особенности экспрессии PD-l1 в клетках стромы опухоли, перитуморальных микрососудах и изолированных кластерах опухолевых клеток в ткани рака молочной железы и их корреляции с клинико-морфологическими характеристиками рака молочной железы
- WHO [Internet]. Breast cancer [cited 2023 Apr 20]. URL: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/breast-cancer.
- Zhang J., Zhang S., Gao S., Ma Y., Tan X., Kang Y., Ren W. HIF-1α, TWIST-1 and ITGB-1, associated with Tumor Stiffness, as Novel Predictive Markers for the Pathological Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Breast Cancer. Cancer Manag Res. 2020; 12: 2209-22. https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S246349.
- Messeha S.S., Zarmouh N.O., Soliman K.F.A. Polyphenols Modulating Effects of PD-L1/PD-1 Checkpoint and EMT-Mediated PD-L1 Overexpression in Breast Cancer. Nutrients. 2021; 13(5): 1718. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13051718.
- Nathanson S.D., Detmar M., Padera T.P., Yates L.R., Welch D.R., Beadnell T.C., Scheid A.D., Wrenn E.D., Cheung K. Mechanisms of breast cancer metastasis. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2022; 39(1): 117-37. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10585-021-10090-2.
- Almozyan S., Colak D., Mansour F., Alaiya A., Al-Harazi O., Qattan A., Al-Mohanna F., Al-Alwan M., Ghebeh H. PD-L1 promotes OCT4 and Nanog expression in breast cancer stem cells by sustaining PI3K/AKT pathway activation. Int J Cancer. 2017; 141(7): 1402-12. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.30834.
- Mansour F.A., Al-Mazrou A., Al-Mohanna F., Al-Alwan M., Ghebeh H. PD-L1 is overexpressed on breast cancer stem cells through notch3/mTOR axis. Oncoimmunology. 2020; 9(1). https://doi.org/10.1080/2162402X.2020.1729299.
- Wang C., Zhu H., Zhou Y., Mao F., Lin Y., Pan B., Zhang X., Xu Q., Huang X., Sun Q. Prognostic Value of PD-L1 in Breast Cancer: A MetaAnalysis. Breast J. 2017; 23(4): 436-43. https://doi.org/10.1111/tbj.12753.
- Karnik T., Kimler B.F., Fan F., Tawfik O. PD-L1 in breast cancer: comparative analysis of 3 different antibodies. Hum Pathol. 2018; 72: 28-34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.humpath.2017.08.010.
- Zhou T., Xu D., Tang B., Ren Y., Han Y., Liang G., Wang J., Wang L. Expression of programmed death ligand-1 and programmed death-1 in samples of invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast and its correlation with prognosis. Anticancer Drugs. 2018; 29(9): 904-10. https://doi.org/10.1097/CAD.0000000000000683.
- Catacchio I., Silvestris N., Scarpi E., Schirosi L., Scattone A., Mangia A. Intratumoral, rather than stromal, CD8+ T cells could be a potential negative prognostic marker in invasive breast cancer patients. Transl Oncol. 2019; 12(3): 585-95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tranon.2018.12.005.
- Evangelou Z., Papoudou-Bai A., Karpathiou G., Kourea H., Kamina S., Goussia A., Harissis H., Peschos D., Batistatou A. PD-L1 Expression and Tumor-infiltrating Lymphocytes in Breast Cancer: Clinicopathological Analysis in Women Younger than 40 Years Old. In Vivo. 2020; 34(2): 639-47. https://doi.org/10.21873/invivo.11818.
- Huang W., Ran R., Shao B., Li H. Prognostic and clinicopathological value of PD-L1 expression in primary breast cancer: a meta-analysis. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2019; 178(1): 17-33. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-019-05371-0.
- Hoffmann L.G., Sarian L.O., Vassallo J., de Paiva Silva G.R., Ramalho S.O.B., Ferracini A.C., da Silva Araujo K., Jales R.M., Figueira D.E., Derchain S. Evaluation of PD-L1 and tumor infiltrating lymphocytes in paired pretreatment biopsies and post neoadjuvant chemotherapy surgical specimens of breast carcinoma. Sci Rep. 2021; 11(1): 22478. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-00944-w.
- Du Q., Che J., Jiang X., Li L., Luo X., Li Q. PD-L1 Acts as a Promising Immune Marker to Predict the Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Breast Cancer Patients. Clin Breast Cancer. 2020; 20(1): 99-111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clbc.2019.06.014.
- Cirqueira M.B., Mendonça C.R., Noll M., Soares L.R., de Paula Carneiro Cysneiros M.A., Paulinelli R.R., Moreira M.A.R., Freitas-Junior R. Prognostic Role of PD-L1 Expression in Invasive Breast Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers (Basel). 2021; 13(23): 6090. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13236090.
- Zubareva E., Senchukova M., Karmakova T. Predictive significance of HIF-1α, Snail, and PD-L1 expression in breast cancer. Clin Exp Med. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10238-023-01026-z.
- Chowdhury S., Veyhl J., Jessa F., Polyakova O., Alenzi A., MacMillan C., Ralhan R., Walfish P.G. Programmed death-ligand 1 overexpression is a prognostic marker for aggressive papillary thyroid cancer and its variants. Oncotarget. 2016; 7(22): 32318-28. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.8698.
- Satelli A., Batth I.S., Brownlee Z., Rojas C., Meng Q.H., Kopetz S., Li S. Potential role of nuclear PD-L1 expression in cell-surface vimentin positive circulating tumor cells as a prognostic marker in cancer patients. Sci Rep. 2016; 6. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep28910.
- Wu Y., Chen W., Xu Z.P., Gu W. PD-L1 Distribution and Perspective for Cancer Immunotherapy-Blockade, Knockdown, or Inhibition. Front Immunol. 2019; 10. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.02022.
- Brierley J., Gospodarowicz M.K., Wittekind Ch. (2017). TNM Classification of Malignant Tumors (8th edition). Oxford, UK; Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 2017.
- Kanugula A.K., Adapala R.K., Jamaiyar A., Lenkey N., Guarino B.D., Liedtke W., Yin L., Paruchuri S., Thodeti C.K. Endothelial TRPV4 channels prevent tumor growth and metastasis via modulation of tumor angiogenesis and vascular integrity. Angiogenesis. 2021; 24(3): 647-56. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-021-09775-9.
- Rodig N., Ryan T., Allen J.A., Pang H., Grabie N., Chernova T., Greenfield E.A., Liang S.C., Sharpe A.H., Lichtman A.H., Freeman G.J. Endothelial expression of PD-L1 and PD-L2 down-regulates CD8+ T cell activation and cytolysis. Eur J Immunol. 2003; 33(11): 3117-26. https://doi.org/10.1002/eji.200324270.
- Gibbons Johnson R.M., Dong H. Functional Expression of Programmed Death-Ligand 1 (B7-H1) by Immune Cells and Tumor Cells. Front Immunol. 2017; 8: 961. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2017.00961.
- Bracamonte-Baran W., Gilotra N.A., Won T., Rodriguez K.M., Talor M.V., Oh B.C., Griffin J., Wittstein I., Sharma K., Skinner J., Johns R.A., Russell S.D., Anders R.A., Zhu Q., Halushka M.K., Brandacher G., Čiháková D. Endothelial Stromal PD-L1 (Programmed Death Ligand 1) Modulates CD8+ T-Cell Infiltration After Heart Transplantation. Circ Heart Fail. 2021; 14(10). https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.120.007982.
- Liu S., Qin T., Liu Z., Wang J., Jia Y., Feng Y., Gao Y., Li K. Anlotinib alters tumor immune microenvironment by downregulating PD-L1 expression on vascular endothelial cells. Cell Death Dis. 2020; 11(5): 309. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-020-2511-3.
- Vanharanta S., Massagué J. Origins of metastatic traits. Cancer Cell. 2013; 24(4): 410-21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2013.09.007.
- Celià-Terrassa T., Kang Y. Distinctive properties of metastasisinitiating cells. Genes Dev. 2016; 30(8): 892-908. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.277681.116.
- Lambert A.W., Pattabiraman D.R., Weinberg R.A. Emerging Biological Principles of Metastasis. Cell. 2017; 168(4): 670-91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2016.11.037.
- Brown C.W., Amante J.J., Mercurio A.M. Cell clustering mediated by the adhesion protein PVRL4 is necessary for α6β4 integrin-promoted ferroptosis resistance in matrix-detached cells. J Biol Chem. 2018; 293(33): 12741-8. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.RA118.003017.
- Lo H.C., Xu Z., Kim I.S., Pingel B., Aguirre S., Kodali S., Liu J., Zhang W., Muscarella A.M., Hein S.M., Krupnick A.S., Neilson J.R., Paust S., Rosen J.M., Wang H., Zhang X.H. Resistance to natural killer cell immunosurveillance confers a selective advantage to polyclonal metastasis. Nat Cancer. 2020; 1(7): 709-22. https://doi.org/10.1038/s43018-020-0068-9.
- Cheung K.J., Padmanaban V., Silvestri V., Schipper K., Cohen J.D., Fairchild A.N., Gorin M.A., Verdone J.E., Pienta K.J., Bader J.S., Ewald A.J. Polyclonal breast cancer metastases arise from collective dissemination of keratin 14-expressing tumor cell clusters. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2016; 113(7): 854-63. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1508541113.
- Wrenn E., Huang Y., Cheung K. Collective metastasis: coordinating the multicellular voyage. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2021; 38(4): 373-99. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10585-021-10111-0.
- Pastushenko I., Blanpain C. EMT Transition States during Tumor Progression and Metastasis. Trends Cell Biol. 2019; 29(3): 212-26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcb.2018.12.001.
- Jiang Y., Zhan H. Communication between EMT and PD-L1 signaling: New insights into tumor immune evasion. Cancer Lett. 2020; 468: 72-81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2019.10.013.
- Sahoo S., Nayak S.P., Hari K., Purkait P., Mandal S., Kishore A., Levine H., Jolly M.K. Immunosuppressive Traits of the Hybrid Epithelial/Mesenchymal Phenotype. Front Immunol. 2021; 12. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2021.797261.
- Rom-Jurek E.M., Kirchhammer N., Ugocsai P., Ortmann O., Wege A.K., Brockhoff G. Regulation of Programmed Death Ligand 1 (PD-L1) Expression in Breast Cancer Cell Lines In Vitro and in Immunodeficient and Humanized Tumor Mice. Int J Mol Sci. 2018; 19(2): 563. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19020563.
- Yu J., Qin B., Moyer A.M., Nowsheen S., Tu X., Dong H., Boughey J.C., Goetz M.P., Weinshilboum R., Lou Z., Wang L. Regulation of sister chromatid cohesion by nuclear PD-L1. Cell Res. 2020; 30(7): 590-601. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41422-020-0315-8.
- Gao Y., Nihira N.T., Bu X., Chu C., Zhang J., Kolodziejczyk A., Fan Y., Chan N.T., Ma L., Liu J., Wang D., Dai X., Liu H., Ono M., Nakanishi A., Inuzuka H., North B.J., Huang Y.H., Sharma S., Geng Y., Xu W., Liu X.S., Li L., Miki Y., Sicinski P., Freeman G.J., Wei W. Acetylationdependent regulation of PD-L1 nuclear translocation dictates the efficacy of anti-PD-1 immunotherapy. Nat Cell Biol. 2020; 22(9): 1064-75. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-020-0562-4.
- Ma R., Liu Y., Che X., Li C., Wen T., Hou K., Qu X. Nuclear PDL1 promotes cell cycle progression of BRAF-mutated colorectal cancer by inhibiting THRAP3. Cancer Lett. 2022; 527: 127-39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2021.12.017.
- Xiong W., Gao Y., Wei W., Zhang J. Extracellular and nuclear PD-L1 in modulating cancer immunotherapy. Trends Cancer. 2021; 7(9): 837-46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trecan.2021.03.003.


