Разрушение биопленок коагулазонегативных стафилококков катионным пептидом варнерином
Автор: Коробов Владимир Павлович, Лемкина Лариса Марковна, Филатова Любовь Борисовна, Полюдова Татьяна Вячеславовна
Журнал: Известия Самарского научного центра Российской академии наук @izvestiya-ssc
Рубрика: Биотехнология
Статья в выпуске: 5-3 т.13, 2011 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Показано, что низкомолекулярный катионный пептид варнерин обладает способностью подавлять формирование биопленок S.epidermidis 33, при этом его действующие концентрации совпадают с таковыми для бактерий планктонной культуры. При более высоких концентрациях пептид способен разрушать и сформировавшиеся в течение 24 ч биопленки.
Низкомолекулярный пептид варнерин, биопленка, стафилококки
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/148200432
IDR: 148200432 | УДК: 579.262:
Текст научной статьи Разрушение биопленок коагулазонегативных стафилококков катионным пептидом варнерином
В лунки планшета вносили по 100 мкл исследуемого стерильного препарата низкомолекулярного пептида варнерина и готовили ряд последовательных двукратных разведений, после чего в каждую лунку добавляли по 10 мкл суспензии клеток S.epidermidis 33, содержащей в 1 мл 1.5-2.0х106 колониеобразующих единиц (КОЕ/мл). Планшеты инкубировали в течение 16-18 ч при 37оС. МПК варнерина определяли путем сравнения со значением МПК референс-образца с известным количеством пептида.
Для исследования влияния пептида варнерина на формирование биопленок в планшеты для ИФА вносили одновременно суспензию клеток индикаторной культуры (107 КОЕ/мл) и варнерин в концентрациях от 0.25 до 256 мкг/мл. После инкубирования при 37оС в течение 24 ч планктонные клетки из лунок удаляли осторожным пипетированием, планшеты трижды промывали 10 мМ фосфатным буфером (рН 7.2) и окрашивали тетразолием MTS [3-(4,5-диметилтиазол-2-ил)-5-(3-карбоксиметокси-фенил)-2-(4-сульфофенил)-2Н-тетразолий, внутренняя соль] для определения количества живых клеток с использованием системы Cell Proliferation Assay (Promega, США) в соответствии с инструкцией фирмы. Детекцию интенсивности окраски проводили на микропланшетном спектрофотометре Benchmark Plus (Bio-Rad, США) при длине волны 490 нм.
Общую биомассу сформировавшихся биопленок определяли окрашиванием 0.1% раствором генци-анвиолета в течение 20 мин, после однократной отмывки не связавшегося красителя 10 мМ фосфатным буфером планшеты высушивали. Экстракцию связавшегося с биопленками красителя проводили этанолом. Количественную оценку этанольных экстрактов осуществляли на микропланшет-ном спектрофотометре при длине волны 570 нм.
Для получения больших количеств биопленок применяли полистироловые вентилируемые чашки Петри (Meus, Piove di Sacco, Италия). Использовали среду LB, содержащую 107 КОЕ/мл бактерий S.epidermidis 33 с логарифмической фазы роста в качестве инокулума. Чашки выдерживали в термостате при 37оС в течение 24 ч.
Для изучения действия низкомолекулярного катионного пептида варнерина на сформированные в течение 24 ч биопленки в контрольные чашки вносили 10 мМ Трис-HCl (рН 7.2), в опытные – препарат варнерина в указанном выше буфере и инкубировали в течение 4 ч и 24 ч. После окончания инкубации среду удаляли и весь объем ее подвергали центрифугированию при 3000g в течение 15 мин. Супернатант использовали для анализа спектра аутолизинов в ренатурируемом ПААГе [17].
Оставшиеся после инкубации с варнерином и буфером (контроль) биопленки для оценки их биомассы окрашивали генцианвиолетом, а для определения количества живых клеток использовали Cell Proliferation Assay, как указано выше.
Для сравнения действия низкомолекулярного пептида варнерина на биопленки и клетки планктонной культуры S.epidermidis 33 последние выращивали на среде LB при 37оС на шейкере Сertomat (Sartorius, Германия) до середины логарифмической фазы роста. Бактерии осаждали (10000 g, 10 мин) на центрифуге 3K30 (“Sigma”, Германия), дважды отмывали в том же режиме 0.01 М Трис - HCl буфером (рН 7.2) и ресуспендировали в буфере до плотности OD 600 = 0.5, используя для измерений кюветы с длиной оптического пути 1 см. Для активации неспецифических аутолитических процессов к препаратам бактерий добавляли низкомолекулярный пептид варнерин. Инкубацию проб проводили на шейкере Sertomat (“Sartorius”, Германия) при 150 об/мин и 37°С в течение 4 ч с измерением оптической плотности ежечасно на спектрофотометре PD-303 (APEL, Япония) при 600 нм. Для получения растворимой части бактериальных препаратов аликвоты сред культивирования центрифугировали, как указано выше.
Полученные супернатанты опытных и контрольных проб планктонных клеток и биопленок концентрировали на центрифужном концентраторе (Eppendorf, США) в 20 раз для биопленок и в 5 раз для планктонной культуры. В концентратах определяли содержание белка [4] и анализировали содержание в них бактериолитических компонентов, используя ренатурируемый электрофорез в 9% ПААГе, содержащем убитые автоклавированием (0.5 атм, 30 мин) и отмытые дистиллированной водой бактерии S.epidermidis 33 (1.6 мг сухого ве-са/мл геля).
После окончания процедуры разделения гели отмывали дистиллированной водой в течение 30 мин, помещали в ренатурирующий буфер (50 мМ MES-NaOH, pH 6.0 и тритон Х-100 0.1%) и инкубировали в течение 16 ч при 37°С. После ренатура-ции гели промывали водой, окрашивали 0.1% метиленовым синим в 0.01% КОН в течение 1 ч и отмывали от красителя водой до проявления прозрачных зон лизиса импрегнированных в гель бактериальных клеток на синем фоне связавших краситель не лизированных бактерий.
РЕЗУЛЬТАТЫ И ИХ ОБСУЖДЕНИЕ
В предварительных экспериментах было проведено сравнение антибактериального действия низкомолекулярного катионного пептида варнерина на клетки планктонной культуры S.epidermidis 33 и образованную ими в течение 24 ч биопленку.
Как видно из рис. 1, варнерин в концентрации 4 мкг/мл проявляет выраженное бактериолитическое действие в отношении планктонных клеток индикаторной культуры уже через 2 ч и лишь через 24 ч снижает количество биомассы и живых клеток в биопленках при одновременном внесении пептида и инокулума на 38 и 36.5% соответственно (рис. 2А,Б).
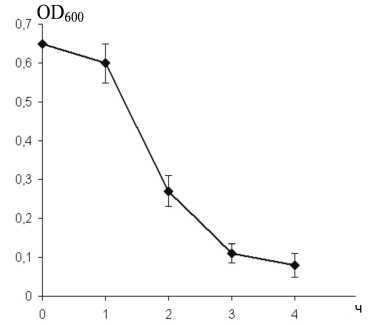
Рис. 1. Лизис планктонной культуры S.epidermidis 33 низкомолекулярным пептидом варнерином (4 мкг/мл).
Действия низкомолекулярного пептида варне-рина при концентрации 4 мкг/мл на сформированную в течение 24 ч биопленку не обнаружено. Однако при увеличении концентрации пептида от 16 до 128 мкг/мл отмечается снижение уровня биомассы и количества живых клеток в образованных в течение суток биопленках (рис. 3).
Полученные нами результаты согласуются с многочисленными литературными данными о значительной резистентности клеток в биопленках к антибактериальным агентам по сравнению с планктонными формами аналогичных бактерий.[5, 7, 1113, 15].
В дальнейших экспериментах на биопленках низкомолекулярный пептид варнерин использовался в концентрации 128 мкг/мл.
При сравнении лизирующего действия пептида на планктонные клетки и биопленку отмечено, что через 4 ч контакта с варнерином (4 мкг/мл) количество жизнеспособных клеток в планктонной культуре падает практически до нуля (рис. 4А), тогда как в биопленке в три раза. Причем, число живых клеток в биопленке остается достаточно высоким даже при 24 ч воздействии варнерина (рис. 5Б).
Сравнение энзимограмм после воздействия вар-нерина на планктонные клетки и биопленки (рис. 4Б и рис. 5В) позволяет обнаружить значительные различия.
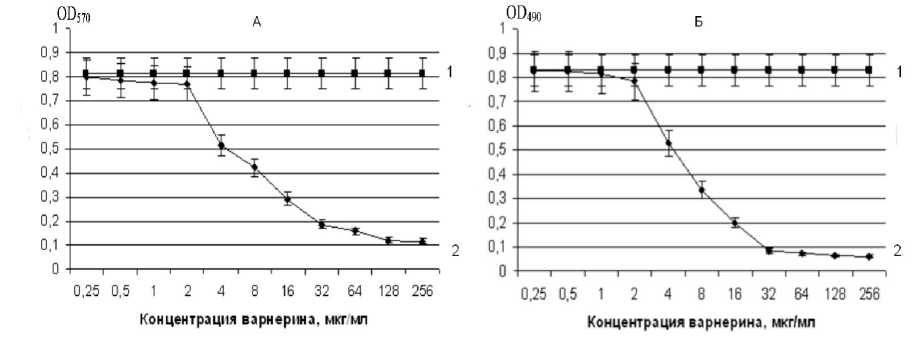
Рис. 2. Действие варнерина на накопление биомассы (А) и жизнеспособность клеточных компонентов (Б) при формировании биопленок S.epidermidis 33 (1 - контроль, 2 - варнерин).
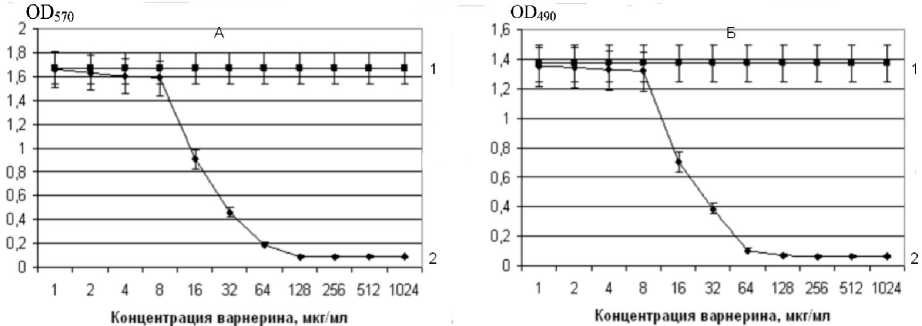
Рис. 3. Действие варнерина на сформированную пленку S.epidermidis 33. А - накопление биомассы, Б - жизнеспособность клеточных компонентов (1 - контроль, 2 - варнерин).
108 КОЕ/мл
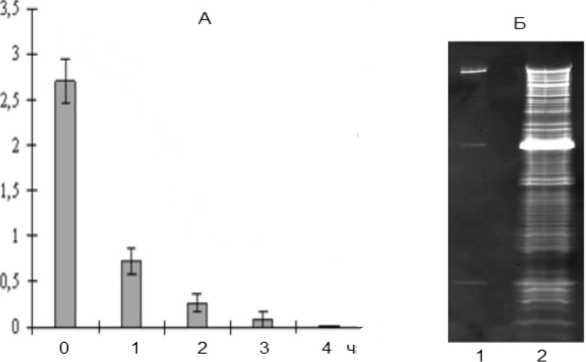
Рис. 4. Действие низкомолекулярного пептида варнерина (4 мкг/мл) на планктонную культуру S. epidermidis 33. А -КОЕ/мл, Б - энзимограмма аутолитических ферментов после 4 ч действия пептида варнерина
Важно отметить, что сам варнерин не обладает какой-либо ферментативной активностью, и это позволяет предположить опосредованность его действия за счет проявления им детергентных свойств и активации аутолитических систем бактериальных клеток [2].
Действительно, как показал энзимографический анализ, супернатанты препаратов планктонных клеток и биопленок S.epidermidis 33, обработанных варнерином, характеризуются гетерогенными спектрами аутолизинов, в составе которых обнаружи- ваются общие группы расщепляющих бактериальные стенки ферментов.
Таким образом, результаты исследований свидетельствуют о том, что низкомолекулярный катионный пептид варнерин обладает выраженным активирующим действием на аутолитические системы как планктонных клеток, так и биопленок бактерий S.epidermidis 33. Это является подтверждением перспектив использования пептида для разработки новых антибактериальных препаратов против стафилококковых инфекций, в том числе, обусловленных образованием биопленок.
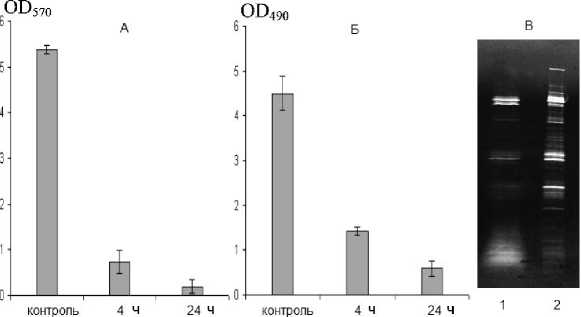
Рис. 5. Действие низкомолекулярного пептида варнерина (128 мкг/мл) на биопленки S.epidermidis 33, сформировавшиеся в течение 24 ч: А – биомасса, Б – жизнеспособные клетки, В – выход аутолизинов (1 – 10 мМ Трис-НС1, 2 – варнерин).
Список литературы Разрушение биопленок коагулазонегативных стафилококков катионным пептидом варнерином
- Коробов В.П., Лемкина Л.М., Полюдова Т.В. Продукция антибактериального фактора широкого спектра действия клетками Staphylococcus warneri//Доклады РАН. 2003. Т. 390. № 5. С. 703-705.
- Коробов В.П., Лемкина Л.М., Полюдова Т.В., Акименко В.К. Выделение и характеристика нового низкомолекулярного антибактериального пептида семейства лантибиотиков//Микробиология. 2010. Т. 79. № 2. С. 228-238.
- Коробов В.П., Полюдова Т.В., Филатова Л.Б. и др. Активация аутолитической активности бактерий S.epidermidis 33 низкомолекулярным катионным пептидом варнерином//Микробиология. 2010. Т. 79. № 1. С. 133-135.
- Сидоренко С.В. Роль бактериальных биопленок в патологии человека//Инфекции в хирургии. 2004. Т. 2. № 3. С. 16-20.
- Anwar H., Strap J.L., Costerton J.W. Eradication of biolm cells of Staphylococcus aureus with tobramycin and cephalexin.//Can. J. Microbiol. 1992. V. 38. P. 618-625.
- Bradford M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of proteindye binding//Anal. Biochem. 1976. V. 72. P. 248-254.
- Ceri H., Olson M.E., Stremick C. et al. The Calgary biolm device: new technology for rapid determination of antibiotic susceptibilities of bacterial biolms//J. Clin. Microbiol. 1999. V. 37. P. 1771-1776.
- Cho B.G., Kim C.H., Lee B.K., Cho. S.H. Comparison of antibiotic resistance of blood culture strains and saprophytic isolates in the presence of biofilms, formed by intercellular adhesion (ica) gene cluster in Staphylococcus epidermidis//J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2005. V. 15. P. 728-733.
- Davey M.E., O'toole G.A. Microbial biofilms: from ecology to molecular genetics//Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2000. V. 64 (4). P. 847-867.
- Donlan R.M., Costerton J.W. Biofilms: survival mechanisms of clinically relevant microorganisms//Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2002. V. 15. P. 167-193.
- Dunne W.M. Evaluating adherent bacteria and biolm using biochemical and immunochemical methods//Handbook of bacterial adhesion: principles, methods, and applications. N.Y., 2000. P. 273-284.
- Dunne W.M., Mason E.O., Kaplan S.L. Diffusion of rifampin and vancomycin through a Staphylococcus epidermidis biofilm//Antimicrob. Agents. Chemother. 1993. V. 37. P. 2522-2526.
- Gilbert P., Brown M.R.W. Mechanisms of the protection of bacterial biolms from antimicrobial agents//Microbial biolms. N.Y., 1993. P. 118-130.
- Kiem S., Oh W.S., Peck K.R et al. Phase variation of biofilm formation in Staphylococcus aureus by IS256 insertion and its impact on the capacity adhering to polyurethane surface.//J. Kor. Med. Sci. 2004. V. 19. P. 779-782.
- Konga K.-F., Vuonga C., Ottoa M. Staphylococcus quorum sensing in biofilm formation and infection//J. Med. Microbiol. 2006. V. 296. P. 133-139.
- Lewis K. Riddle of Biofilm//Resistance Antimicrobial agents and Chemotherapy. 2001. V. 45/N. 4. P. 999-1007
- Mani N., Tobin P., Jayaswal R.K. Isolation and characterization of autolysis-defective mutants of Staphylococcus aureus created by Tn917-lacZ mutagenesis//J. Bacteriol. 1993. V. 75. № 5. Р. 1493-1499.
- Stewart P.S., McFeters G.A., Huang C.T. Biofilm control by antimicrobial agents.//Biofilms II: Process Analysis and Applications. N. Y, 2000. P. 373-405.
- Vuong C., Gerke C., Somerville G.A. et al. Quorum-Sensing Control of Biofilm Factors in Staphylococcus epidermidis//J. Infect. Dis. 2003. V. 188. P. 706-718.
- Xavier J.B., Picioreanu C., Rani S.A. et al. Biofilm-control strategies based on enzymic disruption of the extracellular polymeric substance matrix -a modelling study//Microbiology. 2005. V. 151. P. 3817-3832.


