Protective effect of ghrelin on sodium valproate-induced liver injury in rat
Автор: Sadeghi Niaraki Mandana, Nabavizadeh Fatemeh, Vaezi Gholam H., Alizadeh Ali M, Nahrevanian Hossein, Moslehi Azam, Azizian Saleh
Журнал: Журнал стресс-физиологии и биохимии @jspb
Статья в выпуске: 1 т.9, 2013 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Ghrelin is a peptide that has protective effects on many tissues injury. It has anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidant effects. Sodium valproate is widely used anticonvuisant and anti-depression drug with hepatotoxic side effects. The aim of this study was to evaluated the protective role of ghrelin in liver toxicity due to sodium valproate overdose. Eighteen rats were used in this study and divided in to three groups, containing: control, sodium valproate, and sodium valproate and ghrelin groups. Nitric oxide (NO), prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) and hepatic enzymes AST (aspartate aminotransferase) and ALT (alanine aminotransferase), were assessed and histologic study of liver were performed as indicators of liver damage following sodium valproate toxicity. This study showed the ghrelin decreased ALT and AST to the normal level. Our results show that ghrelin significantly increased NO metabolites and decreased PGE2 level comparison with sodium valproate group, but had no significant change compared to the control group. we showed that ghrelin administration inhibited liver injury in rats due to sodium valproate toxicity.
Ghrelin, liver injury, nitric oxide(no), prostaglandin e2(pge2), sodium valproate
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/14323727
IDR: 14323727
Текст научной статьи Protective effect of ghrelin on sodium valproate-induced liver injury in rat
Valproate (2-propylpentanoic acid) is a widely used anticanvulsant and anti depression drug throughout the word (Shaat et al., 2006).Death due to hepatotoxicity have been reported, mainly in children (Bellringer et al., 1988).
The mechanism by which VPA causes liver damage is belived to be mediated by some of its metabolites (Shaat et al., 2006). VPA is metabolized primarily in the liver by three routes; cytochrome P450, fatty acid, β-oxidation and conjugation to active and inactive metabolites. Some VPA metabolites (β-oxidation) are thought to be potentially hepatotoxic (Liston et al., 2001; Silva et al,. 2002). Less than 5% of metabolites is excreted in the urine (Dlta et al., 1988).
Ghrelin is a newly discovered gut hormone, mainly produced in the stomach (Ariyasu et al., 2001), but also identified in endocrine cells of the gastrointestinal tract (Date et al., 2000).
Ghrelin plays a role in a number of different physiological processes. For example, it enhances growth hormone secretion and increases appetite ( Shiiya et al., 2002), regulates cell proliferation (Yoshihara et al., 2002), stimulates prolaction and adrenocorticotrophic hormone (Kojima et al., 2004), promotes slow wave sleep (Weikel et al., 2003) and memory retention (Carlini et al., 2002).
In the stomach, ghrelin affects gastric acid secretion, motility and exhibits gastroprotective effect (Brzozowski et al., 2004). In mammals, ghrelin plays an important role in the immune system (Yada et al., 2006). Previous study showed ghrelin administration inhibited liver injury in rats due to acetaminophen toxicity (Golestan Jahromi et al., 2010). Ghrelin significantly increased the bioactivition of nitric oxide (Tesauro et al., 2005), mucosal prostaglandin E 2 (PGE 2 ) (Sibilia et al., 2003) and inhibited the activation of Nuclear factorkappa B (NF-KB) and plasma tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) level (Konturek et al., 2006). The antioxidation and anti-inflammatory effects of ghrelin were previously demonstrated (EI Eter et al., 2007). As the main mechanism of VPA toxicity is via inflammation and oxidative stress, this study was designed to evaluate the possible protective effect of ghrelin in hepatocellular damage secondry to VPA toxicity in rats.
MATERIALS AND METHODS Materials
Valproic acid sodium salt and Ghrelin were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (Sigma Chemical
Company, St. Louis, MO, USA).
Animals and experimental protocols
Eighteen male Wistar rats (200-250 g) were used. All animals were kept in an animal room in a controlled temperature and 12:12 h light/dark cycle with free access to food and water. All procedures were approved by the ethical committee of Tehran University of Medical Sciences.
The animals were equally divided into three groups (n=6) including: (A) control group; animals were given saline solution as vehicle, (B) VPA group; rats were given once a day VPA (500 mg/kg B.W i.p) for four consecutive days (Nahrevanian et al., 2009) and (C) VPA+ghrelin group; rats were treated with ghrelin (10 nmol/kg single dose i.p) 1 hour after VPA injection in days 3 and 4 (Tesauro et al., 2005).
Three hours after the last injection of gherlin, rats were anesthetized with i.p injection of ketamine-zylaxine (50 and 8 mg/kg, respectively) (Golestan Jahromi et al., 2010) and the abdomen was opened medially. Then, whole blood samples (1 ml) were taken from the heart. Blood samples were centrifuged (4000 g, 15 min) and serum was collected for serological tests including aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine aminotransferase (ALT). Also, liver middle lob tissue was fixed in a buffered-formaldehyde solution (10%) for histological studies. Other lobs immediately frizzed kept at -70 oC for measurement of PGE2 and NO by ELISA and Griess methods, respectively.
Liver tissues homogenate preparation for determination of PGE2 and NO
Weighed samples of liver tissue (0.5 g) were placed in 1.5 ml microfuge tubes and homogenized using an electrical homogenizer (Model RS541-242, RS Components, Corby, UK) (Tesauro et al., 2005). Then homogenates tested for PGE2 using a high sensitivity PGE2 Chemiluminescence Enzyme Immunoassay (CEI) Kit (Assay Designs Inc., MI, USA) and NO metabolites with the Griess Micro Assay method (Nahrevanian et al.,2009).
Histology and microscopic structural examinations
The grade of histological study was semi quantitatively scored using the following parameters (Ishak et al., 1995):
A*Piecemeal necrosis:
0-Absent,
1-Mild (focal, few portal areas),
2-Mild/moderate (focal ,most portal areas), 3-Moderate (continuous around<50% of tracts or septa),
4-Severe (continuous around>50% of tracts or septa).
B* Confluent necrosis:
0-Absent,
1-Focal confluent necrosis,
2-Centrolobular necrosis in some areas,
3-Centrolobular necrosis in most areas, 4-Centrolobular necrosis + occasional portal-central (P-C) bridging,
5-Centrolobular necrosis + multiple P-C bridging, 6-Panlobular or multilobular necrosis.
C* Focal (Spotty) lytic necrosis, apoptosis,and focal inflammination:
0-Absent,
1-One focus or less per 10× objective,
2-One to four foci per 10× objective,
3-Five to 10 foci per 10× objective,
4-More than 10 foci per 10× objective.
D*Portal inflammation:
0-None,
1-Mild, some or all portal areas,
2-Moderate, some or all portal areas, 3-Moderate/marked, all portal areas, 4-Marked, all portal areas.
**Fibrosis:
0-No fibrosis,
1-Fibrous expansion of some portal areas, with or without short fibrous septa,
2-Fibrous expansion of most portal areas, with or without short fibrous septa,
3-Fibrous expansion of most portal areas with occasional portal-portal (P-P) bridging,
4-Fibrous expansion of portal areas with marked bridging (portal-portal (P-P) as well as portal central (P-C)),
5-Marked bridging (P-P and/or P-C) with occasional noduls (incomplete cirrhosis),
6-Cirrhosis, probable or definite.
Statistical analysis
All values were expressed as Mean±S.E. Statistical analysis performed with analysis of variances (ANOVA) and post hoc Tukey tests using version SPSS 17.0. For the comparison of nonparametric data using Kruskal-Wallis test. P<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
RESULTS
Liver enzymes measurement
Animals injected with VPA alone (group B) showed significantly elevated levels of hepatic enzymes, AST and ALT compared to the control group (group A) (P<0.05) (Table 1). AST and ALT decreased significantly in the group that received ghrelin after VPA administration (group C) compared to the group that received VPA alone (group B) (p<0.05). Ghrelin increased AST and ALT to normale levels (no significant difference with the group A) (P<0.6, P<0.5, P<0.8, respectively) (Table1).
NO metabolites measurement
Our finding showed that levels of NO metabolites of liver tissue in VPA group (group B) had significant change compared to the control group (group A) (107.08±21.12, 141.29±24.21 μΜ/gr.Wet weight, respectively) (p<0.05) (Fig.1), it significantly increased by using ghrelin after VPA administration (109.5±21.14 μΜ/gr.Wet weight) (p<0.05) (Fig.1). Also, our data showed that levels of NO of liver tissue in group that received ghrelin after VPA (group C) had no significant change compared to the control group (P<0.6) (Fig.1).
PGE2 measurement
PGE2 level of liver tissue in VPA group was significantly higher than control group (25.91±2.9, 11.58±1.29 Pg/gr Wet weight, respectively) (p<0.05), but it significantly decreased by using ghrelin after VPA administration (11.68±1.31 Pg/gr Wet weight) (p<0.05) (Fig.2). Our finding showed that levels of PGE2 of liver tissue in group that received ghrelin after VPA (group C) had no significant change compared to the control group (P<0.6) (Fig.2).
Histological study
The microscopic study showed infinitesimal damage in rat liver tissue (0.83±0.3), but did not show any fibrosis in control group. Morphological changes following VPA injected (2.3±0.21) and areas of confluent fibrosis (2.3±0.42) were significantly increased than to the control group (p<0.001, p<0.001, respectively). Treatment with ghrelin has significantly reduced liver injury and fibrosis (1.16±0.47, 0.66±0.21, respectively) compared to the VPA group (p<0.001, p<0.01, respectively) (Table 2, Fig. 3).
Data were expressed as Mean±SEM. n=6, § P<0.05, ALT in VPA group compared to control group, ‖ p<0.05, ALT in VPA+GHR group compared to VPA group, † P<0.05, AST in VPA group compared to control group, ‡ p<0.05, AST in VPA+GHR group compared to VPA group compared to control group.
Table 1: Effects of ghrelin and sodium valporate on levels of hepatic enzymes.
|
Groups |
ALT (U/L) |
AST (U/L) |
|
Control |
65.5±3.86 |
170.8±28.23 |
|
VPA |
80.8±4.14 § |
246±31.18 † |
|
VPA+GHR |
66.4±3.92 ‖ |
184.2±29.12 ‡ |
Data were expressed as Mean±SEM. n=6, § P<0.05, ALT in VPA group compared to control group, ‖ p<0.05, ALT in
VPA+GHR group compared to VPA group, † P<0.05, AST in VPA group compared to control group, ‡ p<0.05, AST in VPA+GHR group compared to VPA group compared to control group.
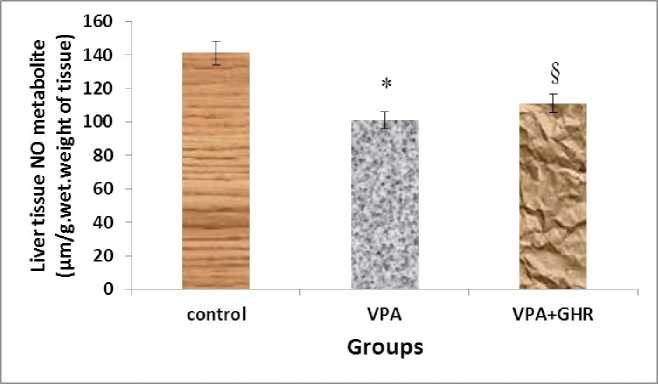
Figure 1: The level of liver tissue NO metabolites in different experimental groups (Mean±SEM, n=6). *p<0.05, liver tissue NO in VPA group compared to control group. §p<0.05, liver tissue NO in VPA+GHR group compared to VPA group.
Table 2: Histological activity index (HAI) was assessed based on the degree of microscopic lesions (Piecerneal necrosis, Confluent necrosis, Focal (Spotty litic necrosis, apoptosis, focal inflamination), Portal inflamination, Fibrosis). Data of each group were reported as Means±SEM based on sum of the scores histological criteria (overall score) using Kruskal-Wallis test (n=6).
|
Groups |
Piecerneal necrosis |
Confluent necrosis |
Focal (Spotty litic necrosis, apoptosis, focal inflamination) |
Portal inflamination |
Overall score |
Fibrosis |
|
Control |
0 |
0 |
0.66±0.21 |
0.16±0.16 |
0.83±0.3 |
0 |
|
VPA |
1.3±0.21 |
0.33±0.33 |
1.5±0.22 |
1.16±0.16 |
2.3±0.21 †† |
2.3±0.42 ‡‡ |
|
VPA+GHR |
0.16±0.16 |
0 |
0.66±0.21 |
0.33±0.21 |
1.16±0.47 ” |
0.66±0.21 § |
†† P<0.001, compared to control group, ” p<0.001, compared to VPA group , ‡‡ P<0.001, compared to control group, § p<0.01, compared to VPA group.
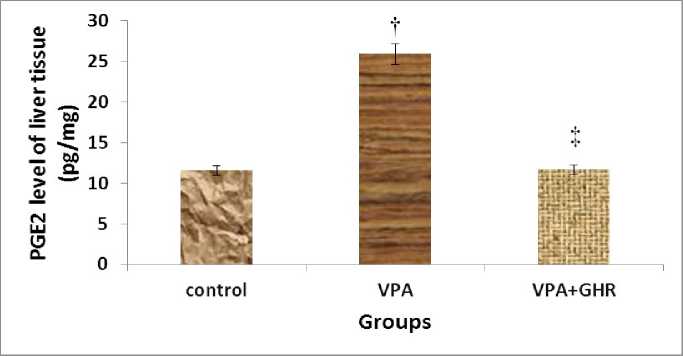
Figure 2: The level of liver tissue PGE2 in different experimental groups (Mean±SEM, n=6). †p<0.05, PGE2 level in VPA group compared to control group, ‡p<0.05, PGE2 level in VPA+GHR group compared to VPA group.
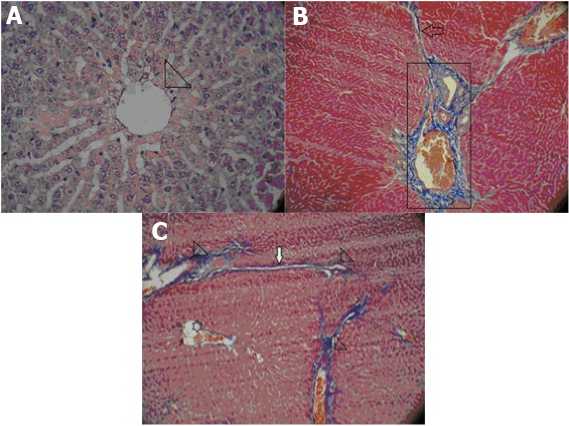
Figure 3: Liver histopathology. Representative slides from corresponding groups are shown (A: control group, Normal liver tissue. Arrowhead shows central vein (H&E ×40), B: VPA group, Aportal tract show fibrosis expension (rectangle) (Masson,s trichrome ×10), C: ghrelin group, Three portal tracts (arrowheads) and a central vein (star) showing portal-portal (p-p) bridging fibrosis (arrow) (Masson,s trichrome ×10).
DISCUSSION
In the present study the hepatic toxicity caused by acute adminiestratin of sodium valproate was investigated; it could indeed be ameliorated by treatment with ghrelin.
Some of GI hormons play a major role in the regulation of inflammatory and fibrojenic process in a variety tissues. Ghrelin is a GI hormone that is also produced by extraintestinal tissues and it has protective effects in different organ including the pancreas, heart, gastrointestinal tract and liver (Golestan Jahromi et al., 2010; Moreno, et al., 2010).
In this study due to induction of liver toxicity by sodium valproate, serum ALT and AST, the diagnostic markers of liver damage, were elevated. These data indicate that VPA causes liver dysfanction. Administration of ghrelin improved liver toxicity and decreased level of these enzyms. Increased liver enzyme activity in this study was in agreement with other previous researcher (Shaat et al., 2006). Plasma transaminases are sensitive indicators of liver cell injury (Tong et al., 2005). Their elevated levels in VPA treated rat may be due to either direct hepatocyte damage or due to oxidative stress leading to apoptosis of hepatocytes.
Kupffer cells are the phagocytic macropages of the liver. When activated, kupffer cells relase numerous signaling molecules, including hydrolytic enzymes, eicosanoids, NO and superoxide (Jaeschke et al., 2002; James et al., 2003). They may also release a number of inflammatory cytokinen, including TNF-α, interlukins, prostaglandins and oxygen radicals are released in liver toxicity (Martinez et al., 1992).
Animal experiments have shown that PGE2, TNF-α, IL-1, IL-6, NO and iNOS are decreased in respons to VPA (Raoj et al., 2007). VPA was found to decrease the expression of COX2 presumably outhor, this inhibition of NF-KB is likely to inhibit other NF-KB regulated genes. That is, NF-KB inhibition by VPA could be expected to decreas TNF-α, IL-1, IL-6, NO, iNOS (Slominany and Slomiany, 2009). A recent study reported that chronic administrations of VPA in rat reduced protein levels of COX-1 and COX-2 total COX activity, and the metabolit of arshidonic produced via COX (Bosetti et al., 2003). Recently, showed that the gastroprotective effect of ghrelin was associated with the increase in NO and PGE2 production (Martinez et al., 1992). Ghrelin also improves endothelial function by inhibiting basal and tumour necrosis factor (TNF-α)-induced, production of chemotactic cytokines, increasing nitric oxide (NO) bioactivity part by its antiinflammatory effect (Li et al., 2004).
In our study, VPA significantly decreases NO metabolites level in the liver tissue but ghrelin elevated it to the normal level. This finding agrees with the reports of Adelinof et. al. In addition to, in our study, PGE2 level of liver tissue was significantly increased in VPA group, but ghrelin reducted it to the control group, while other studies showed decreasing of PGE2 following VPA administration in liver tissue. This discrepancy of findings, may be due to duration and/or dosage of drug (VPA). We also observed piecerneal necrosis, confluent necrosis, spotty litic necrosis, apoptosis, focal inflamination, portal inflamination and fibrosis in the liver tissue due to VPA administration.
Further more, histopatogical study of tissue damage by VPA in the liver confirmed previous finding that, it causes inflammation of the liver capsule, necrosis and steatosis (Tong et al., 2005). Also, in this study we showed that, treatment with ghrelin improved histological changes in the liver.
Inconclusion, we showed that ghrelin administertion inhibited liver injury in rat due to VPA toxicity. The liver protective role of ghrelin may be mediatd at least in immunoreactivity levels in humans.
REFRENCES
Bellringer, ME., Rahman. K., Coleman, R. (1988). Sodium valproate inhibits the movement of secretory vesicles in rat hepatocytes. Biochem J. , 249 , 513-519.
Bosetti, F., Weerasinghe, GR., Rosenberger, T.A., Rapoport, S.I. (2003). Valproic acid down-regulates the conversion of arachidonic acid to eicosanoids via cyclooxygenase-1 and -2 in rat brain. Journal of Neurochemistry ., 85 , 690-696.
Brzozowski, T., Konturek, P., Konturek, S., Kwiecie, S., Drozdowicz, D., Bielanski, W., Pajdo, R., Ptak, A., Nikiforuk, A., Pawlik, W.W., Hahn, E.G. (2004). Exogenous and endogenous ghrelin in gastroprotection against stress-induced gastric damage. Regulatory Peptides. , 120 , 39-51.
Carlini, V., Monzon, M., Varas, M., Cragnolini, A., Schioth, H., Scimonelli, T., de Barioglio, S.R. (2002). Ghrelin increases anxiety-like behavior and memory retention in rats. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. , 299 , 739-743.
Date, Y., Kojima, M., Hosoda, H., Sawaguchi, A., Mondal, M., Suganuma, T., Matsukura, S., Kangawa, K., Nakazato, M. (2000). Ghrelin a novel growth hormone-releasing acylated peptide is synthesized in a distinct endocrine cell type in the gastrointestinal tracts of rats and humans. Endocrinology ., 141 , 4255-4261.
Dlta, C., Jacob, L.Z. (1988). Valproic Acid and the liver review. Clinical Chemistry ., 34 , 890-897.
EI Eter, E., Al Tuwaijiri, A., Hagar, H., Arafa, M. (2007). In vivo and in vitro antioxidant activity of ghrelin: attenuation of gastric ischemic injury in the rat. Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology ., 22 , 1791-1799.
Golestan Jahromi, M., Nabavizadeh, F., Vahedian, J., Nahrevanian, H., Dehpour, A.R., Mehrjardi, A.Z. (2010). Protective effect of ghrelin on acetaminophen-induced liver injury in rat. Peptides Journal ., 31 , 2114-2117.
Ishak, K., Baptista, A., Bianchi, L., Callea, F., Gudat, F., Denk, H., Desmet, V., Korb, B., Macsween, R., Philips, M.J., Portmann, B.G., Poulsen, H., Scheuer, P.J., Schmid, M., Thaler, H. (1995). Histological grading and staging of chronic hepatits. J. hepatology. , 22 , 696-699.
Jaeschke, H., Gores, G., Cederbaum, A., Hinnson, J., Pessayre, D., Lemasters, J. (2002). Mechanisms of hepatotoxicity. Toxicological Sciences . 65 , 166-176.
James, L., Mayeux, P., Hinson, J. (2003). Acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity. Drug Metabolism and Disposition. , 31, 1499-1506.
Kojima, M., Hosoda, H., Kangawa, K. (2004). Ghrelin a novel growth-hormone-releasing and appetite-stimulating peptide from stomach. Best Practice & Research Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism. , 18 , 517-530.
Konturek, P., Brzozowski, T., Walter, B., Burnat, G., Hess, T., Hahn, E., et al. (2006). Ghrelin-induced gastroprotection against ischemia-reperfusion injury involves an activation of sensory afferent nerves and hyperemia mediated by nitric oxide. European Journal of Pharmacology ., 536 , 171181.
Liston, H.I., Makowitz, J.S., De Vane C.I. (2001). Drug glucuronidation in clinical psychopharmacology. J. Clin Psychopharmacol ., 21 , 500-515.
Li, W.G., Gavrila, D., Liu, X., Wang, L., Gunnlaugsson, S., Stoll, L.L., McCormick, M.L., Sigmund, C.D., Tang, C., Weintraub, N.L. (2004). Ghrelin inhibits proinflammatory responses and nuclear factorkappa B activation in human endothelial cells. Circulation ., 109 , 2221-2226.
Martinez, F., Abril, E.R., Earnest, D.L., Watson, R.R. (1992). Ethanol and cytokine secretion. Alcohol ., 9 , 455-458.
Moreno, M., Chaves, J., Sancho-Bru, P., Ramalho, F., Ramalho, L., Mansego, M., Ivorra, C., Dominguez, M., Conde, L., Millán, C., Marí, M., Colmenero, J., Lozano, J.J., Jares, P., Vidal, J., Forns, X., Arroyo, V., Caballería, J., Ginès, P., Bataller, R. (2010). Ghrelin attenuates hepatocellular injury and liver fibrogenesis in rodents and influences fibrosis progression in humans. Hepatology ., 51 , 974-985.
Nahrevanian, H., Hajihosseini, R., Arjmand, M., Farahmand, M., Ghasemi, F. (2009). Evaluation of anti-leishmanial activity by induction of nitric oxide and inhibition of prostaglandin in Balb/c mice infected with leishmania major. Southeast Asian Journal of Tropical Medicine and Public Health. , 40(6) , 1188-1198.
Raoj, S., Bazinet, R.P., Rapoport, S.I., Lee, H.J.
(2007). Chronic treatment of rats with sodium valproate downregulates frontal cortex NF-Kappa B DNA binding activity and COX-2 mRNA. Bipolar Disord. , 9 , 513-20.
Sibilia, V., Rindi, G., Pagani, F., Rapetti, D., Locatelli, V., Torsello, A., Campanini, N., Deghenghi, R., Netti, C. (2003). Ghrelin protects against ethanol-induced gastric ulcers in rats: studies on the mechanism of action. Endocrinology ., 144 , 353-359.
Silva, M.F., Ruiter, J.P., Overmars, H., Bootsma, A.H., Van Gennip, A.H., Jacobs, C., Duran, M., Dealmeida, T.I., Wanders, R.J. (2002). Complete beta oxidation of valproate: cleavage of 3-oxovalproyl-coA by a mitochondrial 3-oxovalproyl-coA thiolase. Biochem J. , 15 , 755760.
Shaat, E.A., Samia, M.A., Madkour, S. (2006). Effect of L-Carntine and deferoxamine on hepatotoxicity, erythrocyte ergothioneine and testicular testosterone synthesis in sodium valproate-treated rats. Bull. Alex. Fac. Med. , 42 , 123-124.
Shiiya, T., Nakazato, M., Mizuta, M., Date, Y., Mondal, M., Tanaka, M., Nozoe, S., Hosoda, H., Kangawa, K., Matsukura, S. (2002). Plasma ghrelin levels in lean and obese humans and the effect of glucose on ghrelin secretion. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism ., 87 , 240244.
Slominany, B.L., Slomiany, A. (2009). Involvement of constitutive nitric oxide synthase in ghrelin-induced cytosolic phospholipase A2 activation in gastric mucosal cell protection against ethanol cytotoxicity. Inflammopharmacol., 17, 245-253.
Tesauro, M., Schinzari, F., Iantomo, M., Rizza, S., Melina, D., Lauro, D., Cardillo, C. (2005). Ghrelin improves endothelial function in patients with metabolic syndrome. Circulation ., 112 , 29862992.
Tong, V., Teng, X.W., Chang, T.K.H., Abbott, F.S. (2005). Valproic Acid I: Time Course of Lipid Peroxidation Biomarkers, Liver Toxicity, and Valproic Acid Metabolite Levels in Rats. Toxicological Sciences ., 86 , 427-435.
Weikel, J., Wichniak, A., Ising, M., Brunner, H., Friess, E., Held, K., Mathias, S., Schmid, D.A., Uhr, M., Steiger, A. (2003). Ghrelin promotes slow-wave sleep in humans. American Journal of Physiology-Endocrinology and Metabolism. , 284 , 407-415.
Yada, T., Kaiya, H., Mutoh, K., Azuma, T., Hyodo, S., Kangawa, K. (2006). Ghrelin stimulates phagocytosis and superoxide production in fish leukocytes. Journal of Endocrinology ., 189 , 5765.
Yoshihara, F., Kojima, M., Hosoda, H., Nakazato, M., Kangawa, K. (2002). Ghrelin: a novel peptide for growth hormone release and feeding regulation. Current Opinion in Clinical Nutrition & Metabolic Care ., 5 , 391-395.
Список литературы Protective effect of ghrelin on sodium valproate-induced liver injury in rat
- Ariyasu, H., Takaya, K., Tagami, T., Ogawa, Y., Hosoda, K., Akamizu, T., Suda, M., Koh, T., Natsui, K., Toyooka, S., Shirakami, G., Usui, T., Shimatsu, A., Doi, K., Hosoda, H., Kojima, M., Kangawa, K., Nakao, K. (2001). Stomach Is a Major Source of Circulating Ghrelin, and Feeding State Determines Plasma Ghrelin-Like Immunoreactivity Levels in Humans. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism., 86, 4753-4758.
- Bellringer, ME., Rahman. K., Coleman, R. (1988). Sodium valproate inhibits the movement of secretory vesicles in rat hepatocytes. Biochem J., 249, 513-519.
- Bosetti, F., Weerasinghe, GR., Rosenberger, T.A., Rapoport, S.I. (2003). Valproic acid down-regulates the conversion of arachidonic acid to eicosanoids via cyclooxygenase-1 and -2 in rat brain. Journal of Neurochemistry., 85, 690-696.
- Brzozowski, T., Konturek, P., Konturek, S., Kwiecie, S., Drozdowicz, D., Bielanski, W., Pajdo, R., Ptak, A., Nikiforuk, A., Pawlik, W.W., Hahn, E.G. (2004). Exogenous and endogenous ghrelin in gastroprotection against stress-induced gastric damage. Regulatory Peptides., 120, 39-51.
- Carlini, V., Monzon, M., Varas, M., Cragnolini, A., Schioth, H., Scimonelli, T., de Barioglio, S.R. (2002). Ghrelin increases anxiety-like behavior and memory retention in rats. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications., 299, 739-743.
- Date, Y., Kojima, M., Hosoda, H., Sawaguchi, A., Mondal, M., Suganuma, T., Matsukura, S., Kangawa, K., Nakazato, M. (2000). Ghrelin a novel growth hormone-releasing acylated peptide is synthesized in a distinct endocrine cell type in the gastrointestinal tracts of rats and humans. Endocrinology., 141, 4255-4261.
- Dlta, C., Jacob, L.Z. (1988). Valproic Acid and the liver review. Clinical Chemistry., 34, 890-897.
- EI Eter, E., Al Tuwaijiri, A., Hagar, H., Arafa, M. (2007). In vivo and in vitro antioxidant activity of ghrelin: attenuation of gastric ischemic injury in the rat. Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology., 22, 1791-1799.
- Golestan Jahromi, M., Nabavizadeh, F., Vahedian, J., Nahrevanian, H., Dehpour, A.R., Mehrjardi, A.Z. (2010). Protective effect of ghrelin on acetaminophen-induced liver injury in rat. Peptides Journal., 31, 2114-2117.
- Ishak, K., Baptista, A., Bianchi, L., Callea, F., Gudat, F., Denk, H., Desmet, V., Korb, B., Macsween, R., Philips, M.J., Portmann, B.G., Poulsen, H., Scheuer, P.J., Schmid, M., Thaler, H. (1995). Histological grading and staging of chronic hepatits. J. hepatology., 22, 696-699.
- Jaeschke, H., Gores, G., Cederbaum, A., Hinnson, J., Pessayre, D., Lemasters, J. (2002). Mechanisms of hepatotoxicity. Toxicological Sciences. 65, 166-176.
- James, L., Mayeux, P., Hinson, J. (2003). Acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity. Drug Metabolism and Disposition., 31, 1499-1506.
- Kojima, M., Hosoda, H., Kangawa, K. (2004). Ghrelin a novel growth-hormone-releasing and appetite-stimulating peptide from stomach. Best Practice & Research Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism., 18, 517-530.
- Konturek, P., Brzozowski, T., Walter, B., Burnat, G., Hess, T., Hahn, E., et al. (2006). Ghrelin-induced gastroprotection against ischemia-reperfusion injury involves an activation of sensory afferent nerves and hyperemia mediated by nitric oxide. European Journal of Pharmacology., 536, 171-181.
- Liston, H.I., Makowitz, J.S., De Vane C.I. (2001). Drug glucuronidation in clinical psychopharmacology. J. Clin Psychopharmacol., 21, 500-515.
- Li, W.G., Gavrila, D., Liu, X., Wang, L., Gunnlaugsson, S., Stoll, L.L., McCormick, M.L., Sigmund, C.D., Tang, C., Weintraub, N.L. (2004). Ghrelin inhibits proinflammatory responses and nuclear factor-kappa B activation in human endothelial cells. Circulation., 109, 2221-2226.
- Martinez, F., Abril, E.R., Earnest, D.L., Watson, R.R. (1992). Ethanol and cytokine secretion. Alcohol., 9, 455-458.
- Moreno, M., Chaves, J., Sancho-Bru, P., Ramalho, F., Ramalho, L., Mansego, M., Ivorra, C., Dominguez, M., Conde, L., Millán, C., Marí, M., Colmenero, J., Lozano, J.J., Jares, P., Vidal, J., Forns, X., Arroyo, V., Caballería, J., Ginès, P., Bataller, R. (2010). Ghrelin attenuates hepatocellular injury and liver fibrogenesis in rodents and influences fibrosis progression in humans. Hepatology., 51, 974-985.
- Nahrevanian, H., Hajihosseini, R., Arjmand, M., Farahmand, M., Ghasemi, F. (2009). Evaluation of anti-leishmanial activity by induction of nitric oxide and inhibition of prostaglandin in Balb/c mice infected with leishmania major. Southeast Asian Journal of Tropical Medicine and Public Health., 40(6), 1188-1198.
- Raoj, S., Bazinet, R.P., Rapoport, S.I., Lee, H.J. (2007). Chronic treatment of rats with sodium valproate downregulates frontal cortex NF-Kappa B DNA binding activity and COX-2 mRNA. Bipolar Disord., 9, 513-20.
- Sibilia, V., Rindi, G., Pagani, F., Rapetti, D., Locatelli, V., Torsello, A., Campanini, N., Deghenghi, R., Netti, C. (2003). Ghrelin protects against ethanol-induced gastric ulcers in rats: studies on the mechanism of action. Endocrinology., 144, 353-359.
- Silva, M.F., Ruiter, J.P., Overmars, H., Bootsma, A.H., Van Gennip, A.H., Jacobs, C., Duran, M., Dealmeida, T.I., Wanders, R.J. (2002). Complete beta oxidation of valproate: cleavage of 3-oxovalproyl-coA by a mitochondrial 3-oxovalproyl-coA thiolase. Biochem J., 15, 755-760.
- Shaat, E.A., Samia, M.A., Madkour, S. (2006). Effect of L-Carntine and deferoxamine on hepatotoxicity, erythrocyte ergothioneine and testicular testosterone synthesis in sodium valproate-treated rats. Bull. Alex. Fac. Med., 42, 123-124.
- Shiiya, T., Nakazato, M., Mizuta, M., Date, Y., Mondal, M., Tanaka, M., Nozoe, S., Hosoda, H., Kangawa, K., Matsukura, S. (2002). Plasma ghrelin levels in lean and obese humans and the effect of glucose on ghrelin secretion. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism., 87, 240-244.
- Slominany, B.L., Slomiany, A. (2009). Involvement of constitutive nitric oxide synthase in ghrelin-induced cytosolic phospholipase A2 activation in gastric mucosal cell protection against ethanol cytotoxicity. Inflammopharmacol., 17, 245-253.
- Tesauro, M., Schinzari, F., Iantomo, M., Rizza, S., Melina, D., Lauro, D., Cardillo, C. (2005). Ghrelin improves endothelial function in patients with metabolic syndrome. Circulation., 112, 2986-2992.
- Tong, V., Teng, X.W., Chang, T.K.H., Abbott, F.S. (2005). Valproic Acid I: Time Course of Lipid Peroxidation Biomarkers, Liver Toxicity, and Valproic Acid Metabolite Levels in Rats. Toxicological Sciences., 86, 427-435.
- Weikel, J., Wichniak, A., Ising, M., Brunner, H., Friess, E., Held, K., Mathias, S., Schmid, D.A., Uhr, M., Steiger, A. (2003). Ghrelin promotes slow-wave sleep in humans. American Journal of Physiology-Endocrinology and Metabolism., 284, 407-415.
- Yada, T., Kaiya, H., Mutoh, K., Azuma, T., Hyodo, S., Kangawa, K. (2006). Ghrelin stimulates phagocytosis and superoxide production in fish leukocytes. Journal of Endocrinology., 189, 57-65.
- Yoshihara, F., Kojima, M., Hosoda, H., Nakazato, M., Kangawa, K. (2002). Ghrelin: a novel peptide for growth hormone release and feeding regulation. Current Opinion in Clinical Nutrition & Metabolic Care., 5, 391-395.


