Response of two tomato cultivars to field-applied proline and salt stress
Автор: Kahlaoui B., Hachicha M., Teixeira J., Misle E., Fidalgo F., Hanchi B.
Журнал: Журнал стресс-физиологии и биохимии @jspb
Статья в выпуске: 3 т.9, 2013 года.
Бесплатный доступ
An experiment was carried out using saline water (6.57 dS.m -1) and subsurface drip irrigation (SDI) on two tomato cultivars ( Solanum lycopersicum, cv. Rio Grande and Heinz-2274) in a silty clay soil. The former is a salinity tolerant and the latter a sensitive cultivar. Exogenous application of proline was done by foliar spray at two concentrations: 10 and 20 mg.L -1, with a control (saline water without proline), during the flowering stage. As a result of the proline applied, significant effects were observed on both cultivars of tomato, particularly with low concentration of proline (10 mg.L -1). It led to increase of leaf area, growth length and fruit yield. Regarding mineral nutrition, Ca 2+ was higher in different organs while low accumulation of Na + occurred. However, Cl - was very low significantly in all tissues of plants of Rio Grande at the higher concentration of proline applied.
Solanum lycopersicum, salt tolerance, exogenous application, proline, tunisia, saline stress
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/14323780
IDR: 14323780
Текст научной статьи Response of two tomato cultivars to field-applied proline and salt stress
Salinity is a major environmental factor limiting plant growth and productivity. In arid and semi-arid regions of the world salinization is exacerbated by the development of soil sodicity, especially those regions with limited rainfall, high evapotranspiration, and high temperature. Sodicity is associated with the use of irrigation water containing high concentrations of sodium. In addition, the increasing demand for water in the world has forced farmers to use low quality water for irrigation, such as water of agricultural drainage. Irrigation with drainage water containing high salinity levels during the whole growing season of the crops, even the tolerant ones, does not produce high yields most of the times. Efforts have been made to control salinity by various technological means, including soil reclamation, drainage, the application of high leaching fractions, and the use of soil amendments (Raddy, 2012). In recent years, much attention has been paid to the development of sustainable agriculture; hence, several materials have been applied as soil amendments to overcome the adverse effects of soil salinity, to improve the physical and chemical properties of soils, to increase their water retention, and to provide the nutrients required during plant growth. Therefore, new approaches are necessary to cope with these problems. One new option is the exogenous application of proline, which let crops tolerate high levels of soil salinity (Ashraf and Foolad, 2007; Ashraf et al., 2008).
Plants facing adverse situations such as high salt concentrations decrease their osmotic potential by accumulating osmolytes that do not perturb enzyme functions so as to maintain continuous water absorption at low soil water potential (Demiral and Turkan, 2006). Accumulation of these compatible solutes (osmoprotectants) such as proline and glycinebetaine, allow turgor maintenance and stabilization of proteins and membranes against destabilizing effects of abiotic stresses including salinity, drought and extremes temperature, all of which cause cellular water depletion. Therefore, the exogenous application of these compounds promises to be an alternative/additional way to genetic engineering to improve yield under environmental stress conditions (Heuer, 2003; Demiral and Turkan, 2006).
Proline accumulation is one of the adaptations of plants to salinity. Several functions are attributed to proline accumulation in response to stress. Besides the biophysical effects of proline as an osmo-compatible solute (Tonon et al., 2004), its biosynthesis can contribute to reduce cellular acidification, allowing the regeneration of NADP+ needed for the maintenance of the respiratory and photosynthetic processes (Larher, 1993). Proline itself may serve also as a nitrogen and carbon source needed in stress recovery (Aziz et al., 1999; Tonon et al., 2004; Demiral and Turkan, 2004) and can also act as a scavenger of hydroxyl radicals, avoiding cellular damage provoked by osmotic or salt-induced oxidative stress (Teixeira and Fidalgo, 2009). Despite these several useful effects, the role of proline accumulation in affecting plant tolerance to salt stress is controversial. For instance, the magnitude of proline increase was found to be inversely related to salt tolerance in tomato (Shannon et al., 1987) and rice cultivars (Lutts et al., 1999).
Tomato is one of the most important horticultural crops in Tunisia, and since its production is concentrated in semi-arid regions, where saline waters are frequently used for irrigation, our aim was focused on determining a valid strategy for improving yield under saline conditions. The objective was to evaluate the response of two cultivars of tomato to exogenous application of proline under field conditions.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Plant material
The experiment was carried out during the summer 2009 (from 2/05 to 27/08). Two tomato cultivars ( Solanum lycopersicum ) were used: a tolerant cultivar to salt, Rio Grande (Kahlaoui et al ., 2011a, b) and a sensitive cultivar to salt, Heinz-2274 (Kahlaoui et al ., 2012). Seeds were provided by the Laboratory of Seeds and Plant Control of the General Direction of Protection and Control of the Agricultural Production and Quality, Tunisia.
Experimental design
The experiment was located at the Cherfech Agricultural Experimental Station located 25 km north of Tunis in the Low Valley of Mejerda River. Climate of the region is Mediterranean with an annual rainfall close to 470 mm and a yearly evapotranspiration average of 1370 mm (PET Penman). The soil was a silty-clay with about 40% clay, 50% silt and 10% sand. The organic matter amount is about 1% and total CaCO 3 is about 40%. The soil pH is around 7-8 and no fertilizer was used in our experiment. The experiment was set using emitters with filters and drip lines buried at 30 cm depth as subsurface drip irrigation (SDI). The transplanting date was 2/05 in single lines, using plants with 5 - 7 leaves. Tomato plants were spaced 1 m between rows and 0.40 m between plants. This experiment was carried out according to a randomized design with two factors (cultivar and proline concentration). Each treatment was replicated three times and each replicate had 10 plants (30 plants per treatment for every cultivar). Treatments were: two exogenous applications of proline at 10 and 20 mg L-1 and a control (without proline application) for every cultivar. Proline spraying was performed 6 times from 30% of flowering at June. In each treatment, three plants/replications were used in statistical analysis.
Irrigation water
The irrigation water came from a well with ECw = 6.57 dS m-1 and SAR=12.81. The water chemical characteristics are described in Table 1. The total water quantity used was 700 mm.
Plant measures and analyses
Determination of plant growth and yield
Shoot length was mesurated by a graduated rule and leaf area was quantified using a planimeter type Delta-T Devices LTd. For every plant, leaves were detached and introduced into the device. Leaf area was expressed in cm2.
Plants used for measures of fructification parameters were preserved for the assessment of yield parameters per plant.
Analysis of Na+, Ca2+ and Cl- in plant tissues
For chemical analyses, tissues from leaves, petioles, stems and roots were used. The organic ions were extracted from dry matter by HNO 3 at room temperature for 48 h. Na+ was analyzed by flame emission, using an Eppendorf spectrophotometer (JENWAY PFP7). Ca2+was determined by atomic absorption spectrophotometry. Cl- was quantified by colorimetry with a Buchler chloridometer.
Statistical analysis
Statistical processing was achieved by the software STATISTICA, Version 5 (Statsoft France, 1997) and the parameters recorded were subjected to analysis of variance with two ways. Means comparison were carried out by the LSD test at the significant level of 0.05 as needed.
RESULTS
Leaf area and shoot length
As seen in Figure 1a, the exogenous application of proline had a significant effect on shoot length of plants of the two cultivars. The higher increase regarding this growth parameter was found with the foliar spray at low concentration of proline, particularly in Rio Grande.
Results concerning leaf area (Fig. 1b), show a significant increase (P ≤ 0.05) in Rio Grande when proline was applied. As to the Heinz-2274 cultivar, a significant increase (P ≤ 0.05) in leaf area was obtained with the lower proline concentration (10 mg L-1) only. At 20 mg L-1, this parameter decreased compared to the control (i.e., without exogenous application of proline).
Mineral nutrition
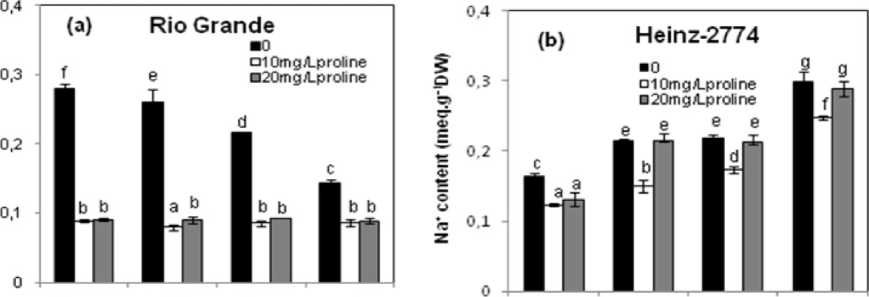
The exogenous application had a significant effect on the Na+ content for the two tomato cultivars. In the cultivar Rio Grande, this content was decreased with low and high concentrations of proline (Fig. 2a). However in the Heinz- 2274, the low concentration of proline decreased Na+ content in all organs of plants. This effect was significantly only in the leaves with the higher concentration of proline (Fig. 2b).
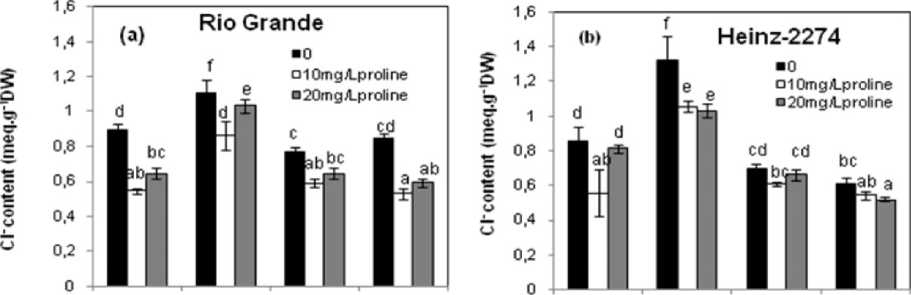
For Cl-, foliar spray significantly reduced the Cl-content in both tomato cultivars with the lower concentration of proline. At high concentration of proline, the effect of exogenous application was significant in all organs of Rio Grande andpetioles and roots of Heinz- 2274 (Fig. 3a and b).
For Ca, the lower concentration of proline led to an increase of Ca content in leaves, petioles and roots of both tomato cultivars. The higher concentration had no significant effect in the petioles of Rio Grande and in the roots of Heinz-2274 (Fig. 4a and b).
Table 1. Chemical characteristics of the irrigation water used.
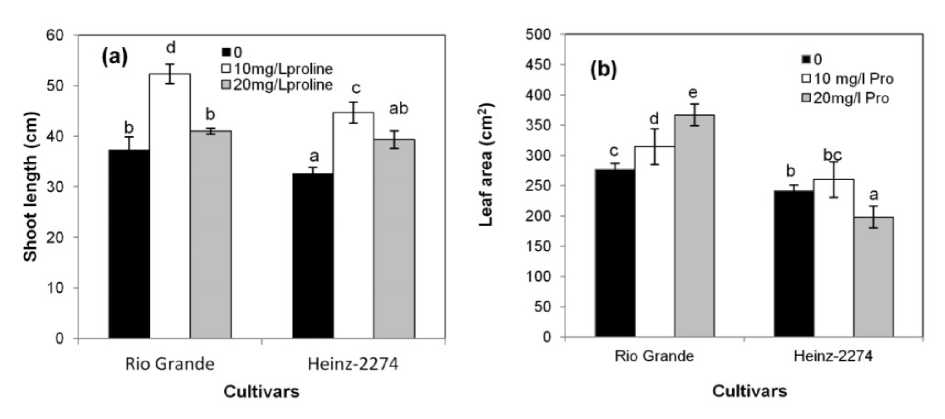
Figure 1. Effect of the exogenous application of proline on (a) shoot length and (b) leaf area of two tomato cultivars (Rio Grande and Heinz-2274) irrigated with saline water (6.57 dS.m-1). All values are the mean of three replications (n=3) and bars with different letters are significantly different at (P ≤ 0.05) according to the LSD test.
|
pH EC dS.m-1 |
Ionic composition (me.L-1) S.A.R HCO3 SO42- Cl- Ca2+ Mg2+ K+ Na+ |
|
7.8 6.57 |
4.2 24.1 37.1 14.7 10.2 1.1 41.2 11 |
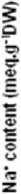
leaves petioles stems roots leaves petioles stems roots
OKjanes Organes
Figure 2. Effect of the exogenous application of proline on Na+, Cl- and Ca2+ contents of different organs of two tomato cultivars (Rio Grande and Heinz-2274) irrigated with saline water (6.57 dS.m-1). All values are the mean of three replications (n=3) and bars with different letters are significantly different at (P ≤ 0.05) according to the LSD test.
leaves petioles stems roots leaves petioles stems roots
Organs Organs
Figure 3. Effect of the exogenous application of proline on Cl- contents of different organs of two tomato cultivars (Rio Grande and Heinz-2274) irrigated with saline water (6.57 dS.m-1). All values are the mean of three replications (n=3) and bars with different letters are significantly different at (P ≤ 0.05) according to the LSD test.
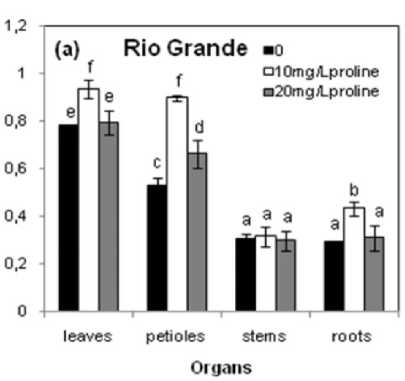
Figure 4. Effect of the exogenous application of proline on Ca2+ contents of different organs of two tomato cultivars (Rio Grande and Heinz-2274) irrigated with saline water (6.57 dS.m-1). All values are the mean of three replications (n=3) and bars with different letters are significantly different at (P ≤ 0.05) according to the LSD test.
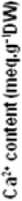
Organs
DISCUSSION
In general, salinity can reduce plant growth or damage the plants through: (i) osmotic effect (causing water deficit), (ii) toxic effect of ions and (iii) imbalance of the uptake of essential nutrients. These modes of action may operate on the cellular as well as on higher organizational levels and influence all aspects of plant metabolism (Patel et al., 2009). Results concerning reduction of shoot length and leaf area development of Heinz-2274 compared to Rio Grande are in accordance with the finding of Patel et al., (2009) and Azuma et al., (2010) who reported that growth of many crops as Delonix regia and pepper under moderate salt stress was affected primarily through a reduction in elongation of stem and leaf area development. Garg and Gupta (1997) reported that salinity causes reduction in leaf area as well as in the photosynthesis rate, which together result in reduced crop growth and yield. Proline is the most common osmolyte accumulating in plants in response to various stress conditions. It covers a wide range of protective roles including osmotic adjustment, stabilizer for cellular structure and reduction of damage to the photosynthetic apparatus. The natural level of proline accumulation in plants varies from species to species. The importance of proline in enhancing plant stress tolerance has recently been substantiated through the exogenous application of proline, which has been reported to offer beneficial effects to plants under stress conditions (Ashraf and Foolad, 2007). Results from the later authors are consistent with our present work on growth parameters regarding the shoot length and leaf area in the lower concentration of proline for the both tomato cultivars. Yamada et al. (2005) reported that exogenous proline (0, 5, 10 and 50 mM) strongly inhibited growth and accelerated leaf senescence of Arabidopsis and petunia. The toxicity of proline was found to be mediated by P5C accumulation in the proline degradation pathway (Hellmann et al., 2000). Plant growth with combined salinity and proline was suppressed presumably not only by salinity but also by proline. Our results of significant decrease of leaf area correspond with these findings.
The exogenous application of compatible solutes offers a valuable tool for studying mechanisms of salt tolerance. One of these mechanisms depends on the plant capacity for the osmotic adjustment, which allows growth to continue under saline conditions (Heuer, 2003). In our study, salinity presumably stimulated the accumulation of Na+ and Cl- in different plant organs (leaves, petioles, stems and roots) of both tomato cultivars. However, this accumulation was dramatically reduced in these plant organs in the presence of the lower proline treatment (10 mgL-1), suggesting its interference in the process of osmotic adjustment. Our data are in accordance with previous results of Ashraf and Foolad (2007), in which the exogenous application of proline resulted in a decrease in Na+ and Cl-accumulation and an increase in growth of barley. Calcium is important during salt stress, e.g., in preserving membrane integrity (Rengel, 1992), signaling in osmoregulation (Patel et al., 2009) and influencing K/Na selectivity (Cramer et al., 1987). In the present study, there was a presumably decrease of Ca2+ content in all the tissues of the two cultivars of tomato with salinization of soil. As a result, Na+ induced Ca2+ deficiency in tissues. It is reported that uptake of Ca2+ from the soil solution may decrease because of ion interactions, precipitation and increase in ionic strength that reduce the activity of Ca2+ (Cramer et al., 1987). However, the exogenous application of proline increased Ca2+ in all tissues of plants in both tomato cultivars.
CONCLUSION
From the results obtained in the present study, it is concluded that proline reduced the impact of salt stress on growth in the two tomato cultivars employed, increased Ca2+ contents and decreased Na+ and Cl- through the application of low concentration of proline (10 mg.L-1). The protective role of proline was more pronounced in the sensitive cultivar of tomato (Heinz-2274). Therefore, the exogenous application of proline by foliar spray might be a useful method to improve growth and productivity of tomato and retard aging process under salt-stressed conditions.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This study was carried out under Tunisian – Portuguese bilateral collaboration project, the INRGREF/ACSAD project for saline water use in agriculture and PISEAU II project for saline water in Center of Tunisia.
Список литературы Response of two tomato cultivars to field-applied proline and salt stress
- Ashraf, M., and Foolad, M.R. 2007. Roles of glycine betaine and proline in improving plant abiotic stress resistance. Environ. Exp. Bot. 59: 206-216.
- Ashraf, M., Athar, H.R., Harris, P.J.C. and Kwon, T.R. 2008. Some prospective strategies for improving crop salt tolerance. Adv. Agron., 97: 45-110.
- Aziz, A., Martin-Tanguy, J. and Larher, F. 1999. Salt stress-induced proline accumulation and changes in tyramine and polyamine levels are linked to ionic osmotic adjustment in tomato leaf discs. Plant Sci., 145: 83-91
- Azuma, R., Ito, N., Nakayama, N., Suwa, R., Nguyen, N.T., Larrinaga-Mayoral, J.A., Esaka, M., Fujiyama, H., Saneoka, H., 2010. Fruits are more sensitive to salinity than leaves and stems in pepper plants (Capsicum annuum L.). Sci. Hortic. 125, 171-178.
- Cramer, G.R., Lynch, J., Lauchli, A., Polito, U.S., 1987. Influx of Na, K+ and Ca into roots of salt-stressed cotton seedlings. Effects of supplemental Ca. Plant. Physiol. 83, 510-516.
- Demiral, T., Türkan, I. 2004. Does exogenous glycinebetaine affect antioxidative system of rice seedlings under NaCl treatment? J Plant Physiol 161: 1089-1100.
- Demiral, T., Türkan, I. 2006. Exogenous glycinebetaine affects growth and proline accumulation and retards senescence in two rice cultivars under NaCl stress. Environ Exp Bot 56: 72-79.
- Garg, B.K., Gupta, I.C., 1997. Saline Wastelands Environment and Plant Growth, Scientific Publishers, Jodhpur, India.
- Hellmann, H., Funck, D., Rentsch, D. and Frommer, W.B. 2000. Hypersensitivity of an Arabidopsis sugar signaling mutant toward exogenous proline application. Plant Physiol. 123: 779-790.
- Heuer, B. 2003. Influence of exogenous application of proline and glycinebetaine on growth of salt -stressed tomato plants. Plant Sci., 165: 693-699.
- Kahlaoui, B., Hachicha, M., Rejeb, S., Misle, E., Rouaissi, M., Rejeb, M.N., Hanchi, B. 2011b. Effect of saline water on tomato under subsurface drip irrigation: yield and fruit quality. Aust. J. Basic Applied Sci. 5(9), 517-529.
- Kahlaoui, B., Hachicha, M., Rejeb, S., Rejeb, M.N. 2012. Effect of drip irrigation and subsurface drip irrigation on tomato crop. Crop Prod. Improve. Agric. Chap. 27, 705-719.
- Kahlaoui, B., Hachicha, M., Rejeb, S., Rejeb, M.N., Hanchi, B., Misle, E., 2011a. Effect of saline water on tomato under subsurface drip irrigation: nutritional and foliar aspects. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 11(1), 69-86.
- Larher F., Leport L., Petrivalsky M., Chappart M. 1993. Effectors for the osmoinduced proline response in higher plants. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry 31, 911-922.
- Lutts, S., Majerus, V., Kinet, J.M. 1999..NaCl effects on proline metabolism in rice (Oriva sativa) seedlings. Physiol. Plant. 105, 450-458.
- Patel, D.A., Bhensdadia, H., Pandey, A.N., 2009. Effect of salinisation of soil on growth, water status and general nutrient accumulation in seedlings of Delonixregia (Fabaceae). Acta Ecol. Sinica 29, 109-115.
- Rengel, Z., 1992.The role of calcium in salt toxicity. Plant Cell Environ. 15, 625-632.
- Shannon, M.C., Gronwald, J.W., Tal, M., 1987. Effects of salinity on growth and accumulation of organic and inorganic ion in cultivated and wild tomato species. J. Amer. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 112, 416-423.
- Teixeira, J., Fidalgo, F. 2009. Salt stress affects glutamine synthetase activity and mRNA accumulation on potato plants in an organ-dependent manner. Plant Physiol Biochem. 47(9): 807-813
- Tononn, G., Kevers, C., Faivre-Rampant, O., Graziani, M., Gaspar, T., 2004. Effect of NaCl and mannitoliso-osmotic stresses on proline and free polyamine levels in embryogenic Fraxinusangustifolia callus. J. Plant Physiol. 161, 701-708.
- Yamada, M., Morishita, H., Urano, K., Shiozaki, N., Kazuko, Y.S., Shinozaki, K. and Yoshida, Y. 2005. Effects of proline accumulation in petunias under drought stress. J. Expt. Bot., 56: 1975-1981.


