Phytostabilization potential of yard long bean in removing cadmium from soil
Автор: Deivanai S., Thulasyammal R.
Журнал: Журнал стресс-физиологии и биохимии @jspb
Статья в выпуске: 2 т.10, 2014 года.
Бесплатный доступ
The effect of cadmium (Cd) on growth, physiology, distribution and tolerance was examined in root, shoot and leaves of yard-long bean ( Vigna unguiculata subsp. sesquipedalis L.). The seeds were grown in pot culture under laboratory conditions for 60 days in Ferriera and Davis nutrient solution with three different concentrations (0.5, 1.0 and 2.0 mM) of cadmium. Cd toxicity was evident from chlorosis in young leaves and increased concentrations of Cd brought significant negative effects on plant growth, photosynthetic rate and protein biosynthesis. Translocation of Cd was found to be more in roots than the above ground parts and the accumulation was in the order of root > shoot > leaf. Low root to shoot translocation of Cd makes the crop ideal for phytostabilization. Relatively high metal tolerance index obtained in the study indicated that the crop has greater tolerance to increase Cd exposure, though accumulation of Cd had altered thickness of root and root biomass. Owing to the crop’s adaptability to high temperature, drought conditions and ability to retain Cd in roots makes it a promising candidate for phytostabilization of soil contaminated by Cd.
Yard-long bean, photosynthetic rate, biomass production, cadmium toxicity, phytostabilization
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/14323868
IDR: 14323868
Текст научной статьи Phytostabilization potential of yard long bean in removing cadmium from soil
Cadmium (Cd) is a nonessential heavy metal found in agricultural soils by the use of pesticides, disposal of sewage sludge into irrigation channels and by continuous application of cadmium containing phosphatic fertilizers (Kabata-Pendias and Dudka 1990). Large amount of Cd in the soil is predominantly through fertilizers, but the amount of Cd present in them varies significantly. However, it is estimated that rock phosphate source contains around 10 mg-500 mg cadmium/Kg P. Though, Cd has not been essentially needed for physiological functions in plant, its high mobility in soil plant system allows them to absorb rapidly by roots and accumulates in shoots (Liu et al., 2010; Lux et al., 2010). Nevertheless, the concentration of Cd in plants varies with species, age, tissue type and its mobility in the soil. According to Adriano (2001) the factors such as pH, total amount of Cd in soil, source of Cd, organic matter, and soil types determine the mobility and availability of Cd in plants. Furthermore, accumulation of this metal poses a potential risk to human and animal health, as it is highly toxic and readily enters into the food chain (Ngayila et al., 2009). On account of toxicity, Cd has gained considerable attention on the agroecosystem as well as on plant growth and development. Available evidences indicated that most plants are sensitive to cadmium exposure and showed visible sign of red or dark red leaf margins, chlorosis, leaf rolls, stunting and necrosis (Benavides et al., 2005). It is also well known that high concentration of Cd in soil significantly alter physiology of plants which ultimately inhibit the growth and decrease the productivity of plants (Zhou et al., 2006). The reduction in growth due to Cd toxicity could be a direct consequence of inhibition in photosynthesis, respiration, water and nutrient uptake (Benavides et al., 2005; Scebba et al., 2006; Zhou et al., 2006; Wong et al., 2008).
Phytoremediation, a technique uses plants to treat soil contaminated with heavy metals, is an emerging technology and has gained popularity because of cost effectiveness, aesthetic advantages as well as long term applicability (Salt et al., 1998; Sarma, 2011). Though the concept was proposed long ago to treat wastewater, it was reintroduced to extract metal from contaminated soil by Utsunamyia (1980) and Chaney (1983). In the last decade extensive researches have been conducted and identified few plant species from the member of Asteraceae, Brassicaceae, Euphorbiaceae, Fabaceae, Lamiaceae, Poaceae and Scrophulariaceae for phytoremediation (Sarma 2011). However, reports on potential use of plants from Leguminosae family in clearing soil polluted with heavy metals is rare and currently, few evidences indicated that plants such as Lupinus albus (Vazquez et al., 2006), Vicia faba (Pichtel and Bradway, 2008) and Trifolium repens (Bidar et al., 2009) are used in re-vegetation and phytosabilization. The efficiency of phytoremediation technology relies on suitability of plants which can propagate easily and grow faster in metal contaminated soils. In this view, the study was initiated to explore the potential of Yard-long bean (Vigna unguiculata subsp. sesquipedalis L.) in phytoremediation. Yard-long bean, a vigorous climbing annual crop belongs to the family Fabaceae, serves as an important food legume where its young leaf, green pods and green seeds are used as vegetables and the haulms are fed to livestock as nutritious supplement to cereal fodder. It is grown primarily for its striking long (35-75 cm) immature pods and also considered as an essential component for intercropping system. The crop is believed to evolve from cowpea (Vigna unguiculata L.) Walp., which is native to subtropical regions and most widely grown in Asia, especially in South and South Eastern Asia, Thailand and Southern China. In addition, the crop is well adapted to warm weather (Hall, 2004) and grows well in poor soil (Hamidou et al., 2007). Besides, we believe that these beneficial features of this crop may play an important role in remediation technology. Therefore the study was initiated to examine i) the impact of cadmium exposure at different concentrations on growth and physiological activities of yard long bean and ii) to assess the effectiveness of yard long bean to be a potential candidate for Cd removal from soil.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Seeds of yard long bean ( Vigna unguiculata subsp. Sesquipedalis ) were sown in plastic pots filled with acid washed riverbed sand and grown under day light conditions with a temperature of 25
± 2oC. Soil in each pot was moistened with distilled water to ensure germination and after the seedling emergence it was supplied with Ferriera and Davis (1987) nutrient solution. On sixth leaf stage, Cadmium (CdCl 2 ) was added to nutrient solution at three concentrations viz., 0.5, 1.0 and 2.0 mM and applied to the growing plants at every alternate day. The nutrient solution without CdCl 2 addition was used as control and the treatment was continued for 6 weeks. Completely randomized design was followed with three replications for each treatment. For each treatment nine plants were randomly selected and harvested after 6 weeks of study.
Growth parameters
After harvest, plants were separated as leaves, root and shoot fractions. Various growth indices such as number of leaves, shoot and root lengths were measured. Fresh weights of root as well as shoot were weighed and the samples were then dried in an oven at 65oC until reaching constant weight to determine the dry weight.
Relative Water Content (RWC)
Leaf relative water content (RWC) was measured according to the method of Weatherly (1950); five leaf samples were collected and weighed to determine their fresh weight (FW). The leaves were rehydrated by placing them in distilled water for 6 h at 25°C in order to obtain turgid weight (TW), followed by oven drying at 60°C for 48 h and reweighed the leaf samples to get their dry weight (DW). The relative water content was calculated using the following formula: Relative Water Content (%) = (FW - DW) / (TW - DW) x 100 Determination of chlorophyll content
Total chlorophyll, chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b were determined for control and Cd treated plants by following the method described by Harbone (1984). Fresh leaves (500 mg) were homogenized in 80% acetone at 4oC. The extract was centrifuged at 10,000 x g for 5 min. Absorbance of the supernatant was read at 646 nm and 663 nm using a UV-Vis spectrophotometer.
Determination of Total soluble protein
Total soluble protein was determined by following the method of Bradford (1976). Fresh plant material of 1.0 g was homogenized in 5 ml of extraction buffer (50 mM Tris-HCl; pH-8, 1 mM PMSF, 10% (v/v) glycerol) and centrifuged at 20,000 rpm at 4˚C for 20 min. Aliquot of the extract was used for determining protein concentration using bovine serum albumin (BSA) as a standard. SDS-PAGE was performed according to Laemmli (1970) and the gels were stained with 0.03% Coomassie Brilliant Blue.
Determination of cadmium ion
Metal content was determined by following Hajiboland (2005); around 0.2 g of powdered plant material was digested with 5 ml of 10% (v/v) nitric acid at 90oC for 1 h. The suspension was cooled and centrifuged at 6000 rpm for 10 min. The nitric acid extraction procedure was repeated thrice. All supernatants were pooled and made up to a known volume (10 ml). The working standards were prepared by serial dilution of the standard stock solutions and used for the calibration of Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometer (AAS). The cadmium concentrations in plant parts such as leaves, shoots and roots were determined by using AA 700- Perkin Elmer’s AAS.
Determination of metal tolerance
Metal tolerance was calculated (Ximenez-Embun et al., 2002) using the mean weight of a plant grown in the presence of a metal divided by the mean weight of a control plant and expressed it as percentage. An index of tolerance of 50% is considered to be the minimum desired biomass production for plants growing in a metal contaminated site.
Statistical analysis
The data collected from different levels of cadmium exposure were compared with the control to determine the morphological and physiological responses in yard long bean using statistical software program SPSS (Version13.0) for windows. Data presented in the text and table is mean ± standard deviation and the error bars in the figure indicate standard deviations. Analysis of variance (ANOVA) was carried out to test significance of the differences between control and treatments followed by a LSD post Hoc multiple comparison of mean.
RESULTS
Effect of excessive Cd uptake on growth and morphology
The progressive levels (0, 0.5, 1.0 and 2.0 mM) of Cd exposure drastically affected the growth and metabolism of yard long bean (Table-1). Excessive concentration of Cd was toxic and it was evident from visible symptoms of chlorosis and leaf senescence. The increasing concentration of Cd in nutrient solution (2.0 mM) have reduced the number of leaves from 12.89 ± 0.5 to 9.78 ± 0.52 as compared to control by 24.13%. The measures of seedling length also varied from 11.0%, 22.9% to 32.5% respectively with 0.5 mM, 1.0 mM and 2.0 mM levels of Cd. The fresh weight and dry weight obtained from plant organs such as root, shoot, leaves and whole plant served as useful indicators for metal uptake. Both, the fresh and dry weights were affected at higher concentrations (i.e.,) 1.0
mM and 2.0 mM of Cd in the nutrient solution. The root fresh weight was reduced approximately by 24.3% and 36.1% when exposed to 1.0 and 2.0 mM of Cd. Mean while the reduction in shoot fresh weight was recorded around 25.0% and 29.9%, whereas the reduction was more pronounced in leaves (29.9% and 36.8%) and whole plant (22.9% and 32.5%). Like fresh weight, dry weights also showed marked difference in the uptake of Cd. Excessive Cd affected the root dry weight (62.3% to 65.3%) and shoot dry weight (55.4% to 61.2%). Analysis of variance had shown a significant differences for seedling length, fresh and dry weights (p <0.05) at 1.0 mM and 2.0 mM of Cd, when comparison was made between control and treatments of various plant organs.
Effect of Cd uptake on physiology of long bean
Cadmium accumulation not only affected the plant growth but also altered physiological functions like RWC, photosynthetic pigment, protein biosynthesis, etc.,. The result on RWC presented in Figure 1a explained a slight decrease at 0.5 mM Cd compared to control and declines sharply at increasing concentrations viz., 1.0 mM and 2.0 mM. The leaf RWC decreased from 9% in 0.5 mM to 28% in 2.0 mM Cd.
The data presented in Fig. 1b showed that Cd treatment markedly altered the concentration of photosynthetic pigment. Estimation of total chlorophyll content decreased in response to progressive Cd concentrations and it ranged from 4.18 mg/L (control) to 0.88 mg/L (2.0 mM Cd). The amount of chlorophyll b was lower than chlorophyll a in control and in all treatments. A significant difference was also noticed for chlorophyll content between control and treatment, among the treatment 1.0 mM and 2.0 mM of Cd severely affected the physiology of the plant.
The effect of Cd on total soluble protein content presented in the Fig. 1c indicated that protein synthesis was also affected greatly by cadmium treatment. Among the plant parts, the protein synthesis was more in leaf tissues (14.95 ± 0.95 mg L-1 to 6.87 ± 1.2 mg L-1 ) , followed by shoot (4.74 ± 0.61 mg L-1 to 4.48 ± 0.62 mg L-1 ) and root (2.56 ± 0.46 mg L-1 to 1.82 ± 0.36 mg L-1 ). Decreased in the total protein content due to Cd treatment is apparent from the banding pattern of SDS-PAGE leaf protein profile (Fig. 1d). A significant difference in plants protein content was noticed between plants treated with cadmium and control as well.
Accumulation of Cd in yard-long bean
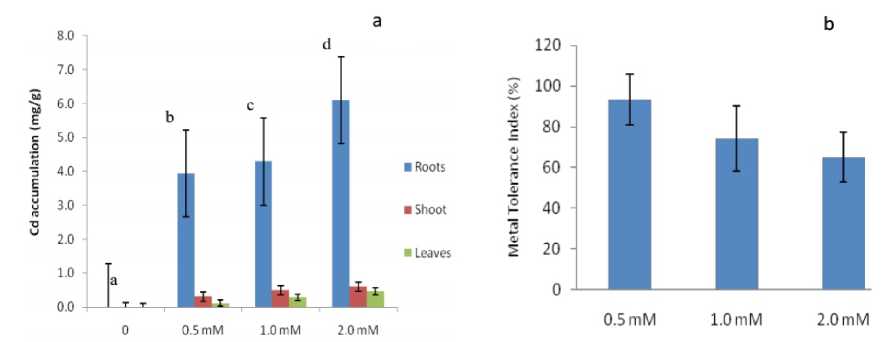
The level of Cd accumulated in the roots, stem and leaves of yard long bean was analyzed and the result is presented in Figure 2a. The plant showed enhanced level of Cd accumulation with increasing Cd concentration. A significant higher amount of Cd was accumulated in all the plant parts compared to control plants. However, wider variations were noticed in the rate of accumulation of Cd among the plant parts. For example, roots retained higher Cd (from 3.9 ± 0.001 mg/g to 6.09 ± 0.03 mg/g)
than shoot (from 0.31 ± 0.01 mg/g to 0.60 ± 0.002 mg/g) and leaves (0.12 ± 0.003 mg/g to 0.46 ± 0.002 mg/g). The result showed that plant species differ greatly in their ability to uptake and transport Cd within the plant. In yard long bean differential mobility of Cd is in the order of root > shoot > leaf. The movement of metals in plants was determined using translocation factor (TF), it is the ratio between Cd concentration in shoots and roots. The ratio between the shoot and root Cd was recorded as 0.08, 0.12 and 0.13 respectively for 0.5 mM, 1.0 mM and 2.0 mM levels of Cd. The result indicated that the TF value for all the treatments were less than 1 evidencing a slow translocation rate of Cd between these organs.
Metal tolerance
Metal tolerance index presented in Fig. 2b revealed the level of tolerance of yard long bean grown in Cd treatment. Considerable higher percentage was noticed for increased concentration of Cd and the tolerance levels were 93.3%, 74.2% and 65.1% respectively for 0.5 mM, 1.0 mM and 2.0 mM concentration of Cd.
Table 1. Effect of different concentration of Cd on growth parameters of yard long bean ( Vigna unguiculata subsp. sesquipedalis L.).
|
Growth parameters |
Cadmium Concentrations |
|||
|
Control |
0.5 mm |
1.0 mM |
2.0 mM |
|
|
No. of leaves |
12.89 ± 0.51a |
11.56 ± 0.81ab |
10.89 ± 0.72ab |
9.78 ± 0.52 b |
|
Root length (cm) |
17.08 ± 1.73a |
14.29 ± 1.20ab |
13.54 ± 0.72ab |
12.73 ± 0.42b |
|
Shoot length (cm) |
73.20 ± 4.72 a |
65.10 ± 2.84ab |
56.48 ± 2.47bc |
49.49 ± 1.85c |
|
Root fresh weight (g) |
2.075 ± 0.19a |
1.876 ± 0.18a |
1.571 ±0.31a |
1.326 ± 0.10a |
|
Shoot fresh weight (g) |
2.453 ± 0.13a |
2.191 ±0.13ab |
1.840 ± 0.24ab |
1.720 ± 0.15b |
|
Leaves fresh weight (g) |
3.557 ± 0.25a |
3.347 ± 0.27ab |
2.493 ± 0.30bc |
2.249 ± 0.29c |
|
Whole plant fresh weight (g) |
8.085 ± 0.42a |
7.414 ± 0.48ab |
5.904 ± 0.58bc |
5.296 ± 0.44c |
|
Root dry weight (g) |
0.167 ± 0.02 a |
0.151 ± 0.01a |
0.063 ± 0.01b |
0.058 ± 0.01b |
|
Shoot dry weight (g) |
0.260 ± 0.02a |
0.254 ± 0.02a |
0.116 ± 0.01b |
0.101± 0.01b |
|
Leaves dry weight (g) |
0.349 ± 0.02a |
0.309 ± 0.02a |
0.220 ± 0.02b |
0.182 ± 0.01b |
|
Whole dry weight (g) |
0.776 ± 0.03a |
0.405 ± 0.02b |
0.399 ± 0.03b |
0.341 ± 0.01b |
Data represent the mean ± SE (n = 9), values followed by different letters in a same line are significantly different at P ≤ 0.05.
proteincontent (mg/L) Relative water content (%)
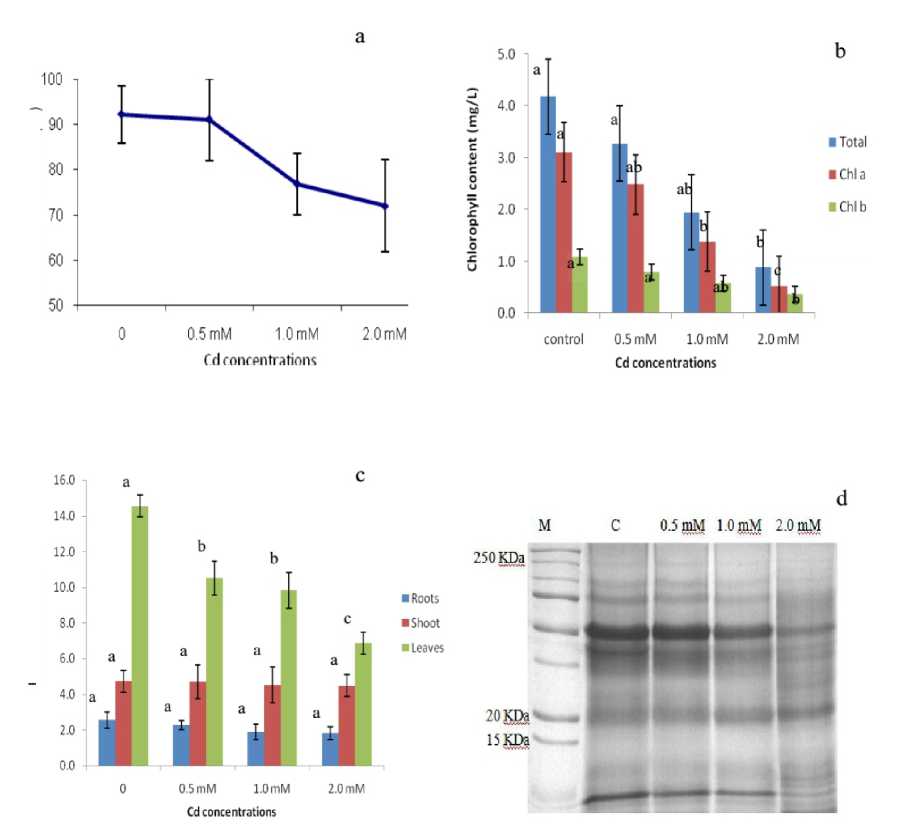
Figure 1. Effect of different concentrations of CdCl 2 on physiology of yard long bean; a) RWC (%), b) chlorophyll content (mg/L), c) protein content (mg/L) in various tissues, d) gel showing protein profiling of SDS PAGE. Values are mean (n = 4) and the error bar represent the standard deviation.
Cd concentrations Cd concentration
Figure 2. a) Cadmium accumulation in root, shoot and leaves (mg/g), and b) Metal tolerance Index (%) of yard long bean grown at different concentration of Cd. Values are mean (n = 9) and the error bar represent the standard deviation
DISCUSSION
Effect of excessive Cd uptake on growth and morphology
In the present study, effect of different levels of cadmium exposure on morphology of yard long bean was investigated. The Cd stress was found to alter the plant growth and development in yard long bean and the most common adverse effect is the appearance of chlorosis and leaf senescence. Karimi et al. (2012) also noticed visible symptoms in Vicia faba grown in soil contaminated with heavy metals like cadmium, lead and nickel. According to them, the appearance of discoloration in leaves is probably due to antagonistic effect between heavy metals and essential nutrients. Reduction in leaf number noticed in the present study coincides with the findings of Pastor et al. (2003) who reported a similar reduction in leaf production, when Lupinus albus was grown in acidic soil treated with Zn .
A retarded development of growth in response to Cd was indicated by noticeable differences in the measures root and shoot length. Variation in root and shoot length may attribute to reduction in cell division and elongation in meristematic tissue which eventually inhibited the plant growth. The present result is in agreement with the earlier findings of Chen et al. (2003) in soybean, Lima et al. (2006) in Pisum sativum, Shafiq et al. (2008) in Leucaena leucocephala as well as Qadir et al. (2004) and Sharma et al. (2010) in Brassica juncea. Besides, excessive Cd affected the root more severely than the shoot growth as a result; the root becomes denser and appears shorter as well as thicker. Lima et al. (2006) demonstrated that root system primarily responds to Cd in soil and restrain its uptake to above ground parts. The result also showed a decrease in fresh and dry weight which may associate with reduction in seedling growth as well as leaf loss. The study is in accordance with the findings of Zornoza et al. (2002) where they noted reduction in shoot and root dry weight in white lupin when grown hydrophonically at 45 µM Cd.
Effect of Cd uptake on physiology of long bean
The Cd treatment has brought significant negative effect on the physiological response of yard long bean and it is evident from the result that Cd treatment had disturbed plant water relationship and mineral nutrition which in turn challenges the structural organization and functional activity of photosynthetic apparatus. The result is in agreement with Rivelli et al. (2012) who showed that reduced water relations in sunflower due to Cd treatment was accompanied by altering the concentration of essential nutrients in tissues.
The photosynthetic pigments; chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b and total chlorophyll in the leaves were sensitive to the cadmium toxicity. Changes in the amount of chlorophyll content per unit area observed in the study were associated with alteration in cell division and chloroplast replication which drastically reduced the number of chloroplasts (Baryla et al., 2001). In the study, reduced chlorophyll content confirmed that excess Cd cause damage to photosynthetic apparatus and developed chlorosis symptoms. Suppression of photosynthetic activity by metal stress is in agreement with earlier reports (Sun et al., 2008; Ogbuchi et al., 2011) and several suggestions were made concerning the effect of Cd on photosynthetic activity: i) inhibition of δ-aminolevulinic acid dehydratase (ALA-dehydratase) and protochlorophyllide reductase associated with chlorophyll biosynthesis, ii) impairment in the supply of Mg2+ and Fe2+ required for chlorophyll synthesis, iii) inhibition of carbonic anhydrase due to Zn2+ deficiency, iv) replacement of Mg2+ ions associated with the tetra-pyrrole ring of chlorophyll molecule (John et al., 2008; Nikolic et al., 2008). Further, earlier works on Cd toxicity in plants have documented that the metal induced changes in CO2 fixation, stomatal conductance, electron transport and enzyme activity there by inhibiting the rate of photosynthesis (Scebba et al., 2006; Hayat et al., 2007).
A decreased in total soluble protein content noticed in the study coincided with the report of John et al. (2008) in Lemna polyrrhiza L exposed to cadmium and lead. The observed reduction in total protein content may attribute to several reasons such as: i) increased protease activity may enhance protein degradation and inhibit protein synthesis (Palma et al., 2002), ii) incorporation of free amino acids into protein (Cheetri et al., 2004) and iii) impairment of photosynthetic activity through cell injury and disruption of cell membrane (Ogbuchi et al., 2011).
Accumulation of Cd in yard-long bean
Accumulation of Cd varied widely with the components of yard long bean; among the plant parts, root region accumulated more Cd than the shoots and the leaves. Accumulation of Cd thus observed in the root is in agreement with the previous observation by Zornoza et al. (2002), Page et al. (2006) and Vazquez et al. (2006) in lupin to heavy metal stress. Similar finding was also reported from various plant species (Zornoza et al., 2002; Benavides et al., 2005; Mendez and Maier 2008; Nedjimi and Daoud 2009) in which the Cd ions were retained mainly in the roots and only small amounts were transported to shoots. The reports also illustrated that the charge of metal ion bound with carboxyl group of mucilage uronic acid restricts the movement across the cell membrane thereby prevents the transport of metal to shoots. Whereas, some authors (Lima et al., 2006; Mishra et al., 2006; Almeida et al., 2007; Sharma et al., 2010) suggested that confinement of Cd in the root tissue may be due to sequestration in vacuoles by glutathione and phytochelatins. Redjala et al. (2009) opinioned that root apoplast probably act as a driving force to extract the metal from the soil. While, Fediuk and Erdei (2002) speculated that the decrease in Cd from root to shoot might be due to the presence of thiol metal complexes which inhibited transportation.
Potential for phytostabilization of soils contaminated by Cd
The study confirmed that yard long bean retained considerable amount of Cd in its root than shoot due to weak translocation through vascular system, indicating defense mechanism of the roots against toxic effect. Indeed, accumulation of Cd in root tissue seems to be interesting in view of phytostabilization technology, where the metal contaminants of the soil are adsorbed and accumulated in roots. According to Mendez and Maier (2008), a plant species recognized for phytostabilization accumulates more metal in root than shoot and limit the metal transfer through food chain. However, the success of phytostabilization depends on the establishment and survival of plants. The ability of the crop to tolerate Cd stress was assessed using metal tolerance index; the index was found to be greater than 50% in all the treatments which ensured desirable biomass production to ameliorate the toxic effect. The result is in agreement with previous result of Kabata and Pendias (2001) and Kopittke et al. (2008) who reported that a maximum tolerable and phyto-toxicity threshold level of plants is around 10 – 100 mg/kg of Cd.
CONCLUSION
The study demonstrated that progressive levels of Cd altered physiological process and significantly modified the morphology of yard long bean. Further, higher concentration of Cd induced synthesis of phytochelatins in the roots and provided greater tolerance which enabled the plants to grow with substantial biomass. In general, Vigna unguiculata is adaptable to high temperature and drought conditions; it seems that the crop can be considered as a promising candidate for phytostabilization. Though pot experiment proved to be effective in clearing Cd contaminants, field trials are necessary to confirm the efficacy of phytostabilization strategy to reclaim soils enriched with cadmium.
Список литературы Phytostabilization potential of yard long bean in removing cadmium from soil
- Adriano, D.C. (2001). Trace Elements in Terrestrial Environments Biogeochemistry Bioavailability and Risk of Metals, second ed. Springer-Verlag, New-York
- Benavides, M.P., Gallego, S.M. and Tomaro, M.L. (2005). Cadmium toxicity in plants. Braz J. Plant Physiol., 17, 21-34
- Bidar, G., Pruvot, C., Garcon, G., Verdin, A., Shirali, P. and Douay, F. (2009). Seasonal and annual variations of metal uptake, bioaccumulation and toxicity in Trifolium repens and Lolium perenne growing in a heavy metal contaminated field. Environ Sci & Pollut Res. Int., 16, 42-53
- Bradford, M.M. (1976). A dye binding assay for protein. Analytical Biochemistry., 72, 248-254
- Chaney, R.L. (1983). Plant uptake of inorganic waste. In Land Treatment of Hazardous Waste, (eds.) J.E. Parr, P.B. Marsh, J.M. Kla, Noyes Data Corp, Park Ridge Il pp 50-76
- Chhetri, D.R., Modak, S. and Safiruddin, A. (2004). Physiological and biochemical response of two ricebean (Vigna umbellata) cultivars to heavy metal stress. Environ & Ecology., 22(1), 27-33
- Ferreira, R.B. and Davies, D.D. (1987). Protein degradation in Lemna with particular reference to ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase 1. The effect of light and dark. Plant Physiol., 83, 869-877
- Hajiboland, R. (2005). An evaluation of the efficiency of cultural plants to remove heavy metal from growing medium. Plant Soil Environ., 51(4), 156-164
- Hall, A.E. (2004). Breeding for adaptation to drought and heat in cowpea. Europ J Agronomy, 21, 447-454
- Hamidou, F., Zombre, G., Guinko, S., Diouf, O. and Braconnier, N.D.A. (2007). Physiological, biochemical and agromorphological responses of five cowpea genotypes (Vigna unguiculata L. Walp.) to water deficit under green house conditions. Biotechnologie, Agronomie, Societe et Environnement, 11(3), 225-234
- Harborne, J.B. (1984). Phytochemical methods: a guide to modern techniques of plant analysis. London, UK, Chapman & Hall
- Hayat, S., Ali, B., Aiman Hasan, S. and Ahmad, A. (2007). Brassinosteroid enhanced the level of antioxidants under cadmium stress in Brassica juncea. Environ Exp Bot, 60, 33-41
- John, R., Ahmad, P., Gadgil, K. and Sharma, S. (2008). Effect of cadmium and lead on growth, biochemical parameters and uptake in Lemna polyrrhiza L. Plant Soil Environ, 54(6), 262-270
- Kabata-Pendias, A. and Dudka, S. (1990). Evaluating baseline data for cadmium in soils and plants in Poland. In: Element concentration cadasters in ecosystems. (Ed). Lieth, H and Markert, B. VCH erlagsgesllschaft, Federal Republic of Germany
- Karimi, R., Chorom, Solhi S., Solhi, M. and Safe, A. (2012). Potential of Vicia faba and Brassica arvensis for phytoextraction of soil contaminated with cadmium, lead and nickel. Afr J Agric Res, 72(2), 3293 -3301
- Kopittke, P.M., Blamey, F.P.C., and Menzies N.W. (2008). Toxicities of soluble Al, Cu and La include ruptures to rhizodermal and root cortical cells of cowpea. Plant Soil, 303, 217-227
- Laemmli, U.K., Molbert, E., Showe, M. and Kelenberger, E. (1970). Form-determining function of genes required for the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. J Mol Bio, 49, 99-113
- Lima, A.I.G., Pereira, S.I.A., Figueira, E.M.A.P., Caldeira, G.C.N. and Caldeira H.D.Q.M. (2006). Cadmium detoxification in roots of Pisum sativum seedlings: relationship between toxicity levels, thiol pool alterations and growth. Environ Exp Bot, 55, 149-162
- Liu, F., Tang, Y., Du, R., Yang, H., Wu, Q. and Qiu R. (2010). Root foraging for zinc and cadmium requirement in Zn/Cd hyperaccumulator plant Sedum alfredii. Plant Soil, 327(1-2), 365-375
- Lux, A., Martinka, M., Vaculik, M. and White, P.J. (2010). White root responses to cadmium in the rhizosphere: a review. J Exp Bot, 62(1), 21-37
- Nedjimi, B. and Daoud, Y. (2009). Cadmium accumulation in Atriplex halimus subsp. Schweinfurthii and its influence on growth, proline, root hydraulic conductivity and nutrient uptake. Flora, 204(4), 316-324
- Ngayila, N., Botineau, M., Baudu, M. and Basly J.P. (2009). Myriophyllum alterniflorum DC. Effect of low concentrations of copper and cadmium on somatic and photosynthetic endpoints: A chemometric approach. Ecol Indicat, 9, 307-312
- Ogbuehi, H.C., Onuh, M.O. and Ezeibekwe, L.O. (2011). Effect of spent engine oil pollution on the nutrient composition and accumulatin of heavy metal in cowpea (Vigna unguiculata L.Walp). Australian Journal of Agricultural Engineering, 2(4), 110-113
- Page, V., Weisskopf, L. and Feller, U. (2006). Heavy metals in white lupin: uptake, root-to-shoot transfer and redistribution within the plant. New Phytol, 171, 329-341
- Palma, J.M., Sandalio, L.M., Javier Corpas, F., Romero Puertas, M.C., McCarthy, I. and Del Rio L.A. (2002). Plant protease protein degradation and oxidative stress: role of peroxisomes. Plant Physiol Biochem, 40, 521-530
- Pastor, J., Hermandez, A.J., Prieto, N. and Fernandez Pascual, M. (2003). Accumulating behavior of Lupinus albus L. growing in a normal and a decalcified calic luvisol polluted with Zn. J Plant Physiol, 160(12), 1457-65
- Pichtel, J. and Bradway, D.J. (2008). Conventional crops and organic amendments for Pb, Cd and Zn treatment at a severely contaminated site. Bioresour Technol, 99, 1242-1251
- Qadir, S., Qureshi, M.I., Javed, S. and Abdin, M.Z. (2004). Genotypic variation in phytoremediation potential of Brassica juncea cultivars exposed to Cd stress. Plant Sci, 167, 1171-1181
- Redjala, T., Sterckeman, T. and Morel, J.L. (2009). Cadmium uptake by roots: Contribution of apoplast and of high low affinity membrane transport system. Environ Exp Bot, 67(1), 235-242
- Rivelli, A.R., De Maria, S., Puschenreiter, M. and Gherbin, P. (2012). Accumulation of cadmium, zinc and copper by Helianthus annuus L.: Impact on plant growth and uptake of nutritional elements. Int J Phytoremediation, 14, 320-334
- Salt, D.E., Smith, R.D. and Raskin, I. (1998). Phytoremediation. Ann Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol, 49, 643-668
- Sarma, H. (2011). Metal hyperaccumulation in plants: a review focusing on phytoremediation technology. J Environ Sci Technol, 4(2), 118-138
- Scebba, F., Arduini, I., Ercoli, L. and Sebastiani, L. (2006). Cadmium effects on growth and antioxidant enzymes activities in Miscanthus sinensis. Biologia Plantarum, 50(4), 688-692
- Shafiq, M., Zafar, I.M., & Athar M. (2008). Effect of lead and cadmium on germination and seedling growth of Leucaena leucocephala. J Appl Sci Environ Manage, 12(2), 61-66
- Sharma, A., Sainger, M., Dwivedi, S., Srivastava, S., Tripathi, R.D. and Singh R.P. (2010). Genotypic variation in Brassica juncea (L.) Czern. cultivars in growth, nitrate assimilation, antioxidant responses and Phytoremediation potential during cadmium stress. J Environ Biol. 31(5), 773-780
- Sun, Y.B., Zhou, Q.X. and Diao, C.Y. (2008). Effects of cadmium and arsenic on growth and metal accumulation of Cd accumulator Solanum nigrum L. Bioresour Technol, 99, 1103-1110
- Utsunamyia, T. (1980). Japanese Patent Application No 55-72959
- Vazquez, S., Agha, R., Granado, A., Sarro, M.J., Esteban, E., Penalosa, J.M. and Carpena, R.O. (2006), Use of white lupin plant for phytostabilization of Cd and As polluted acid soil. Water Air and Soil Pollution, 177(1-4), 349-365
- Weatherley, P.E. (1950). Studies in the water relations of the cotton plant. I. The field measurement of water deficits in leaves. New Phytol, 49, 81-97
- Wong, L., Zhou, Q.X., Ding, L.L. and Sun, Y.B. (2008). Effect of cadmium toxicity on nitrogen metabolism in leaves of Solanum nigrum L. as a newly found cadmium hyperaccumulator. J Hazard Mater, 154, 818-825
- Ximenez-embun, P., Rodriguez-Sanz, B., Madrid-Albarran, Y. and Camara, C. (2002). Uptake of heavy metals by Lupin plants in artificially contaminated sand: preliminary results. Int J Environ Anal Chem, 82, 805-813
- Zhou, W.B., Philippe, J. and Qiu, B.S. (2006): Growth and photosynthetic responses of the bloom-forming cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa to elevated levels of cadmium. Chemosphere, 65, 1738-1746


