Research on proteinase inhibitors of beans Phaseolus vulgaris to make plant protection products from pests and diseases
Автор: Pavlovskaya N.E., Gagarina I.N., Dzumabaeva B.A., Dzangalina E.D.
Журнал: Вестник аграрной науки @vestnikogau
Статья в выпуске: 6 (51), 2014 года.
Бесплатный доступ
An animal body and seed plants have a complex of proteolytic ferments which react in reserve protein breakdown to amino acids in food digestion and seed sprouting. At present a few hundreds of peptidohydrolases of different origin have been described. In regulation of proteolysis inhibitors of proteolytic ferments react. In a living organism they are presented by means of specific protein. Inhibitors have an ability to slow down or stop fermentation. They react in immunity apoptosis, protect plants from parasites protease, regulate ferment strength when sprouting.
Proteinase inhibitors, bean, legumes, protection products
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/147124209
IDR: 147124209 | УДК: 635.652.2:577.175.001.5:632
Текст научной статьи Research on proteinase inhibitors of beans Phaseolus vulgaris to make plant protection products from pests and diseases
Among plant inhibitors the ones of serine proteinase particularly trypsin are widely presented. They are found in seeds of legumes (soy, bean, pea), cereals (wheat, rye, corn), buckwheat, in potato tubers, carrot-roots, apples, cabbage leaves and other sources and are able to perform the following main functions: to act as reserve protein; to control an activity of endogenous ferments; to react in protective reaction [1, 5, 7, 9, 16].
At the same time inhibitors increase a deficit of sulfur-containing amino acids and cause a hypertrophy of pancreas that reduce nutrient value of legumes. The data were received in experiments on soy and bean seed feeding and inhibitor products separated from them [2].
In seeds and other plant storage organs of legume family a level of protein proteinase inhibitors is able to reach 5-10% from total number of water-soluble protein. Bean inhibitors are considered in some scientific works. Protein of antitryptic and antichymotryptic activity was found in seeds of common bean, lima bean, golden gram and multiflora bean [18].
Some of these inhibitors were separated in crystalline state and splitted into components. Inhibitors are used in biotechnology, pharmaceuticals and food production, plant-growing and cattle-breeding. In this respect they play an important role in medicine and gene engineering, particularly to get pest-resistant transgenic plants of vigna, batata, potato, soy, rice [4, 8, 12, 19].
In medicine inhibitors are used to cure pathological processes caused by excessive activation of proteolytic ferments of an organism. The usage of inhibitors in different inflammatory processes, large operative treatment, injuries gives a positive effect [6].
A main task of biotechnology is to search efficient ways of inhibitor production. In this respect one of such sources is bean Phaseolus vulgaris which contains a large quantity of antialimentary compounds used in biology, medicine, agriculture [5, 18].
That is why it is necessary to bioscreen to determine bean varieties and forms having the highest proteinase and amylase inhibitor activity for biopharmaceuticals.
Purpose of research is analysis of bean varieties and lines on proteinase inhibitor content, carrying out of proteinase inhibitor differentiation method and testing of their biological activity.
OBJECTS AND METHODS OF RESEARCH
We studied 24 bean samples of different geographical origin: Oran, Rubin, Oka, Shokoladnitsa varieties from Orel region; Nerussa, lines: 135, 162,179, 202,543/84, 714; also samples from Rumania, Germany, Italy and others.
The material was grown in experimental field GNU VNIIZBK (wide-row sowing, sowing rate 0.35 mln. pieces per ha).
Proteinase inhibitor activity TIA (trypsin inhibitory) and CHIA (chemotrypsin inhibitory) was determined through caseinolytic method of M.L. Kakeid modified by I.I. Benken (1989). Inhibitor activity was calculated from a formula and registered in mcg of delayed tryptic (chemotryptic) units per 1 kg of flour.
Efficiency of proteinase inhibitors makes 18 mg/100 gr.
The method of proteinase inhibitor differentiation and clearing is based on the methodology created by I.O. Melnikova (1982) adapted to bean.
Spectrophotometric method of peroxidase activity determination is based on optical density of reaction products measurement which formed in guaiacol oxidation at a period of time.
Laboratory testing of inhibitor biological activity included testing on peroxidase activity, effect on bug survival of pea beetle Bruchus pisorum L., testing in field included study of the effect on yield and resistance to pests and pea Pisum sativum L. diseases. We used two varieties: sustainable Orpela and susceptible Sprut.
Methods of dispersion analysis and computer programs “Exel” and “Biotest-D” were used in statistical processing of results.
RESULTS OF RESEARCH
It is proved that proteinase inhibitor activity in samples of bean seeds changed insignificantly in years of growing and varied from 6,58 to 11,39 mg/ha on trypsin inhibitor and from 3.75 to 7. 02 mg/ha on chymotrypsin inhibitor. The largest activity among other samples has bean samples of Oran, L-179, Shokoladnitsa, K-15196 and Oka. Their activity on TIA changes from 9,02 in average to 12,48 mg/g (in years of growing). CHTIA is a bit lower and varies from 5.34 to 6.94 mg/ha (Figure 1).
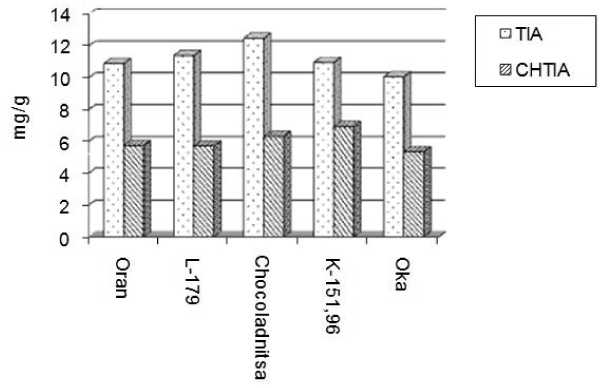
samples
Figure 1 Trypsin and chymotrypsin inhibitor activity of bean seeds
Inhibitor activity was also studied on seed maturity stages. Inhibitors reach the largest activity at full maturity stage. In Figure 2 the changes of trypsin and chymotrypsin inhibitor activity at maturity stages of Shokoladnitsa bean variety are shown. CHTIA activity increases from the stage of middle filling to full maturity. TIA in bean seeds is 2 times higher than chymotrypsin inhibitor activity in tested samples. At the same time TIA and CHTIA in other samples differ insignificantly. So, TIA activity at middle filling stage makes 1.18 mg/ha, CHTIA – 1.05 mg/g, TIA at full filling stage is 3.55mg/ha, CHTIA – 1.25 mg/ha. At maturity stage the activity reaches its maximum level.
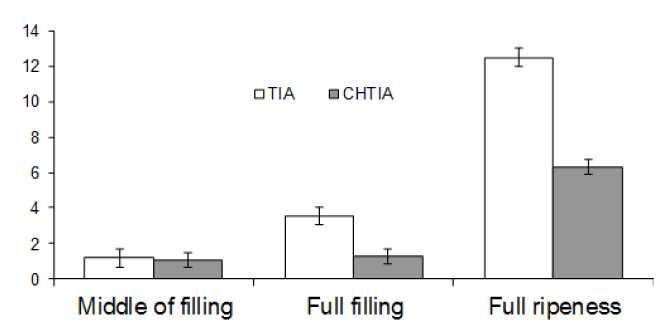
Figure 2 Activity of proteinase inhibitors bean seeds (average data)
Testing of biological activity of differentiated proteinase inhibitors was conducted on pea according to antioxidant system including high molecular ferments and low molecular vitamins [13, 17]. In laboratory experiments the effect of proteinase inhibitors from bean on peroxydase activity was studied. That is the test on peroxydase dependent immunity [3, 13, 15, 17] (table 1).
Table 1 Peroxydase activity in pea seedlings
|
Samples |
Disease free |
Infected |
Fusаrium oxysporum |
|
In 24 hours |
In 24 hours |
In 7 days |
|
|
Control |
74.5 |
71.3 |
100.3 |
|
Inhibitors 10-3 % |
93.5 |
100.0 |
187.0 |
|
Inhibitors 10-4 % |
81.7 |
75.0 |
150.0 |
It was found out that seed steeping in inhibitor solutions leads to peroxidase activity increase in disease free plants. Infection with mushroom spores in 24 hours influences seedlings controversially. In 7 days there was a distinct advantage of the samples with inhibitors in which peroxydase activity increases 1.5-1.8 times. It shows at peroxidase dependent pea immunity improvement treated with proteinase inhibitors and the selective effect of inhibitors on root rot agent Fusarium oxysporum.
Field testing of products based on bean proteinase inhibitors was conducted on sustainable pea variety Orpela and susceptible Sprut. The seeds were seeped in proteinase inhibitor solutions in concentrations (3 х 10-3 %); (3 х 10-4 %); for a control non-treated seeds and industrial product BI-58 (new) were used.
Table 2 Proteinase inhibitor effect on economic indicators of susceptible pea variety sprut
|
Indicator |
Control (nontreated) |
Treated by BI-28 (new) product |
Proteinase inhibitor treated 3х 10-3 % |
|
Pea moth vulnerability % |
37 |
37 |
27 |
|
Plant growth, sm |
61 |
66 |
62 |
|
Numper of productive joints, pieces |
3.4 |
4.5 |
3.2 |
|
Number of beans, pieces |
3.4 |
6.5 |
4.0 |
|
Number of seeds per plant, pieces |
10 |
11.6 |
11.3 |
|
Number of seeds in a bean, pieces |
2.9 |
2.2 |
2.3 |
|
Seed weight, gr |
1.2 |
1.9 |
1.4 |
It was found out that the product did not make a positive effect on pea diseases of powdery mildew, dark and light spotted ascochytosis, rubigo. At the same time vulnerability by pea moth of susceptible pea variety Sprut in the tested sample reduced by 10% in comparison with the non-treated control sample and insecticide BI-28 (new). Inhibitors enlarge bean quantity and seeds per plant and seed weight.
In laboratory conditions we treated pea beetle Bruchus pisorum L. with insecticide «Buldok» and proteinase inhibitors:ТIА 2.69х10-10% and CHTIA 0.32х1010%.

Figure 3 Insecticide and Proteinase Inhibitor Effect on Bug Survival Bruchus pisorum L. Samples: К 1 – “Buldok” control; К 2 – water; О 3 – trypsin inhibitor (2.69%), chymotrypsin (0.32%)
As shown in Figure 3 bug death from the effect of the strongest insecticide “Buldok” is 100%. In the controlled sample with water all bugs are alive, and in the sample with high concentration of trypsin inhibitor (2.69%) species death to 60% is observed. In low concentrations of chymotrypsin inhibitor death reaches 20%.
CONCLUSIONS
-
1. 24 samples of bean were screened to determine proteinase inhibitor activity of seeds.
-
2. Number of inhibitors in seed maturing reaches its maximum in full maternity period.
-
3. Proteinase inhibitors of bean improve peroxydase dependent pea immunity infected with pathogenic agent Fusarium oxysporum.
-
4. TIA and CHIA of bean make an insecticidal effect on pea moth Bruchus pisorum L.
-
5. Proteinase inhibitors of bean stimulate growth and yield of pea of non sustainable
TIA activity depending on variety reaches from 6.58 to 11.39 mg/ha, CHTIA – from 3.75 to 7.02 mg/ha. The largest activity and inhibitor number are observed in bean varieties Oran, Oka, Shokoladnitsa.
varieties.
Список литературы Research on proteinase inhibitors of beans Phaseolus vulgaris to make plant protection products from pests and diseases
- Аhatova А.R., Yarullina L.G., Shpirnaya I.А., Zaikina Е.А., Surina О.B., Tsvetkov V.О., Ibragimov R.E. Hydrolase activity, their inhibitors in plant tissue when infecting with phytopathogene and treatment with resistant inducers/Vestnik of Bashkirskiy gosudarstveniy universitet/, 2012, Volume: 17,№ 3, 2012 P.: 1278-1281
- Benken, I.I. Antinutritional substances of protein origin in soy seeds/I.I.Benken, Т.B.Tomilina//Bulletin VIR -1989.-V.149. -P.3-10.
- Biochemistry of legumes and crops. Monography. -Orel: «Izdat. OrelGAU», 2010. -300 P.: table.81, pict.59. Pavlovskaya N.E., Gagarina I.N., Gorkova I.V., Stepanova S.V.
- Belit, H.-D. Lebensmittel Wissenschaft Technologie/H.-D.Belit, A.Fuchs, L.Grimm//Planta. -1971.-V. 4, № 3. -P.899.
- Domash V.I., Sharpio Т.P., Zabreiko S.А., Sosnovskaya Т.F. Proteolytic ferments and trypsin inhibitors of higher plants in stress conditions//Bioog. Chemistry, 2008. V.56, №3. P.295-357.
- Dunaevskiy Ya.Е., Tsibina Т.А., Belyakova G.А., Domash V.I., Sharpio Т.P., Zabreiko S.А. Beloserskiy М.А. Proteinase inhibiots as antistress proteins of higher plants//Appl. Biochem. and Microbiol. 2005. V.41. №4. P. 392-396.
- Frolova S. А., Titov А. F. Proteolytic activity and trypsin inhibitors in wheat leaves in pre-effect and after-effect period in low hardening temperature//Plant physiology. 2008. №5. P. 549-552.
- Gagarina И.N. Protein complex of bean seeds and testing of biological activity of the components/Аbstract from thesis., Оrel,2005.
- Mosolov, V.V. Proteinase inhibitors and their functions in plants: review/V.V.Моsolov, Т.А.Valueva//Applied biochemistry and microbiology. -2005. -V.41, № 3. -P.261-282.
- Melnikova, I.О. Extraction methods of trypsin and chymotrypsin inhibitors from pea seeds/I.О.Melnikova//Sbornik nauchnih trudov VSGI. -М.,1982. -P. 70-71.
- Puente X.S., Lopez-Otin C.A. Genomic Analysis of Rat Proteases and protease Ingibitors//Genome Res. 2004.Vol.14/P.609-622
- Pavlovskaya N.Е., Gagarina I.N. Innovative approach to protein componrnts use in biotechnology/Vestn.ОGAU, 2008, №1 (10), P.36-38
- Pavlovskaya N.Е., Shalimova О.А., Azarova Е.F., Аndruhina R.М. Methodology guidelines on pea genotype resistance to fusarium and ascochyta leaf blight by means of biochemical tests. Оrel, 2002 -21 p.
- Pavlovskaya N.Е., Zotikov V.I., Borzenkova G.А., Gagarina I.N. and others Physiological and biochemical foundation of plant and pest protection products. Monography, Orel: GNU VNIIZBK, 2013.-188 P.
- Pavlovskaya N.Е., Shalimova О.А., Аzarova Е.F., Аndruhina R.М. Methodological guidelines on pea genotype resistance evaluation to fusarium and ascochyta leaf blight agents by means of biochemical tests. Orel, 2002 -21 P.
- Parfenov I.A. Proteinase inhibitors from potato tubers and their role in plant protection./Аbstract from thesis. Moscow, 2012.
- Pavlovskaya N.Е, Gagarina А.U.and others An plant systemtioxidantАнтиоксидантная система растений. Monography, 2012.-Оrel, ОrelGAU, 100 P.
- Richardson J., Viswanathan K., Lucas A. Serpins, the vasculature, and viral therapeutics//Front. Biosci. 2006. Vol.#11. P.1042-1056
- Wagner, L.P. Phaseolin diversely in the tepalg bean Gray/L.Wagner, J.P.Riehm//Arch. Biochem. and Biophys.-1967.-V.121.-P.672


