Отдаленные результаты лечения атипичной косолапости по методу Понсети
Автор: Вавилов Максим Александрович, Бландинский Валерий Федорович, Громов Илья Валерьевич, Соловьева Екатерина Николаевна, Дубиненков Владимир Борисович, Соколов Александр Григорьевич
Журнал: Гений ортопедии @geniy-ortopedii
Рубрика: Оригинальные статьи
Статья в выпуске: 3 т.28, 2022 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Введение. Врожденная косолапость в структуре пороков развития занимает одно из лидирующих мест у детей. При этом, несмотря на сравнительно невысокую рождаемость, тенденции к уменьшению косолапости в популяции не наблюдается. Наоборот, мы видим увеличение количества патологий стоп, ассоциированных с пороками развития центральной нервной системы, и других патологических синдромов. Атипичная косолапость по классификации Понсети остается актуальной проблемой, требующей от ортопедов своевременной диагностики и тактики лечения. Цель. Акцентировать внимание детских ортопедов на проблеме атипичной косолапости. Обсудить основные ошибки при лечении атипичной косолапости и продемонстрировать количество рецидивов на фоне роста, требующее повторных оперативных вмешательств. Материалы и методы. В клиниках города Ярославля за период с мая 2006 по декабрь 2019 года было пролечено 135 детей (184 стопы) с атипичной косолапостью, что составило 12,1 % от общего числа детей с косолапостью. В анализ вошли только дети, которым мы смогли помочь, используя тактику И. Понсети при атипичной косолапости, что составило 106 детей (147 стоп). Отдаленный срок наблюдений в среднем составил 7,2 года. Остальным детям при оперативной коррекции были выполнены дополнительно релизы и артродезы. Результаты. Рецидивы, потребовавшие повторного оперативного лечения, встретились у 51 ребенка (83 стопы), что составило 48,1 % от общего количества детей с атипичной косолапостью, полеченных в Ярославле. Дискуссия. Введение гипсования по методу И. Понсети в повседневную практику ортопеда требует тщательного соблюдения протокола гипсования, особенно в случае с атипичной косолапостью. Несвоевременное выявление АК, а также несоблюдение протокола гипсования при ТК приводит к формированию ятрогенной атипичной косолапости, что, в свою очередь, увеличивает вероятность больших реконструктивных операций и ухудшает прогноз. Заключение. Метод Понсети в России является «золотым стандартом» лечения косолапости.
Атипичная косолапость, ятрогенная косолапость, метод понсети, рецидив
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/142235349
IDR: 142235349 | УДК: 617.586-007.5-089.4:615.463]-053.2 | DOI: 10.18019/1028-4427-2022-28-3-372-377
Текст научной статьи Отдаленные результаты лечения атипичной косолапости по методу Понсети
Врожденная косолапость в структуре пороков развития занимает одно из лидирующих мест у детей [1–9]. При этом, несмотря на сравнительно невысокую рождаемость, тенденции к уменьшению косолапости в популяции не наблюдается [10-15]. Наоборот, мы видим увеличение количества патологий стоп, ассоциированных с пороками развития центральной нервной системы, и других патологических синдромов [16–18].
Впервые в России лечение косолапости по методу И. Понсети начато с 2004 года в г. Владимире (Г.М. Чочиев). Более активное распространение метод получил в 2006–2008 годах. На данный момент в стране метод
Понсети является «золотым стандартом» для новорожденных детей и стартом лечения косолапости в большинстве случаев [19–25]. При этом количество врожденной атипичной косолапости, по нашим данным и данным зарубежных авторов, составляет 2-3 на 100 детей с косолапостью [26–29], что не всегда вовремя позволяет распознать и адекватно, по всем принципам атипичной косолапости, пролечить данную группу пациентов. Гип- сование детей по методу И. Понсети очень простой и в то же время ответственный метод, требующий беспрекословного соблюдения правил наложения повязки с учетом биомеханики движения костей стопы. Несоблюдение правил гипсования при типичной косолапости и неправильная тактика при гипсовании атипичных стоп приводят к увеличению числа детей, подлежащих большим реконструктивным операциям [24–35].
МАТЕРИАЛЫ И МЕТОДЫ
В клиниках города Ярославля за период с мая 2006 по декабрь 2019 года было пролечено 135 детей (184 стопы) с атипичной косолапостью, что составило 12,1 % от общего числа детей с косолапостью.
В анализ вошли только дети, которых мы пролечили, используя только тактику И. Понсети при атипичной косолапости, что составило 106 детей (147 стоп). Остальные дети, ввиду большого разнообразия стартовых методов лечения и зачастую имевших в анамнезе несколько операций, в анализ не вошли. При атипичной косолапости встречались следующие ассоциации поражения нервной системы и скелета, представленные в таблице 1.
Таблица 1
Ассоциации поражений опорно-двигательной и нервной систем
|
Поражения ОДА и нервной системы |
Дети/стопы |
% |
|
Идиопатическая |
67/76 |
63,3 |
|
Артрогрипоз |
14/28 |
13,2 |
|
Сочетание патологии ЦНС и периферической НС |
10/18 |
9,4 |
|
Амниотические перетяжки |
5/8 |
4,7 |
|
Гемимелии и коалиции |
3/4 |
2,8 |
|
Скелетные дисплазии |
2/4 |
1,9 |
|
Прочие |
5/9 |
4,7 |
|
Всего |
106/147 |
100 |
Итого количество детей с неврологическим дефицитом, артрогрипозом и различными пороками и синдромами, ассоциирующимися с АК, составило 39 человек (71 стопы) или 36,7 % от общего количества первично пролеченных детей с АК по методу И. Понсети.
Возраст начала лечения детей с атипичной косолапостью в клиниках г. Ярославля преобладал с 3 до 12 месяцев, что составило 89 детей (83,9 %). Семьи, как правило, начинали гипсовую коррекцию по месту жительства и, оценивая ситуацию через несколько месяцев от начала терапии, меняли место лечения. Возраст начала лечения в клиниках г. Ярославля представлен в таблице 2.
Таблица 2
Возраст старта лечения в Ярославле детей с АК
|
Возраст на начало лечения |
Кол-во детей |
% |
|
0–3 мес. |
9 |
8,5 |
|
3–6 мес. |
24 |
22,6 |
|
6–12 мес. |
65 |
61,3 |
|
12–36 мес. |
8 |
7,6 |
|
Итого |
106 |
100 |
Отдаленный срок наблюдений в среднем составил 7,2 года. Всем семьям с детьми, пролеченными у нас, предлагались (очно/заочные) осмотры в декре- тированные сроки (табл. 3). При очно/заочных осмотрах на первом году проверялось ношение брейсов, угловые настройки и корректировалось время их ношения. Для оценки эффективности указанной тактики лечения мы использовали три 100-балльные международные шкалы – две шкалы Американского общества хирургов стопы и голеностопного сустава (АО FAS) для заднего и среднего отделов стопы (Midfoot Scale АО, Hindfoot Scale AO) и шкала Laaveg-Ponseti. Детям с атипичными стопами советовалось использовать фиксаторы до 5 лет, а в дальнейшем стрейчинг ахиллова сухожилия на приборе DorsiRamp. Дети с артрогрипозом (учитывая контрактуры вышележащих суставов) чаще не пользовались традиционными брейсами. Их стопы фиксировались в индивидуальных туторах из турбокаста. Периодичность осмотров детей с атипичной косолапостью после курса гипсования: через 2 недели, через 2 месяца, через 4 месяца, далее 1 раз в 3 месяца до 1 года, с 1 года до 5 лет - 2 раза в год, после 5-летнего возраста 1 раз в год до окончания роста.
Таблица 3
|
Варианты лечения |
Количество детей |
|
|
абс. |
% |
|
|
Повторная ахиллотомия |
11 |
13,1 |
|
ПББС. Повторная ахиллотомия |
16 |
19,2 |
|
ПББС. Релиз |
44 |
52,2 |
|
ПББС. Артродез |
10 |
12,1 |
|
ПББС. КДА |
1 |
1,1 |
|
Передний гемиэпифизиодез голеностопного сустава |
2 |
2,3 |
|
Итого |
84 |
100 |
Приводим самые частые причины ошибок лечения атипичной косолапости, встретившиеся в нашей практике, заставившие родителей сменить место лечения ребенка.
Редкость патологии в срезе косолапости, нарушение тактики гипсования (плохое моделирование гипсовой повязки, отсутствие сгибания коленного сустава и, как следствие, соскальзывающие гипсы), невыполнение или слишком раннее выполнение ахиллотомии, несоответствие настройки или модели брейсов и т.д.
Именно по этим вышеуказанным причинам в исторически сформировавшихся центрах лечения косолапости мы видим большое число детей с атипичной косолапостью. Каждый десятый ребенок, лечившийся у нас, потребовал тактики гипсования по типу атипичной. Все вышеперечисленное обусловливает большое количество детей с ятрогенными и врожденными атипичными стопами.
РЕЗУЛЬТАТЫ
Рецидивы, потребовавшие повторного оперативного лечения, встретились у 51 ребенка (83 стопы), что составило 48,1 % от общего количества детей с атипичной косолапостью, полеченных в Ярославле. Всем пролеченным у нас детям с атипичной косолапостью были разосланы анкеты, позволяющие оценить результаты в отдаленном периоде. Часть детей на фоне выявленных рецидивов была прооперирована – 84 ребенка или 79,3 % (см. табл. 3).
Рецидивы атипичной косолапости до 3-х лет лечились с использованием повторного гипсования и ахиллотомии. Транспозиция дистальной инсерции ПББС осуществлялась в возрасте старше 2,5 лет, при условии появления ядра окостенения 3-й клиновидной кости более 5 мм по рентгенограмме. Рецидивы в возрасте от 3 до 6 лет после курса повторного гипсования лечились с использованием различных комбинаций релизов (медиальный, плантарный, задний и, иногда, латеральный). Детям старше 6 лет при одномомент- ной коррекции в реконструкцию стопы, как правило, входил пяточно-кубовидный артродез или клиновидная закрывающая остеотомия кубовидной кости. При коррекции эквинуса на фоне роста использовался однократно аппарат внешней фиксации и у двух детей в подростковом периоде передний гемиэпифизиодез голеностопного сустава с хорошим результатом. Также использовались комбинации вышеуказанных методов.
Из общего пролеченного нами количества детей с АК проведен анализ исходов у 87 пациентов (82 %). Средний срок наблюдения составил 7,2 года.
Как было сказано выше, для оценки эффективности указанной тактики лечения мы использовали три 100-балльные международные шкалы – две шкалы Американского общества хирургов стопы и голеностопного сустава (АО FAS) для заднего и среднего отделов стопы: средние показатели Midfoot Scale АО – 61,2 балла, Hindfoot Scale AO – 58,3 балла, и шкалу Laaveg-Ponseti – средний показатель 65,1 балла.
ДИСКУССИЯ
Незначительное количество атипичной косолапости, по данным литературы, в работе врача не соответствует действительности. Встречаемость косолапости, требующей от врача гипсования с коррекцией кавуса и только потом эквинуса, по нашим наблюдениям, доходит до 10 процентов. При этом метод Понсети в возрасте до 3-х лет при атипичной косолапости остается высокоэффективным и позволяет в большинстве случаев обойтись без больших операций. Исключением являются дети с артрогрипотическими поражениями стоп, где в возрасте 1,5 лет и более приходится дополнять тактику Понсети релизами и, иногда, артродезами. А множественные поражения нижних конечностей осложняют классическую тактику Понсети, приводя к потере коррекции и необходимости повторных курсов гипсования и операциям.
Основными ошибками при лечении атипичной косолапости по И. Понсети были следующие:
-
1) атипичная косолапость в повседневной работе детского ортопеда, при условии средней нагрузки и обслуживании своего региона, встречается не каждый год. Поэтому вероятность ошибки в тактике гипсовой коррекции велика. Ортопед просто не готов к встрече на приеме с данной патологией, что приводит к необходимости смены врача;
-
2) после внедрения метода И. Понсети в повседневную практику врача-ортопеда сменилась классификация врожденной косолапости. И то, что раньше называли атипичной косолапостью, перестало совпадать с тактикой Понсети. Ведь атипичная косолапость по И. Понсети – это ригидная относительно маленькая стопа с выраженным эквинусом заднего отдела и ка-вусом. Первая и вторая причина наблюдались нами у 56 детей / 67 стоп;
-
3) традиционное гипсование в нашей стране, до введения тактики Понсети, предполагало сгибание в коленном суставе до 120–130 градусов. А смена тактики по принципам И. Понсети со сгибанием до 90 градусов в коленном суставе субъективно сложна, и, по мнению
некоторых ортопедов, опасна сосудистыми осложнениями. В связи с этим плохое моделирование гипса и отсутствие сгибания коленного сустава до 90 градусов часто приводит к сползанию гипса и формированию ятрогенной атипичной стопы с выраженным кавусом и ригидным эквинусом. И чем больше ребенок ходит в сползающей гипсовой повязке, тем более ригидной становится деформация (18 детей – 24 стопы).
Оценка проводилась ретроспективно по фото нижних конечностей в гипсах, наложенных по месту жительства. Дети, наблюдаемые нами с атипичной косолапостью, часто с сопутствующим избытком массы и короткой кавусной стопой. Поэтому для хорошей фиксации стопы требуется сгибание коленного сустава до 80–70 градусов (особенно после третьего гипса) и тщательное моделирование гипса от верхней трети бедра до пальцев стопы (рис. 1);
-
4) ортопед, проводя гипсование атипичной косолапости, видя неполную коррекцию, склонен к ранней ахиллотомии (через 3–4 гипса) и после нее получает хорошую тыльную флексию, а, иногда, даже пяточную стопу (рис. 2). Но коррекции кавуса не наступает. При этом стопы получаются короткие, с невыраженным задним отделом и плохо фиксируются брейсами. Это приводит к формированию негативного отношения семьи к брейсам и данной технологии лечения.
Кроме того, отсутствие противоупора натянутого ахиллового сухожилия (после ахиллотомии) по принципу лебедки не позволяет выгипсовать кавус до хорошего сращения ахилла и изменения длины костей голени на фоне роста по отношению к ахиллову сухожилию (13 детей – 19 стоп);
-
5) напротив, невыполненная ахиллотомия при коррекции эквинуса приводит к формированию стопы с косым тараном (рис. 3). А возврат назад и повторный курс гипсования не всегда приводит к исправлению ятрогенной деформации. Бессимптомное плоскостопие зачастую остается (9 детей – 14 стоп);
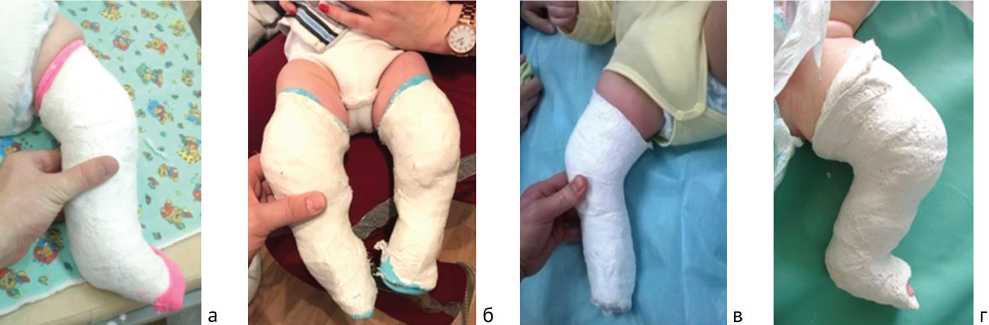
Рис. 1. Примеры гипсования: а–в – по месту жительства без должного сгибания в коленном суставе, приводящие к соскальзыванию гипсовой повязки и формированию ятрогенной атипичной косолапости; г – требуемое положение коленного сустава при гипсовании атипичной косолапости
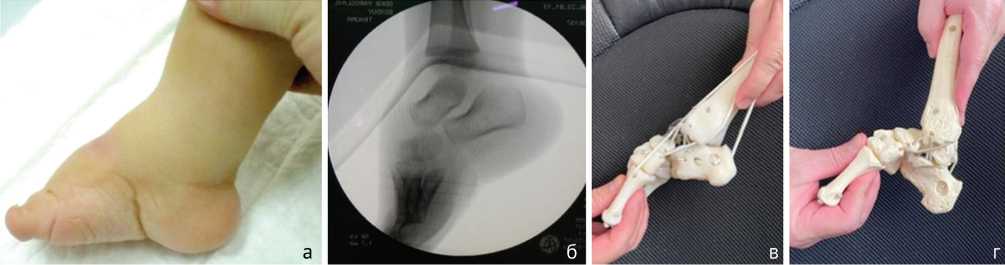
Рис. 2.: а – эквинус и кавус до операции; б – ЭОП-контроль до оперативного лечения, демонстрирующий кавус и эквинус; в – муляж состояния костей стопы после ранней ахиллотомии, до коррекции кавуса; г – внешний вид стопы после выполнения ахиллотомии без коррекции кавуса. Виден выраженный задний отдел стопы при глубокой поперечной подошвенной складке
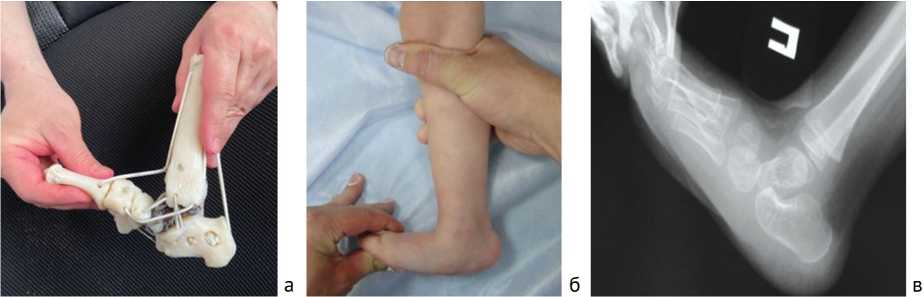
Рис. 3. Попытка исправить деформацию стопы без ахиллотомии: а – муляж; б – внешний вид стопы; в – рентгенологическая картина
-
6) неполная коррекция эквинуса при моделировании гипса (стопа в нейтрали по отношению к голени, а требуется 15–20 градусов тыльной флексии) после ахиллотомии приводит к отсутствию тыльной флексии, что ведет в дальнейшем к плохой фиксации стопы в брейсе. А частое соскальзывание ботинка ведет к рецидиву и дискредитации метода И. Понсети;
-
7) первично лечение косолапости по И. Понсети начинается в возрасте до 1 месяца. При этом за счет незрелой нервной системы мы не видим отклонений формирования, кроме грубых пороков развития. Но на фоне роста иногда ставятся следующие диагнозы: ДЦП, парезы периферической нервной системы, амниотические перетяжки, гемимелии, тарзальные коа-
- лиции, различные по топике объему и характеру, различные синдромы, зачастую не верифицированные (20 детей – 43 стопы от общего числа детей);
-
8) несоответствие брейсов или их настройки по форме стоп после предварительно хорошей гипсовой коррекции при АК. Отведение брейсов при атипичной косолапости должно быть 40 градусов, а не 60–70, как при типичной. А ботинок, предназначенный для фиксации атипичной косолапости, должен быть с силиконовой вкладкой, идеально облегающий стопу после курса гипсования, желательно также использование «седла давления», равномерно распределяющего давление среднего ремешка на кожу передней поверхности голеностопного сустава. При
недостаточно качественной фиксации кожа стопы мацерируется, появляются намины и пролежни. Это ведет к нарушению режима ношения брейсов, а это, в свою очередь, на фоне роста приводит к рецидиву (9 детей / 16 стоп);
-
9) отдельную группу занимают пациенты с артро-грипотической косолапостью – 14 детей (28 стоп). Деформация стоп при данном диагнозе ригидна, как правило, с выраженным кавусом и эквинусом, быстро рецидивирует в процессе роста. А в случае множественного поражения нижних конечностей исправление контрактур коленных суставов мешает коррекции эквинуса, а оперативное вправление тератогенных вывихов головки бедра с последующей длительной иммо-
- билизацией еще быстрее приводит к потере коррекции стоп и необходимости повторной коррекции.
Существующие международные шкалы Midfoot Scale АО, Hindfoot Scale AO и Laaveg-Ponseti оценки позволяют проанализировать отдаленные результаты лечения атипичной косолапости после применения метода Понсети и объективно охарактеризовать эффективность методики гипсования.
Отдаленные наблюдения детей с атипичной косолапостью, оцененные по международным шкалам оценки АО и Laaveg-Ponseti, свидетельствуют об эффективности метода Понсети в ближайшем послеоперационном периоде, но на фоне роста демонстрируют потерю коррекции, требующую активной хирургической тактики.
ЗАКЛЮЧЕНИЕ
Метод Понсети в России является «золотым стандартом» для лечения косолапости. Гипсовая коррекция при врожденной косолапости является высокоэффективной, но при атипичной косолапости требует от ортопеда внимательного отношения и своевременного выявления данной патологии из общего «потока» детей с деформациями стоп. Соблюдение тактики гипсовой коррекции и ношение необходимых моделей брейсов позволяет эффективно лечить и осуществлять корреляцию у детей с атипичной косолапостью. Но при наличии сопутствующей патологии в половине случаев требуются повторные курсы лечения, включающие все имеющиеся в арсенале хирурга методы.
Список литературы Отдаленные результаты лечения атипичной косолапости по методу Понсети
- Кузнечихин Е.П., Ульрих Э.В. Хирургическое лечение детей с заболеваниями и деформациями опорно-двигательной системы. М. : Медицина, 2004. 566 с.
- Ревкович А.С., Рыжиков Д.В., Садовой М.А. Эквино-варо-аддукционная деформация стоп у детей (опыт лечения 228 пациентов) // Современные проблемы науки и образования. 2017. № 6. С. 66. URL: https://elibrary.ru/item.asp?id=32390346 (дата обращения: 12.11.2019).
- Davies T.C., Kiefer G., Zernicke R.F. Kinematics and kinetics of the hip, knee, and ankle of children with clubfoot after posteromedial release // I. Pediatr. Orthop. 2001. Vol. 21, No 3. P. 366-371.
- Swann M., Lloyd-Roberts G.C., Catterall A. The anatomy of uncorrected club feet. A study of rotation deformity // J. Bone Joint Surg. Br. 1969. Vol. 51, No 2. P. 263-269.
- Ponseti I.V., Smoley E.N. Congenital Club Foot: The Results of Treatment // Iowa Orthop. J. 1984. Vol. 4. P. 24-33.
- A radiographic study of skeletal deformities in treated clubfeet / I.V. Ponseti, G.Y. El-Khoury, E. Ippolito, S.L. Weinstein // Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1981. No 160. P. 30-42.
- Dimeglio A. Classification of talipes equinovarus // The Clubfoot: the present and a view of the future. Simons G.W., editor. New York: SpringerVerlag. 1994. P. 92-93.
- Hee H.T., Lee E.H., Lee G.S. Gait and pedobarographic patterns of surgically treated clubfeet // J. Foot Ankle Surg. 2001. Vol. 40, No 5. P. 287-294. DOI: 10.1016/s1067-2516(01)80064-8.
- Hosseinzadeh P., Kelly D.M., Zionts L.E. Management of the Relapsed Clubfoot following Treatment using the Ponseti Method // J. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. 2017. Vol. 25, No 3. P. 195-203. DOI: 10.5435JAAOS-D-15-00624.
- Ponseti I.V., Campos J. Observations on pathogenesis and treatment of congenital clubfoot // Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1972. Vol. 84. P. 50-60. DOI: 10.1097/00003086-197205000-00011.
- The role of collagen in the pathogenesis of idiopathic clubfoot. Biochemical and electron microscopic correlations / V. Ionasescu, J.A. Maynard, I.V. Ponseti, H. Zellweger // Helv. Paediatr. Acta. 1974. Vol. 29, No 4. P. 305-314.
- Ponseti I.V. Treatment of congenital club foot // J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 1992. Vol. 74, No 3. P. 448-454.
- Pirani S., Zeznik L., Hodges D. Magnetic resonance imaging study of the congenital clubfoot treated with the Ponseti method // J. Pediatr. Orthop. 2001. Vol. 21, No 6. P. 719-726.
- Long-term comparative results in patients with congenital clubfoot treated with two different protocols / E. Ippolito, P. Farsetti, R. Caterini, C. Tudisco // J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 2003. Vol. 85, No 7. P. 1286-1294. DOI: 10.2106/00004623-200307000-00015.
- Huber H., Dutoit M. Dynamic foot-pressure measurement in the assessment of operatively treated clubfeet // J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 2004. Vol. 86, No 6. P. 1203-1210. DOI: 10.2106/00004623-200406000-00012.
- Cooper D.M., Dietz F.R. Treatment of idiopathic clubfoot. A thirty-year follow-up note // J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 1995. Vol. 77, No 10. P. 14771489. DOI: 10.2106/00004623-199510000-00002.
- Morcuende J.A., Egbert M., Ponseti I.V. The effect of the internet in the treatment of congenital idiopathic clubfoot // Iowa Orthop. J. 2003. Vol. 23. P. 83-86.
- Soft-Tissue Abnormalities associated with Treatment-Resistant and Treatment-Responsive Clubfoot: Findings of MRI Analysis / D.K. Moon, C.A. Gurnett, H. Aferol, MJ. Siegel, P.K. Commean, M.B. Dobbs // J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 2014. Vol. 96, No 15. P. 1249-1256. DOI: 10.2106/JBJS.M.01257.
- Noonan K.J., Richards B.S. Nonsurgical management of idiopathic clubfoot // J. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. 2003. Vol. 11, No 6. P. 392-402. DOI: 10.5435/00124635-200311000-00003.
- The Effectiveness of the Ponseti Method for Treating Clubfoot associated with Amniotic Band Syndrome / A.M. Carpiaux, P. Hosseinzadeh, R.D. Muchow, HJ. Iwinski, J.L. Walker, T.A. Milbrandt // J. Pediatr. Orthop. 2016. Vol. 36, No 3. P. 284-288. DOI: 10.1097/BPO.0000000000000444.
- Matar H.E., Beirne P., Garg N.K. Effectiveness of the Ponseti method for treating clubfoot associated with myelomeningocele: 3-9 years follow-up // J. Pediatr. Orthop. B. 2017. Vol. 26, No 2. P. 133-136. DOI: 10.1097/BPB.0000000000000352.
- Flexor digitorum accessorius longus muscle in resistant clubfoot patients: introduction of a new sign predicting its presence / S. Shaheen, H. Mursal, M. Rabih, A. Johari // J. Pediatr. Orthop. B. 2015. Vol. 24, No 2. P. 143-146. DOI: 10.1097/BPB.0000000000000129.
- Laaveg S.J., Ponseti I.V. Long-term results of treatment of congenital club foot // J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 1980. Vol. 62, No 1. P. 23-31.
- Treatment of complex idiopathic clubfoot using the modified Ponseti method: up to 11 years follow-up / H.E. Matar, P. Beirne, C.E. Bruce, N.K. Garg // J. Pediatr. Orthop. B. 2017. Vol. 26, No 2. P. 137-142. DOI: 10.1097/BPB.0000000000000321.
- The Timing and Relevance of Relapsed Deformity in Patients with Idiopathic Clubfoot / S.N. Sangiorgio, E. Ebramzadeh, R.D. Morgan, L.E. Zionts // I. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. 2017. Vol. 25, No 7. P. 536-545. DOI: 10.5435JAAOS-D-16-00522.
- Ponseti I.V. Congenital clubfoot: Fundamentals of treatment. 1st Ed. Oxford University Press. 1996. 140 p.
- De Mulder T., Prinsen S., Van Campenhout A. Treatment of non-idiopathic clubfeet with the Ponseti method: a systematic review // J. Child. Orthop. 2018. Vol. 12, No 6. P. 575-581. DOI: 10.1302/1863-2548.12.180066.
- Shah A., Aroojis A., Mehta R. The Ponseti method of treatment for neuromuscular and syndromic (non-idiopathic) clubfeet: evaluation of a programme-based approach at a mean follow-up of 5.8 years // Int. Orthop. 2021. Vol. 45, No 1. P. 155-163. DOI: 10.1007/s00264-020-04677-9.
- The center of pressure path in treated clubfeet / R.A. Brand, SJ. Laaveg, R.D. Crowninshield, I.V. Ponseti // Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1981. No 160. P. 43-47.
- The effect of inturning of the foot on knee kinematics and kinetics in children with treated idiopathic clubfoot / C. Beyaert, T. Haumont, J. Paysant, P. Lascombes, J.M. Andre // Clin. Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2003. Vol. 18, No 7. P. 670-676. DOI: 10.1016/s0268-0033(03)00114-1.
- Gait analysis in children with severe clubfeet: early results of physiotherapy versus surgical release / L.A. Karol, S.E. O'Brien, H. Wilson, C.E. Johnston, B.S. Richards // J. Pediatr. Orthop. 2005. Vol. 25, No 2. P. 236-240. DOI: 10.1097/01.bpo.0000150815.56790.b0.
- Ponseti I.V. Common errors in the treatment of congenital clubfoot // Int. Orthop. 1997. Vol. 21, No 2. P. 137-141. DOI: 10.1007/s002640050137.
- Radical reduction in the rate of extensive corrective surgery for clubfoot using the Ponseti method / J.A. Morcuende, L.A. Dolan, F.R. Dietz, I.V. Ponseti // Pediatrics. 2004. Vol. 113, No 2. P. 376-380. DOI: 10.1542/peds.113.2.376.
- Turco V. Recognition and management of the atypical idiopathic clubfoot // The Clubfoot: The Present and a View of the Future. Simons G.W., editor. New York: Springer-Verlag. 1994. P. 76-77.
- Van Bosse H.J.P. Challenging clubfeet: the arthrogrypotic clubfoot and the complex clubfoot // J. Child. Orthop. 2019. Vol. 13, No 3. P. 271-281. DOI: 10.1302/1863-2548.13.190072.


