Rational economics in comparison to the case of behavioral economics
Автор: Challoumis C., Savić M., Pavlović N.
Журнал: Ekonomski signali @esignali
Статья в выпуске: 1 vol.20, 2025 года.
Бесплатный доступ
This paper aims to represent the special characteristics of rational economics in comparison to the case of behavioral economics. Therefore, this analysis represents these issues and shows the main differences between the two concepts. The mainstream is to show the crucial attributes of both of them and the differences between them. Behavioral economics also take into account subjective characteristics, while rational economics is based more on mathematical norms, but there are also approaches that allow both behavioral economics and behavioral economics as feedback systems can find the most appropriate model.
Rational, behavioral, mainstream, economics, Keynesian, Neoclassical
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/170209518
IDR: 170209518 | УДК: 330.101.3 | DOI: 10.5937/ekonsig2501013C
Текст научной статьи Rational economics in comparison to the case of behavioral economics
Introduction and methodology
In this thesis the rational and the behavioral economics, from the special view of the Keynesian and the Neoclassical approach. This means that as a methodological tool, this paper has used the analysis of the structural elements of the theory of the Keynesian approach and the Neoclassical theory to declare their characteristics. Moreover, the comparison between the two theories is used to determine the differences between them, and for the clarification of their behavior (Azar et al., 2018; Cai, 2017; Campos et al., 2019; Carfora et al., 2021; Challoumis, 2020a; McIsaac & Riley, 2020; Nayak, 2019; Ruiz et al., 2017; Sikka, 2018; Snow, 1988). Therefore, the analysis and the comparison of these two theories showed the rational theory and the behavioral theory in economics (AL-UBAYDLI et al., 2021; Challoumis, 2019a, 2020c; Ginsburgh & Weber, 2020; Grove et al., 2020; Reeves et al., 2019; Waar-denburg et al., 2020). Hence, the identification of attributes of rational and behavioral theory is plausible through this economic analysis.
The rational economic theory
The Keynesian methodology is based on the rational model but there are some issues about the purity of the rationality of the methodology that is used by Keynes. The reason is that there are some controversies. These controversies are about the behavioral and the rational approach of the Keynes methodology (In this section the rational economic approach, and below is presented the behavioral one). Keynes uses as methodology the aspects of long-term expectations, conventions, and animal spirits. According to the Keynesian approach rationality is identified in assumptions (hypotheses). The animal spirits approach is defined by Dow and specifies that the long-term expectations are generated by the conventional optimizing procedure which uses rational criteria. It is not able to model a theory using irrational criteria. Also, Keynes uses the Aristotelian methodology. The interpretation of the Aristotelian method is that any approach to any issue could be made using a variety of starting points. Therefore, any hypothesis that could be made should lead to the same result. Also, there is Challoumis methodology, that is based multiple axiomatics method that uses feedback between the initial hypothesis and the final result. In that way, it is plausible to modify the initial hypothesis or the theory, or the mathematical model until to succeed an adequate result.
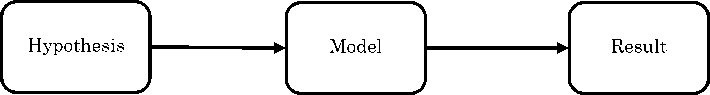
Figure 1: Aristotelian method
A method with feedback is the following one:
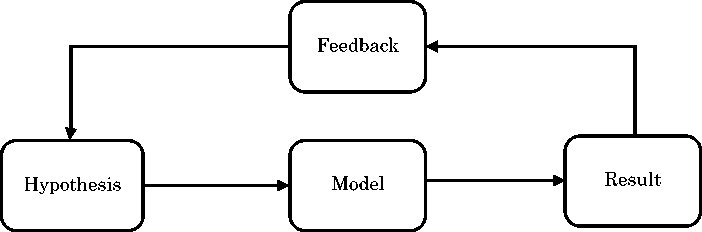
Figure 2: Challoumis method (MSA) (Challoumis, 2018d, 2018a, 2018b, 2019b, 2020c)
This methodology is based on a system of continuous interaction between the initial hypothesis and the final result. (Challoumis, 2019b, 2019c, 2020b, 2020a, 2020c, 2021b, 2021f, 2022). In this way, the maximum reliability of the control system is achieved, as a huge number of verifications can also be carried out by means of code. The theory of Cycle of Money, which achieves the control of GDP with marginal cases, that is, using differential equations, was based on MSA (Multiple Axiomatics Method) (Challoumis, 2019a, 2021d, 2023b, 2021a, 2021c, 2021b, 2021e,
Neoclassical economics methodology
Neoclassical economics use rational methodologies, as the assumptions for the confirmation of any theory. Therefore, the Neoclassical theory is based on the Cartesian/Euclidean approach. This means that the axioms are the basis of any analysis (Blekesaune, 2007; Challoumis, 2020c; Dollery & Worthington, 1996; Gocekli & Comertler, 2021; Guar-dino & Mettler, 2020;
-
• The first feature is known as atomism, or otherwise as reduc-tionism.
-
• The second feature is dualism. Dualism declares that always only one choice is plausible, for instance, true or false, logical, or illogical, etc., excluding with that way any middle ground.
Thence, the two elements to build a rational theorem are going through the atomism/reductionism, and the dualism. In mainstream economics, the Cartesian/Euclidian approach could be determined as the known theory of deductivism/positivism (Altman, 2012; Challoumis, 2019b; Driver, 2017; Hasselman & Stoker, 2017; Ruiz et al., 2017). Then, in mainstream economics, the key is the constant conjunctions that allow rational predictions.
Keynesian economics methodology, as behavioral theory
The Keynesian methodology as mentioned previously has different interpretations depending on the school of thought. Then, from the view of psychology could find application in the role of individuals. According to Winslow, Keynes rejected atomism and used the organic approach. Additionally, to Anna Carabelli, Keynes is based on the opinions and beliefs of economic agents (Challoumis, 2018c, 2020c, 2021b). Therefore, the theory of Keynes includes psychological aspects. Keynes himself uses psychological aspects to underline his theory (Carattini et al., 2018; Kamradt-Scott & McInnes, 2012; Montenegro Martínez et al., 2020; Onur Kulaç, 2017; Rizzo & Throsby, 2006; Sultana et al., 2020). Therefore, in the General Theory of Keynes are referred the phrases like, “psychological laws”, “psychological effect”, “psychological motives”, “psychological characteristics”, “psychological influences”, etc. Forasmuch as we have three basic views which show that Keynes used behavioral aspects in his approach:
-
• Individualism is avowed by Keynes, but the individualism per se is not ignored. Keynes seems to have been avowed the atomic individualism, but philosophically is an individualist in the interpretation of Paley’s dictum . There exist significant behavioral insights exist into Keynes’s work.
-
• The conventions are the second crucial element which shows that Keynes uses behavioral tools in his analysis. In situations of uncertainty, economic agents use conventions to determine their actions. But, in this case is identified that conventions are considered rational if they comply with the uncertainty in a successful manner.
-
• The third element is about the thoughts of Keynes about the behavioral approach. Thence, the comments of Keynes about psychology. Additionally, one more thing that reveals Keynes's behavioral approach is the
affirmations of psychology. Moreover, with the comparison of Keynes’s works is revealed that Keynes is affiliated with behavioral and experimental economics.
Hence, Keynesian theory uses elements from the psychological and behavioral approach, showing that there isn’t only rationalism in Keynes's analysis.
Heuristic and behavioral economics
Mainstream economics, as mentioned in the Neoclassical and Keynesian approach stands on the axioms, the Cartesian/Euclidian approach, the rational choice for the maximization of utility, the individualism, etc.. But are not included in the cognitive limitation, social preferences, the self-control problem, etc. to the rational approach. Neoclassical economics does not involve the choice of consumers in the behavioral explanation. Heuristics claim that by the Keynesian approach, the entrepreneur uses the information that is more representative of the situation, the information that is easy to retrieve, based on the availability of and the confidence of entrepreneurs. It is plausible to perceive human actions as systematic behaviors, not as random actions. This is the point of view where Keynes identified that perfect rationality is not possible, as the heuristic does because there are biases in the judgment subject to uncertainty (Altman, 2012; Challo-umis, 2021b; Gocekli & Comertler, 2021; Guardino & Mettler, 2020; Ruiz et al., 2017). Uncertainty is the key to the behavioral approach of Keynesian theory. In animal spirits, the basic view is the source of instability to the economic decisions, and more precise to the decisions about investments. Overconfidence is one more thing that analyzes the Keynesian approach and shows that has elements of behavioral economics. The degree of confidence determines long-term expectations. There is a divergence between the belief of how confident a person is and the accuracy of positivity of this person. This condition is the point for the application of behavioral economics.
Approximation is an attribute of rational modeling. The assumptions and the axioms used by rationalism are approximations. Two crucial characteristics of rational economics are that economics exists to the perfect competition and the perfect information. These are considered in behavioral economics as cases that should be remodified. There, is a series of things that show that rational economics omit economic parameters according to behavioral economics, which are the following:
-
• The field tests are elements that are important for the application of laboratory experiments. Experiments allow the study of alternative explanations. Therefore, study of economics using field tests allows the examination of the causes of the results, and not stay only in the assumptions without interpretation of their conjunctions, and how each theory leads to its result.
-
• The element of self-awareness is
crucial for the limitation of rationality. The reason for the limitation of rationality is that possibly economists think that they have the appropriate selfawareness, but the truth is that people under pressure or special conditions have a different level of self-awareness. The self is not a self it is an interaction of a series of mechanisms in complicated forms.
-
• The endogenous institutions which are firms’ investments and advertising reveal the changes of consumers by these firms. Therefore, behavioral economics gives an exegesis about the impact of these firms. Without a
behavioral approach, the understanding of the impact of these firms on consumers wouldn’t be able to identify.
-
• The missing psychology is one more aspect that is not included in rational economics. Psychology is inserted into rational economics because affects the choice models and the preferences. The impact of the anomalies on the rational choice appears as the result of a lack of examination of the causes of the results. Moreover, one thing that is also included in behavioral economics is the limited attention. Limited attention affects rational decisions. This is the reason why advertising and organizational structure are used to stimulate attention appropriately and manipulate decision-making.
-
• Neuroscience tries to go deeper into the causes of decisions. The interpretation of this approach is that the study of the brain allows the understanding of the preferences from a neurological approach. Neuroscience reminds us that the mind is extremely complex and gives an exegesis of why we make concrete decisions, indexing the right level of decision-making.
From the previous bullets of behavioral elements of economics, we conclude that all of them are trying to give the exegesis of the results of the economic analysis. On the other hand, mainstream economics are based on the axiomatics and the Car-tesian/Euclidean approach to declare the validation of any economic theory.
Conclusions
There are special characteristics between rational and behavioral economics and differences between them. Thence, rational economics estimate the confirmation of the assumptions that rely on the axiomatics. On the other hand, behavioral economics uses psychology and laboratories to define the decision-making process of the consumers. Then, the approaches between the two cases are different. But both of them have the same aim, to declare each theoretical model, in their way. Their economic tools are not the same. The assumptions and the axioms are easier to apply. At the same time rational economics, estimates in two points the assumption and the confirmation. Then, the assumption has a concrete point of starting from the Euclidean approach. But both of them have a target to confirm the initial point of view (the assumption). Behavioral economics aims at the middle step, meaning the procedure, and not so much at the initial and final point (assumption and confirmation accordingly). Therefore, the target remains the same for rational and behavioral economics, but the economic tools are different.


