Private public partnership in education: a model of human capital management
Автор: Leonidova Galina Valentinovna, Babich Lyubov Vasilyevna
Журнал: Economic and Social Changes: Facts, Trends, Forecast @volnc-esc-en
Рубрика: State and economy
Статья в выпуске: 1 (19) т.5, 2012 года.
Бесплатный доступ
The article considers the issues of human capital use management as one of the most important fictitious assets which provides economic transition to the innovative way of development. The model of cooperation between regional authorities, business and higher educational establishments on the basis of private public partnership is proposed in the article. The implementation of the model will make it possible to provide prospective needs of innovative economy in highly skilled personnel in advance.
Human capital, human capital use, private public partnership in education, higher professional education, personnel training
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/147223323
IDR: 147223323 | УДК: 332.142.4(470.12)
Текст научной статьи Private public partnership in education: a model of human capital management
Modern economies urgently need highly skilled personnel having not only the educational background, but also enterprise, innovative, creative aspirations and motives, able to acquire new knowledge and actively manage the innovation process. To address the key strategic objective of professional education – the ability to react in advance to the long-term needs of innovative economy – there should be a collaboration of the business community and educational institutions, joint work and pooling the efforts of government and administrative bodies, employers and educational institutions on the principles of public-private partnership.
In “the Concepts of long-term socio-economic development of the Russian Federation up to 2020” approved by the Russian Federation Government Decree № 1662-r dated November 17, 2008, “the Basic areas of activity of the Russian Federation Government until 2012 (including the list of implementation projects)” approved by the Russian Federation Government Decree № 1663-r dated November 17, 2008, and the program of anti-crisis measures of the Government of the Russian Federation for 2009, a public-private partnership (PPP) is defined as the basis for the development of economy and education system that is an important condition for achieving the targets of socio-economic development of the Russian Federation.
Activities of PPP in education are regulated by a number of legislative acts1, which define the principles of public-private partnerships:
-
• parity in the resources invested in the program of public-private partnership;
-
• parity responsibility of government and business for projects implementation;
-
• presence of equal leverage and control mechanisms on the part of business and government for the implementation of programs of public-private partnership;
-
• efficient use of resources invested by partners in the education system2.
At the same time there is practically no systematic strategy for implementing PPPs in education, which is expressed by the following:
-
♦ absence of long-term strategies for development of industries and organizations;
-
♦ lack of clearly defined strategic priorities for PPP development;
-
♦ inability of representatives of the education sector to consolidate all the parties concerned to implement the planned programs and projects;
-
♦ undeveloped forms of “horizontal” partnership;
-
♦ predominance of interaction of executive authorities of the state with other social partners on the basis of the model of “managed democracy”3.
In this regard, the study of the model of public-private partnership in education in the Vologda region has become the purpose of this article.
The ideology of the public-private partnership (PPP) is now quite widespread in the world. Public-private partnership, according to V.G. Varnavsky , is an institutional and organizational alliance between government and business in order to implement the socially significant projects and programs in a broad range of industries and R&D, up to the service sector4. In this case the necessary conditions of functioning of such an alliance are legality, clarity, transparency, reasonableness and acceptability of the rules of the game for both sides5. For the state the main reason for the establishment of public-private partnership is first of all an increasing need in services for the delivery of which the state is responsible6. They include higher professional education services demand for which has increased considerably in recent years. Since 2000 up to 2011 there was a positive dynamics of the number of university students and graduates. The values of these parameters per 10 thousand of the region’s population were below the relevant data for Russia 1.3-fold, but comparable with those of developed countries (for example, the number of students per 10 thousand of the population in France was 360 people, in the UK – 380, and in Finland – 590)7. This suggests that the region has good potential to increase the number of specialists with higher education. The proportion of students in the economically active population (per 10 thousand population) which
Table 1. Number of university students per 10 thousand of economically active population, people
|
Territory |
Year |
||||||||
|
1995 |
2000 |
2004 |
2005 |
2006 |
2007 |
2008 |
2009 |
2010 |
|
|
The Russian Federation |
375 |
587 |
803 |
815 |
827 |
826 |
820 |
993 |
983 |
|
NWFD |
404 |
652 |
827 |
841 |
848 |
858 |
841 |
981 |
941 |
|
The Vologda region |
285 |
453 |
653 |
635 |
645 |
684 |
656 |
765 |
741 |
|
Source: Key indicators of regional development of the North-West Federal District. 2009: stat. coll. Vologda, 2009; Russia in figures. 2011: stat. coll. Rosstat. M., 2011. 581 p.; authors’ calculations. |
|||||||||
is one of the direct characteristics of the intellectual potential of the area increased between 1995 and 2011 more than 2.5 times on average both in Russia (from 375 to 982 people) and in its regions (tab. 1) .
Public-private partnerships in education is co-operation between the state / municipal government, educational institutions and businesses to implement projects in the field of education by pooling resources and sharing risk, revenue and expenses. Relationships of PPP parties are partner, equitable in nature and recorded in the documents (agreements, contracts, etc.). Participants in public-private partnerships have right of ownership for the used partnership assets and other proprietary rights, pool their resources to achieve the objectives of the project (program) of the public-private partnership, and then share the responsibilities and risks.
The strategy of socio-economic development of the Vologda region for the period till 2020 defined the purpose of regional system of professional education: addressing the needs of socio-economic complex of the region for skilled personnel and specialists. In this regard, the region adopted the Law “On primary and secondary education”8 and it proceeded to create a multi-level system of public-private partnership. Its main institutional mechanism in professional education are coordinating councils for training (industrial, municipal), and the supervisory boards of trustees of educational institutions.
Currently there are:
-
■ the regional coordinating council for personnel and specialists training at the first vice-governor of the region,
-
■ six industry councils for the following areas: engineering and metal processing, construction, forestry complex; agriculture, trade, services, roads and transportation, education,
-
■ seven municipal councils for personnel training (in the cities of Cherepovets and Vologda, the districts of Veliky Ustyug, Totma, Sokol, Vytegra, Gryazovets)9.
Coordinating councils have become a discussion and negotiation platform for business leaders, heads of educational institutions and relevant departments of problematic issues of training for the regional market.
In addition, the regional government in February 2011 decided to establish a regional system for forecasting staffing requirements for the medium and long term.
The legal basis for the organization of systemic partnership of government, business and vocational training was formed with the participation of the Union of Industrialists and Entrepreneurs: the documents governing the interaction between educational institutions and organizations of employers in training, fixing the educational institution at basic institutions (provision of basic organization, form of cooperation agreements, etc.) are developed and implemented. As part of the coordinating councils’ work there are discussions of the issues related to the development of regulatory frameworks to ensure a favorable tax treatment for employers who invest in the vocational education system.
However, higher education institutions drop out of the PPP area, while in developed countries they are increasingly seen as key partners in federal and regional authorities in implementing the policy of socio-economic development of territories. This is the system of higher vocational education which is building an educational process based on scientific research, is designed to train specialists of a new formation ensuring the establishment of innovative economy, so the “university – enterprise” alliance should become the focus of efficient generation and use of human capital in the region.
It is important to include such an important segment of the regional market as small and medium business, which also remains aloof, into the system of public-private partnerships.
Management model of the region’s human capital use for its innovative development based on public-private partnership is schematically represented in figure 1 .
The implementation of this model is possible in each of the priority industries of the region: mechanical engineering, textile and linen industries, timber industry, etc. For this purpose, the authors believe is necessary to concentrate the industry around one strong institution of higher education (or several if the programs of secondary and higher education are implemented by different institutions) with the active support of the Regional Government.
These entities have their own interests, but these priorities and objectives are coherent, and their interaction has a synergistic effect on the development and effective utilization of human capital in the region (fig. 2) . Each of the partners in this model is supposed to fulfill the functions assigned to it.
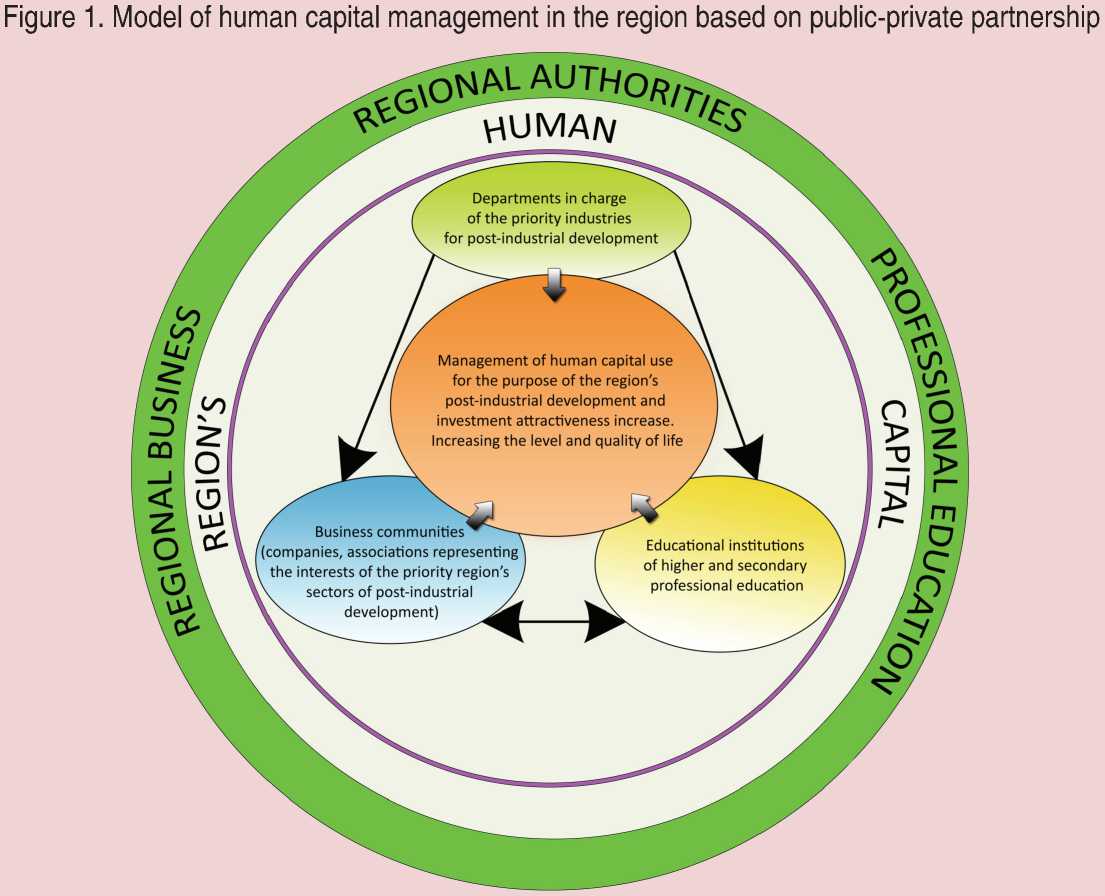
Figure 2. Objectives and functions of public-private partnership participants in education in the interests of the region’s innovative development
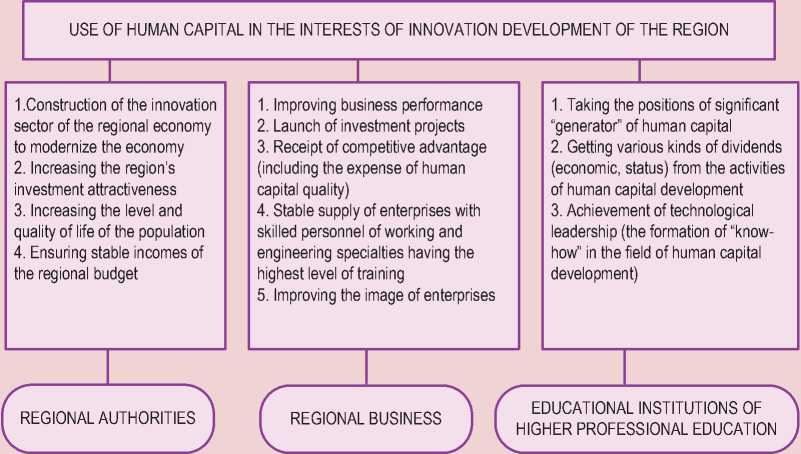
-
1. Designing long-term strategies for the region’s development “Interests configuration” of other PPP subjects makes the laws, applies the tax regulation, motivates them to work together to build and develop human capital, etc.
-
2. Co-financing of joint projects of the subjects for human capital rational use 3. Initiation and regulation of communication processes of PPP participants
-
3. Participation in the creation and development of university-based educational-industrial-technological infrastructure for the innovation activities of companies and the effective use of human capital
-
4. Assistance in the implementation of research works and projects aimed at addressing the problems of specific business
1. Participation in educational and research activities of the university 2. Participation in curriculum development, basic education programs and courses work programs
-
1. Coordination of training plans (training areas, specialties, number of students) 2. Coordination of curriculum, basic educational programs and courses work programs
-
3. Ensuring the quality of graduates training according to the demand of innovative development of the industry and the region 4. Creating educational, industrial and technological infrastructure for the innovation of companies and the effective use of human capital
-
5. Performing research work and projects aimed at addressing the problems of specific business
Thus, the functioning of the PPP is a combination of public and private interests and competencies, which, on the one hand, allows the authorities to solve urgent problems of the region with the financing of infrastructure projects and social programs, on the other it makes it possible for private business to invest and get interested in its profits. Public-private partnerships allow avoiding both drawbacks of direct regulation of the state, and “marketing failures”.
The instruments of public-private partnership able to adjust personnel training mechanism to address specific production problems are targeted training institute and federal target allocation of budget places in universities and federal institutions of secondary vocational education. The resolution of the Government of the Vologda region “On the procedure for determining the size and structure of the reception of students at the expense of the regional budget in the educational institutions of secondary and higher education” No. 1371 dated December 27, 2005 defied an additional mechanism of target contract training. However, the analysis of the order execution shows the insufficiency of legal mechanisms contributing to the employment of graduates in accordance with the trust agreement (the proportion of employed “targetists” of VSPU is 22%). In addition, in some cases there is a passive attitude of universities to interact with companies and organizations to implement the mechanism of targeted training. As can be seen from table 2 Vologda universities have performed the federal quota and targeted training on contracts with companies provided only 82% of the quota.
Another tool of PPP is the institution of “social partnership”. Thus, the paradigm of relations in the Vologda region in primary vocational training is built up as numerous connections of NPO institutions with various enterprises, institutions and organizations.
One of the directions of social partnership implementation is the organization of labor market research by the department of education. Employers and educational institutions agree on targets for admission to professional educational institutions.
Thus, analysis of the situation on the labor market has shown significant differences between the interests of enterprises of different ownership forms that in some way affect the cooperation with them. Large enterprises such as OJSC “Severstal”, OJSC “Cherepovets Steel Rolling Plant”, Vologda Branch of the Northern Railway, OJSC “Vologda bearing plant” and others which are traditionally the partners of educational institutions of professional education, are constantly responding to the offers of cooperation. This is explained by the fact that they are in need of workers and specialists which is due to weak attraction of the job which they offer in the labor market. At the same time there is lack of organization of employers engaged in small-and medium-sized businesses, as well as their mistrust of the quality of professional training that cannot establish a dialogue with this category of employers quickly and effectively. However, in this area there are examples of preparedness for various forms of cooperation, primarily in enterprise trade, catering and domestic services.
However, the share of organizations and companies planning to expand (start) collaboration with institutions of professional education is not more than 50%, and the fact that 35% of com-
Table 2. Target admission by the federal quota and by contracts with agencies and organizations to the universities in the Vologda region in 2009, pers
|
University |
Number of places |
Quota fulfillment |
fulfillment % |
|||
|
by the Federal quota |
by contracts with agencies and organizations |
by the Federal quota |
by contracts with agencies and organizations |
by the Federal quota |
by contracts with agencies and organizations |
|
|
Vologda Institute of Economics and Law |
410 |
- |
464 |
- |
113.1 |
- |
|
Vologda State Pedagogical University |
- |
212 |
- |
114 |
- |
54 |
|
Vologda State Milk Academy named after N.V. Vereshchagin |
165 |
60 |
165 |
60 |
100 |
100 |
|
Vologda State Technical University |
57 |
- |
43 |
- |
75.4 |
- |
|
Total |
632 |
272 |
672 |
174 |
106.3 |
82 |
Source: The concept of Personnel Policy of municipality “The City of Vologda” up to 2020 “Vologda is a city of professionals” [Electronic resource]: adopted by the Resolution of the Administration of the city of Vologda dated 28.09.2010 No. 5165. Available at:
Figure 3. The share of organizations and companies planning to expand (start) cooperation with institutions of professional education, %
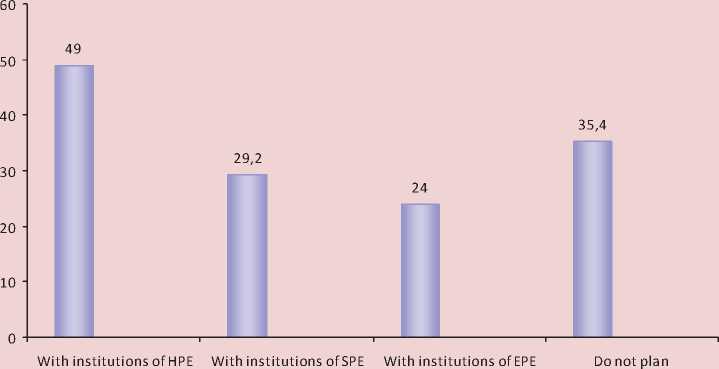
Source: data of expert survey of business leaders and organizations in Vologda, conducted by ISEDT RAS.
panies surveyed in 2007 – 2008 do not plan to cooperate indicates the incomplete effectiveness of the institute of “social partnership” (fig. 3) .
At present, based on one of the elements of the Scientific and Educational Center – the Vologda Branch of SPbSUEE – the legal and institutional issues on building of the state educational institution of the Institute of Regional Development (IRD) are being worked out where the regional government can act as the founder, and the Russian Academy of Sciences can give the scientific leadership. The purpose of the Institute’s activities is targeted training of highly qualified specialists ordered by the regional and municipal governments, business entities, that is, training of the regional administrative elite. The project implementation of the Institute is nothing but a form (model) of the management organization of human capital for innovation development of the industry of mechanical engineering of the region as a whole10.
IRD creation provides:
-
• integration of scientific and educational complex with businesses of the region to carry out joint activities on the development of professional competencies of graduates and the construction of an effective mechanism of interaction between university science, business and government, the formation of effective scientific and educational space11;
-
• scientific and methodological support for continuing education;
-
• integration of scientific and technological potential of the region;
-
• creation of a network of strategic partners who are interested in mutually beneficial cooperation in the field of personnel training;
-
• sustainable development of the region and enhancing its investment attractiveness;
-
• raising the level and quality of life in the region.


Figure 4. The project of the Institute of Regional Development (IRD)
THE CONCEPT OF THE INSTITUTE OF REGIONAL DEVELOPMENT
г-----1
Customers

Interests
Improving the competitiveness of the territory on the basis of development of scientific and technical potential of the region in the prescribed areas
Specialists training with the customer’s requirements (including individual requirements)

Objective
1 Г
Insuring of balance of the interests of government, business, science and education on the basis of their integration

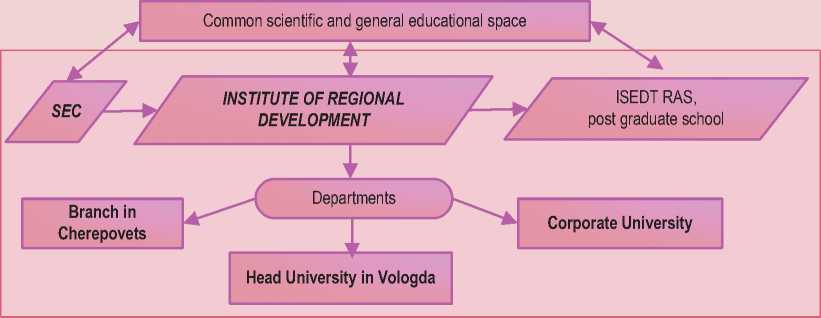

Highly qualified professionals of targeted training
Figure 4 presents a scheme of IRD functioning in the case of engineering industry, which is the basis of innovation development of the region’s economy
As part of IRD activities the partners, i.e. the subjects of human capital use management are:
-
> Department of Industry, Science and Innovation Policy of the regional Government;
-
> Association “Machine-building enterprises of the Vologda region”;
-
> Scientific and educational complex, the core of which is the Vologda branch of “Saint-Petersburg State University of Engineering and Economics” (ENGECON).
In the proposed model the cooperation of participants of public-private partnership is possible in the following areas:
Department of Industry, Science and Innovation Policy of the regional Government;
-
I. Department of Industry, Science and Innovation Policy of the regional Government
– the Vologda Branch of SPbSUEE : through active research policy the Department manages the IRD providing the branch with government orders and grants, allocation the funds for development programs, direct budget financing of projects aimed at developing and efficient use of the region’s human capital.
-
II. Department of Industry, Science and Innovation Policy of the regional Government – Association “Machine-building enterprises of the Vologda region”: the Department motivates companies to cooperate by forming favorable tax treatment.
-
III. Association “Machine-building enterprises of the Vologda region” – the Vologda Branch of SPbSUEE: the Association is involved in efforts to ensure the quality of personnel training (development of curriculum, core educational programs, course work programs). It takes part as a final consumer of educational services in the work of the state certification committee of the university, cofinances the development of university-based educational-industrial-technological infrastructures for innovation of the industry and the efficient use of staff through their involvement in the implementation of research and development.
The Coordinating Council can coordinate the project, its functions are completely in tune with the current branch of personnel training council of the Vologda Oblast (in the direction of machine-building), and which currently regulates the interaction of businesses with educational institutions of primary vocational education. The composition of this body, in our opinion, may include representatives of all PPP participants: from the Department – responsible persons in charge of the region’s machine-building complex, from the Association – companies representatives responsible for staffing and execution of R&D, from the university – the branch Director, deputy Director for Science and head of the issuing department.
Today there is the development of current and future (on medium and long term) plans of IRD development which reflect the structure, scope and quality of personnel training, development of educational, industrial and technological infrastructure and modernization of training facilities of the Branch, professional development of the teaching staff, etc.
It seems that the Institute of Regional Development has to become a center of the modern system of continuing business education in the Vologda region, which is ensured by the following:
-
• programs of higher professional education for training of innovative managers and engineers;
-
• program of secondary professional education for training of mid-level professionals (product engineers, etc.);
-
• Center of Continuing Education implementing training and retraining programs for the existing staff of enterprises;
-
• Youth Scientific and Innovation Center, a key element in the educational and industrial and technological infrastructure of the project, a kind of resource base with modern logistics equipment and providing the possibility of realizing the human potential of talented young people to form a critical mass of human capital capable of solving the problem of improving the territory’s competitiveness;
-
• Center of prevocational training providing target work with talented youth.
The experience of the Vologda branch of SPbSUEE and ISEDT RAS will contribute the project implementation in individualization of the educational process at the first stage – the Scientific and Educational Center (SEC), which has been operating in the region since 2003 on the basis of ISEDT RAS12, in particular such forms of work with talented children and youth as:
-
> the system of remote, part-time training and consulting of gifted children and talented youth with opportunities for educational, scientific and innovative structures of the university;
-
> summer camps for gifted and talented young people;
-
> practice for the students of the Branch and the SEC to establish early contact with prospective employers of the city;
-
> participation of students of the Branch in foreign internships;
-
> students’ and teachers’ academic mobility and participation in international exchange programs;
-
> creation of the Branch’s basic chairs in ISEDT RAS.
The proposed approach will allow the region’s administration to decide the priorities of its innovative development through rational use of such intangible assets as human capital. The project is in compliance with the directions of the Long-term Target Program “Integrated development of professional education system in the Vologda region for 2011 – 2015”:
-
1. Improving the forecasting of staffing needs of the regional economy, formation and distribution of government order for the training of personnel, including the creation of the regulatory framework of formation of state order for regional professional education system based on which the volume and direction of training in professional educational institutions will be determined.
-
2. Increasing demand for the graduates of professional education at the regional labor market through the organization of information and career guidance campaigns to professions and occupations of priority sectors of the economy; concluding contracts with organizations for training, retraining and skills development; career guidance, increasing the prestige of working occupations and professions which are in demand in the labor market.
-
3. Establishing an effective territorial and industry organization of resources of primary and secondary vocational education by building the optimal structure of vocational education institutions, the organization of effective networking of professional educational institutions at all levels (school / NPE / SPE / HPE) and their co-operation with the employers (the equipment of new resource centers of professional education in priority areas of the region’s economic development: construction, engineering and metalworking, agriculture, forestry and wood systems, etc.; upgrading the content of vocational education to meet the needs of regional labor market and employers’ requirements).
The expediency of this is due to the following: first, these mechanisms will provide to coordinate both educational and scientific activity for the solution of practical problems facing the regional economy, second, the possibilities for improving the quality of training and competitiveness of scientific and educational institutions will expand significantly, and third, there will be the prerequisites for the transition to innovation-oriented economy.
Список литературы Private public partnership in education: a model of human capital management
- Varnavsky V.G. Alliance for an indefinite period. Moscow: Feld-Pochta, 2004. No. 29. P. 5-9.
- Gruzdov V.V. Public-private partnerships as a tool for innovative development. Intellectual Property Rights. 2007. No. 2.
- Efimova L.I. Some models of public-private partnerships: trends and international experience: report on the seminar “Public-Private Partnership: new trends in the development of transport infrastructure”. Bulletin of the Euro-Asian Transport Union, 2003. No. 3.
- Ilyin V.A., Gulin K.A., Uskova T.V. Intellectual resources as a factor of innovative development. Economic and social changes: facts, trends, forecast. 2010. No. 3. P. 14-25.
- The concept of long-term socio-economic development of the Russian Federation up to 2020. Approved by the Decree of the Russian Federation Government on November 17, 2008 No. 1662-r.
- Leonidova G.V. Generation of talented youth’s knowledge for the benefit of intelectualization of human capital: the methods and forms. Economic and social change: facts, trends, forecast. 2011. No.13. P. 90-100.
- Leonidova G.V. The problem of formation of the regional scientific and educational space. In: Bulletin of ENGECON. St. Petersburg, 2010. N 1 (36) “Economics”. P. 134-142.
- Orlova E.O., Sovetov P.M. The mechanism of investment interaction of businesses and local governments. Vologda: ISEDT RAS, 2010.
- Public report on the status and performance of the education system of the Vologda region for 2010/2011 academic year. Available at: http://www.edu35.ru/
- RF Government Resolution dated November 11, 2006 No. 671 “On the assertion of a model concession agreement in respect of educational facilities”.
- Guidelines for the implementation of large-scale public-private partnership in education. Moscow: MAKS Press Publishing House, 2010. P. 8-9.
- Development Strategy of Education in the Vologda region up to 2020. Approved by the Regional Government Decree dated March 3, 2009 No. 398.
- Federal Law “On the order of formation and use of target capital of noncommercial organizations”, dated December 30, 2006 No. 275-FL.
- Federal Law “On Autonomous Institutions” dated November 3, 2006 No. 174-FL.
- Federal Law “On Concession Agreements” dated July 21, 2005 No. 115-FL.
- The concept of Personnel Policy of municipality “The City of Vologda” up to 2020 “Vologda is a city of professionals” : adopted by the Resolution of the Administration of the city of Vologda dated 28.09.2010 No. 5165. Available at: http://vologda-portal.ru
- Guidelines for the implementation of large-scale public-private partnership in education. Moscow, 2010. P. 8-9
- Statistical Yearbook of Russia. 2007. Moscow: Rosstat, 2007. P. 786


