Reduced antioxidant status for prolonged period due to repeated stress exposure in rat
Автор: Devaki M, Nirupama R., Yajurvedi H.N.
Журнал: Журнал стресс-физиологии и биохимии @jspb
Статья в выпуске: 2 т.7, 2011 года.
Бесплатный доступ
The objective of the study was to find out whether or not exposure to a stressor after an initial stressful experience augments stress response. Antioxidant status was determined by measuring changes in the activities of the hepatic free radical scavenging enzymes viz, superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione-S-transferase (GST), glucose-6-phosphate-dehydrogenase (G6PDH) and catalase (CAT) and levels of hepatic malondialdehyde (MDA) following exposure to 1 h restraint (RS) and after a gap of 4 h to forced swimming exercise (FS) in rats. The activities of hepatic CAT, SOD, G6PDH and GST were significantly reduced 2 h after RS compared to controls and 4 h after FS the activities of CAT and G6PDH remained at lower levels i.e. they were similar to those found after RS, whereas SOD and GST showed further significant decrease compared to those found after RS. On the other hand the MDA levels, indicative of lipid peroxidation were significantly increased after RS and showed further significant increase after FS. The results reveal that after initial stressful experience, the stress response is augmented due to exposure to another stressor whereas the system does not get habituated to stress exposure.
Cat, g6pdh, gpx, gst, mda, oxidative stress, sod
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/14323517
IDR: 14323517
Текст научной статьи Reduced antioxidant status for prolonged period due to repeated stress exposure in rat
Exposure to stressful situations is among the most common human experiences. It is reported that exposure to stress can stimulate many pathways leading to increased production of the oxygen free radicals (Adachi et al., 1993; Liu, 1999; Irie et al., 2000). These are formed in human body both in physiological and pathological conditions in cytosol, mitochondria, lysosomes, peroxisomes and plasma membrane (Hemmani and Parihar, 1998). Psychological stress is associated with increased reactive oxygen species (ROS) production and oxidative damage and long term exposure to psychological stressors may enhance the risk of many diseases like atherosclerosis, diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis and liver diseases (Kelly, 1999; Liu, 1999; Lu et al., 2003). Stress plays a potential role in aggravating liver diseases viz., hepataic fibrosis and cirrhosis ( Parolo and Rabino, 2001). Other types of stressors are also known to alter antioxidant status and cause tissue damage in experimental animals. For instance, in rats, immobilization for 6 h induced severe bleeding in the stomach and a significant increase in plasma levels of thiobarbituric acid (Liu et al., 1994); 30 minutes cold immobilization increased thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS) and decreased concentration of sulfhydryl (SH) groups in the heart, stomach and brain without change in the liver (Kovacs et al., 1996) ; immobilization for 8 h (Liu et al., 1996) or 6 h ( Oishi and Machida, 2002) caused a significant increase in lipid peroxidation (LPO), oxidative damage of nuclear DNA, decrease in number of neutrophils and activity of catalase (CAT) and superoxide dismutase (SOD); restraint for 6 h resulted in reduction in the level of reduced glutathione (GSH), oxygen radical absorbance and activity of SOD, glutathione-S-transferase activity (GST) (Zaidi et al., 2006); 48 h cold stress (40 C) caused a significant increase in CAT, glutathione reductase (GR) and GSH and decreased SOD activity (Yuksel et al., 2008) ,30 minutes acute immobilization resulted in increased blood corticosterone and glucose levels, activities of MnSOD, CuZn SOD, CAT and glutathione peroxidase (GPx) whereas GR remained unchanged (Djorjevic et al., 2010) and removal of whisker’s lead to an increase in protein carbonyl formation and LPO in the brain, heart, liver, and spleen in mice which were maximized after 12 h (Wang et al., 2007); In these studies alterations in the antioxidant status or oxidative damage have been studied after exposure to a single stressor. It is possible that human beings or animals are exposed to several stressors within a day. Whether exposure to a stressor after an initial stressful experience further alters antioxidant status and thereby enhances oxidative damage or the system gets habituated to stress exposure remains to be understood. Hence the present study aims at investigating effects of restraint followed by forced swimming exercise applied after an interval of 4 h on the activities of CAT, SOD, GPx, GST and concentration of malondialdehyde (MDA) in rat.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Adult male Wistar rats (25) weighing 180-200g were obtained from the inbred colony of the central animal facility of the University of Mysore and were maintained (3 rats/cage) under 12 h: 12 h light and dark cycle. The rats were divided into 3 groups viz., initial controls (n=5), treatment controls (n=10) and stress group (n=10) and were provided rat chow and tap water ab libitum during experimentation.
At each autopsy the adrenal gland and the liver samples were collected and stored at -200C until enzyme assays were conducted. The superoxide dismutase (SOD) (Marklund and Marklund, 1974), glutathione peroxidase (GPx) (Tappel, 1978), catalase (CAT) (Aebi, 1984), glutathione-S-transferase (GST) (Habig et al ., 1974), glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PDH) (Lee, 1982) activities and malondialdehyde (MAD) levels (Ohkawa et al ., 1978) were estimated in the liver sample. The adrenal gland homogenate was used for assay of 3β-hydroxy steroid dehydrogenase (3β-HSDH) activity (Shivanandappa and Venkatesh, 1997). All data were expressed as the mean ± SE and one way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Duncan’s multiple range test were used to test the significant difference between mean values of different groups, fixing the minimum level of significance at P<0.05.
RESULTS
There was a significant increase in the adrenal 3β-HSDH activity following RS compared to controls which showed further significant elevation after exposure to FS compared to RS (Fig1).
The liver CAT and G6PDH activities were significantly reduced following RS compared to initial controls as well as treatment controls and remained at this low level when measured 4 h after FS (Table 1).
The activities of the liver SOD and GST were significantly reduced following RS compared to initial controls and there was a further significant reduction after FS compared to RS group as well as respective controls (Table 1). There was no change in GPx activity either after RS or FS.
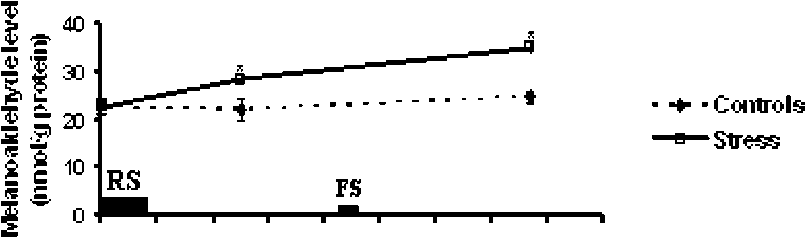
The MDA levels showed a significant increase following RS and further significant increase after FS compared to controls and RS group (Fig 2).
Table 1 Effect of restraint and forced swimming exercise on the activities of liver catalase (CAT), superoxide dismutase (SOD), glucose -6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PDH), glutathione- S transferase (GST) and glutathione peroxidase (GPX) in rat.
|
Group |
CAT (nmol/mg/min) |
SOD (U/mg protein ) |
G6PDH (gmol/mg/min) |
GST (gmol/mg/min) |
Gpx (gmol/mg/min) |
|
Initial controls (Zero hour) |
2.52 ± 0.86a |
19.77 ±1.66a |
0.02±0.01a |
30.9 ±1.78a |
0.16 ± 0.005 |
|
2h after restraint (RS) |
1.44 ± 0.87b |
13.07 ± 0.89b |
0.01± 0.01b |
24.69 ± 1.51b |
0.15±0.12 |
|
Controls for RS group |
2.66 ± 0.107a |
19.87 ± 2.02a |
0.02 ± 0.02a |
26.45 ± 1.52ab |
0.16±0.006 |
|
4h after forced swimming (RS+FS) |
1.26 ± 0.067b |
8.25 ± 2.06 c |
0.01± 0.01b |
15.07±1.38c |
0.13±0.11 |
|
Controls for (RS+FS) |
2.54 ± 0.128a |
20.28 ±2.06 a |
0.02±0.01a |
28.05± 1.51ab |
0.16±0.11 |
|
ANOVA F-Value (df=4,20) |
47.686 P< 0.001 |
11.983 P< 0.001 |
10.286 P< 0.001 |
15.05 P< 0.001 |
NS |
Note: All values are Mean ± SE; Mean values with same superscript letters in a given column are not significantly different, whereas those with different superscript letters are significantly (P<0.05) different as judged by Duncan’s multiple test.
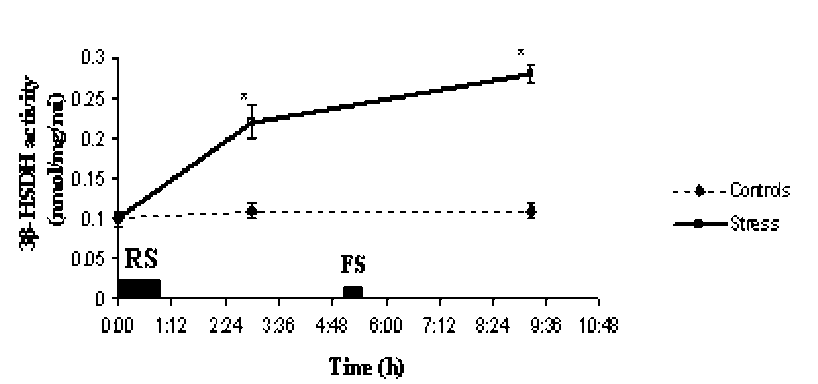
Figure 1 Changes in the adrenal 3β-HSDH activity following exposure to restraint (RS) and later to forced swimming exercise (FS) in rats. * Significant.
0:00 1:12 224 3:36 4:48 6:00 7:12 824 836 10:48
T1me(h)
Figure 2 Changes in the malondialdehyde (MDA) levels following exposure to restraint (RS) and later to forced swimming exercise (FS) in rats. * Significant.
DISCUSSION
Increased adrenocortical activity is considered as an index of stress response in vertebrates as there is an unspecific activation of the hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenalaxis (HPA axis) (Tsigos and Chrousos, 2002) due to stress. Hence, an increase in the activity of 3β-HSDH, a key enzyme of adrenal steroidogenesis in the present study following RS as well as FS indicates that the animals were undergoing stressful experience.
Oxygen free radicals are extremely reactive and unstable and react with lipids, proteins, carbohydrates and nucleic acids in the body
(Sevanian and Hochstein, 1985) and generate a cascade producing lipid peroxidation (LPO), a major mechanism of cell membrane distraction and cell damage (Alession, 1993; Mapp et al., 1995; Sato et al., 1996; Ji , 1999). However biological systems have evolved endogenous defense mechanisms against free radical induced cell damage. Primary antioxidant enzymes viz. GPx, CAT and SOD directly eliminate active oxygen species (hydroxyal radical, superoxide radical, hydrogen peroxide) whereas glutathione reductase, G6PDH and cystosolic GST are secondary enzymes that detoxify ROS by decreasing peroxide levels or maintaining a steady supply of metabolic intermediates like glutathione and NADPH necessary for optimum functioning of primary antioxidant enzymes (Bandyopadhyay et al., 1999). The generation of ROS is a primary event under a variety of stress conditions and the consequence of ROS formation depends on the intensity of the stress. Stressful conditions are known to interfere with antioxidant system by interfering with production or inactivation of antioxidant enzymes (Kono and Fridovich, 1983; Krotz et al., 2002). Hence, changes in the activity of antioxidant enzymes are considered in the present study to assess the effect of repeated acute stress exposure. The SOD converts super oxide radicals into hydrogen peroxide. The ROS scavenging activity of SOD is effective only when its activity is followed by the actions of CAT and GPx, because hydrogen peroxide generated by SOD is further scavenged by CAT and GPx (Halliwell, 2001). Therefore, it is hypothesized that an imbalance in the SOD/CAT results in oxidative alterations. The reduction in the activities of SOD and CAT following RS and FS in the present study indicates decreased antioxidant status due to stress induced by restraint and forced swimming. Further, decreased CAT activity indicates reduced hydrogen peroxide scavenging. In addition, there was also a decrease in potency of secondary antioxidant defense system in stressed rats as shown by decreased activities of G-6-PDH and GST. The fact that RS and FS caused oxidative stress is further supported by increase lipid peroxidation which is an indicator of oxidative damage to the cells. It is reported that lipid peroxidation is a major mechanism of the liver cell injury (Jaeschke et al., 2002; Videla et al., 2003) and is a consequence of imbalance between prooxidant and antioxidant system (Vijayavel et al., 2005).
It is evident from earlier studies (references in introduction) that decreased antioxidant status was observed following one time exposure to an acute stressor. The present study, first time reveals that after a stressful experience, exposure to another stressor results in an enhanced stress response whereas the system does not get habituated to stress exposure.
The facts that restraint induced decreased activity of SOD and GST were further significantly reduced following FS and increase in lipid peroxidation following RS was further increased after FS support this view. It is to be noted that animals or humans face several stressors in a day and such experiences might result in increased liver cell damage, as evidenced by increased LPO in the present study following exposure to second stressor, although after a gap of 4 h. Further in earlier studies, activities of antioxidant enzymes were determined immediately after exposure to stressors. Hence, it is not possible to ascertain whether the stress induced changes are short lived or persist for a longer duration. This is an important fact to be considered because an increase in duration of prevalence of high levels of ROS might lead to increased damage to tissues due to membrane lipid peroxidation. In the present study there was a few hours time interval between completion of stress exposure regime and collection of samples for antioxidant enzyme assays and LPO, i.e., sample was collected 2 h after RS and 4 h after FS and significantly lower antioxidant status and increased LPO were observed. Since, the adverse effects on antioxidant enzymes prevailed a few hours even after completion of stress regime our study shows that stress effects on antioxidant system are not short lived.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The work was supported by a grant from University of Mysore, under the Institution of Excellence scheme funded by Ministry for Human Resource Development, Government of India, through the University Grants Commission.
Список литературы Reduced antioxidant status for prolonged period due to repeated stress exposure in rat
- Adachi, S., Kawamura, K. and Takemoto, K. (1993) Oxidative damage of nuclear DNA in liver of rats exposed to psychological stress. Cancer Research., 53, 4153-4155.
- Aebi, H. (1984) Catalase invitro. Methods in Enzymol., 105, 121-126.
- Alession, H. (1993) Exercise induced oxidative stress. Med Sci Sports Exerc., 25, 218-224.
- Bandyopadhyay, U., Das, D. And Banerjee. R.K. (1999) Reactive oxygen species: oxidative damage and pathogenesis. Curr. Sci., 77 (5), 658-666.
- Djorjevic, J., Djorjevic, A., Adlic, M., Niciforovic, A. and Radojcic, M.B. (2010) Chronic stress differentially affects antioxidant enzymes and modifies the acute stress response in liver of Wistar rats. Physiol Res., (Pre-press), 1-20.
- Habig, W.J., Babst, M.J. and Jacoby, W.J. (1974) Glutathione s-transferase the first step in mercapturic acid formation. JBC., 249, 7130.
- Halliwell, B. (2001) Role of freeradicals in the neurodegenerative diseases: therapeutic implications for antioxidant treatment. Drugs Aging., 18, 685-716.
- Hemnani, T. and Parihar, M.S. (1998) Reactive oxygen species and oxidative DNA damage. Indian J Physiol Pharmacol., 42, 440-452.
- Irie, M., Asami, S., Nagata, S., Miyata, M. and Kasai, H. (2000) Classical conditioning of oxidative DNA damage in rats. J. Neurosci., 288, 13-16.
- Ji LL. (1999) Antioxidants and oxidative stress in excrcise. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med., 22, 283-292.
- Jaeschke, H., Gores, G., Cederbaum, I.A., Hinson, A.J., Pessayre, D. and Lemasters, J.J. (2002) Mechanisms of hepatotoxicity. J Toxicol Sci., 65, 166-176.
- Kelly, G.S. (1999) Nutritional and botanical interventions to assist with the adaptation to stress. AMR., 4, 289-365.
- Kono, Y. and Fridovich, I. (1983) Inhibition and reactivation of Mn-catalase: implications for valence changes at the active site manganese. JBC., 258, 13646-13648
- Kovacs, P., Juranek, I., Stankovicova, T. and Svec, P. (1996) Lipid peroxidation during Acut estress. Pharmazine., SL 1, 51-53.
- Krцtz, F., Sohn, Y.H., Gloe, T., Zahler, S., Riexinger, T., Schiele, M.T., Becker, F.B., Theisen, K., Klauss, V and Pohl. U. (2002) NAD(P)H oxidase-dependent platelet superoxide anion release increases platelet recruitment. Blood., 100, 917-924.
- Lee, C.Y. (1982) Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase from mouse. Methods Emzymol., 89, 252-257.
- Liu, J., Wang, X. and Mori, A. (1994) Immobilization stress-induced antioxidant defence changes in rat plasma: effect of treatment with reduced glutathione. JBC., 26(4), 511-517.
- Liu, J., Wang, X., Mark, K., Shigenaga., Helen, C., Yeo., Mori, A., Bruce, N. and Ames. (1996) Immobilization stress causes oxidative damage to lipid, protein, and DNA in the brain of rats. FASEB., 10, 1532-1538.
- Liu, J.K. (1999) Stress, ageing, brain oxidative damage. Neurochem Res., 24, 1479-97.
- Lu, L.G., Zeng, M.D., Mao, Y.M., et al. (2003) Relationship between clinical and pathologic findings in patients with chronic liver diseases. World J Gastroenterol., 12, 2796-2800.
- Mapp, P.I., Grootveld, M.C. and Blake, D.R. (1995) Hypoxia, oxidative stress and rheumatoid arthritis. Br Med J., 51, 419-436.
- Marklund & Marklund, G. (1974) Involvement of the superoxide anion radical in the autoxidation of pyrogallol and a convenient assay for superoxide dismutase. EJB., 47, 469-547.
- Ohkawa, H., Ohishi, N. and Yagi, K. (1978) Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by Thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal. Biochem., 95, 351-358.
- Oishi, K. and Machida, M. (2002) Different effects of immobilization stress on the mRNA expression of antioxidant enzymes in rat peripheral organs. Scand J Clin Lab Invest., 62, 115-122.
- Parolo, M. and Rabino, G. (2001) Oxidative stressrelated molecules and liver fibrosis. J Hepatol., 35, 297-306.
- Sato, M., Ramarathnam, N., Suzuki, Y., Ohkubo, T.,Takeuchi, M. and Ochi, H. (1996) Variental differences in the phenolic content and superoxide radical scavenging potential of wines from different sources. J Agr Food Chem., 44, 37-40.
- Sevanian, A. and Hochstein, P. (1985) Mechanisms and consequences of lipid peroxidation in biological system. Annu. Rev. Nutr., 5, 365-390.
- Shivanandappa, T. and Venkatesh, S. (1997) A colorimetric assay method for 3 hydroxy-5-steroid dehydrogenase. Anal Biochem., 254, 57.
- Tappel A.L. (1978) Glutathione peroxidase and hydroperoxidase. Methods in Enzymol., 52, 506-513.
- Tsigos, C. and Chrousos, G.P. (2002) Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis, neuroendrocrine factors and stress. J. Psychosom. Res., 53(4), 865.
- Videla, L.A., Fernandez, V., Tapia, G. and Varela, P. (2003) Oxidative stress-mediated hepatotoxicity of iron and copper: role of kupffer cells. Biometals., 16(1), 103-111.
- Vijayavel, K., Anbuselvam, C. and Balasubramanian, M. P. (2005) Naphthaleneinduced hematological disturbances and oxidative stress in an estuarine edible crab, Scylla serrata. Environ Toxicol., 20, 464-466.
- Wang, L., Muxin, G., Nishida, H., Shirakawa, C., Sato, S. and Konishi, T. (2007) Psychological stress induced oxidative stress as a model of sub-healthy condition and the effect of TMC. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med., 4(2), 195-202.
- Yuksel, S., Dilek, A. and Ozfer, Y.(2008) Antioxidative and metabolic responses to extended cold exposure in rats. Acta Biol Hung., 59(1), 57-66.
- Zaidi S.M.K.R., Al-Qirim T.M. and Banu,N. (2006) Effect of antioxidant vitamins on glutathione depletion and lipid peroxidation induced by restraint stress in the rat liver. Drug in R&D., 6(3), 157-165.


