Parasites fauna and structure of the component para-site communities minnow phoxinus phoxinus (l.) from river and Sea-u Karalake and curves on the island Kolguev
Автор: Dorovskikh G.N., Stepanov V.G.
Журнал: Arctic and North @arctic-and-north
Рубрика: Biological Sciences
Статья в выпуске: 12, 2013 года.
Бесплатный доступ
The collection of the material was produced by the conventional method in July 1992, and 2004 from Crooked Lake to Kolguev rivers Sea-U and Halmer-U, August 2003 − from the Kara. We studied 63 copies minnow 1+. In the studied reservoirs parasitofauna minnow impoverished and largely random nature, community immature parasites. In July and August, the community formed parasites.
Fish parasites, parasitic fauna, component community, phoxinus phoxinus, minnow
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/148320345
IDR: 148320345 | УДК: 639.3.09
Текст научной статьи Parasites fauna and structure of the component para-site communities minnow phoxinus phoxinus (l.) from river and Sea-u Karalake and curves on the island Kolguev
Previously, it was shown that in most southern watersespecialyin the Kama River basin, upstream Vychegda and in the tributaries of the upper reaches of the Northern Dvina River minnow parasitofauna homogeneous component of its community of parasites mature (balanced) [2, 4 -7].
This part of the report is devoted to the description of the parasite community structure and its parasites of the northern waters of the studied.
MaterialsandMethods
Minnow caught by a net of the riverbeds Sea-Yu (plot coordinates the collection of material -67 ° 59 's. Lat., 59 ° 46' east. Etc.), Kara (68 ° 52 '. W., 64 ° 51' in the . etc.) and its tributary Hal-mer-U (68 ° 07 's. lat., 64 ° 42' east. etc.) from crooked Lake to Kolguev (Fig. 1). Dates of catching fish and sample sizes are shown in Table. 1. Age 1 + fish. Minnow caught in 10-20 minutes. and immediately fixed in 10% solution of formalin into the plastic bottle. Processing of the samples carried out by conventional methods, allowing for the dissection of fish fixed in formalin. It is mandatory for the parasites viewed sediment from the tanks in which the fish was kept until the autopsy.
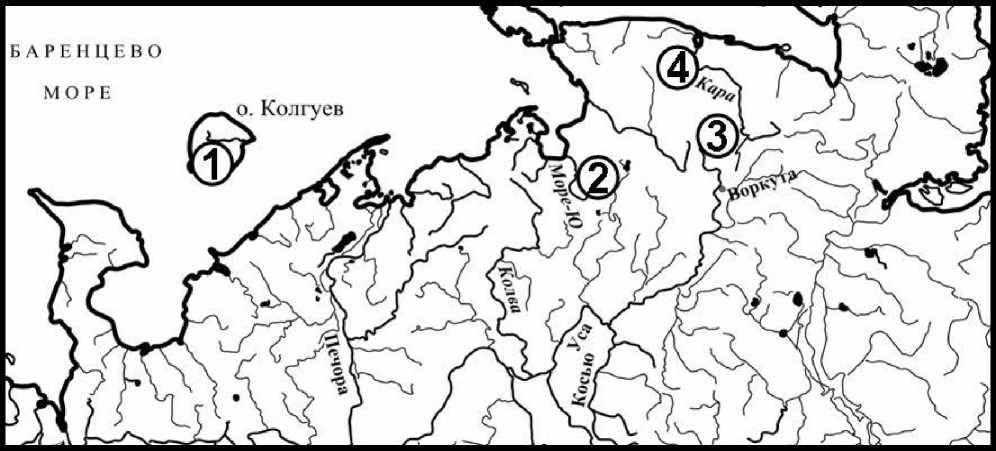
Pic. 1. Themap-schemeoftheregionрайонасбораматериала: 1 — The lake krivoeon the island Kolguev; 2 — River-sea-U; 3 — riverHalmer; 4 — riverKara
Terminology and calculation method of the constructing indices of graphs showing the structure of the component parasitic communities are set out in the previous publications [4, 5].
ResultsandDiscussions
From the surveyed reservoirs found 16 species of parasites (Table 1). In each of the studies revealed locations from 3 to 10 species thereof. Most of all parasites was observed in fish from the river Halmer-U (10 species), then from Crooked Lake (8), from the river Sea-N (7). Do minnows of the Kara met three kinds of parasites. Interestingly, the grayling Thymallus thymallus (L.) from the same locations in August 1991 found only Proteocephalus thymalli (Annenkowa-Chlopina, 1923).
Table 1
The Parasite fauna of Golyana
|
Type of parasite |
Lake Krivoe Island Kolgyev 10 July 1992 n = 20 |
Rivers |
||
|
Sea-U 2 July 2004 n = 15 |
Halmer-U 26 July 2004 n = 18 |
KARA 24 August 2003 n = 10 |
||
|
Myxobolus musculi Keysselitz, 1908 |
- |
1(0,07) |
- |
2(0,8) |
|
M. lomi Donec et Kulakowskaja, 1962 |
- |
- |
2(0,11) |
- |
|
Trichodina sp. |
- |
- |
+ |
- |
|
Dactylogyrus borealis Nybelin, 1936 |
3(0,15) |
1(0,07) |
3(0,22) |
- |
|
Gyrodactylus aphyae Malmberg, 1957 |
1(0,05) |
?(0,13) |
?(1,94) |
- |
|
G.macronychus Malmberg, 1957 |
1(0,05) |
- |
- |
- |
|
G.laevis Malmberg, 1957 |
5(0,35) |
- |
?(0,11) |
- |
|
G.pannonicus Molnar, 1968 |
?(0,11) |
|||
|
G.magnificus Malmberg, 1957 |
- |
1(0,07) |
- |
- |
|
Proteocephaluslongicollis (Zeder, 1800) |
3(0,3) |
- |
- |
- |
|
Allocreadium isoporum (Looss, 1894) |
- |
1(0,07) |
2(0,17) |
- |
|
A. transversale (Rudolphi, 1802) |
1(0,05) |
- |
- |
- |
|
Phyllodistomum folium(Olbers, 1926) |
1(0,05) |
- |
- |
- |
|
Diplostomum phoxini Faust, 1918 larvae |
20(74,7) |
15(11,3) |
18(63,8) |
10(20,8) |
|
Rhipidocotyle campanula (Dujardin, 1845) larvae |
- |
- |
4(0,9) |
- |
|
Raphidascaris acus (Bloch, 1779) larvae |
- |
1(0,13) |
1(0,06) |
4(2,2) |
In all waters except the Kara found Gyrodactylus aphyae and Dactylogyrus borealis. Allo-creadium isoporum observed in the rivers and the sea-Yu-Yu Halmer, Myxobolus musculi - in rivers Sea and Kara-Yu, G. laevis - in the river Halmer-U and Crooked Lake. Only the fish out of the riversea Yu registered G. macronychus, in the river Halmer-U - Myxobolus lomi, Trichodina sp., G. pannonicus, Rhipidocotyle campanula, in Crooked Lake - Proteocephalus longicollis, Allocreadium transversale, Phyllodistomum folium. At all points of the collection of the material met only Meta-cercariae Diplostomum phoxini. A fish out of water courses attended by all land larvae Raphidas-caris acus. The last two types, apparently, and form the core of the parasite minnow rivers studied.
As you can see, the set of parasites in the northern waters of the minnow, in the comparison with those of the more southern basins [5-7], random and significantly depleted. Are not found microsporidia, parasites, clams, leeches and crustaceans. Less rich in the species composition myxosporeans, monogeneans, trematodes and nematodes. Marked one cestode species P. Longicollis, and that is not typical minnow.
P. longicollis –is the parasite whitefish, who went to the parasitic representative for carps. Do minnows from the lake on the island Kolguev marked cestode egg-laying birds [1], in contrast to fish from the river Hunt (Lake vera), which found plerocercoids [8]. Only in the minnow from Lake Crooked found fluke A. transversale. Its definitive hosts - vyunovye and minnows [Scriabin, Koval, 1966 op. by: 10]. This kind of flukes previously registered with the fish of the Pechora river basins, Mezen and Northern Dvina [3], but in the monitored streams it is not found.
Apparently, studied parasitic communities are in a state of formation [in: 2]. Indeed, not only worms P. longicollis and A. transversale are able to lay, but also all of the collected specimens A. isoporum and Dactylogyrus borealis from the river Halmer-U. Copies of the D. borealis from the River Halmer-U is fully formed with rounded eggs in the ovary, but have not started laying eggs. All members of the district. Gyrodactylus with embryos.
In all communities, the number of the species dominated by autogenous species, the number of individuals and biomass - allogeneic (Table 2). Types of specialists dominated in all respects. The only exception was a parasitic community of the Kara, in which the number of the species in the lead-species generalists.
In a clear dominant communities, both in the number of thebindividuals and biomass, is an allogeneic specialist Diplostomum phoxini. The presence of a pronounced type-dominant point and the high value of the index Berger-Parker. The index values of Shannon and evenness of species below 0.5. The listed features are characteristic of immature fish parasite communities. [2]
By the number of thebparasite species and their community minnow biomass of the studied water bodies are divided into two groups. This is the community component of the rivers Sea-Yu and Kara other than these minimum values of parameters, and those of the river Halmer-U and Crooked Lake, characterized by their maximum values. In the parasite communities of the last minnow ponds number of species groups, allocated by the ratio of their biomass is three, from the river Sea-U - two of the Kara - one (Fig. 2). Apparently, the latter species later split into two groups. Anyway, the two types of biomass values lie on the boundary between 1 and 2 groups of them. Then in all communities in the Group 1 includes only D. phoxini. The amount of error of the regression equations that describe the location of the points, the biomass of the species in the community, less than a critical value - 0.25 [2].
Table 2
Characteristics of the component parasite communities of the minnow
|
Indicators |
Lake Krivoe Island Kolgyev |
rivers |
||
|
Sea-U |
Halmer-U |
KARA |
||
|
studied fish |
20 |
15 |
18 |
10 |
|
The total number of species of parasites |
8 |
7 |
8 |
3 |
|
The total number of individuals of parasites |
1515 |
177 |
930 |
228 |
|
The total notional value of biomass |
239,2 |
28,1 |
144,8 |
36,1 |
|
Number of autogenous species |
7 |
6 |
7 |
2 |
|
The number of species of allogeneic |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
|
Proportion of individuals with autogenous species |
0,013 |
0,045 |
0,038 |
0,126 |
|
The share of biomass autogenous species |
0,042 |
0,078 |
0,053 |
0,117 |
|
The proportion of individuals of species of allogeneic |
0,987 |
0,955 |
0,962 |
0,874 |
|
The share of biomass types of allogeneic |
0,958 |
0,922 |
0,947 |
0,883 |
|
The number of species experts |
5 |
4 |
6 |
1 |
|
The proportion of individuals of species experts |
0.995 |
0,977 |
0,995 |
0,874 |
|
The share of biomass types of specialists |
0.966 |
0,955 |
0,992 |
0,883 |
|
The number of generalist species |
3 |
3 |
2 |
2 |
|
The proportion of individuals of species generalist |
0,005 |
0,023 |
0,005 |
0,126 |
|
The share of biomass generalist species |
0,034 |
0,045 |
0,008 |
0,117 |
|
Dominant species by number of individuals |
Diplostomumphoxini |
|||
|
Dominant view on the value of biomass |
Diplostomum phoxini |
|||
|
Characteristics of the dominant species |
ал/с |
|||
|
Berger-Parker index by number of individuals |
0,987 |
0,955 |
0,962 |
0,874 |
|
Berger-Parker index of biomass |
0,958 |
0,922 |
0,947 |
0,883 |
|
Evenness of species by number of individuals |
0,044 |
0,135 |
0,095 |
0,411 |
|
Evenness of species in biomass |
0,107 |
0,206 |
0,123 |
0,403 |
|
Shannon index on the number of individuals |
0,092 |
0,262 |
0,197 |
0,452 |
|
Shannon index values for biomass |
0,222 |
0,400 |
0,256 |
0,443 |
|
Error of the regression equations |
0,075 |
0,145 |
0,084 |
0,246 |
Previously mentioned the natural variation in the species diversity index component parasite communities of fish in the geographical coordinates [9], traces the relation of the states of these communities with the geological age (Quaternary history) areas [2]. It is shown that in the basin of the Kama River, the upper reaches of the river Vychegda tributaries of the upper reaches of the Northern Dvina and Pechora river bed in the Pechora lowland parasite fauna minnow homogeneous component of its community of the mature parasites [5-7]. In the studied northern waters parasite fauna minnow impoverished and largely random nature, community immature parasites. The number of species of fish parasites, their biomass indices Shannon equalization species that characterize the component from the community parasites minnow northern reservoirs investigated below, and Berger-Parker index higher than that of the community channel unbalanced Upper Pechora [4] . These observations support the conclusion made earlier that the immature parasitic communities are geologically young areas, mature or occupy an intermediate position between them - in the older [2]. In addition, if the characteristics of the balanced component parasite communities minnow strictly enough established [5-7], the way was clear for those of immature parasites communities it still to be clarified.
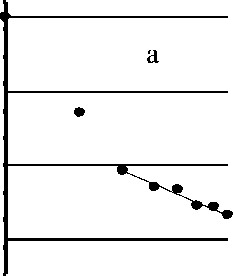
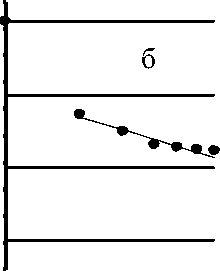
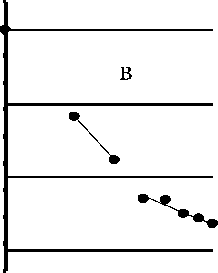
Pic. 2. Variation curves of the conditional parasite biomass minnow:
and - the fish caught July 10, 1992 from Crooked Lake, b - 2 July 2004 from the River Sea-Yu, in - 26 July 2004 from the river Halmer-U d - August 25, 2003 from the Kara
Список литературы Parasites fauna and structure of the component para-site communities minnow phoxinus phoxinus (l.) from river and Sea-u Karalake and curves on the island Kolguev
- Anikieva L.V., Dorovskikh G.N. Phenotypic variability of the parasite salmonid fishes Proteocephalus longicollis (Zeder, 1800) of the common minnow (Phoxinus phoxinus) / / Ecological and parasitological studies of the animals and plants of the European North. Petrozavodsk: Karelian Research Centre of RAS, 2001. Pp. 58-63.
- Dorovskikh G.N.The parasites of the freshwater fish of the north-east of the European part of Russia (fauna, ecology parasitic communities, zoogeography): Author. dis. ... Dr. biol. Science. St. Petersburg.: Zool. Institute of Russian Academy of Sciences, 2002. 50p.
- Dorovskikh G.N. Zoogeography of fish parasites of major rivers in the northeastern Europe (monograph). Syktyvkar: Publishing House of the Syktyvkar University Press, 2011. 142p.
- Dorovskikh G.N. Stepanov, V. The structure of the component parasite communities grayling Thymallus thymallus (L.) (Salmoniformes, Thymallidae) and minnow Phoxinus phoxinus (L.) (Cypriniformes, Cyprinidae) from the upper reaches of the Pechora River / / Proceedings of the Russian Academy of Sciences. Biology Series. 2009. Number three. p. 358-367.
- Dorovskikh G.N. Stepanov V.G. Theseasonal dynamics of the community structure of parasites minnow Phoxinus phoxinus (L.) in the upper watersheds of the Northern Dvina River / / Fish and fish. households in. 2009. Number three. Pp. 33-43.
- Dorovskikh G.N. Stepanov V.G. Seasonal dynamics and structure of the parasite comcomponent parasite communities minnow Phoxinus phoxinus (L.) of the Pechora River. 1 / / Parasitology. , 2011. T. 45, no. 4. S. 277-286.
- Dorovskikh G.N. Stepanov V.G. The seasonal dynamics of the community structure of parasites minnow Phoxinus phoxinus (L.) in the river basin of Luz / / Fish and fish. households in. , 2011. Number 9. S. 41-48.
- Pugachev O.N. The parasites of the freshwater fish north-east Asia. Leningrad: Publishing House of Zool. Institute of the USSR Academy of Sciences, 1984. 156.
- Pugachev O.N. The parasites of freshwater fishes of North Asia (fauna, ecology parasitic communities, zoogeography): Author. dis. ... Doctor. biol. Science. St. Petersburg.: Zool. Institute of Russian Academy of Sciences, 1999. 50p.
- Pugachev O.N. The catalog of the parasites of the freshwater fishes of northern Asia. Trematodes. St. Petersburg.: Publishing House of the Zool. Institute of Russian Academy of Sciences, 2003. 224p. (Proceedings of the Zoological Institute of the RAS. T. 298).


