Research in the functioning of the regional budgetary system
Автор: Pechenskaya Mariya Aleksandrovna
Журнал: Economic and Social Changes: Facts, Trends, Forecast @volnc-esc-en
Рубрика: Public finance
Статья в выпуске: 5 (41) т.8, 2015 года.
Бесплатный доступ
The state regulation conducted in accordance with the current economic policy plays a leading role in the formation and development of the economic structure of modern society. The financial system carries out control activities in the market economy through financial mechanisms by means of financial levers and incentives to achieve financial objectives. Regional public finance, as a major part of the RF financial system, is of great importance for the reproductive process during the transfer to effective market organization of the economy. The state budget is the main link of the financial system. It is an incomparable by its amount monetary fund, winch has huge investment potential and can quantitatively and qualitatively affect the efficiency of social production. The use of this potential to a great extent will determine a development direction and regional economy sustainability. The stability of the budget system is seen in the concept of long term socio-economic development of Russia until 2020 as a vital condition for the solution of strategic economic and social objectives of financial provision of innovative development of the economy...
Public finance in the region, budget policy, budget, interbudgetary relations, budgetary security, problems of public administration efficiency, market reforms trends, budgetary system crisis, role of private capital
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/147223760
IDR: 147223760 | УДК: 336.143 | DOI: 10.15838/esc/2015.5.41.10
Текст научной статьи Research in the functioning of the regional budgetary system
This publication is part of a series of articles devoted to the 25th anniversary since the foundation of the Institute of Socio-Economic Development of Territories of RAS.
The adoption of the RF Budget and Tax codes in 1998 and the legislative consolidation of multi-tiered budget and tax systems required scientific solution of key objectives, such as redistribution of powers between levels of government . In this regard, in 1999–2001 the Institute of Socio-Economic Development of Territories of RAS performed the research in the problems of formation of regional and local budgets and allocation of expenditure and revenue powers and authority between levels of the budgetary system (E.A. Prokof’ev, S.N. Dubov). Based on the 1999–2000 data the research associates estimated the tax potential of municipal entities and considered the options of financial aid distribution to the Vologda Oblast districts, aimed at leveling the fiscal capacity of population in the region and encouraging the local governments to improve the efficiency of the available revenue base use. The research results sent to the Vologda Oblast Department of Finance were taken into account when drafting the regional budget for 2002.
The extensive scientific work was conducted by the Institute together with the Foundation for Enterprise Restructuring and Financial Institutions Development (Moscow) under “Regional Fiscal Technical Assistance Project” initiated by the International Bank for Reconstruction and Development. Some findings of this study were disclosed the monograph “Regional Public Finance: Conditions, Factors and Prospects” (V.A. Ilyin, M.F. Sychev, S.N. Dubov, E.A. Durnova, L.V. Kostyleva) in 2001. It presented the results of estimated state of public finance in the Vologda Oblast in 1997–2000, the analysis of influence of various factors and proposes directions for future development of the system of budget resources and extra budgetary funds of the region. The research team was focused on the identification of state of public finance in the region.
The year of 2003 witnessed a new phase of the municipal governance level reform enshrined in the federal law “On general principles of local government organization in the Russian Federation” No. 131-FZ of October 6, 2003. In this regard, ISEDT RAS initiated the research in the local self-government system in terms of the new law implementation (T.V. Uskova, E.D. Amelin, A.A. Kol’ev, S.N. Dubov). The researchers analyzed severe shocks in local self-government the country had been experiencing since 1991. First, the local government system was changed radically due to the adoption of the 1991 RSFSR law “On local self-government in RSFSR”, namely the changes in competence of local councils and the substitution of the collegial control body (the Executive Committee) by the head of local administration, acting according to the principle of unity of command. Second, the local authorities underwent radical restructuring in autumn of 1993: the “presidential reform” of local self-government involved the cease of local councils’ activity and the construction of a new system of local self-government on the basis of the Presidential decrees. Some provisions were not consistent with the Constitution. Third, in 1995 with the adoption and the entry into force of the federal law “On general principles of local self-government organization in the Russian Federation” there was a new phase of local government reorganization.
Since January 1, 2006 a number of Russian regions, including the Vologda Oblast, has been creating a two-tier model of local selfgovernment in a pilot mode. In the region there are 372 municipal formations, of which 2 – urban districts, 26 – municipal districts and 344 – urban and rural settlements. The reform of municipalities was aimed at transforming their spatial boundaries, streamlining the budgetary organization, changing the principles of exercising the powers and the conditions of forming the local budgets revenue and expenditure and developing the new methods of the budget process. According to the reforms, the local authorities were to obtain clear boundaries and an independent revenue base. In this regard, it was very relevant to carry out the comprehensive assessment of reform processes at the local level and current state of municipal finances. The ISEDT RAS research was focused on the analysis of changes in the fiscal autonomy of local selfgovernments in revenues and expenditures due to the municipal reform and the reform of interbudgetary relations, as well as the assessment of compliance of the results with the stated principles (M.A. Pechenskaya). The evaluation of state of municipal finance of the Vologda Oblast in 2003–2010 showed that the fiscal autonomy of municipalities had decreased. The deterioration in the financial condition of municipalities was manifested in the following:
-
• reduction in the proportion of local budgets’ own revenues in gross regional product (up to 3% in 2006 against 6% in 2004);
-
• significant redistribution of tax revenues from the local budget in favor of the regional one (71% in 2010 against 34% in 2004);
-
• only 4% of the local taxes are allocated to territorial budgets
-
• significant increase in the importance of the intergovernmental transfers system (from 25.9% in revenues in 2003 to 64.2% in 2010);
-
• increase in the differentiation according to the degree of fiscal autonomy of 3 types of municipal entities: urban districts, municipal districts and settlements;
-
• increase in the dependence of local governments’ power execution on financial assistance, but not on quality of management activities (more than 95% of the municipalities receive subsidies to equalize fiscal capacity and budget balance).
To strengthen research in the fiscal direction, in 2009 ISEDT RAS created a sector of public finance in the structure of the Department of Socio-Economic Development and Governance in Territorial Systems and the graduate school had a new specialty – 08.00.10 “Finance, monetary circulation and credit” .
Due to the crisis phenomena in the economy since the end of 2008 the sector has been focused on identifying threats to the formation of territorial budgets and the development of methods to raise the level of budgetary security of territories. It is the question of sustainable development of Russian regions in the context of their budget provision has grown particularly acute in the period when the formation and the execution of subnational budgets occurred in conditions of severe imbalance.
To assess the level of budgetary security of the region the sector elaborated the method including 4 directions of evaluation (fiscal position, debt load, inter-budgetary relations and budget management quality). On its basis the researchers estimated the level of budgetary security of the Northwestern Federal District subjects. The calculation results are presented in Table 1.
Table 1. Integral estimation of the budgetary security level of the Northwestern Federal District subjects in 2006–2010, calculated by ISEDT RAS
|
Subject |
2006 |
2007 |
2008 |
2009 |
2010 |
|||||
|
Point |
Level assessment |
Point |
Level assessment |
Point |
Level assessment |
Point |
Level assessment |
Point |
Level assessment |
|
|
Saint Petersburg |
35.2 |
high |
35.5 |
high |
36.0 |
high |
28.0 |
average |
33.1 |
high |
|
Murmansk Oblast |
26.5 |
average |
27.3 |
average |
25.7 |
average |
23.5 |
average |
30.0 |
average |
|
Leningrad Oblast |
30.2 |
high |
31.2 |
high |
30.5 |
high |
26.9 |
average |
30.0 |
average |
|
Komi Republic |
31.1 |
high |
27.4 |
average |
30.2 |
high |
24.1 |
average |
27.0 |
average |
|
Pskov Oblast |
30.1 |
high |
29.7 |
average |
30.8 |
high |
26.7 |
average |
26.7 |
average |
|
Arkhangelsk Oblast |
29.2 |
average |
27.6 |
average |
26.4 |
average |
16.6 |
low |
26.3 |
average |
|
Vologda Oblast |
32.7 |
high |
31.0 |
high |
32.6 |
high |
14.9 |
low |
26.0 |
average |
|
Novgorod Oblast |
28.4 |
average |
31.7 |
high |
29.6 |
average |
27.8 |
average |
24.8 |
average |
|
Kaliningrad Oblast |
33.2 |
high |
31.3 |
high |
33.3 |
high |
24.4 |
average |
24.5 |
average |
|
Republic of Karelia |
23.3 |
average |
26.5 |
average |
27.8 |
average |
15.6 |
low |
24.2 |
average |
Istochniki: Povarova A.I., Pechenskaya M.A. Metody povysheniya byudzhetnoi obespechennosti regiona : zaklyuchitel’nyi otchet o NIR [Methods to Improve Budget Sufficiency of the Region : Final Research Reports]. Vologda, 2010. 130 p.; Povarova A.I. Metody povysheniya byudzhetnoi obespechennosti regiona [Methods to Improve Budget Sufficiency of the Region]. Vologda: ISERT RAN, 2011. 39 p.
According to the assessment, Saint Petersburg was in the lead by level of fiscal capacity. Before the crisis, the Kaliningrad Oblast (the second leader in the district in 2006–2008), the Vologda Oblast and the Leningrad Oblast demonstrated a high level persistently. The Komi Republic can be also considered as a self-sufficient region. These results were due to the high growth rate of consolidated budge revenues, the prudent debt policy of regional authorities, the minimization of accounts payable and interest costs and the improved quality of management of certain stages of the budget process.
However, the reduction in the integral assessment of the fiscal capacity level in 2009 caused by the drop in own revenues of consolidated budgets with all the special effects, which include: high budget deficit, reduced provision of the Oblasts with budgetary resources, increasing amount of receivables on payments to the budget and debt liabilities and increased dependence on allocations from the federal government. In these circumstances even Saint Petersburg failed to maintain the status of a wealthy Oblast. The Vologda Oblast, the Arkhangelsk Oblast and the Republic of Karelia that suffered most from the crisis moved into the category of regions with low fiscal capacity.
The regions dependent on transfers, such as the Novgorod Oblast and the Pskov Oblast, were unexpectedly characterized by a high budgetary provision level. However, this can not be assessed unambiguously. The significant inflow of financial assistance led to the positive development of certain components of the budget systems of these subjects. However, both areas are little dependent on a limited circle of taxpayers, characterized by a low level of interest expenses and payables. The regions have an apparent advantage, such as higher realism of budget planning in comparison with, for example, the Vologda Oblast.
It should be noted that since 2010 the Institute has annually prepared an expert opinion on the Vologda Oblast draft laws “On regional budget” and sent them to the Government and the Legislative Assembly of the region, together with a detailed analysis of the project and proposals for improving the budget process.
In the same year, relying on the monitoring of the status of regional budget systems, the public finance sector prepared a monograph “Public Finance of the regions: Modernization Priorities” (T.V. Uskova, A.I. Povarova, V.S. Orlova), analyzing the efficiency of the measures taken by the NWFD subjects to adapt regional finances to the crisis consequences.
The financial and economic crisis affected export-resource regions and regions of iron and steel and engineering industries most severely, particularly the Vologda Oblast, the Murmansk Oblast, the Kaliningrad Oblast and the Republic of Karelia. This initiated the research in the influence of metallurgical corporation owners’ interests on the socioeconomic development of regions and the study of the budgetary crisis causes. The work was performed under the supervision of ISEDT RAS Director Doctor of Economics, Professor V.A. Ilyin. The comprehensive analysis of activities of the leading Russian ferrous metallurgy enterprises, which are the main taxpayers in the Vologda, Lipetsk



and Chelyabinsk oblasts revealed the ineffectiveness of the country’s fiscal policy. The authors proposed the options for changes in its paradigm. One of the basic postulates of the research is the following: the actual problems associated with the decrease in the metallurgical corporations’ contribution to socio-economic development of the Russian Federation and its regions lie in the principles of modern tax policy.
The preprint “Influence of Metallurgical Corporation Owners’ Interests on SocioEconomic Development” (V.A. Ilyin, A.I. Povarova, M.F. Sychev) published in 2012 tried to address a number of pressing issues. Why is the use of the largest production capacities of ferrous metallurgy of the country not accompanied by the significant acceleration of socio-economic development of the Russian regions, where these facilities are located? Why do budgets not grow as much as incomes of metallurgical corporation owners? How do the interests of corporation owners and territorial communities differ? How is it possible to harmonize interests of the society and the owners?
The results of the further study were reflected in the monograph “Budgetary Crisis of the regions” (V.A. Ilyin, A.I. Povarova) in 2013. The authors’ calculations, based on the results of analytical developments of the famous domestic experts and the ISEDT RAS research, indicated the potential to increase the revenues of the country’s consolidated budget in the upcoming 2–3 years by 14–18 trillion rubles, or 45–70% ( tab. 2 ).
The next book to continue the research on this topic – “Problems of Public Administration Efficiency. Trend of Market Transformation. Crisis of the Budgetary System. Role of Private Capital. Strategy 2020: Problems of Realization” (2014; V.A. Ilyin, A.I. Povarova) – aroused interest not only among scholars but also among practitioners. The letter ISEDT RAS Director V.A. Ilyin received from Deputy of the State Duma of the Federal Assembly of the Russian Federation, Member of the State Duma Committee on Defense, Member of the State Council, Chairman of the Liberal Democratic Party of Russia V.V. Zhirinovsky, thanked the monograph authors for a clear civic position, based on
Table 2. Possible increase in budget revenue calculated by ISEDT RAS, trillion rubles per year
|
Source |
Factual value |
Proposed option |
RF consolidated budget |
Budgets of state non-budgetary funds |
Federal budget |
Budgets of RF subjects |
|
Abolition of export VAT refund |
18% |
0 1) |
1.1 |
1.1 |
||
|
Abolition of exemptions on VAT for the financial sector of the economy |
0% |
18%2) |
3.0–5.0 |
3.0–5.0 |
||
|
Abolition of privileges on property tax for natural monopolies |
0% |
2.2%2) |
0.2 |
0.2 |
||
|
Increase in tax rates on dividends |
5–9% |
13–15%1) |
0.2–0.5 |
0.2–0.5 |
||
|
Introduction of a progressive scale of income tax |
13%** |
13–50%3) |
2.0–4.5 |
2.0–4.5 |
||
|
Introduction of hard currency repatriation tax |
– |
20%4) |
0.5 |
0.5 |
||
|
Abolition of the annual income margin above which insurance premiums are not paid |
568 thousand rubles |
0 5) |
0.6 |
0.6 |
||
|
Introduction of luxury tax, with subsequent redistribution between RF subjects |
– |
0.26) |
0.2 |
|||
|
Abolition of the budget rule, the use of all oil and gas revenues for economical development |
25% |
0 7) |
5.7 |
5.7 |
||
|
Total |
13.5–18.3 |
0.6 |
10.3–12.3 |
2.6–5.4 |
||
Sources: Ilyin V.A., Povarova A.I. Byudzhetnyi krizis regionov: monografiya [Budgetary Crisis of the Regions”: Monograph]. Vologda: ISERT RAN, 2013. 128 p. |
||||||
the serious economic analysis. “The topic of your research is constantly kept in sight of the Liberal Democratic Party... The idea to consolidate the state and strengthen its role in the economical management becomes critically important during the sanctions,” – said Vladimir Zhirinovsky.
The special place in the ISEDT RAS works is taken by the research in the regulation of inter-budgetary relations of the territories as an integral part of budgetary policy of the federal state. There are such research works, as “Federation Subject and Federal Center: Problems and Ways to Improve Budgetary Relations” (2012), “Improvement of Methods of regional Budgets Formation” (2013; M.A. Pechenskaya).
The evaluation of the impact of inter-budgetary relations management is based on the dissertation research of the article author, one of the first graduates of the ISEDT RAS Scientific and Education Center. The PhD thesis, meeting the requirements of the specialty “Finance, monetary circulation and credit” for the first time in ISEDT RAS, was defended at the Institute of Economics RAS Dissertation Council (Moscow) in 2014. The hypothesis of the dissertation research is as follows: the effective regulation of inter-budgetary relations in the Oblast can be achieved through the expansion of organizational and economic tools for its implementation and strengthening the stimulating function of inter-budgetary relations.
In terms of the fiscal policy orientation on the outcome and the conduct of large-scale administrative reforms the issue to estimate state and municipal regulation becomes particularly urgent. The thesis presents the method to evaluate the degree of compliance of the objectives set by the state in the sphere of inter-budgetary regulation in the region to the acquired results. On the basis of this method ISEDT RAS carried out the first stage of the monitoring devoted to the effectiveness of inter-budgetary regulation on the example of the Vologda Oblast (figure).
The evaluation of financial autonomy of local budgets of the region showed that since 2006 the independence of municipal authorities in addressing budget issues had increased by 15%, however in 2012 it accounted for only 52%. It is primarily caused by the centralization of revenues, especially tax, at higher levels.
Assessment of the degree of inter-budgetary regulation effectiveness in the Vologda Oblast (calculated by the author’s method)
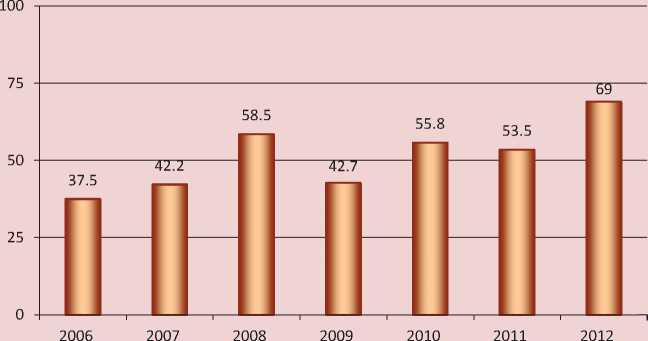
(75-100%) - high degree of effectiveness
(50-75%) - average degree of effectiveness
(25-50%) - low degree of effectiveness
(0-25%) - extremely low degree of effectiveness
Sources: Pechenskaya M.A. Otsenka rezul’tativnosti regulirovaniya mezhbyudzhetnykh otnoshenii (na primere Vologodskoi oblasti): dissertatsiya na soiskanie uch. st. kand. ekon. nauk [Assessment of the Inter-Budgetary Relations Regulation Efficiency (Case Study of the Vologda Oblast) : Ph.D. in Economics Dissertation]. Moskow, 2014. 168 p.
The assessment of adequacy of budgetary resources shows that the municipalities lack funds to finance current expenditures and stimulate the formation of innovative development budgets. Own revenues cover only 40% of the operating costs. Moreover, the powers and authorities are distributed between budgetary system levels at the expense of local budgets: up to 5% of the expenditure commitments not provided with relevant revenue sources are transferred to the lower level.
The quality and the efficiency of planning in the region in the period under analysis remained not enough high, therefore, were evaluated by 66%in 2012, largely due to the prevailing practice of under-funding of the approved budget allocations to local budgets.
The evaluation revealed problems in the Oblastal system of fiscal equalization of the municipalities. Thus, the gap in budgetary provision amounted to 4.2 times. After the provided donations it decreased slightly – to 3.4 times. However, the implementation of subsidiary support promoted differe ntiation of the local municipalities – to 4.3 times, indicating the preference to co-finance investment projects of the developed, but not developing municipalities. Thus, in 2006–2012 the evaluation of inter-budgetary regulation in the Vologda Oblast disclosed a low and medium degree of its efficiency. In 2012 the regulation results were consistent with the objectives only by 69%.
The loss of balance between the centralization of financial resources and the federalization of budgetary relations in Russia

indicates rather ineffective inter-budgetary regulation. Own budgetary resources necessary for the execution of powers and the enhancement of low potential are withdrawn from the region. This makes the subnational governments more vulnerable in terms of financial autonomy; they have to seek for additional budget resources to execute their powers and authorities and promote the formation of development budgets that are able to create and develop economic growth points.
The wide range of problems associated with various aspects to improve the efficiency of state regulation of the inter-budgetary relations are discussed in the monograph “Inter-Budgetary Relations: State, Regulation, Performance Assessment” (2015; M.A Pechenskaya).
The budget crisis of regions encouraged the research in the problems of budget risks management. The public finance sector employees classified the factors influencing the formation of public finance risks of the territories in the research work “Improving the System to Manage Budget Risks in the Territorial Budget Systems” (2014; A.I. Povarova, A.V. Galukhin, A.A. Toropilov). According to the method of fiscal risks identification revised by the authors, they studied the formation and the execution of the federal budget and the Vologda Oblast budget in 2014–2017, the management decisions on minimization of public finance risks in Russia and the region and formulated a set of measures to enhance the management of fiscal risks in the region.
The direction to study public finance is developing. A.V. Galukhin is completing the dissertation devoted to financial sustainability of a profitable part of regional budgets. The elaboration of the issue to regulate inter-budgetary relations will be continued in the doctoral dissertation of the article author (there already is a work plan for 2015–2017 and a “road” map).
To continue the research in the effectiveness of public administration the sector has prepared a monograph “Systemic Problems of regional Budgets” (M.A. Pechenskaya, A.I. Povarova), which will address the transformation processes in tax competence of the territorial authorities and the system of intergovernmental transfers and their impact on the systemic crisis of territorial budgets.
Moreover, the research in the impact of economic sectors on the budget has moved from the steel industry to the oil and gas corporations. Nowadays V.A. Ilyin supervises the analysis of the impact of largest Russian oil and gas enterprises on the socio-economic development of territories. The role of the government’s monetary policy in the economy is considered.
In conclusion we note that the search for reserves to enhance the country’s economic dynamics always remains relevant. Fiscal capacity of Russian territories, ISEDT RAS has been studying for the past 17 years, is one of the most important reserves of this kind.
Список литературы Research in the functioning of the regional budgetary system
- Ilyin V.A., Povarova A.I., Sychev M.F. Vliyanie interesov sobstvennikov metallurgicheskikh korporatsii na sotsial’no-ekonomicheskoe razvitie: preprint . Vologda: ISERT RAN, 2012. 104 p.
- Ilyin V.A., Povarova A.I. Byudzhetnyi krizis regionov: monografiya . Vologda: ISERT RAN, 2013. 128 p.
- Ilyin V.A., Povarova A.I. Problemy effektivnosti gosudarstvennogo upravleniya. Tendentsii rynochnykh transformatsii. Krizis byudzhetnoi sistemy. Rol’ chastnogo kapitala. Strategiya-2020: problemy realizatsii: monografiya . Vologda: ISERT RAN, 2014. 188 p.
- Povarova A.I., Pechenskaya M.A. Metody povysheniya byudzhetnoi obespechennosti regiona: zaklyuchitel’nyi otchet o NIR . Vologda, 2010. 130 p.
- Uskova T.V., Amelin D.E., Kol’ev A.A., Dubov S.N. O reformirovanii sistemy upravleniya Vologodskoi oblasti v svete realizatsii novogo zakona “Ob obshchikh printsipakh organizatsii mestnogo samoupravleniya v Rossiiskoi Federatsii”: otchet o NIR . Vologda, 2004. 210 p.
- Obshchestvennye finansy regiona: sostoyanie, faktory, perspektivy . Team of author under the supervision of V.A. Ilyin and M.F. Sychev. Vologda: VNKTs TsEMI RAN, 2000. 156 p.
- Pechenskaya M.A. Mezhbyudzhetnye otnosheniya: sostoyanie, regulirovanie, otsenka rezul’tativnosti: monografiya . Vologda: ISERT RAN, 2015. 164 p.
- Pechenskaya M.A. Otsenka rezul’tativnosti regulirovaniya mezhbyudzhetnykh otnoshenii (na primere Vologodskoi oblasti): dissertatsiya na soiskanie uch. st. kand. ekon. nauk . Moskow, 2014. 168 p.
- Povarova A.I. Metody povysheniya byudzhetnoi obespechennosti regiona . Vologda: ISERT RAN, 2011. 39 p.
- Prokof’ev A.E. Problemy formirovaniya mestnykh byudzhetov i raspredeleniya raskhodnykh i dokhodnykh polnomochii mezhdu urovnyami byudzhetnoi sistemy: otchet o NIR . Vologda, 1999. 84 p.
- Dubov S.N. Problemy formirovaniya regional’nykh i mestnykh byudzhetov i raspredeleniya raskhodnykh i dokhodnykh polnomochii mezhdu urovnyami byudzhetnoi sistemy: zaklyuchitel’nyi otchet o NIR . Vologda, 2001. 79 p.
- Uskova T.V., Povarova A.I., Orlova V.S. Obshchestvennye finansy regionov: prioritety modernizatsii . Vologda: ISERT RAN, 2010. 168 p.


