Response of the coelomocyte of metaphire posthuma to chlorpyrifos toxicity
Автор: Saha Subrata, Mukherjee Suman
Журнал: Журнал стресс-физиологии и биохимии @jspb
Статья в выпуске: 1 т.21, 2025 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Background: Chlorpyrifos, a widely used organophosphorus pesticide, poses significant environmental risks due to its persistence in soil and adverse effects on non-target organisms such as earthworms. This study investigates the toxicological impact of chlorpyrifos on the earthworm species Metaphire posthuma under controlled laboratory conditions. We assessed acute toxicity, growth rate, and immune responses, including coelomocyte viability. Earthworms were collected, maintained in a controlled environment, and exposed to varying concentrations of chlorpyrifos.
Soil biodiversity, earthworm health, chlorpyrifos toxicity, coelomocyte
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/143183775
IDR: 143183775
Текст научной статьи Response of the coelomocyte of metaphire posthuma to chlorpyrifos toxicity
Environmental contamination by pesticides and other organochemicals is of growing concern in India and worldwide. A variety of pesticides are used extensively in India, sometimes at higher application rates than those used internationally (Sharma et al ., 2019). Monitoring programs are being eloped to help predict or give early warning of ecosystem degradation. Earthworms have been selected as a suitable representative soil organism as they are key components of the soil biota and they contribute to the overall productivity of agricultural soils through their feeding, casting, and burrowing activities (Blouin et al ., 2013). The use of biomarkers in environmental monitoring is now becoming a routine method for examining the toxicity of chemicals. Biomarkers are a biological response that can be related to exposure to, or the toxic effect of an environmental chemical or chemicals (Oost et al ., 2002). Biomarkers can be used as an early warning indicator of environmental contamination and adverse effects on populationsand provide a link between the presence of a chemical and toxic effect (Turesky and Lu, 2020).
Chlorpyrifos, a broad-spectrum organophosphorus insecticide, is considered an ideal substitute for virulent organophosphorus insecticides such as methamidophos (Solomon et al ., 2014). Recently, with the prohibition of virulent organophosphorus insecticides in the production of vegetables, the use of chlorpyrifos caused soil, groundwater, and surface water contamination at many sites because of the long-persist of chlorpyrifos in the soi (Wołejko et al ., 2022)l. In the field situation, chlorpyrifos could persist in the soil for longer periods (Wołejko et al ., 2022) and chlorpyrifos had been found to persist for up to two years in soil (Lee et al ., 2012). Newer products such as sustained-release pellets, which release low levels of pesticides into the soil over a much longer period, can persist for up to 18 months (Frederiksen et al ., 2008). The wide use of chlorpyrifos may result in a hazard to the environment.
Earthworm, as an important organism in the soil ecosystem, is an important indicator of pesticide pollution. Acute and chronic toxicity tests using earthworms have been traditionally used to assess the toxicity of contaminants in soils to terrestrial invertebrates (ISO 11268-1, 1993; ISO 11268-2, 1998). Until recently, the measured common endpoint when evaluating the toxicity of chlorpyrifos to earthworms were ecologically relevant toxicity criteria, such as mortality, body growth, and cocoon production. A study onthe chronic toxicity of chlorpyrifos on Aporrectodeacaliginosa found that chlorpyrifos could greatly affect the fecundity of A. caliginosa (Bart et al., 2018).
Invertebrates exhibit different immune mechanisms against environmental pathogens. In earthworms, the cellular functions of innate and adaptive immunity are affected by different coelomocytes located in the coelomic cavity whose discrete characteristics like those of other functional cell types depend largely upon available techniques and assay (Engelmann et al ., 2002). The coelomic fluid contains different types of coelomocytes and their nomenclature is based mainly on morphological and cytochemical criteria (Vetvicka and Sima, 2009) through more recent studies attempt to determine superficial and functional markers for cell classification. In general,there are three main coelomocyte types-melanocytes,free chloragogen cells with nutritive and accessory functions, and either hyaline or granular amoebocytes, both representing effectors immunocytes involved in a broad of defense functions (Engelmann et al ., 2002).
In contrast to adaptive immunity, which isa highly sophisticated system based on antigen-specific T and B cells and antibodies and which is observed in vertebrates only, many innate immunity mechanisms are unserved from invertebrates to vertebrates (Bilej Martinand and Prochazkova, 2010). Cellular mechanisms of invertebrate immunity include adhesion, aggregation, and nodule formation, encapsulation of foreign objects and form of invertebrate immunity also includes wound repair, clotting, and coagulating responses. Apart from these cellular mechanisms, invertebrate possesses a broad range of antimicrobial peptides and enzyme activation base cascades; humoral defense also includes lectin-like and pattern recognition molecules that are designated to recognize a few highly conserved structures present in many different microorganisms (Bilej et al., 2010).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Collection and laboratory maintenance of animal
Earthworms of the species, Metaphire posthuman were collected from college campuses and maintained in a laboratory in a culture medium. Earthworms were cultured in the laboratory at room temperature (20 ° C) on moist soil mixed with decayed leaves and well-decomposed cow manure. Distilled water was given to reach 60% of the maximum water-holding capacity. Water content was readjusted weekly (Fig.1A). Soil was changed every four weeks and earthworms were maintained until required for experimentation. The earthworms used in this experiment were adults with well-developed clitella. The individual fresh weights of the adult earthworms used in the experiment varied between 350 and 400 mg.
Determination of earthworm acute test
The soil for the experiment consisted of 70% quartz sand, 20% Kaolin clay, 10% sphagnum peat, and calcium carbonate to adjust the pH to 6.0±0.5. The soil was prepared by adding different concentrations of pesticides (dry weight basis). Chlorpyrifos was added at different concentrationsof chlorpyrifos on a percentage basis. The desired amount of pesticide was thoroughly mixed into the soil as an aqueous solution to give the working concentration of pesticide and the soil was placed into glass jars.Ten adult worms were placed in 1 L glass containers filled with test substrate.To prevent the worms from escaping, test containers were covered with a polythene sheet with integrated gauze (+1 mm) to ensure optimal ventilation. After 1, 2, 3, and 4 days of incubation, surviving worms were stored by hand. The test endpoint was mortality.Four replicates wereapplied for the acute tests.A control treatment was in parallel, also represented by four replicates.
Pesticidal treatment
The soil of the container was artificially contaminated by adding different sublethal concentrations of pesticides chlorpyrifos was added with sublethal concentrations of 1, 10, and 100mg/kg soil. 10 earthworms were added to each container. Soil changes every 2 days and earthworms were placed in fresh contaminated soil. The animals were exposed to a sublethal concentration of chlorpyrifos to determine total coelomocyte count (TCC), adhesion and the phagocytic response of coelomocytes.
Earthworm growth test
The soil of the container was contaminated by adding different sublethal concentrations of pesticides such as 1, 10, and 100 mg/kg soil for varied spans of exposure to determine the earthworm growth rate (Zhou et al ., 2007). Ten worms were added to each container. Soil was changed every 2 days and earthworms were placed into fresh contaminated soil. Earthworms were weighed every day during the experiment to determine the effect of pesticide on growth before weighing, all worms were sorted out of the soil, washed with top wells and left on wet filter paper then blotted off and weighed using an electronic weighing balance. Worms were then returned to the soil. During all experiments, moisture content was checked weekly and maintained at 50% by adjusting the weight of the container against the weight of the container against the weight known from the previous day prior to sampling the experiment lasted for 7 days.
Extrusion of coelomocyte
The coelomocytes were extruded from coelomic fluid following the method (Diogène et al., 1997). Before experimentation, the animal was placed in an empty sterile 50 ml centrifuge tube. The earthworms are then immersed in 25 ml extrusion medium (71.2mM guaiacol glycerol ether, 2% v/v ethanol, and a supplement of antibiotic and antimycin agent: 100µg/ml penicillin G sodium salt, 100µg/ml streptomycin sulfate and 25 ng/ml amphotericin). The animals were maintained for three minutes in the extrusion solution with gentle up and down strokes. During this step, coelomocytes were released from the coelomic cavity of the earthworms through pores in their integument. After that, each earthworm was rinsed with ice-cold MHBSS-GGE. Following the extrusion procedure, the cell suspensions were always kept on ice. Cells from individual earthworms were centrifuged at 500×g/7min at 4 °C; the coelomocytes were finally re-suspended in a fixed volume of MHBSS-GGE.
Microscopic study and photo documentation
The coelomocyte was extruded from coelomic fluid following the method (Diogène et al., 1997). A part of the freshly collected coelomic fluid was placed on a glass slide in a moist chamber and the coelomocytes were allowed to settle. The supernatant of the coelomic fluid was carefully removed by micropipette. Phase contrast image analyses of live cells were carried out under a microscope with a digital image recording facility at different magnifications.
Determination of total coelomocyte count (TCC)
Coelomocytes were isolated following the method (Diogène et al ., 1997) . The extruded coelomocyte and its count were determined using an improved Neubauer hemocytometer (Burch et al ., 1999).
Coelomocyte viability
Coelomocyte viability was determined by trypan blue extrusion following the method (Burch et al ., 1999). Resuspended coelomocytes were mixed at a ratio of 1:1 with 0.04% trypan blue and vortexed. 20µl of this mixture was transferred to a glass microscope slide with a cover slip tire coelomocytes were determined by dye exclusion and reported as present live coelomocytes per total cells counted.
Adhesion assay of coelomocyte
The adhesion behavior of coelomocytes was determined by following method (Gupta and Yadav, 2016). The coelomic fluid of the earthworm was obtained by immersing the earthworm in 25 ml of extrusion medium for 2 minutes with gentle up-down strokes. The viability of the coelomocyte was checked by trypan blue staining following the principle of dye exclusion and uniform density. Coelomocytes were incubated in a humid chamber for 150 minutes over a glass surface for complete adhesion. The supernatant fluid of the post-incubated sample was carefully removed by micropipette. Gentle jetting of the extrusion medium was applied to remove the nonadherent coelomocyte population settled over the slide due to gravity and was enumerated by a Neubauer hemocytometer. Adherent and nonadherent cell populations were examined microscopically. Phase contrast image analyses of adherent and non-adherent cells were carried out microscopically. Light microscopic analyses were carried out after cytofixation and stained with Giemsa’s stain or hematoxylin-eosin stain. Digital documentation of cell images was carried out with a camera fitted with a microscope.
Determination of phagocytic response ofcoelomocyte
The coelomic fluid of the earthworm was obtained by immersing the earthworm in 25 ml of extrusion medium for 2 mins with gentle up and down strokes. The coelomic fluid was incubated with yeast ( Saccharomyces cerevisiae ) suspension of a concentration of 10 6 cells per 1ml, as 3:1, at a temperature of 30 °C during 3 hrs, according to a modified method of (Diogène et al., 1997).The slides were analyzed in the light microscope with a phase contrast device at 1 hr intervals, calculating the percentage of coelomocytes containing phagocyted yeast cells, according to the formula (Hendawi et al . 2004).
. . . .... number of coelomocytes with phagocytes yeast cells
Phagocyte tic activity (%) =-----------------;------------—;---;-------- j \ г total number of coelomocytes
Determination of nitric oxide
Nitric oxide production was determined in coelomocytes spectrophotometrically following the method of Hahn et al. (2001). To 1 ml of cell suspension (1x10 6 ceiis/mi), 1 ml of Griess reagent was added and incubated for 30 minutes at 37˚C. Optical density was determined spectrophotometrically at 540 nm. The molar concentration of nitrite in the sample was determined from the standard curve prepared using a known concentration of sodium nitrite and the result was expressed as цМ NO/10 6 cells/ml.
RESULTS
Assessment of chlorpyrifos on acute toxicity for M.posthuma
In all exposure periods, a clear concentration relationship was observed that earthworm mortality increased with increasing concentrations of each contaminant. Acute toxicity tests have been traditionally used to assess the toxicity of contaminants in soils to earthworms. The most common endpoint measured when evaluating acute toxicity of chemicals to earthworm LC50 (the concentration that is lethal to 50% of individuals). The endpoint “LC50” shows effects at relatively high pollutant concentrations and indicates the maximum damage likely to an organism. In this study, LC5o on earthworm by chlorpyrifos assessed is 200mg/kg (4 d), which is similar to the previous report (Griffith et al. 2019).
Impact of chlorpyrifos on growth of M . posthuma
In the present study, toxicity tests demonstrated that chlorpyrifos has anadverse impact on growth and reproduction in earthworms, but this is largely dependent on pesticide concentration and exposure period. Earthworm growth decreased with increased concentrations of pesticide (Table 1). The average weight gain of earthworms exposed to chlorpyrifos was generally lower than the controls with respect to high doses of exposure for a longer span.
Microscopic study of coelomocyte
In the classification morphological, as well as behavioral features and phagocytic activity of coelomocytes were taken into consideration. Three main types of coelomocytes were distinguished as eleocytes, amoebocytes and granulocytes. Amoebocytes are polymorphic having centrally placed nuclei whose shape varies from oval to kidney-like (Figure 2A). Their cytoplasm contains few granules. Eleocytes circulating coelomocytes having normal or oval surface area. Their small, spherical nuclei are located eccentrically (Figure 2B). Granulocytes are spherical with respect to surface area. Nuclei are spherical in shape and centrally located and the cytoplasm contains fine granules (Figure 2C). Exposure to a pesticide of 100 mg/kg of soil resulted in an apparent loss of cytoplasmic plasticity and disintegration of the cell membrane (Figure 2a). Granulocytes exhibited signs of cellular degradation and damage as evident from a microscopic study (Figure 2b). Eleocytes exhibited signs of cellular disintegration in response to pesticide treatment (Figure 2c).
Total celomocyte count
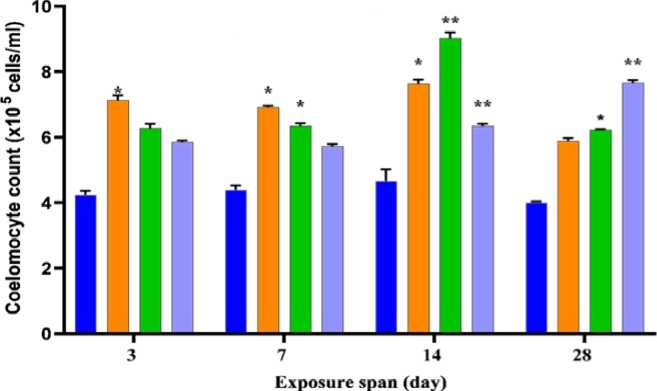
The total count of coelomocytes in the blood of M. posthumawasrecorded as 4.2×105cells/ml (Figure 4). An increase in coelomocyte density was recorded against all concentrations of pesticide for varied spans of exposure (Figure 4). Intense increasesin total count were recorded as 9×105 cells/ml against 10 mg/kg soil per 14 days of exposure (Figure 4). The overall increase in cell count was recorded against control for all the concentrations of chlorpyriphos for all spans of exposure of M. posthuman (Figure 4).
Adhesion response of coelomocyte
Coelomocytes, the chief effector cells present in the coelomic fluid of M. posthuman composed of diverse subpopulations namely adherent (Figure 3A) and nonadherent types. The efficacy of Coelomocytes for discrimination and adherence over nonself surface was shifted by sublethal concentrations of chlorpyrifos. In the controlled populations, 35% of coelomocytes adhered over the glass surface after incubation for 150 minutes (Figure 5). Coelomoctes of M. posthuma exposed to chlorpyrifos for a dose of 100 mg/kg soil for 28 days expressed lowest percentage of adherent cell as 2% as compared to control (Figure 5). A steady depletion of the efficacy of Coelomocytes for surface adhesion against all concentrations of pesticide indicated a possible alteration in cell surface characteristics.
Phagocytic response of coelomocyte
Phagocytosis is considered as the primary line of cellular defense in annelids and therefore any factor that affects this activity would influence the general immune status of the animal (Adamowicz & Wojtaszek, 2001). Coelomocytes are reported to perform phagocytosis of non-self particulates under toxin exposure (Figure 3 B&C). Coelomocytes of invertebrates are capable of phagocyting invading microorganisms and pathogens under proper elicitation. Coelomocytes of M. posthuma exposed to 100mg/kg soil chlorpyrifos formulations for 28 days expressed the lowest value of phagocytosis percentage (Figure 6). The animal exposed to 100mg/kg soil of pesticide exhibited low phagocytic percentage for an increasing span of exposures (Figure 6). Phagocytic response expressed a decreasing trend under pesticide exposure as evident from phagocytosis percentage in control and treated sets (Figure 6).
Nitric oxide activity
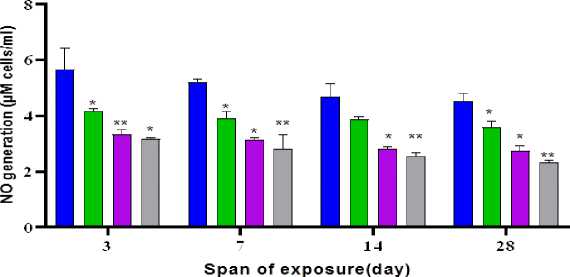
A decrease in intra-coelomocyte nitric oxide production was observed under pesticide exposure. The lowest concentrations of intracoelomocyte nitric oxide were recorded as 3.5 µM/106cells, 2.7 µM NO/106 cells and 2.32 µM No/106 cells against 1mg/kg, 10mg/kg and 100mg/kg of chlorpyrifos for 28 days of exposure respectively (Figure 7). M. posthuma exposed to chlorpyrifos formulations showed a decreasing trend in value of 5 µM NO/106cells (Figure 7)
intracoelomocyte No production against the control

Figure 1 . (A): Rearing and treatment of Metaphire posthuman . (B): Measurement of the weight of M. posthuman . (C) Extrusion of coelomocyte of M. posthuman .
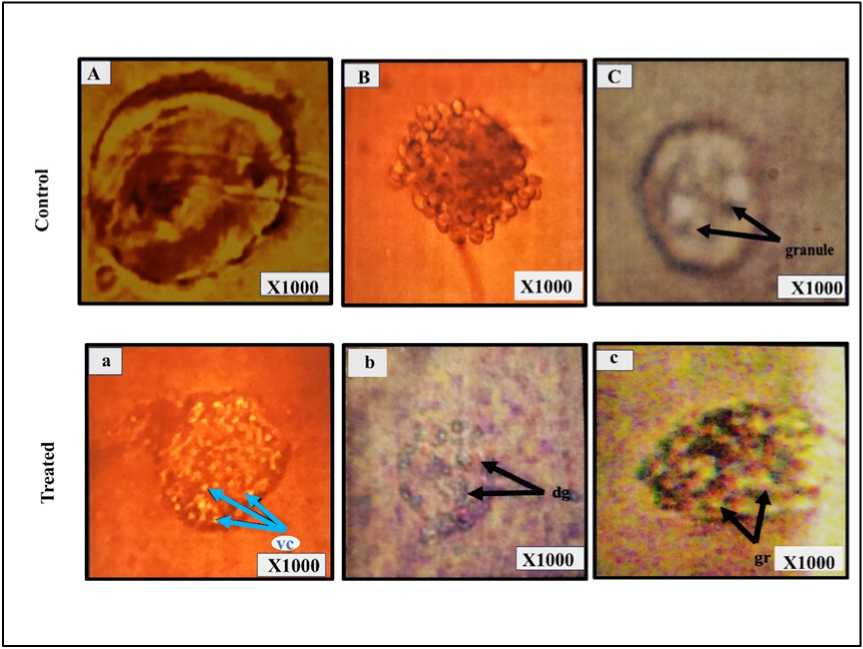
Figure 2. Microscopic view of Coelomocyte (A: Amoebocyte, B: Eleocyte, C: Granulocyte) of control M.posthuma.
Microscopic view of pesticide exposed coelomocyte (a: Amoebocyte exhibiting vacuolation (vc) b: Eleocyte showing cellular disintegration (dg) c: Granulocyte exhibiting granulation (gr).
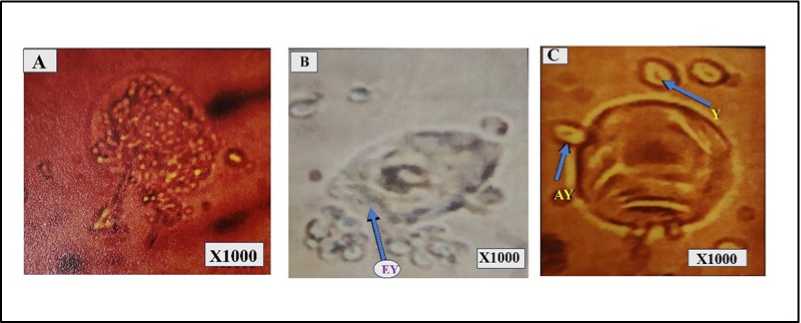
Figure 3. Microscopic view of Coelomocyte (A: Amoebocyte, B: Eleocyte, C: Granulocyte) of control M. posthuma .
Microscopic view of pesticide exposed coelomocyte (a: Amoebocyte exhibiting vacuolation (vc) b: Eleocyte showing cellular disintegration (dg) c: Granulocyte exhibiting granulation (gr).
Table 1. Growth of adult M. posthuma exposed to chlorpyrifos in vivo.
|
Treatment with chlorpyrifos (mg/kg) |
Mean weight per earthworm (kg) |
|||
|
3rd day |
7th day |
14th day |
28th day |
|
|
Control |
1.4±0.012 |
1.266±0.034 |
1.2995±0.011 |
1.307±0.01 |
|
1 mg/kg |
1.7195±0.007 |
1.2417±0.078 |
1.1915±0.015 |
1.244±0.073 |
|
10 mg/kg |
1.859±0.04 |
1.2707±0.068 |
1.350±0.044 |
1.2848±0.037 |
|
100 mg/kg |
1.3538±0.025 |
1.2252±0.058 |
1.148±0.088 |
0.9635±0.027 |
■ Control
■ 1 mg
■ 10 mg
■ 100 mg
Figure 4. Dynamics of coelomocyte count of M. posthuma exposed to chlorpyrifos in vivo. Data is represented as Mean± S.D. Statistical significance is shown at p<0.05*, p<0.01**, P<0.001***.
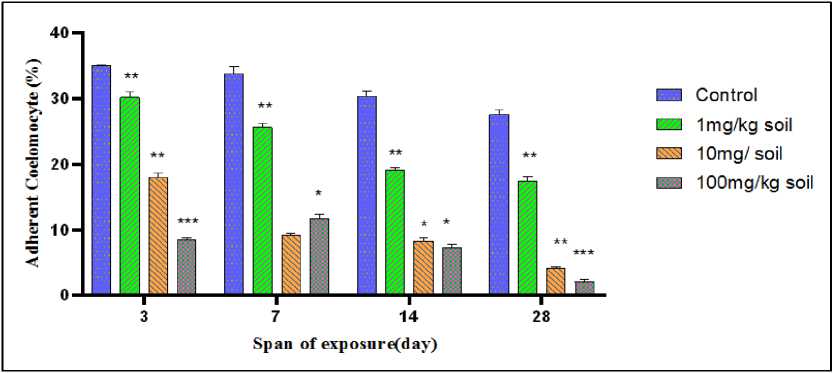
Figure 5. Nonself surface adhesion of coelomocyte of M. posthuma exposed to chlorpyrifos in vivo . Data is represented as Mean± S.D. Statistical significance is shown at p<0.05*, p<0.01**, P<0.001***.
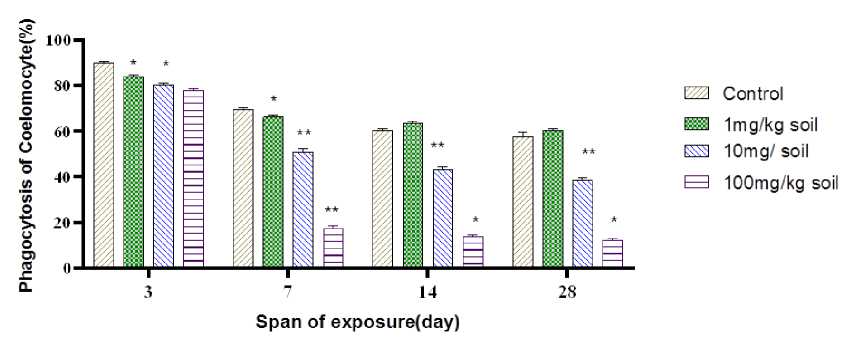
Figure 6. Phagocytic response of coelomocyte of M. posthuma exposed to chlorpyrifos in vivo . Data is represented as Mean± S.D. Statistical significance is shown at p<0.05*, p<0.01**, P<0.001***.
Control
1 mg/kg soil
1 Omg/ soil
1 OOmg/kg soil
Figure 7. Generation of intracoelomocyte nitric oxide of M. posthuma exposed to chlorpyrifos in vivo . Data is represented as Mean± S.D. Statistical significance is shown at p<0.05*, p<0.01**, P<0.001***.
DISCUSSION
The immune system in all organisms provide protection against infection agents and tumors and rejects non-self-components. This is accomplished through a system of recognition, to distinguish self from non-self, and response, to eliminate invading organisms or foreign bodies. Invertebrates rely mainly on innate defenses implemented through a nonlymphoid system. Many chemicals introduced into the environment as a result of industrial or agricultural activity have been implicated in ecotoxicological effects via immunotoxic mechanisms in exposure to agrochemicals and mixtures of domestic and industrial waste.
Chlorpyrifos is an organophosphate insecticide and its use has changed drastically over the last ten years. Direct application of chlorpyrifos to soil, and vegetation can result in exposure to nontargetedorganisms like earthworms. The present study has arrived for assessment of the toxicological effects of chlorpyrifos on M. posthuma under controlled laboratory conditions. Acute toxicity tests have been traditionally used to assess the toxicity of contaminants in soils to earthworms. The animals are sensitive to toxic exposures of chlorpyrifos and the LC 50 value is assessed as 200mg/kg for 4 days.
Physiological responses of M. posthuma exposedto chlorpyrifos were examined in depth. When compared to the control, the live M. posthuma exhibited decreased pattern in growth with increased concentration of pesticide (Table 1). Reduction in the growth of pesticide exposed earthworms may be due to the onset of stress. The density of circulatorycoelomocytes is an indicator of stress and coelomocyte count is considered as a valuable tool in monitoring the health status of M. posthuma distributed in bio-unsafeenvironments. The total coelomocyte count in the blood of M. posthuma was recorded as 4.2×105 cells/ml (Figure 4). Overall increase in coelomocyte count was recorded against control and the drastic alteration in total coelomocyte count is suggestive of a status of cellular stress of the animal in its natural habitat.
Microscopic observation of pesticide exposed coelomocyte is indicative of the disintegration of cell membrane, loss of cytoplasmic plasticity along with sign of cellular disintegration (Figure 2a, 2b, and 2c). Exposure of M. posthuma to chlorpyrifos resulted inthe appearance of pathological symptoms in amoebocyte, eleocyte and granulocyte subpopulations. Morphological impairment of Coelomocytes is indicated to possible disruption of normal functioning of the coelomocyte subpopulation.
Coelomocytes are immunocompetent cells of the blood of earthworms which are capable of expressing immune logical responses through surface adhesion during the exposure of toxins and parasites. The present study involves exposure of the Coelomocytes of M. posthuma to varied concentrations of chlorpyrifosinvivo. Impairment in nonself surface adherence of Coelomocyte (Figure-5) is indicative of a shift of immunological responses in M. posthuma under the sublethal exposure of chlorpyrifos.
Phagocytosis is an important immunological marker of various environmental toxins. The present study exhibited an inhibitory effect of chlorpyrifos on the phagocytic efficiency of Coelomocytes at varied sublethal concentrations (Figure 6). The decrement in phagocytic efficacy of coelomocytes could eventually render the earthworm more vulnerable to microbial infections under chlorpyrifos exposure.
Invertebrates are capable of producing reactive nitrogen species (RNS) like nitric oxide (NO) upon contact with xenobiotics. The nitric oxide bears the potential to kill microorganisms by combining with superoxide anion to form highly reactive peroxynitrite, a strong bactericidal reagent. Sublethal concentrations of chlorpyrifos suppress the generation of nitric oxide in coelomocytes (Figure 7). The pesticide-induced decline in the generation of nitric oxide may lead to the growth of microorganisms in the blood.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
The authors thankfully acknowledge the support received from Post Graduate Department of Zoology, A.B.N. Seal College, Cooch Behar and Bidhannagar College for completion of the work.
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
The authors declare that they have no potential conflicts of interest.
Список литературы Response of the coelomocyte of metaphire posthuma to chlorpyrifos toxicity
- Adamowicz, A. and Wojtaszek, J. (2001). Morphology and phagocytotic activity of coelomocytes in Dendrobaenaveneta (Lumbricidae). Zool. Pol., 46.
- Bart, S., Amosse, J., Lowe, C. N., Mougin, C., Pery, A. R. R. and Pelosi, C. (2018). Aporrectodea caliginosa, a relevant earthworm species for a posteriori pesticide risk assessment: current knowledge and recommendations for culture and experimental design. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 25(34), 33867.
- Bilej, M., Prochazkova, P., Silerova, M. and Roubalova, R. (2010). Earthworm Immunity. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, 708, 66-79.
- Bilej, M., and Prochazkova, P. (2010). Earthworm Immunity. In K. Söderhäll (Ed.), Invertebrate Immunity (pp. 66-79). Springer US.
- Blouin, M., Hodson, M., Delgado, E. A., baker, G., Brussard, L., Butt, K., Dai, J., Dendooven, L., Epres, G., Tondoh, E., Cluzeau, D. and Brun, J.J. (2013). A review of earthworm impact on soil function and ecosystem services. European Journal of Soil Science, 64, 161-182.
- Burch, S. W., Fitzpatrick, L. C., Goven, A. J., Venables, B. J. and Giggleman, M. A. (1999). In Vitro Earthworm Lumbricusterrestris Coelomocyte Assay for Use in Terrestrial Toxicity Identification Evaluation. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 62(5), 547-554.
- Diogene, J., Dufour, M., Poirier, G. and Nadeau, D. (1997). Extrusion of earthworm coelomocytes: Comparison of the cell populations recovered from the species Lumbricusterrestris, Eisenia fetida and Octolasiontyrtaeum. Laboratory Animals, 31, 326336.
- Engelmann, P., Pal, J., Berki, T., Cooper, E. L. and Nemeth, P. (2002). Earthworm leukocytes react with different mammalian antigen-specific monoclonal antibodies. Zoology, 105(3), 257-265.
- Frederiksen, H., Hansen, H., Borggaard, O. and Pedersen, M. (2008). Starch-encapsulated chlorpyrifos: Release rate, insecticidal activity and degradation in soil. Journal of Microencapsulation, 19, 319-331.
- Griffith, C., Thai, A. and Larive, C. (2019). Metabolite biomarkers of chlorothalonil exposure in earthworms, coelomic fluid, and coelomocytes. Science of The Total Environment, 681.
- Gupta, S. and Yadav, S. (2016). Immuno-defense Strategy in Earthworms: A Review Article. International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences, 5, 1022-1035.
- Hendawi, M., Sauve, S., Ashour, M., Brousseau, P. and Fournier, M. (2004). A new ultrasound protocol for extrusion of coelomocyte cells from the earthworm Eisenia fetida. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 59(1), 17-22.
- Lee, K. Y., Strand, S. E. and Doty, S. L. (2012). Phytoremediation of Chlorpyrifos by Populus and Salix. International Journal of Phytoremediation, 14(1), 48-61.
- Oost, R., Porte, C., den Brink, N. and Den Brink, P. (2002). Biomarkers in environmental assessment. Ecotoxicological Testing of Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems; Emerging Techniques, Trends, and Strategies.
- Sharma, A., Kumar, V., Shahzad, B., Tanveer, M. Sidhu, G. P. S., Handa, N., Kohli, S. K., Yadav, P. Bali, A. S., Parihar, R. D., Dar, O. I., Singh, K. Jasrotia, S., Bakshi, P., Ramakrishnan, M., Kumar S., Bhardwaj, R. and Thukral, A. K. (2019) Worldwide pesticide usage and its impacts on ecosystem. SN Applied Sciences, 1(11), 1446.
- Solomon, K., Mackay, D. and Anderson, J. (2014). Evaluation of evidence that the organophosphorus insecticide chlorpyrifos is a potential persistent organic pollutant (POP) or persistent, bioaccumulative, and toxic (PBT). Environmental Sciences Europe, 26.
- Turesky, R. J. and Lu, K. (2020). Biomarkers of Environmental Toxicants: Exposure and Biological Effects. Toxics, 8(2), 37.
- Vetvicka, V. and Sima, P. (2009). Origins and functions of annelide immune cells: the concise survey. Invertebrate Survival Journal, 6.
- Wotejko, E., Lozowicka, B., Jablonska-Trypuc, A., Pietruszynska, M. and Wydro, U. (2022). Chlorpyrifos Occurrence and Toxicological Risk Assessment: A Review. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(19), 12209.
- Zhou, S.P., Duan, C., Fu, H., Chen, Y.H., Wang, X.-H. and Yu, Z. (2007). Toxicity assessment for chlorpyrifos-contaminated soil with three different earthworm test methods. Journal of Environmental Sciences (China), 19, 854-858.


