Physiological responses of Sigmadocia carnosa (Dendy, 1889) and Mycale mytilorum (Annandale, 1911) to osmotic challenge
Автор: Badusha M., Hashim K. A.
Журнал: Журнал стресс-физиологии и биохимии @jspb
Статья в выпуске: 1 т.19, 2023 года.
Бесплатный доступ
The sponge species Sigmadocia carnosa (Dendy, 1889) and Mycale mytilorum (Annandale, 1911) belong to the class demospongiae were collected from the Vizhinjam port of South India and examined for ouabain sensitive Na+, K+-ATPase specific activity in tissue homogenates. The total protein contents including stress proteins in the tissues were measured with the help of a modified Biuret assay. A species specific activity of Na+, K+-ATPase was found in the tested marine sponges. A time dependent significant increase in Na+, K+-ATPase activity was found in Sigmadocia carnosa at diluted sea water. The Na+, K+-ATPase activity in Mycale mytilorum also showed significant rise particularly during 1 and 4 hour at diluted sea water exposure. The total protein contents in both species showed no significant change during exposure to dilute sea water.
Sigmadocia carnosa, mycale mytilorum, na+-k+-atpase activity, osmotic challenge, protein content
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/143179379
IDR: 143179379
Текст научной статьи Physiological responses of Sigmadocia carnosa (Dendy, 1889) and Mycale mytilorum (Annandale, 1911) to osmotic challenge
Sponges are the most primitive of multicellular animals. Neither true tissue nor organs are present, and the cells display a considerable degree of independence. In 18th century the biologists noticed the flow of water and contractile activity in sponges and from that time onwards considered the sponges as animals. The sponges have significant traditional uses because of their importance for bath and domestic purposes as they have immense capacity to hold water in their capillaries which are made up of sponging fibres. Among marine invertebrates, Porifera (sponges) are potential source of novel bioactive compounds to provide future drugs against malaria, cancer and a range of viral diseases. A number of sponge-derived nitrogenous compounds and proteins as antimalarials have been discovered during the last decade. So the characterization of the response of sponges to various types of physiological or environmental stress conditions with regard to the nitrogenous compounds is relevant in future pharmacological studies.
The marine sponges have an ionic gradient across the tissues, inward sodium, and outward potassium (Prosser, 1967). Since the early 1900s, ecological, chemical, mechanical and electrical stimuli were applied to sponges to determine the speed at which they could respond (Parker, 1910; Emson, 1966; Prosser, 1967; Ellwanger and Nickel, 2006). The demosponges are fully capable of responsiveness and signaling (Sakaraya et al., 2007 and Srivastava et al., 2010). One of the most obvious examples of ecological adaptation is salt tolerance. When the salinity of an aquatic habitat is higher or lower than the body fluids of the organisms living in it, those organisms transport salts across their epithelia to keep osmolarity within physiological levels (Krogh, 1946). Most studies have focused on the Na+, K+-ATPase, but other proteins also being investigated (Towle, 1997; Marshall, 2002 and Evans et al., 2005). The Na+, K+-ATPase was discovered in leg nerves of crabs (Skou, 1957). This is a transmembrane protein that utilizes the energy from the ATP hydrolysis transporting, in the best studied cases, 3Na+ from the cytoplasm to the extracellular compartment and 2K+ in the opposite direction, carrying both cations against their respective gradients while maintaining also an electrical gradient. The role of Na+, K+-ATPase in osmoregulation is not fully elucidated, and varies depending on the organism or cell type under consideration (Towle 1997; Evans et al., 2005 Marshall, 2002). The most frequent source of evidence for a given protein to be considered relevant in osmo-regulation is when its expression or activity is altered after the organism has gone from high to low salt, or vice versa. The salt-regulated proteins may not be directly responsible for the movement of ions from the medium into the organism (or vice versa). Rather, usually several of them act in collaboration with each other setting up electrochemical gradients across various membranes that, in combination, are able to keep a fitting osmotic equilibrium for the organism. However, the mechanisms of hyper and hypo-osmotic regulation are not well understood. In this paper we focus on the enzyme whose involvement in osmoregulation have been most recognized, the Na+, K+-ATPase. Our interest on the Na+, K+-ATPase and its role in osmoregulation stems from our work on the marine sponges Sigmadocia carnosa and Mycale mytilorum.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Sample collection
Sponges were removed from the substrate with a knife or chisel, preferably using protective gloves and protective clothing. Sigmadocia carnosa (Dendy, 1889) (Plate.2) and Mycale mytilorum (Annandale, 1911) (Plate.3) sponge species were collected from Vizhinjam port of Thiruvananthapuram district (Fig.1). Vizhinjam is a natural port, which is located close to the international ship route, which is 10 nautical miles from the international shipping lane. The Vizhinjam port is endowed with a natural seawater depth of up to 24 m as close as one nautical mile from the seacoast (Plate.1). Kovalam beach is just 3 Km from Vizhinjam.
Outline of characters used for Demospongiae identification
The experimental models belong to the Phylum: Porifera Grant and Class: Demospongiae Sollas inhabiting the Vizhinjam regions of South India. Their distribution is also extended to Indian Ocean and Indo-
Australian regions. They have been identified as follows: 1. Sigmadocia carnosa (Dendy, 1889) 2. Mycale mytilorum (Annandale, 1911). Sponge spicules were prepared for optical microscope examination.
Sponge identifications are primarily based on morphology. Some of these morphological characters vary substantially between widely separated populations, or those living in different habitats, indicating no more than eco phenotypic variation within the species, whereas other features are much more consistent between individuals irrespective of their geographic distribution. There are many morphological characters which can be used to aid in sponge identification including shape, distribution of surface pores, colour, ornamentation of the surface, texture, structure and composition of the organic skeleton and water canal system, and the structure, composition, size and geometry of the inorganic skeleton. In addition, several non-morphological features have proven useful practical tools in sponge taxonomy.
The demospongiae are the largest class in the phylum Porifera. Their "skeletons" are made of spicules consisting of fibers of the protein spongin, the mineral silica, or both. Where spicules of silica are present, they have a different shape from those in the otherwise similar glass sponges. The demosponges include 90% of all species of sponges and are predominantly leuconoid in structure. There are many diverse orders in this class, including all of the large sponges. Most are marine dwellers, but several live in freshwater environments. Some species are brightly coloured, and there is great variety in body shape; the largest species are over 1 metre (3.3 ft) across. They reproduce both sexually and asexually.
Model species-1
Sigmadocia carnosa (Dendy, 1889) (Plate.2)
Classification
Kingdom : Animalia
Phylum : Porifera Grant
Class : Demospongiae Sollas
Order : Haplosclerida Topsent
Family : Adociidae de Laubenfels
Genus : Sigmadocia de Laubenfels
Species : Sigmadocia carnosa (Dendy, 1889)
This is sessile, erect, rising in to small tubular processes: thickness of tubes about 5mm. Oscules terminal, diameter 2mm and compound. Colour pale yellow when alive. Consistency is compressible with good resiliency. Dermal skeleton well developed and detachable consists of unispicular reticulation. The main skeleton is a reticulation of multispicular primary fibres and uni or bi spicular connectives. Meshes rectangular and rather regular in the peripheral parts but rather confused in deeper regions. Diameter of primary fibres is about 0.042 mm and that of connectives, 0.021mm. The spicules of this sponge show the following features (1) Oxeas: Slightly curved, sharply pointed, maximum width at central part and the size of oxeas is 0.07-0.13×0.002-0.006 mm [length minimum and maximum×width minimum and maximum] (2) Sigmas: C or S shaped, tips sharply pointed and chord length is 0.011-0.02 mm (Fig 2.).
Model species-2
Mycale mytilorum (Annandale, 1911) (Plate.3)
Classification
Kingdom : Animalia
Phylum : Porifera Grant
Class : Demospongiae Sollas
Order : Poecilosclerida Topsent
Family : Ophlitaspongiidae de Laubenfels
Genus : Mycale Gray
Species : Mycale mytilorum (Annandale, 1911)
This is structurally the most diverse order comprising of the maximum number of species. Sponge is encrusting or massive. Colour brick red when alive. Texture is slimy when alive and with good resiliency. Surface even, oscules rare, present only on the thickest part and highly contractile. Pores are minute, oval in outline and highly contractile. Subtylostyles are scattered in the dermal region along with microscleres and refringent granules. Main skeleton is irregular. The spicules of this sponge shows the following features (1) Subtylostyles: straight or slightly curved, head conspicuous, circular or oblong, shaft straight, maximum width at the central part, the size is 0.166-0.288×0.002-
0.008 [length minimum and maximum×width minimum and maximum] and head length is 0.04-0.06 mm (2) Sigmas: C or S shaped and chord length: 0.03-0.036 mm. (3) Anisochelas: It is rare and chord length is 0.012-0.024 mm (Fig 3.).
Sponge Maintenance
Marine sponges were brought in to the laboratory and were stabilized for 12 hours in sea water.
Experimental Protocol
The experiment was designed to study the osmotic response of two marine sponges namely Sigmadocia carnosa and Mycale mytilorum , which were exposed to dilute sea water (50% SW). From each sponge species an approximate weight of 25 g body part was taken and marked as groups 1-4 and were kept into 4 glass troughs. Group 1 sponge mass kept at full strength sea water and was served as control. The other three groups of sponges were exposed to 50% diluted SW for varied time intervals (1, 2 and 4 hrs).
Sampling and Analysis
After exposure to specific time intervals approximately 300 mg sponge mass was excised and kept in TNT buffer (pH 7.5) and stored at -80 °C.
Sample Preparation
Stored sponge mass was then homogenized in TNT buffer (pH 7.5) and kept at 4 °C. After centrifugation at 700 g for 10 minutes, the supernatant obtained was collected, this served as the source of Na+, K+-ATPase.
Quantification of Na+, K+ -ATPase Specific Activity
The ouabain sensitive Na+,K+-ATPase specific activity was measured in tissue homogenates as described earlier (Peter et al. , 2000). Briefly, about 300 mg tissue was homogenized in storage buffer (pH 7.5) and centrifuged at 700 g for 10 minutes. The supernatant obtained was used to measure the specific activity of Na+, K+-ATPase in samples with or without ouabain. The tissue samples with duplicates were added to a 96-well microplate containing assay mixture with KCl (medium A) or ouabain (medium E) and incubated at 37 °C where the reaction was initiated by the addition of ATP. After terminating the reaction with 8.6 % TCA, the liberated inorganic phosphate content was measured with a Span Autoreader 4011 at 700 nm and expressed in µmol Pi h-1 mg protein. The protein contents in the tissues were measured with the help of a modified Biuret assay (Alexander and Ingram, 1980) with Bovine Serum Albumin as standard.
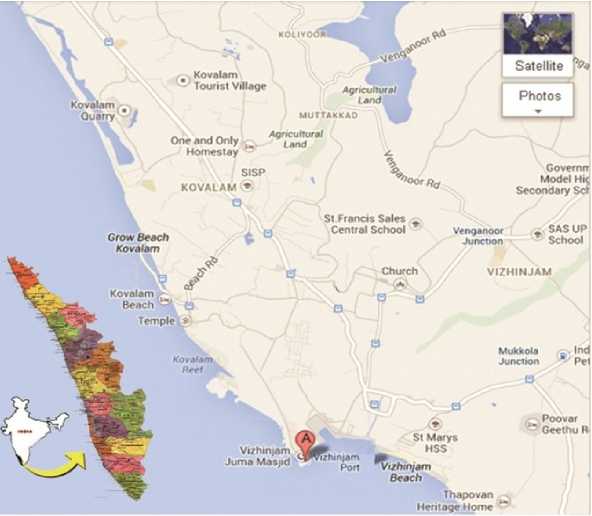
Figure 1. Location map of the sampling site
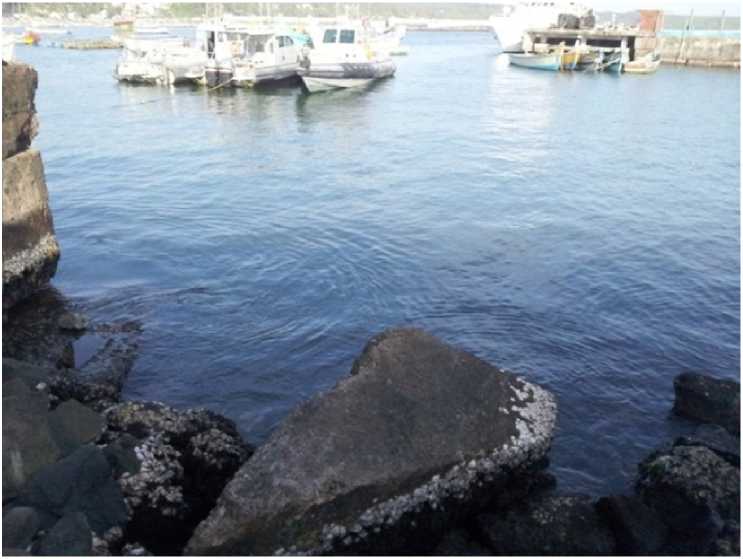

Plate 1. Sampling site (Vizhinjam)
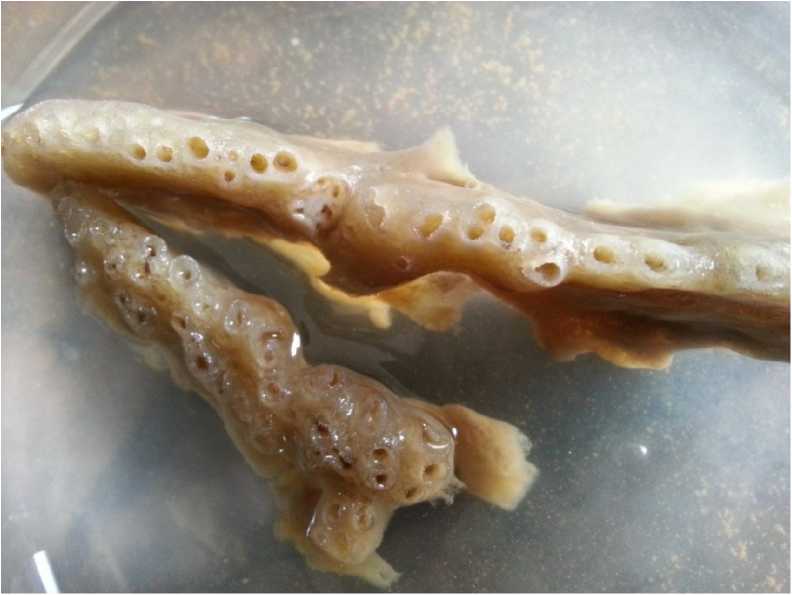
Plate 2. Sigmadocia carnosa (Dendy, 1889)
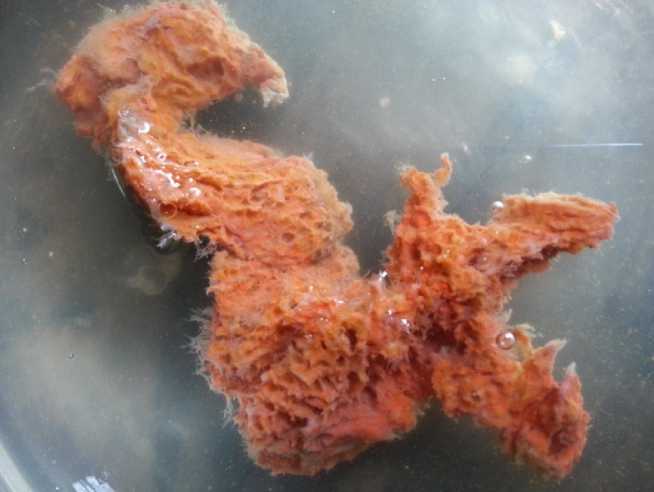
Plate 3. Mycale mytilorum (Annandale, 1911)
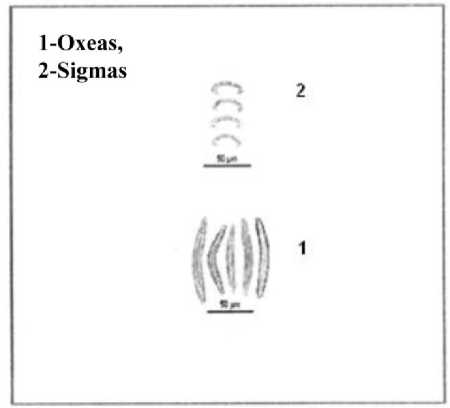
Figure 2. Spicules of Sigmadocia carnosa (Dendy, 1889)
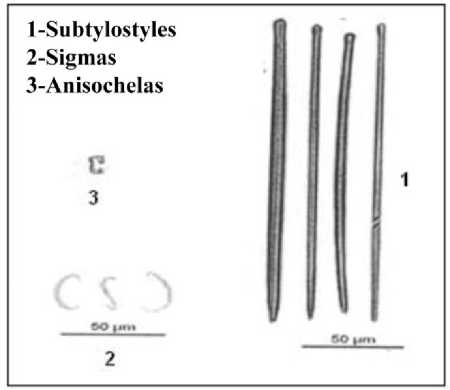
Figure 3. Spicules of Mycale mytilorum (Annandale, 1911)
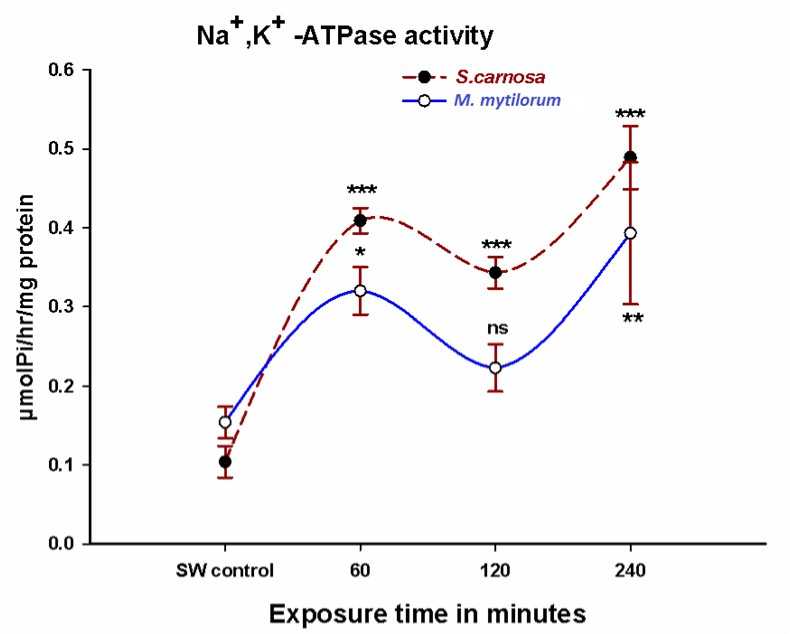
Figure 4. Na+, K+-ATPase activity in Sigmadocia carnosa and Mycale mytilorum exposed to diluted sea water (50%SW) in varied time intervals (060,120,240 minutes). (*P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 when compared to control)
Table 1. Total protein contents in Sigmadocia carnosa and Mycale mytilorum exposed to dilute sea water (50% SW) in varied time intervals (060, 120, 240 minutes). Each value is mean ± SE of tests.
|
Status |
S. carnosa |
M. mytilorum |
|
Control (SW) |
1.328 ± 0.08 |
1.630 ± 0.06 |
|
1hr (50%SW) |
1.238 ± 0.05ns |
1.495 ± 0.05ns |
|
2hr (50% SW) |
1.430 ± 0.18ns |
1.635 ± 0.06 |
|
4hr (50% SW) |
1.238 ± 0.02ns |
1.628 ± 0.12ns |
RESULTS
A significant time dependent increase in Na+,K+-ATPase activity was found in Sigmadocia carnosa when exposed to dilute sea water (Fig.4). The Na+,K+-ATPase activity in Mycale mytilorum also showed significant increases at 1 and 4 hour after 50% diluted sea water exposure, though at 2 hour exposure the enzyme activity remains unaffected (Fig 4).
The total protein contents in Sigmadocia carnosa and Mycale mytilorum , however, showed no significant change upon exposure to dilute sea water (Table 1).
DISCUSSIONS
Na+, K+-ATPase is a transmembrane protein found in higher eukaryotes that transports Na+ and K+ across the plasma membrane that maintains ionic gradients (Skou, 1957). These gradients, in turn, facilitate other secondary active transport systems such as Na+amino acid and Na+glucose co-transport in animals (Crane, 1977). Na+, K+-ATPase is responsible for maintenance of two electrochemical gradients across the plasma membrane by its electrogenic activity of exporting 3 Na+ from the cell and importing 2 K+ into the cell during each reaction cycle. This fundamental role has generated wide interest and numerous physiological, molecular, and pharmacological studies (Horisberger et al., 1991). Na+, K+-ATPase is limited to multicellular organisms, and thus may be a key molecule in metazoan evolution; it is present in simple multicellular organisms and is essential for nerve function (Shenk and Steele, 1993).
Measurement of the specific activity of Na+, K+-ATPase required to evaluate the purity or to express the actual specific enzyme activity. Accordingly an accurate determination of both inorganic phosphate and protein content is necessary. Sponges differ from other invertebrates in the maintenance of an almost protozoan like independence of their constituent cells. For this reason they are considered the most primitive of the multicellular animals. They lack organs but have well developed connective tissue in which differentiated cells perform a variety of functions. There are many morphological characters which can be used to aid in sponge identification. Their skeletons are made of spicules consisting of fibers of the protein spongin, the mineral silica,or both.
In this study the marine sponge species Sigmadocia carnosa (Dendy, 1889) and Mycale mytilorum (Annandale, 1911) were used as experimental models. The experiment was designed to find out the osmotic response of two marine sponges which were exposed to dilute SW (50% SW). The ouabain-sensitive Na+, K+-ATPase specific activity was measured in tissue homogenates. The protein contents in these sponges were also measured using modified Biuret assay with Bovine Serum Albumin as standard. The responses of the Na+, K+-ATPase activity which corresponds to sodium pump activity responded to hypo-osmotic challenges. The rise in Na+, K+-ATPase activity clearly indicate that the tested marine sponges can tolerate hypo-osmotic challenges physiologically as it can rely on sodium pump activity during osmotically challenged environmental conditions, which would ultimately help them to survive in adverse environments.
CONCLUSION
Physiological responses of Sigmadocia carnosa and Mycale mytilorum to osmotic challenge was studied by measuring the ouabain sensitive Na+, K+-ATPase specific activity in tissue homogenates and the protein contents in the tissues with the help of a modified biuret assay. The rise in Na+, K+-ATPase activity in the sponge species Sigmadocia carnosa and Mycale mytilorum after hypo-osmotic challenge clearly indicate that sodium pump activity occurs in this primitive metazoan species, which would help them in tolerance to hypo-osmotic solutions.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
We are thankful to University of Kerala for the financial support. The authors express sincere thanks to the department of Zoology, University of Kerala, Kariavattom Campus for all the facilities provided throughout the study. The facilities provided by Research Department of Zoology, NSS College, Pandalam are deeply acknowledged. The laboratory facilities provided by Prof. Dr. M. C. Subhash Peter, Department of Zoology, University of Kerala, Kariavattom Campus are greatly acknowledged. We obliged to Prof. Dr. P. A. Thomas, Former Principal Scietist, Central Marine Fisheries Research Institute for his immense support in sponge species identification.
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
The authors declare that they have no potential conflicts of interest.
Список литературы Physiological responses of Sigmadocia carnosa (Dendy, 1889) and Mycale mytilorum (Annandale, 1911) to osmotic challenge
- Alexander J.B. and Ingram, G.A. (1980). A comparison of five methods commonly used to measure protein concentration of fish sera. J. Fish. Biol., 16, 115-122.
- Annandale N. (1911). Some sponges associated with gregarious mollusks of the family Vermetidae. Records of the Indian Museum, Calcutta, 6, 47-55.
- Crane R.K. (1977). The gradient hypothesis and other models of carrier-mediated active transport. Rev. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol., 78, 99-159.
- Dendy A. (1889). Report on a Second Coll.ection of Sponges from Gulf of Mannar. Annals and Magazine of Natural History, 3, 73-99.
- Ellwanger K. and Nickel M. (2006). Neuroactive substances specifically modulate rhythmic body contractions in the nerveless metazoon Tethya wilhelma (Demospongiae, Porifera). Frontiers in Zoology, 3, 710-1186.
- Emson R.H. (1966). The reactions of the sponge Cliona celata to applied stimuli. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology, 18, 805-827.
- Evans D.H., Piermarini P.M. and Choe K.P. (2005). The multifunctional fish gill: dominant site of gas exchange, osmoregulation, acid-base regulation and excretion of nitrogenous waste. Physiol., 85, 97-177.
- Horisberger J.D., Jaunin P., Reuben M.A., Lasater L.S., Chow D.C., Forte J.G., Sachs G., Rossier B.C. and Geering K. (1991). The H, K-ATPase b-subunit can act as a surrogate for the b-subunit of Na, Kpumps. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 266, 19131-19134.
- Krogh A. (1946). The active and passive exchanges of inorganic ions through the surfaces of living cells and through living membranes generally. Proc. R. Soc. Lond B., 133, 140-200.
- Marshall W.S. (2002). Na+, Cl-, Ca2+ and Zn2+ transport by fish gills: retrospective review and prospective synthesis. J. Exp. Zool., 293, 264-283.
- Parker G.H. (1910). The reactions of sponges with a consideration of the origin of the nervous system. The Journal of Experimental Zoology, 8, 765-805.
- Peter M.C.S., Lock R.A.C. and Wendelaar Bonga S.E. (2000). Evidence for an osmoregulatory role of thyroid hormones in the Fresh water Mozambique tilapia; Oreochromis mossambicus. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol., 120, 157-167
- Prosser C.L. (1967). Ionic analysis and effects of ions on contractions of sponge tissues. Zeit vergleichliche Physiologie, 54, 109-120.
- Sakaraya O., Armstrong K.A., Adamska M., Adamski M., Wang I., Tidor B., Degnan B.M., Oakley T.H. and Kosik K.S. (2007). A post-synaptic scaffold at the origin of the animal kingdom. Public Library of Science, 1(2).
- Shenk M.A. and Steele R.E. (1993). A molecular snapshot of the metazoan Eve. Trends in Biochemical Sciences, 18, 459-563.
- Skou J.C. (1957). The influence of some cations on an adenosine triphosphatase from peripheral nerves. Biochim. Biophys. Acta., 23, 394-401.
- Srivastava M., Simakov., Chapman J., Fahey B., Gauthier M., Mitros T., Richards G.S., Conaco C., Dacre M., Hellsten U., Larroux C. and Putnam N. (2010). The Amphimedon queenslandica genome and the evolution of animal complexity. Nature, 466, 720-727.
- Towle D.W. (1997). Transport-related ATPase as probes of tissue functions in three terrestrial crabs of Palau. J. Exp. Zool., 218, 89-95.


