Отслеживание состояния целеориентированного диалога на основе БЕРТ
Автор: Гуляев П.А., Елистратова Е.А., Коновалов В.П., Куратов Ю.М., Пугачев Л.П., Бурцев М.С.
Журнал: Труды Московского физико-технического института @trudy-mipt
Рубрика: Информатика и управление
Статья в выпуске: 3 (51) т.13, 2021 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Отслеживание состояния диалога (Dialogue State Tracking) является одним из ключевых компонентов виртуальных помощников, таких как Alexa или Siri. Для выполнения различных задач этим помощникам необходимо поддерживать всё большее количество сервисов и API. В этой работе мы представляем систему отслеживания целеориентированного диалога с помощью языковой модели BERT с использованием методов обучения понимания вопросно-ответных систем. На вход модель принимает историю диалогов с описанием выделяемых полей и сервисов, а также возможными значениями полей. Языковая модель позволяет переиспользовать информацию о выделяемых слотах в мультидоменных диалогах и масштабироваться на выделение полей, не участвовавших в процессе обучения. Наша модель достигает общей целевой точности 53,97% для набора данных SGD, что превосходит базовую модель.
Диалоговые системы, состояние диалога, интенты, слоты, берт
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/142231492
IDR: 142231492 | УДК: 004.891.3 | DOI: 10.53815/20726759_2021_13_3_48
Текст научной статьи Отслеживание состояния целеориентированного диалога на основе БЕРТ
Появление на рынке таких виртуальных помощников, как Яндекс Алиса, Amazon Alexa и Google Assistant, подтолкнуло разработчиков к созданию дополнительных возможностей по взаимодействию с их приложениями (интерфейсов) на. естественном языке. Такие услуги, как заказ такси или бронирование столика, теперь возможно осуществлять через диалог с виртуальным помощником. Отслеживание состояния диалога (Dialogue State Tracking -DST) является ключевым компонентом в таких системах. DST отвечает за. перевод высказываний на естественном языке в семантическое представление языка, в частности,
«Московский физико-технический институт (национальный исследовательский университет)», 2021
за извлечение намерений (intents) и пар (слот, значение), соответствующих цели пользователя. Например, если целью пользователя является заказ такси (intent: OrderTaxi), то слотами могут быть адрес, число_пассажиров и многие другие. Для разработки целеориентированных диалоговых систем было выпущено большое количество диалоговых корпусов NegoChat [1], ATIS [4] и многие другие. Однако однодоменные наборы данных (все диалоги, набор данных в которых представлен одной темой) не отображают реальную картину мира, где диалог может вращаться вокруг разных доменов.
Разработка корпуса мультидоменных диалогов (Multi-WOZ) поставила новые задачи перед системами DST [5]. Этот набор данных содержит диалоги, в которых домен диалога изменяется в течение диалога. Например, пользователь может начать диалог, попросив забронировать ресторан, а затем попросить заказать такси до ресторана. В этом случае DST должен определять домен, слот и соответствующее значение после каждой реплики пользователя с учетом истории разговора, если это необходимо.
Google представила новый и наиболее крупный на данный момент корпус диалогов Schema-Guided Dialogue (SGD) [13]. Он содержит более 16 000 диалогов в обучающей выборке, охватывающих 26 сервисов (сервис объединяет в себе несколько однотипных целей), принадлежащих 16 доменам. Для того, чтобы измерить способность модели к адаптации под новые домены, тестовые наборы содержат сервисы и домены, которых не было в тренировочной выборке.
Для каждого сервиса, представленного в диалогах, в SGD предоставляется схема, дающая краткие описания сервиса, всех его слотов и намерений (интентов) на естественном языке. Состояние каждого диалога состоит из трех полей: текущее намерение (actin e_intent), запрашиваемые слоты (requested_ slots) и значения слотов (slot_values). SGD предлагает при предсказании состояния диалога, распознавать и использовать семантику представленных описаний целей и слотов. Таким образом обеспечивается обобщение на новые схемы, не участвовавшие в процессе обучения. Авторы также предложили базовую модель DST для всех сервисов и API, обеспечивающую общую точность 41,1% (при обучении и оценке на всем наборе данных) и 48,6% точности (при обучении и оценке на однодоменных диалогах) [13]. Предложенная модель кодирует намерения, слоты и значений слотов, введенных в схему, в векторное представление. Этот подход имеет следующий недостаток - представления должны быть рассчитаны заранее с использованием BERT в качестве кодировщика. Так как этот кодировщик не участвует в процессе обучения, векторные схемы не подлежат обучению.
Для отслеживания состояния диалога мы предлагаем модель GOLOMB (GOaL-Oriented Multi-task BERT-based dialogue state tracker) [2] - целеориентированная мультизадачная модель на базе BERT. GOLOMB была сделана на основе современных вопросноответных нейронных архитектур с применением BERT [6]. При таком подходе, получая на вход текст и вопрос по нему, модель учится выделять подстроку в тексте как ответ на заданный вопрос. Мы переформулировали эту задачу для отслеживания состояния диалога. Мы используем историю диалога как текст, по которому задаётся вопрос. ‘Вопросом’ является описание домена, слота и интента, для которых мы ищем ‘ответ’ - значение слота, представленное в истории диалога. Для предсказания состояния диалога наша мультизадачная модель решает несколько классификационных задач и задачу поиска подстроки. Для каждой задачи существует свой классификатор, реализованный как полносвязный слой нейронной сети без функции активации. Такой подход позволяет одновременно обучаться на информации из истории диалогов и схемы, описывающих выделяемые значения. Наш подход устойчив к изменениям в схеме и не требует дообучения модели для новых намерений и слотов. Кроме того, наша модель не требует предварительно рассчитанного векторного представления схемы. Наш подход превосходит базовую модель по основной метрике общая целевая точность (joint goal accuracy), достигая 53.97% на валидационных данных.
2. Цель исследования
Основной задачей данного исследования было получить качество модели на метрике joint goal accuracy для всего датасета (SGD-A11) выше, чем качество, которое выдавало базовое решение. Общая целевая точность базовой модели составляет 41.1%.
3. Обзор решений
Главной задачей отслеживания состояния диалога является выделение слотов, их значений, а также намерений пользователей, в зависимости от которых пользователь упоминает те или иные слоты. Пары слотов и их значений формируют состояние диалога. Состояние диалога в дальнейшем используется в качестве значений аргументов для вызова внешних API или как условия для выбора следующего действия диалоговой системы. Классические системы отслеживания состояния диалога комбинировали семантику, извлеченную системой распознавания естественного языка с контекстом предыдущих реплик для оценки текущего состояния диалога [7], [8], [9] или совместно обучали системы распознавания речи и отслеживания состояния диалога [10], [15].
В ранних задачах по отслеживанию состояния диалога, таких как DSTC2 или WoZ, требовалось выделять состояние диалога только из одного домена, т.е. диалог мог вестись только на одну заранее заданную тему. В то же время в этих задачах были известны все возможные значения всех слотов - они задавались в онтологии. Таким образом, задача системы отслеживания состояния диалога сводилась к перебору и выбору нужных пар слот-значение. Модели, предложенные для решения этих задач, были сильно привязаны к онтологии источников данных и не имели возможности быстрой адаптации к новым доменам данных. Так, например, в работе [16] использовалось обучение представлений слов независимо для каждой пары слот-значение.
Ранее обнаружили, что в датасете WoZ в 38.6% реплик появляются значения, которые имеют менее 20 упоминаний по всей обучающей выборке, таким образом для многих слотов не хватает данных для обучения, что сильно снижает joint goal accuracy [17]. Для решения этой проблемы в предложенной модели GLAD (Global-Locally Self-Attentive Dialogue State Tracker) было добавлено использование общих параметров для всех слотов. Таким образом, информация, извлеченная из одних слотов, используется при обучении других слотов, что улучшает качество отслеживания состояния и даёт возможность работы с мультидоменными диалогами. Тем не менее модель использовала общие для всех слотов параметры, так и параметры, обучаемые индивидуально для каждого слота.
С развитием технологий отслеживания состояния диалога, была поставлена более сложная задача на новых данных - MultiWoZ. В ней системе необходимо выделять состояние из диалогов, в которых пользователь может переключаться между доменами или даже упоминать несколько доменов одновременно. С ростом числа возможных слотов и их возможных значений перебор всех пар становился трудозатратным, а обучение специфичных для слотов значений менее эффективным. Усовершенствованная версия GLAD - GCE (Globally-Conditioned Encoder), модель, в которой все параметры распространялись между всеми слотами, превзошла предыдущую модель на задачах WoZ и MultiWoZ [18]. А модель StateNet, которая формирует представление истории диалога, основанного на последнем высказывании пользователя и действии системы, определяет близость этого представления к предлагаемому значению слота из множества возможных кандидатов [19].
В [20] формируется представление истории диалога с помощью иерархической LSTM, после чего объединяются подходы независимого выбора значения слота из числа предлагаемых кандидатов и выбора значения слота из всех значений этого слота, обозначенных в обучающей выборке.
Проблемой большинства представленных выше моделей является необходимость наличия словаря со всеми поддерживаемыми моделью значениями: модели не способны выделить значения вне словаря. В [21] предложили модель PtrNet, использующую сеть указа- телей на основе индексов (index-based pointer) для различных слотов, позволяющую обрабатывать значения вне словаря. А в [12] отслеживали состояние диалога с помощью biGRU кодировщика и декодировщика. Кодировщик делал векторное представление для каждого токена во всей истории диалога. Декодировщик генерировал значение слота, используя soft-copy механизм, объединяющий внимание на историю диалога и выбор значения из словаря. Также авторами были исследованы возможности применения zero и few-shot обучения для отслеживания состояния диалогов на доменах, которых не были или почти не были представлены в обучающей выборке.
Для эффективной работы с неизвестными значениями и использования подходов без обучающих примеров подходят предобученные языковые модели, где BERT является одной из самых распространённых архитектур. В [11] адаптировали BERT для работы с отслеживанием состояния диалога: модель предсказывала начальный и конечный токен значения для каждого слота.
4. Модель
В данном разделе представлено детальное описание предлагаемой модели GOLOMB. Архитектура модели представлена на рис. 1.
На вход модели подаётся описание слота и его домена, далее следует история диалога, описание возможных намерений пользователя и возможные значения для категориального слота. BERT-кодировщик преобразует входную последовательность в контекстные представления на уровне предложений и токенов. Эти представления затем подаются в следующие выходные классификаторы для специализированных задач:
-
1) Классификаторы:
-
• Классификатор намерений (intent classifier). Предсказывает активные намерения.
-
• Классификатор требуемых слотов (requested slot gate). Предсказывает список требуемых слотов в этой реплике.
-
• Классификатор наличия слота (slot gate). Предсказывает, будет ли слот представлен в контексте.
-
• Классификатор категориальных слотов (categorical slot filler). Предсказывает слот, выбирая самый вероятный из списка предсказанных.
2) Выделение подстроки в тексте:
4.1. Описание онтологии используемых данных
е Заполнитель слотов подстроками из текста (free-form slot filler). Предсказывает значение слота, находя нужную подстроку в тексте.
Каждый классификатор реализован как полносвязный слой без функций активаций.
Состояние целеориентированного диалога - это представление выделенных целей пользователя. Состояние диалога используется для того, чтобы определить релевантный сервис для удовлетворения целей пользователя и определить параметры запуска этого сервиса исходя из запросов пользователя. В общем случае состояние диалога состоит из трех полей: активные намерения (acti-ue intents), требуемые слоты (requested slots), и их значения (slot -values).
Диалог в наборе данных SGD представлен последовательностью реплик Пользователя и Системы. Каждая пара реплик Пользователь-Система организована в фреймы, где каждый фрейм соответствует одному сервису. Для каждого сервиса в соответствующем фрейме поддерживается отдельное состояние диалога. Параметр обновление состояние (state update) определяется как разница между значениями слота, присутствующими в текущем сервисном фрейме, и фрейме для того же сервиса, но для предыдущего полвзователвского высказывания. Задача - прогнозирование обновления состояния.
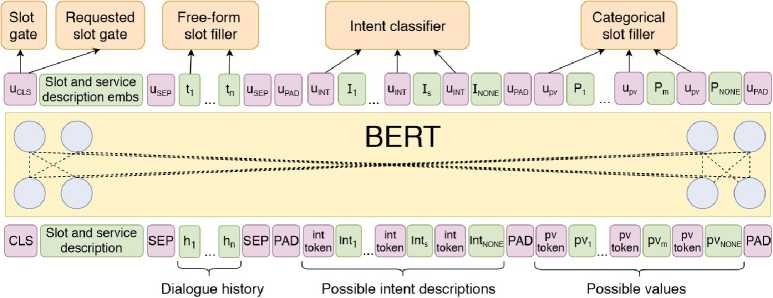
Рис. 1. Архитектура, модели GOLOMB. Классификатор slot gate решает, должен ли слот попасть в обновлённое состояние диалога. Requested slot gate предсказывает, был ли слот запрошен пользователем. Классификатор intent classifier выбирает активное намерение (intent) пользователя. В зависимости от того, является ли слот категориальным или пекатегориальпым, используются различные классификаторы. Для пекатегориалыюго слота, используется free-form slot filler, который выбирает позиции начала и конца, значения слота, в истории диалога. Для категориального слота, categorical slot filler выбирает значение слота, среди представленных возможных значений
Входные значение BERT
За основу мы взяли модель BERT, обученную отвечать на вопросы (SQuAD) [14], который состоит из вопроса, и контекста. В нашем случае контекст - это история диалога, а вопрос - это конкатенация описаний слотов и доменов. В табл. 1 показан шаблон, по которому составляются входные данные.
В качестве входных значений для BERT передаются [CLS [-токен, затем конкатенация слота и описание домена с историей диалога (текущая реплика пользователя с предшествующей ей репликой системы), разделенные специальным токеном [SEP ]. Далее мы дополняем вход токенами [PAD] пока не достигнем значения таж_ hist_ len (по умолчанию max_hist_len = 250). Далее добавляем описание всех возможных используемых намерений, разделяя значения токеном [int]
Затем, если слот категориальный, мы перечисляем все возможные значения этого слота ри^ , 1 Д к Д mau_num_cat_slot_uaLues = 11. разделяя зшгчепия токеном [ри]. Также к намерениям и категориальным слотам добавляется дополнительное значение NONE, на случай, если слот или интент не представлены в данной реплике. Вся сформированная строка кодируется с помощью BERT и результаты передаются на вход различным классификаторам (см. рис. 1).
Таблица!
Компоненты входной последовательности для GOLOMB
Вопрос Контекст Возможные намерения Возможные значения слота
Описания слота и сервиса История диалога
Описания всех возможных намерений для данного сервиса Возможные значения слотов (только для категориальных слотов)
Классификаторы GOLOMB
Пусть Д - полносвязная сеть, ж - выход BERT. Все выходы выполняют линейное преобразование соответствующих эмбеддингов. ж - вектор из Rn, am- произвольное поло- жительное целое число. Тогда, выход при Т, Тт,т : R” ^ Rm превращает ж в вектор предсказаний у Е Rm:
Тт,т (ж) = У, (1)
где Тт,т ~ полносвязный слой без функции активации.
^Г,т(ж) = \¥т,тХ + Ьт,т. (2)
Классификатор наличия слота
Прогнозирование состояния диалога происходит в два этапа. Сперва для каждого слота данного сервиса происходит предсказание статуса слота. Если статус слота спрогнозирован как попе, то значение этого слота в состоянии диалога не изменяется. Если предсказание dontcare, тогда этому слоту назначается специальное значение dontcare. Иначе, мы переходим ко второму этапу, на котором происходит предсказание значения слота. Статус слота прогнозируется сетью Tstatus применительно к [CLS ]-токену. Логиты Zstatus нормализуются при помощи софтмакс для того чтобы получить вероятностное распределение трех возможных статусов. Наиболее вероятный статус считается активным.
1 status — 7status,3(uCLS ). (Ч
Значения слотов в состоянии диалога представлены в виде массива (list). Для категориальных слотов этот массив имеет только одно значение (значение из схемы). Вариативность значения слота допускается для некатегориальных слотов.
Классификатор категориальных слотов
Для прогнозирования значений категориальных слотов применяется полносвязная сеть к каждому возможному эмбеддингу значения слота upv, чтобы получить логит:
lposval = ^cat_slot,1(upv ), 1 < 3 < т + 1, (4)
где т - максимальное число возможных значений категориального слота. Дополнительное значение соответствует значению NONE. Вычисленные логиты объединяются в вектор и нормализуются с помощью softmax-преобразования для получения распределения по всем возможным значениям.
Заполнитель слотов подстроками из текста
Чтобы получить интервал для некатегориального значения слота, мы прогнозируем распределение начала и конца интервала по представлениям токенов ti истории диалога:
lstart = Тstart,l^^i), 1< ^ < п, (5)
lstop = ^stop,1(tj ), 1< 3< И, ( 6)
где и - размер скрытого состояния (обычно 384 или 512, как требуется для входа BERT).
Классификатор требуемых слотов
Это слоты, значения которых запрашиваются пользователем в текущей реплике. Является ли слот требуемым или нет определяется с помощью применения Treq siot к [CLS ] токену. Полученные логиты нормализуются для получения метрики в пределах [0,1]. Во время прогнозирования все слоты с оценкой больше 0.5 считаются требуемыми.
lreq_slot — Treq_slot,2(uC LS ). (7)
Классификатор намерений
Активные намерения - это намерения, соответствующие текущей реплике. Чтобы предсказать активное намерение пользователя для данного сервиса, мы применяем полностью связанный слой к каждому эмбеддингу Uint, а затем получаем распределение вероятностей при помощи софтмакс:
intent — ^intent,1 ('Hint'), 1< j < S + 1,
где s - число возможных интентов плюс значение NONE.
5. Настройка экспериментов5.1. Набор данных Schema-Guided Dialogue
Т а б л и ц а 2
Информация о количестве некоторых параметров датасета для Schema-Guided-Dataset (SGD)
|
Тренировочные/Валидационные |
|||
|
Однодоменные |
Мультидоменные |
Смешанные |
|
|
диалогов |
5 403/836 |
10 739/1646 |
16 142/2482 |
|
реплик |
82 588/11 928 |
247 376/36 978 |
329 964/48 726 |
|
слотов |
201/134 |
214/132 |
214/136 |
|
доменов |
14/16 |
16/15 |
16/16 |
|
сервисов |
24/17 |
26/16 |
26/17 |
|
намерений |
35/28 |
37/26 |
37/28 |
Мы используем набор диалоговых данных Schema-Guided Dialogue (SGD) для демонстрации качества нашей модели. Это крупнейший общедоступный мультидоменный корпус. SGD включает в себя 34 сервиса, принадлежащих 16 различным доменам, с более чем 18 000 диалогов (общее количество для обучающей и валидационной выборки).
Набор данных состоит из однодоменных и мультидоменных диалогов. Однодоменный диалог предполагает взаимодействие только с одним сервисом, мультидоменный диалог имеет взаимодействие с двумя или более различными сервисами. В табл. 2 иллюстрируется статистика набора данных.
Авторы SGD также предложили онтологический (schema-guided) подход для мультидоменного целенаправленного диалога. Онтология определяет интерфейс для внутреннего API как список пользовательских намерений и слотов, а также их описание на естественном языке. Каждый диалог в наборе данных отслеживается одной или несколькими схемами, относящимися к диалогу (одна схема соответствует одному сервису). Модель будет использовать схему сервиса в качестве входных данных для создания прогнозов относительно намерений и слотов, перечисленных в схеме. Описания слотов и намерений на естественном языке позволяют модели обрабатывать новые сервисы.
5.2. Обучение
Мы используем предварительно обученную модель BERT (bert-large-cased-whole-word-masking-f inetuned-squad) с 24 слоями размерностью 1024, 16 головами self-attention и 340 миллионами параметров. Мы обновляем параметры модели, используя алгоритм оптимизации Adam с weight decay [23]. Начальный коэффициент обучения (learning rate) оптимизатора модели 3.5е — 5. Мы обучаем модель на 5 эпохах с размерами батча 8 и шагом обновления градиента (gradient accumulation step) равным 12 на графическом процессоре Tesla V100 32GB. Наша реализация модели основана на семействе моделей трансформеров из библиотеки HuggingFace [24]. Во время обучения, мы получаем значительное количество примеров, когда слот не присутствует в обновлении состояния, и модель должна предсказать либо пустую подстроку, либо значение NONE. Эти примеры (мы называем их «отрицательными») заставляют модель делать константные прогнозы. Чтобы смягчить эту проблему, мы вводим cat_ neg_ sampling _prob (по умолчанию 0.1) и noncat_neg_ sampling _prob (по умолчанию 0.2) - вероятности генерации «пустых» значений примеров для категориальных и некатегориальных слотов соответственно. Кроме того, количество некатегориальных примеров значительно преобладает над количеством категориальных. Мы решаем проблему классового дисбаланса, делая отдельные батчи для категориальных и некатегориальных примеров.
6. Метрики качества
Для оценки задачи отслеживания состояния диалога были использованы следующие метрики:
• Active Intent Accuracy: Часть пользовательских реплик, для которых было правильно предсказано активное намерение.
• Requested Slot Fl: Макро-усреднённое (macro-averaged) Fl для запрашиваемых пользователем слотов на всех репликах.
• Average Goal Accuracy: Для каждой реплики пользователя модель предсказывает одно значение для каждого слота, присутствующего в состоянии диалога. Слоты, которые имеют непустое значение в истинных метках диалога, используются для подсчета точности - средней точности правильного предсказания значения слота. Для некатегориальных слотов используется приближённое совпадение, чтобы поощрять модель за частичные совпадения с разметкой диалога.
• Joint Goal Accuracy: Это средняя точность правильного предсказания сразу всех значений слотов для одной реплики.
7. Эксперименты и результаты
Результаты оценки показаны в табл. 3. Сравнение между нашей моделью и базовой моделью [13] по метрике Joint Goal Accuracy приведено на рис. 2.
Т а б л и ц а 3
Сравнение качества между базовой моделью и нашей моделью на валидации и на тесте
|
Active Int Асе |
Req Slot Fl |
Avg GA |
Joint GA |
|
|
GOLOMB, качество на валидации |
0.660 |
0.969 |
0.817 |
0.539 |
|
Базовая модель, качество на валидации |
0.908 |
0.973 |
0.740 |
0.411 |
|
GOLOMB, качество на тесте |
0.747 |
0.971 |
0.750 |
0.465 |
Как видно из табл. 3, наша модель превосходит базовую модель по joint и average goal accuracy, но базовая модель показывает лучшие результаты на requested slot Fl и active intent accuracy. Возможная причина значительного превосходства базовой модели в определении активных намерений заключается в том, что базовая модель использует выход [CLS ] токена для предсказания намерения. Мы тоже пытались использовать выход токена [CLS ] для классификации намерений, и это приводило к улучшению точности определения намерений. Однако в этой модели основная метрика - joint goal accuracy - ухудшалась.
На рис. 2 показано сравнение между GOLOMB и базовой моделью по joint goal accuracy и average goal accuracy. Наша модель показывает лучшую производительность на каждом домене по joint goal accuracy. Наиболее близкие оценки соответствуют домену Events, где обе модели показали хорошую точность, что связано с большим количеством обучающих диалогов в данном домене. Наибольшая разница наблюдается у домена Services, где GOLOMB показал значительное превосходство. Тем не менее лучший результат был достигнут на домене Banks, сервисы которого не были представлены в обучающей выборке.
■ GOLOMB Joint Goal
GOLOMB Average Goal
C Baseline Joint Goal
Baseline Average Goal
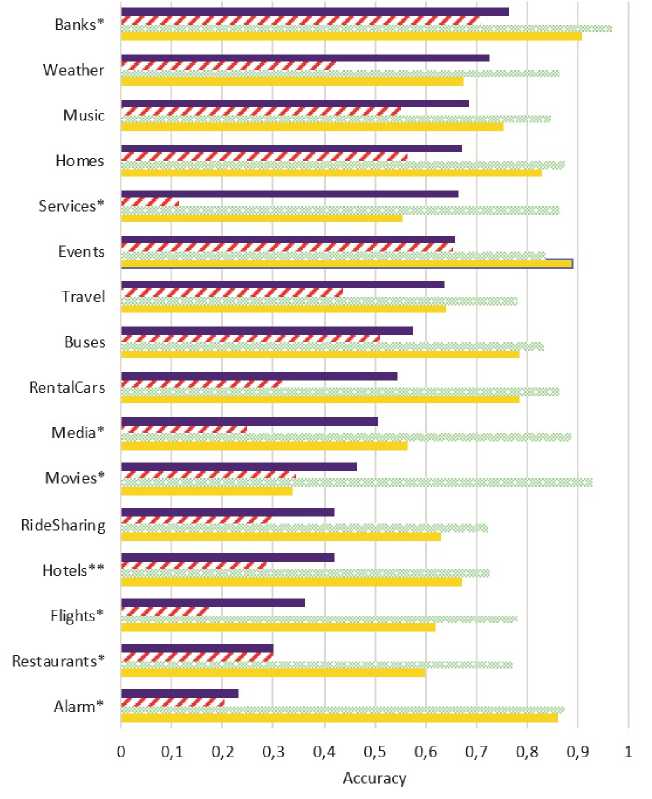
Рис. 2. Сравнение качества, для каждого домена, по joint goal accuracy и average goal accuracy между базовой моделью и нашей моделью. Знак ’*’ обозначает домен, сервисы которого содержатся в тестовой выборке, по не содержатся в тренировочной, ’**’ обозначает домен, один сервис которого модель видела, в тренировочных данных, а. второй - пет. Все сервисы остальных доменов содержатся в тренировочных данных
На. домене Alarm модель демонстрирует худшую оценку joint goal accuracy, однако также она. демонстрирует относительно хорошую среднюю точность. Наиболее вероятным объяснением первого результата, является то, что во время обучения модель не видела, примеров из этого домена. Кроме того, высокая средняя точность сигнализирует о том, что есть несколько слотов, где модель делает больше ошибок, чем на. остальных.
Частота ошибок между различными слотами показана, на. рис. 3. Неудивительно, что на. слоте location получилась самая большая частота, ошибок - 12%, так как он появляется сразу в трех доменах: Hotels, Restaurants и Travel, при том, что только домен Travel встречался в тренировочных данных. У слота, date вторая по величине частота, ошибок и этот слот также появляется сразу в трех доменах, одного из которых - Restaurants - в трени- ровочной выборке не было. У слотов destination и destination_ city частота ошибок 6% и 4% соответственно. Эти слоты часто заполнялись местами отправления вместо мест назначения. Тем не менее ошибки в разметке пунктов отправления и назначения встречались часто в датасете SGD, таким образом, модель могла выучить неправильные метки.
location date destination destinationcity eventname picku p_city to_location therapistname rest aura nt name pi ckupjocation ha svegeta ria noptio ns city_of_event city number of seats type category placename origincity passengers director
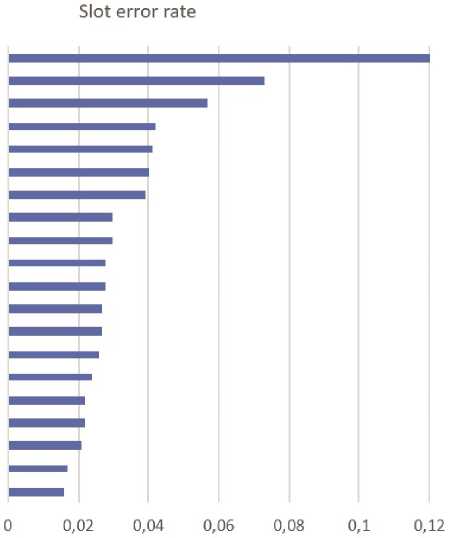
Рис. 3. Первые 20 слотов, отсортированных по частоте ошибок на тестовых данных. На слоте location, который появляется в доменах Hotels, Restaurants и Travel, модель выдала, наибольший процент ошибок - 12%. А на слоте director, который появляется в доменах Media и Movies вышел минимальный процент ошибок - 1.6%
В мультидоменных диалогах мы заметили, что наша, модель часто допускает ошибки на. репликах, где происходит переключение домена. Как правило, неправильное выделение состояния происходит в ситуации, когда, слот был выделен для одного домена, и его значение необходимо перенести в слот в новом домене. Проблема заключается в том, что в текущем контексте нет упоминания о значении нового слота, и наша, модель не может найти это значение слота, исходя из архитектуры модели. Например, пользователь сначала, бронирует время заезда, в отель и алгоритм записывает это время как время начала, брони. После чего пользователь заказывает такси и просит довезти его по адресу к этому времени. Но алгоритм уже выделил это поле как время заезда, в отель и ему требуется повторное упоминание этого времени при заказе такси (рис. 4).
|
User: "Yes, that would be great. Can 1 have a number and address for the office?" |
|
|
User State: |
"service": "Services_4", "activejntent": "BookAppointment", "requested_slots": ["address", "phone_number" ] |
|
System: "1 have booked your appointment. The number is 707-526-2525 and the address is 2455 bennett valley road # B208." |
|
|
User: "1 would need a cab to get there." |
|
|
User State: |
"service": "RideSharing_r, "activejntent": "GetRide", "slot_values": {"destination": ["2455 bennett valley road # B208"]} |
Рис. 4. Пример смены домена, в диалоге
8. Исследование вклада отдельных компонент модели
Результаты исследования вклада каждого отдельного компонента в общую производительность модель представлены в табл. 4. Были проведены следующие эксперименты.
Т а б л и ц а 4
Исследование вклада отдельных компонент модели
|
Описания |
CLS для кат. слотов |
PV для кат. слотов |
Интенты |
SQuAD преобучение |
Active Int Асе |
Req Slot Fl |
Avg GA |
Joint GA |
|
|
(а) |
- |
+ |
- |
- |
- |
- |
0.969 |
0.782 |
0.460 |
|
(Ь) |
+ |
+ |
- |
- |
- |
- |
0.969 |
0.778 |
0.464 |
|
(с) |
+ |
- |
+ |
- |
- |
- |
0.969 |
0.814 |
0.524 |
|
(d) |
+ |
- |
+ |
+ |
- |
0.657 |
0.969 |
0.820 |
0.535 |
|
Финальная модель |
+ |
- |
+ |
+ |
+ |
0.660 |
0.969 |
0.817 |
0.539 |
Здесь «Описания» обозначают использование описаний слотов и доменов онтологии на естественном языке. Для предсказания значений категориальных слоёв использовались два подхода. Первый использует для предсказания выход u cls ~ полносвязный слой над CLS-выходом BERT. Второй подход, вошедший в финальную архитектуру модели, использует выходы иру для выбора значения слота среди возможных.
• CLS для категориальных слотов. Наша первая версия модели использовала ucls-выход для предсказания значений категориальных слотов. В качестве классификатора использовался полносвязный слой по \CLS]-токену BERT с m + 1 выходами, где m - максимальное число различных значений для одного категориального слота и значение NONE. Если у слота было k < m значений, то значения между к + 1 и m заполнялись значениями —INF, чтобы получать нулевую вероятность для этих значений при использовании softmax-функции поверх m + 1 выходов. Также мы использовали только названия слотов и доменов, не используя их описание в онтологии.
• CLS для категориальных слотов + описание онтологии схемы. Мы добавили в модель использование описания слотов и доменов на естественном языке. К нашему удивлению это увеличило качество не так значительно, как мы ожидали.
• PV для категориальных слотов + описание онтологии схемы. Добавление возможных категориальных значений, разделённых специальными токенами pv на вход BERTEncoder увеличило качество модели на 6% на метрике joint goal accuracy.
9. Заключение
е PV для категориальных слотов + описание онтологии схемы + интенты. Мы добавили предсказание намерений пользователей, также передавая их на вход BERTEncoder с специальными разделителями u^nt (аналогично категориальных слотам). Несмотря на то, что предсказание намерений невелико, это увеличило joint goal accuracy на, 1%.
е PV для категориальных слотов + описание онтологии схемы + интенты + предобучение BERT на наборе данных SQuAD. Перед обучением на основном наборе данных мы предобучили BERTEncoder на SQuAD наборе данных и несмотря на то, что average goal accuracy уменьшилось, мы увеличили значение ключевой метрики joint goal accuracy.
В этой работе мы представляем единую модель на основе BERT для отслеживания состояния мультидоменного диалога. Наша модель устойчива к изменениям в схеме и не требует дообучения при появлении в данных новых намерений и слотов. Модель согласуется с реальными сценариями, предложенными виртуальными помощниками, и достигла существенных улучшений по сравнению с базовой моделью.
Список литературы Отслеживание состояния целеориентированного диалога на основе БЕРТ
- Konovalov V. [et al.\. The negochat corpus of human-agent negotiation dialogues // Proceedings of the Tenth International Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation (LREC'16). 2016. P. 3141-3145.
- Guhjaev P. [et al.\. Goal-oriented multi-task bert-based dialogue state tracker // arXiv preprint arXiv:2002.02450. 2020.
- Budzianowski P. [et al.\. MultiWOZ-A Large-Scale Multi-Domain Wizard-of-Oz Dataset for Task-Oriented Dialogue Modelling // arXiv preprint arXiv:1810.00278. 2018.
- Hemphill C.T., Godfrey J. J., Doddington G.R. The ATIS spoken language systems pilot corpus // Speech and Natural Language: Proceedings of a Workshop Held at Hidden Valley, Pennsylvania, June 24-27, 1990. 1990.
- Eric M. [et al.\. Multiwoz 2.1: Multi-domain dialogue state corrections and state tracking baselines. 2019.
- Devlin J. [et al.\. Bert: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding // arXiv preprint arXiv:1810.04805. 2018.
- Thomson В., Young S. Bavesian update of dialogue state: A POMDP framework for spoken dialogue systems // Computer Speech k, Language. 2010. V. 24, N 4. P. 562-588.
- Wang Z., Lemon O. A simple and generic belief tracking mechanism for the dialog state tracking challenge: On the believabilitv of observed information // Proceedings of the SIGDIAL 2013 Conference. 2013. P. 423-432.
- Williams J.D. Web-stvle ranking and SLU combination for dialog state tracking // Proceedings of the 15th Annual Meeting of the Special Interest Group on Discourse and Dialogue (SIGDIAL). 2014. P. 282-291.
- Henderson M., Thomson В., Williams J.D. The second dialog state tracking challenge // Proceedings of the 15th annual meeting of the special interest group on discourse and dialogue (SIGDIAL). 2014. P. 263-272.
- Chao G.L., Lane I. Bert-dst: Scalable end-to-end dialogue state tracking with bidirectional encoder representations from transformer // arXiv preprint arXiv:1907.03040. 2019.
- Wu C.S. [et al.\. Transferable multi-domain state generator for task-oriented dialogue systems // arXiv preprint arXiv:1905.08743. 2019.
- Rastogi A. [et al.\. Towards scalable multi-domain conversational agents: The schema-guided dialogue dataset // Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. 2020. V. 34. N 05. P. 8689-8696.
- Rajpurkar P. [et al.}. Squad: 100,000+ questions for machine comprehension of text // arXiv preprint arXiv: 1606.05250. 2016.
- Zilka L., Jurcicek F. Incremental LSTM-based dialog state tracker // 2015 Ieee Workshop on Automatic Speech Recognition and Understanding (Asru). IEEE, 2015. P. 757-762.
- Mrksic N. [et al.}. Neural belief tracker: Data-driven dialogue state tracking // arXiv preprint arXiv:1606.03777. 2016.
- Zhong V., Xiong C., Socher R. Global-locallv self-attentive encoder for dialogue state tracking // Proceedings of the 56th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers). 2018. P. 1458-1467.
- Nouri E., Hosseini-Asl E. Toward scalable neural dialogue state tracking model // arXiv preprint arXiv:1812.00899. 2018.
- Ren L. [et al.}. Towards universal dialogue state tracking // arXiv preprint arXiv:1810.09587. 2018.
- Goel R., Paul S., Hakkani-Tur D. Hvst: A hybrid approach for flexible and accurate dialogue state tracking // arXiv preprint arXiv:1907.00883. 2019.
- Xu P., Hu Q. An end-to-end approach for handling unknown slot values in dialogue state tracking // arXiv preprint arXiv:1805.01555. 2018.
- Peters M.E. [et al.\. Deep contextualized word representations // arXiv preprint arXiv:1802.05365. 2018.
- Loshchilov I., Hutter F. Decoupled weight decay regularization // arXiv preprint arXiv:1711.05101. 2017.
- Wolf T. [et al], HuggingFace's Transformers: State-of-the-art natural language processing // arXiv preprint arXiv:1910.03771. 2019.


