Растворимость фосфатов редкоземельных металлов в карбонатно-щелочных системах
Автор: Герасв С.А., Литвинова Т.Е., Масанина М.Н., Гордиманова Э.А.
Журнал: Вестник Южно-Уральского государственного университета. Серия: Металлургия @vestnik-susu-metallurgy
Рубрика: Физическая химия и физика металлургических систем
Статья в выпуске: 1 т.24, 2024 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Статья посвящена исследованию процесса растворения фосфатов некоторых редкоземельных металлов (РЗМ) в карбонатно-щелочных системах. В качестве объекта исследования рассмотрены модельные осадки фосфатов тяжелых РЗМ - гольмия и иттербия; РЗМ средней массы - самария и гадолиния; легкого РЗМ - неодима, а также иттрия, который не является лантаноидом. Фосфаты РЗМ представляют собой примесные компоненты, входящие в состав промышленного отхода фосфогипса (ФГ). По различным оценкам ежегодно в России образуется от 10 до 15 млн тонн такого отхода, что влечет за собой возникновение экологических проблем в местах его захоронения. Для рационального использования минерального сырья необходимо разработать такое решение, которое позволит переработать фосфогипс в коммерчески ценные продукты, одним из которых может быть концентрат редкоземельных металлов. Редкоземельные металлы получили широкое применение в различных отраслях: оборона, энергетика, электроника, металлургия, катализ и другие. Однако малые объемы производства и отсутствие полного цикла производства некоторых РЗМ вынуждают осуществлять их закупку за рубежом. Таким образом, исследование направлено на достижение экономической стабильности и технологического суверенитета Российской Федерации. В статье представлено описание влияния температуры, концентрации карбонатного раствора, межфазного отношения и скорости перемешивания на процесс растворения фосфатов РЗМ. В рассматриваемом концентрационном диапазоне при температуре 90 °С максимальные равновесные степени извлечения в раствор составили: E(Ho) = 75,6 %; E(Yb) = 85,5 %; E(Nd) = 62,5 %; E(Gd) = 71,6 %; E(Y) = 73,1 %; E(Sm) = 46,1 %. Результаты экспериментального исследования относятся к части термодинамического анализа системы REEPO4 - K2CO3, которые в дальнейшем могут быть использованы при моделировании процесса попутного извлечения РЗМ из техногенных отходов, в частности фосфогипса, методом жидкостной карбонатно-щелочной конверсии.
Редкоземельные металлы, лантаноиды, фосфогипс, карбонат калия, изотермы растворимости
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/147243229
IDR: 147243229 | УДК: 669 | DOI: 10.14529/met240101
Текст научной статьи Растворимость фосфатов редкоземельных металлов в карбонатно-щелочных системах
Одно из актуальных направлений для исследований в области переработки минерального сырья – это повышение комплексности переработки [1, 2]. В промышленном масштабе до сих пор не внедрен ни один способ, который позволил бы рационально использовать апатитовый концентрат при переработке его в ортофосфорную кислоту [3, 4]. Часть производств организована по дигидратному методу (1), что влечет за собой образование отхода дигидрата сульфата кальция, другая часть производств – по полугидратному методу (2), приводящему к появлению отхода полугидрата сульфата кальция [5, 6]:
Ca5 (PO 4 )3 F + 5H 2 SO 4 + 10H 2 O ^ 5CaSO 4 • 2H 2 O Ф + 3H 3 PO 4 + HF T ; (1)
Ca5(PO 4 )3F + 5H 2 SO 4 + 2,5H 2 O ^ 5CaSO 4 • 0,5H 2 O Ф + 3H 3 PO 4 + HF T . (2)
Дигидрат и полугидрат сульфата кальция имеют схожий состав, отличающийся лишь содержанием структурной воды. В случае захоронения открытым способом эти отходы и вовсе могут иметь одинаковый состав в силу протекания процессов дегидратации (3) и гидратации (4), обусловленных аналогичным влиянием условий окружающей среды на них [7, 8]:
CaSO4 • 2H 2 O ^ CaSO4 • 0,5H 2 O + 1,5H 2 O; (3)
CaSO4 • 0,5H2O + 1,5H2O ^ CaSO4 • 2H 2 O. (4)
Таким образом, полугидрат и дигидрат сульфата кальция следует рассматривать как одну группу отходов (фосфогипс), области применения и способы переработки которых должны быть основаны на общем подходе.
Одним из путей утилизации фосфогипса в мировой практике является использование его в качестве добавки в строительные смеси, материала для дорожного покрытия или, например, подкисляющего агента в сельском хозяйстве. Однако применение отхода в качестве добавки в лучшем случае решает только проблему утилизации и никоим образом не позволяет увеличить глубину переработки исходного сырья, что приводит к потере ценных компонентов [9, 10].
Согласно данным рентгенофазового анализа различных проб отвального фосфогипса, в его состав входит от 0,1 до 0,8 % редкоземельных металлов в пересчете на оксиды [11, 12], причем нахождение их зафиксировано преимущественно в виде фосфата трехвалентного металла [13, 14]. Хотя ФГ содержит относительно небольшое количество РЗМ, тем не менее он является перспективным источником для их извлечения, поскольку:
-
1) является безопасным вторичным сырьем с точки зрения радиационного фона [15];
-
2) в сравнении с другими РЗМ-содержа-щими источниками, расположенными на территории Российской Федерации, отвалы ФГ являются доступными [16, 17].
Например, в рудах месторождения Томтор (Якутия) содержится изобилие редкоземельных металлов: от 7 до 10 % РЗМ в пересчете на оксидную форму, тем не менее из-за отсутствия инфраструктуры вблизи месторождения добыча и переработка ископаемого сырья не представляется возможной [18].
Существует множество способов химической переработки ФГ, основанных на кислотном выщелачивании. Технологические схемы предполагают получение РЗМ и гипса как потенциального строительного материала [19, 20]. Комплексной переработки эти методы не предусматривают и не приводят к сокращению количества отвалов [21].
Карбонатная конверсия фосфогипса предполагает его обработку крепкими растворами карбонатов натрия или аммония с получением сульфата щелочного металла или аммония и фосфомела (конверсионного мела) [22, 23]. К недостаткам способа следует отнести неудовлетворительные реологические показате- ли и фильтруемость мелкодисперсной пульпы фосфомела и потери РЗМ [24].
Прием использования карбонатно-щелочных сред является перспективным для переработки фосфатно-карбонатных сырьевых источников [25–27] за счет образования растворимых карбонатных комплексов состава REE (CO 3 ) 2 [28–30].
Тем не менее поведение малорастворимых соединений РЗМ в карбонатно-щелочных средах изучено далеко не в полной мере [31, 32] и носит, скорее, отрывочный характер.
В этой связи необходимо осуществить экспериментальное подтверждение теоретических исследований с целью определения практических значений растворимости фосфатов различных групп РЗМ: тяжелых – гольмия и иттербия; средних – самария и гадолиния; легких – неодима, а также иттрия, который не является лантаноидом [33].
Цель настоящего исследования – установить влияние ряда параметров на растворимость фосфатов РЗМ в карбонатно-щелочных средах: температуры, времени, концентрации карбоната калия, межфазного отношения и скорости перемешивания.
Методология
Изучено влияние температуры, скорости и продолжительности перемешивания, концентрации карбоната в растворе на растворимость фосфатов гольмия, иттербия, неодима, гадолиния, иттрия и самария.
В качестве исходных образцов были отобраны навески модельных фосфатов гольмия, иттербия, самария, гадолиния, неодима и иттрия, которые были предварительно получены осаждением РЗМ ортофосфорной кислотой (0,2 М) из нитратных сред (0,2 М):
REE 3+ + H 3 PO 4 ^ REE PO 4 Ф + 3H + . (5)
После осаждения модельные осадки направлялись на фильтрование, промывку и сушку, а также на рентгенофазовый анализ для подтверждения состава.
Предварительное исследование растворимости фосфатов редкоземельных металлов было опробовано в среде карбоната калия и аммония, а также в среде карбоната и гидрокарбоната натрия. В ряду: карбонат калия, карбонат аммония, карбонат натрия, гидрокарбонат натрия наблюдается снижение растворимости фосфатов РЗМ, что может указывать на влияние природы катиона. Снижение растворимости в среде гидрокарбонат-иона, вероятно, связано с малой стабильностью гидрокарбонатных комплексов РЗМ, вследствие чего экспериментальные исследования, представленные в данной статье, проводились именно в среде карбоната калия.
Изучение растворимости было проведено в изотермических условиях на лабораторном оборудовании HEL Auto-MATE Reactor System.
Параметры, при которых осуществлялось построение изотерм растворимости, выбирались из следующих соображений.
-
1. Температура
-
2. Время
-
3. Концентрация карбонатного раствора
-
4. Межфазное отношение
-
5. Интенсивность перемешивания
Большинство известных способов переработки фосфогипса в мел методом жидкостной карбонатно-щелочной конверсии подразумевают ведение процесса при температуре 50–90 °С [34]. Выбор температуры 90 °С для исследования влияния концентрации на степень извлечения РЗМ обусловлен увеличением скорости процесса (согласно уравнению Аррениуса) и смещением химического равновесия в сторону образования карбонатного комплекса (принцип Ле Шателье), поскольку процесс является эндотермическим.
Изотермы растворимости представляют собой зависимость равновесной концентрации (степени извлечения) РЗМ от концентрации карбонатного раствора. В этой связи время должно быть подобрано таким образом, чтобы дальнейшее его увеличение не приводило к росту растворимости.
Растворимость карбоната калия в воде составляет 110,5 г на 100 г воды, следовательно, технически представляется возможным исследовать растворимость осадков РЗМ в широком диапазоне его концентрации, в то время как растворимость карбоната натрия (21,8 г на 100 г воды) и карбоната аммония (96 г на 100 г воды) значительно ниже и не позволит рассмотреть поведение фосфатов РЗМ в области высоких концентраций.
Межфазное отношение (ж : т) оказывает существенное влияние на растворимость, причем попытки проведения эксперимента при стехиометрических соотношениях не привели к ожидаемому результату.
Параметр обеспечивает интенсификацию процесса растворения и влияет на отвод про- дуктов (карбонатных комплексов РЗМ) с поверхности твердого фосфата РЗМ. Экспериментально было установлено, что число оборотов оказывает воздействие на процесс растворения и при значении выше 650 об/мин возрастания степени извлечения не наблюдается. Растворение REEPO4, равно как и REE2(CO3)3, протекает в диффузионном режиме. Скорость перемешивания, учитывая опыт, установлена 650 об/мин.
Анализ концентрации РЗМ в растворе производился методом трилонометрического титрования в присутствии индикатора арсеназо (III) по формуле
_ C Трилон Б ' V T рилон Б
C REE = у ,
V a
где C Трилон Б – концентрация титранта, экв/л; V Трилон Б – объем трилона Б, ушедшего на титрование пробы, мл; V a – объем аликвоты, взятой на анализ, мл.
Результаты эксперимента
Согласно анализу термодинамических параметров (энтальпия, энтропия, энергия Гиббса), фосфаты редкоземельных металлов способны растворяться в среде карбонат-иона, причем наиболее вероятными продуктами процесса являются карбонатные комплексы [35]. При этом реакция имеет эндотермический характер, а значит, повышение температуры позволит не только повысить скорость, но и сместить химическое равновесие в сторону образования комплекса. На примере фосфата иттербия (III) (рис. 1) представлено несколько кинетических кривых при разных T . Увеличение температуры приводит к увеличению скорости, а также к увеличению степени извлечения в раствор в состоянии системы, близком к равновесному.
Скорость перемешивания пульпы (рис. 2) и межфазное отношение (рис. 3) оказывают воздействие на процесс растворения фосфатов редкоземельных металлов. Анализ экспериментально полученных зависимостей для фосфатов гольмия (III), иттербия (III) и неодима (III) свидетельствует о том, что при n > 500 об/мин и ж : т > 2000 мл/г дальнейшее увеличение этих параметров не проводит к возрастанию E , таким образом, построение изотерм растворимости осуществлялось при n = 650 об/мин и ж: т = 2100 мл/г.
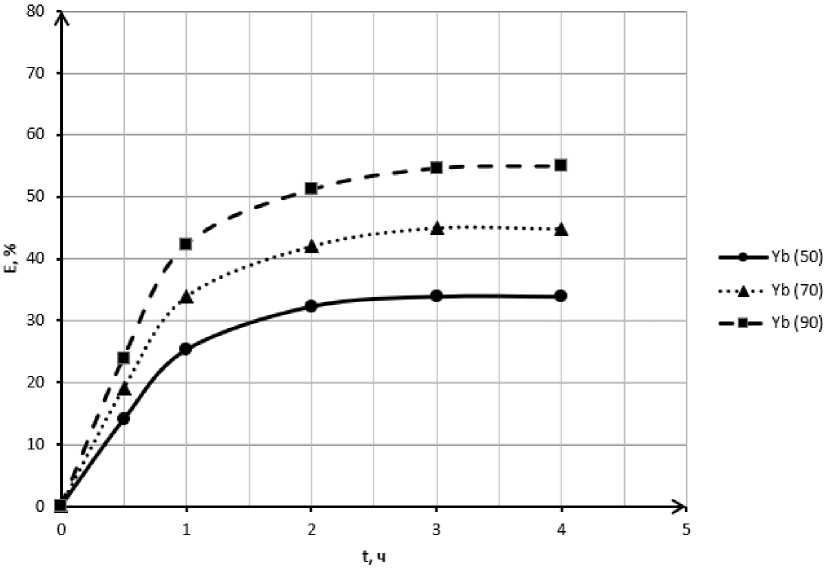
Рис. 1. Влияние температуры на растворимость YbPO 4 Fig. 1. An influence of temperature on YbPO 4 dissolution
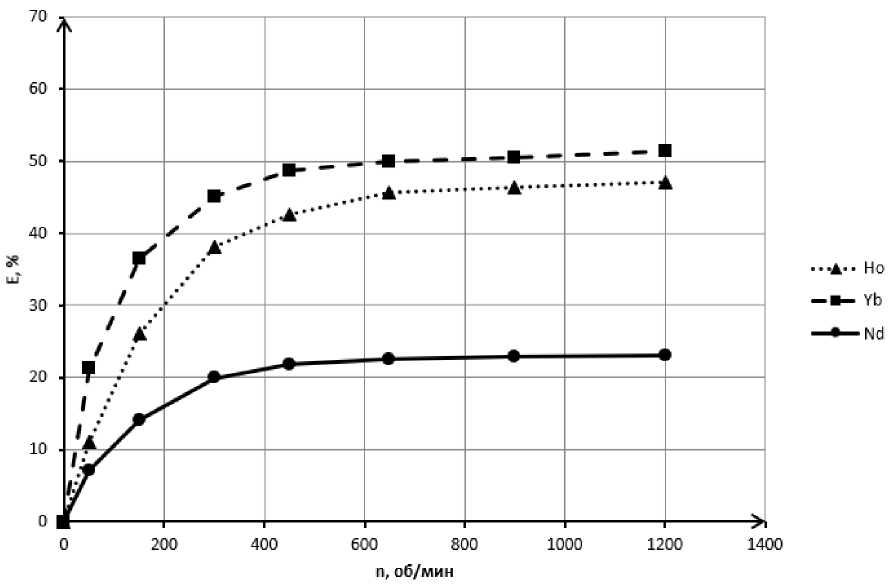
Рис. 2. Влияние скорости перемешивания на растворимость REE PO 4 Fig. 2. An influence of mixing rate on REE PO 4 dissolution
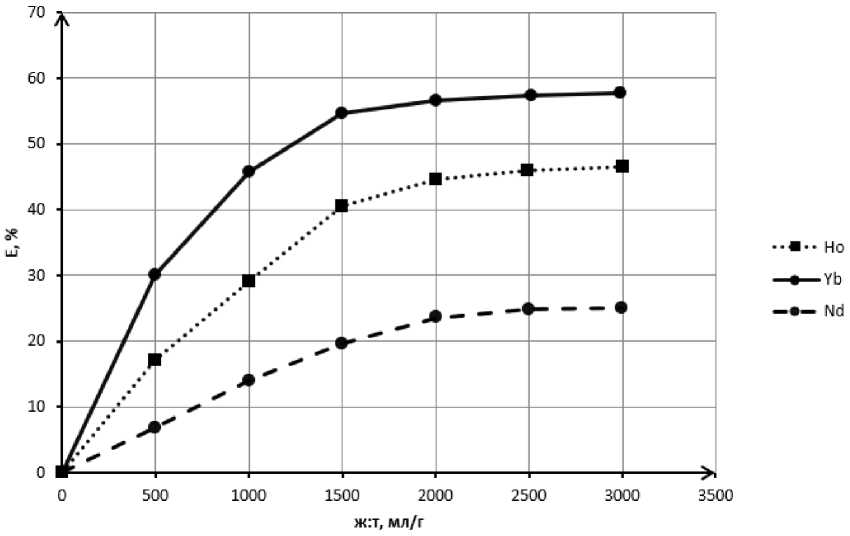
Рис. 3. Влияние межфазного отношения на растворимость REE PO 4 Fig. 3. An influence of liquid to solid ratio on REE PO 4 dissolution
Известные литературные данные полагают полное растворение REEPO4 в карбонатных средах уже при 1 М K2CO3, однако использование раствора такой концентрации не приводит к полному растворению, поэтому рассмотрено влияние концентрации карбонат- иона на растворимость. Эксперимент проводили при T = 90 °C, скорости перемешивания 650 об/мин, ж :т = 2100 мл/г и продолжительности перемешивания 6 ч. На рис. 4 показаны зависимости E-C для фосфата иттербия (III).
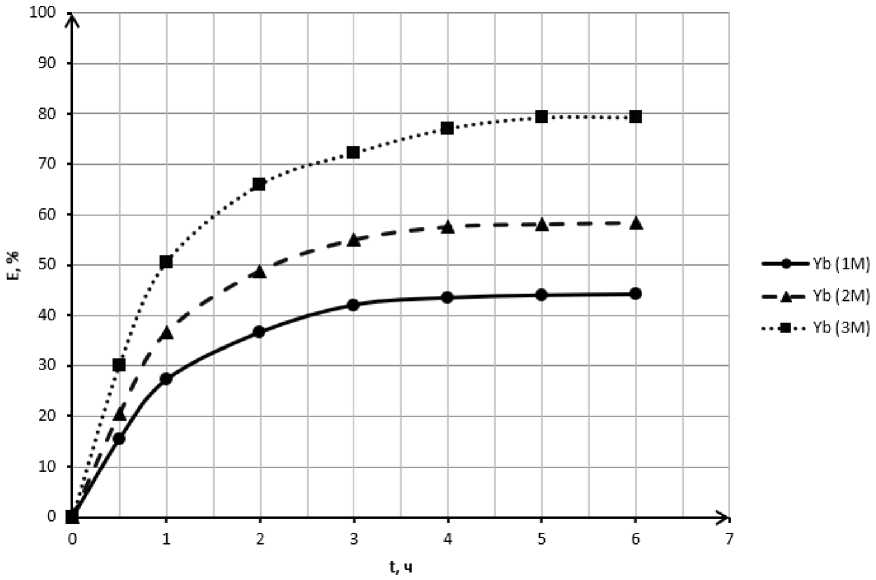
Рис. 4. Влияние концентрации карбонат-иона на растворимость YbPO 4 Fig. 4. An influence of carbonate-ion concentration on YbPO 4 dissolution
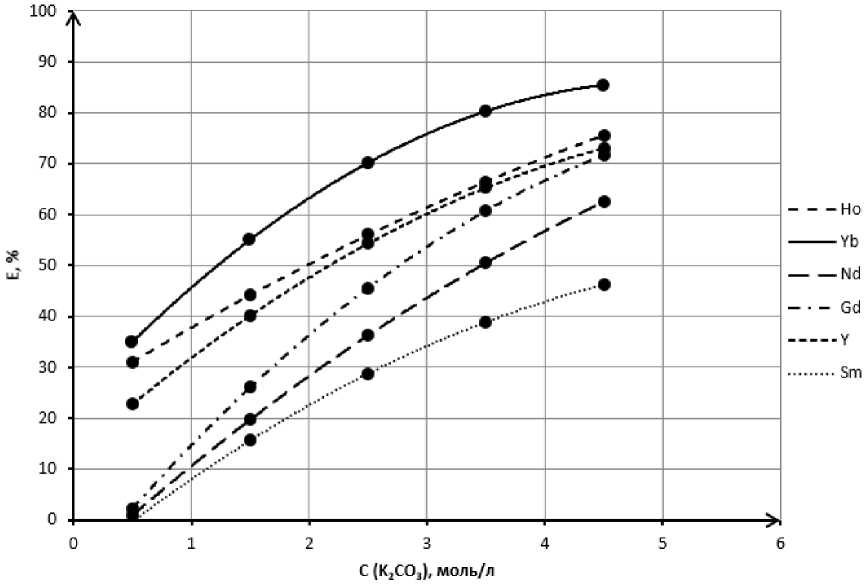
Рис. 5. Изотермы растворимости REE PO 4 в карбонатно-щелочной среде
Fig. 5. Isotherms of REE PO 4 dissolution in carbonate-alkaline media
Степень извлечения некоторых редкоземельных металлов в раствор при различной концентрации карбоната калия
Degree of extraction of some rare earth metals into solution at different potassium carbonate concentrations
1-я стадия:
2 REE PO 4 + 3CO 3 2 - → REE 2 (CO 3 ) 3 + 2PO 3 4 - ; (7) 2-я стадия:
REE 2 (CO 3 ) 3 + CO 3 2 - → 2 REE (CO 3 ) 2 - ; (8)
Σ :
REE PO 4 + 2CO 3 2 - → REE (CO 3 ) 2 - + PO 3 4 - . (9)
Отрицательное значение стандартной энергии Гиббса процесса комплексообразования РЗМ указывает на возможность протекания процесса, однако растворение при стандартных условиях на протяжении длительного времени (более суток) не приводит к переходу РЗМ в жидкую фазу, что свидетельствует о том, что скорость процесса низка при данных условиях. Таким образом, вести процесс следует при повышенной температуре.
Установлено влияние межфазного отношения, которое также указывает на протекание процесса с низкой скоростью при стехиометрических соотношениях. Такое влияние может свидетельствовать о том, что процесс комплексообразования – последовательный процесс перехода фосфата в карбонат, а карбоната – в комплекс.
Выводы
Растворение осадков РЗМ в среде карбо-нат-иона технически осуществимо, причем в случае попутного извлечения редких земель из фосфогипса возможно достичь равновесной концентрации рассмотренных металлов в растворе, поскольку время конверсии фосфогипса по ранее разработанной технологии совпадает с равновесным временем, при котором были экспериментально получены изотермы.
С учетом результатов, опубликованных ранее, метод растворения осадков РЗМ в среде карбонат-иона является универсальным, поскольку позволяет перевести РЗМ в жидкую фазу из осадков, образованных различными анионами: сульфатами, карбонатами, фосфатами.
Применительно к технологии жидкостной карбонатно-щелочной конверсии фосфогипса представляется целесообразным ведение процесса конверсии при тех же параметрах, что и ранее разработанных, за исключением межфазного отношения (его необходимо увеличить).
Дальнейшее выделение РЗМ из щелока возможно осуществить за счет разрушения карбонатных комплексов с образованием вторичных осадков РЗМ, однако в литературе описана трудность разделения смеси РЗМ на отдельные элементы, которая вызвана малым различием в ионном радиусе атома (различия в радиусе атомов соседних элементов составляют всего лишь 0,01–0,03 Å) [12]. Таким образом, их разделение методом осаждения является перспективной и сложной задачей.
Список литературы Растворимость фосфатов редкоземельных металлов в карбонатно-щелочных системах
- Chernysh Y., Yakhnenko O., Chubur V., Roubík H. Phosphogypsum Recycling: A Review of Environmental Issues, Current Trends, and Prospects. Appl. Sci. 2021;11:1575. DOI: 10.3390/app11041575
- Gschneidner K.A., Jr. The Rare Earth Crisis – The Supply/Demand Situation for 2010–2015. Mater. Matters. 2011;6:32–37.
- Cheremisina O., Sergeev V., Ponomareva M., Ilina A., Fedorov A. Kinetics Study of Solvent and Solid-Phase Extraction of Rare Earth Metals with Di-2-Ethylhexylphosphoric Acid. Metals. 2020;10:687. DOI: 10.3390/met10050687
- Sergeev I.B., Ponomarenko T.V. Incentives for creation the competitive rare-earth industry in Russia in the context of global market competition. Journal of Mining Institute. 2015;211:104.
- Cheremisina O., Sergeev V., Fedorov A., Alferova D. Concentration and Separation of Heavy Rare-Earth Metals at Stripping Stage. Metals. 2019;9:1317. DOI: 10.3390/met9121317
- Husein Malkawi D.A., Husein Malkawi A.I., Bani-Hani K.A. Slope Stability Analysis for the Phosphogypsum Stockpiles: A Case Study for the Sustainable Management of the Phosphogypsum Stacks in Aqaba Jordan. Sustainability. 2022;14(23):15763. DOI: 10.3390/su142315763
- Bingqi W., Lin Y., Tong L., Jianxin C. Study on the Kinetics of Hydration Transformation from Hemihydrate Phosphogypsum to Dihydrate Phosphogypsum in Simulated Wet Process Phosphoric Acid. ACS Omega. 2021;6(11):7342–7350. DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.0c05432
- Cheremisina O., Ponomareva M., Sergeev V., Mashukova Y., Balandinsky D. Extraction of Rare Earth Metals by Solid-Phase Extractants from Phosphoric Acid Solution. Metals. 2021;11:991. DOI: 10.3390/met11060991
- Li P., Zhang X., Zhong M., Fan Z., Xiong J., Zhang Z. Phosphogypsum-Based Ultra-Low Basicity Cementing Material. Materials. 2022;15:6601. DOI: 10.3390/ma15196601
- Kim P., Anderko A., Navrotsky A., Riman R.E. Trends in Structure and Thermodynamic Properties of Normal Rare Earth Carbonates and Rare Earth Hydroxycarbonates. Minerals. 2018;8:106. DOI: 10.3390/min8030106
- Kurkinen S., Sami Virolainen S., Sainio T. Recovery of rare earth elements from phosphogypsum waste in resin-in-leach process by eluting with biodegradable complexing agents. Hydrometallurgy. 2021;201:105569. DOI: 10.1016/j.hydromet.2021.105569
- Pathapati S.V.S.H., Free M.L., Sarswat P.K. A Comparative Study on Recent Developments for Individual Rare Earth Elements Separation. Processes. 2023;11:2070. DOI: 10.3390/pr11072070
- Salavati-Niasari M., Javidi J., Davar F. Sonochemical synthesis of Dy2(CO3)3 nanoparticles, Dy(OH)3 nanotubes and their conversion to Dy2O3 nanoparticles. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2010;17:870–877. DOI: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2010.02.013
- Kaczorowska M.A. The Latest Achievements of Liquid Membranes for Rare Earth Elements Recovery from Aqueous Solutions – A Mini Review. Membranes. 2023;13:839. DOI: 10.3390/membranes13100839
- Mukaba J.-L., Eze C.P., Pereao O., Petrik L.F. Rare Earths’ Recovery from Phosphogypsum: An Overview on Direct and Indirect Leaching Techniques. Minerals. 2021;11:1051. DOI: 10.3390/min11101051
- Cheremisina O.V., Sergeev V., Fedorov A.T., Alferova D.A. Separation of rare-earth metals and titanium in complex apatite concentrate processing. Obogashchenie Rud. 2020;5:30–34. DOI: 10.17580/or.2020.05.05
- Pyagai I., Zubkova O., Babykin R., Toropchina M., Fediuk R. Influence of Impurities on the Process of Obtaining Calcium Carbonate during the Processing of Phosphogypsum. Materials. 2022;15:4335. DOI: 10.3390/ma15124335
- Okrugin A., Zhuravlev A. Mineralogical and Geochemical Evidence of Paragenetic Unity of Igneous Silicate and Carbonatite Rocks of the Tomtor Massif in the North-East of the Siberian Platform. Minerals. 2023;13:211. DOI: 10.3390/min13020211
- Daminescu D., Duteanu N., Ciopec M., Negrea A., Negrea P., Nemeş N.S., Pascu B., Lazău R., Berbecea A. Kinetic Modelling the Solid–Liquid Extraction Process of Scandium from Red Mud: Influence of Acid Composition, Contact Time and Temperature. Materials. 2023;16:6998. DOI: 10.3390/ma16216998
- Guan Q., Sui Y., Liu C., Wang Y., Zeng C., Yu W., Gao Z., Zang Z., Chi R.-a. Characterization and Leaching Kinetics of Rare Earth Elements from Phosphogypsum in Hydrochloric Acid. Minerals. 2022;12:703. DOI: 10.3390/min12060703
- Zeng Cx., Guan Qj., Sui Y. Kinetics of nitric acid leaching of low-grade rare earth elements from phosphogypsum. J. Cent. South Univ. 2022;29(6):1869–1880. DOI: 10.1007/s11771-022-5049-y
- Li X., Lv X., Xiang L. Review of the State of Impurity Occurrences and Impurity Removal Technology in Phosphogypsum. Materials. 2023;16:5630. DOI: 10.3390/ma16165630
- Balaram V. Potential Future Alternative Resources for Rare Earth Elements: Opportunities and Challenges. Minerals. 2023;13:425. DOI: 10.3390/min13030425
- Lv X., Xiang L. The Generation Process, Impurity Removal and High-Value Utilization of Phosphogypsum Material. Nanomaterials. 2022;12:3021. DOI: 10.3390/nano12173021
- Millero F., Schreiber D. Use of the ion pairing model to estimate activity coefficients of the ionic components of natural waters. American Journal of Science. 1982;282:1508–1540. DOI: 10.2475/ajs.282.9.1508
- Lee J.H., Robert H.B. Examination of comparative rare earth element complexation behavior using linear free-energy relationships. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta. 1992;56:1127–1137. DOI: 10.1016/0016-7037(92)90050-S
- Liu X., Byrne R.H. Comprehensive Investigation of Yttrium and Rare Earth Element Complexation by Carbonate Ions Using ICP–Mass Spectrometry. Journal of Solution Chemistry. 1998;27:803–815. DOI: 10.1023/A:1022677119835
- Luo Y.R., Byrne R.H. The Ionic Strength Dependence of Rare Earth and Yttrium Fluoride Complexation at 25°C. Journal of Solution Chemistry. 2000;29:1089–1099. DOI: 10.1023/A: 1005186932126
- Ohta A., Kawabe I. Rare earth element partitioning between Fe oxyhydroxide precipitates and aqueous NaCl solutions doped with NaHCO3: Determinations of rare earth element complexation constants with carbonate ions. Geochemical journal. 2000;34:439–454. DOI: 10.2343/geochemj.34.439
- Rao R., Chatt A. Studies on Stability Constants of Europium(III) Carbonate Complexes and Application of SIT and Ion-Pairing Models. Radiochimica Acta. 1991;54(4):181–188. DOI: 10.1524/ract.1991.54.4.181
- Devine C.D. The stability constants of some carboxylate complexes of the trivalent lanthanons; 1969. DOI: 10.2172/4619812
- Han K. Characteristics of Precipitation of Rare Earth Elements with Various Precipitants. Minerals. 2020;10:178. DOI: 10.3390/min10020178
- Jowitt S.M. Mineral economics of the rare-earth elements. MRS Bulletin. 2022;47:276–282. DOI: 10.1557/s43577-022-00289-3
- Kang C.-U., Ji S.-W., Jo H. Recycling of Industrial Waste Gypsum Using Mineral Carbonation. Sustainability. 2022;14:4436. DOI: 10.3390/su14084436
- Chirkst D.E., Cheremisina O.V. Solubility of cerium (III) phosphate at different temperatures and concentrations of ortho-phosphoric acid. Journal of Mining Institute. 2006;169(4):227–230.


