Первый опыт применения новой генерации активного робота в первичном тотальном эндопротезировании коленного сустава
Автор: Лычагин А.В., Грицюк А., Рукин Я.А., Елизаров М.П., Грицюк А.А., Гавловский М.Я., Томбоиди К.Х.
Журнал: Кафедра травматологии и ортопедии @jkto
Рубрика: Оригинальное исследование
Статья в выпуске: 1 (55), 2024 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Введение. Тотальное эндопротезирование коленного сустава с помощью робота является быстро развивающейся областью, в настоящее время появляются новые системы роботов поэтому в этой статье обобщается текущий статус роботизированной технологии, обсуждаются ее преимущества и недостатки.Целью исследования явилось сравнение преимуществ и недостатков новой активной роботизированной системы и их влияние на общую длительность операции.Материалы и методы. Проведено проспективное одноцентровое исследование результатов интраоперационного тайминга у 45 пациентов (12 мужчин и 33 женщины, со средним возрастом 65,9±7,4 лет, средний ИМТ - 31,3±4,7 кг/м2 с применением CJ150 CUVIS Joint® при тотальной артропластике колена, в сравнении с T-Solution One.Результаты. При проведении сравнительного анализа, выявлено статистически достоверное уменьшение общего времени операции при применении новой системы CUVIS на 33,7% меньше (111,5±15,9 мин, 168,2±29,9 мин, при р
Коленный сустав, робот, роботизированное тотальное эндопротезирование коленного сустава
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/142241715
IDR: 142241715 | УДК: 617.3 | DOI: 10.17238/2226-2016-2024-1-22-29
Текст научной статьи Первый опыт применения новой генерации активного робота в первичном тотальном эндопротезировании коленного сустава
THE DEPARTMENT OF TRAUMATOLOGY AND ORTHOPEDICS
Тотальное эндопротезирование коленного сустава остается одной из наиболее часто выполняемых хирургических процедур во всем мире: только в Великобритании (до пандемии COVID-19) ежегодно выполняется более 100 000 случаев [1]. В то время как тотальное эндопротезирование тазобедренного сустава было описано как операция века из-за превосходной удовлетворенности пациентов, превышающей 90% через 10 лет [2, 3], артропластика коленного сустава дает несколько худшие результаты [4].
Хотя принцип оптимального выравнивания при тотальном эндопротезировании коленного сустава остается предметом дискуссий [5, 6], ключевыми факторами успешного тотального эндопротезирования коленного сустава являются точное позиционирование имплантата с точной резекцией большеберцовой и бедренной костей, в сочетании с мягкотканым балансом [7, 8, 9].
С ростом осведомленности об артропластике как варианте лечения и с тем, что большинство пациентов сообщают о высоком уровне удовлетворенности, количество выполненных тотальных артропластик коленного сустава продолжает расти. Средний возраст пациентов, перенесших тотальное эндопротезирование коленного сустава, снижается [10], а с учетом еще более высоких функциональных ожиданий и требований, предъявляемых к имплантату, необходимость точности резекции кости, позиционирования имплантата и балансировки связок имеет первостепенное значение, помимо удовлетворенности пациентов и выживаемости имплантатов.
Последние технологические достижения, в том числе роботизированное тотальное эндопротезирование коленного сустава и трехмерная печать индивидуальных имплантатов и инструментов, направлены на оптимизацию этих хирургических факторов. Навигация при тотальном эндопротезировании коленного сустава хорошо известна, и лежащий в ее основе принцип позволяет хирургам оценить анатомию кости пациента на экране в реальном времени во время операции, чтобы точно выполнить резекцию кости и балансировку связок. Ранее в Великобритании и США от 3 до 5% всех выполненных артропластик коленного сустава использовали навигацию, тогда как в Австралии этот показатель выше — 30% [11].
Роботизированное тотальное эндопротезирование коленного сустава основано на принципах навигации и позволяет хирургам выполнять предоперационное планирование и с большой точностью выполнять хирургическое вмешательство с помощью интраоперационной роботизированной руки, которая, в зависимости от типа робота, либо автономно выполнит заранее заданные резекции, либо поможет хирургу в этом [12, 13] (Song et al, 2013; Hampp et al, 2019; Salt et al, 2019).
Активные роботизированные системы используют предоперационные данные (в виде компьютерной томографии или магнитно-резонансная томография) в сочетании с интраоперационным анатомическим картированием для выполнять заранее запланированные костные резекции самостоятельно. Хирургический робот ROBODOC, ныне известный как TSolutionOne (THINK Surgical Inc., Фремонт, Калифорния, США), является хорошо известным примером полностью активной системы. Эта система использует предоперационную компьютерную томографию для создания виртуальной модели, на которой хирург может планировать разрезы кости для достижения желаемого выравнивания, расположение и размер имплантата [15, 16]. Авторы статьи использовали в течение 5 лет данную систему и накопили некоторый опыт ее применения [17, 18].
Тотальное эндопротезирование коленного сустава с помощью робота является быстро развивающейся областью, в настоящее время появилась более новая система активного робота CJ150
CUVIS Joint® (CUREXO Inc., Cеул, Республика Корея), которая претерпела некоторые принципиальные изменения, поэтому в этой статье обобщается текущий статус роботизированной технологии в тотальном эндопротезировании коленного сустава, обсуждаются ее преимущества и ограничения, а также оцениваются последние данные, касающиеся результатов роботизированной тотальной артропластики коленного сустава.
Целью исследования явилось сравнение преимуществ и недостатков новой активной роботизированной системы и их влияние на общую длительность операции.
Материалы и методы:
Проведено проспективное одноцентровое исследование в клинике травматологии, ортопедии и патологии суставов университетской клинической больницы №1 кафедры травматологии, ортопедии и хирургии катастроф ФГАОУ ВО Первого МГМУ им. И. М. Сеченова (Сеченовский университет) в 2023 г.
Критерии включения пациентов в исследование:
– Пациенты старше 18 лет с гонартрозом 3-4 степени по классификации Kellgren-Lawrence и болевым синдромом выше 5 баллов по 10-балльной ВАШ;
– Риск анестезиологического пособия по шкале АSА не более III;
– Наличие письменного информированного согласия на выполнение операции ТЭКС по предложенной методике;
Критерии невключения:
– Риск анестезиологического пособия по шкале АSА более III;
– Индекс массы тела (ИМТ) больше 45 кг/м2;
– Деформация коленного сустава (не более вальгус-варус 10°), первичные дефекты костной ткани;
Критерии исключения пациентов из исследования:
– Отказ пациента от дальнейшего участия в исследовании;
– Несоблюдение пациентом предписанного режима.
Согласно критериям включения и невключения для клинического исследования методом сплошной выборки отобрано 45 пациентов (12 мужчин и 33 женщины) для проведения роботизированного тотального эндопротезирования коленного сустава с применением активного робота CJ150 CUVIS Joint®. Средний возраст пациентов составил 65,9±7,4 лет (критерий Шапиро-Уилка, р=0,307), средний ИМТ (кг/м2) – 31,3±4,7 (p=0,099).
Во время операции проводили хронометрию этапов хирургического вмешательства согласно принятому протоколу и результаты заносили в базу данных. При анализе результатов исследования, из базы данных пациентов, оперированных при помощи активной роботической системой T-Solution One® (THINK Surgical, Inc., США) было выбрано 45 пациентов
(10 мужчин и 35 женщин) с подобными средними данными возраста (66,7±7,4 лет) и ИМТ (31,9±5,4 кг/м2), и результаты были сравнены между собой.
Статистическая обработка клинического материала проводилась с помощью программы IBM SPSS Statistics 23 (SPSS Inc., Чикаго, Иллинойс): группировка данных, вычисление интенсивных и экстенсивных показателей, определение средней ошибки относительных величин, определение нормального распределения критерием Шапиро-Уилка, при оценке различий между двумя зависимыми выборками, взятыми из закона распределения, отличного от нормального - критерий Уилкоксона.
Методика операции: Положение пациента и анестезия в обеих группах не различались. Роботизированная хирургическая (ортопедическая) система CJ150 CUVIS Joint® принципиально состоит основных элементов (Рисунок 1), и помогает хирургам в планировании и проведении эндопротезирования коленных суставов.
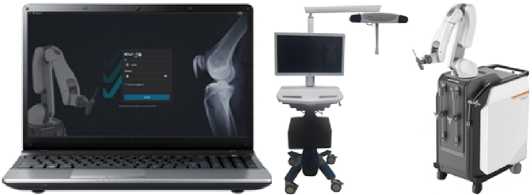
Рисунок 1 – Основные элементы системы CJ150 CUVIS Joint®: а – консоль планирования, б – основная консоль, в – манипулятор
-
1. Консоль планирования – компьютер, который дает возможность хирургу обрабатывать DICOM file сканы КТ пациента, на основании которых разрабатывается предоперационный план, рассчитываются оси нижней конечности и коленного сустава, подбирается и позиционируется имплантат, намечаются линии резекции бедренной и большеберцовой костей с учетом индивидуальных анатомических особенностей пациента.
-
2. Основная консоль – состоит из подвижного интерактивного монитора, для управления всей системой вместе с манипулятором и инфракрасной камерой системы OTS (Оптическая Система Слежения) во время операции.
-
3. Манипулятор - состоит из подвижной опоры, руки манипулятора, на крайнем звене которого фиксируется хирургический режущий инструмент.
Роботизированная хирургическая технология первичного тотального эндопротезирования коленного сустава включает 3 этапа (Рисунок 2):
Этап 1. Предоперационное планирование.
-
а) КТ нижней конечности – выполняется с захватом тазобедренных и голеностопных суставов в положении 175 градусов сгибания в коленных суставах с фиксированным калибровочным стержнем с шагом в 1 мм;
-
б) Предоперационное планирование – начинается с анализа результатов КТ оперируемого сустава и всей нижней конечности пациента, для определения размеров костей, точного определения осей конечности и различных деформаций на всех срезах конечности – процедура сегментации, выполняется на данной системе в автоматическом режиме, но проверяется хирургом;
-
в) Используя консоль планирования, хирург создает трехмерную (3D) модель сустава пациента, выбирает имплантат, определяет оптимальное размещение и выравнивание, создает персонализированный операционный план и сохраняет его на USB-носителе.

а б в
Рисунок 2 – Схема технологии: а – КТ, б - консоль планирования, в - манипулятор
Этап 2. Предоперационная подготовка робота включает:
-
а) Нестерильную часть – включение системы, загрузка OPERATING file и тестирование системы управления робота;
-
б) одевание и фиксация стерильных чехлов на манипуляторе, сборка и тестирование маркеров робота и конечности (Рисунок 3).
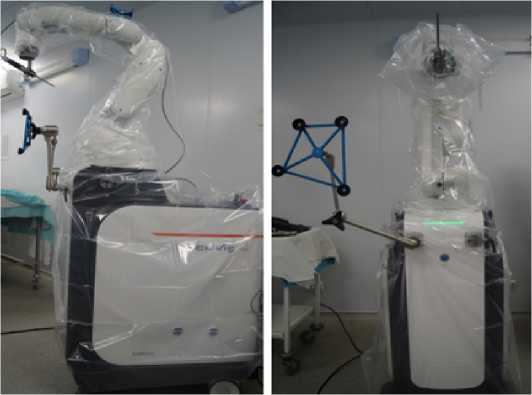
Рисунок 3 – Вид манипулятора в стерильном чехле: а – вид сбоку, б – вид спереди
Этап 3. Этап хирургической операции, данный этап рассмотрим на клиническом примере. Пациентка П., 70 лет, диагноз:
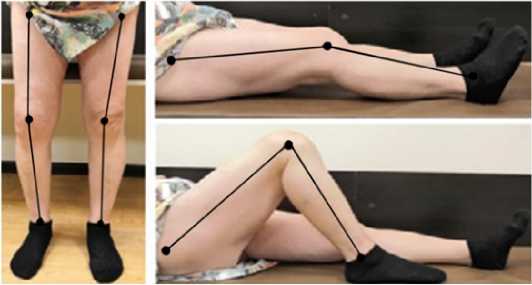
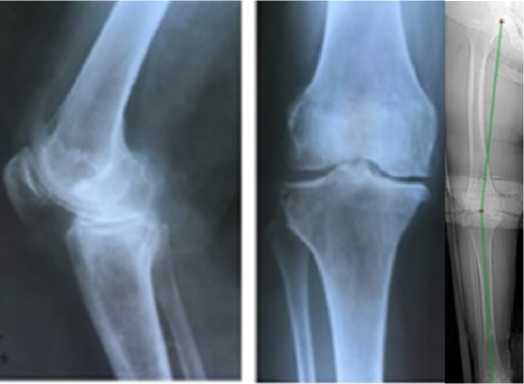
посттравматический правосторонний гонартроз III стадия, варусная деформация, комбинированная контрактура коленного сустава, болевой синдром. Вид пациента, функция сустава и рентгенограммы представлены на Рисунках 4-5.
а б в
Рисунок 4 - Вид пациента и функция конечности до операции: а – вид спереди, б – вид сбоку в сгибании, в – вид сбоку в разгибании
а
б
Рисунок 5 - Рентгенограммы коленного сустава (а) и топограмма (б)
Операция начинается с медиа-парапателлярного доступа к коленному суставу с вывихом надколенника кнаружи, при этом удалять остеофиты на бедренной и большеберцовой кости запрещается (Рисунок 6).
Далее приступают к установке винтов Шанца, на которые устанавливают бедренный и большеберцовый костные маркеры и приступают к сбору данных и оцифровке контрольных точек – костной регистрации (Рисунок 7).
Процесс регистрации представляет из себя совмещении точек компьютерной томографии и соответствующего виртуального прототипа бедренной и большеберцовой костей, которые были созданы при планировании операции (Рисунок 8).
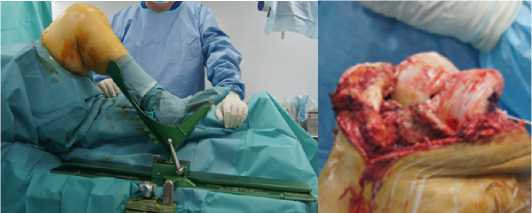
Рисунок 6 – Вид коленного сустава перед операцией: a -конечность фиксирована в специальном держателе, б – выполнен медиальный парапателлярный доступ к коленному суставу
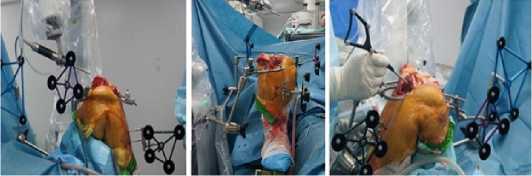
б в
Рисунок 7 – Интраоперационная картина: а - установка маркеров, б – фиксация робота, в - оцифровка контрольных точек
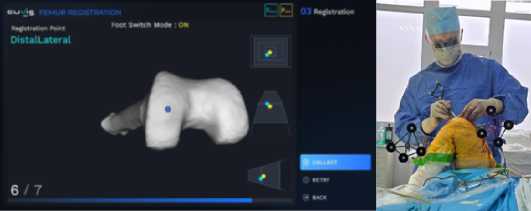
а б
Рисунок 8 – А – вид панели основной консоли при оцифровке, б – хирург, выполняющий процедуру костной регистрации
После окончания костной регистрации робот выполняет резекцию бедренной и большеберцовой костей (Рисунок 9 а), затем хирургический робот отсоединяют от конечности пациента и после незначительной резекции костных опилов (краевые заусенцы снимаются хирургическим рашпилем (Рисунок 9 б), коленный сустав готов к примерке протеза и проверке сгибательно-разгибательных промежутков.
Далее после установки примерочных конпонентов коленного сустава, хирург проверяет баланс связок, при необходимости выполняет мягктканные релизы, и фиксирует результат на мониторе и в памяти компьютера (Рисунок 10).
При необходимости коррекции оси или баланса мягких тканей выполняют ререзекцию, или релиз мягких тканей до приемлемого положения имплантата и конечности. После чего выполняется окончательна имплантация коленного протеза (Рисунок 11).
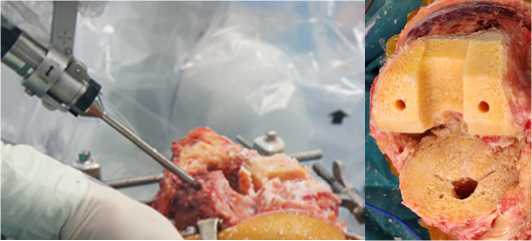
Рисунок 9 – Интраоперационная картина: а – резекция кости, б - вид кости после резекции
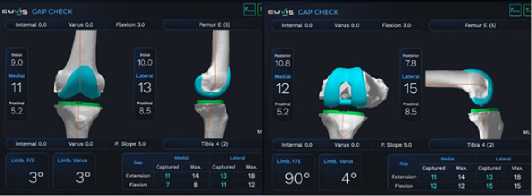
Рисунок 10 – Вид монитора при определении параметров сгибательно-разгибательного промежутков и осей конечности: а- в положении разгибания, б – в положении сгибания
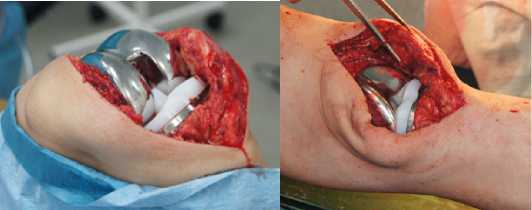
Рисунок 11 – Вид операционной раны после имплантации протеза коленного сустава
В послеоперационном периоде проводили лечение, направленное на заживление раны и раннюю реабилитацию коленного сустава, на 2-3 сутки выполняли контрольную рентгенографию и после восстановления полного объема движений на 7-12 сутки топограмму нижних конечностей (Рисунок 12).
Результаты.
При проведении сравнительного анализа, результаты которого приведены в Таблице 1 и на Рисунке 13.
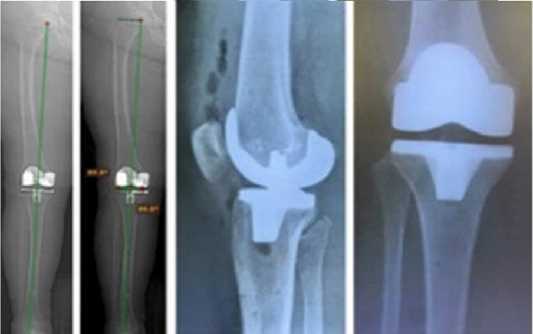
Рисунок 12 - Рентгенологическое обследование после операции: а – топограммы, б - рентгенограммы после роботизированного эндопротезирования коленного сустава.
Таблица 1
Сравнительный анализ хронометрии этапов операции
|
Этапы операции (мин.) |
Группы пациентов |
Р* |
|
|
CUVIS |
T-Solution One |
||
|
Подготовка робота |
14,32±4,6 |
42,52±7,4 |
0,000 |
|
Доступ |
10,85±2,3 |
10,08±2,5 |
0,135 |
|
Установка трекеров |
5,09±0,3 |
- |
- |
|
Фиксация |
12,4±3,7 |
18,32±6,2 |
0,003 |
|
Костная регистрация |
12,64±5,4 |
22,99±9,6 |
0,001 |
|
Резекция кости |
19,79±2,1 |
27,15±7,9 |
0,000 |
|
Примерка |
5,62±0,6 |
6,65±0,5 |
0,241 |
|
Цементирование |
15,02±1,34 |
17,49±4,2 |
0,544 |
|
Ушивание |
15,77±1,9 |
17,94±5 |
0,311 |
|
Общее время |
111,5±15,9 |
168,2±29,9 |
0,000 |
* - критерий Уилкинсона
Выявлено, что имело место статистически достоверная разница общего времени операции, которое было при применении новой системы CUVIS на 33,7% меньше, чем при T-Solution One, среднее время операции на 56 минут (при р <0,001).
Результат складывается из времени подготовки робота к операции которое в 3 раза больше, время, потраченное на хирургический доступ в обеих группах, практически совпало, время установки трекеров компенсировалось более простым методом фиксации. Костная регистрация (в 1,8 раза) и скорость резекции кости системы (в 1,4 раза) CUVIS гораздо более быстрые и результаты статистически значимые. Примерка, цементирование протеза и время ушивания раны были примерно одинаковыми и статистически значимой разницы не имели.
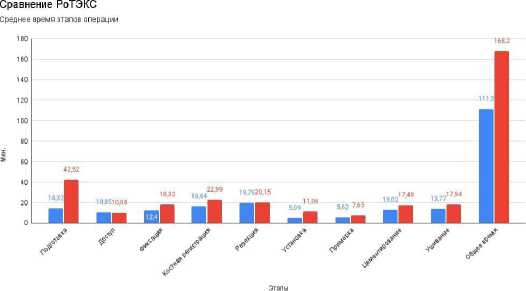
■ Cuvis ■ T-SolulionOne
Рисунок 13. Гистограмма сравнения времени этапов операции
Обсуждение.
В большей части статей по теме нашего исследования содержат данные о точности выравнивания оси конечности и положения имплантата, в сравнении с общепринятой мануальной техникой. Исследования в которых сравниваются, подобные роботизированные системы мы не обнаружили. Полностью активные или автономные системы получили несколько ограниченное распространение по сравнению с полуактивными системами, отчасти в результате неоднозначных результатов, описанных в литературе.
Song E.K. et al., (2013) провели рандомизированное исследование с участием 100 пациентов и обнаружили, что в группе с роботизированной помощью увеличение времени операции было больше на 25 минут, чем при мануальной технике, но никаких проблем это в дальнейшем пациентам не доставило [19].
Аналогичным образом, Liow M.H.L., et al., (2014) рандомизировали 60 пациентов и оценили двухлетние результаты роботизированной и традиционной тотальной артропластики коленного сустава. Они сообщили, что, несмотря на большую длительность операции, оценки функциональных шкал колена и уровень удовлетворенности пациентов не различались между двумя группами, хотя в группе с роботами было небольшое улучшение показателей качества жизни по сравнению с обычной группой [20, 21].
Опасения по поводу полностью автономных систем связаны с более длительным временем операции и наложения жгута, а также травмой мягких тканей. Liow et al, (2017) обнаружили, что среднее время наложения жгута составляет 91 минуту, и отметили, что 6,5% пациентов после роботизированной ТЭКС развился тромбоз глубоких вен, который они объяснили тем, что ногу жестко удерживали в держателе [15].
В большом рандомизированном контролируемом исследовании с 10-летним периодом наблюдения вверх (724 колена), Kim Y.H., et al., (2020) обнаружили, что у группы с роботами было более длинное время жгута (75 против 38 минут), что остается часто встречающейся проблемой для роботизированного тотального коленного сустава [22].
Park S.E., Lee C.T. (2007) рандомизировали 72 пациента на полностью активную роботизированную и традиционную тотальную артропластику коленного сустава и обнаружили более высокий уровень осложнений в группе с роботизированной поддержкой, однако повреждения мягких тканей были ятрогенными [23].
Таким образом, основной проблемой активных роботов было увеличение времени операции, но мы можем сказать, что новая генерация активного робота значительно «быстрее» предыдущей за счет следующих нововведений:
-
1. Автоматизирована предоперационная подготовка;
-
2. Удобный интерфейс и схема регистрации;
-
3. Фиксация и позиционирование робота проще;
-
4. Можно менять скорость перемещения фрезы во время операции;
-
5. Интраоперационная проверка оси конечности, сгибательно-разгибательных промежутков;
-
6. Меньшие габариты и большая маневренность.
Заключение. Будущее тотального эндопротезирования коленного сустава, несомненно, связано с роботизированными технологиями, которые показывают бурный рост, хотя в какой степени и в каком объеме это будет зависеть от дальнейших высококачественных исследований, оценивающих долгосрочные результаты, осложнения, выживаемость и анализ затрат и выгод.
Список литературы Первый опыт применения новой генерации активного робота в первичном тотальном эндопротезировании коленного сустава
- National Joint Registry. National Joint Registry 17th annual report. 2020. https://reports.njrcentre.org.uk/portals/0/pdfdownloads/njr%2017th%20annual%20report%202020.pdf (accessed 30 May 2023).
- Learmonth ID, Young C, Rorabeck C. The operation of the century: total hip replacement. Lancet. 2007;370(9597):1508–1519. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(07)60457-7.
- Ramaskandhan J, Smith K, Kometa S, Chockalingam N, Siddique M. Total joint replacement of ankle, knee, and hip: how do patients perceive their operative outcomes at 10 years? Foot Ankle Orthop. 2021;6(3):247301142110227. https://doi.org/10.1177/24730114211022735.
- Rodriguez-Merchan EC. Patient satisfaction following primary total knee arthroplasty: contributing factors. Arch Bone Joint Surg. 2021;9(4):379–386. https://doi.org/10.22038/ABJS.2020.46395.2274.
- Haddad FS. Evolving techniques: the need for better technology. Bone Joint J. 2017:99-B (2):145-146. https://doi.org/10.1302/0301-620X.99B2.38085/
- Roussot MA, Vles GF, Oussedik S. Clinical outcomes of kinematic alignment versus mechanical alignment in total knee arthroplasty: a systematic review. EFORT Open Rev. 2020;5(8):486–497. https://doi.org/10.1302/2058-5241.5.190093.
- Devers BN, Conditt MA, Jamieson ML et al. Does greater knee flexion increase patient function and satisfaction after total knee arthroplasty? J Arthroplasty. 2011;26(2):178–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ARTH.2010.02.008/
- Khan M, Osman K, Green G, Haddad FS. The epidemiology of failure in total knee arthroplasty. Bone Joint J. 2016;98-B(1_Supple_A):105–112. https://doi.org/10.1302/0301-620X.98B1.36293.
- Abdel MP, Ledford CK, Kobic A, Taunton MJ, Hanssen AD. Contemporary failure aetiologies of the primary, posterior-stabilised total knee arthroplasty. Bone Joint J. 2017;99B:647–652. https://doi. org/10.1302/0301-620X.99B5.BJJ-2016-0617.R3/
- Kurtz SM, Lau E, Ong K et al. Future young patient demand for primary and revision joint replacement: National projections from 2010 to 2030. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009;467(10):2606–2612. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-009-0834-6.
- Picard F, Clarke J, Deep K, Gregori A. Computer assisted knee replacement surgery: is the movement mainstream? Orthop Muscul Syst. 2014;3(2):1–6. https://doi.org/10.4172/2161-0533.1000153.
- Song EK, Seon JK, Yim JH, Netravali NA, Bargar WL. Roboticassisted TKA reduces postoperative alignment outliers and improves gap balance compared to conventional TKA. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2013;471(1):118–126. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11999-012-2407-3.
- Hampp EL, Chughtai M, Scholl LY et al. Robotic arm assisted total knee arthroplasty demonstrated greater accuracy and precision to plan compared with manual techniques. J Knee Surg. 2019;32(3):239–250. https://doi.org/10.1055/S-0038-1641729.
- Sultan AA, Samuel LT, Khlopas A et al. Robotic-arm assisted total knee arthroplasty more accurately restored the posterior condylar offset ratio and the insall-salvati index compared to the manual technique; a cohortmatched study. Surg Technol Int. 2019; 34:409-413
- Liow MHL, Chin PL, Pang HN, Tay DKJ, Yeo SJ. THINK surgical TSolution-One®(Robodoc) total knee arthroplasty. 2017a; 3:63. https://doi.org/10.1051/sicotj/2017052.
- Prakash R, Agrawal Y. Robotic technology in total knee arthroplasty. Br J Hosp Med (Lond). 2023 Jun 2;84(6):1-9. doi: 10.12968/hmed.2022.0491. Epub 2023 Jun 23. PMID: 37364881.
- Лычагин А. В., Грицюк А. А., Рукин Я. А., Елизаров М. П. История развития робототехники в хирургии и ортопедии (Обзор литературы)// Кафедра травматологии и ортопедии. 2020;1(39):13-19. DOI 10.17238/issn2226-2016.2020.1.13-19. – EDN TRLXFQ. [Lychagin A. V., Gritsyuk A. A., Rukin YA. A., Elizarov M. P. Istoriya razvitiya robototekhniki v khirurgii i ortopedii (Obzor literatury)// Kafedra travmatologii i ortopedii. 2020;1(39):13-19. DOI 10.17238/issn2226-2016.2020.1.13-19. – EDN TRLXFQ.]
- Лычагин А. В., Грицюк А.А., Рукин Я. А., Елизаров М. П., Грицюк А.А., Гавловский М.Я., Богатов Т. В. Клиническая эффективность и точность выравнивания механической оси при роботизированном тотальном эндопротезировании коленного сустава. Гений ортопедии. 2023;29(5):487-494 https://doi.org/10.18019/1028-4427-2023-29-5-487-494. EDN: QKZVVF [Lychagin A. V., Gritsyuk A.A., Rukin YA. A., Elizarov M. P., Gritsyuk A.A., Gavlovskii M.YA., Bogatov T. V. Klinicheskaya ehffektivnost’ I tochnost’ vyravnivaniya mekhanicheskoi osi pri robotizirovannom total’nom ehndoprotezirovanii kolennogo sustava. Genii ortopedii. 2023;29(5):487-494. https://doi.org/10.18019/1028-4427-2023-29-5-487-494. EDN: QKZVVF.]
- Song EK, Seon JK, Yim JH, Netravali NA, Bargar WL. Roboticassisted TKA reduces postoperative alignment outliers and improves gap balance compared to conventional TKA. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2013;471(1):118–126. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11999-012-2407-3.
- Liow MHL, Xia Z, Wong MK et al. Robot-assisted total knee arthroplasty accurately restores the joint line and mechanical axis: a prospective randomised study. J Arthroplasty. 2014;29(12):2373–2377. https:// doi.org/10.1016/j.arth.2013.12.010.
- Liow MHL, Goh GSH, Wong MK et al. Robotic-assisted total knee arthroplasty may lead to improvement in quality-of-life measures: a 2-year follow-up of a prospective randomized trial. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2017b;25(9):2942–2951. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-016-4076-3.
- Kim YH, Yoon SH, Park JW. Does robotic-assisted TKA result in better outcome scores or long-term survivorship than conventional TKA? A randomized, controlled trial. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2020; 478(2): 266–275. https://doi.org/10.1097/CORR.0000000000000916.
- Park SE, Lee CT. Comparison of robotic-assisted and conventional manual implantation of a primary total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2007;22(7):1054–1059. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ARTH.2007.05.036.


