Research of the oxidative process of gold-containing sulfide materials roasting for the development of an optimal mode
Бесплатный доступ
Now, in world practice, sulphide refractory gold-containing materials are subjected to oxidative roasting mainly with low productivity and subsequent cyanidation provides a high degree of metal recovery. Of particular importance is oxidative calcination to increase the extraction of valuable components (Au, Ag, Mo, W, Cu, Zn) from metal-containing intermediate products. Today, new technologies and technological schemes are being developed around the world in the field of processing gold-bearing ores to increase the degree of extraction and reduce processing costs in order to reduce the cost of the product, and special attention is paid to reducing the content of a valuable component in the tailings of processes, as well as special attention paid to reduce the content of a valuable component in the tailings of production processes. In this aspect, the development of new technologies and the improvement of existing technologies to increase the extraction of valuable components are urgent tasks of the science and practice of the mining and metallurgical industry. The aim of the research was to develop an effective technology for processing sulfide materials in suspension in a kiln to intensify the process and increase the yield of valuable components.
Oxidative calcination, drying, fluidized bed furnace, sulfides, suspended calcination, refractory ores, gold-arsenic ores, biooxidation cake, desulfurization, recovery, fluidized bed, humidity, pyrometallurgy, undeoxidation, sintering of pieces
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/14125808
IDR: 14125808 | УДК: 669.213 | DOI: 10.24411/2181-0753-2020-10003
Текст научной статьи Research of the oxidative process of gold-containing sulfide materials roasting for the development of an optimal mode
Technological furnaces are very widely used in all metallurgical industries. In metallurgical furnaces due to fuel combustion, the process of heating the processed material is implemented. The heat transfer mechanism is very difficult, because in these devices, in contrast to heat exchangers, a significant contribution to the total heat transfer of the radiant (radiation) component. Sometimes this heat transfer mechanism is prevailing. The organization of the movement of the resulting flue gases and the use of heat of the exhaust gases, in turn, significantly affects the contribution to the total heat transfer of the convective component. Therefore, the design of metallurgical furnaces involves taking into account the characteristics of the supplied fuel, calculating the combustion process taking into account the hydrodynamics of the movement of
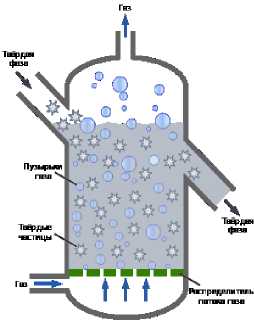
Fig. 1 Diagram of a fluidized bed furnace
flue gases, choosing the design of the furnace, taking into account the characteristics of fuel-burning devices.
These tasks involve the use of a wide variety of knowledge in technology, chemistry and physics.
The industrial scale oxidative roasting process has changed significantly over the past hundred years. The main processes on which roasting is based are as follows:
-
• Rotary kiln and multi-hearth kiln
-
• Fluidized bed roasting (single and multi-stage)
-
• Circulating fluidized bed
-
• Oxygen fluidized bed
At present, the process of oxidative roasting in a fluidized bed furnace is widespread in the world. It works by supplying air to the furnace at a sufficient speed to “liquefy” these particles. Air enters the process through the nozzle grill in the ventilation chamber at the bottom of the furnace. The speed of air required to fluidize the particles will vary from ore to ore depending on density. The fluidization of these particles provides better mixing, which provides a more efficient oxidation of pyrite to hematite. The fluidized bed design also provides a more uniform temperature in the reactor along with increased rates of heat and mass transfer in the system [1, 2].
Along with better particle mixing, the fluidized bed also provides higher throughput per unit area, better temperature control and better gas composition control, unlike other roasting units. All these improvements have made it more rational and efficient when applied to commercial operation. The giant companies Yellowknife, Campbell Red Lake, and Jerritt Canyon are widely using fluidized bed roasting in North America. All of these facilities operated for a certain period and then were closed for various reasons, including emissions problems. The scheme of the fluidized bed furnace can be seen in Figure 1.
In the analysis of existing technologies for oxidative roasting of various metal-containing sulfide materials, inefficiency associated with:
Sulphide particles in the process of oxidative roasting of gold-bearing refractory ores are undeoxidized due to low temperature inside the furnace
О
w
or insufficient process time;
In the process with increasing temperature in the process, sintering of gold particles begins, which leads to a further decrease in the degree of extraction of a valuable component;
The process of oxidative roasting of molybdenum concentrates is carried out at a temperature of 550-600ºС, with an increase in the roasting temperature, sulfide particles are oxidized to MoO 2 and MoO 3 . If the temperature rises to avoid under-oxidation of sulfides, the formation of sintered particles begins.
The above disadvantages of existing technologies are the basis for the development of more efficient methods for the oxidative burning of sulfide materials.
The experiments of oxidative roasting of sulfur and carbon-containing difficultly processed semi-products of BIOX and concentrate (charge) are carried out in a laboratory furnace of high-speed roasting. When performing work, the variables are the following parameters: Duration of roasting (20.30, 40 min.). Furnace temperature (550, 600, 650 ° С).
Based on the data obtained, the rational composition of sulfide sulfur and carbon-containing difficult-to-process BIOX intermediates and concentrates is calculated. Analyzed data after oxidative roasting of sulfide materials HMP-3 in different conditions.
A methodology has been developed for conducting studies on the oxidative roasting of molybdenum sulfide materials of the Scientific and Production Association of Rare Metals and Hard Alloys of the Almalyk Mining and Metallurgical Combine.
:-------------------------------------------------------------------------♦
To determine the best roasting mode, the process is carried out under different conditions. For example, we keep the temperature inside the furnace from 450 ° C to 750 ° C. We carry out 7 tests in this range (450, 500, 550, 600, 650, 700, 750 ° С). The duration of the process is also set from 45 minutes to 120 minutes. At each temperature regime, we conduct a minimum of 8 experiments to ensure the reliability of the research results. All samples after oxidative roasting are given for chemical analysis.
In laboratory conditions, several experiments were carried out on roasting sulfide gold-containing biocakes in the conditions of GMZ-3 intensive oxidative roasting in suspension. The purpose of the work is to determine the optimal roasting mode for the proposed design industrial furnace. Below are the results of several experiments of oxidative roasting, depending on the humidity of the mixture, temperature and duration of the process. In this case, the optimal mode of oxidative roasting is determined by the degree of desulfurization and the degree of extraction of a valuable component from sulfide concentrates.
Experiments were performed to determine the effect of the humidity content in the charge and temperature on the degree of desulfurization and the degree of extraction of a valuable component. Roasting was carried out for 60 minutes. 6 samples were taken with different humidity,%: 47, 40, 34, 17.5, 10 and 5-3. The experimental results are shown in the table 1.
Table 1
The results of experiments to determine the dependence of the desulfurization degree (Des) and the valuable component extraction on the humidity content of the material
|
Experim ent No. |
Т, °С |
Humidity, % |
|||||||||||
|
47 |
40 |
34 |
17,5 |
10 |
5-3 |
||||||||
|
Q Ф |
ɛ, % |
Q Ф |
ɛ, % |
Q Ф |
ɛ, % |
Q Ф |
ɛ, % |
Q Ф |
ɛ, % |
Q Ф |
ɛ, % |
||
|
1 |
500 |
76.2 |
36.8 |
78.9 |
37 |
83.2 |
37.6 |
83.9 |
38.6 |
87.5 |
71.3 |
98.2 |
78.5 |
|
2 |
550 |
78.7 |
38.6 |
80,9 |
38.9 |
83.7 |
39.5 |
84.9 |
40.3 |
93 |
77.5 |
99.3 |
79.2 |
|
3 |
600 |
81.2 |
41.5 |
83.5 |
41.9 |
84.7 |
42.3 |
86.4 |
43.3 |
99.2 |
80.3 |
100 |
81.1 |
|
4 |
650 |
83.3 |
42.4 |
86.5 |
42.8 |
86.6 |
43.4 |
88.3 |
48.2 |
99.7 |
81 |
100 |
82.7 |
|
5 |
700 |
85.7 |
43.7 |
88.2 |
44.2 |
90.2 |
45.0 |
92.1 |
45.7 |
100 |
79.5 |
100 |
82 |
Consider roasting at 500 ° C for 60 minutes. Figure 2 and Table 2 show that with a charge humidity of 47%, the degree of desulfurization is 76.2% and the degree of extraction is 36.8% and with a decrease in humidity in the charge, the degree of desulfurization and recovery increases, with W- 3-5% the degree of desulfurization is 98.2% and the degree of recovery of 78.5%. In more detail, the results of roasting at 500 ° C and Ƭ = 60 min. are given in table 2.
And the same experiment was carried out at different temperatures, °С: 550, 600, 650, 700-750. Consider roasting at 650 ° C for 60 min. The results of roasting at 650 ° C and Ƭ = 60 min are shown in table 3.
♦■
Table 2
Results of experiments to determine the dependence of the desulfurization degree and the valuable component extraction on the humidity content of the material
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
|
|
W |
47 |
40 |
34 |
17.5 |
10 |
3-5 |
|
Desulf. |
76.2 |
78.9 |
83.2 |
83.9 |
87.5 |
98.2 |
|
Extraction |
36.8 |
37.0 |
37.6 |
38.5 |
71.3 |
78.5 |
From table 3 it is seen that with a mixture humidity of 47%, the degree of desulfurization is 83.3%
Научно-практический электронный журнал ОБОГАЩЕНИЕ
«ТЕСНика» №2 2020 года W XJ*/ ПОЛЕЗНЫХ ИСКОПАЕМЫХ and the degree of extraction is 42.5% and with a
decrease in humidity in the mixture, the degree of desulfurization and recovery increases. at W-3-5%, the degree of desulfurization is 100% and the recovery is 88.5%.
Table 3
Results of experiments to find the optimal parameters of oxidative roasting in a new furnace for intensive roasting
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
|
|
W |
47 |
40 |
34 |
17.5 |
10 |
3-5 |
|
Desulf. |
83.3 |
86.5 |
86.6 |
88.3 |
99.7 |
100 |
|
Extraction |
42.4 |
42.8 |
43.4 |
48.2 |
82.1 |
82.5 |
The best temperature for the degree of desulfurization and recovery is 650 ° C. Since with a decrease in temperature the degree of desulfurization and extraction of a valuable component decreases (see table 2) and with an increase in temperature, the degree of desulfurization and extraction of a valuable component increases (see table 3).
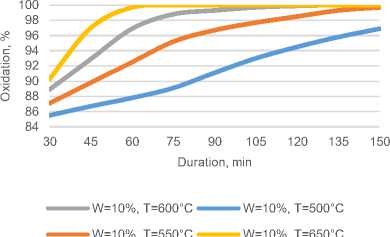
Fig. 4. Effect of temperature and process duration on the oxidation state of sulfide compounds
even with low humidity content in the charge, the degree of extraction is not more than 81%.
To determine the optimal conditions for the oxidative roasting of various sulfide materials such as gold-containing biooxidation and molybdenum cake, a series
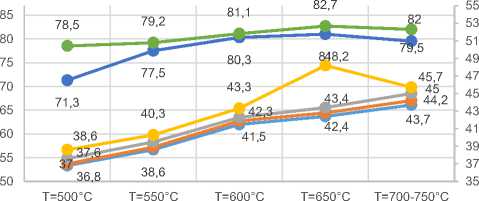
—•—W=10% • W=5-3% • W=47%
• W=40%
• W=34%
W=17,5%
Fig. 2 Dependence of the degree of extraction of a valuable component on the humidity content of the material
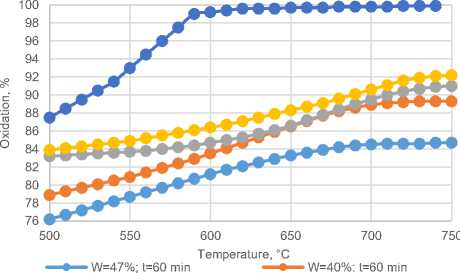
• W=34%; t=60min е W=17,5%; t=60 min
^2^W=10%; t=60 min
Fig. 3. Dependence of the degree of oxidation on the temperature of the feed material with different humidity content of the feed material
But it must be borne in mind that when the temperature rises above 650 ° C or a longer time, sintering of particles occurs and the degree of extraction decreases.
So in the case of roasting at 700-750 ° C and
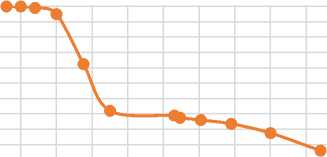
5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50
W, %
-
• t=60 min; T=600°C
Fig.5. Effect of humidity of the concentrate on the oxidation state of sulfides of laboratory experiments with different roasting conditions were carried out and theoretical data for each material were considered.
Sulphide gold-containing bio-cake was fired in a new type of furnace for intense roasting under different conditions:
-
- with different process durations (from 60 minutes to 150 minutes);
-
- with different temperatures inside the oven (from 450ºС to 750ºС);
-
- material humidity (40% to 3%);
As a result of a series of experiments, dependences of the degree of oxidation on various factors of the oxidative roasting process were revealed, such as duration, process temperature, humidity, and composition of the supplied material.
The results of the study are given in the following figures 6-8.
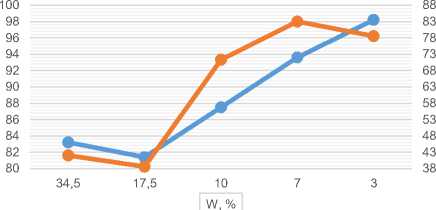
Figure 6 shows that with a decrease in the humidity content of the material during oxidative roasting, an increase in the degree of oxidation of sulfides is observed. And of course, the process temperature also directly affects the degree of desulfurization.
• Oxidation • Au extraction
temperature roasting of sulfide concentrates.
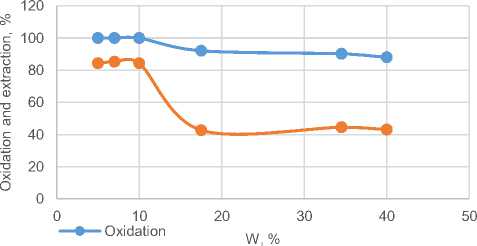
Fig. 8 Dependence of the degree of oxidation and extraction of a valuable component on the humidity of the material at a temperature at a temperature of 700ºС
Figures 6 - 8 show that with a decrease in the humidity content of the material, the extraction of a valuable component increases, with increasing temperature, the extraction of a valuable component also increases, but at a temperature of 700º there is a decrease in the degree of extraction, it is assumed that this is due to sintering of pieces.
Fig. 6. Dependence of material humidity on the degree of oxidation and extraction of a valuable component at a temperature at a temperature of 500ºС
Figures 7 and 8 show the results of various experiments to find optimal conditions for the oxidative burning of sulfide bio-cakes HMP-3 SC NMMC. These curves show only the oxidation state of the material. Of course, the degree of oxidation directly affects the extraction of a valuable component, but there are
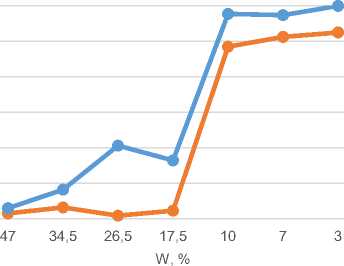
• Au extraction, % • Oxidation, %
Fig. 7 Dependence of material humidity on the degree of oxidation and extraction of a valuable component at a temperature at a temperature of 600ºС suggestions that in the processes of oxidative roasting at high temperature sintering of pieces begins, and this leads to a further decrease in the degree of extraction.
Therefore, we investigated the degree of extraction and the factors affecting it. The following curves show the effect of various factors on the degree of recovery. And with this, it is possible to clarify and determine the optimal conditions for intensive low-
Conclusion.
As a result of laboratory studies on the low-temperature intensive calcination of the biological oxidation product in suspension, it was determined that calcination at 600 ° С for 90 min and subsequent sorption cyanidation of the calcine increase the yield recovery of gold to 82.7%. It was determined that, depending on the nature of the concentrate and roasting conditions, the degree of sulfur removal is 90-95%, the degree of arsenic removal is also 90-95%. In cinders along with cyclone dust and inertial filters that work in air cooling, the following remains: sulfide sulfur 0.5–3.0%, arsenic 0.5– 1.5%, a yield of calcined material of 75-90% is proposed. Organic carbon and carbon monoxide 0.20.3% remain in cinders.
Список литературы Research of the oxidative process of gold-containing sulfide materials roasting for the development of an optimal mode
- Khasanov A.S., Tolibov B.I., Yuldoshev S.M. History and development of furnace technology. Materials of the republican scientific and technical conference "New composite and nanocomposite materials: structure, properties and application", - Tashkent. April 5-6, 2018. -P247-248.
- Khasanov A.S., Tolibov B.I., Yuldoshev S.M. Improving the use of heat in smelting and roasting processes in metallurgy. Materials of the Republican scientific and technical conference "New technologies for drilling, production and processing in oil and gas complexes", - Karshi. April 27-28, 2018. -P272-279.
- Khasanov A.S., Tolibov B.I. Improving the use of heat during melting and roasting processes in metallurgy // Gorniy Vestnik Uzbekistana. - Navoi, 2018. -№3. -P. 85-92. (https://www.researchgate.net/publication/341371612_Soversenstvovanie_ispolzovania_tepla_pri_plavilnyh_i_obzigovyh_processah_v_metallurgii).
- Khasanov A.S., Tolibov B.I. Roasting of molybdenum cakes in a new type of furnace for intense roasting // Gorniy Vestnik Uzbekistana. -Navoi, 2018. - No. 4. - S.131-135.
- Khasanov A.S., Tolibov B.I. Investigation of the possibility of the oxidation of sulfide materials in the furnace for intensive roasting // Gorniy zhurnal No. 9, 2018. -C85-89. (http://rudmet.net/media/articles/Article_MJ_09_18_pp.85-89.pdf).


