Переломы дистального метафиза плечевой кости у детей: этиопатогенез, клиника, диагностика, лечение
Автор: Амаири О.Н., Ахтямов И.Ф., Цой И.В., Андреев П.С.
Журнал: Вестник медицинского института "РЕАВИЗ": реабилитация, врач и здоровье @vestnik-reaviz
Рубрика: Клиническая медицина
Статья в выпуске: 5 т.14, 2024 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Актуальность. Переломы дистального метафиза плечевой кости – самые распространённые среди травм костей локтевого сустава у детей, наблюдаются в 64–70% случаев. Цель — обобщение, систематизация литературных данных и представление современ-ных взглядов на эпидемиологию, этиологию, патогенез, диагностику и лечение надмыщелковых и чрезмыщелковых переломов плече-вой кости у детей. Материалы и методы. Системный поиск литературы был проведён по базам данных PubMed, PubMed Central, Web of Science, Scopus, MEDLINE, eLIBRARY, РИНЦ, Google Scholar, Cyberleninka, eLibrary и др. В исследование включались публикации о пере-ломах дистального метафиза плечевой кости, лечении надмыщелковых и чрезмыщелковых переломов плечевой кости у детей в воз-растной категорнии от 1 года до 17 лет включительно. Результаты. Дистальные метефизарные переломы плечевой кости являются самыми частыми среди переломов локтевого сустава у детей. Лечение переломов без смещения I-типа по Gartland проводится кон-сервативно. Предпочтительным методом лечения переломов со смешением (типа II, III и VI по Gartland) является закрытая репозиция с чрескожным остеосинтезом спицами. При неуспешных попытках выполнения закрытой репозиции или при развитии серьёзных сосуди-сто-неврологических нарушений применяется открытая репозиция с ревизией области перелома. Оперативные вмешательства с остеосинтезом дистальных переломов плечевой кости в разы увеличились за последние годы, но значительно уменьшилось количе-ство корригирующих остеотомий в лечении посттравматических деформаций. Заключение. Правильный подход в диагностике и лечении дистальных метефизарных переломов плечевой кости у детей, разумный выбор метода оперативного лечения и техники остеосинтеза обеспечивают положительные результаты лечения, уменьшают риск развития осложнений на протяжении всех этапов периода лечения.
Надмыщелковые переломы, чрезмыщелковые переломы, переломы дистального метафиза плечевой кости у детей, переломы локтевого сустава у детей
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/143183996
IDR: 143183996 | УДК: 616.717.4-001.5-053.2(048.8) | DOI: 10.20340/vmi-rvz.2024.5.CLIN.1
Текст обзорной статьи Переломы дистального метафиза плечевой кости у детей: этиопатогенез, клиника, диагностика, лечение
Переломы у детей и подростков до 18 лет составляют более 15% от травматических переломов всех остальных возрастных групп населения, и частота их только растёт [1]. Переломы верхних конечностей у детей встречаются чаще других (76– 80%) [2]. На переломы костей локтевого сустава приходится около 20% всех интраартикулярных переломов, и наиболее часто они встречаются в детском возрастном периоде. Переломы дистального метаэпифизарного конца плечевой кости могут сочетаться с повреждениями ростковой зоны с нарушением формирования анатомической конфигурации, деформацией плечевой кости и ограничением функции локтевого сустава даже при восстановлении нарушений анатомических структур [3–5].
Цель — обобщение, систематизация литературных данных и представление современных взглядов на эпидемиологию, этиологию, патогенез, диагностику и лечение надмыщелковых и чрезмыщелковых переломов плечевой кости у детей.
Материалы и методы
Системный поиск литературы был проведён по базам данных PubMed, PubMed Central, Web of Science, Scopus, MEDLINE, eLIBRARY, РИНЦ, Google Scholar, Cyberleninka, eLibrary и др. по ключевым словам и словосочетаниям: надмыщелковые переломы, чрезмыщелковые переломы у детей, переломы дистального эпиметафиза плечевой кости у детей, переломы локтевого сустава у детей, pediatric supracondylar fractures, pediatric transcondylar fractures, distal humeral fractures in children, pediatric supracondylar type I-IV fractures, pediatric elbow fractures, переломы дистального метафиза плечевой кости у детей. Критерии включения: публикации о переломах дистального метафиза плечевой кости у детей в возрастной категорнии от 1 года до 17 лет включительно. В обзор первично было отобрано 186 источников и публикаций, из них критериям включения соответствовали 71. Рассмотрены источники на русском, английском, испанском и немецком языках, сообщающия об эпидемиологических статистических, клинико-диагностических данных и методах лечения при надмыщелковых и чрезмыщелковых переломах у детей.
Результаты и обсуждение
Статистика. По данным литературы, на долю дистальных метафизарных (надмыщелковых и чрезмыщелковых) переломов плечевой кости у детей приходится около 13,9%, они занимают первое место (32,35%) в возрасте от 3 до 6 лет, второе место – от 0 до 2 лет и от 7 до 11 лет (25% и 11,61% соответственно) [6]. Данные переломы являются самыми частыми среди переломов локтевого сустава у детей (64–70%) [7, 8]. Классическим механизмом травмы является падение на вытянутую руку с опорой на кисть (при разгибательном переломе) или в результате приземления на локоть при согнутой верхней конечности (при сгибательном). Согласно данным большинства литературных источников, разгибательный тип перелома встречается в подавляющем большинстве случаев (98%) и чаще возникает в недоминирующей конечности. Сгибательный тип встречается чаще у детей старшего возраста [9–11].
Анатомические особенности. При падении на вытянутую и отведённую кнаружи руку локтевой отросток, фиксированный в локтевой ямке, действует как точка опоры, а при травматичном чрезмерном разгибании в локтевом суставе дистальный конец плечевой кости начинает ломаться сначала спереди, затем перелом прогрессирует кзади. Если сила воздействия высокая, то задний кортикальный слой разрывается и происходит смещение дистального фрагмента кзади с формированием угла, открытого кзади (разгибательный перелом). Соответственно при сгибательном виде смещение дистального фрагмента происходит вперед. Надмыщелковая область расположена в дистальном метадиафизарном отделе плечевой кости. Она ограничена сзади локтевой ямкой, спереди – венечной ямкой и с обеих сторон соответствующими надмыщелковыми гребнями, которые заканчиваются медиальными и латеральными колоннами мыщелка и надмыщелками, являющимися зоной крепления различных мышц верхней конечности. Через данную зону проходят плечевая артерия, срединный, лучевой и локтевой нервы [12, 13].
Диагностика. Пострадавшие дети поступают обычно с жалобами на боли в локтевом суставе после падения на вытянутую и отведённую кнаружи (реже, на согнутую в локтевом суставе) руку. Верхняя конечность находится в вынужденном полусогнутом в локтевом суставе положении, движения ограничены за счёт выраженного болевого синдрома, здесь же отмечаются экхимоз, отёк мягких тканей, деформация нижней трети плеча и локтевого сустава. Пальпация и осевые нагрузки резко болезненны. Особое внимание следует уделять образованию кожных складок, ямочки на задней поверхности плеча. Этот признак (pucker sign) появляется, когда проксимальный фрагмент перелома пересекает плечевую мышцу, стягивая глубокую дерму. Поэтому, при наличии данного признака следует предположить и исключить наличие серьёзного смещения и повреждения мягких тканей, плечевой артерии, срединного нерва или развития компарт-мент-синдрома в данной области. Следовательно, при осмотре верхней конечности важно тщательно проводить оценку сосудисто-неврологического статуса, проверить пульс на плечевой и лучевой арте- риях обеих конечностей, оценить моторные и сенсорные функции пальцев кисти, а при снижении или отсутствии пульса на лучевой артерии следует проводить ультразвуковое исследование-Doppler сосудов верхней конечности. Имеются данные о возникновении сосудистых нарушений в 10–20% случаев переломов со смещением. Smuin D.M. и соавт. (2017 г.) сообщили об отличных результатах и отсутствии сосудисто-неврологических осложнений, используя при пальпации области перелома во время первичного осмотра в максимально коротком сроке времени от момента травмы до операции – не более 16 часов – технику постепенного закрытого пальпаторного освобождения мягких тканей, подвергаемых ишемии в результате смещения фрагментов.
Заключительный диагноз ставится с помощью рентгенографических исследований, позволяющих определить характер перелома и вид его смещения [14–16].
Рентгенодиагностика. Для правильной постановки диагноза необходимо произвести лучевую диагностику локтевого сустава: рентгенографию, компьютерную томографию, ультразвуковое исследо-вание-Doppler сосудов верхней конечности, магнитно-резонансную томографию и электромиогра-фические исследования при подозрении на развитие нейроваскулярных повреждений. Рентгенограммы в двух проекциях – прямой и боковой – позволяют определить тип перелома (разгибательный или сгибательный), степени смещения, ротации и фрагментации. При нестабильных, оскольчатых переломах, а также при риске сосудистоневрологических и мягкотканых повреждений, показано проведение компьютерной и магнитнорезонансной томографий. В связи с возможной комбинацией надмыщелковых переломов с переломами костей предплечья необходимо также получить прямое и боковое рентгенографические изображения этого сегмента. Адекватные знания нормы показателей соотношений элементов локтевого сустава с учётом возрастной рентгенанатомии (зон роста) дистального отдела плечевой кости, проксимального отдела лучевой и локтевой костей помогут более точно интерпретировать рентгенограмму костей локтевого сустава у детей. В прямой проекции надмыщелковой области дистального отдела плечевой кости можно увидеть поперечную или косую линии перелома. Их бывает сложно идентифицировать, иногда не удаётся даже заметить их при переломах без смещения [17].
Рентгенологическим индексом, характеризиру-ющим наличие аддукционных или абдукционных смещений дистального меатэпифиза плечевой кости, является плече-головчатый угол Баумана – угол между осью диафиза плечевой кости, и линией, проходящей через зону роста головчатого возвышения (рис. 1). У детей в норме он равен 67°–75° у мальчиков и 65°–75° у девочек. Вместе с углом Баумана для оценки варусной или вальгусной деформации при переломах (Cubitus varus и cubitus valgus) используется несущий угол (плечелоктевой) (рис. 2), образующийся пересечением линии, проведённой через центральную ось диафиза плечевой кости, и линии, проведённой через центральную ось диафиза локтевой кости. По данным радиографических исследований локтевого сустава (Goldfarb и др., 2012 г.), у детей и подростков в среднем этот угол равен 11°–21°, но для достоверности рекомендуется сравнить с рентгеновскими данными здоровой руки [18].
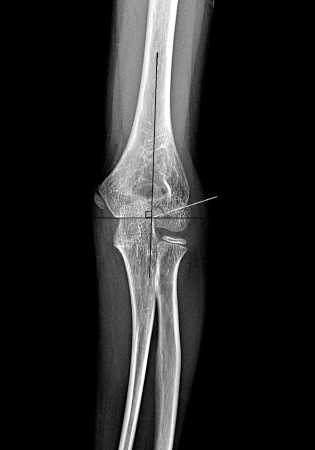
Рисунок 1. Рентгенограмма локтевого сустава в прямой проекции: угол Баумана. Пациент О' 10 лет
Figure 1. X-ray of the elbow joint in the anteroposterior (AP) view:
Baumann's angle. Patient О 10 years old
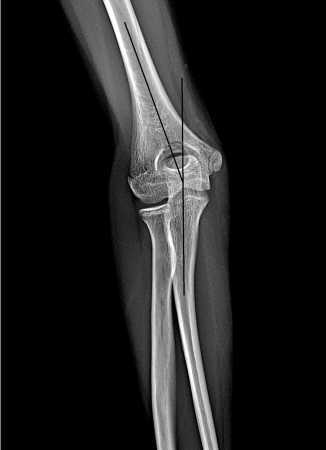
Рисунок 2. Рентгенограмма локтевого сустава в прямой проекции:
несущий угол (плечелоктевой). Пациент 2 11 лет
Figure 2. X-ray of the elbow joint in the AP view: carrying angle (hu-meroulnar). Patient 2 11 years old
Для определения степени смещения дистального фрагмента плечевой кости в сагиттальной плоскости (сгибательный или разгибательный перелом) служит передняя плечевая линия (Anterior Humeral Line-AHL-The Rogers’ line), проведённая вдоль переднего кортикального слоя плечевой кости (рис. 3, 4). В норме она пересекает среднюю треть головки. При разгибательном типе перелома, как правило, она проходит спереди головки, а при сгибательном – сзади. AHL также является простым и полезным параметром для оценки качества репозиции надмыщелковых переломов у детей со смещением. В своей работе Kao H.K. и соавт. (2016 г.) сообщают об особенностях наблюдений, где у пациентов, у которых AHL пересекала среднюю и заднюю трети головки отмечалось раннее улучшение сгибания и общего объёма движений в локтевом суставе [19]. В диагностике перелома головки (вывиха/подвывиха), перелома шейки лучевой кости немаловажна ра-диокапителлярная линия (лучеголовчатая линия) (рис. 3), проведённая через центр лучевой кости, которая в норме проходит через центр головчатого возвышения плечевой кости. Это соотношение сохраняется при сгибании и разгибании конечности в локтевом суставе. Блоко-плечевой угол или передний угол суставной поверхности дистального отдела плечевой кости (рис. 4) образуется продольной линией диафиза плечевой кости и осевой линией мыщелка и составляет около 40° [20–22].
Симптом задней жировой подушечки. В согнутом локтевом суставе задняя жировая подушечка прилегает к локтевой ямке. Внутрисуставной перелом любой кости в локтевом суставе вызывает кровотечение из места перелома. Возникшие в результате кровоизлияния гематомы или отёк поднимут жировую подушку от ямки локтевого сустава. Это создает положительный симптом задней жировой подушечки (рис. 5). В нескольких исследованиях сообщалось о роли симптома задней жировой подушечки в выявлении скрытых несмещённых внутрисуставных или понадкостничных переломов данной области [23]
Классификация переломов. До настоящего времени не существует единой классификации переломов дистального эпиметафиза плечевой кости у детей. Большинство авторов предлагают применять классификации, основанные на анатомической номенклатуре. Согласно этой классификации переломы, локализирующиеся внутри от линии прикрепления локтевой капсулы, считаются внутрисуставными (метафизарные и эпиметафизарные), а переломы вне капсулы локтевого сустава – внесуставны-ми (переломы внутреннего, наружного надмыщелка и надмыщелковые переломы) [24].
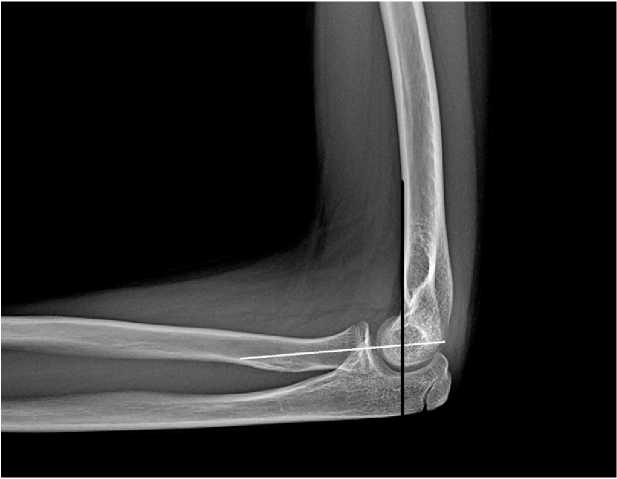
Рисунок 3. Рентгенограмма локтевого сустава в боковой проекции: передняя плечевая линия (черная линия) в норме пересекает среднюю треть головки; лучеголовчатая линия (белая линия) проходит через центр головчатого возвышения плечевой кости. Пациент 9 12 лет
Figure 3. X-ray of the elbow joint in the lateral view: anterior humeral line (black line) normally intersects the middle third of the capitellum; radio-capitellar line (white line) passes through the center of the capitellum of the humerus. Patient 9 12 years old
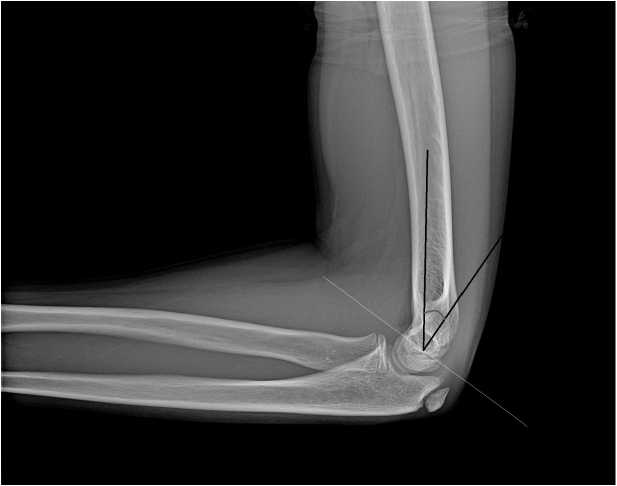
Рисунок 4. Рентгенограмма локтевого сустава в боковой проекции: блоко-плечевой угол. Пациент & 12 лет
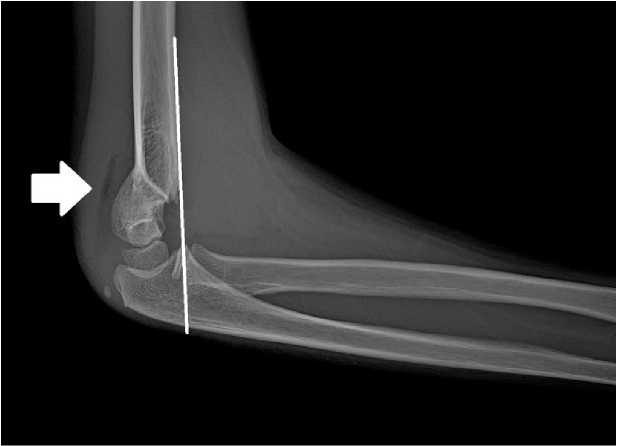
Рисунок 5. Рентгенограмма локтевого сустава в боковой проекции: чрезмыщелковый перелом плечевой кости по Gartland II типа. Передняя плечевая линия не пересекает головку, дистальный фрагмент смещен кзади (белая линия). Симптом задней жировой подушечки (стрелка). Пациент & 9 лет
Figure 5. X-ray of the elbow joint in the lateral view: Gartland type II supracondylar fracture of the humerus. The anterior humeral line does not intersect the capitellum, and the distal fragment is displaced posteriorly (white line). Posterior fat pad sign (arrow). Patient & 9 years old
По данным зарубежной литературы многие авторы характеризуют переломы дистального метафиза плечевой кости у детей как внесуставные экс-тракапсулярные (надмыщелковые) и внесуставные интракапсулярные (чрезмыщелковые) на разных уровнях колонны мыщелка плечевой кости, применяя один и тот же термин (supracondylar – надмыщелковые). К внутрисуставным переломам относится эпиметафизарная локализация переломов с повреждением суставной поверхности (эпифизиолизы, остеоэпифизиолизы), классификацию которых по- дробно описали Robert B. Salter и W. Robert Harris (1963 г.) [25–30].
Одной из самых распространённых и актуальных классификаций дистальных метафизарных переломов является классификация Gartland (1959 г.), которая была модифицирована другими авторами неоднократно (Wilkins, De Boeck, Leitch и др.). В зависимости от степени смещения переломы делятся: на тип I – без смещения; тип II – частичное смещение; и тип III – полное смещение [31, 32]. Модифицированная классификация Gartland представлена в таблице 1.
Таблица 1. Модифицированная классификация Gartland Table 1. Modified Gartland classification
|
Тип перелома |
Характеристика |
|
I-тип |
Без смещения или минимально смещен |
|
II-тип |
Угловое смещение с сохранением заднего кортикального слоя. |
|
Il-a |
Угловое смещение. |
|
ll-b |
Ротационное смещение |
|
Ill-тип |
Полностью смещен, отсутствует значимый кортикальный контакт, но периостальный шарнир (медиальный / лате- |
|
ральный) сохранен. |
|
|
lll-a |
Медиальный периостальный шарнир сохранен. Дистальный фрагмент смещен заднемедиально. |
|
lll-b |
Латеральный периостальный шарнир сохранен. Дистальный отломок смещен заднелатерально |
|
lV-тип |
Не имеет периостального шарнира и нестабилен как при сгибании, так и при разгибании, т.е. имеет разнонаправлен- |
|
ную нестабильность |
|
|
De Boeck-тип |
Медиальный столбец плечевой кости оскольчатый и нестабильный, потеря угла Баумана |
В практике часто используется AO/ASIF классификация (Мюллер М.Е. с соавт., 1996 г.), описывающая детали перелома и характер смещения костных отломков. АО классификация основана на принципе разделения переломов на три группы по тяжести повреждения от наиболее простого к сложному. При этом каждая группа подразделяется ещё на подгруппы в зависимости от локализации, линии, типа излома, характера смещения и количества фрагментов. Для более специфичного описания переломов детского возраста создана АО комплексная классификация переломов длинных трубчатых костей у детей (PCCF), где каждая кость имеет код: к примеру плечевая кость – (1), лучевая – (2r), а локтевая – (2u) и т.д. Локализация перелома шифруется следующим образом: проксимальный концевой сегмент (1), диафизарный сегмент (2) и дистальный концевой сегмент (3). Переломы концевого сегмента-эпифиза и метафиза обозначаются буквами (Е) и (М). Далее указывается характер линии перелома кодом (1–9), степень тяжести: простой (1) и осколчатый (2) перелом и вид смещения (I–IV). АО классификация переломов дистального метафизар-ного отдела плечевой кости у детей (внесуставных надмыщелковых и чрезмыщелковых) учитывает схему Gartland (табл. 2), а для эпифизарных (внутри-сутавных) переломов использует классификацию Salter-Harris. Для эпифизиолиза дистального конца плечевой кости по SH I-типа применяется код
(13-E/1.1), для внесуставного метаэпифизеолиза по SH-II типа – (13-E/2.1), для эпифизарных переломов по SH III-типа – (13-E/3.1), для простых (двухфраг-ментных) эпиметафизарных по SH IV-типа – (13-E/4.1), а для оскольчатых (межмыщелковых) переломов по SH IV-типа – (13-E/4.2) [33–36].
Лечение переломов без смещения (тип I по Gartland) или с минимальным смещением у детей обычно проводится консервативно с помощью иммобилизации гипсовой повязкой локтевого сустава при сгибании на 90° в среднефизиологическом положении между супинацией и пронацией от пальцев до верхней трети плеча в течение 3–5 недель. Не рекомендуется иммобилизовать локтевой сустав под углом меньше 90° сгибания, поскольку это может увеличить кровяное давление сосудов предплечья и затруднить кровоток в дистальных отделах плечевой кости. В первые дни после травмы, когда нарастает отёк мягких тканей, следует избегать наложения циркулярной гипсовой повязки во избежание развития компартмент-синдрома и сосудистой недостаточности. С этой целью необходимо осмотреть состояние кожных покровов и устранить места сдавления не позже 24 часов с момента наложения гипсовой иммобилизации. Рентгеновский контроль состояния отломков нужно провести через одну и три–четыре недели после травмы, а после снятия гипса начать разработку локтевого сустава [37].
Таблица 2. Комплексная классификация АО переломов дистального метафиза плечевой кости у детей по схеме Gartland Table 2. Comprehensive AO classification of fractures of the distal humeral metaphysis in children according to the Gartland scheme
|
Код перелома |
Расшифровка |
Описание перелома |
|
13-M/3.1 I |
Простой перелом дистального метафиза плечевой кости без смешения (Gartlan I-тип) |
Передняя плечевая линия на боковой рентгенограмме (линия Rogers) пересекает центр головчатого возвышения. В передне-задней проекции зазор вальгус-но-варусного смещения не превышает 2 мм |
|
13-M/3.1 II |
Простой неполный перелом дистального метафиза плечевой кости с угловым смещением, но с сохранением заднего или переднего кортикального слоя (Gartlan II-тип) |
Передняя плечевая линия на боковой рентгенограмме НЕ пересекает центр головчатого возвышения. В передне-задней проекции зазор вальгус-но-варусного смещения превышает 2 мм. |
|
13-M/3.2 II |
Оскольчатый неполный перелом дистального метафиза плечевой кости с угловым смещением, но с сохранением заднего или переднего кортикального слоя (Gartlan II-тип) |
Имеются более 2х фрагментов. Передняя плечевая линия на боковой рентгенограмме НЕ пересекает центр головчатого возвышения. В передне-задней проекции зазор вальгус-но-варусного смещения превышает 2 мм |
|
13-M/3.1 III |
Простой полный перелом дистального метафиза плечевой кости с полным смещением (Gartlan III-тип) |
Полностью смещен, отсутствует значимый кортикальный контакт, но с минимальными соприкосновением и соосностью между фрагментами. |
|
13-M/3.2 III |
Оскольчатый полный перелом дистального метафиза плечевой кости с полным смещением (Gartlan III-тип) |
Имеются более 2х фрагментов с минимальными соприкосновением и соосностью между фрагментами |
|
13-M/3.1 IV |
Простой полный перелом дистального метафиза плечевой кости с полным смещением, имеет разнонаправленную нестабильность (Gartlan IV-тип) |
Полностью смещен, абсолютно отсутствует контакт или соосность между фрагментами |
|
13-M/3.2 IV |
Оскольчатый полный перелом дистального метафиза плечевой кости с полным смещением, имеет разнонаправленную нестабильность (Gartlan IV-тип) |
Имеются более 2х фрагментов. Полностью смещен, абсолютно отсутствует контакт или соосность между фрагментами |
Переломы II-a типа по Gartland – без ротационной деформации – можно лечить консервативно с помощью гипсовой иммобилизации после проведения закрытой репозиции при отсутствии противопоказаний. Moraleda и соавт. описали отдалённые результаты переломов Gartland типа-II, пролеченных с иммобилизацией и без попыток репозиции. Авторы описали незначительную деформацию локтевого сустава в 26% случаев, боль или нестабильность у 17% пациентов, а также умеренное увеличение объёма разгибания в локтевом суставе и невыраженное ограничение сгибания локтевого сустава, которое присутствовало почти у всех пациентов. При этом авторы считают, что у большинства пациентов функциональные результаты были неплохими [38]. Однако при данном виде перелома противопоказаниями к консервативному лечению, очевидно, могу быть оскольчатый перелом медиального столбца, наличие обширных отёков, сосудистоневрологических нарушений и когда не удаётся репонировать дистальный отломок с помощью закрытой репозиции [19].
Закрытую репозицию следует производить слегка согнув верхнюю конечность в локтевом суставе, чтобы уменьшить риск нейроваскулярных повреждений. Затем необходимо устранять смещения в корональ-ной (фронтальной) плоскости: медиальное или латеральное ротационное смещения с коррекцией ва- русно/вальгусной и угловой деформаций дистального фрагмента. При наличии ротационного смещения, варусной или вальгусной деформаций пронация предплечья помогает устранить заднемедиальное смещение (внутреннюю ротацию), одновременно фиксируя медиальную сторону кортикального слоя дистального фрагмента, а супинация помогает устранять заднелатеральнее смещение (наружную ротацию). Деформация в сагиттальной плоскости устраняется гиперфлексией дистального отломка при переломах разгибательного типа и с помощью разгибания при переломах сгибательного типа.
Pham и соавт. описали свои результаты при лечении надмыщелковых переломов II-b и III типа по Гартланду с помощью метода Блаунта (Blount). Авторы выявили вторичное смещение в 5% случаев, варусную деформацию в 2%, ни одного случая с компартмент-синдромом и получили удовлетворительные результаты по критериям Флинна (Flynn) – в 90% случаев. Авторы пришли к выводу, что метод Блаунта является разумным вариантом для лечения надмыщелковых переломов плечевой кости типа II-b и III у детей. Muccioli и соавт. также описали хорошие результаты с техникой Блаунта [39, 40].
Для лечения супракондилярных переломов плечевой кости со смещением (типа Гартланда-II и -III и сгибательного типа) AAOS (Американская академия хирургов-ортопедов) в своём практическом руко- водстве (Лечение надмыщелковых переломов плечевой кости у детей) рекомендует закрытую репозиция с остеосинтезом спицами. Park M.J. и соавт. в своей публикации – AAOS целесообразные критерии в лечении надмыщелковых переломов плечевой кости у детей (AAOS Appropriate Use Criteria: Management of Pediatric Supracondylar Humerus Fractures) рекомендуют даже при неосложнённых переломах Gartland II выполнение закрытой репозиции с фиксацией спицами. Поскольку наблюдались вторичные смещения дистального фрагмента кзади через неделю консервативного лечения с гипсовой иммобилизацией [41, 42].
Эти рекомендации не обошлись без научной критики. Проводились исследования для оценки применимости рекомендаций AAOS в клинической практике. По результатам исследований авторы пришли к выводу, что AAOS рекомендует неотлож-ное/экстренное вмешательство чаще, чем в проведённых исследованиях, основываясь больше на классификации переломов. В руководстве AAOS возраст пациента и передняя линия плечевой кости (AHL) как критерий вмешательства конкретно не рассматриваются, в то время как в проведённых исследованиях авторы акцентировали внимание на возрасте, классификации переломов, сопутствующей травме, требующей хирургического вмешательства, и пересечении AHL головки плечевой кости [43, 44].
При разнонаправленной нестабильности дистального фрагмента (тип-IV по Gartland) выполнение удовлетворительной закрытой репозиции является большим вызовом. Novais E.N. и соавт. описали технику джойстика (Joystick Technique) для закрытой репозиции при переломах Gartland IV. С этой целью одну спицу диаметром 2,0 мм вводят чрескожно через головку плечевой кости под контролем рентгеноскопии. Эта спица работает как джойстик для обеспечения анатомической репозиции и должна быть расположена посередине дистального фрагмента. После достижения репозиции джойстик проводят через линию перелома до проксимального медиального кортикального слоя. Вторая и третья спицы вводятся с латеральной стороны в расходящемся порядке, чтобы пересечь место перелома максимально раздельно. Авторы считают данный метод безопасным и эффективным, позволяющим избежать травматичности многократных безуспешных попыток закрытой репозиции и дальнейшей открытой репозиции [45].
Надмыщелковые и чрезмыщелковые переломы традиционно рассматриваются как показание для оказания неотложной хирургической помощи из-за риска развития сосудисто-неврологических осложнений. До сих пор ведутся споры о том, можно ли безопасно отсрочить репозицию при отсутствии сосудисто-неврологических нарушений. С другой стороны, следует также принять во внимание, что выполнение операции в ночное время, с неадекватным оборудованием или неопытным персоналом потенциально может увеличить количество хирургических ошибок. Без сомнения, случаи с открытым переломом, сильным отёком и признаками повреждения нервов и сосудов требуют неотложного вмешательства. При надмыщелковых переломах III-тип Gartland у детей хирургическое вмешательство может быть отложено до 24 часов, что даёт возможность оперировать в дневное время, а не в ночные часы, а, следовательно, более точно оценить сосудисто-неврологический статус и выраженность отёка [46, 47].
По данным многих авторов, положительные результаты лечения надмыщелковых и чрезмыщелковых переломов плечевой кости у детей со смещением чаще наблюдались при закрытой репозиции с иммобилизацией гипсовой лонгетой или с фиксацией спицами. При остеосинтезе перекрещенными медиальной и латеральной спицами обеспечивается стабильная фиксация, и меньше вероятность деформации или потери репозиции, однако при этом остаётся риск повреждения локтевого нерва [48, 49]. Было показано, что размер спицы влияет на стабильность фиксации. Так, диаметр спицы 2 мм обеспечивает большую биомеханическую прочность по сравнению со спицами 1,5 мм [50]. Chuang Liu и соавт. провели сравнительные исследования стабильности разных способов фиксации. Результаты показали, что наилучшую устойчивость к поступательным силам обеспечивали интрамедуллярные медиальные и латеральные эластичные штифты, затем боковая внешняя фиксация, затем фиксация спицами соответственно. Однако стабильность фиксации перекрещенными двумя или тремя спицами против торсионных сил превосходят фиксацию интрамедуллярными штифтами и боковую внешнюю фиксацию, при этом фиксация тремя перекрещенными спицами (двумя латеральными и одной медиальной, или двумя медиальными и одной латеральной) в зависимости от линии перелома обеспечивает наибольшую стабильность. Kow R.Y. и др. сообщили об удовлетворительных косметических и функциональных результатах без повышенного риска осложнений при лечении надмыщелковых переломов плечевой кости боковой внешней фиксацией (двумя стержнями) с комбинацией чрескожным остеосинтезом одной латеральной спицей по сравнению с классическим остеосинтезом перекрещенными спицами [51, 52].
При исследовании результатов лечения внесу-ставных переломов дистального отдела плечевой кости у подростков с помощью закрытой репозиции с фиксацией спицами и после открытой репозиции с фиксацией спицами, Phillip Bell и др. сообщают о том, что закрытая репозиция приводит к удовлетворительным клиническим и рентгенологическим результатам, позволяет быстрое восстановление функции и уменьшает количество осложнений [53]. S. Pesenti и соавт. в ретроспективных когортных исследованиях оценки методов фиксации надмыщелковых переломов у детей сообщают, что проведение открытой репозиции надмыщелковых переломов у детей через малоинвазивный доступ с фиксацией медиальной спицей увеличивает время операции, но снижает риск развития вторичного смещения, развития ятрогенного повреждения локтевого нерва и улучшает стабильность фиксации перелома [54].
Лечение метафизарных переломов дистального отдела плечевой кости у детей методом чрескост-ного остеосинтеза по Илизарову, несмотря на сложность методики, позволяет добиться точной закрытой репозиции, стабильной фиксации, раннего полноценного функционального лечения и является малотравматичным и эффективным методом [55, 56]. В литературе имеются также данные о применении в лечении надмыщелковых и чрезмыщелковых переломов фиксации винтом, двумя винтами, винтом с одной спицей или более [53, 57].
Показанием для открытой репозиции могут служить открытые переломы, безуспешность закрытой репозиции и наличие сосудисто-неврологических нарушений, требующих ревизию в области перелома. В литературе описаны различные оперативные доступы и методики при надмыщелковых и чрезмыщелковых переломах. Хирургический доступ может быть как медиальным, так и латеральным, либо комбинированным с двух сторон, а также существует и передний и задний доступ локтевого сустава. В лечении дистальных метафизарных переломов плечевой кости у подростков применяются также открытая репозиция с внутренней фиксацией накостным остеосинтезом (одной или двумя пластинками) и фиксация винтами [53, 58].
Осложнения. Эти переломы могут иметь осложнения, такие как до лечения (неврологические, сосудистые и компартмент синдром), и осложнения после лечения (ранние: потеря репозиции, неврологические, сосудистые, синдром сдавления, инфицирование; поздние: угловая деформация, снижение объёма движения в локтевом суставе, оссифи-цирующий миозит, аваскулярный некроз блока, ложный сустав и др.) [59].
Нейроваскулярные осложнения могут развиваться при всех видах переломов даже без смещения, но, как правило, чаще происходят при переломах с полным смещением (III-IV типа по Gartland), по данным литературы травматическая неврапраксия происходит с частотой 11,3% случаев. Нейропатия переднего межкостного нерва чаще развивается при надмыщелковых переломах разгибательного типа, а повреждение локтевого нерва чаще встречается при сгибательном типе и ятрогенно при медиальном доступе чрескожного остеосинтеза [60]. Травма лучевого нерва характерена при переломах с заднемедиальным смещением [61].
Варусные деформации локтевого сустава возникают в 10-70% случаев после надмыщелковых и чрезмыщелковых переломов. В зависимости от характера смещения деформация может быт вальгусной (Cubitus Valgus), варусной (Cubitus Varus) или по сагиттальной оси (Recurvatum Deformity) [62]. Salonen и соавт. утверждают, что оперативные вмешательства с остеосинтезом дистальных переломов плечевой кости увеличились в четыре раза с 1987 по 2016 год, за этот же период значительно уменьшилось количество корригирующих остеотомий [63].
Заключение
Надмыщелковые и чрезмыщелковые переломы являются самыми частыми среди переломов локтевого сустава у детей. Разгибательные переломы существенно чаще встречаются, чем сгибательные. Из предложенных классификаций наиболее актуальной и практичной является классификация Gartland и основанная на ней классификация переломов дистального отдела АО-комплексная классификация переломов длинных трубчатых костей у детей (PCCF). Их критерии помогают более точно установить верный диагноз, определить тактику лечения и наиболее характерные осложнения.
Лечение дистальных метефизарных (надмыщелковых и чрезмыщелковых) переломов без смещения I-типа по Gartland, по мнению многих авторов, проводится консервативно путём иммобилизации гипсовой лангетой. Стабильные переломы со смещением (типа II), поддающиеся стабильной репозиции, можно лечить консервативно после проведения закрытой репозиции, но в связи с риском вторичного смещения следует фиксировать закрытыми методами спицами. Предпочтительным методом лечения нестабильных переломов со смешением (типа III и VI по Gartland), по мнению многих авторов, является закрытая репозиция с чрескожным остеосинтезом спицами. При неуспешных попытках выполнения закрытой репозиции или при развитии серьёзных сосудисто-неврологических нарушений нужно применить открытую репозицию с ревизией области перелома.
Правильный подход в диагностике и лечении дистальных метефизарных переломов плечевой кости, разумный выбор метода оперативного лечения и техники остеосинтеза обеспечивают положительные результаты лечения, уменьшают риск развития осложнений на протяжении всех этапов лечения и количество оперативных вмешательств в лечении посттравматических деформаций.
Список литературы Переломы дистального метафиза плечевой кости у детей: этиопатогенез, клиника, диагностика, лечение
- Wang H, Feng C, Liu H, et al. Epidemiologic Features of Traumatic Fractures in Children and Adolescents: A 9-Year Retrospective Study. Biomed Res Int. 2019;2019:8019063. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/8019063
- Merckaert S, Chaibi E, Meriem S et al. Epidemiology of Pediatric Upper Extremity Fractures in Tertiary Care Center in Switzerland [published online ahead of print, 2020 Feb 27]. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2020;10.1097/PEC.0000000000002047. https://doi.org/10.1097/PEC.0000000000002047
- Морозов С.Ю., Тучик Е.С., Морозов Ю.Е. Судебно-медицинские аспекты оценки переломов костей, составляющих локтевой сустав у детей. Медицинская экспертиза и право. 2015;1:31-35. Morozov S.Yu., Tuchik E.S., Morozov Yu.E. Forensic assessment of fractures of bones of an elbow joint in children. Meditsinskaya ekspertiza i pravo. 2015;(1):31-35. (In Russ).
- Hussain S, Dar T, Beigh AQ, et al. Pattern and epidemiology of pediatric musculoskeletal injuries in Kashmir valley, a retrospective single-center study of 1467 patients. J Pediatr Orthop B 2015;24:230–237.
- Issin A, Kockara N, Oner A, Sahin V. Epidemiologic properties of pediatric fractures in a metropolitan area of Turkey. Medicine (Baltimore) 2015;94:e1877.
- Baig MN. A Review of Epidemiological Distribution of Different Types of Fractures in Paediatric Age. Cureus. 2017;9(8):e1624. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.1624
- Rodríguez-Martínez JJ, Mora-Ríos FG, Mejía-Rohenes LC. Pediatric traumatic elbow frequency in Hospital Regional General Ignacio Zarago-za. Rev Esp Med Quir. 2018;23(2):87-92.
- Tepeneu N.F. Fractures of the Humeral Condyles in Children. A Review Journal of Medical and Psychological Trauma. 2018;1(1):3-13.
- Pilla NI, Rinaldi J, Hatch M, Hennrikus W. Epidemiological Analysis of Displaced Supracondylar Fractures. Cureus. 2020;12(4):e7734. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.7734
- Okubo H, Nakasone M, Kinjo M et al. Epidemiology of paediatric elbow fractures: a retrospective multi-centre study of 488 fractures. J Child Orthop. 2019;13(5):516-521. https://doi.org/10.1302/1863-2548.13.190043
- Anjum R, Sharma V, Jindal R et al. Epidemiologic pattern of paediatric supracondylar fractures of humerus in a teaching hospital of rural India: A prospective study of 263 cases. Chin J Traumatol. 2017;20(3):158-160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjtee.2016.10.007
- Wilkins KE. Fractures and dislocations of the elbow region. In: Rockwood CA Jr, Wilkins KE, King RE, editors. Fractures in children. 3rd ed. Philadelphia: JB Lippincott; 1991. p. 526–617.
- Ryan LM, Bachur RG, Wiley JF. Evaluation and management of supracondylar fractures in children. UpToDate. Waltham (MA): UpToDate. 2009.
- Smuin DM, Hennrikus WL. The Effect of the Pucker Sign on Outcomes of Type III Extension Supracondylar Fractures in Children. J Pediatr Orthop. 2017;37(4):e229-e232. https://doi.org/10.1097/BPO.0000000000000893
- Louahem D, Cottalorda J. Acute ischemia and pink pulseless hand in 68 of 404 gartland type III supracondylar humeral fractures in children: Urgent management and therapeutic consensus. Injury. 2016;47(4):848-852. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.injury.2016.01.010
- Franklin CC, Skaggs DL. Approach to the pediatric supracondylar humeral fracture with neurovascular compromise. Instr Course Lect. 2013;62:429-433.
- Dhoju D, Shrestha D, Parajuli N et al. Ipsilateral supracondylar fracture and forearm bone injury in children: a retrospective review of thirty one cases. Kathmandu Univ Med J (KUMJ). 2011 Apr-Jun;9(34):11-6. https://doi.org/ 10.3126/kumj.v9i2.6280. PMID: 22610861
- Goldfarb CA, Patterson JM, Sutter M, Krauss M, Steffen JA, Galatz L. Elbow radiographic anatomy: measurement techniques and normative data. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2012;21(9):1236-1246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jse.2011.10.026
- Kao HK, Lee WC, Yang WE, Chang CH. Clinical significance of anterior humeral line in supracondylar humeral fractures in children. Injury. 2016;47(10):2252-2257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.injury.2016.06.037
- Weiland A. In: The elbow and its disorders. 3. Morrey B, editor. Philadelphia: WB Saunders; 2000. p. 13–42.
- Johnson, Thomas R., Lynne S. Steinbach, eds. Essentials of musculoskeletal imaging. American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, 2004.
- Madjar-Simic I, Talic-Tanovic A, Hadziahmetovic Z, Sarac-Hadzihalilovic A. Radiographic assessment in the treatment of supracondylar hu-merus fractures in children. Acta Inform Med. 2012;20(3):154-159. https://doi.org/10.5455/aim.2012.20.154-159
- Samelis PV, Papagrigorakis E, Ellinas S. Role of the Posterior Fat Pad Sign in Treating Displaced Extension Type Supracondylar Fractures of the Pediatric Elbow Using the Blount Method. Cureus. 2019;11(10):e6024. Published 2019 Oct 29. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.6024
- Баиров Г. А. Детская травматология. 2-е изд. СПб.: Питер, 2000. Bairov G.A. Detskaya travmatologiya. 2nd ed. Saint Petersburg: Piter; 2000. (In Russ).
- Amir S, Jannis S, Daniel R. Distal humerus fractures: a review of current therapy concepts. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2016;9(2):199-206. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12178-016-9341-z
- Ul Islam S, Glover AW, Waseem M. Challenges and Solutions in Management of Distal Humerus Fractures. Open Orthop J. 2017;11:1292-1307. https://doi.org/10.2174/1874325001711011292
- Jupiter JB, Mehne DK. Fractures of the distal humerus. Orthopedics. 1992;15(7):825-833.
- Juan P. Simone 44 - Low Transcondylar Fractures of the Distal Humerus, Editor(s): Bernard F. Morrey, Joaquin Sanchez-Sotelo, Mark E. Mor-rey,Morrey's the Elbow and its Disorders (Fifth Edition), Elsevier, 2018:440-449. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-323-34169-1.00044-9 (https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780323341691000449)
- Cepela DJ, Tartaglione JP, Dooley TP, Patel PN. Classifications In Brief: Salter-Harris Classification of Pediatric Physeal Fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2016;474(11):2531-2537. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-016-4891-3
- Beckmann NM, Crawford L. Salter-Harris I fracture of the distal humerus in a neonate: imaging appearance of radiographs, ultrasound, and arthrography. Radiol Case Rep. 2017;12(3):571-576. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radcr.2017.04.013
- Alton TB, Werner SE, Gee AO. Classifications in brief: the Gartland classification of supracondylar humerus fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2015;473(2):738-741. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-014-4033-8
- Barton KL, Kaminsky CK, Green DW, Shean CJ, Kautz SM, Skaggs DL. Reliability of a modified Gartland classification of supracondylar hu-merus fractures. J Pediatr Orthop. 2001;21(1):27-30. https://doi.org/10.1097/00004694-200101000-00007
- Meinberg EG, Agel J, Roberts CS, Karam MD, Kellam JF. Fracture and Dislocation Classification Compendium-2018. J Orthop Trauma. 2018;32 Suppl 1:S1-S170. https://doi.org/10.1097/BOT.0000000000001063
- Slongo TF, Audigé L; AO Pediatric Classification Group. Fracture and dislocation classification compendium for children: the AO pediatric comprehensive classification of long bone fractures (PCCF). J Orthop Trauma. 2007;21(10 Suppl):S135-S160. https://doi.org/10.1097/00005131-200711101-00020
- Joeris A, Lutz N, Blumenthal A, Slongo T, Audigé L. The AO Pediatric Comprehensive Classification of Long Bone Fractures (PCCF). Acta Orthop. 2017;88(2):123-128. https://doi.org/10.1080/17453674.2016.1258532
- Audigé L, Slongo T, Lutz N, Blumenthal A, Joeris A. The AO Pediatric Comprehensive Classification of Long Bone Fractures (PCCF). Acta Orthop. 2017;88(2):133-139. https://doi.org/10.1080/17453674.2016.1258534
- Battaglia TC, Armstrong DG, Schwend RM. Factors affecting forearm compartment pressures in children with supracondylar fractures of the humerus. J Pediatr Orthop. 2002;22(4):431-439.
- Moraleda L, Valencia M, Barco R, González-Moran G. Natural history of unreduced Gartland type-II supracondylar fractures of the humerus in children: a two to thirteen-year follow-up study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2013;95(1):28-34. https://doi.org/10.2106/jbjs.l.00132
- Pham TT, Accadbled F, Abid A, et al. Gartland types IIB and III supracondylar fractures of the humerus in children: is Blount's method effec-tive and safe? J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2017;26(12):2226-2231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jse.2017.05.018
- Muccioli C, ElBatti S, Oborocianu I, et al. Outcomes of Gartland type III supracondylar fractures treated using Blount's method. Orthop Trau-matol Surg Res. 2017;103(7):1121-1125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.otsr.2017.06.011
- Park MJ, Ho CA, Larson AN. AAOS Appropriate Use Criteria: Management of Pediatric Supracondylar Humerus Fractures. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2015;23(10):e52-e55. https://doi.org/10.5435/JAAOS-D-15-00408
- Howard A, Mulpuri K, Abel MF, et al. The treatment of pediatric supracondylar humerus fractures. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2012;20(5):320-327. https://doi.org/10.5435/JAAOS-20-05-320
- Yang J, Wang T, Tian NF, et al. Supracondylar humeral fractures in children: American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons appropriate use criteria versus actual management in a teaching hospital. J Child Orthop. 2019;13(4):404-408. https://doi.org/10.1302/1863-2548.13.190081
- Wang JH, Morris WZ, Bafus BT, Liu RW. Pediatric Supracondylar Humerus Fractures: AAOS Appropriate Use Criteria Versus Actual Manage-ment at a Pediatric Level 1 Trauma Center. J Pediatr Orthop. 2019;39(8):e578-e585. https://doi.org/10.1097/BPO.0000000000001096
- Novais EN, Andrade MA, Gomes DC. The use of a joystick technique facilitates closed reduction and percutaneous fixation of multidirection-ally unstable supracondylar humeral fractures in children. J Pediatr Orthop. 2013;33(1):14-19. https://doi.org/10.1097/BPO.0b013e3182724d07
- Abbott MD, Buchler L, Loder RT, Caltoum CB. Gartland type III supracondylar humerus fractures: outcome and complications as related to operative timing and pin configuration. J Child Orthop. 2014;8(6):473-477. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11832-014-0624-x
- Shon H-C, Kim JW, Shin H-K, et al. Does the timing of surgery affect outcomes of Gartland type III supracondylar fractures in children? Pediat-ric Traumatology, Orthopaedics and Reconstructive Surgery. 2019;7(2):25-32. https://doi.org/10.17816/PTORS7225-32
- Brauer CA, Lee BM, Bae DS, Waters PM, Kocher MS. A systematic review of medial and lateral entry pinning versus lateral entry pinning for supracondylar fractures of the humerus. J Pediatr Orthop. 2007;27(2):181-186. https://doi.org/10.1097/bpo.0b013e3180316cf1
- Kamara A, Ji X, Liu C, Liu T, Wang E. The most stable pinning configurations in transverse supracondylar humerus fracture fixation in chil-dren: A novel three-dimensional finite element analysis of a pediatric bone model. Injury. 2021;52(6):1310-1315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.injury.2021.01.012
- Gottschalk HP, Sagoo D, Glaser D, Doan J, Edmonds EW, Schlechter J. Biomechanical analysis of pin placement for pediatric supracondylar humerus fractures: does starting point, pin size, and number matter?. J Pediatr Orthop. 2012;32(5):445-451. https://doi.org/10.1097/BPO.0b013e318257d1cd
- Liu C, Kamara A, Liu T, Yan Y, Wang E. Mechanical stability study of three techniques used in the fixation of transverse and oblique metaph-yseal-diaphyseal junction fractures of the distal humerus in children: a finite element analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020;15(1):34. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13018-020-1564-4
- Kow RY, Zamri AR, Ruben JK, Jamaluddin S, Mohd-Nazir MT. Humeral Supracondylar Fractures in Children: A Novel Technique of Lateral External Fixation and Kirschner Wiring. Malays Orthop J. 2016;10(2):41-46. https://doi.org/10.5704/MOJ.1607.008
- Bell P, Scannell BP, Loeffler BJ, et al. Adolescent Distal Humerus Fractures: ORIF Versus CRPP. J Pediatr Orthop. 2017;37(8):511-520. https://doi.org/10.1097/BPO.0000000000000715
- Pesenti S, Ecalle A, Gaubert L, et al. Operative management of supracondylar humeral fractures in children: Comparison of five fixation methods. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2017;103(5):771-775. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.otsr.2017.05.008
- Швед С. И., Сысенко Ю. М., Знаменский Г. Б. Лечение переломов плечевой кости у детей методом чрескостного остеосинтеза по Илизарову. Гений ортопедии. 1996;1:66-70. Shved S. I., Sysenko Yu. M., Znamensky G. B. Treatment of humeral fractures in children by the method of transosseous osteosynthesis according to Ilizarov. Genius of Orthopedics. 1996;1:66-70. (In Russ).
- Gugenheim JJ Jr. The Ilizarov fixator for pediatric and adolescent supracondylar fracture variants. J Pediatr Orthop. 2000;20(2):177-182.
- Dabash S, Gerzina C, Prabhakar G, Thabet AM, Jeon S, Heinrich SD. Screw fixation for supracondylar humerus fractures in children: a report of seventeen cases. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2019;29(3):575-581. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-018-2316-6
- Ersan O, Gonen E, İlhan RD, Boysan E, Ates Y. Comparison of anterior and lateral approaches in the treatment of extension-type supracondy-lar humerus fractures in children. J Pediatr Orthop B. 2012;21(2):121-126. https://doi.org/10.1097/BPB.0b013e32834dd1b2]
- Vaquero-Picado A, González-Morán G, Moraleda L. Management of supracondylar fractures of the humerus in children. EFORT Open Rev. 2018;3(10):526-540. https://doi.org/10.1302/2058-5241.3.170049
- Babal JC, Mehlman CT, Klein G. Nerve injuries associated with pediatric supracondylar humeral fractures: a meta-analysis. J Pediatr Orthop. 2010;30(3):253-263. https://doi.org/10.1097/BPO.0b013e3181d213a6
- Wang SI, Kwon TY, Hwang HP, Kim JR. Functional outcomes of Gartland III supracondylar humerus fractures with early neurovascular compli-cations in children: A retrospective observational study. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017;96(25):e7148. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000007148
- Koch PP, Exner GU. Supracondylar medial open wedge osteotomy with external fixation for cubitus varus deformity. J Pediatr Orthop B. 2003;12(2):116-122. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.bpb.0000049571.52224.c8
- Salonen A, Niemi ST, Kannus P, Laitakari E, Mattila VM. Increased incidence of distal humeral fracture surgery and decreased incidence of respective corrective osteotomy among Finns aged 0 to 18 years between 1987 and 2016: a population-based study. J Child Orthop. 2019;13(4):399-403. https://doi.org/10.1302/1863-2548.13.190049


