Priorities of the strategic management and planning of the Northern Sea Route
Автор: Evgeniy E. Plisetskiy
Журнал: Arctic and North @arctic-and-north
Рубрика: Problems of the northern sea route development
Статья в выпуске: 22, 2016 года.
Бесплатный доступ
The article is devoted to the analysis of the main socioeconomic indicators of 10 subjects of the Russian Federation, with the coastal areas adjacent to the water area of the Northern Sea Route. The author studied the strategy of socio-economic development of the North and Far East Russia. The planned development of the NSR provides alignment of a unified system of public-private management of transportation artery and the implementation of other strategic activities. It is necessary to establish a single governing body, modernization of the Arctic transport system, production of high-tech products and marine technology for the home market, building a rear port infrastructure, container terminals, customs warehouses and logistics centers.
Northern Sea Route, regions, development strategies
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/148318675
IDR: 148318675 | УДК: 338.49/338.47 | DOI: 10.17238/issn2221-2698.2016.22.103
Текст научной статьи Priorities of the strategic management and planning of the Northern Sea Route
The Northern Sea Route (NSR) is one of the determining factors of sustainable socioeconomic development of the Arctic zone of the Russian Federation. At the same time NSR not only provides national security and strengthens Russia's geopolitical presence in the Arctic, but it is also an important transport corridor, a key element of the entire infrastructure. In this connection, not by chance, on the 8th of December 2015 at the session of the Commission on the development of the Arctic Marine Board at the Government of the Russian Federation, Dmitry Rogozin said that without a serious modernization of infrastructure of seaports, including checkpoints, providing them with modern logistic, energy facilities, the creation of modern systems of communication, navigation, maritime safety, the Northern sea Route and its competitiveness would not have any perspective [1]. Processing the updated integrated development strategy for the Northern Sea Route it is very important to consider the existing policy, its priorities and development of the transport corridor founded by the federal and regional documents.
Northern Sea Route in the strategic management and planning
Analysis of the main socio-economic indicators in 10 subjects of the Russian Federation1, a part of the NSR, shows that a high proportion of regions in the total area of the territory of Russia
(almost 49%) and a significant share in the total volume of extraction of mineral resources (almost 30%), these regions are characterized by low rates of population, employment and retail turnover, as well as the low rates of housing and agricultural production (pic. 1).
Инвестиции в основной капитал;
13,2
Оборотрозничной торговли; 6,8
■ Ввод в действие общей площади жилых домов; 4,7
Продукция с/х 4,4
Производство и распределение электроэнергии; 10,0
■ Обрабатывающие производства; 5,8
-
■ Добыча полезных ископаемых; 29,0
-
■ Основные фонды в экономике; 14,7
Среднегодовая численность занятых в экономике; 7,7
■ Численность населения; 6,9
Площадь территории; 49,1
Валовой региональный продукт; 11,1
Picture 1. The share of 10 researched areas in the index of social and economic development 2013 , % 2
Three biggest positions are: territory(49% of the RF), resource extraction (29%), investments in main capital (13.2%)
Similarly, not a high proportion of the studied regions and the total volume of foreign trade turnover with foreign countries (Table 2). For example, the proportion of the Nenets, Yamalo-Nenets, Chukotka Autonomous District, the Arkhangelsk and Murmansk regions, Kamchatsky Krai in the total volume of the Russian exports, according to Rosstat, does not exceed 0.5%. The volume of transit traffic through the NSR grew from 110 ths. tons in 2010 by more than 10 times in 2013 (1.16 million tonnes), a decrease took place due to a number of economic reasons in 2014 and the turnover was 274 thousand tons. The mining company, transporting bulk cargoes of the Kovdor from Murmansk could not reach an agreement on prices and transported 200 thousand tons less than in previous years. A gas company Novatek moved its business from Vitino port on the Kola Peninsula in the port of Ust-Luga near St. Petersburg — the enterprise sees no reason to use the NSR to transport gas condensate, as it was in previous years 3.
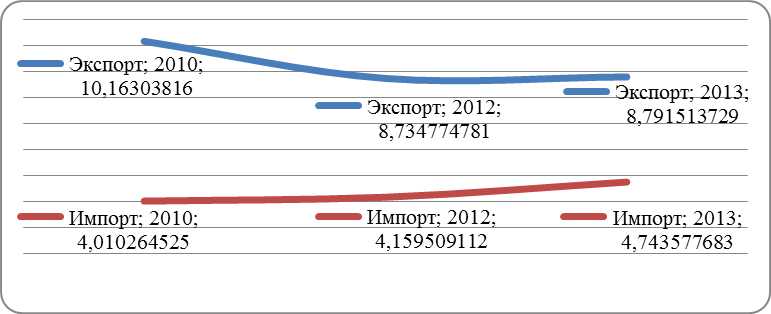
Picture 2. The share of 10 areas in foregn trade index, % . Blue line is export, red line is import
Targeted and integrated development of the NSR is capable of providing a wide diversification of the economy of the northern areas, it creates new jobs, stimulates the development of Russian oil and gas extraction on the Arctic shelf and maintains the pace of growth of the productive forces of the Far North.
The planned development of the NSR can not be achieved without building a single publicprivate management of transportation, determining organizational, legal, administrative, institutional and economic approaches. First, we should talk about the formation of a single governing body that would deal with the control and coordination of the activities carried out by the sovereign agencies and commercial organizations for the development of the NSR. According to the law adopted in 2012 № 132-FZ “On Amendments to the legislative acts of the Russian Federation regarding the state control of merchant shipping in the waters of the Northern Sea Route”4, it has been a number of measures for the development of the NSR, including the establishment of the administration in the form of a federal state fiscal institution (FSFI). Decree of the Russian Government dated by the15th of March 2013 № 358-p: such administration has been established for the organization of sailing along the NSR. The main objectives of its activities are to ensure the safety of navigation and protection of the marine environment from pollution from ships in the waters of the NSR. You may notice that the powers reserved for the institutions that do not allow it to become the only operator on the development of the NSR.
For comparison, it is worth paying attention to the management model of the Panama Channel. Thus, the powers of the Administration of the Panama Channel are to ensure work, administration, management, maintenance and modernization of the Channel, as well as the implementation of related services, permitted by the legislation. The Panama Channel Authority is responsible for the management, maintenance, use and conservation of water resources of the channel in full coordination with the relevant governmental and non-governmental organizations 5.
The existing system of public administration of the NSR is presented in the relevant documents on strategic and program-oriented federal and regional planning and looks like that ( pic. 3 ):
Стратегия развития Арктической зоны Российской
Федерации до 2020
\ года у
•Государственная программа социальноэкономического развития Арктической зоны Российской Федерации на период до 2020 года

Транспортная стратегия Россшгекой Федерации на период до 2030года
Государственная программа Российской Федерации «Развитие транспортной системы», а также Государственные программы РФ «Охрана окружающей среды» на 2012 - 2020 годы», «Развитие судостроения на 2013 - 2030 годы»;
ФАИП на 2015 год и на плановый период 2016 и 2017 годов

Стратегии социальноэкономического развития субфедерального уровня
Региональные стратегии социальноэкономического развития у
Государственные программы субъектов РФ
Picture 3. NSR strategic management today
The main priorities of the NSR development are incorporated in strategic planning documents: “Strategy of development of the Russian Arctic and national security untill 2020” (“Strategy 2020”); strategies of social and economic development of the RF subjects, in terms of improving the management and realization of specific projects in the social, economic and other spheres.
One of the complex socio-economic targets of the Russian Arctic listed in the “Strategy 2020” is the modernization and development of infrastructure and the Arctic transport system , which provides: excellence, availability of transport infrastructure in the areas of the Arctic continental shelf development, the restructuring and growth of cargo volumes for the NSR, improving the legal framework of the Russian Federation and the state regulation of navigation along the NSR, improving the management and safety of navigation in the Russian Arctic, the modernization of Arctic ports and the creation of new industrial complexes, governmental support of the “northern delivery”, export of goods and products, establishment of modern information and telecommunication infrastructure. The development of infrastructure of the NSR and navy, including the icebreakers will solve the problems of transport maintenance in the Arctic and the Eurasian transit during the econd phase (until 2020) of the “Strategy 2020”.
A key tool for the implementation of the “Strategy 2020” is the “State program of socioeconomic development of the Russian Arctic for the period untill 2020”6, real investment which, unfortunately, has been postponed by now. Priorities of state policy in the “Strategy 2020” directly related to the development of the NSR are: the active interaction among the Arctic States on maritime delimitation, increased efforts of Arctic states in the creation of a single regional System for Search and Rescue and to prevent man-made disasters and elimination of their consequences, including the coordination of rescue forces, Business Plan for the organization and effective use of transit and cross-polar air routes in the Arctic, as well as in the use of the NSR for the international navigation, the improvement of social and public administration of economy, the development of the resource base of the Russian Arctic, modernization and development of infrastructure, the Arctic transport system and the fisheries in the Russian Arctic.
As part of the Russian state program “Environmental protection” for 2012-2020 provides for measures to ensure comprehensive data on the marine environment, the oceans and seas for the implementation of various kinds of sea activities in Russia (navigation along the Northern Sea Route, fishing, navy and National defense).
State program of the Russian Federation “Development of shipbuilding for the 2013-2030 years” means state support measures aimed at support of the high-tech production in Russia, high-tech products of civilian marine technology for the Russian market. Construction and modernization of icebreakers, creation of new ports, modernization of port infrastructure, the development of the basic production and port infrastructure are one of the priorities of the “Transport Strategy of the Russian Federation for the period untill 2030”. The subprogram “Sea and river transport” includes measures to ensure the waterways and hydro facilities, search and rescue, maintenance of navigation, hydrographic support of shipping along the NSR.
According to the federal targeted investment program for 2015 and the plan of 2016-2017, (Ref. Ministry of Economic Development of Russia,December 25, 2014 № 32639-EE/D17i) it was scheduled more than 20 activities related to work on reconstruction and construction of infrastructure facilities of seaports and airport complexes along the NSR with the total volume of financing for more than 30 billion rubles (pic . 4 ).
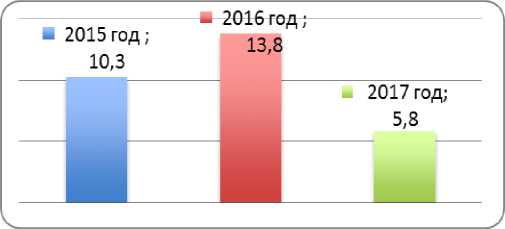
Picture 4. Budget for the NSR development projects 2015—2017, billions of rubles7.
The increase in the volume of cargo transportation by sea route is planned to 63,7 million tons by 2020, and an increase in technical equipment – up to 40.5% in 2020. The Federal Target Program “Development of Transport System of Russia (2010-2020)” provided measures for navigation and hydrographic support of navigation along the NSR and the development of the largest seaports, including Arkhangelsk, Murmansk and Sabetta.
Regional strategies of the NSR development
The Strategy of socio-economic development of the North-West Federal District until 2020 has one of the priority directions and it is the development of transport and notes the need for articulating the development of all types of transport, terminals and warehouse infrastructure that makes the complex of major hubs like St. Petersburg, Murmansk, Vologda, Arkhangelsk and Kaliningrad. Here, the main events are marked: modernization and construction of port terminals for coal, container, oil and petroleum products in the framework of the project “Integrated development of the Murmansk transport hub”; design and construction of passenger terminal for cruise ships in the port of Murmansk; construction of a seaport in Belomorsk, which will include two cargo areas - specialized coal complex and universal complex; development of the Northern Sea Route and the Arctic port infrastructure; reconstruction and construction of facilities in the seaport of Arkhangelsk; building ports, including container terminals, customs, warehouses and logistics centers.
Prospects for the development of water transport in Siberia were identified in the Strategy of socio-economic development of Siberia until 2020, linked to the further development of the Northern Sea Route in terms of infrastructure development of the Arctic ports. Strategy and aims of the NSR development were identified in the Strategy of socio-economic development of the Far East and the Baikal region for the period up to 2025: transport support of the development of Arctic oil and gas fields, providing northern delivery of socially important goods, the development of large-scale regional and transit traffic.
The Strategy of Social and Economic Development of the Russian Federation and its subjects has designated priorities for the development of the transport corridor. Strategy for SocioEconomic Development of the Murmansk region untill 2020 and up to 2025 clearly captures the role of the NSR as a strategic driver of the region and an important element in the system of international transport corridors. Intensification of navigation along the NSR will open up regional markets of the most dynamically developing Asia-Pacific region in addition to the traditional European and North American markets. In this context, a key challenge is the development of the Murmansk transport service to provide navigation along the Northern Sea Route. Meeting the challenge will increase cargo handling at ports of the Murmansk region from 28,160,000 tons in 2012 to 70,0 mln tons in 2025. There is a priority investment projects until 2020, aimed at the development of infrastructure of the NSR and initiated by the Ministry of Transport of Russia, FSUE “Rosmorport”, the sovereign-governmental Atomic energy Corporation “Rosatom” with a financiation of more than 280 billion rubles 8. At the same time, the use of targeted program planning in the field of infrastructure development is not provided in the Murmansk region.
The Strategy of socio-economic development of the Arkhangelsk region until 2030 pointed out the geographical position of the Arkhangelsk region and the access to the northern seas was celebrated as an important competitive advantage of the Arkhangelsk sea port - a strategic transport hub that could allow export to foreign markets and transit of goods. Priority projects in the region for the transport infrastructure development are: the construction of deep water port in Arkhangelsk, reconstruction of terminals and the sea approach channel (the projects included in the Strategy of the transport complex development of the Northwestern Federal District). Government programs have been designed in order to implement these plans for the development and reconstruction of the ports and the NSR but have not been approved.
The Strategy for socio-economic development of the Nenets Autonomous District until 2030 has clearly defined the place of the region as an integral part of the Russian Arctic, the goals and objectives of the state policy for this period: introduction of new techniques and technologies for use of marine minerals and water biological resources, as well as providing the necessary infrastructure to operate the extraction inductry in the Arctic; to ensure cargo delivery along the Northern Sea Route; use of the state support for building new icebreakers, safety and rescue vessels, coastal safety infrastructure; safety control for navigation and traffic control in areas of heavy traffic. The NAD priority mineral extraction projects are also associated with the active development of the NSR capacity, namely: construction of a large (capacity of 12 million tons) plant for oil processing in Indigirka; building a gas chemical complex on the Barents Sea coast (also in Indigirka). The territory of the NAD is considered as a convenient “jumping zone” for offshore platforms and communications center for vessels along the NSR. Application of any tools to enable the development of the NSR infrastructure has not been provided in the document.
Priorities of the NSR in the Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous District could be defined according to Strategy of social and economic development until 2020 and they are mainly related to the role of the transport path in the operation of the Russia's largest center for the LNG - Uzhno-Tambeyskoye gas field near the village of Sabetta and construction of a port terminal there. At the same time, the Strategy does not fix any strategic activities in the field of the NSR development.
The draft Strategy for socio-economic development of the Krasnoyarsky Krai up to 2020 is focused on the development and preservation of the NSR and “Yenisei-NSR” transport system. It is done to ensure the active extraction of oil and gas and future extraction of mineral resources on the Arctic continental shelf. A special role is devoted to the Port of Dikson that is sees “as the security guarantor of the ships along the Northern Sea Route and the support base for its development” and, in the long-term perspective, the Strategy mantiones building new oil terminal and port in Khatanga. The use of any targeted tools for the NSR development is not provided in the draft.
Development of the NSR infrastructure is done according to the Development schemes for productivity of transport and energy of the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia) untill 2020 and it is, primarily, related to the river and sea ports’ capacity, river and sea routes and the Northern Sea Route, the modernization of the fleet of the Lena, Yana and Kolyma shipping companies; their completion with the ships for mixed “river-sea” navigation; safety of navigation along the NSR and the restoration of navigation and hydrographic infrastructure serving the shipping in the Western and Eastern sectors of the Arctic. Investments in water transport for the period of 2007—2020 are going to be around 10 billion rubles for water transport, new vessels of the “river-sea” class with a total deadweight of 52—64 thousand tons, construction, improvement and renewal of the passenger vessels, and etc. The Strategy is supported by the subprogram “Water transport” of the state program “Development of transport complex of the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia) for 20122016” with thе funding more than 6 billion rubles.
In the Strategy for socio-economic development of the Kamchatsky Krai until 2025 marine economic activity stands is one of four priority directions of regional development that directly affect the NSR infrastructure, development of transport and port infrastructure, carrying out primary processing of the freight traffic, the development of regional programs for the ship repair complex. The Strategy is the subprogram “Development of Water Transport” of the State Program “Development of transport system in the Kamchatsky Krai in 2014-2025”, which aims to create a modern cargo and passenger fleet, renew water transport and etc. The total volume of financing is about 700 million rubles.
The Strategy for Socio-Economic Development of Primorsky Krai until 2025 focuses on the transport and logistics cluster in the region, port-hub on the basis of the port complex Vostochny — Nakhodka, complex development of Vladivostok and Nakhodka transport hub, that ends the NSR in the east of the country and will serve the transnational distribution, providing cargo transportation to/from South-East Asian countries. The total volume of the planned investments for the development of the cluster is 62 billion rubles. But unfortunately all these has no planned funding.
The strategic the federal and the regional planning documents, objectives and actions for the development of particular elements of the NSR should be reviewed in terms of their interlinkages, the redistribution of finanacing and prioritization. At the same time, only two areas (the Kamchatsky Krai and the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia) among the 9 regions are carrying out (partly) the renewal and development of the NSR infrastructure with the help of targeted programs.
Conclusion
The analysis of the existing strategic development management system allows SMEs to make the following conclusions. First of all, necessary to form a unified governing body SMP (Development Institute), which would be engaged in the control and coordination of the activities carried out by state agencies and commercial organizations-mi (or empowering the existing SME Administration).
There is a need to develop a comprehensive strategy of development of SMEs and co-sponding her state program defining long-term objectives, targets, deadlines (stages) before the implementation of 2025-2030. Taking into account the interests of coastal regions and business, the priority areas (elements) of development funding responsible executors.
One of the prerequisites for SMEs active work in the medium term become approved in June 2015. The Chairman of the Russian Government Dmitry Medvedev approved "Comprehensive Development Project of the Northern Sea Route", aimed at co-building the conditions for implementation of investment projects, the increase in transit cargo-flow [2].
Список литературы Priorities of the strategic management and planning of the Northern Sea Route
- Rogozin D. provyol sovmestnoe zasedanie Goskomissii po voprosam razvitiya Arktiki i Morskoj kollegii pri Pravitelstve. 8 dekabrya 2015. URL: http://government.ru/news/21070/ (Accessed: 03 February 2015).
- Medvedev D.A. podpisal kompleksnyj proekt razvitiya Severnogo morskogo puti. 8 iyunya 2015. URL: http://www.interfax.ru/russia/446380; http://tass.ru/ekonomika/2027639 (Accessed: 02 February 2016).


