Постуральная устойчивость у лиц с латентными триггерными зонами шейной мускулатуры
Автор: Мухаметова Эльвира Ришатовна, Милицкова Ална Дмитриевна, Балтина Татьяна Валерьевна
Журнал: Ульяновский медико-биологический журнал @medbio-ulsu
Рубрика: Физиология
Статья в выпуске: 4, 2019 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Выделяют множество причин развития постуральных нарушений, среди которых дисфункция мышц шейного отдела позвоночника является наиболее спорной. Цель исследования. Выявить влияние латентных миогенных триггерных зон шейной мускулатуры на постуральную устойчивость. Материалы и методы. Использовался метод компьютерной стабилографии. Латентные миогенные триггерные зоны (лМТЗ) определялись по наличию в мышце шеи уплотненного узелка или пучка и по повышенной болевой чувствительности в этой области. Оценка постуральной устойчивости у испытуемых с лМТЗ осуществлялась с помощью стандартного стабилографического тестирования и теста Ромберга. В стандартной пробе оценивались как классические, так и векторные показатели. Результаты. Показано, что у испытуемых с множественными лМТЗ (4 и более) достоверно изменяются только векторные показатели. Так, установлено снижение качества функции равновесия, а также повышение средней линейной скорости центра давления и увеличение нормированной площади векторограммы по сравнению показателями в группе контроля и группе с единичными лМТЗ (от 1 до 3), что указывает на снижение постурального контроля у лиц с множественными лМТЗ...
Латентные миогенные триггерные точки, постуральный контроль, стабилография, тест ромберга
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/14116395
IDR: 14116395 | УДК: 612.829.34 | DOI: 10.34014/2227-1848-2019-4-114-123
Текст научной статьи Постуральная устойчивость у лиц с латентными триггерными зонами шейной мускулатуры
Введение. Сенсорная информация, получаемая от зрительной, вестибулярной и соматосенсорной систем, формирует внутреннюю концепцию о положении, движении и взаимодействии тела с окружающим пространством. Каждый из сенсорных входов обеспечивает функционально специфическую информацию, и ни один из них не работает независимо. Напротив, они образуют между собой широкие связи и формируют мультимодальный сенсорный вход на разных уровнях нейроак-сиса [1], который анализируется как единое целое. Такая мультисистемная интеграция компенсирует нарушения одного из входов. Дисфункция или снижение проприоцепции может значительно снизить контроль движений, регуляцию баланса и вертикальной позы и требует компенсаторной сверхрегуляции других сенсорных систем (зрительной, вестибулярной).
Шейный отдел играет важную роль в постуральной устойчивости ввиду большого количества механорецепторов и обширных связей с вестибулярной, зрительной, центральной нервной системами [2]. Так, у пациентов с напряженной шейной мускулатурой при вибрации мышц шеи отмечается более выраженная постуральная неустойчивость по сравнению с лицами без подобных изменений в шейных мышцах [3]. Предполагается, что доминирование проприоцептивной сигнализации от мышц шейного отдела, которая возникает вследствие боли и ригидности шейной мускулатуры, способствует возникновению головокружения [4]. Известно, что в латентных мио-генных триггерных зонах (лМТЗ) обнаружи- вается повышенное количество воспалительных нейромедиаторов по сравнению со здоровой мышцей, а также повышенная локальная активность ноцицепторов и механорецепторов [5–7], вследствие чего возникает подпороговая ноцицептивная сигнализация. Это приводит к изменению соматосенсорной сигнализации от шейного отдела и нарушению интеграции импульсов в системе постурального контроля. Ранее не изучалась степень влияния лМТЗ на постуральную устойчивость. Однако лМТЗ имеют высокую распространенность [8–10] и являются предикторами возникновения активных МТЗ с их болевыми симптомами [11]. Существуют данные, которые позволяют предположить, что афферентация от измененной шейной мускулатуры может вызывать ощущение девиации тела и нарушение ориентации в пространстве [4, 12–14].
Цель исследования. Выявить влияние латентных миогенных триггерных зон на постуральную устойчивость.
Материалы и методы. Было обследовано 79 чел. (39 мужчин, 40 женщин) в возрасте от 18 до 30 лет с лМТЗ мышц шеи. В исследование не вошли лица, имеющие травмы шеи в анамнезе, активные жалобы на боль в шее в течение 6 мес., неврологическую патологию в анамнезе, приступы головокружения, принимающие нейролептики, анксиолитики, антидепрессанты и седативные препараты. Контрольную группу составили 28 чел. (10 мужчин, 18 женщин), которые не предъявляли жалобы на спонтанную боль в области шеи и головы, а также на боль, вызванную пальпацией мышц шеи.
Исследование было одобрено локальным этическим комитетом Казанского федерального университета (протокол № 7 от 4 декабря 2017 г.) и соответствует принципам Хельсинкской декларации. После получения сведений о целях, методах и этапах исследования всеми испытуемыми подписано информированное согласие.
Перед исследованием проводился сбор анамнеза, включающий отоневрологическое тестирование, соматический и неврологический осмотр. Тестирование осуществлялось в дневное время. Все испытуемые имели нор- мальное или скорректированное до нормального зрение. Проводилась оценка на предмет субъективно хорошего самочувствия, отсутствие чувства голода, наличие удовлетворительного сна (не менее 7–8 ч).
В ходе осмотра выявлялись лМТЗ исследуемых мышц в точках пальпации. Болезненность в мышцах оценивалась самими испытуемыми по визуально-аналоговой шкале (ВАШ) [15].
Минимальными критериями для идентификации латентной триггерной зоны в данном исследовании были: 1) пальпируемый уплотненный пучок или узелок в мышце и 2) гиперсенситивная точка в уплотненном пучке скелетной мышцы [9, 16, 17].
Стабилографическая оценка постуральной устойчивости проводилась у всех испытуемых в тот же день, что и осмотр, с использованием компьютерного стабилоанализатора «Стабилан – 01-2» (ОКБ «Ритм», Таганрог), состоящего из двух блоков: воспринимающего (стабилоплатформа) и регистрирующего (компьютер и программно-методическое обеспечение StabMed 2.11) с частотой дискретизации 50 Гц.
Стабилометрическая диагностика проводилась с использованием двух тестов: стаби-лографического и теста Ромберга.
Для оценки выраженности нарушений функции равновесия испытуемого в европейской стойке применялся стабилографический тест, запись производилась в один этап. Определялись следующие стабилографические показатели: Qx – разброс (величина девиации) центра давления (ЦД) во фронтальной плоскости, мм; Qy – разброс (величина девиации) ЦД в сагиттальной плоскости, мм; S – нормированная во времени площадь статокинезиограммы, мм2/с; КФР – качество функции равновесия, % (в норме варьирует от 85 до 100 %); ЛСС – средняя линейная скорость, мм/с.
Тест Ромберга состоял из двух проб – с открытыми и закрытыми глазами. В первой пробе испытуемый стоял с открытыми глазами, при этом ему необходимо было сосчитать количество чередующихся кругов разного цвета и назвать количество белых кругов. Во второй пробе участник в положении стоя с закрытыми глазами считал количество звуковых сигналов, которое выбиралось программой рандомно. Коэффициент Ромберга (КР) рассчитывался как отношение площади стато-кинезиограммы, полученной в первой пробе, к площади статокинезиограммы во второй.
Достоверных различий постурографиче-ских показателей между испытуемыми с наличием лМТЗ в 1–3 мышцах шеи, а также между лицами с лМТЗ в 4 и более мышцах шеи выявлено не было, в связи с чем испытуемые были разделены на следующие подгруппы: группа А – лМТЗ в 1–3 мышцах шеи (43 чел.); группа Б – лМТЗ в 4 и более мышцах шеи (36 чел.).
Статистическая обработка проводилась с использованием программного обеспечения
IBM SigmaPlot. Использована оценка нормальности распределения и описательная статистика. Результаты представлены в виде средних значений показателей с указанием стандартной ошибки средней (M±m). Статистически значимыми считались различия при p<0,05.
Результаты. При оценке классических стабилографических показателей были получены следующие результаты: среднеквадратическое отклонение ЦД во фронтальной и сагиттальной плоскостях было достоверно ниже в группе А (1–3 лМТЗ) по сравнению с контрольной группой и с группой Б (p≤0,001) (рис. 1а).
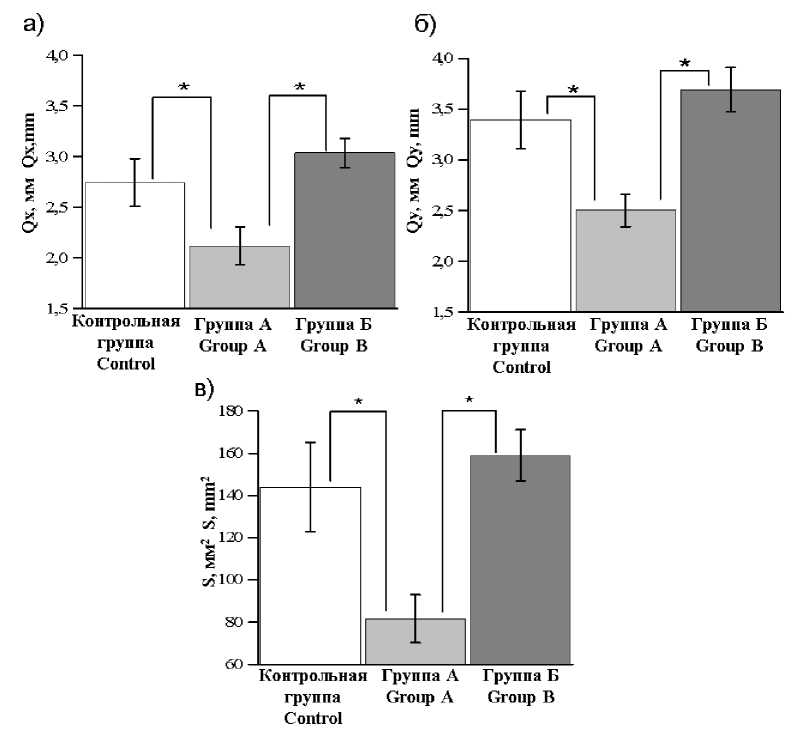
Рис. 1. Классические стабилографические показатели у лиц с латентными триггерными зонами мышц шеи и в контрольной группе: а) разброс центра давления во фронтальной (Qx, мм) и сагиттальной плоскостях (Qy, мм); б) площадь статокинезиограммы (S, мм2).
* – достоверное отличие между сравниваемыми группами при р<0,05
Fig. 1. Classical posturography indices in individuals with latent trigger zones of the neck muscles and in the control group: a) variation of pressure center in frontal (Qx, mm) and sagittal planes (Qy, mm); b) statokinesiogram area (S, mm2).
* – difference between the compared groups is significant (p<0.05)
Как видно из рис. 1, в контрольной группе отклонение по осям X и Y составило 2,7±0,2 и 3,3±0,3 мм соответственно, в группе Б – 3,0±0,1 и 3,7±0,2 мм. Достоверных отличий между контрольной группой и группой Б не выявлено.
В группе А площадь статокинезиограммы (82±11 мм2) оказалась меньше, чем в контрольной группе (144±21 мм2, p≤0,001) и в группе Б (159±12 мм2, p≤0,001) (рис. 1б).
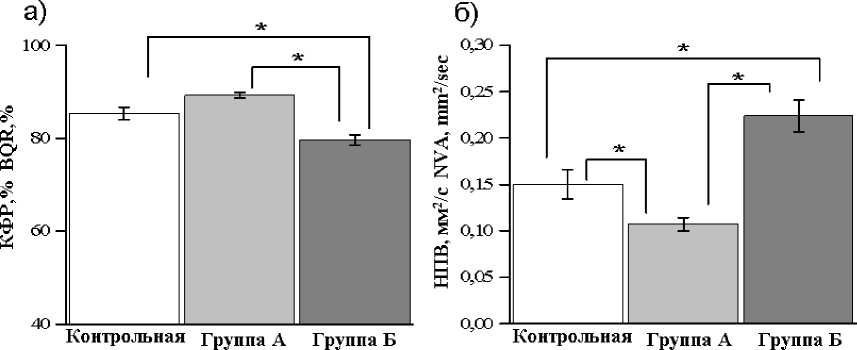
Качество функции равновесия (КФР) в группе А (89±0,6 %) было достоверно выше по сравнению с группой Б (80±1 %, p≤0,001), а в группе Б – ниже по сравнению с контрольной группой (85±1 %, p≤0,001). Достоверных различий данного показателя между группой А и контрольной группой выявлено не было (рис. 2а).
Уровень нормированной площади век-торограммы (НПВ) в группе А составил 0,10±0,007 мм2/с, что достоверно меньше, чем в группе Б (0,22±0,01 мм2/с, p<0,001) и в контрольной группе (0,15±0,01 мм2/с, p<0,001). Между контрольной группой и группой Б также отмечено достоверное отличие (p<0,001) (рис. 2б).
группа Group A Group В группа Group A Group В
Control Control
Control
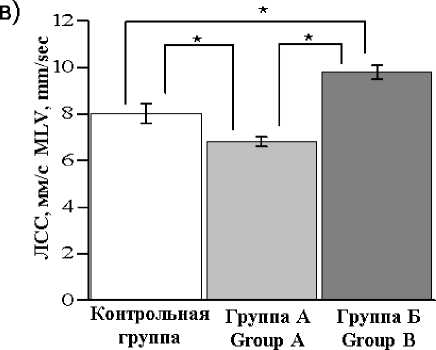
Рис. 2. Векторные стабилографические показатели у лиц с латентными триггерными зонами мышц шеи и в контрольной группе: а) показатель качества функции равновесия (КФР, %);
б) нормированная площадь векторограммы (НВП, мм2/с); в) линейная средняя скорость (ЛСС, мм/с).
* – достоверное отличие между сравниваемыми группами при р<0,05
Fig. 2. Vector posturography indices in individuals with latent trigger zones of the neck muscles and in the control group: a) an indicator of the equilibrium function quality (EFQ, %);
-
b) vectorogram normalized area (VNA, mm2/sec); c) linear mean velocity (LMV, mm/sec).
* – difference between the compared groups is significant (p<0.05)
Наибольшее значение линейной средней скорости выявлено в группе Б – 9,7±0,3 мм/с, что достоверно выше по сравнению с контрольной группой (8±0,4 мм/с, p≤0,001) и группой А (6,8±0,1 мм/с, p≤0,001). Значения данного показателя в группе контроля и в группе А также достоверно различались (p≤0,001) (рис. 2в).
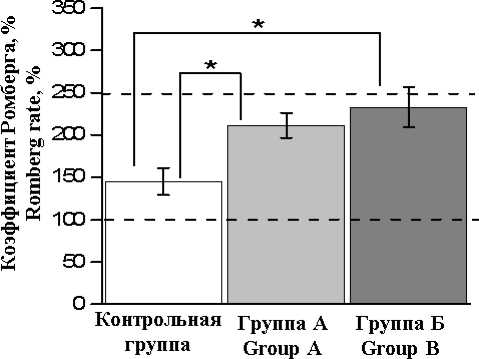
Коэффициент Ромберга в группах А (211±15 %) и Б (233±23 %) превышал аналогичный показатель в контрольной группе (145±16 %, p<0,006) (рис. 3).
Control
Рис. 3. Показатель коэффициента Ромберга у лиц с латентными триггерными зонами мышц шеи и в контрольной группе.
* – достоверное отличие между сравниваемыми группами при р<0,05
Fig. 3. Romberg coefficient in individuals with latent trigger zones of the neck muscles and in the control group.
* – difference between the compared groups is significant (p<0.05)
Обсуждение. В данном исследовании сравнивались показатели постурального контроля у лиц с лМТЗ шейной мускулатуры и здоровых испытуемых. Достоверных различий в классических показателях между контрольной группой и группой с лМТЗ, количество которых 4 и более, выявлено не было. Однако векторные показатели в этой группе достоверно отличались.
КФР является наименее вариабельным стабилометрическим показателем по сравнению с площадью эллипса статокинезио-граммы. КФР характеризует специфическое свойство системы поддержания вертикальной позы человека [18].
Ранее было показано, что лица с первичной длительно персистирующей хронической болью в шее имеют постуральный дефицит по сравнению с контрольной группой [19]. В другом исследовании впервые было показано, что мышечная утомляемость является превалиру- ющим фактором по сравнению с болью [20]. Также сообщалось о влиянии интенсивности боли на постуральный контроль [21–23]. В частности, повышенная скорость смещения ЦД [24] и нарушения движения [21] были обнаружены только для интенсивности боли больше 4 по 10-балльной ВАШ. В данном исследовании испытуемые не предъявляли активных жалоб на головную боль, боль в шее и спине, болезненность мышц шеи выявлялась исключительно при пальпации и прессуре указанных мышц, среднее значение выраженности боли составляло около 50 мм из 100 по ВАШ. Предполагается, что боль при пальпации лМТЗ связана с сенсибилизацией нейронов, возникающей из-за подпороговой активации из зоны уплотнения [25].
Более того, при анализе ряда классических и векторных показателей (площадь эллипса, средняя линейная скорость) было показано их снижение в группе с лМТЗ в количес- тве от одной до трех. Вероятно, это связано с формированием подпороговой ноцицептивной импульсации с лМТЗ, приводящей к активации механизмов дестабилизации положения шеи при их небольшом количестве, в результате чего улучшается постуральный контроль. Это подтверждается исследованиями с использованием воротников, фиксирующих шейный отдел позвоночника, в которых было показано улучшение показателей смещения ЦД у молодых здоровых испытуемых при стабилизации шеи [26]. Возможно, стабилизация шейного отдела позвоночника приводит к компенсации постуральной неустойчивости системы и, вероятно, благоприятно влияет на систему баланса.
При усложнении задачи в виде исключения зрительного контроля у всех субъектов с лМТЗ выявлено достоверное ухудшение коэффициента Ромберга. Наши результаты демонстрируют, что у субъектов с лМТЗ могут возникать субклинические проявления недостаточности постурального контроля. Более того, результаты этого исследования подкрепляют существующие предположения о том, что дефицит постурального контроля является вторичным по отношению к боли в шее. Таким образом, наши результаты показали, что постуральная неустойчивость при более сложной задаче, такой как тест Ромберга, харак- терна для лиц с наличием лМТЗ в мышцах шеи. Это может быть связано с тем, что при выполнении более сложных задач неточность информации, идущей от проприоцептивных рецепторов шейного отдела в ЦНС, не может быть компенсирована информацией из других источников (например, зрительного входа). Было показано, что возможно нарушение чувствительности афферентных мышечных веретен за счет изменения возбудимости мотонейронов спинного мозга при активации ноцицепторов в мышцах и суставах [27–30]. Таким образом, различия в постуральной эффективности, обнаруженные между тремя группами испытуемых, могут отражать разную степень возмущения фузимоторной системы, определяющую различия в точности проприоцептивного входа [29, 30].
Выводы:
Список литературы Постуральная устойчивость у лиц с латентными триггерными зонами шейной мускулатуры
- Bronstein A.M. Multisensory integration in balance control. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2016; 137: 57-66.
- Jones K.D., Horak F.B., Winters-Stone K., Irvine J.M., Bennett R.M. Fibromyalgia is associated with impaired balance and falls. Journal of clinical rheumatology: practical reports on rheumatic & musculoskeletal diseases. 2009; 15 (1): 16-21.
- Hasvold T., Johnsen R. Headache and neck or shoulder pain-frequent and disabling complaints in the general population. Scand. J. Prim. Health Care. 1993; 11 (3): 219-224.
- Hain T.C. Cervicogenic causes of vertigo. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2015; 28 (1): 69-73.
- Oostendorp R.A.B., van Eupen A.A.J.M., Elvers J.W.H., Bernards J.A. Effects of restrained cervical mobility on involuntary eye movements. J. Man Manip. Ther. 1993; 1 (4): 148-153.
- Reid S.A., Rivett D.A. Manual therapy treatment of cervicogenic dizziness: a systematic review. Man ther. 2005; 10 (1): 4-13.
- Reid S.A., Rivett D.A., Katekar M.G., Callister R. Sustained natural apophyseal glides (SNAGs) are an effective treatment for cervicogenic dizziness. Man Ther. 2008; 13 (4): 357-366.
- Sola A.E., Rodenberger M.L., Gettys B.B. Incidence of hypersensitive areas in posterior shoulder muscles. A survey of two hundred young adults. Am. J. Phys. Med. 1955; 34 (6): 585-590.
- Sciotti V.M., Mittak V.L., DiMarco L., Ford L.M., Plezbert J., Santipadri E., Ball K. Clinical precision of myofascial trigger point location in the trapezius muscle. Pain. 2001; 93 (3): 259-266.
- Wade B. Trigger points in the upper trapezius or normal subtrapezial anatomy? Physiother. Can. 2001; 53 (3): 219-222.
- Chen S.M., Chen J.T., Kuan T.S., Hong T.S., Hong C.Z. Decrease in pressure pain thresholds of latent myofascial trigger points in the middle finger extensors immediately after continuous piano practice. J. Musculoskelet Pain. 2000; 8 (3): 83-92.
- Herdman S.J., Clendaniel R. Vestibular rehabilitation. FA Davis; 2014.
- Ryan G.M.S., Cope S. Cervical vertigo. Lancet. 1955; 266 (6905): 1355-1359.
- Croft P.R., Lewis M., Papageorgiou A.C., Thomas E., Jayson I.M., Macfarlane G.J., Silman A.J. Risk factors for neck pain: a longitudinal study in the general population. pain. 2001; 93 (3): 317-325.
- Scott J., Huskisson E.C. Graphic representation of pain. pain. 1976; 2 (2): 175-184.
- Gerwin R.D., Shannon S., Hong C.Z., Hubbard D., Gevirtz R. Interrater reliability in myofascial trigger point examination. Pain. 1997; 69 (1-2): 65-73.
- Simons D.G. Review of enigmatic MTrPs as a common cause of enigmatic musculoskeletal pain and dysfunction. J. Electromyogr Kinesiol. 2004; 14 (1): 95-107.
- Усачев В.И., Доценко В.И., Кононов А.Ф., Артемов В.Г. Новая методология стабилометрической диагностики нарушения функции равновесия тела. Вестник оториноларингологии. 2009; 3: 19-22.
- Silva A.G., Cruz A.L. Standing balance in patients with whiplash-associated neck pain and idiopathic neck pain when compared with asymptomatic participants: a systematic review. Physiother. Theory Pract. 2013; 29 (1): 1-18.
- Cheng C.H., Chien A., Hsu W.L., Yen L.W., Lin Y.H., Cheng H. Y. Changes of postural control and muscle activation pattern in response to external perturbations after neck flexor fatigue in young subjects with and without chronic neck pain. Gait Posture. 2015; 41 (3): 801-807.
- Matre D., Arendt-Neilsen L., Knardahl S. Effects of localization and intensity of experimental muscle pain on ankle joint proprioception. Eur. J. Pain. 2002; 6 (4): 245-260.
- Sipko T., Kuczynski M. Intensity of chronic pain modifies postural control in low back patients. Eur. J. Pain. 2013; 17 (4): 612-620.
- Vuillerme N., Pinsault N. Experimental neck muscle pain impairs standing balance in humans. Exp. Brain. Res. 2009; 192 (4): 723-729.
- Ruhe A., Fejer R., Walker B. Altered postural sway in patients suffering from non-specific neck pain and whiplash associated disorder-A systematic review of the literature. Chiropr. Man Therap. 2011; 19 (1): 13.
- Mense S., Gerwin R.D. (ed.). Muscle pain: diagnosis and treatment. Springer Science & Business Media; 2010.
- Schikora N., Klunter H., Delank S., Eysel-Gosepath K. Influence of cervical spine stabilization via stiff neck on the postural system in healthy patients: compensation or decompensation of the postural system? Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2010; 267: 1623-1628.
- Pedersen J., Sjolander P., Wenngren B.I., Johansson H. Increased intramuscular concentration of brady-kinin increases the static fusimotordrive to muscle spindles in neck muscles of the cat. Pain. 1997; 70 (1): 83-91.
- Thunberg J., Hellstrom F., Sjolander P., Bergenheim M., Wenngren B., Johansson H. Influences on the fusimotor-muscle spindle system from chemosensitive nerve endings in cervical facet joints in the cat: possible implications for whiplash induced disorders. Pain. 2001; 91 (1-2): 15-22.
- Johansson H., Sjolander P., Djupsjobacka M., Bergenheim M., Pedersen J. Pathophysiological mechanisms behind work-related muscle pain syndromes. Am. J. Ind. Med. 1999; 36 (S1): 104-106.
- Sjolander P., Johansson H., Djupsjobacka M. Spinal and supraspinal effects of activity in ligament afferents. J. Electromyogr Kinesiol. 2002; 12 (3): 167-176.


