Психонейроиммуноэндокринология и иммунный гомеостаз: ось кишечник - головной мозг, ожирение и когнитивные функции
Автор: Булгакова Светлана Викторовна, Романчук Наталья Петровна, Помазанова Оксана Станиславовна
Журнал: Бюллетень науки и практики @bulletennauki
Рубрика: Медицинские науки
Статья в выпуске: 12 т.6, 2020 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Новые компетенции психонейроиммуноэндокринология и психонейроиммунология играют стратегическую роль в междисциплинарной науке и межведомственном планировании и принятии решений. Внедрения многовекторных нейротехнологий искусственного интеллекта и принципов цифрового здравоохранения, будут способствовать развитию современного нейробыта и нейромаркетинга. Наличие инновационных технологий, таких как секвенирование следующего поколения и коррелированные инструменты биоинформатики, позволяют глубже исследовать перекрестные нейросетевые взаимосвязи между микробиотой и иммунными реакциями человека. Иммунный гомеостаз - это баланс между иммунологической толерантностью и воспалительными иммунными реакциями - является ключевой особенностью в исходе здоровья или болезни. Здоровая микробиота - это качественное и количественное соотношение разнообразных микробов отдельных органов и систем, поддерживающее биохимическое, метаболическое и иммунное равновесие макроорганизма, необходимое для сохранения здоровья человека. Функциональные продукты питания, здоровая биомикробиота, здоровый образ жизни и управляемое защитное воздействия окружающей среды, искусственный интеллект и электромагнитная информационная нагрузка/перегрузка - ответственны за работу иммунной системы человека и ее способности своевременного иммунного ответа на пандемические атаки. Ожирение продолжает оставаться одной из основных проблем современного здравоохранения из-за своей высокой распространенности и полиморбидности. Помимо кардиометаболических заболеваний, поражения опорно-двигательной системы, лица с ожирением демонстрируют нарушения когнитивных функций, имеют высокий риск развития депрессии, тревоги. Микробиота кишечника является посредником между воздействием окружающей среды (пища, образ жизни) и физиологией хозяина и ее изменение может частично объяснить перекрестную связь между вышеуказанными патологиями. Известно, что западные модели питания являются основной причиной эпидемии ожирения, которая также способствует дисбиотическому дрейфу микробиоты кишечника, это, в свою очередь, способствует развитию осложнений, связанных с ожирением. Экспериментальные исследования на животных моделях и, в меньшей степени на людях, показывают, что микробиота связана с ожирением и может вносить вклад в эндокринные, нейрохимические изменения и развитие системного воспаления, лежащие в основе самого ожирения и связанных с ним заболеваний. Тем не менее в настоящее время остается ряд вопросов. Моделирование оси микробиота-кишечник-мозг, обеспечивает мозг информацией из кишечника не только через нервную систему, но и через непрерывный поток микробных, эндокринных, метаболических и иммунных сообщений. Коммуникационная сеть дает важные ключи к пониманию того, как ожирение и диабет могут воздействовать на мозг, провоцируя нервно-психические заболевания. Обзор литературы посвящен анализу данных о взаимосвязи оси кишечник-головной мозг, ожирения и когнитивных функций, иммунного гомеостаза и новых компетенций: психонейроиммунологии и психонейроиммуноэндокринологии.
Микробиота, головной мозг, гипоталамо-гипофизарно-надпочечниковая ось, настроение, когнитивные функции, ожирение, иммунный гомеостаз, психонейроиммунология, психонейроиммуноэндокринология
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/14117712
IDR: 14117712 | УДК: 612.017.11 | DOI: 10.33619/2414-2948/61/15
Текст обзорной статьи Психонейроиммуноэндокринология и иммунный гомеостаз: ось кишечник - головной мозг, ожирение и когнитивные функции
Бюллетень науки и практики / Bulletin of Science and Practice
Микроорганизмы, населяющие кишечник млекопитающих (собирательно называемые микробиотой), включают бактерии, вирусы, простейшие, археи и грибы. Причем бактерии составляют большинство. Это чрезвычайно сложная экосистема. В частности, микробиота кишечника взрослого человека, по оценкам, включает более 1000 различных видов бактерий с более чем 7000 штаммов. Коллективный геном микробиоты (называемый микробиомом) превышает размер генома человека и считается виртуальным органом, который участвует в физиологическом функционировании хозяина [1]. Кишечные микробы играют роль в физиологии человека через несколько механизмов, включая их вклад в метаболизм питательных веществ и ксенобиотиков (например, синтез витаминов, переваривание олиго- и полисахаридов, лекарств и т. д.), а также в регуляцию иммунных и нейроэндокринных функций. Некоторые из этих эффектов опосредуются продуктами бактериального метаболизма, такими как короткоцепочечные жирные кислоты (SCFA), включая пропионат, бутират или ацетат, которые влияют на кишечный барьер, воспалительный тонус и метаболический гомеостатический контроль в различных тканях [2].
Большое количество исследований сообщают, что изменения кишечной микробиоты (так называемый дисбиоз) связаны не только с заболеваниями, поражающими кишечник, такими как воспалительное заболевание кишечника (ВЗК), но и с патологией других органов и систем. К ним относятся, помимо прочего, метаболические заболевания (например, диабет 2 типа (СД2) и ожирение), ревматоидный артрит и психические расстройства. В связи с тем, что возникновение заболевания, по-видимому, сопровождается сдвигами нормальной микробиоты человека в сторону дисбиотического состава, который может усугубить болезнь, создавая порочный круг, необходимо знать общие характеристики здоровой микробиоты на уровне популяции, что до сих пор неясно и вызывает дискуссии. Напротив, в физиологических условиях микробиота кишечника сосуществует в симбиозе с хозяином, внося свой вклад в гомеостатический контроль организма через регуляцию иммунной, эндокринной и нервной систем [3–4].
Ожирение — это многофакторное состояние, которое зависит от внутренних индивидуальных факторов, а также от переменных окружающей среды. Однако считается, что резкое увеличение распространенности ожирения за последние 40 лет является следствием изменений образа жизни, таких как гиподинамия и питание с высоким содержанием жиров и углеводов. Кроме того, нездоровые пищевые привычки связаны с изменениями кишечной микробиоты, что также может вносить свой вклад в патофизиологию, лежащую в основе ожирения, и его метаболические и психологические осложнения [5]. В обзоре литературы мы проведем анализ роли микробиоты в регулировании оси кишечник-головной мозг и ее влиянии на настроение и изменения когнитивных функций, связанных с ожирением. Рассмотрим механизмы, с помощью которых микробиота может изменять коммуникацию между кишечником и головным мозгом, уделяя особое внимание воздействию на ось гипоталамус-гипофиз-надпочечники (HPA), иммунную систему и нейротрансмиссию.
Ось кишечник-головной мозг
Ось кишечник- головной мозг представляет собой сложную двунаправленную коммуникационную систему (Рисунок 1) [6], опосредованную гормональными, иммунологическими и нервными сигналами между кишечником и мозгом. Это также путь, посредством которого микробиота кишечника может влиять на процессы развития нервной системы и функции мозга. Нарушение регуляции оси кишечник – головной мозг связано с метаболическими заболеваниями, а также психическими и непсихическими расстройствами. В свою очередь, эти нарушения часто связаны с изменениями в составе или функции кишечной микробиоты, что также может способствовать нарушению молекулярного диалога между кишечником и мозгом [6].
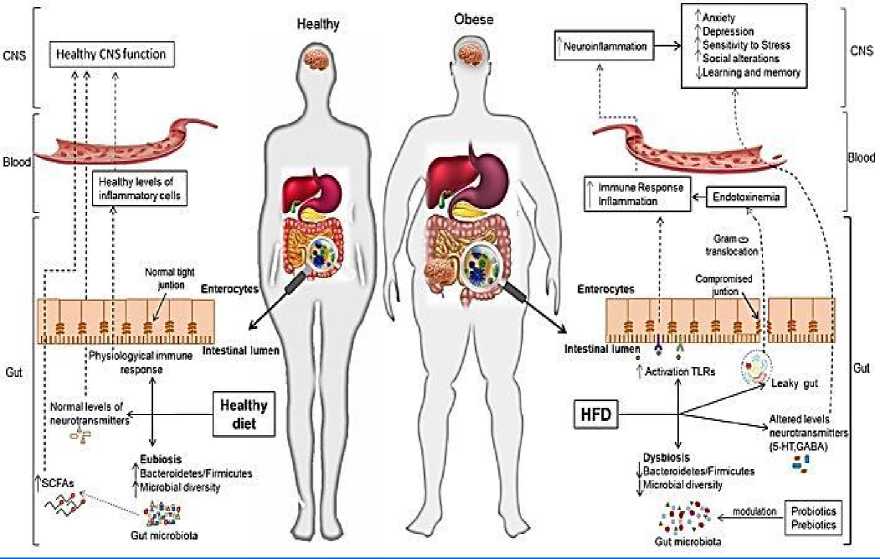
Рисунок 1. Взаимодействие между микробиотой и осью кишечник-мозг при ожирении и связанных с ним психических расстройствах [6].
Микробиота кишечника способствует регулированию оси кишечник-мозг и поддержанию ее функциональности, в то время как ее изменение (дисбиоз) из-за факторов образа жизни (нездоровое питание, стресс) связано с ожирением и его неблагоприятными последствиями для настроения и когнитивных функций. Считается, что здоровый режим питания (например, богатый клетчаткой, овощами и т. д.) увеличивает разнообразие микробиоты кишечника и, таким образом, способствует целостности эпителия кишечника, здоровому иммунному гомеостазу и нормальной функции ЦНС через ось кишечник–мозг.
Напротив, западная диета (богатая простыми сахарами и насыщенными жирами), по-видимому, снижает микробное разнообразие, активирует процессы воспаления и приводит к развитию синдрома повышенной проницаемости кишечника. Это способствует дислокации компонентов грамотрицательных бактерий, что усиливает системное воспаление, вызывает нейровоспаление и изменения в ЦНС. Применение диетических стратегий (например, пробиотиков, более здорового питания, богатого клетчаткой, пребиотиков и т. д.) может благотворно повлиять на ожирение и психические расстройства за счет восстановления здоровой микробиоты и ее регулирующей роли в системе кишечник–мозг [3, 6].
Ось кишечник-мозг образована центральной нервной системой (ЦНС), кишечной иннервацией, которая включает внешние волокна вегетативной нервной системы (ВНС) и внутренние нейроны кишечной нервной системы (КНС), ось HPA и микрофлору кишечника.
Внешняя иннервация желудочно-кишечного тракта соединяет кишечник с мозгом через блуждающие нервы и спинномозговые волокна, в то время как мозг отправляет эфферентные симпатические и парасимпатические волокна в желудочно-кишечный тракт [7]. Ось HPA является частью лимбической системы и главным регулятором стрессовой реакции. Кроме того, ось HPA регулирует различные процессы в организме, включая функцию кишечника во время пищеварения. Кортикотропин-рилизинг-фактор (CRF), высвобождаемый осью HPA, и различные представители его семейства (например, CRF, урокортин 1, урокортин 2 и урокортин 3), как известно, влияют на функцию желудочно-кишечного тракта: перистальтику кишечника, его проницаемость и воспалительные процессы [8].
Другие процессы в организме, регулируемые осью HPA, — это иммунные функции, эмоции и настроение. Это подтверждается различными исследованиями, демонстрирующими тот факт, что активация стрессовой реакции через ось HPA приводит к секреции глюкокортикоидов (ГК), которые, в свою очередь, также модулируют иммунитет [9]. Исследования показывают, что расстройства настроения обычно связаны с нарушением регуляции оси HPA. Стресс также связан с желудочно-кишечными заболеваниями, такими как ВЗК или колит [10].
Существует несколько механизмов, с помощью которых микробиота кишечника может способствовать регулированию коммуникации и функции этой оси, включая способность модулировать иммунные медиаторы (например, цитокины и хемокины) и передачу сигналов блуждающего нерва, а также генерировать или регулировать синтез нейроактивных метаболитов эндокринной системы (например, глюкокортикоиды, нейропептиды и т. д.) или их рецепторы [6]. Например, Bravo J. A. et al. (2011) отметили, что L. rhamnosus JB-1 изменял рецепторы мРНК ГАМК в различных областях мозга связанных со стрессом, тревогой и депрессивным поведением у нормальных здоровых животных. Они определили блуждающий нерв как конститутивный модулятор коммуникационного пути между кишечной микробиотой и мозгом, когда животные, подвергшиеся ваготомии, не могли проявлять нейрохимические и поведенческие эффекты [11]. Desbonnet L. et al. (2008) лечили крыс Sprague-Dawley в течение 14 дней штаммом B. infantis [12]. Введение этой бактерии нативным крысам значительно ослабляло секрецию интерферона (IFN)-γ, фактора некроза опухоли (TNF)-α и интерлейкина (IL)-6 после стимуляции митогеном иммунных клеток цельной крови. Также отмечалось заметное увеличение плазменных концентраций триптофана и кинуреновой кислоты, снижение уровня 5-HIAA во фронтальной коре и показателей DOPAC в миндалевидной коре у крыс, получивших Bifidobacterium , по сравнению с контрольной группой. Эти результаты показывают, что модуляция кишечной микробиоты может вызывать изменения иммунной, нейроэндокринной и моноаминергической активности.
cc ) ® I
Кишечная иннервация
Функциональность желудочно-кишечного тракта (перистальтика кишечника, секреторные функции, кровоток) регулируется комплексным действием как ЦНС, так и КНС. В то время как ЦНС контролирует функции кишечника посредством внешней иннервации ВНС, КНС может действовать автономно и независимо от головного мозга. Внешняя иннервация состоит из блуждающих (тела клеток первого порядка находятся в узловых и яремных ганглиях) и спинномозговых афферентов (тела первого порядка — в грудопоясничных и пояснично-крестцовых ганглиях задних корешков), которые проецируются в центре ствола головного или спинного мозга для передачи сенсорной информации из кишечника в ЦНС. В свою очередь, ЦНС посылает как симпатические имульсы, которые в основном вызывают тормозящее действие на желудочно-кишечный тракт, так и парасимпатические, оказывающие как тормозящее, так и возбуждающие эффекты [13]. Хотя КНС получает окончания внешних эфферентных волокон, она также способна действовать как независимая нервная система. Фактически, она состоит из миллионов нейронов, включая внутренние первичные афферентные нейроны (IPAN), которые являются сенсорными, интернейронами и мотонейронами, содержащимися в миентеральном и подслизистом сплетениях. Эти разные популяции нейронов работают совместно для регуляции гастроинтестинальной инервации [14].
Кишечные нейроны отделены от содержимого просвета кишечника, включая микробиоту, барьером эпителиальных клеток, слизистым слоем, секрецией ионов и жидкости. Тем не менее, на моделях животных показано, что микробиота кишечника взаимодействует с кишечной иннервацией несколькими путями, которые могут включать промежуточные взаимодействия с иммунными и энтероэндокринными клетками (EEC) [13]. Например, EEC продуцируют гормоны кишечника (например, холецистокинин (CCK) или глюкагоноподобный пептид 1 (GLP-1) в ответ на бактериальные стимулы, которые также модулируют активность кишечных нейронов. В свою очередь, синапсы кишечных нейронов на EEC обеспечивают трофическое действие. Таким образом, микробиота может влиять на КНС через свое прямое взаимодействие с EEC. Точно так же КНС улавливает иммунные сигналы, в первую очередь вызванные взаимодействиями кишечной микробиоты и иммунной системы, оценивает микробную молекулярную среду, а затем активирует иммунный ответ, который может изменять микрофлора.
Ряд исследований подтвердили влияние кишечной микробиоты на ось кишечник-мозг и, следовательно, на ЦНС через нейронные пути. Прямые доказательства роли кишечной микробиоты в регуляции нервной системы получены при сравнении животных без микроорганизмов (GF) с животными, колонизированными традиционным способом. Dupont J. R. et al. (1965) продемонстрировали, что архитектура и размер мышечно-кишечного (Ауэрбаха) сплетения отличались у крыс GF [15]. Anitha M. et al. (2012) показали, что в мышечно-кишечном сплетении толстой кишки и в дистальном отделе подвздошной кишки наблюдалось уменьшение количества нитрергических нейронов у 4-недельных мышей GF [16]. Многочисленные исследования, сравнивающие модели GF с обычными животными, также предоставляют доказательства того, что микробиота может влиять на развитие КНС. Кроме того, микробиота кишечника также участвует в поддержании кишечного барьера, поскольку у животных GF наблюдается более медленная регенерация эпителиальных клеток, что также может влиять на транслокацию молекул в кровоток. и процесс передачи сигналов от кишечника к мозгу и его функции [17].
В соответствии с этими результатами, распознавание кишечной микробиоты Toll-Like рецепторами (TLR) необходимо для стимулирования пролиферации эпителиальных клеток и регулирования врожденного иммунитета. TLR также экспрессируются энтеросолюбильными нейронами в желудочно-кишечном тракте и, следовательно, представляют собой сигнальные молекулы, которые могут опосредовать перекрестную связь между микробиотой и КНС [18]. TLR2 и TLR4 играют важную роль в кишечной иннервации и функции тонкого кишечника. Имеются доказательства того, что перераспределение белка плотных соединений zonula occludens-1 (ZO-1) непосредственно усиливается активацией TLR2, указывая тем самым, что TLR2 может усиливать целостность эпителия. TLR2 также участвует в регуляции физиологии желудочно-кишечного тракта и кишечной нейрохимии, поскольку у мышей с нокаутом TLR2 наблюдается уменьшение числа нейронов дистального отдела подвздошной кишки, глиальных клеток и области мышечно-кишечного ганглия, а также структурные аномалии в подслизистом сплетении [19]. Подобные изменения наблюдались у мышей с нокаутом TLR4, показывая уменьшение транзита in vivo в сочетании с важными изменениями в нейрохимии [19–20].
Кроме того, было показано, что TLR2 играет важную роль в серотонинергической системе тонкого кишечника. Так, Latorre E. et al. (2016) обнаружили, что активация TLR2 ингибирует переносчик серотонина (SERT), тем самым увеличивая содержание серотонина (5-HT) в тонком кишечнике [21]. Нарушение регуляции серотонинергической системы было связано с хроническими воспалительными заболеваниями кишечника (ВЗК) или диареей [22]. Кроме того, TLR2 может активироваться пищевыми насыщенными жирными кислотами и индуцированным питанием с высоким смодержанем жиров (HFD), кишечным дисбиозом, что приводит к чрезмерному росту потенциальных патогенов, таких как протеобактерии , продуцирующие липополисахариды (LPS) [23].
Центральная нервная система (ЦНС)
Связь между ЦНС и кишечником опосредуется секрецией нейронами сигнальных молекул, иммунными клетками и энтерохромаффинными клетками (ЭК), сильно влияющими на микробиоту кишечника. ЦНС, состоящая из головного и спинного мозга, отвечает за интеграцию и координацию всей поступающей в организм эндогенной и экзогенной информации. Как объяснялось ранее, существует двунаправленная передача информации от кишечника к ЦНС и от ЦНС к кишечнику через афферентные и эфферентные нервные, эндокринные и иммунологические сигналы между ЦНС и системой ЖКТ. Известно, что эта коммуникация регулирует энергетический баланс с помощью сигналов насыщения [24].
SCFA бутират выступает в качестве основного источника энергии для клеток толстой кишки, усиливает барьерную функцию кишечника и оказывает противовоспалительное действие. Введение бутирата натрия также оказывает антидепрессивный эффект, связанный с повышенной экспрессией нейротрофического фактора мозга (BDNF), который снижается при расстройствах настроения [27]. Таким образом, в различных исследованиях показано, что SCFA, образующиеся в результате метаболической активности микробиоты кишечника, обладают потенциальными полезными эффектами, действуя через ось кишечник-мозг. Желчные кислоты также играют роль в регуляции метаболического пути за счет связывания со специфическими рецепторами, такими как рецептор Фарнезоида X (FXR), участвующий в производстве холестерина, метаболизме глюкозы и синтезе желчных кислот, или TGR5 (рецептор, связанный с G-белком, специфичный для желчных кислот), участвующий в расходе энергии в коричневой жировой ткани, предотвращении ожирения и инсулинорезистентности. Кроме того, микробиота участвует в синтезе желчных кислот и превращает первичную желчную кислоту во вторичные желчные кислоты. Это очевидно у животных GF, у которых разнообразие желчных кислот ниже, чем у контрольных животных [28].
Центральная регуляция периферической иммунной системы
ЦНС регулирует транскрипцию генов периферического иммунного ответа через ось HPA или через симпатическую нервную систему (SNS). Этот механизм позволяет ЦНС модулировать активность внутренних физиологических процессов для оптимальной адаптации к внешним условиям, например, катастрофе в окружающей среде. В этой ситуации ось HPA продуцирует глюкокортикоиды, которые на периферии модифицируют метаболические процессы и подавляют краткосрочный провоспалительный и противовирусный иммунный ответ. SNS использует другой путь, который позволяет ЦНС модулировать врожденную иммунную систему через нервные волокна, выделяющие норадреналин (NA) в первичные и вторичные лимфоидные органы, участвующие в гематопоэзе и взаимодействиях между антигенпрезентирующими клетками и лимфоцитами [29]. Накопленный адреналин может высвобождаться в системный кровоток из надпочечников, стимулируемых нервными волокнами SNS, подавляя опосредованный интерфероном противовирусный ответ I типа и регулируя транскрипцию провоспалительных цитокинов [30].
[31]. Другой пример — секреция триптазы и гистамина (продуктов тучных клеток) в тонкую кишку человека в ответ на стресс, вызванный холодной болью. Другие продукты тучных клеток могут секретироваться в просвет кишечника, включая серотонин и кортикотропин релизинг гормон (CRH) [32].
Иммунная модуляция ЦНС
Хроническая инфекция Helicobacter pylori вызывает у мышей тревожное поведение, вызывает структурные и функциональные изменения в КНС, в режимах питания, увеличивая частоту и уменьшая количество потребляемой пищи. Последние связаны со снижением экспрессии POMC в дугообразном ядре и увеличением TNF-α в медианном возвышении [33]. Инфекция Campylobacter jejuni также вызывает тревожное поведение без увеличения воспалительных маркеров. В последнем случае коммуникация между кишечником и мозгом может быть опосредована активацией восходящих путей блуждающего нерва [34]. Хроническая инфекция Trichuris muris также вызывает тревожное поведение у мышей, снижает экспрессию BDNF в гиппокампе, что сопровождается умеренным повышением TNF-α и IFN-γ, а также кинуренина в плазме. Введение Bifidobacterium longum восстановило поведенческие изменения и BDNF, но не уровни цитокинов и кинуренина, доказывая, что вмешательство в микробиоту кишечника изменяет поведение [33].
Влияние микробиоты кишечника на ЦНС: роль нейромедиаторов
Мозг является основным модулятором гомеостаза кишечника, контролируя его моторику, секрецию кислоты, бикарбонатов и слизи [24]. Влияние кишечной микробиоты на ЦНС и поведение было продемонстрировано в интервенционных исследованиях с пробиотиками или антибиотиками на грызунах и в немногочисленных работах на людях. Например, известно, что некоторые пробиотические штаммы, принадлежащие к родам Bifidobacterium и Lactobacillus , улучшают настроение и уменьшают симптомы тревоги у пациентов с ВЗК и синдромом хронической усталости [35].
Кроме того, дисбактериоз кишечника связан с кишечным и системным воспалением, способствующим расстройствам настроения, таким как депрессия, при воспалительных состояниях, таких как синдром раздраженного кишечника (СРК) [8] и, предположительно, при ожирении. Механизмы, с помощью которых пробиотики могут опосредовать эти эффекты, включают их возможные иммунорегуляторные свойства, описанные выше, и их способность изменять нейротрансмиссию 5-HT (нейромедиатор моноаминов, производный триптофана, поступающий с пищей). Этот нейротрансмиттер хорошо известен своей ролью в познании и настроении. Однако 95% 5-HT продуцируется в кишечнике, в частности ЭК слизистой оболочки и окончаний нейронов КНС. Классические функции, приписываемые 5-HT в желудочно-кишечном тракте, связаны с его участием в моторике, секреции и восприятии боли GI. 5-HT также оказывает нейропротекторное, трофическое и провоспалительное действие в кишечнике [22].
Регулирование настроения и познания зависит от доступности триптофана в ЦНС, которая, в свою очередь, зависит от доступности периферической ее фракции, изменяющейся у мышей GF. Clarke G. et al. (2013) продемонстрировали, что отсутствие кишечной микробиоты у мышей GF в молодом возрасте увеличивало уровень триптофана в плазме, что указывает на возможный гуморальный путь, с помощью которого микробиота может влиять на серотонинергическую нейротрансмиссию в ЦНС [36]. Кроме того, они наблюдали увеличение 5-HT и его основного метаболита, гидроксииндолуксусной кислоты, в гиппокампе по сравнению с нормальными животными. Тем не менее, колонизация животных GF была недостаточной, чтобы обратить вспять нейрохимические последствия для ЦНС у взрослых из-за отсутствия микробиоты в раннем возрасте, даже несмотря на то, что исходные значения доступности триптофана были восстановлены. Nishino R. et al. (2013) также показали, что у мышей GF, подвергшихся воздействию среды SPF в течение 24 часов, развивалась нормальная (SPF) микробиота, что сопровождалось снижением тревожного поведения и увеличением уровней ADE, DA и 5-HT в мозге [37]. Другие авторы показали, что животные GF демонстрируют значительное снижение 5-HT в сыворотке по сравнению с нормальными мышами (без специфических патогенов, SPF) [38]. Yano J. M. et al. (2015) отметили, что спорообразующие бактерии (Sp) из микробиоты мышей и человека способствуют биосинтезу 5-HT ЭК толстой кишки [38]. Эти авторы также показали, что повышенная концентрация в просвете кишечника конкретных микробных метаболитов увеличивает 5-HT в толстой кишке и крови у мышей GF. Взаимодействия хозяина и микробиоты очень важны для регулирования основных биологических процессов, связанных с 5-HT. Agusti et al. (2017) показали, что 5-HT значительно снижается в гиппокампе мышей, получавших HFD, и это коррелирует с ангедонически-депрессивным поведением [5]. Введение B. pseudocatenulatum CECT 7765 ослаблял депрессивно-подобное поведение, связанное с ожирением, и значительно увеличивало концентрацию 5-HT в гиппокампе, изменяя микробиоту кишечника. Использование пробиотиков у животных с депрессией показало эффективность. Например, штамм Bifidobacterium infantis восстановил тест принудительного плавания (FST) и снизил провоспалительные цитокины, регулирующие метаболизм триптофана и нейротрансмиттеров в ЦНС в модели депрессии у крыс, вызванной разлучением с матерью [12].
На уровень ГАМК также может влиять микробиота кишечника. Bravo J. A. и др. (2011), показали, что введение L. rhamnosus JB-1 изменяет рецепторы мРНК ГАМК в различных областях мозга мышей [11]. Экспрессия рецептора GABA b1b была увеличена в кортикальной поясной извилине и прелимбической области, тогда как она снизилась в гиппокампе, миндалине и голубом пятне. В префронтальной коре (PFCx) и миндалевидном теле наблюдалось снижение мРНК GABA Aα2, но увеличение в гиппокампе. Это сопровождалось ослаблением стресса, тревоги и депрессивного поведения у здоровых животных. Результаты того же исследования подтвердили, что связь между микробиотой и мозгом частично происходила через блуждающий нерв, который передавал информацию в ЦНС. Это подтверждено тем фактом, что животные, подвергнутые ваготомии, не показали нейрохимических и поведенческих эффектов.
Таким образом, блуждающий нерв был идентифицирован как конститутивный модулятор коммуникационного пути между кишечной микробиотой и мозгом. Другие авторы также показали, что компоненты микробиоты способны продуцировать молекулы, которые действуют как локальные нейротрансмиттеры в ENS, например, ГАМК, 5-HT, ацетилхолин, мелатонин, гистамин [39].
Ось HPA
Считается, что микробиота кишечника играет роль в механизмах, управляющих стрессовой реакцией через ось HPA, дерегуляция которой также связана с ожирением. Эта связь была впервые доказана у пациентов с синдромом Кушинга, для которых характерен высокий уровень кортизола, глюкозы, гипертония и ожирение верхней части тела [40].
Взаимосвязь между микробиотой кишечника и реакцией на стресс через ось HPA первоначально была обнаружена у животных GF и намеренно колонизированных грызунов. Sudo N. et al. (2004) показали, что реакция на стресс через ось HPA была усилена у животных GF по сравнению с животными SPF и сопровождалась увеличением экспрессии BDNF в коре и гиппокампе [41].
Высокоинтенсивная реакция на стресс была спровоцирована колонизацией кишечника штаммом B. infantis и частично обращена SPF на ранней стадии, но не в более позднем возрасте. Это открытие указывает на то, что воздействие микробов на ранней стадии развития необходимо для того, чтобы система HPA стала полностью восприимчивой к ингибирующей регуляции со стороны нервной системы. O’Mahony S. M. et al. (2009) показали, что стресс в раннем возрасте, вызванный разлучением с матерью, также вызывает изменения в фекальной микробиоте, подтверждая идею о том, что стресс на ранних стадиях развития изменяет микробиоту кишечника. С другой стороны, модификация кишечной микробиоты пробиотиком также может модулировать реакцию на стресс [42]. Например, Ait-Belgnaoui et al. (2012) продемонстрировали, что пероральный прием L. Farciminis подавлял вызванную стрессом повышенную проницаемость кишечника, эндотоксемию и предотвращал стрессовую реакцию оси HPA и нейровоспаление [23].
Как мы указывали выше, стресс является важным фактором ожирения и пищевого поведения, который также может быть взаимосвязан с микробиотой [23]. Многочисленные исследования подтверждают, что ось HPA играет важную роль в возникновении метаболических изменений и развитии ожирения [6, 43]. Существует положительная связь между стрессом, увеличением веса, ожирением и индексом массы тела (ИМТ), базальной глюкозой, базальным инсулином и резистентностью к инсулину [44]. Кроме того, связь между стрессом и метаболической дисфункцией сильнее у людей с более высоким ИМТ [44], что позволяет предположить, что стресс увеличивает риск ожирения, особенно у людей с более высоким ИМТ. Ряд исследований показали, что стероиды надпочечников повышают уровень глюкозы и инсулина, а также увеличивают потребление высококалорийной пищи [6, 44]. Хронически высокие уровни ГК и инсулина способствовали увеличению потребления вкусной пищи и отложению жира в брюшной полости [45]. Следовательно, стресс может вызвать метаболическую дисфункцию и изменить пищевое поведение; кроме того, люди, страдающие ожирением, более чувствительны к стрессу.
Роль микробиоты во взаимосвязи между стрессом и ожирением была продемонстрирована, при введении потенциальных пробиотических бактерий животным моделям с ожирением. Так, Agusti A. et al. (2017) продемонстрировали, что базальные уровни кортикостерона были значительно увеличены у мышей с ожирением, вызванным HFD [5]. У животных с ожирением также наблюдался повышенный уровень кортикостерона в ответ на острый социальный стресс, что позволяет предположить, что мыши с ожирением были более восприимчивы к этим стрессовым ситуациям. Введение B. pseudocatenulatum CECT 7765 снижало уровни кортикостерона у мышей, получавших HDF, указывая на то, что вмешательство, нацеленное на кишечник, способно обратить вспять профиль анксиогенного ожирения [6].
Влияние ожирения на когнитивные функции и настроение
Ожирение может способствовать когнитивным нарушениям и поведенческим изменениям, что отчасти может быть объяснено нейровоспалительными процессами, связанными с избытком веса [46]. Ожирение в детстве и подростковом возрасте может иметь особо важное значение, поскольку это критические периоды для развития нервной системы и пластичности нейронов. В это время возможно изменение функций мозга с последующим нарушением поведения и настроения во взрослом возрасте [47].
На разнообразие и стабильность микробиоты кишечника может влиять диета с высоким содержанием жиров (HFD) или высоким содержанием углеводов, что приводит к дисбактериозу, который является типичным изменением, наблюдаемым при ожирении. Считается, что дисбиотическая микробиота изменяет связь между кишечником и головным мозгом, способствуя возникновению тревоги, депрессии, меняет чувствительность к стрессу, социальное поведение, нарушению памяти и снижению внимания или исполнительной функции. Использование некоторых пробиотиков продемонстрировало снижению тревоги и депрессии (Рисунок 2) [6, 47].
Ожирение, микробиота и питание могут влиять на эпизодическую и семантическую память [48]. Память позволяет нам хранить информацию. Мы можем запоминать автобиографическую и эпизодическую информацию, исторические даты, различные типы языка. Ученые продемонстрировали влияние HFD или питания с высоким содержанием сахара на память. Например, перекармливание в неонатальном периоде может привести к повреждению гиппокампа (основная структура, участвующая в процессах памяти), вызывая микроглиоз этой области всего через 14 дней перекармливания, который может сохраняться во взрослой жизни [49]. У подростков были описаны нарушения памяти после 4 недель HFD [50]. Введение сахарозы крысам в период полового созревания и подросткового возраста может вызвать дефицит распознавания [10].
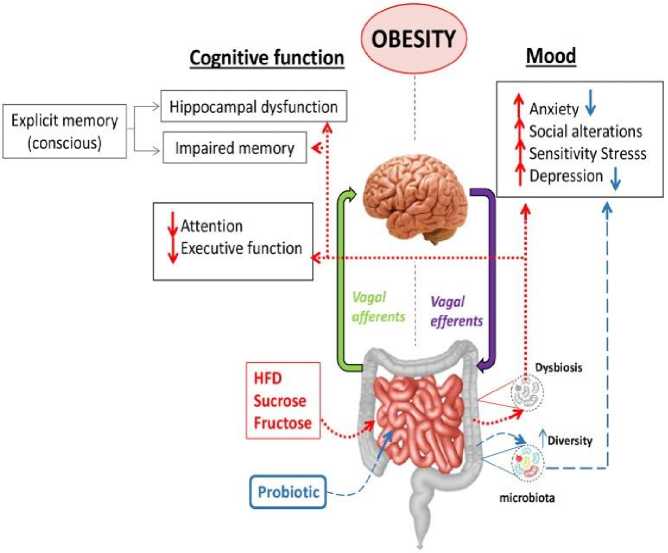
Рисунок 2. Настроение и когнитивные изменения при ожирении: роль оси кишечник-мозг [6, 47].
Однако, Heyward F. D. et al. (2012) обнаружили, что мыши, получавшие HFD в течение 23 недель, демонстрировали не отличающееся от контроля распознавание новых объектов, но, в тоже время, когнитивные нарушения в задаче запоминания местоположения объектов (OLM) [51]. Также Krishna S. et al. (2015) показали, что память у самок мышей при распознавании новых объектов не пострадала после употребления HFD пищи [52]. Underwood E. L. et al. (2016) обнаружили, что оба пола мышей, получавшие HFD в течение 12
cc) ® I недель, в равной степени испытывали сложность в решении когнитивных задач [53].
На животных моделях проведен ряд исследований о влиянии диеты, богатой насыщенными жирами, на пространственное обучение и память. Так, Collison K. S. et al. (2010) кормили взрослых мышей рационом, обогащенным трансжирными кислотами (TFA), глутаматом натрия (MSG) или их комбинацией (TFA + MSG). TFA + MSG вызвали снижение пространственного познания [54]. Подобные результаты были получены Guimarães E. D.et al. (2017) с использованием нового теста памяти на распознавание объектов у взрослых крыс, которым подкожно вводили глутамат натрия в течение первых 5 дней жизни для стимуляции развития ожирения [55]. У животных-подростков также доказана взаимосвязь между HFD и пространственным когнитивным дефицитом [56]. Интересно, что этот тип диеты не влияет на пространственные способности во взрослом возрасте, и этот когнитивный дефицит можно исправить с помощью упражнений [57]. У взрослых животных ограничение калорийности пищи (CR) защищает ЦНС. Пространственная память была значительно увеличена в группе CR и существенно уменьшилась в группе с высококалорийным питанием (HC), демонстрируя, что длительное потребление высоких калорий вызывает аутофагию в гиппокампе, что может увеличить риск когнитивных нарушений [58]. В тоже время, Mielke J. G. et al. (2006) обнаружили отсутствие влияния HFD на пространственную память [59].
Остается открытым вопрос: когнитивные нарушения предшествуют ожирению или являются следствием ожирения? Чтобы проверить эту гипотезу, крысам в возрасте от 4 до 20 недель, предрасположенным к ожирению (1 группа) и резистентным к ожирению (2 группа), давали стандартную пищу. В возрасте 12 недель крысы 1 группы показали значительное ухудшение памяти по сравнению со 2 группой. Также были исследованы изменения бессознательной памяти, связанные с ожирением. Бессознательная память относится к непреднамеренным действиям, хранящимся в нашем мозге. У грызунов дополнительное количество холестерина в рационе (0,5% от сухой массы) значительно улучшило краткосрочную и долгосрочную память [20]. Однако добавление фруктозы, в том числе в сочетании с HFD, значительно ухудшало оба вида памяти у мышей. Кроме того, эффекты HFD на формирование страха могут различаться у самок и самцов мышей. Hwang L. L. et al. (2010) продемонстрировали, что HFD вызывает больше когнитивных нарушений у самцов мышей, чем у самок [60].
Исследования на животных выявили взаимосвязь между ожирением, нейровоспалением и нарушениями памяти. Например, Wang S. et al. (2016) использовали противовоспалительное средство, чтобы показать, что хроническое лечение реином (основной ингредиент растения ревеня с противовоспалительными свойствами) предотвращает вызванное HFD ухудшение распознавания [61]. У крыс, подвергшихся воздействию ревеня, также наблюдалось повышенное бактериальное разнообразие в подвздошной кишке, что также могло способствовать или отражать положительные эффекты лечения [6]. Wang S. et al. (2017) продемонстрировали, что сапонин, активный компонент чая с противовоспалительным действием, ограничивает неблагоприятные изменения микробиоты кишечника, снижает массу тела, улучшает толерантность к глюкозе и предотвращает ухудшение процессы распознавания у мышей, получавших HFD; он также снизил нейровоспаление, глиоз и дефицит BDNF в гиппокампе [56].
Ряд исследователей показали, что у людей ожирение связано со снижением когнитивных функций и повышенным риском нейродегенеративных заболеваний во время старения [6, 62]. Gunstad J. et al. (2007) продемонстрировали, что взрослые с ИМТ более 25кг/м2 в возрасте от 22 до 82 лет имеют более низкие результаты теста управляющих функций, чем взрослые с нормальным весом (ИМТ 18,5–24,9 кг/м2), и некоторые различия. в тесте на внимание, что предполагает связь между повышенным ИМТ и сниженными когнитивными функциями независимо от возраста [63]. Ряд исследований с участием детей с ожирением обнаружили у них изменения во внимании и переключении внимания, а также в зрительно-пространственных способностях по сравнению с детьми с нормальным весом [6, 64].
Кроме того, потребление жиров и сахара в разные периоды жизни также может ухудшать познавательные способности. Например, Francis H. M. и Stevenson R. J. (2011) показали, что у здоровых студентов бакалавриата с высоким (по их самоотчетам) потреблением жира и рафинированного сахара возникают проблемы с памятью, связанные с функцией гиппокампа [7]. Точно так же Beilharz et al. (2015) обнаружили, что гиппокампальная память чувствительна к высокоэнергетической диете [65]. Cournot M. et al. (2006) показали, что более высокий индекс массы тела был связан с более низкими показателями когнитивных функций у здоровых лиц средних лет, не страдающих деменцией [66]. Другое исследование австралийской когорты детей школьного возраста обнаружило, что более высокое потребление западной диеты в возрасте 14 лет было связано с ухудшением когнитивных функций через 3 года [67]. Crichton G. E. et al. (2012) показали, что ежедневное употребление нежирной пищи может улучшить когнитивные способности [68].
Доказана связь НЖК с когнитивными нарушениями. Потребление НЖК в молодом, среднем и более старшем возрасте увеличивает уязвимость к когнитивным нарушениям и даже неврологическим заболеваниям. Точно так же более высокое потребление углеводов, особенно простых сахаров, было связано с нарушением когнитивных функций [69]. Повышенное потребление полиненасыщенных жирных кислот (ПНЖК) и более высокое соотношение ПНЖК и НЖК были связаны с улучшением функций памяти (также у детей) и снижением риска нарушений памяти [6].
Есть также ряд исследований, говорящих о благотворном влиянии пробиотиков на когнитивные функции человека. Например, коктейль из различных пробиотиков ( Bifidobacterium bifidum W23, Bifidobacterium lactis W52, Lactobacillus acidophilus W37, Lactobacillus brevis W63, Lactobacillus casei W56, Lactobacillus salivarius W24 и Lactobacillus salivarius ) улучшил когнитивное состояние у людей с нормальным настроением [70]. Исследование здоровых женщин, получавших ферментированное молоко с пробиотиками, показало, что пробиотики способны модулировать активность мозга (измеренную с помощью фМРТ) в областях мозга, участвующих в опосредовании когнитивных функций [71].
Беспокойство и депрессия при ожирении
Тревога и депрессия — самые распространенные психические расстройства в развитых странах [72]. Они часто возникают в результате неправильной адаптации к стрессу. Кроме того, в исследованиях на животных и людях доказана двунаправленная связь этих состояний с ожирением и связанными с ним метаболическими нарушениями (например, диабетом 2 типа, сердечно-сосудистыми заболеваниями).
В исследованиях на животных изучалось влияние стресса и западных диет, ведущих к ожирению, на настроение, а также их возможный механизм. Santos R. O. et al. (2016) продемонстрировали, что диета с высоким содержанием углеводов, применяемая в течение 12 недель, была анксиогенной и вызывала депрессивные симптомы после воздействия стресса [73]. Хронический стресс также может увеличить потребление пищи, содержащей сахар и жир, в качестве компенсирующего механизма (комфортная пища) для уменьшения тревожности, связанной со стрессом, что может привести к перееданию и ожирению в долгосрочной перспективе [74]. В поддержку этой гипотезы другие исследования показали, что введение HFD взрослым крысам снижает тревожность [75]. Недавнее исследование также показывает, что сочетание ожирения (вызванного диетой) с хроническим легким стрессом (например, 8-часовое голодание или лишение воды, путаница дня и ночи) вызывает депрессию и тревожное поведение, а также подавляет передачу сигналов лептина/LepRb [76]. Это предлагается как возможный механизм, опосредующий негативные последствия ожирения и стресса для настроения [76]. В связи с этим Haque Z. et al. (2013) также указывают на то, что лептин важен для регуляции настроения и эмоций. Они наблюдали, что животные, подвергшиеся стрессу (иммобилизация в течение 2 часов), демонстрировали поведенческие дефициты, но они были устранены экзогенным лептином [77]. Finger B.C. et al. (2010) показали, что мыши с дефицитом лептина (ob/ob) проявляют более высокий уровень беспокойства [78].
Связь между ожирением и поведенческими нарушениями дополнительно подтверждается тем, что некоторые методы лечения ожирения обладают анксиолитическим действием. Так, некоторые препараты (сибутрамин, дулоксетин, пиоглитазон, ондансетрон, 3-метокси-Np-толилхиноксалин-2-карбоксамид (QCM-4), агонист GPR120), применяемые для лечения ожирения, ослабляли поведенческие изменения у мышей [6]. Эти результаты показывают, что ожирение и эмоциональные расстройства, такие как тревога и депрессия, могут иметь общую основу, в частности, микробиоту, играющую роль в регуляции системного воспаления. В поддержку этого мнения некоторые штаммы пробиотиков с антидепрессивными эффектами также показали эффекты снижения веса, предполагая, что модуляция состава микробиоты или их функции может быть полезной при депрессии, связанной с ожирением [79]. Так, Ohland C. L. et al. (2013) показали, что введение штамма Lactobacillus helveticus восстановило соотношение Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes у мышей, получавших HFD со снижением тревожного поведения [80]. Abildgaard A. et al. (2017) показали, что смесь восьми различных штаммов Bifidobacterium и Lactobacillus снижает депрессивно-подобное поведение у мышей, получавших HFD, в сочетании с пониженными уровнями IL-6 и TNF-α в сыворотке [81]. Следовательно, положительные эффекты некоторых из этих штаммов бактерий могут быть частично опосредованы их способностью снижать системное воспаление, влияющее как на ожирение, так и на расстройства настроения.
Эпидемиологические и клинические исследования на людях также подтверждают двунаправленную связь между ожирением, режимами питания и расстройствами настроения (Рисунок 2). Систематические обзоры и метаанализ продольных исследований показывают, что ожирение увеличивает риск возникновения депрессии на 55% [82], а депрессия увеличивает риск возникновения ожирения на 58% [83]. Ряд интервенционных исследований показывают, что улучшение качества питания (средиземноморская диета) привело к снижению симптомов депрессии у взрослых [84], дополнительно подтверждая роль диеты при депрессии. Кроме того, депрессия была связана с изменениями в микробиоте кишечника [85].
Глобальная распространенность диабета растет, и клиническое, социальное и экономическое бремя, связанное с этой эпидемией, усугубляется значительным сочетанием диабета с нервно-психическими заболеваниями, особенно депрессией. Важно отметить, что не только распространенность расстройств настроения повышена у пациентов с сахарным диабетом 2 типа, депрессивные пациенты также более склонны к развитию диабета. Эта взаимная связь требует молекулярного и системного анализа взаимодействий диабет-мозг для руководства профилактическими и терапевтическими стратегиями [86]. Моделирование оси микробиота-кишечник-мозг, обеспечивает мозг информацией из кишечника не только через нервную систему, но и через непрерывный поток микробных, эндокринных, метаболических и иммунных сообщений. Коммуникационная сеть дает важные ключи к пониманию того, как ожирение и диабет могут воздействовать на мозг, провоцируя нервно-психические заболевания. Кишечная микробиота управляет множеством функций организма, тесно связанных с иммунной, метаболической и нервной системами, а дисбактериоз кишечника нарушает гомеостаз между этими системами [86].
У пациентов с тяжелыми психическими расстройствами, включая тяжелую депрессию, биполярное расстройство и шизофрению, наблюдаются различные изменения микробиоты кишечника и повышенная проницаемость кишечника, нарушение регуляции НРА и субклиническое воспаление [87]. Дисрегуляция оси НРА возникает как следствие психосоциального стресса, особенно травматических жизненных событий [87].
Заключение
Установленные связи, между ожирением и когнитивными нарушениями в эпидемиологических и экспериментальных исследованиях, указывают на общие факторы риска и патофизиологические механизмы и могут быть связаны с изменениями кишечной микробиоты, вызванными питанием, которые, в свою очередь, могут способствовать нейровоспалению и дисрегуляции нейроэндокринной системы, связанной с ожирением, сопутствующими психическими нарушениями. Эта гипотеза была подтверждена на экспериментальных моделях, которые исследовали эффективность ряда пробиотиков или веществ, изменяющих микробиоту кишечника, как в уменьшении ожирения, так и в снижении связанных с ним психических расстройств. Эти исследования, однако, не помогают нам понять, играют ли вмешательства, влияющие на экосистему кишечника, основную или второстепенную роль в снижении психических нарушений, связанных с ожирением. Фекальные трансплантаты, однако, предоставили более прямые доказательства роли дисбиотической микробиоты в нейроповеденческих изменениях, поскольку колонизация худых мышей микробиотой мышей с ожирением, вызванной HFD, привела к неврологическим осложнениям ожирения.
До сих пор не хватает полного понимания механизмов, с помощью которых микробиота может влиять на ось кишечник-мозг и, следовательно, на функцию головного мозга, исследования пролили свет на множество факторов, в том числе на регуляцию кишечного барьера, воспаление и передачу сигналов через TLR, которые распознают бактериальные стимулы и опосредуют связь с КНС, регуляцию энтероэндокринной секреции и стрессовую реакцию HPA, и производство и регулирование уровней нейромедиаторов хозяина и их рецепторов. Однако необходимы дальнейшие исследования для прогресса в идентификации молекулярных мишеней/путей, которые могут быть благоприятно модулированы вмешательствами на основе микробиоты, чтобы помочь уменьшить осложнения, связанные с ожирением.
Новые компетенции психонейроиммуноэндокринология и психонейроиммунология играют стратегическую роль в междисциплинарной науке и межведомственном планировании и принятии решений. Внедрение многовекторных нейротехнологий искусственного интеллекта и принципов цифрового здравоохранения, будут способствовать развитию современного нейробыта и нейромаркетинга.
В исследовании Д. В. Романова, Н. П. Романчук (2014), «Ранняя диагностика когнитивных нарушений» решена одна из актуальных задач современной медицины - раннее распознавание когнитивных нарушений. Рассматриваются подходы к диагностике, обсуждаются вопросы патогенеза и систематики когнитивных нарушений, психометрические и патопсихологические методики оценки когнитивных расстройств, подходы к комплексному психофармакологическому лечению и профилактике когнитивных расстройств. Результаты ориентируют врача на использование мультидисциплинарного подхода к пониманию проблемы нейродегенераций и формированию научно-обоснованных алгоритмов ведения таких пациентов [88].
Функциональные продукты питания с помощью биомаркеров и технологий искусственного интеллекта являются целевой питательной средой как для организма в целом, так и для биомикробиоты в частности [89]. Микробиологическая память будет оставаться стабильной, когда рацион функционального (здорового) диетического питания и здоровая биомикробиота остаются почти неизменными [89]. Персонализированные функциональные диеты на основе алгоритмов искусственного интеллекта улучшают гликемические реакции на диетические продукты. Другие персонализированные терапевтические применения диетической-иммунно-метаболической оси включают функциональные пробиотические добавки и/или функциональное диетическое планирование, основанное на профилях микробиома. Микробиота представляет собой ключевой элемент, потенциально способный влиять на функции антигена вызывать защитный иммунный ответ и на способность иммунной системы адекватно реагировать на антигенную стимуляцию (эффективность вакцины), действуя в качестве иммунологического модулятора, а также природного адъюванта вакцины. Иммунная система человека и микробиота совместно эволюционируют, и их сбалансированное системное взаимодействие происходит в течение всей жизни. Эта тесная ассоциация и общий состав, и богатство микробиоты играют важную роль в модуляции иммунитета хозяина и могут влиять на иммунный ответ при вакцинации [89].
Иммунный гомеостаз — это баланс между иммунологической толерантностью и воспалительными иммунными реакциями — является ключевой особенностью в исходе здоровья или болезни. Здоровая микробиота — это качественное и количественное соотношение разнообразных микробов отдельных органов и систем, поддерживающее биохимическое, метаболическое и иммунное равновесие макроорганизма, необходимое для сохранения здоровья человека [90]. Механизмы, с помощью которых микробиота может изменять коммуникацию между кишечником и головным мозгом, являются главными из-за воздействия на ось HPA, иммунную систему и нейротрансмиссию. Наличие инновационных технологий, таких как секвенирование следующего поколения и коррелированные инструменты биоинформатики, позволяют глубже исследовать перекрестные нейросетевые взаимосвязи между микробиотой и иммунными реакциями человека.
Функциональные продукты питания, здоровая биомикробиота, здоровый образ жизни и управляемое защитное воздействия окружающей среды, искусственный интеллект и электромагнитная информационная нагрузка/перегрузка — ответственны за работу иммунной системы человека и ее способности своевременного иммунного ответа на пандемические атаки [90].
Список литературы Психонейроиммуноэндокринология и иммунный гомеостаз: ось кишечник - головной мозг, ожирение и когнитивные функции
- Wang Y., Kasper L. H. The role of microbiome in central nervous system disorders // Brain, behavior, and immunity. 2014. V. 38. P. 1-12. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbi.2013.12.015
- Topping D. L., Clifton P. M. Short-chain fatty acids and human colonic function: roles of resistant starch and nonstarch polysaccharides // Physiological reviews. 2001. DOI: 10.1152/physrev.2001.81.3.1031
- Тренева Е. В., Булгакова С. В., Романчук П. И., Захарова Н. О., Сиротко И. И. Мозг и микробиота: нейроэндокринные и гериатрические аспекты // Бюллетень науки и практики. 2019. Т. 5. №9. С. 26-52. DOI: 10.33619/2414-2948/46/03
- Романчук Н. П., Пятин В. Ф., Волобуев А. Н., Булгакова С. В., Тренева Е. В., Романов Д. В. Мозг, депрессия, эпигенетика: новые данные // Бюллетень науки и практики. 2020. Т. 6. №5. С. 163-183. DOI: 10.33619/2414-2948/54/21
- Agusti A., Moya-Perez A., Campillo I., Montserrat-De La Paz S., Cerrudo V., Perez-Villalba A., Sanz Y. Bifidobacterium pseudocatenulatum CECT 7765 ameliorates neuroendocrine alterations associated with an exaggerated stress response and anhedonia in obese mice // Molecular neurobiology. 2018. V. 55. №6. P. 5337-5352. DOI: 10.1007/s12035-017-0768-z
- Agustí A., García-Pardo M. P., López-Almela I., Campillo I., Maes M., Romaní-Pérez M., Sanz Y. Interplay between the gut-brain axis, obesity and cognitive function // Frontiers in neuroscience. 2018. V. 12. P. 155.
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2018.00155
- Francis H. M., Stevenson R. J. Higher reported saturated fat and refined sugar intake is associated with reduced hippocampal-dependent memory and sensitivity to interoceptive signals // Behavioral neuroscience. 2011. V. 125. №6. P. 943.
- DOI: 10.1037/a0025998
- Dai C., Zheng C. Q., Jiang M., Ma X. Y., Jiang L. J. Probiotics and irritable bowel syndrome // World Journal of Gastroenterology: WJG. 2013. V. 19. №36. P. 5973.
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i36.5973
- Zheng G., Wu S. P., Hu Y., Smith D. E., Wiley J. W., Hong S. Corticosterone mediates stress-related increased intestinal permeability in a region-specific manner // Neurogastroenterology & Motility. 2013. V. 25. №2. P. e127-e139.
- DOI: 10.1111/nmo.12066
- Reichelt A. C., Killcross S., Hambly L. D., Morris M. J., Westbrook R. F. Impact of adolescent sucrose access on cognitive control, recognition memory, and parvalbumin immunoreactivity // Learning & memory. 2015. V. 22. №4. P. 215-224.
- DOI: 10.1101/lm.038000.114
- Bravo J. A., Forsythe P., Chew M. V., Escaravage E., Savignac H. M., Dinan T. G.,.. Cryan J. F. Ingestion of Lactobacillus strain regulates emotional behavior and central GABA receptor expression in a mouse via the vagus nerve // Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 2011. V. 108. №38. P. 16050-16055.
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1102999108
- Desbonnet L., Garrett L., Clarke G., Bienenstock J., Dinan T. G. The probiotic Bifidobacteria infantis: an assessment of potential antidepressant properties in the rat // Journal of psychiatric research. 2008. V. 43. №2. P. 164-174.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2008.03.009
- Browning K. N., Travagli R. A. Central nervous system control of gastrointestinal motility and secretion and modulation of gastrointestinal functions // Comprehensive physiology. 2011. V. 4. №4. P. 1339-1368.
- DOI: 10.1002/cphy.c130055
- Furness J. B., Callaghan B. P., Rivera L. R., Cho H. J. The enteric nervous system and gastrointestinal innervation: integrated local and central control // Microbial endocrinology: The microbiota-gut-brain axis in health and disease. Springer, New York, NY, 2014. P. 39-71.
- DOI: 10.1007/978-1-4939-0897-4_3
- Dupont J. R., Jervis H. R., Sprinz H. Auerbach's plexus of the rat cecum in relation to the germfree state // Journal of Comparative Neurology. 1965. V. 125. №1. P. 11-18.
- DOI: 10.1002/cne.901250103
- Anitha M., Vijay-Kumar M., Sitaraman S. V., Gewirtz A. T., Srinivasan S. Gut microbial products regulate murine gastrointestinal motility via Toll-like receptor 4 signaling // Gastroenterology. 2012. V. 143. №4. P. 1006-1016. e4.
- DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2012.06.034
- Hyland N. P., Cryan J. F. Microbe-host interactions: Influence of the gut microbiota on the enteric nervous system // Developmental Biology. 2016. V. 417. №2. P. 182-187.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2016.06.027
- Koppel N., Balskus E. P. Exploring and understanding the biochemical diversity of the human microbiota // Cell chemical biology. 2016. V. 23. №1. P. 18-30.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2015.12.008
- Brun, P., Giron, M. C., Qesari, M., Porzionato, A., Caputi, V., Zoppellaro, C.,.. & Pizzuti, D. Toll-like receptor 2 regulates intestinal inflammation by controlling integrity of the enteric nervous system // Gastroenterology. 2013. V. 145. №6. P. 1323-1333.
- Apryatin S. A., Sidorova Y. S., Shipelin V. A., Balakina A., Trusov N. V., Mazo V. K. Neuromotor activity, anxiety and cognitive function in the in vivo model of alimentary hyperlipidemia and obesity // Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine. 2017. V. 163. №1. P. 37-41.
- DOI: 10.1007/s10517-017-3732-z
- Latorre E., Layunta E., Grasa L., Castro M., Pardo J., Gomollón F.,.. Mesonero J. E. Intestinal serotonin transporter inhibition by toll-like receptor 2 activation. A feedback modulation // PLoS One. 2016. V. 11. №12. P. e0169303.
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0169303
- Mawe G. M., Hoffman J. M. Serotonin signaling in the gastrointestinal tract // Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013. V. 10. P. 473-486.
- DOI: 10.1038/nrgastro.2013.105
- Ait-Belgnaoui A., Durand H., Cartier C., Chaumaz G., Eutamene H., Ferrier L.,.. Theodorou V. Prevention of gut leakiness by a probiotic treatment leads to attenuated HPA response to an acute psychological stress in rats // Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2012. V. 37. №11. P. 1885-1895.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2012.03.024
- Carabotti M., Scirocco A., Maselli M. A., Severi C The gut-brain axis: interactions between enteric microbiota, central and enteric nervous systems // Annals of gastroenterology: quarterly publication of the Hellenic Society of Gastroenterology. 2015. V. 28. №2. P. 203. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25830558
- Müller T. D., Nogueiras R., Andermann M. L., Andrews Z. B., Anker S. D., Argente J., Batterham R. L., Benoit S. C., Bowers C. Y., Broglio F., Casanueva F. F., D'Alessio D., Depoortere I., Geliebter A., … Tschöp M.H. Ghrelin // Molecular Metabolism V. 4. №6. P. 437-460
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molmet.2015.03.005
- Valentino M. A., Lin J. E., Snook A. E., Li P., Kim G. W., Marszalowicz G.,.. Waldman S. A.A uroguanylin-GUCY2C endocrine axis regulates feeding in mice // The Journal of clinical investigation. 2011. V. 121. №9.
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI57925
- Wei Y. B., Melas P. A., Wegener G., Mathé A. A., Lavebratt C. Antidepressant-like effect of sodium butyrate is associated with an increase in TET1 and in 5-hydroxymethylation levels in the Bdnf gene // International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology. 2015. V. 18. №2.
- DOI: 10.1093/ijnp/pyu032
- Tomkin G. H., Owens D. Obesity diabetes and the role of bile acids in metabolism // Journal of Translational Internal Medicine. 2016. V. 4. №2. P. 73-80.
- DOI: 10.1515/jtim-2016-0018
- Nance D. M., Sanders V. M. Autonomic innervation and regulation of the immune system (1987-2007) // Brain, behavior, and immunity. 2007. V. 21. №6. P. 736-745.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbi.2007.03.008
- Cole S. W., Hawkley L. C., Arevalo J. M., Sung C. Y., Rose R. M., Cacioppo J. T. Social regulation of gene expression in human leukocytes // Genome biology. 2007. V. 8. №9. P. R189.
- DOI: 10.1186/gb-2007-8-9-r189
- Yang H., Stephens R. L., Tache Y. TRH analogue microinjected into specific medullary nuclei stimulates gastric serotonin secretion in rats // American Journal of Physiology-Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology. 1992. V. 262. №2. P. G216-G222.
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.1992.262.2.G216
- Santos J., Saperas E., Nogueiras C., Mourelle M., Antolín M., Cadahia A., Malagelada J. R. Release of mast cell mediators into the jejunum by cold pain stress in humans // Gastroenterology. 1998. V. 114. №4. P. 640-648.
- DOI: 10.1016/S0016-5085(98)70577-3
- Bercik P., Collins S. M. The effects of inflammation, infection and antibiotics on the microbiota-gut-brain axis // Microbial endocrinology: the microbiota-gut-brain axis in health and disease. Springer, New York, NY, 2014. P. 279-289.
- DOI: 10.1007/978-1-4939-0897-4_13
- Goehler L. E., Park S. M., Opitz N., Lyte M., Gaykema R. P. Campylobacter jejuni infection increases anxiety-like behavior in the holeboard: possible anatomical substrates for viscerosensory modulation of exploratory behavior // Brain, behavior, and immunity. 2008. V. 22. №3. P. 354-366.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbi.2007.08.009
- Shadnoush M., Hosseini R. S., Mehrabi Y., Delpisheh A., Alipoor E., Faghfoori Z.,.. Moghadam J. Z. Probiotic yogurt affects pro-and anti-inflammatory factors in patients with inflammatory bowel disease // Iranian journal of pharmaceutical research: IJPR. 2013. V. 12. №4. P. 929. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24523774
- Clarke G., Grenham S., Scully P., Fitzgerald P., Moloney R. T., Shanahan F.,.. Cryan J. T. The microbiome-gut-brain axis during early life regulates the hippocampal serotonergic system in a sex-dependent manner // Molecular psychiatry. 2013. V. 18. №6. P. 666-673.
- DOI: 10.1038/mp.2012.77
- Nishino R., Mikami K., Takahashi H., Tomonaga S., Furuse M., Hiramoto T.,.. Sudo N. Commensal microbiota modulate murine behaviors in a strictly contamination-free environment confirmed by culture-based methods // Neurogastroenterology & Motility. 2013. V. 25. №6. P. 521-e371.
- DOI: 10.1111/nmo.12110
- Yano J. M., Yu K., Donaldson G. P., Shastri G. G., Ann P., Ma L.,.. Hsiao E. Y. Indigenous bacteria from the gut microbiota regulate host serotonin biosynthesis // Cell. 2015. V. 161. №2. P. 264-276.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.02.047
- Portune K. J., Beaumont M., Davila A. M., Tomé D., Blachier F., Sanz Y. Gut microbiota role in dietary protein metabolism and health-related outcomes: the two sides of the coin // Trends in Food Science & Technology. 2016. V. 57. P. 213-232.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tifs.2016.08.011
- Nieuwenhuizen A. G., Rutters F. The hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal-axis in the regulation of energy balance // Physiology & behavior. 2008. V. 94. №2. P. 169-177.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2007.12.011
- Sudo N., Chida Y., Kubo C. Postnatal microbial colonization programs the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal system for stress response in mice // J Psychosom Res. 2005. V. 58. №6. P. S60-S60.
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2004.063388
- O'Mahony S. M., Marchesi J. R., Scully P., Codling C., Ceolho A. M., Quigley E. M.,.. Dinan T. G. Early life stress alters behavior, immunity, and microbiota in rats: implications for irritable bowel syndrome and psychiatric illnesses // Biological psychiatry. 2009. V. 65. №3. P. 263-267.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2008.06.026
- Пятин В. Ф., Романчук Н. П., Булгакова С. В., Романов Д. В., Сиротко И. И., Давыдкин И. Л., Волобуев А. Н. Циркадианный стресс Homo sapiens: новые нейрофизиологические, нейроэндокринные и психонейроиммунные механизмы // Бюллетень науки и практики. 2020. Т. 6. №6. С. 115-135.
- DOI: 10.33619/2414-2948/55/16
- Sinha R., Jastreboff A. M. Stress as a common risk factor for obesity and addiction // Biological psychiatry. 2013. V. 73. №9. P. 827-835.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2013.01.032
- Warne J. P. Shaping the stress response: interplay of palatable food choices, glucocorticoids, insulin and abdominal obesity // Molecular and cellular endocrinology. 2009. V. 300. №1-2. P. 137-146.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mce.2008.09.036
- Guillemot-Legris O., Muccioli G. G. Obesity-induced neuroinflammation: beyond the hypothalamus // Trends in Neurosciences. 2017. V. 40. №4. P. 237-253.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tins.2017.02.005
- Agustí A., García-Pardo M. P., López-Almela I., Campillo I., Maes M., Romaní-Pérez M., Sanz Y. Interplay between the gut-brain axis, obesity and cognitive function // Frontiers in neuroscience. 2018. V. 12. P. 155.
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2018.00155
- Noble E. E., Hsu T. M., Kanoski S. E. Gut to brain dysbiosis: mechanisms linking western diet consumption, the microbiome, and cognitive impairment // Frontiers in behavioral neuroscience. 2017. V. 11. P. 9.
- DOI: 10.3389/fnbeh.2017.00009
- De Luca S. N., Ziko I., Sominsky L., Nguyen J. C., Dinan T., Miller A. A.,.. Spencer S. J. Early life overfeeding impairs spatial memory performance by reducing microglial sensitivity to learning // Journal of neuroinflammation. 2016. V. 13. №1. P. 1-15.
- DOI: 10.1186/s12974-016-0578-7
- Del Rio D., Morales L., Ruiz-Gayo M., Del Olmo N.Effect of high-fat diets on mood and learning performance in adolescent mice // Behavioural brain research. 2016. V. 311. P. 167-172.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbr.2016.04.052
- Heyward F. D., Walton R. G., Carle M. S., Coleman M. A., Garvey W. T., Sweatt J. D. Adult mice maintained on a high-fat diet exhibit object location memory deficits and reduced hippocampal SIRT1 gene expression // Neurobiology of learning and memory. 2012. V. 98. №1. P. 25-32.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nlm.2012.04.005
- Krishna S., Keralapurath M. M., Lin Z., Wagner J. J., de La Serre C. B., Harn D. A., Filipov N. M. Neurochemical and electrophysiological deficits in the ventral hippocampus and selective behavioral alterations caused by high-fat diet in female C57BL/6 mice // Neuroscience. 2015. V. 297. P. 170-181.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2015.03.068
- Underwood E. L., Thompson L. T. A high-fat diet causes impairment in hippocampal memory and sex-dependent alterations in peripheral metabolism // Neural plasticity. 2016. V. 2016.
- DOI: 10.1155/2016/7385314
- Collison K. S., Makhoul N. J., Inglis A., Al-Johi M., Zaidi M. Z., Maqbool Z.,.. Shoukri M. Dietary trans-fat combined with monosodium glutamate induces dyslipidemia and impairs spatial memory // Physiology & behavior. 2010. V. 99. №3. P. 334-342.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2009.11.010
- Guimarães E. D. S. G., de Caires Júnior L. C., Musso C. M., Macedo de Almeida M., Gonçalves C. F., Pettersen K. G.,.. Mourao-Júnior C. A. Altered behavior of adult obese rats by monosodium l-glutamate neonatal treatment is related to hypercorticosteronemia and activation of hypothalamic ERK1 and ERK2 // Nutritional neuroscience. 2017. V. 20. №3. P. 153-160.
- DOI: 10.1179/1476830515Y.0000000004
- Wang S., Huang X. F., Zhang P., Newell K. A., Wang H., Zheng K., Yu Y. Dietary teasaponin ameliorates alteration of gut microbiota and cognitive decline in diet-induced obese mice // Scientific Reports. 2017. V. 7. №1. P. 1-13.
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-12156-2
- Klein C., Jonas W., Iggena D., Empl L., Rivalan M., Wiedmer P.,.. Steiner B. Exercise prevents high-fat diet-induced impairment of flexible memory expression in the water maze and modulates adult hippocampal neurogenesis in mice // Neurobiology of learning and memory. 2016. V. 131. P. 26-35.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nlm.2016.03.002
- Dong W., Wang R., Ma L. N., Xu B. L., Zhang J. S., Zhao Z. W.,.. Zhang X. Autophagy involving age-related cognitive behavior and hippocampus injury is modulated by different caloric intake in mice // International journal of clinical and experimental medicine. 2015. V. 8. №7. P. 11843. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26380026
- Mielke J. G., Nicolitch K., Avellaneda V., Earlam K., Ahuja T., Mealing G., Messier C. Longitudinal study of the effects of a high-fat diet on glucose regulation, hippocampal function, and cerebral insulin sensitivity in C57BL/6 mice // Behavioural brain research. 2006. V. 175. №2. P. 374-382.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbr.2006.09.010
- Hwang L. L., Wang C. H., Li T. L., Chang S. D., Lin L. C., Chen C. P.,.. Chiou L. C. Sex differences in high-fat diet-induced Obesity, metabolic alterations and learning, and synaptic plasticity deficits in mice // Obesity. 2010. V. 18. №3. P. 463-469.
- DOI: 10.1038/oby.2009.273
- Wang S., Huang X. F., Zhang P., Wang H., Zhang Q., Yu S., Yu Y. Chronic rhein treatment improves recognition memory in high-fat diet-induced obese male mice // The Journal of nutritional biochemistry. 2016. V. 36. P. 42-50.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2016.07.008
- Булгакова С. В., Романчук Н. П. Участие гормонов в процессах когнитивного и социальноэмоционального старения // Бюллетень науки и практики. 2020. Т. 6. №8. С. 97-129.
- DOI: 10.33619/2414-2948/57/09
- Gunstad J., Paul R. H., Cohen R. A., Tate D. F., Spitznagel M. B., Gordon E. Elevated body mass index is associated with executive dysfunction in otherwise healthy adults // Comprehensive psychiatry. 2007. V. 48. №1. P. 57-61.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.comppsych.2006.05.001
- Martin A., Booth J. N., Young D., Revie M., Boyter A. C., Johnston B.,.. Reilly J. J. Associations between Obesity and cognition in the pre-school years // Obesity. 2016. V. 24. №1. P. 207-214.
- DOI: 10.1002/oby.21329
- Beilharz J. E., Maniam J., Morris M. J. Diet-induced cognitive deficits: the role of fat and sugar, potential mechanisms and nutritional interventions. Nutrients 2015; 7: 6719-38.
- DOI: 10.3390/nu7085307
- Cournot M. C. M. J., Marquie J. C., Ansiau D., Martinaud C., Fonds H., Ferrieres J., Ruidavets J. B. Relation between body mass index and cognitive function in healthy middle-aged men and women // Neurology. 2006. V. 67. №7. P. 1208-1214.
- DOI: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000238082.13860.50
- Nyaradi A., Foster J. K., Hickling S., Li, J., Ambrosini G. L., Jacques A., Oddy W. H. Prospective associations between dietary patterns and cognitive performance during adolescence // Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry. 2014. V. 55. №9. P. 1017-1024.
- DOI: 10.1111/jcpp.12209
- Crichton G. E., Murphy K. J., Howe P. R., Buckley J. D., Bryan J. Dairy consumption and working memory performance in overweight and obese adults // Appetite. 2012. V. 59. №1. P. 34-40.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.appet.2012.03.019
- Roberts R. O., Roberts L. A., Geda Y. E., Cha R. H., Pankratz V. S., O'Connor H. M.,.. Petersen R. C. Relative intake of macronutrients impacts risk of mild cognitive impairment or dementia // Journal of Alzheimer's disease. 2012. V. 32. №2. P. 329-339.
- DOI: 10.3233/JAD-2012-120862
- Steenbergen L., Sellaro R. van H. S., Bosch J. A., Colzato L. S. // A randomized controlled trial to test the effect of multispecies probiotics on cognitive reactivity to sad mood. Brain Behav Immun. 2015. V. 48. P. 258-264.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbi.2015.04.003
- Tillisch K., Labus J., Kilpatrick L., Jiang Z., Stains J., Ebrat B.,.. Mayer E. A. Consumption of fermented milk product with probiotic modulates brain activity // Gastroenterology. 2013. V. 144. №7. P. 1394-1401. e4.
- DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2013.02.043
- World Health Organization Depression and Other Common Mental Disorders: Global Health Estimates. Geneva. 2017.
- Santos R. O., Trindade S. C., Maurer L. H., Bersch A. M., Sautter C. K., Penna N. G.Physicochemical, antioxidant and sensory quality of brazilian blueberry wine // Anais da Academia Brasileira de Ciências. 2016. V. 88. №3. P. 1557-1568.
- DOI: 10.1590/0001-3765201620140491
- Oliveira C. et al. Hypercaloric diet modulates effects of chronic Stress: a behavioral and biometric study on rats // Stress. 2015. V. 18. №5. P. 514-523.
- DOI: 10.3109/10253890.2015.1079616
- McNeilly A. D., Stewart C. A., Sutherland C., Balfour D. J. High fat feeding is associated with stimulation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis and reduced anxiety in the rat // Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2015. V. 52. P. 272-280.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2014.12.002
- Yang J. L., Jiang H., Pan F., Ho C. S., Ho R. C. The effects of high-fat-diet combined with chronic unpredictable mild stress on depression-like behavior and leptin/leprb in male rats // Scientific reports. 2016. V. 6. P. 35239.
- DOI: 10.1038/srep35239
- Haque Z., Akbar N., Yasmin F., Haleem M. A., Haleem D. J. Inhibition of immobilization Stress-induced anorexia, behavioral deficits, and plasma corticosterone secretion by injected leptin in rats // Stress. 2013. V. 16. №3. P. 353-362.
- DOI: 10.3109/10253890.2012.736047
- Finger B. C., Dinan T. G., Cryan J. F. Leptin-deficient mice retain normal appetitive spatial learning yet exhibit marked increases in anxiety-related behaviours // Psychopharmacology. 2010. V. 210. №4. P. 559-568.
- DOI: 10.1007/s00213-010-1858-z
- Schachter J., Martel J., Lin C. S., Chang C. J., Wu T. R., Lu C. C.,.. Young J. D. Effects of obesity on depression: a role for inflammation and the gut microbiota // Brain, Behavior, and Immunity. 2018. V. 69. P. 1-8.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbi.2017.08.026
- Ohland C. L., Kish L., Bell H., Thiesen A., Hotte N., Pankiv E., Madsen K. L. Effects of Lactobacillus helveticus on murine behavior are dependent on diet and genotype and correlate with alterations in the gut microbiome // Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2013. V. 38. №9. P. 1738-1747.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2013.02.008
- Abildgaard A., Elfving B., Hokland M., Wegener G., Lund S. Probiotic treatment reduces depressive-like behaviour in rats independently of diet // Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2017. V. 79. P. 40-48.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2017.02.014
- De Wit L., Luppino F., van Straten A., Penninx B., Zitman F., Cuijpers P. Depression and obesity: a meta-analysis of community-based studies // Psychiatry research. 2010. V. 178. №2. P. 230-235.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.psychres.2009.04.015
- Parletta N., Zarnowiecki D., Cho J., Wilson A., Bogomolova S., Villani A.,.. Segal L. A Mediterranean-style dietary intervention supplemented with fish oil improves diet quality and mental health in people with depression: A randomized controlled trial (HELFIMED) // Nutritional neuroscience. 2019. V. 22. №7. P. 474-487.
- DOI: 10.1080/1028415X.2017.1411320
- Lassale C., Batty G. D., Baghdadli A., Jacka F., Sánchez-Villegas A., Kivimäki M., Akbaraly, T. Healthy dietary indices and risk of depressive outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies // Molecular psychiatry. 2019. V. 24. №7. P. 965-986.
- DOI: 10.1038/s41380-018-0237-8
- Cenit M. C., Sanz Y., Codoñer-Franch P. Influence of gut microbiota on neuropsychiatric disorders // World journal of gastroenterology. 2017. V. 23. №30. P. 5486. https://dx.doi.org/10.3748%2Fwjg.v23.i30.5486
- Farzi A., Hassan A. M., Zenz G., Holzer P. Diabesity and mood disorders: Multiple links through the microbiota-gut-brain axis // Molecular aspects of medicine. 2019. V. 66. P. 80-93.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mam.2018.11.003
- Misiak B., Łoniewski I., Marlicz W., Frydecka D., Szulc A., Rudzki L., Samochowiec J. The HPA axis dysregulation in severe mental illness: Can we shift the blame to gut microbiota? // Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology and Biological Psychiatry. 2020. P. 109951.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2020.109951
- Романов Д. В., Романчук Н. П. Ранняя диагностика когнитивных нарушений. Самара. 2014. 34 с.
- Романчук Н. П. Здоровая микробиота и натуральное функциональное питание: гуморальный и клеточный иммунитет // Бюллетень науки и практики. 2020. Т. 6. №9. С. 127-166.
- DOI: 10.33619/2414-2948/58/14
- Булгакова С. В., Романчук Н. П. Иммунный гомеостаз: новая роль микро- и макроэлементов, здоровой микробиоты // Бюллетень науки и практики. 2020. Т. 6. №10. С. 206-233.
- DOI: 10.33619/2414-2948/59/22


