Reflection of expenditure priorities in regions’ budget planning
Автор: Klimanov V.V., Timushev E.N., Vantrusov V.A.
Журнал: Economic and Social Changes: Facts, Trends, Forecast @volnc-esc-en
Рубрика: Public finance
Статья в выпуске: 4 т.18, 2025 года.
Бесплатный доступ
The paper investigates the extent to which the strategic and budgetary documents of constituent entities of the Russian Federation reflect a multi-scenario approach to forecasting budget parameters and identify spending priorities. The analysis is based on the example of the regions included in the Northwestern Federal District. The relevance of the study is due to the fact that budget policy as a whole has a multi-scenario nature. Therefore, in order to increase the effectiveness of public administration on the part of the authorities, it is important to assess the risks of budget execution and develop a response plan to minimize their negative consequences, which requires, among other things, prioritization of expenditures. The paper uses methods of structural and substantive analysis of regulatory and program documents of strategic and budgetary planning at the level of constituent entities of the Russian Federation, the method of rating regional budget planning documents according to the authors’ criteria and the method of grouping budget expenditures within regional projects, which are a decomposition of federal projects. The scientific significance of the study lies in formulating the problem of using a multi-scenario approach in the development of budget planning documents and reflecting spending priorities in them, assessing the severity of this problem at the regional level and common ways to address it. The novelty of the work lies in the fact that for the first time all the main documents of budget forecasting and planning in the regions of the Northwestern Federal District have been studied. It has been established that the vast majority of budget forecasts and the main directions of budget policy are presented only in the basic version. Strategic and budget planning documents virtually do not offer a multivariate forecast of regional budget revenue and expenditure items. Consequently, spending priorities are not set properly. It is shown that a significant proportion of actual regional expenditures coincide with federal priorities and they reflect the list of expenditure obligations stipulated in federal legislation. The theoretical significance of the study lies in substantiating the need to apply a multi-scenario approach to the disclosure of budget policy priorities at the regional level, the practical significance consists in updating the details of documents for medium- and long-term strategic and budgetary planning – in preparing a separate section with disclosure of information on a multi-scenario approach to forecasting and on priority areas of spending
Strategy, budget forecast, prioritization, socio-economic development strategy, budget forecast for the region, main directions of budget policy, national project, multi-scenario approach
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/147251832
IDR: 147251832 | УДК: 332.1, 336.5 | DOI: 10.15838/esc.2025.4.100.6
Текст научной статьи Reflection of expenditure priorities in regions’ budget planning
In practice, regional budget execution often deviates from the originally approved parameters. In some cases, the ratio of fact and plan is rather significant for both budget surpluses and deficits, although this value is often absent in the financial statements due to current changes to the approved budget or the consolidated budget statement.
The dynamics of the main revenue items of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation, especially taxes, is difficult to predict and depends on factors that are often not manageable at the regional level. Budgetary policy as a whole has a “multi-scenario” nature, as it is determined by the economic and the socio-political situation, which are developing non-linearly and difficult to predict.
Consequently, strategic and budgetary planning documents, including at the regional level, should specify the risks associated with budget execution and management responses by public authorities based on the unpredictability and uncertainty of external factors. At the stage of budget planning, the variability of its execution should be provided, which determines the scenarios for generating revenues and spending. The priorities set in the context of government programs and functional expenditure areas should increase the transparency of public administration and become a clearer guide for the financial authority in terms of budget execution.
In general, it is very difficult to identify the priority areas of budget expenditures of the RF constituent entities on the basis of existing documents. At the same time, to ensure the effectiveness of public finance management, it is necessary that regional-level documents clearly define those areas of public policy that are of strategic importance to the region.
The aim of our work is to establish the extent to which the strategic and budgetary documents of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation reflect a multi-scenario approach to forecasting budget parameters and identify spending priorities. The empirical analysis is based on the materials of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation, which are part of the Northwestern Federal District (NWFD). At the same time, an analysis of similar documents in other territories of the Russian Federation shows that the regions as a whole differ insignificantly from each other in terms of the degree of completeness and detail of disclosure of budget spending priorities in the documents. Consequently, the results obtained and the conclusions drawn on their basis can be extended to most of the RF constituent entities.
We have set the following tasks to achieve the goal, according to which the study is divided into three parts:
-
1) analysis of strategic and budget planning documents for the NWFD;
-
2) assessment of the completeness of disclosure of budget spending priorities in the materials directly accompanying the budget preparation – the “Main directions of budget and tax policy” of the RF constituent entities;
-
3) identification of current priorities and expenditure items that coincide with federal priorities based on the actual materials of the laws on regional budgets for 2025–2027.
The conceptual basis of our research is the provisions of the theory of financial management, according to which, in conditions of uncertainty, the most effective way to manage financial resources involves the working out of several development scenarios, assessing the likelihood of implementation and drawing up a program of actions depending on the goals set. In this context, the main scientific interest was to determine to what extent the provisions of the theory – the need for a scenario approach for more effective management of financial resources – are respected in the practice of budgetary policy at the level of the RF constituent entities. The motivation for our study was to pose the problem of using a multiscenario approach in the development of budget planning documents and reflecting spending priorities in them, as well as to assess the severity of this problem in practice.
Literature review
The key documents of long-term strategic planning at the regional level are the socio-economic development strategy of the RF constituent entities and the budget forecast of the RF consti- tuent entities for the long term. The latter is often attached to the budget law at the stage of its drafting and submission to the legislature. In addition, the main documents on the basis of which the draft budget is drawn up annually include the main directions of budgetary and tax policy of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation.
The regions are developing their own government programs, including regional projects aimed at achieving national goals at the federal level. In this case, the budget planning quality depends on the possibility of a competent combination of both federal tasks, but solved at the level of a particular region, and purely regional priorities. However, the problem of planning quality is felt even more strongly at the municipal level, where there are fewer powers than at the regional level, due to the continuing shortcomings in their separation (Levina, 2023). At the intra-regional level, the quality of budget planning depends on both the solution of region-wide and purely local problems. The problem of limited capacity of municipalities to independently determine budget spending priorities remains relevant (Pechenskaya, 2015), which is associated with the high centralization of budget resources. Despite the severity of this problem, our research focuses on the specifics of planning and prioritizing expenditures at the regional level.
The quality of budget planning in the region largely depends on the level of forecasting, the role of which is often underestimated in practice. Meanwhile, it affects the financial stability of public authorities at different levels of government. G. Kaplanoglou and V. Rapanos cite institutional problems of fiscal policy, including errors in budget forecasting, among the causes of the Greek financial and economic crisis of the 2010s (Kaplanoglou, Rapanos, 2013). Although in practice, it is carried out by the financial department of the relevant territory, in scientific research with a practical bias, various options for assessing future events are possible, including considering the complex of intergovernmental relations in the budgetary system as a whole. This is a more complex, but also promising approach, as it involves a comprehensive view of the problem. For example, a group of international researchers examined scenario options for the allocation of federal intergovernmental transfers in Mexico to address the challenges of sustainable development at the regional level (Guerrero et al., 2022). In our work, we do not separately consider the issue of uncertainty in the distribution of intergovernmental transfers, focusing on the more general problem of accounting for different scenarios in the dynamics of revenues and expenditures of regional budgets as a whole, and priority expenditure items.
The literature review shows how important forecasting and planning are for the sustainability of the budget process. Negative internal factors: unrealistic forecasting, complexity of methodology, and unreliability of forecasts (Foster, Miller, 2000), as well as opportunistic behavior (Benito et al., 2015), sometimes affect the severity of the budget crisis more than external factors, such as falling tax revenues or federal intergovernmental transfers (Mitchell, Stansel, 2016). There are many works in the literature on public choice (Hoang, Maher, 2022) that demonstrate the priority in practice of current expenditures over long-term commitments in conditions of limited funds and low budget sustainability. Thus, high-quality forecasting and planning increase the level of trust in the state and reduce the uncertainty of fiscal policy.
The uncertainty of socio-economic development implies the working out of different budget execution options. But, oddly enough, the category of priority of budget expenditures as such is rarely mentioned in the literature on public finance.
Usually, a much more general topic is touched upon – the factors influencing the composition of expenses. A variant of their typology is given in (Facchini, 2018), where the structure of budget expenditures is generally explained in terms of the paradigms of demand for public goods (demand factors), intentions and opportunities for their provision by public authorities (a group of supply factors) and in terms of institutional conditions. Nevertheless, the priority of certain expenditure items comes to the fore during periods of economic or social upheaval. For example, at the stage of recovery from the 2008–2009 crisis, forecasts for the consolidation of government spending were made and discussed to maintain financial stability, which was shaken as a result of anticrisis injections into the economy (Ortiz et al., 2010). Similarly, during the period of coronavirus infection, a large number of papers appeared with an operational analysis of budgetary responses to the crisis and recommendations on the ways out of it (Andrew et al., 2020; Klimanov et al., 2021). Thus, in the current macroeconomic situation, which is characterized by external uncertainty and sanctions pressure, it is especially important to implement a multi-scenario approach to forecasting and planning the parameters of the budgets of the RF constituent entities and determining spending priorities.
As for long-term planning documents at the regional level in Russia, there are relatively few studies that provide a comprehensive analysis of socio-economic development strategies for all regions. One of them is a study by K.V. Budaeva, which is a comprehensive comparative analysis of strategizing practices at the regional level (Budaeva, 2017). It is notable for the fact that it was carried out at the dawn of the modern stage of federal regulation of strategic planning and documents the ways in which the regions approached the creation and implementation of laws on strategic planning and socio-economic development strategies. In most works, as a rule, the documents of a limited number of regions are the object of analysis and one or another aspect of the problem is considered. For example, there are studies examining regional strategies from the perspective of industry analysis, in particular when looking for an answer to the question of how the regional strategy highlights problems in the field of education and outlines ways to solve them (Belyakov, 2017). A number of works pays attention to the quality of the creation of individual sections of strategies, for example, devoted to issues of spatial development in the region – theoretical and methodological foundations and practice of compilation using the example of the subjects of the Ural Federal District (Antipin et al., 2023). A.G. Ataeva’s research is aimed at improving the methodological support for strategy development (Ataeva, 2019). The cited work is also interesting because it addresses the problem of the applicability of forecasting methods at the stage of scenario development according to a number of criteria, such as accuracy, objectivity and, which is important, applicability to achieve the goals of the region.
Strategic documents and supporting program documents show the importance to correctly solve methodological problems, in particular, such as the adequacy of goals and objectives on the one hand and targets on the other hand. Otherwise, there is a high risk of failure to achieve the planned goals. N.Yu. Oding and coauthors draw attention to this using the example of federal programs for reforming the system of intergovernmental relations (Oding et al., 2016). The works of B.S. Zhikharevich focus on various issues of developing strategies for the socio-economic development of regions, as well as cities. The characteristics of the text of the regional strategy were determined by the methods of expert discussion and survey: what should be in it to consider a high-quality strategy (Zhikharevich, 2024). Let us single out the qualities of the strategy that have been noted by experts and are of particular interest from the point of view of this work: clarity of priorities and compliance of the strategy’s provisions with presidential decrees and national development goals. As we can see, the criterion of multiscenarity (variability) as such, is not specified here, although it could have been taken into account by experts by default based on the predictive nature of the strategy itself as a goal-setting document.
Thus, the scientific literature rarely study the development strategies of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation precisely from the point of view of completeness of reflecting the priority areas of budget expenditures, increasing financial stability and reducing the level of uncertainty. Our research is aimed at filling this gap. The problem of financial support for achieving the goals reflected in regional strategies is one of the main obstacles to improving programmatic and targeted management of public finances in Russia and strategic planning in general. Moreover, we are not talking about the availability or lack of financial resources, but rather about the methodological issues of their accounting and distribution in the context of the multi-scenario nature of the budget process. In previous studies, we have found that regional government programs, the main tool for program-oriented management, do not rely sufficiently on budget forecasting, which makes them less realistic, and therefore carries a high risk of not achieving the goals of the socioeconomic development strategy (Klimanov et al., 2017). In the field of forecasting, there is an almost universal use of an exclusively one-scenario approach to long-term budget forecasting, even in the case of working out several scenarios of socioeconomic development in a regional strategy. According to A.B. Zolotareva and I.A. Sokolov, strategies for the socio-economic development of regions in practice serve as a declaration of intent rather than a tool to improve the effectiveness of public administration, because they usually do not contain an estimate of the funds needed to achieve the stated goals, nor a forecast of their receipt in the medium and long term (Zolotareva, Sokolov, 2018). These shortcomings can be eliminated through the development and implementation of the budget forecast of the RF constituent entities for a longterm period.
In contrast to socio-economic development strategies, a much smaller amount of scientific research is devoted to budget forecasts of the subjects of the Russian Federation. Experts cite the formality of development1, descriptive nature, lack of transparency of forecast calculations, absence or lack of elaboration of a multi-scenario approach among the main disadvantages of the current regional budget forecasts (Mikhailova, Eremina, 2018). N. Barbashova notes the weakness of the methodology for their development and, in terms of costs, suggests an original way of calculating the future value of expenditure obligations, taking into account the number of consumers of the relevant public goods (Barbashova, 2022). Earlier, I.Yu. Arlashkin, A.N. Deryugin, and K.A. Proka proposed a less formalized approach to forecasting the same main items of expenditure, taking into account the number of different population groups, factors concerning the amount of insurance premiums paid for the unemployed population and obligations assumed at the federal level, but which are expenditure obligations of regions (Arlashkin et al., 2015).
The main directions of budget and tax policy, developed for three years, unlike the strategies of socio-economic development and budget forecast, belong to the documents of medium- rather than long-term budget planning. As far as we know, they have not yet been a separate object of scientific research, especially based on materials from a large number of regions. Nevertheless, in our opinion, it is in the “Main Directions ...” that the mediumterm revenue prospects and spending priorities should necessarily be reflected. This will allow them to become documents on which not only the budget for the next year is based, but also its execution, including necessary adjustments, in the current year.
Thus, each of the reviewed documents fulfills its task within the framework of public administration. The literature review shows that they still have certain disadvantages at the level of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation. At the same time, in terms of reflecting different scenarios and prioritizing budget expenditures, these documents are characterized by a low degree of study. This represents a significant gap in scientific knowledge. Meanwhile, the implementation of a multi-scenario approach to budget forecasting and planning is important to ensure financial stability and reduce uncertainty.
Methodology of the research
As part of the first task, we have collected and analyzed the current strategies of socio-economic development, budget forecasts for the long term, and the main directions of budget and tax policy for 2025–2027 for the RF constituent entities that are part of the Northwestern Federal District. The subject of the analysis is to identify the availability of funding to solve the tasks of socio-economic development, reflect the multi-scenario approach to forecasting budget revenue receipts and prioritize expenditures in the event of a pessimistic forecast scenario. We applied the methods of regulatory legal acts analysis, structural, and substantive analysis.
As part of the solution of the second task, we identified and examined documents regulating the main directions of budget and tax policy of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation (“Main directions ...”) in all regions of the Northwestern Federal District, with the exception of the Pskov and Novgorod regions. We carried out the analysis of the “Main directions ...” by an expert method based on the consensus of our team, based on the accumulated experience in analyzing budget planning documents at the federal level and at the level of other Russia’s regions. We revealed the compliance of the provisions of the document with three criteria: 1) the clarity of priority spending areas; 2) the completeness of the disclosure of priorities; 3) the originality of the identified areas.
In the latter case, we assessed how much the priority spending areas reflect regional specifics and do not copy federal priorities. The rating scale varies from 0 to 10: the clearer and more detailed the spending priorities are and the more they differ from the federal priorities, the higher the score we assign to the document. We prioritized one or another area of expenditure based on the wording of the document. The corresponding direction may reflect both federal priorities and purely regional ones (the latter is much less common). The document itself does not provide for such differentiation in any way. The methodology we use is definitely subjective, which affects results, but this is justified by the task at hand (a qualitative assessment of the completeness of disclosure of spending priorities). At the same time, the task we are solving is quite simple and, therefore, intuitive. The “Main Directions...” themselves are easy to construct, and the allocated spending priorities, if they are outlined, are in most cases clear and easy to read.
The paper also estimates the volume of expenditures of the regional budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation, which are part of the Northwestern Federal District, which are carried out within the framework of regional projects developed for the implementation of federal projects, which in turn are part of national projects. This is the solution to the third task. The appendices to the regional laws on the budget for 2025–2027 have been analyzed in terms of disclosing the volume of budget allocations by target items (state programs and non-program areas of activity), groups and subgroups of types of expenditures. The affiliation of an expenditure item to federal projects is estimated using the target expenditure item code according to the current list of budget classification codes2. The data are collected and organized for all regions of the Northwestern
Federal District, except for Saint Petersburg, whose budget for 2025–2027 presents the required information in a slightly different format.
Results
The priorities of budget expenditures in Russia are currently determined by the national development goals, which are set out in Presidential Decree 309, dated May 7, 2024 “On the national development goals of the Russian Federation for the period up to 2030 and for the future up to 2036”. The share of federal budget expenditures on financing national projects is 13.8–14.3% of total expenditures in 2025–2027 ( Tab. 1 ). For comparison, this indicator was slightly lower – 9.4–10.0% in 2020–2024.
Table 1. Federal budget expenditures on national projects
|
National project |
Billion rubles |
% |
||||
|
2025 |
2026 |
2027 |
2025 |
2026 |
2027 |
|
|
Ja “Family” |
2832.9 |
2 883.4 |
2 843.7 |
49.1 |
45.7 |
44.7 |
|
I “Infrastructure for life” |
1168.4 |
1 359.1 |
1 413.1 |
20.3 |
21.6 |
22.2 |
|
Yu “Youth and children” |
458.1 |
547.4 |
550.3 |
7.9 |
8.7 |
8.7 |
|
D “Long and active life” |
369.8 |
284.2 |
284.7 |
6.4 |
4.5 |
4.5 |
|
T “Efficient transport system” |
131.4 |
165.5 |
202.2 |
2.3 |
2.6 |
3.2 |
|
C “Data economy and digital transformation of the state” |
129.1 |
161.8 |
167.0 |
2.2 |
2.6 |
2.6 |
|
Ch “Environmental well-being” |
48.6 |
109.3 |
124.2 |
0.8 |
1.7 |
2.0 |
|
E “Efficient and competitive economy” |
206.8 |
162.0 |
99.2 |
3.6 |
2.6 |
1.6 |
|
P “Tourism and hospitality” |
44.0 |
70.8 |
81.9 |
0.8 |
1.1 |
1.3 |
|
M “International cooperation and export” |
45.3 |
49.4 |
52.5 |
0.8 |
0.8 |
0.8 |
|
L “Personnel” |
17.9 |
15.6 |
17.3 |
0.3 |
0.2 |
0.3 |
|
Expenses for the block of national projects to ensure technological leadership |
313.2 |
494.4 |
520.2 |
5.4 |
7.8 |
8.2 |
|
Total expenses within the framework of national projects |
5 765.50 |
6 302.90 |
6 356.40 |
100.0 |
100.0 |
100.0 |
|
For reference: |
||||||
|
Federal budget expenditures according to the Federal Budget Act |
41 469.50 |
44 022.20 |
45 915.60 |
- |
- |
- |
|
Share of expenditures under national projects in total federal budget expenditures |
13.9% |
14.3% |
13.8% |
- |
- |
- |
Source: Main directions of budget, tax, and customs tariff policy for 2025 and for the planning period of 2026 and 2027. Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation.
Analysis of strategic and budget planning documents
Strategies for the socio-economic development of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation are long-term strategic planning documents at the regional level, developed within the framework of goal setting. They usually set general priorities for the development of regions. Despite their wide coverage, they often contain redundant information, making it difficult to identify the truly most important, often unique priorities for a particular region.
The strategies for the socio-economic development of the NWFD regions set out priority areas that often repeat the priorities reflected in the decrees of the President of the Russian Federation. Tasks and main activities are defined for each of them. A list of regional government programs and priority projects can be presented separately (Arkhangelsk Region), federal projects in which the region can participate (Republic of Karelia) are highlighted, and the need for the region to participate in national and federal projects to achieve the goals of the strategy (Republic of Karelia) is noted. The frequent reference to federal priorities in the strategies of all regions is due to the institutional foundations of intergovernmental relations in Russia, primarily the low level of spending powers of the regions.
The assessment of budget resources in the strategy – the total cost of implementation – is not presented in detail. It either does not exist at all (Kaliningrad Region, Pskov Region), or is given in general and/or in aggregated areas for achieving the goal of socio-economic development (Komi Republic, Nenets Autonomous Area, Vologda Region, Arkhangelsk Region, Leningrad Region, Saint Petersburg), or only for some proposed development projects (Murmansk Region). The amount of funding for individual priorities and tasks is usually not specified. Only in rare cases
(the Republic of Karelia), the amount of financial resources is determined for each priority area and program.
Despite the common features, the strategies meet the unique conditions of a particular region: competitive advantages are spelled out (Vologda Region), regional specifics are emphasized – international and interregional cooperation and the development of export activities (Kaliningrad Region). There may be an excessive number of the development areas – the creation of a tourism brand, food security (Novgorod and Pskov regions), which makes it difficult to identify truly priority areas. Nevertheless, due to their complex nature, socio-economic development strategies are not (and hardly can be) a full-fledged document of longterm, let alone medium-term budget planning. This task should be solved by the budget forecast of the region.
The budget forecast of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation for a long-term period is a strategic planning document containing the following information: a forecast of the main characteristics of the budget, indicators of financial support for national projects and state programs, basic approaches to shaping budget policy for a long-term period, as well as other indicators characterizing the budget. In accordance with paragraph 2 of Article 170.1 of the Budget Code of the Russian Federation, such a forecast is projected for a period of up to 12 years.
Budget forecasts have been publicly released in all subjects of the Northwestern Federal District, with the exception of the Nenets Autonomous Area. In contrast to the strategies, the budget forecasts of all regions in one format or another show the volume of financial support for government programs and non-programmatic areas of activity, highlight the largest expenditure items for the coming years, determine the financing of government programs, as well as national projects. In all regions, the demand for increased cost efficiency is emphasized, which is ensured by spending in the format of government programs. In all regions of the Northwestern Federal District, the budget forecast is presented in the baseline scenario in accordance with the forecast of the socio-economic development of the region, with the exception of the Vologda and Murmansk regions. However, even in the documents of those regions, only the total amount of expenditures is shown in a two-way representation, including the total amount of expenditures in the form of government programs. The amount of proposed funding in terms of programs is reflected only in the baseline scenario. It is noteworthy that the Vologda Region budget forecast details the volume of intergovernmental transfers to municipalities, which increases the overall variability of the forecast, but obviously does not disclose the complete and necessary information in the program presentation.
The importance of prioritizing costs is also mentioned, but in general terms and in the context of ensuring the implementation of the RF Presidential decrees. Less frequently (for example, in the Pskov Region and Saint Petersburg), the relationship between the budget forecast and the regional development strategy is emphasized. However, spending priorities are usually not disclosed in detail. Only in a number of cases (Republic of Karelia, Komi Republic, Arkhangelsk Region) is the funding of government programs that are priority for the region provided separately. More often, information is provided that is of particular interest, but does not reveal the real priorities: financial support for national projects implemented in the region (Komi Republic, Murmansk Region), retrospective values of the region’s credit ratings and the main directions of budget spending, but not in a programmatic format, but aggregated in the context of functional areas of expenditure (Murmansk Region) and others.
A number of explanations can be offered for the regions’ rejection of the multi-scenario budget forecast and the allocation of priority expenditures in them. First of all, reflecting several scenarios for the development of events (conservative, basic, targeted), which also presupposes a choice of priorities, is excluded in the minimum federal requirements for a budget forecast3. We believe that the desire of the regions to simplify the development of such documents plays an important role in the absence of both regulatory and practical necessity: most entities have a low level of financial independence. Financial authorities do not see the need to develop a detailed version of the budget forecast. The differentiation of documents found in terms of other elements: regional financing of national projects, credit ratings values can be explained by managerial competencies and the initiative of specialists from the financial department of the respective region.
Thus, the budget forecasts of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation are a simple statement of future events without their cost estimation in various versions of the forecast. As a rule, they do not have a clear list of priority areas with appropriate amounts of funding.
When drawing up the “Main directions of budget and tax policy” (hereinafter referred to as the MDBTP), the provisions of the goal-setting documents are disclosed, the results of the implementation of budget policy in the current year are taken into account, as well as the approaches of the financial authority to the preparation of the draft budget and its main characteristics, including the projected parameters. Consequently, the MDBTP should reflect the priorities of the regional budget policy. In practice, they define only the general principles on which the region’s tax and budget policy is based, but not the vision of various financing scenarios for clearly identified government priorities.
In all the reviewed documents of the Northwestern Federal District regions, budget policy is guided by the priority of goals and objectives set by the President of the Russian Federation and the provisions of national and federal projects. Such priorities are usually characterized as unconditional. Special attention is paid to priority financing of the implementation of national goals in accordance with presidential decrees, the implementation of measures stipulated in the President’s messages to the Federal Assembly, full financial support for the implementation of priority tasks for the regions (the list of which, however, is not always clearly defined) and the achievement of planned results of regional projects. Although the need to implement budget expenditures based on the principle of prioritization is emphasized, there is usually no specification of priority areas.
Assessing the completeness of disclosure of budget spending priorities in the materials directly accompanying the budget preparation – the “Main directions of budget and tax policy” of the constituent entity of the Russian Federation
A common problem for the regions is the limited disclosure of the MDBTP priorities. Even if the priorities themselves are clearly identified, the average expert assessment by the criterion of completeness, set by us, was only 6.1, with a maximum of 10.0 ( Tab. 2 ).
Table 2. Expert assessment of the MDBTP of the Northwestern Federal District regions
|
Region |
Clarity of priority spending areas |
Completeness of priority disclosure |
Originality of the selected areas; reflection of regional specifics |
Overall average score |
|
Republic of Karelia |
7 |
6 |
7 |
6.7 |
|
Komi Republic |
7 |
5 |
8 |
6.7 |
|
Arkhangelsk Region |
7 |
7 |
8 |
7.3 |
|
Vologda Region |
8 |
6 |
7 |
7.0 |
|
Kaliningrad Region |
8 |
7 |
6 |
7.0 |
|
Leningrad Region |
6 |
6 |
8 |
6.7 |
|
Murmansk Region |
8 |
7 |
9 |
8.0 |
|
Novgorod Region |
||||
|
Pskov Region |
||||
|
Saint Petersburg |
6 |
6 |
8 |
6.7 |
|
Nenets Autonomous Area |
8 |
5 |
8 |
7.0 |
|
The average for all regions considered |
7.2 |
6.1 |
7.7 |
- |
|
Source: own compilation. |
||||
In some regions, the priorities of fiscal policy are not only very clearly but also quite fully outlined. For example, the priorities of the Kaliningrad Region include supporting the region’s economy, including the implementation of infrastructure projects, stimulating investment and entrepreneurship. In the Vologda Region, the main priority belongs to the governor’s initiatives in addition to national development goals, while budget policy in each of the areas (security and law enforcement, national economy, housing and communal services, social sphere) is relatively highly detailed.
In other regions of the Northwestern Federal District, although the priority spending areas are clearly identified, they are done so in relatively little detail. In addition to increasing wages and maintaining the achieved wage levels for certain categories of employees, specific priorities are outlined such as the development of infrastructure in closed administrative-territorial formations, the implementation of master plans for key settlements in the Arctic zone, cost recovery for utilities (Murmansk Region), the formation of a comfortable urban environment, the entrepreneurship development, and the formation of a motivation system for healthy lifestyle, reduction of unsuitable housing stock (Nenets Autonomous Area), ensuring wages not lower than the minimum wage, annual wage indexation; maintaining established social support measures (Komi Republic).
For comparison, the regional priorities of budget expenditures in Saint Petersburg and the Leningrad Region are noticeably less clearly and fully disclosed, where only the strategic prioritization of expenditures and the development of project management principles are mentioned. There is no detailed description of those and other areas.
It is quite difficult to explain the revealed interregional differentiation according to the criteria for disclosure of spending priorities in the MDBTP. Nevertheless, we can note that the priorities are most clearly reflected in the regions that pay great attention to the specifics of their development in spatial and sectoral aspects (Kaliningrad, Vologda, Murmansk regions). In addition, the most original spending priorities are observed in the northern regions of Russia (Murmansk Region, Nenets Autonomous Area, Komi Republic), which is largely related to certain areas of budget provision within the framework of the state policy for the development of the Arctic zone of the Russian Federation. It is noteworthy that the high-income regions of the city of Saint Petersburg and the Leningrad Region do not pay much attention to prioritization of expenses, although more fiscally independent regions could be expected to reflect priorities more fully.
It is difficult to assess the originality of the identified spending areas, given that in all regions they largely mirror federal priorities. Nevertheless, for some regions, as we have shown, a number of identified spending areas are quite specific. We also note that the regions are trying to find a balance between federal and regional goals. For example, the Arkhangelsk Region emphasizes the priority of financing regional goals aimed at ensuring the implementation of national projects and decrees of the President of the Russian Federation.
Identifying priority areas and volumes of regional expenditures that coincide with federal priorities based on the actual materials of the laws on the regional budget for 2025–2027
The Novgorod and Pskov regions have the largest share of expenditures carried out within the framework of national projects (about 20–25%; Figure ). The share of such funds in the expenditures of the other regions is much lower. In all regions, the largest amount of spending is directed within the
Share of expenditures under national projects in the total expenditures of budgets of the subjects of the Northwestern Federal District of the Russian Federation in 2025, %
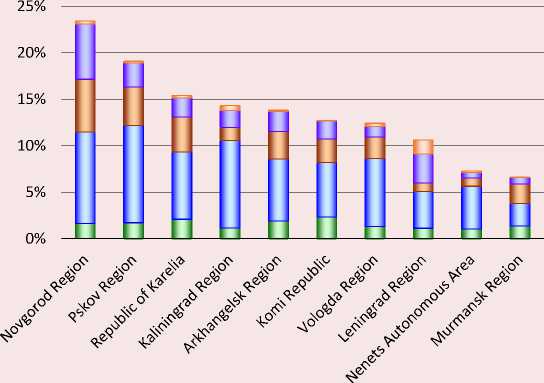
-
□ Other national projects
-
□ Ja “Family”
-
□ Yu “Youth and children”
-
□ I “Infrastructure for life”
-
□ D “Long and active life”
According to: data from the laws on the regions’ budget for 2025–2027.
framework of the national project “Infrastructure for Life” (an average of 6.8% for all regions), significantly less – for the projects “Youth and children”, “Family” and “Long and active life” (2.7, 2.2, and 1.6%, respectively).
The revealed structure of expenditures of regional budgets within the framework of national projects repeats the list of their spending powers (obligations) provided for in federal legislation4. Interregional differentiation exists, but it is not so widespread ( Tab. 3 ).
The high share of expenditures within the framework of the national project “Infrastructure for life” is due to the fact that through it expenses for the construction and repair of highways are carried out (the federal project “Regional and local road network”). It is one of the main expenditure obligations at the regional level. Expenditures in the field of education within the framework of the national project “Youth and children” are also quite voluminous. Funds are allocated for the repair and modernization of schools, upgrading their technical facilities (the federal project “All the best for children”), additional costs are incurred for individual, “advanced” schools (federal project “Leading schools”), professional development and additional education for teachers (federal project “Teachers and mentors”). Measures similar to maternity capital at the regional level (federal project “Family support”) and state support programs for large families (federal project “Family with many children”) are funded at approximately the same level as part of the national project “Family”.
Table 3. Share of expenditures under national and federal projects in the total expenditures of the budgets of the RF constituent entities in 2025, %
|
National (federal) project |
.55 ТБ СП ^ ОС |
S’ ОС Ё |
S5 ОС со CD х: |
S5 ОС СП |
ОС "ей |
ОС _| |
ОС со СП Е 1 |
ОС |
ОС |
СП CD со ел CD CD 2 |
СО CD CD "ел со |
|
D “Long and active life” |
2.1 |
2.3 |
1.9 |
1.3 |
1.1 |
1.1 |
1.4 |
1.6 |
1.7 |
1.1 |
… |
|
I “Infrastructure for Life” |
7.2 |
5.8 |
6.7 |
7.3 |
9.4 |
3.9 |
2.4 |
9.9 |
10.5 |
4.6 |
… |
|
I8 “Regional and local road network” |
6.0 |
5.2 |
5.8 |
5.7 |
8.0 |
3.0 |
1.5 |
8.2 |
8.6 |
4.0 |
… |
|
U “Youth and children” |
3.7 |
2.6 |
2.9 |
2.3 |
1.4 |
0.9 |
2.1 |
5.7 |
4.1 |
0.9 |
… |
|
U4 “All the best for children” |
2.0 |
1.0 |
1.0 |
1.4 |
0.7 |
0.3 |
0.9 |
2.2 |
1.4 |
0.2 |
… |
|
U5 “Leading schools” |
0.0 |
0.0 |
0.0 |
0.0 |
0.0 |
0.0 |
0.0 |
1.3 |
1.5 |
0.0 |
… |
|
U6 “Teachers and mentors” |
1.2 |
1.3 |
1.2 |
0.7 |
0.5 |
0.6 |
1.0 |
0.8 |
1.0 |
0.7 |
… |
|
Ja “Family” |
2.0 |
1.9 |
2.2 |
1.1 |
1.8 |
3.1 |
0.7 |
5.9 |
2.6 |
0.6 |
… |
|
Ja1 “Family support” |
0.5 |
0.9 |
1.0 |
0.1 |
0.2 |
2.6 |
0.1 |
2.3 |
0.2 |
0.2 |
… |
|
Ja2 “Large family” |
0.4 |
0.3 |
0.8 |
0.4 |
1.1 |
0.3 |
0.2 |
1.6 |
1.8 |
0.0 |
… |
|
Other national projects |
0.3 |
0.1 |
0.1 |
0.3 |
0.5 |
1.5 |
0.1 |
0.3 |
0.2 |
0.2 |
… |
|
Total expenditures under national projects |
15.4 |
12.7 |
13.8 |
12.4 |
14.3 |
10.6 |
6.6 |
23.4 |
19.1 |
7.3 |
… |
|
Total expenses, billion rubles |
73.5 |
124.5 |
151.7 |
166.4 |
149.3 |
268.6 |
142.1 |
65.2 |
58.1 |
29.5 |
1491.5 |
|
Source: own compilation. |
Conclusions
The scientific significance of the study is to assess the importance of a multi-scenario approach in budget planning at the level of the RF constituent entities and the reflection of budget spending priorities in various documents. We have studied all the main documents of budget forecasting and planning at the regional level – strategies of socio-economic development, budget forecasts and the main directions of budget policy of the RF constituent entities from the Northwestern Federal District. This is the first time this has been done. The analysis of those documents allowed obtaining the following results.
We have established that prioritizing the goals and objectives of the state policy of the RF constituent entities only within the framework of socio-economic development strategies is insufficient. The vast majority of the budget forecasts are presented in the baseline scenario in accordance with the forecast of socio-economic development. Even in the Vologda and Murmansk regions, where a multi-scenario approach to budget forecasting is applied, only the total amount of expenditures is shown, including the total amount of expenditures in the form of government programs. The MDBTP of all the regions considered also use only a baseline scenario of the forecast of budget parameters.
We revealed the low clarity of priority spending areas and the incompleteness of the disclosure of priorities in the MDBTP. Even if some areas of expenditure differ in comparative detail and are designated as priorities, there is no projected amount of funding for them. This diminishes the substantive value of such documents. Consequently, the priorities of budget expenditures at the regional level are not always explicitly indicated.
For the first time, we identified the actual priority areas of regional expenditures that coincide with federal priorities, and gave an estimate of their volumes by region based on the materials of the law on the regional budget of each region, that is, based on current empirical data. The paper establishes that the structure of expenditures of regional budgets within the framework of national projects repeats the list of their expenditure obligations stipulated in the federal legislation. Nevertheless, the revealed differentiation among regions in terms of spending areas requires additional research.
A variable approach to budget planning and clear priorities of regional public policy increase transparency and predictability of government actions, reduce uncertainty, strengthen financial stability and generally have a beneficial effect on the effectiveness of public administration. However, we have found that the RF constituent entities have poorly implemented a multi-variant approach to forecasting and planning budget revenue and expenditure items, and spending priorities remain vagely defined. This situation is probably due to the same factors that we proposed in terms of analyzing the budget forecasts of the regions, namely the lack of direct requirements from the federal level and the lack of interest from the regions in complicating the development of the relevant documents unnecessarily. Apparently, the dependence of the financial stability of the region on the recommendations of the theory of budget planning is not confirmed by the practice of budget policy. This may be due to the low administrative (in terms of separation of powers) and financial independence of the regions.
The answer to the question of what exactly prevents the introduction of a multi-scenario approach and allocation of expenditure priorities in the framework of budget planning at the regional level may be the subject of further research. From a practical point of view, it is relevant to develop possible methodological recommendations for regions on information disclosure in terms of the multi-scenario approach and the use of certain forecasting methods.


