Reocinetical analysis polyetoxysiloxane polymers with zirconyl oxychloride
Автор: Kuvatov D.G., Mustafoev O.Sh., Akhundjanov K.A.
Журнал: Экономика и социум @ekonomika-socium
Статья в выпуске: 1-1 (56), 2019 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/140241387
IDR: 140241387
Текст статьи Reocinetical analysis polyetoxysiloxane polymers with zirconyl oxychloride
Wide interest to nanotechnologies last time is explained, at last by 3 circumstances. Many of key questions are connected to the structure i.e. atoms arrangement inside the nanostructure [1-4]. The structural nanoformations on the base of network polysilaxane polymers which are formed in the course of reaction-active polyetoxysilane oligomers. Hardening, forming the network structures inside of nanoparticles is of special interest. Investigation of hardening macro kinetics for these systems, besides the applied aspects (determination of gel- formation points, “vitality” fibre etc) is of significant scientific interest because it gives information on the mechanism and physicschemical regularities of nanoparticles formation on the base of three – dimensional polymers network structures. In nanoscale the relative stability of structure various elements can change depending both kinetic and thermodynamic factors. This implies the necessity of careful investigation of kinetics and thermodynamics of phase transitions in nanostructural systems in the course of three-dimensional polyetoxysiloxane polymers formation, which synthesis process can proceeds without of second component addition in catalyst presence [5-7].
The main goal of this investigation is the investigation of rheokinetic regularities of three-dimensional polymeric nanostructures on the base of tetraetoxysilane under varying of catalyst content in reaction system with the use of viscosimetry method, which allows observing the process of structure formation up to fluidity loss by the system under investigation.
Experimental. Polyetoxysiloxane oligomer was investigated, obtained on the base of TEOS. Reaction system compositions are:
Polyetoxysiloxane (PES) oligomer formation reaction was carried out at 250C 24 h. The oligomer obtained was colorless liquid with viscosity 0,14 Pa. Hardening reaction – nanoparticles formation was carried out in isothermical conditions at 250C under catalyst content varying. Modification of nanostructures on PES base in the hardening process was carried out by insertion of various quantities of zirconyl chloride in hardening systems. Viscosity changes in the process of hardening was estimated on rotation viscosimeter “Rheotest-2” (Germany) with working unit of coaxial cylinders in the conditions of high shear velocities (D=656sec-1).
Results and Discussion. The mechanism of oligomer obtaining and its further hardening occurs by sol-gel process scheme, including hydrolysis reaction followed by alcoxy or hydroxysilanes condensation [1-3]. At the beginning under alcoxy group hydrolysis, silanol groups ≡ Si-OH are formed and under condensation on hydroxyl and alcoxyl groups ≡ Si-O-Si ≡ chains are formed. Under the further hydrolysis and condensation siloxane network of hydrogel is formed by oligomers cross-linking. The process goes through nuclei formation and particles growth followed their agglomeration.
The structure formed is on porous network with the pores size 1-10nm; which is similar to ceolites structure with specific surface (S s.a ) depending on synthesis conditions 130-1260 m2 g-1.
Thus at well controlled hydrolysis conditions (solvent, catalyst, temperature) and tetraalcoxysilane condensation in the presence of transformed polymer it is possible to get materials where organic polymers are included homogeneously in silica three-dimensional network, forming two-phase system. In display of physical and chemical properties by these systems both organic and inorganic phases play the important role. Synergism between two phases can be explained exceptionally by domens size influence and interface properties. As inorganic component zirconyl chloride was used which participates in the beginning stage of sol-gel reaction and in polymerization process it includes in the structure of network polymer simultaneously with hybrid silica formation. In this case this component from the beginning is dispergated homogeneously by ionic-bonding interaction that leads to homogeneous matrix with sol-gel reaction completion. The common scheme of three-dimensional polymeric micro-spherical silica gel consists of three stages. On the first stage hydrolytic polycondensation of initial alcoxysilanes takes place with the formation of PES oligomer. On the second stage hydrosol is formed by addition of components to regulate of porosity in alcohol solutions. After hydrosol drying at 1200 C hydrogel is formed followed with xerogel- silica gel formation. It was of significance to investigate the kinetics of sol-gel process of porous microspherical polymer-silica sorbent obtaining to investigate the effect of some factors, influencing on sol-gel process and properties of reaction end product.
On the structure on xerogel forming, hardening reaction kinetics and mechanism structural features of reacting components and their ratio with hardening in reaction system influence. In the hardening process the complex of chemical and physical-mechanical properties changes. Schematically PES oligomer hardening process can be divided into 2 stages.
On the first stage the growth of linear macromolecules and their branding take place, but common network enveloping all material volume is absent. On the second stage such network is formed. Eventually, in the systems with the increasing of topological complexity of molecules in the course of reaction, when the transition takes place in the scope of liquid phase from liquid aggregate state in hard (high-elastic or glass-like) the velocity of network polymer formation process will be determined at the every stage of functional groups interaction and various relaxation processes. Formation of concrete topological forms developing at polyfunctional molecules (oligomers) condensation depends on the nature of substances reacting and ratio of different elementary reaction velocities and determines the concrete value of the optical transformation degree, which is responsible for fluidity loss-the moment, which is named by various terms- “structurizing”, gel-formation. On the Figure1 the experimental data of dynamical viscosity for hardening PES with various catalyst content (3,6,9,12,15% in relation to oligomer) depending on time. As the initial reagents 10% PES oligomer in ethanol and ammonia hydroxide as a catalyst were used.
It is seen from rheokinetical curves that it is possible to escape 3 steps of PES oligomer gel formation the initial induction period when the system remains the viscous Newtonian liquid with practically constant viscosity the stage of intensive gel-formation with rapid increasing of all parameters measured and completing period when the limiting values of dynamical viscosity is reached and the gel formed is stabilized. The time constants, characterizing these steps are determined: t o - the end of induction period t 1/2 -half period of gel formation process to the time of full process proceeding. As it is seen from the results cited in the table 1 and figure 2 this clearly give the main regularities of gel formation process namely the existence of induction period, auto catalytically character of viscosity increase and obtaining of limiting gel state.
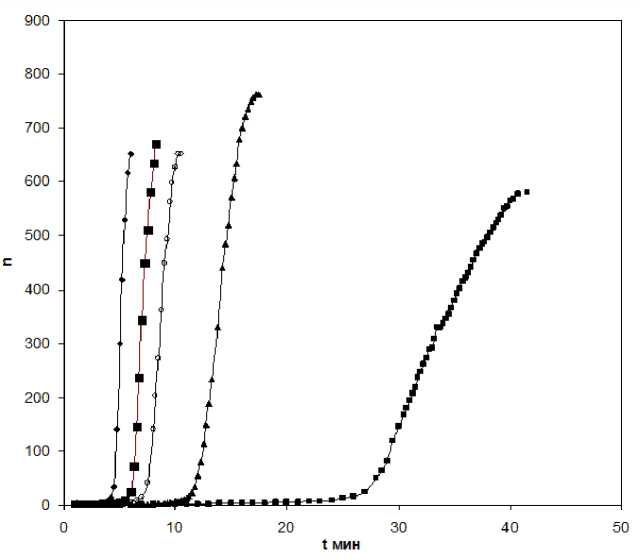
Figure 1. The dependence of dynamical viscosity of PES oligomer hardening process time depending on catalyst. Catalyst water solution of ammonia: 1) ■- 3% 2)A- 6% 3) о - 9% 4) ■ -12% 5) ^ - 15%
Table 1. The dependence of PES oligomer hardening time on catalyst (I)
and zirconyl chloride (II) on catalyst content gap
|
I Catalyst content,% |
t 0 c. |
t 1/2 C |
t K C |
|
3 |
240 |
1980 |
3960 |
|
6 |
240 |
830 |
1050 |
|
9 |
60 |
515 |
570 |
|
12 |
60 |
410 |
495 |
|
15 |
60 |
300 |
360 |
|
II Zirconyl chloride content, % |
|||
|
- |
60 |
515 |
570 |
|
0,8 |
60 |
480 |
585 |
|
1,7 |
60 |
490 |
590 |
|
3,5 |
60 |
495 |
590 |
|
5 |
120 |
585 |
615 |
|
6,7 |
120 |
610 |
625 |
From the data cited it is seen clearly the catalyst influence on PES oligomer gel formation kinetics. The decrease of catalyst leads to significant increase of time constants. It is especially distinctly expressed at 3% catalyst addition.
Experimentally by viscosimetry method the determination of full gel formation process due to hardening and loss of system flow. The T k value is determined by calculation through extrapolation. Mathematical treatment of experimental results obtained allowed deriving the equation describing the change of dynamical viscosity on time as follow: η = η 0 exp(k η t) [8].
On the Figure 2 the influence of zirconyl chloride solution on the process of PES oligomer hardening is shown. As it is seen from Figure 2 and Table 1 the increase of 5% zyrconyl chloride concentration in system in hardened system leads to slowing down of gel formation reaching point. It can be explained by the chemical interaction of zirconyl chloride with silanol groups of PES oligomer product hydrolysis that possibly fades the part of active centers and leads to less cross linked structure of polymer.
The duration and velocity of mixing in sol-gel process of polymer zirconyl silica sorbents obtaining were investigated. On the form of the sorbent obtained influence significantly viscosity, velocity and mixing duration. It was shown that the optimal mixing velocity under hybride sorbent obtaining with zirconyl chloride addition is 2700 v/m and duration up to 4 min. Decrease of mixing velocity leads to increase of sorbent PMSS particles up to 20 µ m and decrease of mixing duration leads to obtaining of non-spherical and integration of sorbent form. Increase of mixing time leads to decrease of hybrid sorbent parts to 1 µ m.
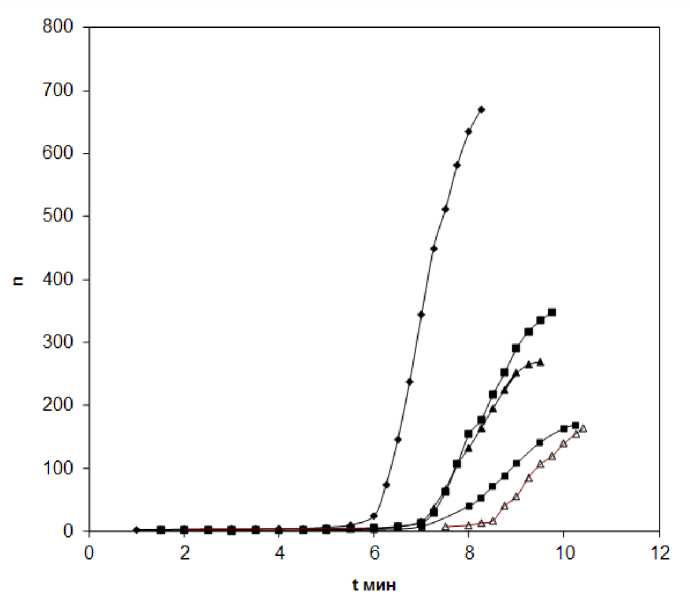
Figure 2. Dependence of dynamical viscosity on time of hybrid oligomer PES hardening process and quantity of zyrconyl chloride.
-
1) ♦ - without additives ; 2) ■ - 1,7%; 3) A-3%; 4) ■ - 5%; 5) A - 6,7%
So, in can be noted that zirconyl chloride solution influences actively on the process of PES oligomer hardening and slowing down the the hardening process, forming more spatial polymer network.
Conclusion. The rheokinetical regularities of polyetoxysilane oligomers hardening under varying of catalyst content in system and modifying reagent were investigated. It was shown, that introduction of zirconyl chloride in systems and increase of its content leads to slowing down of gel formation process and formation of less cross-linked structures.
Some technological parameters of obtaining and regulation of polymer zirconylsilica nanostructural particles were estimated.
Список литературы Reocinetical analysis polyetoxysiloxane polymers with zirconyl oxychloride
- Antonio Sánchez-Fernández, Laura Peña-Parás, Elisa M. Mendoza, Alejandra Leyva. Spectroscopic and Thermal Studies of Polyalkoxysilanes and Silica-Chitosan Hybrid Materials//Journal of Materials Science Research; Vol. 5, N1; 2016
- Georgi Chernev, Elena Todorova, Stoyan Jambazov, Isabel M.M. Salvado, Juliana Ivanova. Synthesis and structure of sol-gel silica-polysacharide hybrids.//Journal of chemical technology and Metallurgy, 49, 2, 2014, 128-132
- Jen-Taut Yeh, Chin-Lai Chen, Kuo-Shien Huang. Synthesis and properties of chitosan-SiO2 hybrid materials.//Materials Letters 61 (2007) 1292-1295
- Hong Zhao, Jianhong Xu, Wenjie Lan, Tao Wang, Guangsheng Luo. Microfluidic production of porous chitosan-silica hybrid microspheres and its Cu(II) adsorption performance. China. Chemical Engineering Journal 229 (2013) 82-89
- Tetyana M Budnyak, Ievgen V Pylypchuk, Valentin A Tertykh, Elina S Yanovska and Dorota Kolodynska. Synthesis and adsorption properties of chitosan-silica nanocomposite prepared by sol-gel method. Budnyak et al. Nanoscale Research Letters (2015)
- Victoria Puchol, Jamal El Haskouri, Julio Latorre, Carmen Guillem, Aurelio Beltrán, Daniel Beltrán and Pedro Amorós. Biomimetic chitosan-mediated synthesis in heterogeneous phase of bulk and mesoporous silica nanoparticles.//This journal is (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry 2009
- Grazielle S. Silva; Pedro C. Oliveira; Domingos S. Giordani; Heizir F. de Castro/Chitosan/siloxane hybrid polymer: synthesis, characterization and performance as a support for immobilizing enzyme. Escola de Engenharia de Lorena, Universidade de São Paulo, CP116, 12602-810 Lorena-SP, Brazil 2011
- Gorbunova, Yu.; Kerber, M.L.; Balashov, I.N.; Kazakov, S.I.; Malkin, Ya. Visokomol. Soed. 2001, A 43, (8), 1339.


