Protein profile analysis by SDS-page in different elicited edible sprouts
Автор: Thappa Ch., Guleria S., Sharma K.
Журнал: Журнал стресс-физиологии и биохимии @jspb
Статья в выпуске: 3 т.19, 2023 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Sprouts are the low processed food, having the high nutritional value and health promoting components. Various studies reported that the bioactive composition of various sprouts enhanced by elicitation with different elicitors. In the present investigation, the protein profiling by SDS-PAGE of different sprouts (mungbean, chickpea, broccoli and knolkhol) which were elicited with different elicitor viz salicylic acid (SA), methyl salicylate (MeSA) and neem leaf extract (NE) were performed. Results of the study showed that in all the sprouting seeds variety of bands were obsereved ranging from 8.31 to 112 kDa. The significant increase in intensity of protein bands was observed in 1% MeSA and 20 mM SA treatments in mung bean and chickpea sprouts, whereas, in the case of broccoli and knolkhol sprouts, only SA (200 µM) treated sprouts showed increased protein band intensity. This quantitative increase may be due to an increase in the synthesis of some proteins during elicitation. Elicitation can enhance the polyphenolic such as phenolic, flavanoids, vitamins, amino acids and glucosinolates content in sprouts by regulating the expression level of gene which are responsible for the synthesis of various enzymes which are required for the production of secondary metabolites. Moreover, our previous studies also reported that elicitation with different elicitors effectively increases the biological activities of sprouts. Therefore, from this study it may be concluded that the elicitation is an effective approach for the enhancement of nutritional and bioactive composition of seed.
Elicitation, elicitors, sprouts, antioxidant, sds-page
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/143180558
IDR: 143180558
Текст научной статьи Protein profile analysis by SDS-page in different elicited edible sprouts
Due to their high nutritional values and health benefits, sprouts have become more popular among people all over the world. Sprouts are low processed food, the quality and potential bioactivity are mainly determined by seed quality and conditions of germination (Swieca et al ., 2014). It has been widely reported that sprouts provide higher nutritive value than raw seeds and their production is simple and inexpensive. Sprouts have long been used in diet as “health food”. Many studies have shown that the germination of seed increases the biological activity of sprouts due to the accumulation of bioactive components in cereal, pulses, vegetables seeds (Gan et al ., 2017). During germination, sprouts accumulate the large of bioactive compounds by the anabolic and catabolic process. It was also observed that the seed germination, reduces the non-digestible and anti-nutritional factors present in the raw seed (Baenas et al ., 2015). In sprouts, bioactive component level increase which providing the many biological activities like antioxidant, antidiabetic, anti-inflammatory, hyplipidemic and anticarcinogenic activities. As a result, sprouts are beneficial to human health. Based on these evidences, many researches have focused on approaches targeted at enhancing the amount of bioactive components in sprouts (Swieca et al ., 2012).
Germination is one of the most common and effective process for improving the quality of legumes and vegetables (Pajak et al., 2014). There are several reports about the effect of germination methods on the nutraceutical value of legumes including: soybean, mung bean or lentil. Modification of chemical composition and selected bioactivities of plant food by elicitors is cost-effective and socially acceptable. Sprouting of seeds may be regarded as a natural bioreactor or biotechnological module (Gawlik-Dziki et al., 2012). Seed and seedlings treatments for improving plant vigour are being developed and used. Increasingly, commercial seed treatment approaches are developing to view seed treatments as a means to increase substantial value of seed and to improve plant growth and productivity (Andarwulan and Shetty, 1999). Thus, elicitation of sprouts seems to be a promising alternative to other conventional biotechnological techniques used for improving the yield of plant secondary metabolites and the nutraceutical potential of low-processed food. Therefore, the main aim of this research paper to know the impact of elicitation on protein content of different sprouts using SDS-PAGE method.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Collection of plant material
Seeds of chickpea ( Cicer arietinum var. GNG1581), mung bean ( Vigna radiate var. IPM-02-3), broccoli ( Brassica oleracea var. Jammu Broccoli-07) and knolkhol ( Brassica oleracea var. G40) were procured from the Division of Plant Breeding and Genetics and Division of Vegetable Science and Floriculture, FoA, SKUAST-J, Chatha. The seeds were then washed several times with distilled water before soaking in distilled water overnight at 25ºC. The seeds were then kept in petri dishes lined with absorbent paper and germinated under controlled conditions (broccoli and knolkhol a period of 16 hours in dark and 8 hours in light for 5 days, 22-25ºC, 60-75% relative humidity; mungbean 6 days in the dark, 25–27°C, 80–85% relative humidity; chickpea: 12-15 ˚C, 40% relative humidity for 6 days in dark). Each day, seedlings were watered with 5 mL of distilled water.
Elicitors
The elicitors used in the study were salicylic acid (SA), methyl salicylate (MeSA) and neem leaf extract (NE). Different working concentrations of salicylic acid (20 mM and 200 µM) and methyl salicylate (1% and 0.2%.) used in the study for elicitation of sprouts. Neem leaf extract was prepared according to Paul and Sharma (2002). 400 g (fresh weight) of mature leaves were homogenized in a pre-chilled pestle and mortar using chilled, sterilized distilled water. The extract was filtered through four layers of moistened muslin cloth. The final volume was adjusted to 1000 mL with distilled water. The filtrate was then centrifuged at 2000 g, 4 ˚C for 15 min. The supernatant thus obtained was denoted as concentrated neem extract. This extract was then diluted with distilled water to prepare a 1:2 dilution of the concentrated neem extract.
Determination of total protein content and SDS-PAGE profileExtract preparation
For total protein estimation, extraction was carried out in phosphate buffer (pH 7.0). One gram of sprouts were homogenized in 4 mL of pre-chilled phosphate buffer and centrifuged at 12,000 rpm for 20 min at 4˚ C. Supernatant was stored at -20˚and used as enzyme source. Moreover, protein extraction for SDS-PAGE profiling was carried out in pre-chilled Tris-HCl sample buffer (pH 6.6). One gram of sprout sample was homogenized in 4 mL of Tris-Cl buffer in a pre-chilled mortar and pestle. Then the homogenate was centrifuged at 12,000 rpm for 20 min at 4˚ C. Supernatant was stored at -20˚C.
Total protein content
Total protein content of control and optimized elicitor treated spouts was determined according to the method reported by Bradford (1976).
Preparation of Bradford reagent 100 mg of Coomassie Brilliant Blue G-250 was dissolved in 50 mL of methanol to which 100 mL of 85% (v/v) phosphoric acid (H 3 PO 4 ) was added and the final volume was made up to 1 liter with distilled water. The reagent was filtered using Whatman No. 1 filter paper and stored in a dark bottle at 4 °C.
Estimation of protein content: 20 µL of extract was taken and the volume was raised to 1000 µL by adding 980 µL of distilled water. The final reaction mixture was prepared by adding 5 mL of Bradford reagent. After 10 min. incubation at room temperature, the absorbance of the reaction mixture was measured at 595 nm using double beam UV-VIS spectrophotometer. The protein content was determined from the standard curve prepared from BSA (5 to 50 μg):
y = 0.006x – 0.038: R2= 0.999
The results were expressed as milligram BSA equivalents (mg BSAEs) per gram fresh weight.
SDS-PAGE profiling of proteins
Preparation of Reagents
-
> Acrylamide/ bisacrylamide solution: 30% acrylamide solution was prepared
-
> Gel casting buffers: For discontinuous gels, the buffers required were resolving gel and stacking gel: Resolving gel buffer: 1.5 M Tris-HCl (pH 8.8), Stacking gel buffer: 0.5 M Tris-HCl (pH 6.8)
-
> 2X loading buffer: Following constituents were used for the preparation of loading buffer: Bromophenol blue (0.1 mL), 2-Mercaptoethanol (5.0 mL), Glycerol (10 mL), SDS (2.0 g), Tris-HCl stock, pH 6.8 (25 mL). Then the final volume was made upto 100 mL with distilled water and buffer was stored in a tightly sealed bottle at 4˚C.
^ 1X Running buffer: This was prepared using the following reagents:Tris-HCl (25 mM), Glycine (250 mM), SDS: 0.1 % (w/v), 10% Sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS), 10% Ammonium persulfate (APS), TEMED (Tetramethylethylenediamine).
Preparation of Gels
12% separating or resolving gel was prepared by adding the following solutions (total volume 15 mL): Millipore water: (4.9 mL), 30% acrlyamide/bisacrylamide (6 mL), 1.5 M Tris-HCl, pH 8.8 (3.8 mL), 10% SDS: 150 µL, 10% APS (150 µL), TEMED (6 µL). After adding TEMED, solution was mixed well and quickly transferred to the casting chamber between the glass plates and filled upto 0.7 cm below the bottom of the comb. Then, a small layer of isopropanol was added on top of the gel prior to polymerization to straighten the level of the gel and for prevention of air bubble formation in stacking gel. Once the gel was polymerized, stacking gel (5%) was prepared by mixing the following component solutions (total volume 6 mL): Millipore water (4.1 mL), 30% acrylamide/bisacrylamide (1 mL), 1.0 M Tris-HCl stock solution, pH 6.8 (750 µL), SDS (60 µL), APS (60 µL) TEMED (6 µL). The isopropanol layer was then removed by using filter paper and the gel was washed with Millipore water. The stacking gel was then quickly transferred using 1 mL pipette and then the comb was placed. After solidification of the gel, the comb was carefully removed and the wells were washed with Millipore water.
Procedure
The banding patterns of total soluble proteins extracted from sprout samples of different crops were detected by the sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacyrlamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) performed according to Sambrook et al. (1989), on 12% separating gels and 5% stacking gels in vertical Electrophoretic unit. Twenty microliters of each extracted sample were loaded per well. Gels were run at 50 mA for five hours, fixed and stained with methanol, glacial acetic acid, distilled water prepared in the ratio of 4.5: 1: 4.5. Destaining was performed with methanol, acetic acid and distilled water solution prepared in the ratio 2:1:7. Relative molecular weights of the polypeptides were determined by using protein marker (BLUeye Prestained protein Ladder, Sigma).
Statistical analysis
All of the tests were repeated three times. The results were calculated as the average of three independent germination experiments. Data were subjected to one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and significant differences between samples were determined by the least significant differences (LSD) test at p ≤ 0.05 probability level, using R Studio software (version 3.4.1, 2017).
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Total protein was extracted in phosphate buffer (pH 7.0) quantified by the Bradford method. The protein yield was expressed as milligram BSA equivalents (mg BSAEs) per gram as shown in Table 1. Total protein in mung bean was found to be in the range of 7.67 to 27.30 mg BSAEs/g FW. MeSA (1%) treated mung bean sprouts showed the highest soluble protein content (27.30 mg BSAEs/g FW) followed by the SA (20 mM) treatment. Similarly, in chickpea sprouts, the total protein content was in the range of 29.03 to 38.59 mg BSAEs/g FW. Highest protein content was observed in the SA (20 mM) (38.59 mg BSAEs/g FW) treatment, followed by the MeSA (1%). In the case of broccoli and knolkhol total protein content was found to be in the range of 0.31 to 1.13 mg BSAEs/g FW. The highest total protein content was observed in the SA (200 µM) treatment (broccoli: 1.13 mg BSAEs/g FW; knolkhol: 0.54 mg BSAEs/g FW) followed by the MS (0.2 %) treatments.
To elucidate whether elicitation can lead to modifications of the sprout’s protein profile, the SDS gel electrophoresis pattern of mung bean, chickpea, broccoli, and knolkhol sprouts was performed using 5 percent stacking and 12 percent separating gels (Plates 1-4). It was observed that the type and quantity of elicitor solution used had a significant impact on the qualitative electrophoretic profiles of different sprouts, as well as some quantitative changes in the protein band intensity. A variety of bands ranging from 8.31 to 112 kDa were observed in all sprouting seeds. In mung bean sprouts, MeSA (1%) concentration showed greater intensity protein bands. In the case of chickpea, intense bands were seen in almost every elicitor solution applied, with proteins bands ranging from 13.18 to 112 kDa but MeSA (1%) showed a darker 112 kDa band as compared to other treatments. Similarly, elicitation also showed the impact on protein content in broccoli and knolkhol sprouts. In the case of broccoli and knolkhol, less intense bands were seen in almost every elicitor solution applied, with proteins bands ranging from 8.31 to 99 kDa. Overall results of SDS-PAGE protein profiling of control and elicited sprouts in the present study showed that the intensity of protein bands increased in elicited sprouts as compared to control. This quantitative increase may be due to an increase in the synthesis of some proteins during elicitation. However, no qualitative difference was observed in the SDS-PAGE profile of the elicited sprouts as compared to the control. Penas et al. (2015) also found similar results, where some quantitative differences in the protein bands intensity were found but no significant difference was observed in the qualitative electrophoretic profile of lentil sprouts. However, qualitative differences were observed in a similar study by Azooz et al. (2013) where the priming of fava bean seeds with 100 mg/L of ascorbic acid prior to their germination under salt stress resulted in the expression of new protein bands. In a similar finding by Fercha et al. (2014), quantitative differences between the control and the elicited wheat seeds were observed when the seeds germinated under salt stress were elicited with 0.5 mmol/L of ascorbic acid. The results of the previous studies suggest that significant and more pronounced changes in the protein composition and quantity of sprouts could be obtained by the combination of elicitation with additional stress conditions. In the present study, no significant qualitative changes have been observed in the protein composition of elicited sprouts, which may be due to the reason that combination of elicitation with additional stress conditions was not applied and also minor changes in the protein profile cannot be visualized by onedimensional SDS-PAGE. The quantitative changes observed in the present study may be due to the synthesis/hydrolysis of proteins during germination.
Table 1. Total protein content of different sprouts
|
Treatments |
Mung Bean Sprouts |
Chickpea Sprouts |
Broccoli sprouts |
Knolkhol sprouts |
|
Protein content (mg BSAEs/g FW) |
Protein content (mg BSAEs/g FW) |
Protein content (mg BSAEs/g FW) |
Protein content (mg BSAEs/g FW) |
|
|
Control |
7.67±2.73a |
29.03±5.20a |
0.81±0.112a |
0.31±0.01a |
|
NE |
14.0a±2.03a |
38.73±1.73a |
0.84±0.09a |
0.41±0.09a |
|
SA(20 mM) |
17.15±1.31b |
38.59±6.09a |
1.13±0.01b |
0.54±0.08b |
|
MS (1%) |
27.30±2.58b |
37.84±5.7a |
1.08±0.05b |
0.52±0.2b |
The superscript alphabet b shows the values significantly different from control ((p≤0.05) BSAEs: Bovine serum albumin equivalents; FW: fresh weight
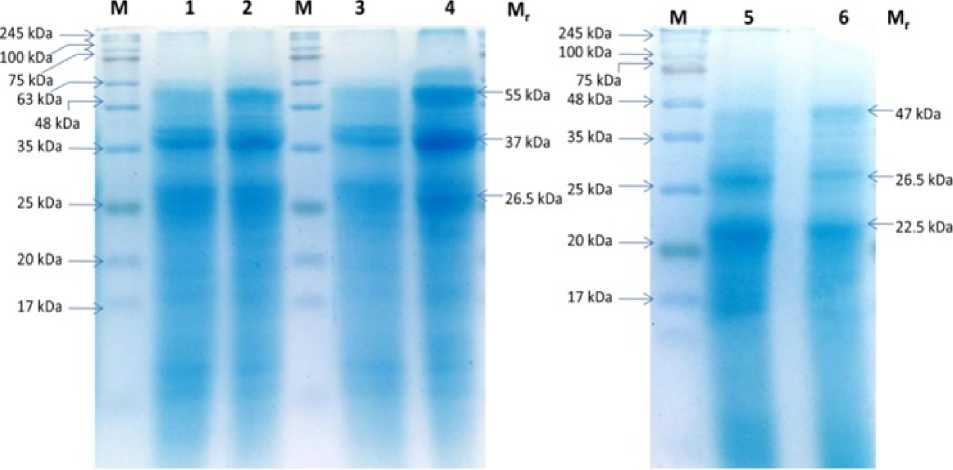
Figure 1. SDS-PAGE profiling of proteins from mung bean sprouts. Lane M , marker; Lane 1, 3,5 represents control; lane 2, sprouts elicited with salicylic acid (20 mM), Lane 4, sprouts elicited with methyl salicylate (1.0%), Lane 6, sprouts elicited with neem leaf extract (NE) and Mr, relative molecular weight.
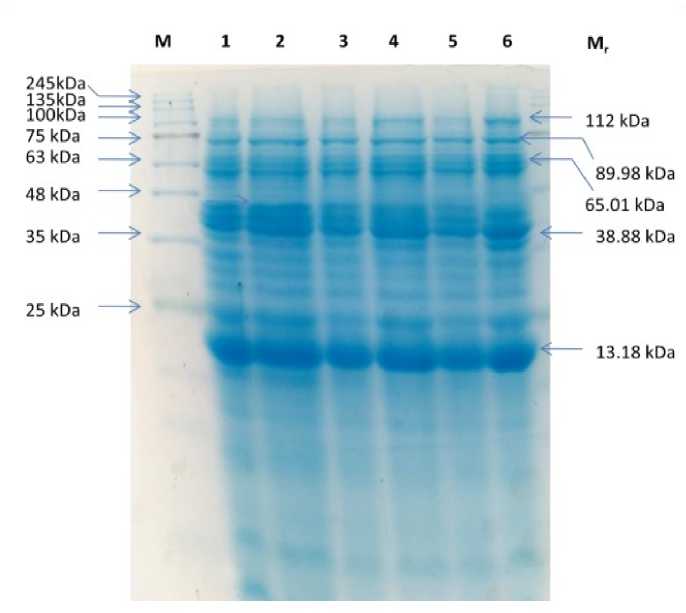
Figure 2. SDS-PAGE profiling of proteins from chickpea sprouts. Lane M , marker; Lane 1, 3,5 represents control; lane 2, sprouts elicited with neem leaf extract (NE), Lane 4, sprouts elicited with salicylic acid (20 mM), Lane 6, sprouts elicited with methyl salicylate (1.0%) and Mr, relative molecular weight.
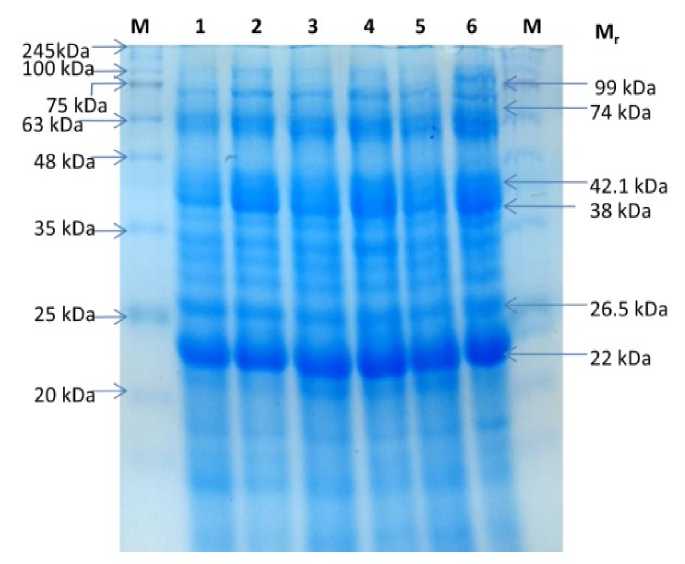
Figure 3. SDS-PAGE profiling of proteins from broccoli sprouts. Lane M , marker; Lane 1, 3,5 represents control; lane 2, sprouts elicited with neem leaf extract (NE), Lane 4, sprouts elicited with methyl salicylate (0.2%), Lane 6, sprouts elicited with salicylic acid (200 µM) and Mr, relative molecular weight.
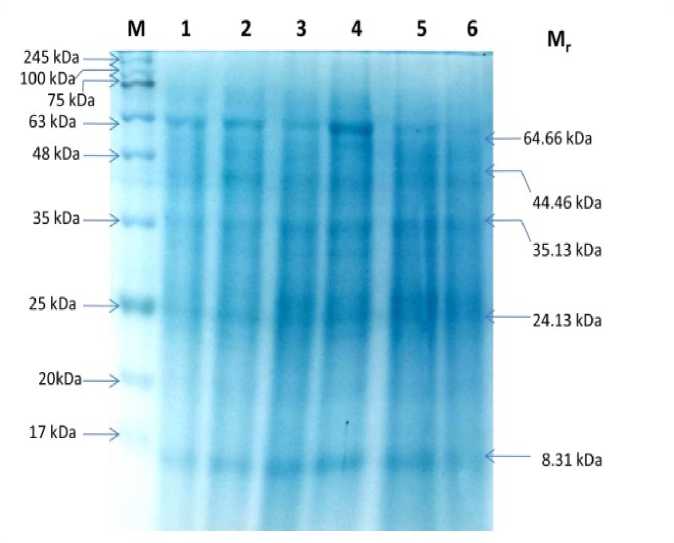
Figure 4. SDS-PAGE profiling of proteins from knolkhol sprouts. Lane M , marker; Lane 1, 3,5 represents control; lane 2, sprouts elicited with methyl salicylate (0.2%), Lane 4, sprouts elicited with salicylic acid (200 µM), Lane 6, sprouts elicited with neem leaf extract (NE) and Mr, relative molecular weight.
CONCLUSION
The present study shows that elicitation influences the protein content of seed during sprouting. The significant increase in intensity of protein bands was observed in 1% MeSA and 20 mM SA treatments in mung bean and chickpea sprouts, whereas, in the case of broccoli and knolkhol sprouts, only SA (200 µM) treated sprouts showed increased protein band intensity. This quantitative increase may be due to an increase in the synthesis of some proteins during elicitation. During sprouting, the hydrolysis and synthesis of proteins occur, which enhance the nutritional activity of the seed. Our previous studies also showed that elicitation with the same elicitor effectively increased the bioactive composition and biological properties of mungbean, chickpea, broccoli and knolkhol sprouts. Elicitation may be a feasible and cost-effective method for increasing the nutritional content of sprouts.
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest
Список литературы Protein profile analysis by SDS-page in different elicited edible sprouts
- Andarwulan, N. and Shetty, K. (1999). Improvement of pea (Pisum sativum) seed vigour response by fish protein hydrolysates in combination with acetyl salicylic acid. Process Biochemistry, 35: 159-165.
- Azooz, M. M., Alzahrani, A. M. and Youssef, M. M. (2013). The potential role of seed priming with ascorbic acid and nicotinamide and their interactions to enhance salt tolerance in broad bean (Vicia faba' L.). Australian Journal of Crop Science, 7: 2091-2100.
- Baenas, N., Ferreres, F., Garcia-Viguera, C. and Moreno, D. A. (2015). Radish sprouts Characterization and elicitation of novel varieties rich in anthocyanins. Food Research International, 69: 305-312.
- Bradford, M. M. (1976). A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Analytical Biochemistry, 72: 248-254.
- Fercha, A., Capriotti, A. L., Caruso, G., Cavaliere, C., Samperi, R., Stampachiacchiere, S. and Lagana, A. (2014). Comparative analysis of metabolic proteome variation in ascorbate-primved and unprimed wheat seeds during germination under salt stress. Journal of Proteomics, 108: 238-257.
- Gan, R.Y., Lui, W.Y., Wu, K., Chan, C.L., Dai, S.H., Sui, Z.Q. and Corke, H. (2017). Bioactive compounds and bioactivities of germinated edible seeds and sprouts: An updated review. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 59, 1-14.
- Gawlik-Dziki, U., Swieca, M. and Sugier, D. (2012). Enhancement of antioxidant abilities and the lipoxygenase and xanthine oxidase inhibitory activity of broccoli sprouts by biotic elicitors. Acta Scientiarum Polonorum - Hortorum Cultus, 11: 1325.
- Pajak, P., Socha, R., Gakowska, D., Roznowski, J. and Fortuna, T. (2014). Phenolic profile and antioxidant activity in selected seeds and sprouts. Food Chemistry, 143: 300-306.
- Paul, P.K. and Sharma, P.D. (2002). Azadirachta indica leaf extract induces resistance in barley against leaf stripe disease. Physiological and Molecular Plant Pathology, 61: 3-13.
- Penas, E., Limon., R. I., Martinez-Villaluenga, C., Restani, P., Pihlanto, A. and Frias, J. (2015). Impact of Elicitation on Antioxidant and Potential Antihypertensive Properties of Lentil Sprouts. Plant Foods for Human Nutrition, 70: 401-7.
- Sambrook, J., Fritsch, E.F. and Maniatis, T. (1989). SDS-Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of proteins. In: Ford N, Nolan C, Ferguson M, editors. Molecular cloning. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press. pp. 18.47-45.
- Swieca, M., Surdyka, M. , Gawlik-Dziki, U. , Ztotek, U. and Baraniak, B. (2014). Antioxidant potential of fresh and stored lentil sprouts affected by elicitation with temperature stresses. International Journal of Food Science and Technology, 49: 1811-1817.
- Swieca, M., Gawlik-Dziki, U., Kowalczyk, D. and Ztotek, U. (2012). Impact of germination time and type of illumination on the antioxidant compounds and antioxidant capacity of Lens culinaris sprouts. Scientia Horticulturae, 140: 87-95.


