Результаты работы нового спектрополяриметра для наблюдения солнечного радиоизлучения в диапазоне 50-500 МГц
Автор: Муратова Н.О., Муратов А.А., Кашапова Л.К.
Журнал: Солнечно-земная физика @solnechno-zemnaya-fizika
Статья в выпуске: 3 т.5, 2019 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Наземные наблюдения в метровом радиодиапазоне представляют большой интерес для понимания процессов, происходящих в короне Солнца. Мы представляем основные принципы работы, схему и результаты первых наблюдений Солнечного спектрополяриметра метрового диапазона (ССМД), запущенного для наблюдения Солнца в диапазоне 50-500 МГц в апреле 2016 г. Основной задачей при конструировании прибора было создание современного цифрового спектрополяриметра, способного измерять полный вектор Стокса для спорадических явлений, наблюдаемых в диапазоне 50-500 МГц. Для приема радиоизлучения используется логопериодическая скрещенная антенна, принимающая горизонтальную и вертикальную поляризационные компоненты одновременно. Основой ССМД является цифровая часть, алгоритм работы которой построен на базе архитектуры FX-коррелятора. В основе получения динамических амплитудных спектров (зависимость амплитуды от частоты и времени) лежит алгоритм быстрого преобразования Фурье (БПФ), реализованный по принципу поточной схемы и работающий в режиме реального времени...
Радиоспектрометр, спектрометр с быстрым преобразованием фурье, fx-коррелятор, инструменты, солнце, поляризация, параметры стокса, метровый диапазон
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/142222483
IDR: 142222483 | УДК: 523.9, | DOI: 10.12737/szf-53201901
Текст научной статьи Результаты работы нового спектрополяриметра для наблюдения солнечного радиоизлучения в диапазоне 50-500 МГц
Ускоренные частицы в солнечной короне являются источником большого количества явлений, возникающих при взаимодействии магнитных полей и плазмы. При этом нетепловые электроны, ускоренные в солнечной атмосфере, излучают радиоволны в широком диапазоне и приводят к возникновению множества видов радиовсплесков [Wild et al., 1963; Железняков, 1964; Kundu, 1965]. Интерес к изучению событий этого вида не утихает уже много десятилетий. С одной стороны, до сих пор остаются нерешенными важные для физики солнечной короны задачи, связанные с пониманием природы радиовсплесков. С другой стороны, уже имеющиеся в распоряжении методы позволяют делать оценки параметров плазмы во время событий, связанных с такими геоэффективными явлениями, как корональные выбросы массы или увеличение потока электронов в солнечных космических лучах [Tsvetkov et al., 2018]. Для исследования явлений в этом диапазоне широко распространены так называемые динамические спектры, демонстрирующие распределение значений какого-либо параметра в зависимости от времени и частоты. Метровое излучение большинства известных радиовсплесков поляризовано [Железняков, 1964; McLean et al., 1985], а полную информацию о поляризации излучения дает полный вектор Стокса [Born, Wolf, 1965]. В настоящее время спектральные наблюдения в метровом диапазоне проводятся на ряде инструментов: Culgoora (18–1800 МГц, Австралия) [Prestage et al., 1994]; Learmonth (25– 180 МГц, Австралия) [ Solar/3/1]; Hiraiso (25–2500 МГц, Япония) [Kondo et al., 1995]; AMATERAS (150–500 МГц, Япония) [Iwai et al., 2012]; спектрограф ИЗМИРАН (25–270 МГц, Россия) [] и др. Помимо отдельных инструментов существует и мировая сеть спектрографов e-CALLISTO, наблюдающих в метровом и дециметровом диапазонах. В распоряжении данной сети имеются радиоспектрографы с частотным диапазоном 45–870 МГц, расположенные в разных точках земного шара. Один из спектрографов сети e-CALLISTO [Benz et al., 2009] ведет наблюдения в Радиоастрофизической обсерватории (ур. Бадары). Однако этот аналоговый спектрограф измеряет только интенсивность горизонтальной поляризационной компоненты. Большинство радиоспектрографов наблюдает либо одну поляризационную компоненту (линейную или круговую) вектора электрического поля, либо один параметр Стокса, реже они наблюдают два параметра. Это связано с тем, что наблюдения полного вектора Стокса накладывают особые условия на характеристики приемной системы устройства, особенно на соотношение ширины канала и наблюдаемой частоты, требуя при этом высокой чувствительности. Также метровый диапазон чувствителен к ионосферным эффектам, а кроме того, «загрязнен» сигналами других многочисленных радиоустройств. Стремительное развитие электроники и появление новых доступных серийных микросхем и процессов позволяют продвинуться в решении поставленной задачи. Мы представляем результаты первого этапа создания и введения в режим регулярных наблюдений солнечного спектрополяриметра метрового диапазона (ССМД) 50–500 МГц. В работе представлены концепции построения спектрополяриметра, обсуждаются цифровая и аналоговая части, полученные на первом этапе характеристики прибора и результаты наблюдений. В заключении приводятся планы и задачи по усовершенствованию нового прибора.
БАЗОВАЯ КОНЦЕПЦИЯ ССМД
При разработке была поставлена задача создания радиоспектрополяриметра, измеряющего все параметры Стокса ( I , Q , U , V ) солнечного радиоизлучения, наблюдаемого в диапазоне 50–500 МГц. Получение всех параметров Стокса дает возможность полного описания состояния поляризации радиоизлучения. В настоящее время не существует аналогичных радиоспектрографов с такими характеристиками.
В качестве приемной антенны ССМД мы используем скрещенную 2×16-элементную логопериодическую антенну [ /] (рис. 1, a, б). Она отличается высокой прочностью, небольшой стоимостью и способна перекрыть широкий частотный диапазон. Еще одно ее преимущество — данная модель принимает одновременно горизонтальную и вертикальную компоненты поляризации. Представим плоскую электромагнитную волну, падающую на антенну в виде двух взаимно перпендикулярных компонент вектора электрического поля:
E x = a 1 cos ( т + 5 1 ) , E y = a 2 cos( t + 5 2).
Через амплитуды а 1 , а 2 и разность фаз δ=δ 1 –δ 2 выражения (1) мы можем определить параметры вектора Стокса [Born, Wolf , 1965] . Для квазимоно-хроматических волн данные параметры примут следующий вид:
I = ^а^ + ^ a2Y Q = Oo^-(a2^, U = 2( a , a2 cos5^,
V = 2 ( a 1 a 2 sin 5^.
Для дальнейших вычислений нам удобнее воспользоваться эквивалентной формой записи, поэтому выразим эти параметры через элементы матрицы когерентности
** **
xx yy , xx y y ,
U = EE* \ + ( E E V V = i Ue^E J - ( e E J . xy yx xy yx
Здесь Е х и E y — аналитические сигналы; * — комплексное сопряжение; < > — усреднение по времени; I — полная интенсивность; Q — разница интенсивностей линейных составляющих 0° и 90°; U — разница интенсивностей линейных составляющих 45° и 135°; V — разница интенсивностей левой и правой круговых поляризаций.
Далее мы подробнее остановимся на аналоговой и цифровой частях ССМД.

Рис. 1. 2×16-элементная скрещенная логопериодическая антенна CLP5130-1X, на мачте которой закреплен герметичный корпус, содержащий блок аналоговой электроники ССМД ( а ); блок ССМД (внешний вид), содержащий аналоговую и цифровую электронику и расположенный в тоннеле под антенной ССМД ( б )
HYB 90
50-500 МГц I
2LP513O-IX, 10-12 дБ
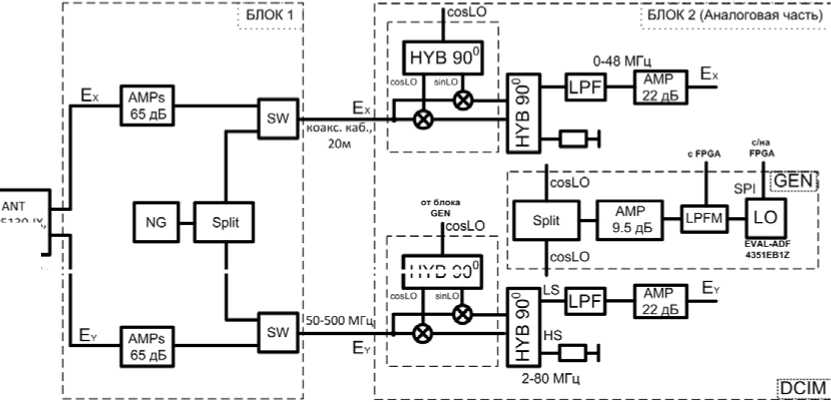
Рис. 2 . Блок-схема аналоговой части ССМД
АНАЛОГОВАЯ ЧАСТЬ ССМД
Электронику ССМД можно условно разделить на два блока. Первый блок расположен на мачте антенны в герметично закрытом корпусе (рис. 1, а ) и содержит аналоговую электронику. Антенна (ANT) принимает одновременно горизонтальную и вертикальную компоненты поляризации в диапазоне 50– 500 МГц при усилении антенны 10–12 дБ. Далее (рис. 2) каскад усилителей усиливает эти сигналы на 65 дБ (AMPs). В дальнейшем предполагается использовать схему калибровки, включающую в себя два СВЧ-коммутатора (SW), генератор шума (NG) и СВЧ-разветвитель (Split) и находящуюся в этом же корпусе.
Усиленные сигналы по коаксиальным 20-метровым кабелям поступают на второй блок ССМД, содержащий вторую часть устройств аналоговой схемы и цифровую электронику. Второй блок располагается в тоннеле под антенной ССМД. Для дальнейшей обработки (рис. 2, БЛОК 2 (аналоговая часть)) мы переносим сигналы Ех и Ey в область пониженных частот, используя супергетеродинную схему, при этом диапазон 50–500 МГц разбивается на 10 поддиапазонов, обрабатываемых устройством последовательно. Мы переносим наш диапазон в более низкочастотную область, поскольку частота дискретизации сигналов в цифровой части составляет 100 МГц (максимальная частота дискретизации аналого-цифрового преобразователя (АЦП) — 125 МГц). В схеме понижения частоты используется один местный гетеродин (LO, блок GEN), в роли которого выступает оценочная плата синтезатора частот EVAL-ADF4350EB1Z [], контролируемая и перестраиваемая с помощью FPGA (Field-Programmable Gate Array — программируемая пользователем вентильная матрица) по трехпроводному SPI-интерфейсу (Serial Peripheral Interface — последовательный периферийный интерфейс). Генерируемый синтезатором частот сигнал затем разветвляется для Ех- и Ey-каналов. Помимо полезного сигнала, синтезатор генерирует вторые, третьи и другие гармоники высших порядков. Для того чтобы избежать влияния этих гармоник, мы добавляем на выход платы синтезатора частот плату с матрицей фильтров (LPFM), собранную на элементах поверхностного
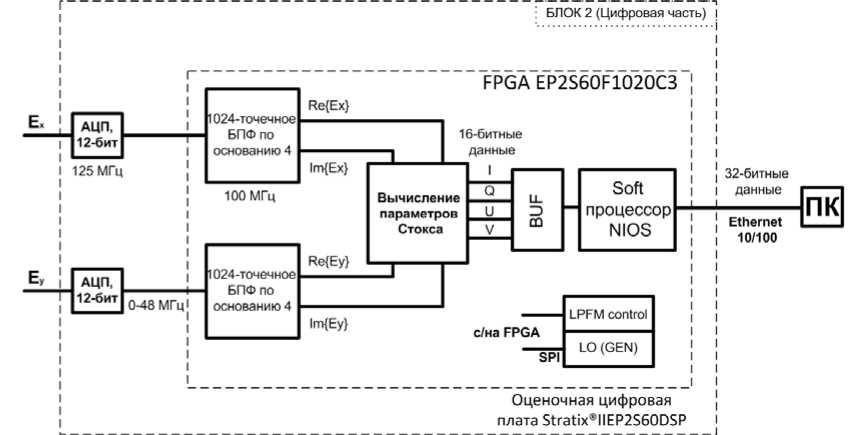
Рис. 3. Блок-схема цифровой части ССМД
монтажа — фильтрах и двух СВЧ-коммутаторах, которые осуществляют выбор фильтра, необходимого для данной полосы частот. Блок LPFM контролируется при помощи FPGA. При смешении сигналов на выходе смесителя наряду с полезным пониженным по частоте сигналом мы получим зеркальный канал. Чтобы подавить его, в схеме понижения частоты (блок DCIM) мы применили архитектуру Хартли [Hartley, 1928] , которая предполагает использование двух квадратурных мостов 90° (HYB), а также двух смесителей. Входной квадратурный мост и два смесителя размещены на одной плате — это исключает дополнительные искажения сигнала. После выходного квадратурного моста частотный диапазон сигналов Е х и E y составляет 2–80 МГц. Затем эти сигналы проходят через НЧ-фильтр (LPF), после которого их диапазон составляет 2–48 МГц. Теперь сигналы готовы к обработке цифровой частью ССМД, которая находится в одном корпусе с вышеописанными устройствами аналогового блока схемы.
ЦИФРОВАЯ ЧАСТЬ ССМД
Цифровая часть ССМД реализована на оценочной цифровой плате Stratix®IIEP2S60DSP компании Altera (c июня 2015 г. — корпорация Intel [https://www. ]). Обработанные аналоговой частью сигналы Ех и Ey предварительно усиливаются на 22 дБ, а затем оцифровываются 12-битными АЦП, расположенными на оценочной плате (рис. 3). Как уже упоминалось выше, частота дискретизации сигналов 100 МГц, а наблюдаемый диапазон частот ССМД 50–500 МГц, поэтому ранее была использована схема понижения частоты. Полосы оцифрованных Ех- и Ey-сигналов предварительно разбитого 50–500 МГц диапазона составляют 46 МГц, каждый такой поддиапазон последовательно поступает на FPGA EP2S60F1020C3, где обрабатывается блоком быстрого преобразования Фурье (БПФ), работающим на тактовой частоте 100 МГц. Кроме цифровой обработки сигналов, которая является основной функци- ей FPGA, она осуществляет функции контроля и перестройки платы синтезатора частот по 3-проводному SPI-интерфейсу, управления входными АЦП и матрицей фильтров (LPFM), а также контроля передачи данных по локальной сети Ethernet с цифровой платы на персональный компьютер (ПК). Остановимся подробнее на блоке цифровой обработки.
Рассмотрим выражение (3). В природе сигналы вещественны. Нам необходимо получить из вещественных сигналов аналитические и комплексносопряженные им компоненты. Далее, согласно (3), нам необходимо найти две автокорреляционных функции (АКФ) и две взаимнокорреляционных (ВКФ). Теорема Винера — Хинчина утверждает, что спектр мощности сигнала W (ω) связан с его АКФ B S (τ) преобразованием Фурье [Баскаков, 2003; Wilson et al., 2009] :
W ( to ) = J B S ( t ) e - j toT d t , (4)
-от где
W ( to ) = S ( to ) S * ( to ) ,
B S ( t ) = J S ( t ) S * ( t -t ) dt .
-от
Взаимный спектр мощности W UV (ω) и ВКФ B UV (τ) двух сигналов аналогичным образом связаны преобразованием Фурье:
от
W uv ( to ) = J B uv ( t ) e j d t , (5)
-от где
Wuv (to) = U(to) V* (to) , от
B uv ( t ) = J U ( t ) V * ( t -t ) d T .
-от
Используя утверждения (4) и (5) при создании блока цифровой обработки ССМД, мы применили архи-
Основные параметры ССМД
|
Параметр |
Значение |
|
Частотный диапазон |
50–500 МГц |
|
Число каналов |
4608 |
|
Ширина поддиапазона |
46 МГц |
|
Число каналов в поддиапазоне |
471 (для последнего 369) |
|
Ширина канала (шаг) |
97.66 кГц (97.66 кГц) |
|
Частота дискретизации |
100 МГц |
|
Разрядность данных на входе (выходе) |
12 бит (32 Бит) |
|
Тип измеряемой поляризации |
полный вектор Стокса ( I , Q , U , V ) (сохраняются I - и V -компоненты) |
|
Временное разрешение |
1 секунда |
|
Временной диапазон наблюдений |
00:00–10:00 UT |
|
Объем записанных данных в день |
1.2 ГБ |
тектуру FX-коррелятора [Romney, 1999]. Вначале мы получаем спектры сигналов, а затем вычисляем компоненты Стокса. Для вычисления спектров Ех и Ey, мы реализовали в FPGA 1024-точечный алгоритм БПФ по основанию 4. Учитывая характеристики устройств аналоговой схемы, мы используем 471 (а для последнего поддиапазона — 369) частотный канал из 512 вычисленных БПФ для каждого поддиапазона. Соответственно для диапазона 50–500 МГц мы получаем 4608 каналов. Данный алгоритм реализован при использовании поточной архитектуры [Rabiner et al., 1975] и работает в режиме реального времени, что позволяет обрабатывать поступившие на вход сигналы без потери данных. Учитывая (3)–(5) мы получаем параметры Стокса и производим накопление (BUF). Накопленные 32-битные данные передаются с оценочной платы на компьютер через LAN Ethernet 10/100. Для передачи данных мы используем микропроцессор NIOS [], который также является частью прошивки FPGA. Управление микропроцессором осуществляется пакетом программ, созданных в Eclipse IDE на языке С. Прошивка для FPGA выполнена на языке Veri-logHDL на программном обеспечении (ПО) QuartusII [] и занимает 20 % логических ресурсов чипа EP2S60F1020C3 и 30 % ресурсов памяти. ПО для отображения данных на ПК и их записи выполнено в Qt SDK (Software Development Kit — пакет средств разработки []) на языке C++.
ОСНОВНЫЕ ПАРАМЕТРЫ ССМД
В приведенной выше таблице указаны основные параметры ССМД. Как было сказано в предыдущих разделах, для того чтобы обработать диапазон 50– 500 МГц, исходя из частоты обработки данных FPGA 100 МГц, мы разбиваем его на поддиапазоны размером по 46 МГц. Необходимо отметить, что изначально ширина каждого поддиапазона для обработки с помощью БПФ составляет 50 МГц, но из-за особенностей аналоговой схемы мы перекрываем поддиапазоны и сокращаем ширину до 46 МГц (до 36 МГц для последнего). Таким образом, из 512 ка- налов, вычисленных при помощи БПФ, мы используем для каждого поддиаппазона 471 (а для последнего — 369) канал, полный спектр содержит 4608 каналов. Ширина канала составляет 97.66 кГц при шаге 97.66 кГц. На входе устройства после АЦП данные имеют 12-битную разрядность, таким образом, динамический диапазон цифровой части составляет 72 дБ. На выходе цифровой части разрядность данных составляет 32 бита. Временное разрешение ССМД — 1 с. Его снижают такие факторы, как скорость работы устройств на цифровой плате и Ethernet соединения, применение последовательной, а не прямой обработки частотного диапазона 50–500 МГц. ССМД вычисляет полный вектор Стокса, но на данный момент на ПК фиксируются I и V (интенсивность и круговая поляризация). В дальнейшем планируется фиксировать все четыре параметра. Как отмечалось ранее [Железняков, 1964; Akabane et al., 1961; Chin et al., 1971], при наблюдении линейной поляризации (Q- и U-параметры Стокса) необходимо учитывать эффект Фарадея и рассчитывать ширину канала так, чтобы уменьшить эффект размытия поляризации в канале, связанный с конечностью ширины полосы приемной аппаратуры. Опираясь на предварительные расчеты и практические измерения, проведенные другими исследователями, для увеличения вероятности регистрации линейной поляризации мы выбрали ширину канала 10 кГц. На первом этапе создания прибора с целью повышения чувствительности было принято решение заложить ширину канала равной 97.66 кГц, что позволило тестировать и отлаживать работу прибора для таких важных параметров, как полная интенсивность и круговая поляризация. Объем записанных данных составляет 1.2 Гб в день, данные доступны в формате bin, в настоящий момент идет работа по их размещению на сервере института.
ПЕРВЫЕ РЕЗУЛЬТАТЫ НАБЛЮДЕНИЙ
Прибор был успешно запущен в режим регулярных наблюдений в Радиоастрофизической обсерва-
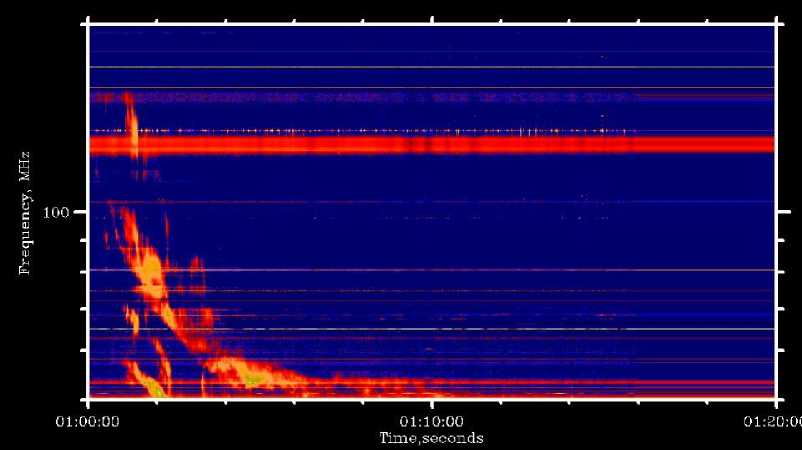
Рис. 4. Радиовсплеск II-типа (интенсивность I ), зарегистрированный ССМД 10.07.2016
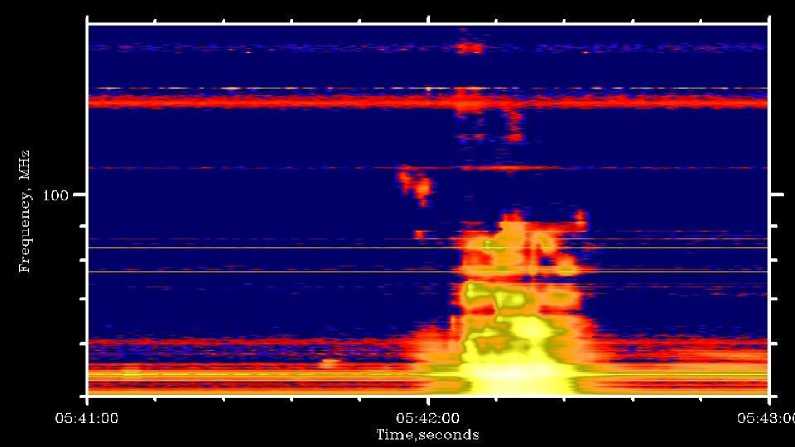
а
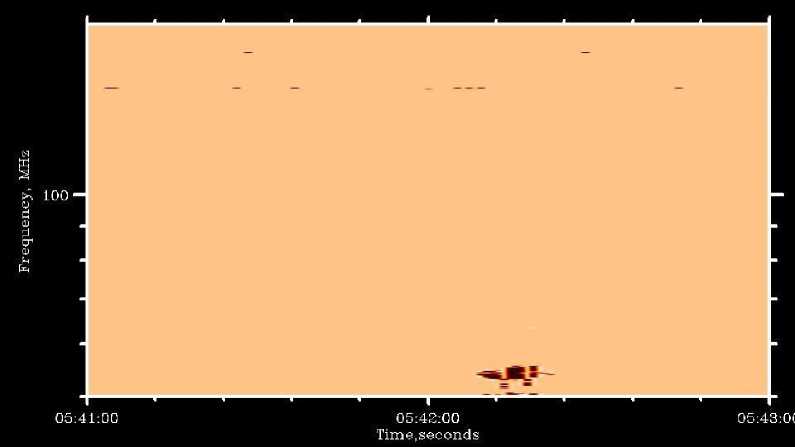
Рис. 5. Радиовсплеск III-типа, зарегистрированный ССМД 23.07.2016: a — интенсивность I ; б — круговая поляризация V
б
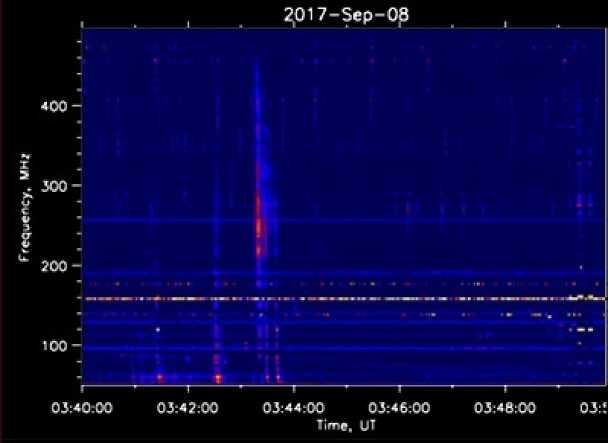
Рис. 6. Радиовсплеск III-типа (спектр интенсивности I ), зарегистрированный ССМД 08.09.2017
тории ИСЗФ СО РАН (уp. Бадары) в апреле 2016 г. Одним из первых явлений, зарегистрированных прибором, был радиовсплеск с медленным частотным дрейфом, или радиовсплеск II типа, наблюдавшийся во время солнечной вспышки 10 июля 2016 г. (см. рис. 4). Во время другой солнечной вспышки 23 июля 2016 г. были зарегистрированы радиовсплески с быстрым частотным дрейфом, или всплески III типа. ССМД зафиксировал также наличие круговой поляризации. Динамические спектры этих двух параметров показаны на рис. 5. Приведенные выше события не являются артефактами. Это подтверждается тем, что они были зарегистрированы также приборами сети eCALLISTO и радиоспектрографом обсерватории Лер-монт [] (Австралия). Наблюдения в период повышенной солнечной активности в сентябре 2017 г. показали, что спектрограф обладает достаточной чувствительностью во всем заявленном диапазоне (рис. 6).
Для проведения анализа в настоящее время доступны только спектры интенсивности I . Наблюдения круговой поляризации ( V -параметр Стокса) пока тестируются с целью уточнения знака поляризации. Однако благодаря регулярным наблюдениям на сегодняшний день накоплен достаточный материал для составления каталога радиовсплесков, наблюдавшихся на ССМД в 2016–2018 гг.
ЗАКЛЮЧЕНИЕ
Разработан, создан и введен в режим регулярных наблюдений оригинальный прибор, позволяющий получать динамические спектры солнечного радиоизлучения в диапазоне 50–500 МГц с временным разрешением 1 с и шириной канала 97.66 кГц. Первые наблюдения на новом приборе показали, что он может регистрировать различные по динамическим и яркостным характеристикам радиовсплески. В ближайшее время для проведения научного анализа планируется сделать доступными наблюдения круговой поляризации. Также планируются регулярные наблюденияй полного вектора Стокса и улучшение характеристик спектрографа с учетом опыта, полученного в результате первых наблюдений.
Работа выполнена в рамках базового финансирования ФНИ II.16.
Список литературы Результаты работы нового спектрополяриметра для наблюдения солнечного радиоизлучения в диапазоне 50-500 МГц
- Баскаков С.И. Радиотехнические цепи и сигналы. М.: Высшая школа, 2003. 462 с.
- Железняков В.В. Радиоизлучение Солнца и планет. М.: Наука, 1964. 560 с.
- Akabane K., Cohen M.H. Polarization measurements of type III bursts and Faraday rotation in the corona // Solar Phys. 1961. V. 133. P. 258-268.
- Benz A.O., Monstein C., Meyer H., et al. A world-wide net of solar radio spectrometers: e-CALLISTO // Earth, Moon, and Planets. 2009. V. 104, iss. 1-4. P. 277-285. DOI: 10.1007/s11038-008-9267-6
- Born M, Wolf E. Principles of Optics. London: Pergamon Press, 1965. 808 p.
- Chin Y.C., Lusignan B.B., Fung P.C.W. Polarization measurements of solar type III radio bursts at 25.3 MHz // Solar Phys. 1971. V. 16, iss. 1. P. 135-151.
- DOI: 10.1007/BF00154509
- Hartley R. Modulation System. US patent, no. 1666206, 1928.
- Iwai K., Tsuchiya F., Morioka A., Misawa H. IPRT/AMATERAS: A new metric spectrum observation system for solar radio bursts // Solar Phys. 2012. V. 277, iss. 2. P. 447-457. -y.
- DOI: 10.1007/s11207-011-9919
- Kondo T., Isobe T., Igi S., et al. Hiraiso Radio Spectrograph (HiRAS) for monitoring solar radio bursts // J. Communications Research Laboratory. 1995. V. 42, N 1. P. 111-119.
- Kundu M.R. Solar Radio Astronomy. N.Y.: Interscience Publ., 1965. 660 p.
- McLean D.J., Labrum N.R. Solar Radiophysics: Studies of Emission from the Sun at Metre Wavelengths. N.Y.: Cambridge University Press, 1985. P. 516.
- Prestage N.P., Luckhurst R.G., Paterson B.R., et al. A new radiospectrograph at Culgoora // Solar Phys. 1994. V.150. P. 393-396.
- DOI: 10.1007/BF00712901
- Rabiner L.R., Gold B. Theory and Application of Digital Signal Processing. New Jersey: Englewood Cliffs, Prentice-Hall, Inc. Publ., 1975. 777 p.
- Romney J.D. Cross-correlators. synthesis imaging in radio astronomy II. A collection of lectures from the Sixth NRAO/NMIMT Synthesis Imaging Summer School. ASP Conf. Ser. Socorro, New Mexico, USA, 1999. V. 180. P. 57-78.
- Tsvetkov Ts., Miteva R., Petrov N. On the relationship between filaments and solar energetic particles // J. Atmos. Solar-Terr. Phys. 2018. V. 179. P. 1-10. 10.1016/j.jastp. 2018.06.005.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jastp.2018.06.005
- Wild J.P., Smerd S.F., Weiss A.A. Solar bursts // Ann. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. // 1963. V. 1, N 1. P. 291-366.
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev.aa.01.090163.001451
- Wilson T.L., Rohlfs K., Hüttemeister S. Tools of Radio Astronomy. Berlin: Springer-Verlag Publ., 2009. 520 p.
- URL: http://www.izmiran.ru/stp/lars/?LANG=ru (дата обращения 9.02.2019).
- URL: https://www.analog.com/en/index.html (дата обращения 30 июля 2019).
- URL: https://www.intel.com (дата обращения 30 июля 2019).
- URL: https://www.sws.bom.gov.au/Solar/3/1 (дата обращения 30 июля 2019).
- URL: http://www.cd-corp.com/eng/cma/clp5130.pdf (дата обращения 30 июля 2019).
- URL: https://www.qt.io (дата обращения 30 июля 2019).
- Akabane K., Cohen M.H. Polarization measurements of type III bursts and Faraday rotation in the corona. Solar Phys. 1961, vol. 133, pp. 258-268
- Baskakov S.I. Radiotekhnicheskie tsepi i signaly [Radio circuits and signals]. Moscow, Vysshaya Shkola Publ., 2003. 462 p. (In Russian).
- Benz A.O., Monstein C., Meyer H., Manoharan P.K., Ramesh R., Altyntsev A., et al. A world-wide net of solar radio spectrometers: e-CALLISTO. Earth, Moon, and Planets. 2009, vol. 104, iss. 1-4, pp. 277-285.
- DOI: 10.1007/s11038-008-9267-6
- Born M., Wolf E. Principles of Optics. London: Pergamon Press, 1965, 808 p.
- Chin Y.C., Lusignan B.B., Fung P.C.W. Polarization measurements of solar type III radio bursts at 25.3 MHz. Solar Phys. 1971, vol. 16, iss. 1, pp. 135-151.
- DOI: 10.1007/BF00154509
- Hartley R. Modulation System. US patent, no. 1666206, 1928.
- Iwai K., Tsuchiya F., Morioka A., Misawa H. IPRT/AMATERAS: A new metric spectrum observation system for solar radio bursts. Solar Phys. 2012, vol. 277, iss. 2, pp. 447-457. -y.
- DOI: 10.1007/s11207-011-9919
- Kondo T., Isobe T., Igi S., Watari S., Tokimura M. The Hiraiso Radio Spectrograph (HiRAS) for monitoring solar radio bursts. J. Communications Research Laboratory. 1995, vol. 42, no. 1, pp. 111-119.
- Kundu M. R. Solar Radio Astronomy. N.Y.: Interscience Publ., 1965. 660 p.
- McLean D.J., Labrum N.R. Solar Radiophysics: Studies of Emission from the Sun at Metre Wavelengths. N.Y.: Cambridge University Press, 1985, 516 p.
- Prestage N.P., Luckhurst R.G., Paterson B.R., Bevins, C.S., Yuile, C.G. A new radiospectrograph at Culgoora. Solar Phys. 1994, vol.150, pp. 393-396.
- DOI: 10.1007/BF00712901
- Rabiner L.R., Gold B. Theory and Application of Digital Signal Processing. New Jersey: Englewood Cliffs, Prentice-Hall, Inc. Publ, 1975, 777 p.
- Romney J.D. Cross-correlators. synthesis imaging in radio astronomy II. A collection of lectures from the Sixth NRAO/NMIMT Synthesis Imaging Summer School. ASP Conf. Ser. Socorro, New Mexico, USA, 1999, vol. 180, pp. 57-78.
- Tsvetkov Ts., Miteva R., Petrov N. On the relationship between filaments and solar energetic particles. J. Atmos. Solar-Terr. Phys. 2018, vol. 179, pp. 1-10. 10.1016/j.jastp. 2018.06.005.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jastp.2018.06.005
- Wild J.P., Smerd S.F., Weiss A.A. Solar Bursts. Annual Review of Astronomy and Astrophysics. 1963, vol. 1, no. 1, pp. 291-366.
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev.aa.01.090163.001451
- Wilson T.L., Rohlfs K., Hüttemeister S. Tools of Radio Astronomy. Berlin: Springer-Verlag Publ. 2009, 520 p.
- Zheleznyakov V.V. Radio Emission of the Sun and Planets. Oxford, Pergamon Press, 1970, 712 p. (ed.: J.S. Hey).
- URL: https://www.analog.com/en/index.html (accessed 30 July 2019).
- URL: https://www.intel.com (accessed 30 July 2019).
- URL: https://www.sws.bom.gov.au/Solar/3/1 (accessed 30 July 2019).
- URL: http://www.cd-corp.com/eng/cma/clp5130.pdf (accessed 30 July 2019).
- URL: http://www.izmiran.ru/stp/lars/?LANG=ru (accessed 30 July 2019).
- URL: https://www.qt.io (accessed 30 July 2019).


