Risk management in foreign currency operations of business entities
Автор: Šmigić Miladinović Jasmina
Журнал: Ekonomski signali @esignali
Статья в выпуске: 2 vol.17, 2022 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Risk is an integral part of everyday business. Doing business outside the borders of the national economy implies settlements and payments in different currencies and carries with it the occurrence of risks of changes in exchange rates, interest rates on the international market and the like. Globalization has led to the fact that economic entities are necessarily directed to do business with foreign economic entities, either in the role of buyer or in the role of seller. In both cases, payment is implied, but also settlement in domestic and foreign currency, since in the Republic of Serbia the official currency is the dinar, and most foreign exchange operations are performed in euros and dollars. The problem can arise on several grounds, due to the mismatch between the realization of business and payments, due to the overestimation or underestimation of the domestic currency in relation to the foreign currency, but also due to numerous other reasons. Having in mind the above, the aim of this paper is to point out the need for risk management in foreign exchange operations of economic entities, which significantly affects the stability of the financial and overall economic system of a particular national economy.
Risk, risk management, foreign exchange operations, currency
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/170204017
IDR: 170204017 | DOI: 10.5937/ekonsig2202001S
Текст научной статьи Risk management in foreign currency operations of business entities
In situations mentioned in previous section, very important issue is the reality of foreign exchange rate. For example if we have the situation of overestimated local currency we are supporting import and othervise, if we have the situation of underestimated local currency we are supporting export. -lso, a lot of factor, including political stability, geopolitical relations, offer and demand etc. are influ-encing on the exchange rate.
The level of the risk is directly proportional to the level of dependence of one national economy to other national economies, ie. it is depending of the level of import and export, beside the factor of proper estimation of local currency.
-
- risk of change in the exchange rate and possibilities for its overcoming
-ccording to the National Bank of Serbia [NBS, 2022] the risk of changes in the exchange rate occurs with all businessmen who have a currency mismatch of assets and liabilities in conditions of more or less fluctuating exchange rates. Due to the nature of the business, the risk of changes in the exchange rate is most pronounced among businessmen engaged in foreign trade.
For the importer - who has the obligation to pay imports in foreign currency on a certain day in the future - the risk of exchange rate change means the risk that the domestic currency weakens, so on the day of his foreign currency obligation he must pay more dinars than planned and record a loss. -t the same time, the importer would benefit if the domestic currency strengthened, because in the future it would settle its obligation with less dinars.
For the exporter, on the contrary, the strengthening of the domestic currency means a potential loss because when exchanging foreign currency from exports for domestic currency he gets a smaller amount of dinars, while weakening the domestic currency means a potential gain for him - when exchanging foreign currency from exports he gets more dinars.
What importers and exporters have in common is that, due to the risk of changes in the exchange rate, they do not know in advance what their final financial result will be. That is why they cannot calculate the risk of a change in the price of their products in advance, which makes it difficult for them to plan their business. Therefore, the basic function of hedging against exchange rate risk is to eliminate the consequences of uncertainty regarding the movement of the exchange rate in the future.
For businessmen - importers and exporters, the specific advantages of contracting protection against exchange rate risk are the following: [NBS, 2022]
-
- the possibility of a clear calculation of cash flows in the future,
-
- the possibility of forming the prices of their products that certainly enable the realization of business plans,
-
- business stability and the ability of the company to focus on its core business.
The best way to protect against exchange rate risk is complete harmonization of the currency structure of cash inflows and outflows of the company, because it eliminates foreign exchange risk from business (natural insurance against exchange rate risk or so-called natural hedging).
This way of protection against the risk of changes in the exchange rate is the best because it is free and exclusively related to the business of the company itself. However, there are few businessmen who can provide this type of protection.
-ccording to the NBS, Businessmen who cannot provide "natural hedging" can use instruments of hedging against foreign exchange risk in the form of various contracts, which are based on buying or selling currency at a predetermined rate. Since the price of these instruments - contracts is practically derived from another financial instrument (exchange rate, interest rates, indices, etc.), they are called financial derivatives.
Diagram 1. Foreign Exchange Risks classification
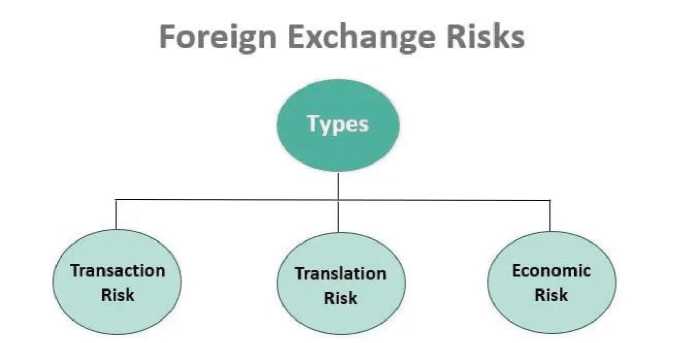
Source: -uthor
Foreign exchange risks can be classified into the following three types of risks:
-
1. transaction,
-
2. translation and
-
3. economic risk.
Transaction Risk exposure occurs only when there is a temporal coincidence between the "assumption" of the obligation and its payment. Features of transaction risk:
-
- Inconsistency between the currency in which the price is expressed and the currency in which the costs are expressed;
-
- Gains or losses are caused by differences between the planned exchange rates used in determining the price and the exchange rates realized during the collection, when the conversion from the currency of sale to the currency of costs. Gains and losses are the difference between the amount of risk converted at the planned rate and the actual exchange rate;
-
- Determining the time of currency conversion is very important if you want to link items in the currency to be converted.
Therefore, transactional currency risk can be defined as: risk that may lead to non-realization of planned earnings in financial transactions in which the selling price and costs are not in the same currency, due to opposite changes in exchange rate value compared to the exchange rate used in determining price and, that is, between the period of determining prices and charging for the service rendered.
Banks that have decided to operate in the international market in the long run are constantly faced with this risk, so this is one of their key decisions at which level they will recognize transaction risk. It primarily depends on the type of business in question and the instability of the currency in question.
Understanding foreign exchange risk and developing a definition of currency risk for many multinational corporations and banks begins with translational exposure , also known as accounting or balance sheet exposure.
This exposure in the narrowest sense grows out of the need to translate the assets, receivables, capital and liabilities of a given corporation (bank) denominated in foreign currency as the balance sheet and income statement of its subsidiaries - entities established in foreign countries, that is, the domestic currency.
Translation is performed on the basis of valid accounting standards established by the Ministry of Finance, or by an officially elected accounting and bookkeeping body, internal or international.
The accounting effect of foreign exchange exposure is only part of the currency risk faced by international corporations and banks. The starting point for understanding and managing this type of exposure is in the accounting methods used to "translate" the given positions in the balance sheet and income statement denominated in different currencies into one common-parent currency.
The differences between realized and unrealized effects have important bookkeeping and tax standards.
High volume of direct investments abroad, increasing presence of -merican corporations and banks on all continents, liberalization of capital movements around the world, deregulation of banking and financial systems, as well as the abolition of foreign exchange controls in most leading developed countries, after many years of debates. they forced the -merican authorities to deal in more detail with the bookkeeping and accounting of
Šmigić Miladinović J., Risk Management in Foreign Currency Operations of Business Entities foreign currency-foreign exchange positions.
Economic, future or expected exposure to foreign exchange risk implies future relative changes in currency prices, which could have an impact on the effects of the bank's operations in the near or distant future. Thus, the essence of economic exposure to exchange rate risk comes down to thison risk exposure resulting from a real change in the exchange rate in relation to the currencies of competitors, ie, which has the opposite effect on competitive costs, sales, profits and market share.
Important characteristics of economic exposure to currency risk are:
-
- That it occurs before an economic transaction and usually determines whether it will occur,
-
- That it is related to real, not nominal changes in exchange rates,
-
- It can generally be said that it does not appear in the financial statements,
-
- That it can affect our domestic sales in local currency,
-
- To strive to have different time spans.
Considering the future effects of changes in real exchange rates is a very important, but at the same time complex task of forecasting by economic entities involved or wishing to 8oin the international exchange. This work is extremely important for long-term arrangements such as the establishment of branches or subsidiaries abroad, when it is necessary to assess longterm economic and financial trends, and within them the effects of changes in real exchange rates. There are methods for predicting changes in exchange rates and which can be classified into two groups:
-
1. Econometric models with the help of mathematical patterns,
-
2. Sub8ective assessments of a team of experts or individuals of relative variables on the movement of course height.
-
3. Some of the financial instruments used for reducing the risk of change in foreign currency
The important fact is that economic exposure to exchange rate risk is a dynamic category, difficult to design and part of the overall exchange rate risk. In this context, an adequate professional-analytical approach to the concept of total foreign exchange risk by the bank's management team is necessary, bearing in mind both the static and dynamic aspects of this category of bank risk exposure.
Some of the basic financial instruments used to hedge exchange rate risk are:
-
- foreign exchange futures (forwards) - which allow the purchase or sale of one currency for another at a predetermined rate with an execution date on a specific day in the future;
-
- Side panels currency swaps -which involve contracting the simultaneous purchase and sale of two currencies at predetermined rates on two different dates in the future;
-
- currency options - which give the option buyer the right (but not the obligation) to buy or sell a certain currency at a predetermined rate within a predetermined period or on a predetermined day in the future, for which the option buyer pays a premium.
The price of foreign exchange forwards or swaps is usually a calculation category. It is determined based on the current exchange rate of the currency being bought/sold and the difference in interest rates on the two currencies. This formula starts from the assumption of equalizing the yield of two currencies within the contract. Therefore, buyers of foreign currency, which bear a lower interest rate than, for example. dinars, in the future they pay foreign currency at a higher forward rate than the current one (compensation of the seller's income). This forward exchange rate should not be viewed as a prediction of exchange rate movements in the future, but as a calculation category derived from the interest rate differential. -ccording to one of the selected methodologies, a calculator is calculated for calculating the forward price for determining the forward price of individual currency pairs, which can be used to determine the amount of the forward exchange rate depending on the maturity of the transaction and selected interest rates.
Forward purchase of foreign currency for a businessman means additional costs if the current exchange rate on the date of execution of the transaction is lower than the agreed forward exchange rate (since the purchase of foreign exchange at the current exchange rate on the date of execution may be cheaper). Forward sale of foreign exchange for a businessman means giving up potential extra profit if on the date of the transaction the current exchange rate is higher
Šmigić Miladinović J., Risk Management in Foreign Currency Operations of Business Entities than the agreed forward exchange rate (since more dinars can be obtained for selling foreign exchange on the market at the current exchange rate).
Both cases represent an opportunity cost of forward sale of foreign currency, which should be viewed as a small price that the company may pay for the purchase of certainty, ie for security and responsibility towards itself, shareholders and employees.
For a businessman who wants to protect himself from the movement of the exchange rate in one direction, but above all does not intend to give up potential profits if the exchange rate would move in the opposite direction, it is recommended to buy adequate options .
When concluding a contract on forward purchase of foreign currency, businessmen should pay attention to what kind of forwards are offered to them. In our market, banks often offer so-called. covered forwards, according to which the payment of all or part of the dinar equivalent is requested in advance, whereby the businessman received the purchased currency on the desired date in the future. In this way, banks protect themselves from credit risk - the risk that a businessman will not fulfill his obligation in the future, but in re- turn offer a more favorable forward price. Which forward will be more favorable to the businessman depends on whether he currently has dinars for forward purchase of foreign currency, whether and in what amount interest and interest rates are used on the dinar deposit, which are used in calculating the forward exchange rate, as the methodology of calculating that exchange rate. In order to compare the cost-effectiveness of classic forward foreign exchange purchases and covered forward foreign exchange purchases, we provide a calculator for comparing the prices of forward foreign exchange purchase agreements.
The question also arises: How to compensate the deficit of one currency with the surplus of another, while protecting against the risk of exchange rate changes?
In this case, the company has the possibility of concluding currency swaps in which the businessman would sell foreign exchange for dinars in the first leg, and after a certain time, he would buy that foreign exchange at the forward exchange rate. In this way, the businessman eliminates the risk of changes in the exchange rate in his business and gets a basis for calculating the price of his product. -n example of currency swaps can be found in the publication Financial Derivatives.
4. Most valuable currencies in the world
It is often said that the value of some good is depending by its usefulness and the demand for it. So, it can be said that currencies that are most demanded are also the most valuable. But except that, economist that are dealing with monetary issues like to said, that when we are talking about currency worth we can say that "everything is in the trust". The value of one currency is the picture of its national economy strenght. In picture below, we are presenting the most demanded (traded) currencies in the world.
Picture 1. The most traded currencies in the world in 2016.
Most Traded Currencies By Value (2016)
B= United States Dollar 87.6%
И Euro 31.3%
| | Japanese Yen 21.6%
£E= British pound 12.8% iM Australian Dollar ^Д 6.9%
-
■♦I Canadian Dollar Д 5.1%
-
a Swiss Franc 4 8%
-
^1 Chinese Yuan 4.0%
2.2%
2.1%
I’| Mexican Peso 15 Swedish Krona И New Zealand Dollar n^ Singapore Dollar □ Hong Kong Dollar ifS Norwegian Krone Ж South Korean Won
Q Turkish Lira Indian Rupee ^g Russian Ruble и Brazilian Real 6^ South African Rand
2 2%
1.8%
1.7%
1.7%
1.6%
1.4%
11%
11%
10%
10%
0% 10% 20% 30% 40% 50% 60% 70% 80% 90% 100%
% Daily Share
Source: Ban к for International Settlements (BIS)
• The total sum is 200% because each currency trade always involves a currency pair.
Source: [BIS, 2016]
-s expected, the most traded currencies, on the daily bases, are US Dollar and Euro. The total percentage sum is 200% because each transaction has 2 directions - one currency for other.
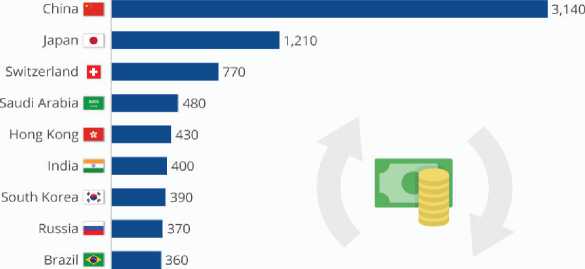
-lso, interesting can be to see which country is holding most of foreign currencies at total (doesn’t matter which). It is shown in Picture 2 where we can see that China is the country with most foreign currencies holding in foreign money reserves.
Picture 2. Top 10 countries with foreign money reserves
China's the Biggest Foreign Currency Holder
Ranking of states holding most foreign currency reserves worldwide (in billion dollars)
10 Singapore ^ |^^J 290
® ® ® As of March 2018, figures rounded
@statistacharts Source: IWF
Source: [Statista, 2022]
5. Conclusion
The risk of changes in the exchange rate occurs with all businessmen who have a currency mismatch of assets and liabilities in conditions of more or less fluctuating exchange rates. Due to the nature of the business, the risk of changes in the exchange rate is most pronounced among businessmen engaged in foreign trade.
The best way to protect against exchange rate risk is complete harmonization of the currency structure of cash inflows and outflows of the company, because it eliminates foreign exchange risk from business (natural insurance against exchange rate risk or so-called natural hedging).
Foreign exchange risks can be classified into the following three types of risks:transaction, translation and economic risk. Each of them must be concidered and managed on the proper way in order to be reduced.
Список литературы Risk management in foreign currency operations of business entities
- (2016) Bank for International Settlements (BIS). available at: https://www.visualcapitalist.com/ most-traded-currencies-2016/, 22.04.2022
- (2022) World Bank: Annual Report
- Council for Cooperation between Science and Economy International Sources of Funding. available at: https://nip.rs/sr/finansiranie/medunarodni-izvori-finansiranie (in original: Savet za saradnju nauke i privrede: Međunarodni izvori finansiranja; dostupno na: https://nip.rs/sr/finansira
- Loesche, D. (2022) China Holds the Most Foreign Currency Reserves. Statista, published on Jun 28, available at: https://www.statista.com/chart/14471/china-holds-the-mostforeign-currency-reserves/, 23.04.2022
- National Bank of Serbia (NBS) (2022) Frequently asked questions. https://nbs.rs/en/finansiisko-trziste/devizni-hedging/pitania-jodgovori/index.html. 22.04.2022
- Samuels, M.J. (1995) Financial Statements Analysis in Europe. London: Chapman & Hall
- Sylvestre, J., Urbancic, F.R. (1994) Effective methods for cash flow analysis. Healthcare Financial Management: Journal of the Healthcare Financial Management Association, Jul, 48(7), 62
- Tobias, A. (2021) The Future of Finance and the Global Economy: Facing Global Forces, Shaping Global Solutions. IMF, available at: https://www.imf.org/en/News/Articles/2021/09/27/sp092721-the-future-of-finance-and-the-global-economy


