Разметка стилобата Парфенона и других дорических храмов Аттики
Автор: Щетников Андрей Иванович
Журнал: Schole. Философское антиковедение и классическая традиция @classics-nsu-schole
Статья в выпуске: 1 т.10, 2016 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Анализируя результаты обмеров стилобата Парфенона с помощью алгоритма Евклида для поиска общей меры двух величин, мы пришли к выводу о том, что этот стилобат размечался с помощью фута длиной 0,286 м. Такой фут укладывается 15 раз в межосевом промежутке рядовых колонн, 108 раз в ширине и 243 раза в длине стилобата, что даёт отношение ширины к длине, в точности равное 4 к 9. Такой же фут длиной 0,286 м мы извлекли из анализа размеров Гефестейона. Однако приложение такого же метода анализа к другим дорическим храмам Аттики эпохи Перикла дало для каждого из этих храмов свою собственную длину фута, отличную от всех остальных.
Греческая археология, античные храмы, индуктивная метрология
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/147103437
IDR: 147103437
Текст научной статьи Разметка стилобата Парфенона и других дорических храмов Аттики
ВведениеОткрытие мер длины из памятников архитектуры
Меры длины с древнейших времён привязывались к размерам человеческого тела, о чём говорят их названия — пядь, фут, локоть, шаг, сажень. Такие меры каждый человек «всегда носил с собой» в самом прямом смысле. Однако локти у разных людей хотя и не сильно, но всё же различаются по длине. Поэтому предполагается, что каждый культурный народ в какое-то время своей истории обзаводился своими стандартными узаконенными мерами длины, веса и объёма.
ΣΧΟΛΗ Vol. 10. 1 (2016)
Некоторые мерные линейки сохранились до наших дней с глубокой древности. Таков египетский «фараонов локоть», более полутора десятков экземпляров которого найдено в различных гробницах — все эти изготовленные из дерева мерные локти имеют длину 52,5 ± 0,2 см. Однако от большинства древних культур никаких вещественных мер длины до нас не дошло. Отсюда возникает желание восстановить эти меры через размеры предметов, изготовленных с их помощью. К таким предметам относятся в первую очередь памятники древней архитектуры.
Систематическое изложение идей индуктивной метрологии было осуществлено знаменитым английским археологом Уильямом Мэтью Флиндерсом Питри (1853–1942). В молодости он вместе с отцом участвовал в обмерах Стоунхенджа и уже тогда пришёл к мысли о том, что такие обмеры должны проводиться по правилам, принятым для аналогичных процедур в естественных науках, с указанием методики и погрешностей измерений. Свои идеи он изложил в книге Inductive metrology, or the recovery of ancient measures from the monuments, изданной в 1877 году.
Из современной литературы по индуктивной метрологии прежде всего следует указать статьи Coulton (1974 и 1975), посвящённые методологическим основаниям этого подхода, с привязкой к храмам античной Греции. Статистические подходы к извлечению древних мер из памятников архитектуры обсуждаются в книге Pakkanen 2013.
Принципы индуктивной метрологии
Когда мы работаем с обмерами древнего памятника архитектуры, нас в конечном счёте интересуют не таблицы и чертежи, в которые сведены эти обмеры, а замысел архитектора, воплощённый в постройке. Тем самым мы исходно предполагаем, что такой замысел у архитектора имелся, и он был запечатлён в чертежах, масштабных моделях и плазах, с указанием соответствующих размеров, которыми должны были руководствоваться организаторы и исполнители строительных работ.
В основе метрологических изысканий лежит предположение о том, что во всех или хотя бы в некоторых конструктивно значимых частях постройки в исходном проекте и при строительстве использовалась одна и та же мера длины, которая укладывалась в этих частях нацело либо в каких-то дробных отношениях, выражаемых небольшими целыми числами. В этих изысканиях мы ищем идеальные пропорции частей, выражаемые отношениями целых чисел, и вещественную длину модуля, на основе которого была осуществлена постройка.
Однако к какой бы точности воспроизведения базовых размеров не стремились строители, в любом случае эта разметка велась с некоторой погрешностью. Некоторая погрешность содержится также в результатах обмеров, произведённых археологами. Неизбежное наличие этой погрешности мы тоже должны учитывать в своём анализе.
Большинство древних памятников архитектуры дошло до наших дней или с заметными повреждениями, или вообще в развалинах. В этом случае уже выполнение самих обмеров и установление точных базовых размеров оказывается весьма трудной задачей, предполагающей мысленную реконструкцию замысла. И отнюдь не всегда эту задачу удаётся решить с требуемой для последующего анализа точностью, о чём также не следует забывать.
Разметка стилобата дорических храмовПринципы разметки стилобата
Периптер — это античный храм, со всех четырёх сторон окружённый колоннадой, так называемым перистасисом . Важная особенность дорического перистасиса состоит в том, что в нём проход между угловой и двумя соседними с ней рядовыми колоннами обычно делается меньше проходов между рядовыми колоннами. Это угловое сокращение нужно для того, чтобы капители колонн правильно сопрягались с чередующимися элементами фриза — триглифами и метопами. Кроме того, в некоторых дорических храмах угловые колонны имеют чуть больший диаметр по сравнению с рядовыми, для исправления оптических иллюзий, утончающих угловую колонну.
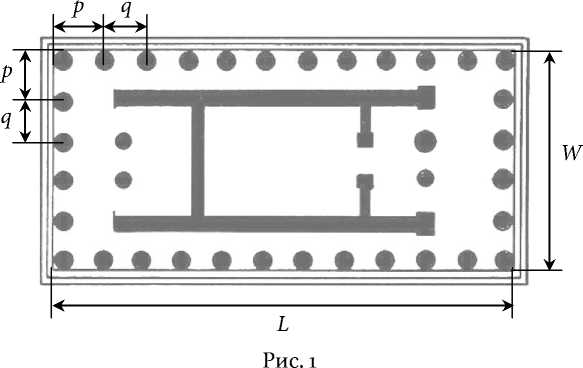
Верхняя ступенька ступенчатого цоколя, на котором стоит храм, называется стилобатом. Пусть в храме стоит NW колонн по фасадам и NL колонн по бокам, включая угловые. Для дальнейших расчётов существенным будет предположение о том, что разметочные шаги на фасадах и по бокам храма являются одинаковыми. Некоторые дорические храмы имеют неодинаковые шаги рядовых колонн на боках и на фасадах (см. Coulton 1974, 64); мы такие храмы в этой статье рассматривать не будем. Обозначим продольное расстояние от угла стилобата до оси первой рядовой колонны через p, a расстояние между осями рядовых колонн через q (рис. 1).
N W колонн, стоящих на фасаде стилобата, образуют N W – 1 межосевой промежуток, из которых NW – 3 промежутка имеют длину q ; аналогично и для боковой стороны. Выразим ширину стилобата W и его длину L через шаги p и q :
W = ( N w - 3)- q + 2 p, (1)
L = ( N l — a)- q + 2 p . (2)
При таком описании разметки стилобата нам не нужно знать ни диаметров колонн, ни других размеров, входящих в общую систему пропорций храма. Здесь положение угловой колонны не задано, но оно определяется её диаметром. При этом по заданным шагам p и q можно рассчитать размеры стилобата L и W . И обратно, зная размеры стилобата, мы в принципе можем рассчитать шаги p и q и сопоставить их между собой.1
Гипотеза и метод расчёта
Базовая гипотеза, на которой мы будем основываться ниже, состоит в том, что оба шага p и q всегда содержат целое число модульных единиц. Отсюда следует, что как размеры стилобата, так и разность шагов d = p – q всегда измеряются целым числом единиц.
Здесь нужно сделать важное замечание. Понятно, что каковы бы ни были шаги p и q , нам всегда удастся подобрать достаточно маленькую мерку, которая с хорошей точностью уложится в p и q нацело. Но такой вариант, когда эта мерка, к примеру, будет иметь размер около 2 см и при этом 215 раз уложится в q и 243 раза уложится в p , нам не подходит. Мы ищем достаточно большую меру, которая нацело уложится в рядовом шаге колонн q , в относительно небольшой разности шагов d , и тем самым в прочих разметочных расстояниях p , W , L .
Теперь обсудим дальнейшую программу действий. Пусть шаги p и q уже известны из обмеров; найдём их разность d. Мы предполагаем, что искомый модуль, которым производилась разметка стилобата, нацело укладывается в шаге q. Если разность d с хорошей точностью укладывается в q, то она и является искомой общей мерой p и q, вымеряющей также стороны стилобата. Будем считать, что «хорошая точность» достигается, если разность между q и nd составляет меньше 0,2d.
Если же остаток слишком велик, надо посмотреть, сколько раз он укладывается в d , и если он уложится в d с хорошей точностью целое число раз, надо принять этот остаток за разметочный модуль и посчитать, сколько раз он уложился в шагах p и q , а затем и в размерах стилобата.
Процедура, которую мы здесь описываем, в математике называется алгоритмом Евклида для поиска наибольшей общей меры двух величин (см. Щетников 2003). В случае, когда два отрезка заданы с абсолютной точностью, они могут не иметь общей меры, как сторона и диагональ квадрата, и алгоритм Евклида никогда не придёт к завершению. Но в случае, когда два отрезка отложены и измерены с некоторой погрешностью, нет смысла искать меру меньшую, чем эта погрешность.
Разметка стилобата Парфенона«Стофутовый Парфенон»
Из античных источников мы знаем, что храм Афины, стоявший на Акрополе до греко-персидских войн, назывался ἑκατόµπεδον — стофутовый. Этот же эпитет был перенесён и на новый Парфенон. Примером может служить фраза Плутарха ( Перикл 13), который говорит, что «стофутовый Парфенон сооружали Калликрат и Иктин».
Каким бы ни был фут, который применялся при этом строительстве, расстояние в 100 футов примерно равно 30 метрам. Рассматривая результаты обмеров Парфенона, можно заметить, что приблизительно стофутовой является его ширина, измеренная по стилобату — верхней ступеньке основания, на которую опираются опоясывающая храм колоннада (30,9 м). Впрочем, примерно такую же длину имеет и целла — находящаяся внутри храма зала, в которой стояла статуя Афины (29,9 м).
Зная, что ширина стилобата Парфенона примерно равна 100 футам, англичане Джеймс Стюарт и Николас Ревет в опубликованной в 1762 году книге The Antiquities of Athens and Other Monuments of Greece поступили очень просто, разделив эту ширину на 100 и объявив полученный отрезок аттическим футом. Это же рассуждение повторили Hultch 1882 и Penrose 1888. С тех пор утверждение «ширина стилобата Парфенона равна 100 аттических футам» кочует из одной публикации в другую. При этом мало кто помнит о том, что «аттический фут в 30,9 см» — это условная мера длины, существование которой не подтверждено никакими вещественными свидетельствами.
Однако ряд античных либо восходящих к античности источников прямо указывает на то, что Парфенон назывался стофутовым только по переносу имени. Грамматик Гарпократион (II в. н. э.) в своём лексиконе пишет так: «Парфенон называется стофутовым за свою красоту и соразмерность, а не за свои размеры». Византийская энциклопедия, известная как Etimologicum Magnum , даёт слову EKaTcpneSov такое толкование: «Храм в Афинах, имеющий по сто футов на каждой стороне. По нему же называется и Парфенон».
От размеров стилобата — к разметочному модулю
Стилобат Парфенона имеет расстановку колонн 8 х 17 и размеры 30,89 х 69,54 м (Penrose 1888, Balanos 1938, OpXavSog 1978). Эти размеры с высокой точностью соотносятся между собой как 4 : 9, поскольку 2% • 30,89 = 69,50.
Обмеры шагов колонн приводят к средним значениям q = 4,29 м, p = 4,72 м. Разность этих шагов d = 0,43 м укладывается в шаге q с хорошей точностью 10 раз. Тем самым мы можем предположить — и это предположение является основным в настоящей работе, — что при разметке стилобата была использована мера длины, приблизительно равная 0,43 м. Эту меру естественно назвать локтем . Длина и ширина стилобата размечаются в таких локтях как
11 + 14 • 10 + 11 = 162,
11 + 5 • 10 + 11 = 72.
Отношение целых чисел 162 : 72 изящным образом сокращается до 9 : 4, что служит ещё одним косвенным подтверждением правильности наших рассуждений.2
Уточним длину локтя, разделив обмерный полупериметр стилобата, выраженный в метрах, на полупериметр, выраженный в целочисленных локтях:
(69,54 + 30,89): (162 + 72) = 0,429 м.
Витрувий в Десяти книгах об архитектуре в качестве основной единицы разметки везде приводит футы, составляющие % локтя; в футах составля- лись и дошедшие до нас античные сметы на проведение строительных работ. Если основной единицей разметки стилобата у строителей Парфенона служил не локоть, а фут, то длина этого фута была равна % • 0,429 = 0,286 м.3 Это вполне себе нормальная стопа, 44 размер обуви. Выраженные в этих футах, размеры стилобата составляют 243 х 108 футов с разметкой
16% + 14 • 15 + 16% = 243, 16% + 5 • 15 + 16% = 108.
Разметка плит и внутренних портиков
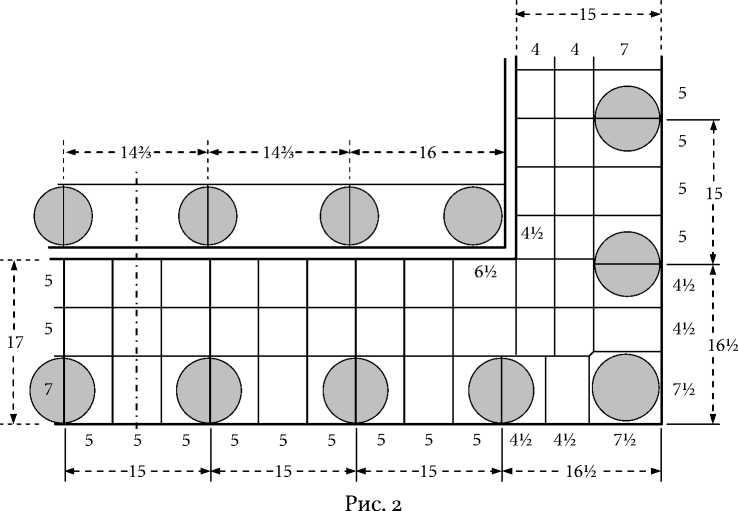
На шаге q = 15 футов укладываются три плиты внешнего обрамления стилобата. Продольный размер одной такой плиты равен 5 футам. Эти плиты составляются в обрамляющую стилобат ленту шириной 2,01 м. Фут укладывается в этой ширине с хорошей точностью 7 раз, поскольку 7 • 0,286 = 2,00 м. Ширина ступеней стилобата по фасаду равна 4,84 м, с боковой стороны — 4,26 м. Эти размеры также близки к размерам, кратным одному футу, поскольку 17 • 0,286 = 4,86 м, 15 • 0,286 = 4,29 м. Полная идеализированная схема раскладки плит стилобата показана на рис. 2; здесь все размеры приведены к целому или полуцелому числу футов.4
За каждым из двух фасадов Парфенона находится внутренний портик из шести колонн, поднятый над уровнем стилобата на две ступени. Колонны стоят на второй ступени, ширина которой равна 21,72 м, что с хорошей точностью равно 76 футам, поскольку 76 • 0,286 = 21,74 м. Угловой шаг колонн портика составляет 4,57 м, что с хорошей точностью составляет 16 футов: 16 • 0,286 = 4,58 м. Тогда рядовой шаг колонн портика 4,19 м будет равен (76 -2 • 16): з = 14% фута, что также показано на рис. 2.
Другие дорические храмы Аттики
Принцип разметки стилобата дорического храма, который мы обсуждали выше, формулируется так: разметочная мера нацело укладывается как в рядовом, так и в угловом шаге колонн, поэтому она укладывается нацело в длине и ширине стилобата. Попробуем подойти с этим принципом к другим дорическим храмам. Если его удастся обнаружить в нескольких храмах, это существенно прибавит нам уверенности в том, что строители этих храмов руководствовались этим принципом на самом деле.5 Естественно начать с храмов, построенных в Аттике в то же самое время, что и Парфенон.
Храм Гефеста в Афинах
Это хорошо сохранившийся храм, стоящий на агоре в Афинах. Его расстановка колонн 6 х 13 - одна из самых распространённых в дорическом пери- стиле. Размеры стилобата Гефестейона равны 13,71 х 31,77 м (Dinsmoor 1941, Plommer 1950).
Расчётные шаги колонн q = 2,58 м, p = 2,98 м хорошо согласуются с обмерными значениями 2,58 и 3,01 м. Разность обмерных значений равна 0,43 м — здесь опознаётся уже известный нам локоть, выявленный из обмеров Парфенона. Он с хорошей точностью укладывается 6 раз в рядовом шаге, поскольку 6 • 0,43 = 2,58 м, что даёт разметку стилобата
7 + 10 • 6 + 7 = 74, 7 + 3 • 6 + 7 = 32-
Отношение шагов 7 : 6 отличается от отношения 11 : 10, установленного для Парфенона. В футах это даёт разметку стилобата
10% + 10 • 9 + 10% = 111, 10% + 3 • 9 + 10% = 48.
Уточним величину фута Гефестейона с помощью соотношения
(31,77 + 13,71): (111 + 48) = 0,286 м-
Мы убедились, что в разметке стилобата Гефестейона использовался тот же самый фут, что и в разметке стилобата Парфенона . Единство места и времени служит веским основанием, чтобы сделать вывод о том, что этот результат не является случайным совпадением.
Храм Ареса в Афинах
Этот дорический храм, построенный в северной части афинской агоры ок. 440 г. до н. э., был разобран в конце I в. до н. э., так что от него сохранился только каменный фундамент, вскрытый раскопками, а также отдельные мраморные детали. Dinsmoor (1940) показал, что храм имел такую же расстановку колонн 6 х 13, как и Гефестейон, и вообще был с ним чрезвычайно схожим, хотя и имел несколько большие размеры. На основании данных раскопок он рассчитал шаги колонн p = 3,12 и q = 2,69 м, а также размеры стилобата 14,32 х 33,15 м.
Отношение всех размеров храма Ареса к соответствующим размерам храма Гефеста является практически одинаковым: 33,15 : 31,78 = 1,043; 14,32 : 13,71 = 1,044; 3,12 : 2,98 = 1,047; 2,69 : 2,58 = 1,043.6 Поэтому здесь можно предпо- лагать наличие той же самой разметочной схемы 111 : 48. Но тогда приходится сделать вывод о том, что при разметке храма Ареса применялся другой фут, увеличенный по сравнению с футом Гефестейона; длина этого фута рассчитывается из соотношения
(33,15 + 14,32): (111 + 48) = 0,299 м.
Храм Посейдона на мысе Сунион
Храм Посейдона на мысе Сунион, построенный в эпоху Перикла, до наших дней дошёл сильно повреждённым. По его фасадам стояло 6 колонн. Поскольку часть основания храма полностью разобрана, подсчитать число колонн по боковым сторонам и измерить длину стилобата напрямую оказывается невозможным. Ниже мы воспользуемся результатами обмеров и расчетов из статьи Plommer 1950, в которой приводится ряд доводов за то, что по боковым сторонам в храме Посейдона стояло по 13 колонн.
Будем исходить из рядового шага 2,52 м, установленного прямым обмером, и рассчитанного Plommer’ом углового шага 2,93 м. Разность этих шагов, равная 0,41 м, по своей величине предположительно является «локтем храма Посейдона». Она с хорошей точностью 6 раз укладывается в рядовом шаге, поскольку 6 • 0,41 = 2,46 м, так что мы предположительно опять имеем дело с отношением шагов 7 : 6.
Предполагая для храма Посейдона ту же самую схему разметки 111 : 48, что и в храмах Гефеста и Ареса, рассчитаем длину фута через ширину стилобата 13,40 м:
13,40 : 48 = 0,279 м.
Для проверки сосчитаем произведения 9 • 0,279 = 2,51 м, 10% • 0,279 = 2,93 м, что прекрасно согласуется с результатами обмеров. Отсюда длина стилобата, если бы он сохранился целиком, была бы равна 111 • 0,279 = 30,97 м.7
Храм Немезиды в Рамнунте
Это ещё один дорический храм, построенный в Аттике в ту же самую эпоху и дошедший до наших дней в развалинах. Он имеет расстановку колонн 6 х 12. Размеры стилобата, приведённые у разных авторов, несколько различаются: Гэнди, проводивший измерения в 1813 году, когда стилобат ещё был целым, указывает размеры 10,02 х 21,46 м (пересчитано из английской си- стемы мер в статье Miles 1989); сам Miles восстанавливает размеры 9,96 х 21,43 м- Этот храм является малым — он примерно в полтора раза меньше по своим размерам, нежели храмы Гефеста, Ареса и Посейдона.
В ситуации неточного обмера стилобата нам будет удобнее исходить из измеренных рядового шага 1,90 м и углового шага 2,17 м (Miles 1989). Разность этих шагов равна 0,27 м. Предположим, что это как раз один фут разметки. В таком случае сами шаги разметки с хорошей точностью оказываются равными 7 и 8 футов, поскольку 7 • 0,27 = 1,89 м, 8 • 0,27 = 2,16 м. Длина и ширина стилобата размечаются в футах как
8 + 9 • 7 + 8 = 79, 8 + 3 • 7 + 8 = 37-
Теперь мы можем уточнить длину фута для этого храма:
(2,17 + 1,89): (8 + 7) = 0,271 м.
При такой длине фута размеры стилобата должны быть равны 10,01 х 21,38 м, что вполне согласуется с результатами обмеров, указанными выше.
Афинский храм Аполлона на Делосе
Остров Делос находился в непосредственной сфере политического и культурного влияния Афин, ежегодно отправлявших сюда своё священное посольство. Храм Аполлона, построенный на Делосе афинянами ок. 420 до н. э., до наших дней дошёл в развалинах. Храм выполнен по схеме дорического амфипростиля с 6 колоннами на переднем и заднем фасадах; по бокам колонн нет. Ширина стилобата 9,69 м, шаг q между рядовыми колоннами равен 1,83 м (Jones 2001), и на каждый из двух угловых шагов p остаётся 2,10 м. Разница шагов составляет 0,27 м, это предположительный модуль (фут) постройки. Он с хорошей точностью укладывается 7 раз в шаге q , поскольку 7 • 0,27 = 1,89 м, так что разметка колонн на фасаде произведена по схеме
8 + 3 • 7 + 8 = 37-
Уточнённое значение фута равно 9,69 : 37 = 0,262 м, при этом 7 • 0,262 = 1,83 м. Обмерная длина стилобата составляет 17,01 м, что равно 65 футам: 65 • 0,262 = 17,03 м.
Разметка фасада здесь произведена в точности так же, как в храме Немезиды, но разметочный фут взят чуть более коротким, 0,262 м против 0,271 м, поэтому и ширина фасада получилась чуть меньшей, 9,69 м против 10,01 м.
Заключение
На примере нескольких храмов, построенных архитекторами одного времени и одного круга, мы видим, что величина фута, которым размечался стилобат, не воспроизводится от храма к храму, но каждый раз является новой. Исключения бывают, как в случае Парфенона и Гефестейона, но они только подтверждают общее правило. И правдоподобным выглядит предположение о том, что разметочный фут каждый раз изготавливался заново непосредственно перед началом строительства.8
Приложение: немного математики
Исходя из формул (1) и (2), выразим шаги q и p через размеры стилобата:
_ L - W
q = N - N ’ LW
( N l - 3) W - ( N w - 3) L 2( N l - N w )
Обозначим через A число, показывающее, сколько раз разность d = p – q укладывается в рядовом шаге q . Исходя из (3) и (4), мы получаем, что
A = q = 2( L - W )
d ( N l - 1) W - ( N w - 1) L "
Размеры стилобата L и W имеют некоторую погрешность, которая складывается из неточностей исходной разметки и неточностей последующего обмера. Для примера рассмотрим небольшой дорический периптер с расстановкой колонн 6 x 11 и с размерами стилобата 10,62 х 20,67 м- Формула (3) показывает, что погрешности в 10 см в измерении каждого из размеров L и W соответствует погрешность в 2 см в расчёте рядового шага q .
Формула (4) заметно более чувствительна к погрешностям измерений сторон стилобата. Здесь погрешности в 10 см в измерении каждого из размеров L и W соответствуют погрешности в 3 и 8 см в расчёте шага p. При этом формула (5) оказывается ещё более чувствительной к погрешностям измерения стилобата. Для данных нашего примера расчётное значение A равно 7,05. И мы можем сказать: «Наверное, в этом храме шаги p и q относятся между собой как 8 : 7». Но допустим теперь, что измеренное значение длины стилобата L изменится всего на +3 см, с 20,67 на 20,70 м. Тогда расчётное отношение A изменится с 7,05 на 7,46, и мы будем спрашивать себя, не надо ли приблизить A целочисленным отношением 15 : 2. Точно так же, изменение ширины стилобата W всего на +2 см с 10,62 до 10,64 м приведёт к изменению расчётного отношения A с 7,05 на 7,60, и мы опять не сможем с уверенностью утверждать, что шаги p и q относятся между собой как 8 : 7.
Список литературы Разметка стилобата Парфенона и других дорических храмов Аттики
- Витрувий. Об архитектуре. Пер. Ф. А. Петровского. М.: Всесоюзная академия архитектуры, 1936 (репр. Едиториал УРСС, 2003).
- Хазанов, Д. Б. (1958) “Модуль и масштаб в греческой архитектуре,” Вопросы теории архитектурной композиции. Москва: Госостройиздат, 5-56.
- Щетников, А. И. (2003) Алгоритм Евклида и непрерывные дроби. Новосибирск: АНТ.
- Balanos, N. M. (1938) Les monuments de l’Acropole. Relèvement et conservation. Paris.
- Bankel, H. (1984) “Das Fuß maß des Parthenon,” Parthenon-Kongreß Basel, 4-8 April 1982. Mainz: von Zabern.
- Brigo, R. (2008) “La matematica e l’architettura del Partenone,” BABesch 83, 99-105.
- Coulton, J. J. (1974) “Towards understanding Doric design: the stylobate and intercolumniations,” The Annual of the British School at Athens 69, 61-86.
- Coulton, J. J. (1975) “Towards understanding Greek temple design: general considerations,” The Annual of the British School at Athens 70, 59-99.
- Coulton, J. J. (1977) Ancient Greek architects at work: Problems of structure and design. Ithaca: Cornell UP.
- Coulton, J. J. (1984) “The Parthenon and Periclean doric,” Parthenon-Kongreß Basel, 4-8 April 1982. Mainz: von Zabern, 40-44.
- Coulton, J. J. (1989) “Modules and measurements in ancient design and modern scholarship,” Munus non ingratum. Proceedings of the International Symposium on Vitruvius’ De architectura and the Hellenistic and Republican Architecture (Leiden 1987). Leiden, 85-89.
- Dinsmoor, W. B. (1940) “The temple of Ares at Athens,” Hesperia 9, 1-52.
- Dinsmoor, W. B. (1941) “Observations on the Hephaisteion,” Hesperia, Suppl., 1-171.
- Dinsmoor, W. B. (1950) The architecture of Ancient Greece. NY: Norton & Co.
- Dinsmoor, W. B. (1961) “The basis of Greek temple design: Asia Minor, Greece, Italy,” Atti del settimo Congresso Internationale di archeologia Classica, Roma-Napoli 1959, Rome, 355-368.
- D’Ooge, M. L. (1908) The Acropolis of Athens. NY, London: Macmillan.
- Dörpfeld, W. (1884) “Der Tempel von Sunion,” Mittheilungen des Deutschen Archaologischen Instituts, Athenische Abteilung 9, 324-337.
- Dörpfeld, W. (1890) “Metrologische Beiträge V. Das äginätisch-attische Maßsystem,” Mittheilungen des Deutschen Archaologischen Instituts, Athenische Abteilung 15, 167-187.
- Hultsch, F. (1882) Griechische und römische Metrologie. Berlin (repr. Graz 1971). Jones, M. W. (2001) “Doric measure and architectural design 2: A modular reading of the classical temple,” American Journal of Archaeology 105, 675-713.
- Koldewey, R., Puchstein O. (1899) Griechische Tempel in Unteritalien und Sicilien. Berlin.
- Koenigs, W. (1979) “Zum Entwurf dorischer Hallen,” Istanbuler Mitteilungen 29, 209-237.
- Korres, M. (1994) “Der Plan des Parthenon,” Mitteilungen des Deutschen Archäologischen Instituts, Athenische Abteilung 109, 53-120.
- Miles, M. M. (1989) “A reconstruction of the temple of Nemesis at Rhamnous,” Hesperia 58, 137-249.
- McAllister, M. H. (1959) “The temple of Ares at Athens,” Hesperia 28, 1-64.
- Naredi-Rainer, P. (1982) Architektur und Harmonie: Zahl, Mass und Proportion in der abendländischen Baukunst. Köln: DuMonte.
- Ορλάνδος, Α. (1978) Η αρχιτεκτονική του Παρθενώνος. Αθήναι.
- Pakkanen, J. (2013) Classical Greek architectural design: a quantitative approach. Foundation of the Finnish Institute at Athens.
- Penrose, F. C. (1888) An investigation of the principles of Athenian architecture, or the results of a recent survey conducted chiefly with reference to the optical refinements exhibited in the construction of the ancient buildings at Athens. London.
- Petrie, W. M. F. (1877) Inductive metrology, or the recovery of ancient measures from the monuments. Sounders (repr. Cambridge UP, 2013)
- Plommer, W. H. (1950) “Three Attic temples,” The Annual of the British School at Athens 45, 66-112.
- Robertson, D. S. (1929) Greek and Roman architecture. Cambridge UP.
- Schneider, L., Höcker, C. (1990) Die Akropolis von Athen: antikes Heiligtum und modernes Reiseziel. Köln: DuMont.
- Sonntagbauer, W. (1998) “Zum Grundriß des Parthenon,” Jahreshefte des Österreichischen Archäologischen Institutes 67, 133-169.
- Waele, J. de (1998) “Der klassische Tempel in Athen: Hephaisteion und Poseidontempel,” BABesch 73, 83-94.
- Waele, J. de (2001) “Planänderung oder Korrektur am Parthenon?” Belgian Archaeology in a European Setting I, Leuven UP, 99-112.
- Wesenberg, B. (1995) “Die Metrologie der griechischen Architektur: Probleme interdisziplinärer Forschung,” Ordo et mensura III: 3. Internationaler Interdisziplinärer Kongress für Historische Metrologie vom 17. bis 21. November 1993 im Städtischen Museum Simeonstift Trier, Scripta Mercaturae Verlag, 199-222. Zwarte, R. de (1996) “Der ursprungliche Entwurf fur das Hephaisteion in Athen. Eine modulare architektonische Komposition des 5. Jhs. v. Chr.,” Bulletin Antieke Beschaving 71, 95-102.


