Роль генов семейства Argonaute в эффектах активатора РНК-интерференции эноксацина на продолжительность жизни Drosophila melanogaster
Автор: Пакшина Н.Р., Яковлева Д.В., Уляшева Н.С., Прошкина Е.Н., Москалев А.А.
Журнал: Известия Коми научного центра УрО РАН @izvestia-komisc
Рубрика: Научные статьи
Статья в выпуске: 6 (64), 2023 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Эпигенетические механизмы играют ведущую роль в регуляции генной экспрессии и координации биологических процессов, влияя на скорость старения и продолжительность жизни организма. Важную роль в реализации этих механизмов играют малые РНК, которые подавляют активность своих мишеней путем РНК-интерференции и обеспечивают противовирусную защиту. Эноксацин является уникальным индуктором факторов РНК-интерференции с потенциальной геропротекторной активностью. Установлено, что его эффекты опосредованы микроРНК, но возможно участие и других видов некодирующих РНК. В данном исследовании мы изучили влияние эноксацина на продолжительность жизни Drosophila melanogaster и впервые проанализировали вклад в его эффект генов семейства Argonaute, которые специфично обеспечивают биогенез и функционирование микроРНК, киРНК и пивиРНК.
Малые рнк, рнк-интерференция, эноксацин, продолжительность жизни, старение, гены argonaute, drosophila melanogaster
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/149143620
IDR: 149143620 | УДК: 577.24 | DOI: 10.19110/1994-5655-2023-6-103-114
Текст научной статьи Роль генов семейства Argonaute в эффектах активатора РНК-интерференции эноксацина на продолжительность жизни Drosophila melanogaster
Эпигенетика изучает наследуемые изменения экспрессии генов или клеточного фенотипа, не связанные с изменениями нуклеотидной последовательности генома. Эпигенетические механизмы включают в себя метилирование ДНК, модификацию РНК и гистонов, структуру хроматина и некодирующие РНК [1]. Предполагается, что нарушение их слаженной работы является одной из ведущих причин старения. Дисбаланс в эпигенетических механизмах вызывает обширные изменения генной экспрессии и состояние геномной нестабильности [2, 3].
Многочисленные исследования свидетельствуют о важной роли малых РНК в эпигенетической регуляции [1, 4, 5]. К данной группе некодирующих РНК относятся микроРНК, короткие интерферирующие РНК (киРНК), Piwi-взаимо- действующие РНК (пивиРНК), отличающиеся по размеру, функции и белкам Argonaute, с которыми они взаимодействуют. МикроРНК регулируют экспрессию генов с помощью РНК-интерференции - посттранскрипционного процесса путем нацеливания на специфические мРНК и последующего ингибирования трансляции и деградации этих молекул [1, 6]. Они участвуют в развитии организма, дифференцировке клеток, регуляции клеточного цикла, старении, метаболизме, апоптозе, и их экспрессия меняется при некоторых заболеваниях человека [1, 7]. КиРНК также осуществляют деградацию молекул-мишеней мРНК посредством РНК-интерференции. Кроме того, они участвуют в защите генома от активности мобильных генетических элементов и вирусов [8]. ПивиРНК описаны как важные регуляторы поддержания зародышевой линии. Они необходимы для подавления активности мобильных генетических элементов в зародышевых клетках [9], а также могут воздействовать на экспрессию генов посредством влияния на метилирование ДНК и модификации хроматина [10]. К белкам, обеспечивающим биогенез и функционирование малых РНК, относятся Drosha и представители семейства Dicer и Argonaute [11]. Имеются данные, указывающие на роль данных белков в регуляции стрессоустойчивости и продолжительности жизни (далее – ПЖ) модельных организмов [12].
Поиск терапевтических подходов, нацеленных на эпигенетические механизмы, является перспективной задачей современной биологии и медицины, так как изменения в этих механизмах имеют обратимый характер и тесно сопряжены с заболеваниями человека [13]. В настоящее время описан ряд веществ, обеспечивающих регуляцию метилирования ДНК, модификаций гистонов, транскрипционных регуляторов, которые способны влиять на скорость старения и предупреждать развитие возрастных патологических процессов [14-20]. Проводятся исследования, направленные на идентификацию низкомолекулярных соединений для ингибирования или активации экспрессии микроРНК [21, 22]. Эти молекулы также обладают потенциалом для замедления старения и предупреждения возраст-зависимых заболеваний [23–25].
Эноксацин является первым низкомолекулярным активатором факторов РНК-интерференции [21]. Данное соединение относится к семейству синтетических антибактериальных соединений на основе фторхинолонового скелета. Оно проявляет активность в отношении спектра грамотри-цательных и грамположительных бактерий [26]. Основной механизм его действия заключается в модификации процессинга микроРНК и усилении деградации мРНК посредством микроРНК и киРНК [21, 23, 27]. Но он также может влиять на функцию пивиРНК через микроРНК [28].
С использованием модели Drosophila melanogaster мы проверили геропротекторную активность эноксаци-на и оценили вклад конкретных путей биогенеза малых РНК в его эффект. Дрозофила в контексте данного исследования представляет собой уникальный модельный объект. У нее имеются белки семейства Argonaute, которые отвечают за биогенез конкретных типов малых РНК. Argonaute-1 (AGO1) необходим для синтеза и функционирования микроРНК, Argonaute-2 (AGO2) - для киРНК, бел- ки Argonaute-3 (AGO3), Aubergin (aub) и piwi осуществляют биогенез пивиРНК [29]. Для определения их роли мы сопоставили влияние эноксацина в разных концентрациях на ПЖ дрозофил линии дикого типа и дрозофил с нокдауном генов Argonaute, кодирующих эти белки.
Материалы и методы
Линии Drosophila melanogaster и получение особей с нокдауном генов Argonaute
Линии, использованные в работе, представлены в табл. 1. Они содержатся в коллекции лабораторных линий плодовых мушек Drosophila Института биологии ФИЦ Коми НЦ УрО РАН.
Условия содержания и обработки эноксацином
Для содержания дрозофил использовали климатические камеры KBF720-ICH (Binder, Германия). Животных содержали при температуре +25 °С, относительной влажности воздуха 60 %, 12-часовом режиме освещения. Состав питательной среды, на которой содержали контрольных и опытных животных при проведении экспериментов, был адаптирован из работы Xia и de Belle [30]: вода - 1 л, кукурузная мука – 92 г, сухие дрожжи – 32.1 г, агар-агар – 5.2 г, глюкоза - 136.9 г; для снижения микробиологической нагрузки 5 мл 10 %-ного раствора нипагина, разбавленного в 96 %-ном этаноле, 5 мл 50 %-ной пропионовой кислоты.
Раствор эноксацина в концентрациях 0.1, 0.5, 1, 5, 10, 50, 100, 500 мкг/мл наносили на поверхность питательной среды дрозофил в количестве 30 мкл на пробирку. В качестве растворителя использовали 1 мкмоль/л раствор NaOH. В контроле на среду наносили только 1 мкмоль/л NaOH.
Анализ продолжительности жизни
Для анализа ПЖ дрозофил собирали в течение 24 ч после вылета имаго. С использованием наркоза углекислым газом (Genesee Scientific, США) мух усыпляли, сортировали по полу и рассаживали в пробирки по 30 особей. Самцы и самки жили раздельно. Начиная с первого дня жизни имаго ежедневно вели подсчет числа умерших особей, два раза в неделю мух переносили на свежую среду.
Результаты представляли в виде кривых дожития и рассчитывали медианную ПЖ (длительность жизни наиболее типичных представителей выборки) и возраст 90 % смертности (показатель максимальной ПЖ). При статистической обработке данных применяли непараметрические методы, так как распределение продолжительности жизни не подчиняется нормальному закону. Для сравнения функций дожития использовали критерий Колмогорова-Смирнова [31]. Для оценки достоверности различий по медианной ПЖ – критерий Гехана-Бреслоу-Вилкоксона [32]. Для оценки статистической значимости различий максимальной ПЖ применяли метод Ванг-Аллисона [33]. Поправка Бонферрони использовалась для корректировки множественных сравнений [34]. Обработку данных проводили с помощью программы Statistica, версия 6.1 (StatSoft, США), статистической среды R, версия 2.15.1 (The R Foundation) и онлайн-приложения OASIS 2 (Online application for survival analysis) [35].
Линии Drosophila melanogaster , использованные для получения особей с РНК-интерференцией генов Argonaute
Drosophila melanogaster lines used to obtain individuals with RNA interference of the Argonaute genes
Table 1
|
Линии |
Генотип |
Описание |
Источник, номер линии |
|
Canton-S |
Линия дикого типа |
Центр линий дрозофил в Блумингтоне, США (#64349) |
|
|
P{CaryP} attP40 |
у[1] v[1]; P{y[+t7.7]=CaryP} Msp300[attP40] |
Контрольная линия для линий с РНК-интерференцией |
Центр линий дрозофил в Блумингтоне, США (#36304) |
|
P{CaryP} attP2 |
y[1] v[1]; P{y[+t7.7]=CaryP}attP2 |
Контрольная линия для линий с РНК-интерференцией |
Центр линий дрозофил в Блумингтоне, США (#36303) |
|
RNAi-AGO1 |
y[1] v[1]; P{y[+t7.7] v[+t1.8]=TRiP. HM04006}attP2 |
Экспрессирует дцРНК для РНК-интерференции AGO1 под контролем промотора UAS в векторе VALIUM1. Конструкция в третьей хромосоме |
Центр линий дрозофил в Блумингтоне, США (#31700) |
|
RNAi-AGO2 |
y[1] sc[*] v[1] sev[21]; P{y[+t7.7] v[+t1.8]=TRiP.HMS00108}attP2 |
Экспрессирует дцРНК для РНК-интерференции AGO2 под контролем промотора UAS в векторе VALIUM20. Конструкция в третьей хромосоме |
Центр линий дрозофил в Блумингтоне, США (#34799) |
|
RNAi-AGO3 |
y[1] v[1]; P{y[+t7.7] v[+t1.8]=TRiP. HMC02938}attP40 |
Экспрессирует дцРНК для РНК-интерференции AGO3 под контролем промотора UAS в векторе VALIUM20. Конструкция во второй хромосоме |
Центр линий дрозофил в Блумингтоне, США (#44543) |
|
RNAi-piwi |
y[1] v[1]; P{y[+t7.7] v[+t1.8]=TRiP. HMJ21827}attP40/CyO |
Экспрессирует дцРНК для РНК-интерференции piwi под контролем промотора UAS в векторе VALIUM20. Конструкция во второй хромосоме |
Центр линий дрозофил в Блумингтоне, США (#57819) |
|
RNAi-aub (1) |
y[1] v[1]; P{y[+t7.7] v[+t1.8]=TRiP. JF01390}attP2 |
Экспрессирует дцРНК для РНК-интерференции aub под контролем промотора UAS в векторе VALIUM1. Конструкция во второй хромосоме |
Центр линий дрозофил в Блумингтоне, США (#31606) |
|
RNAi- aub (2) |
y[1] sc[*] v[1] sev[21]; P{y[+t7.7] v[+t1.8]=TRiP.HMS00611}attP2 |
Экспрессирует дцРНК для РНК-интерференции aub под контролем промотора UAS в векторе VALIUM20. Конструкция в третьей хромосоме |
Центр линий дрозофил в Блумингтоне, США (#33728) |
|
GAL4-da |
w[*]; P{w[+mW.hs]=GAL4-da.G32}2; P{w[+mW.hs]=GAL4-da.G32}3a |
Повсеместная экспрессия GAL4 |
Центр линий дрозофил в Блумингтоне, США (#55849) |
Результаты и их обсуждение
Влияние эноксацина на продолжительность жизни особей Drosophila mela-nogaster дикого типа
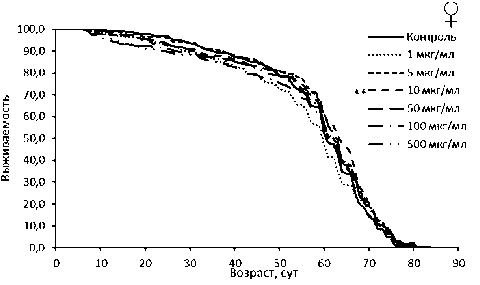
Мы изучили влияние активатора РНК-интерференции эноксацина на ПЖ дрозофил линии дикого типа Canton-S . У самцов в двух биологических повторностях из трех (табл. 2) наблюдали увеличение медианной ПЖ дрозофил на 8-20 % (p < 0.05) и возраста 90 % смертности на 3–12 % (p < 0.05) при применении вещества в концентрациях 10-500 мкг/мл. У самок при этих же концентрациях также обнаружен положительный эффект. Медианная ПЖ повысилась на 5-8 % (p < 0.05), а возраст 90 % смертности - на 3-12 % (p < 0.05). На основании наших результатов можно говорить о геропротекторном потенциале эноксацина. Этот результат согласуется с данными других авторов, где показано, что эноксацин продлевает жизнь нематодам [21]. Тем не менее положительный эффект не всегда воспроизводился во всех биологических повторностях и при их совмещении был выражен слабо (табл. 2, рис. 1).
Влияние нокдауна генов Argonaute на эффект эноксацина
Для изучения вклада генов семейства Argonaute в эффект эноксацина мы изучили его влияние на ПЖ особей Drosophila melanogaster с нокдауном генов семейства Argonaute , кодирующих белки
Таблица 2
Параметры продолжительности жизни особей Drosophila melanogaster линии Canton-S при обработке эноксацином
Table 2
Lifespan parameters of Drosophila melanogaster Canton-S lines treated with enoxacin
|
Повторность |
C m |
Самцы |
Самки |
||||
|
M |
90 % |
N |
M |
90 % |
N |
||
|
1 |
Контроль |
63 |
68 |
136 |
68 |
76 |
143 |
|
1 |
63 |
69 |
143 |
68 |
76 |
152 |
|
|
5 |
63 |
68 |
142 |
69 |
76 |
142 |
|
|
10 |
60** |
68 |
143 |
68 |
76 |
147 |
|
|
50 |
61** |
67 |
148 |
64* |
76 |
156 |
|
|
100 |
61** |
68 |
141 |
64* |
74 |
152 |
|
|
500 |
63 |
68 |
144 |
64 |
76 |
146 |
|
|
2 |
Контроль |
50 |
60 |
144 |
60 |
67 |
136 |
|
1 |
49 |
60 |
144 |
60 |
68 |
112 |
|
|
5 |
53 |
63 |
125 |
61 |
69* |
133 |
|
|
10 |
53 |
60 |
144 |
63** |
71* |
143 |
|
|
50 |
54*** |
64* |
138 |
65*** |
75*** |
136 |
|
|
100 |
55* |
62* |
134 |
64* |
75** |
137 |
|
|
500 |
60*** |
67*** |
139 |
62 |
69 |
109 |
|
|
3 |
Контроль |
49 |
60 |
143 |
57 |
67 |
148 |
|
1 |
46 |
57 |
143 |
57 |
64 |
141 |
|
|
5 |
52 |
64 |
145 |
59 |
72 |
135 |
|
|
10 |
54*** |
66** |
145 |
61* |
71 |
148 |
|
|
50 |
51 |
64 |
137 |
60 |
68 |
141 |
|
|
100 |
50 |
61 |
134 |
58 |
67 |
137 |
|
|
500 |
42*** |
58 |
121 |
60* |
68 |
145 |
|
Примечания. Cm – концентрация эноксацина, мкг/мл; М – медианная ПЖ (сут); 90 % – возраст 90 % смертности (сут); N – количество особей в выборке.
Условные обозначения. * – различия с контролем статистически значимы при p < 0.05, ** – различия с контролем статистически значимы при p < 0.01, *** – различия с контролем статистически значимы при p < 0.001, достоверность различий для М указана по критерию Геха-на-Бреслоу-Вилкоксона с поправкой Бонферрони, достоверность различий для 90 % – по тесту Ванг-Аллисона с поправкой Бонферрони.
Note. Cm - concentration of enoxacin, µg/mL; M - median lifespan (days); 90 % - age of 90 % mortality (days); N - number of individuals in the sample.
Symbols. * - differences with control are statistically significant at p < 0.05; ** - differences with control are statistically significant at p < 0.01; *** - differences with control are statistically significant at p < 0.001, the significance of differences for M is indicated by the Gehan-Breslow Wilcoxon test with Bonferroni correction, the significance of differences for 90 % is indicated by the Wang-Allison test with Bonferroni correction.
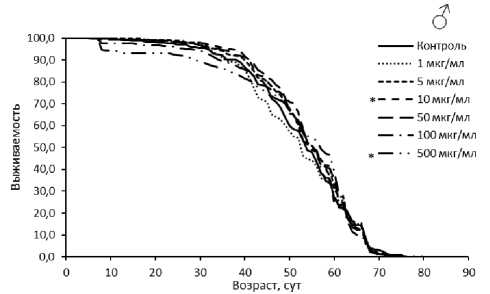
Рисунок 1. Кривые выживаемости самцов (А) и самок (Б) Drosophila melanogaster линии Canton-S при обработке эноксацином.
Условные обозначения. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01 – критерий Колмогорова-Смирнова с поправкой Бонферрони.
Figure 1. Survival curves for male (A) and female (Б) Canton-S Drosophila melanogaster treated with enoxacin.
Symbols. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01 – Kolmogorov-Smirnov test with Bonferroni correction.
биогенеза малых РНК, включая микроРНК ( AGO1 ), киРНК ( AGO2 ), пивиРНК ( AGO3, aub, piwi ).
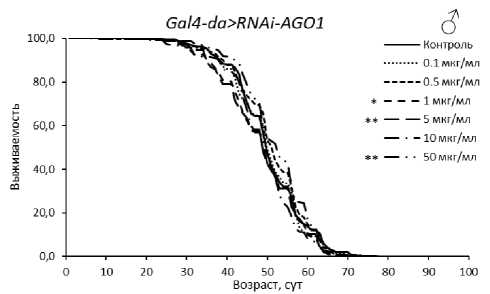
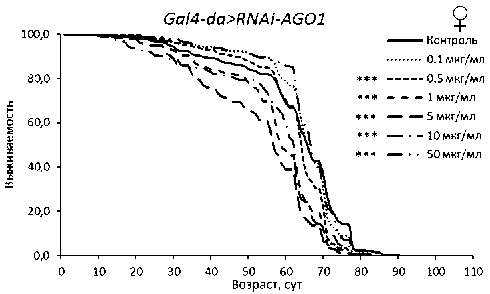
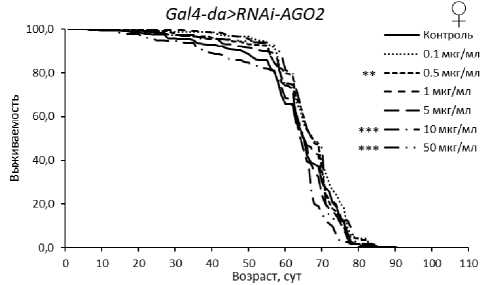
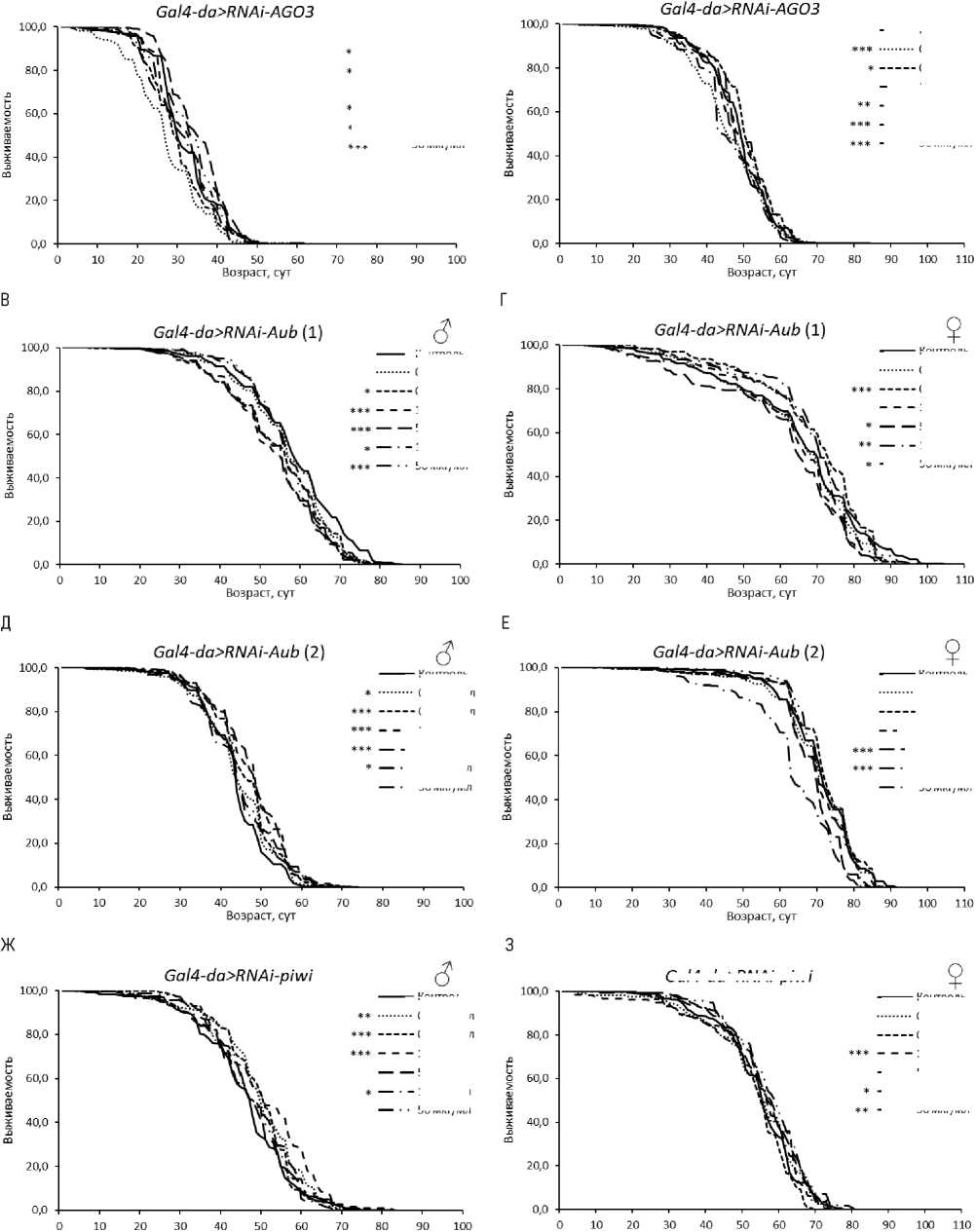
У самцов с нокдауном гена AGO2 обнаружен положительный эффект эноксацина в концентрациях 1, 10 и 50 мкг/мл в одной из повторностей (табл. 3, рис. 2). Также увеличение ПЖ при потреблении эноксацина наблюдали у мух с РНК-интерференцией aub® (при 0.5-50 мкг/мл вещества) и piwi (при 0.1-1 мкг/мл) (табл. 3, рис. 3). В перечисленных случаях медианная ПЖ была увеличена на 6–23 % (р < 0.05), а возраст 90 % смертности - на 5-23 % (р < 0.05). Эти данные указывают на то, что активность генов AGO2 , aub и piwi у самцов не снижает эффект эноксацина по сравнению с линией дикого типа.
У самцов с нокдауном AGO1, AGO3 и aub(1) эноксацин в изучаемых концентрациях либо имел менее выраженный и разнонаправленный эффект (между повторностями) на длительность жизни, либо воспроизводимо снижал медианную ПЖ на 3–13 % (p < 0.05) и возраст 90 % смертности на 5–17 % (p < 0.05). Данный результат говорит о возможном участии этих генов, отвечающих за биогенез и функционирование микроРНК и пивиРНК, в геропротекторном действии эноксацина.
У самок воспроизводимый положительный эффект энок-сацина наблюдался только при концентрации 0.5 мкг/мл у дрозофил с нокдауном aub(1) (р < 0.05). В остальных генотипах эноксацин либо укорачивал жизнь мух, либо не оказывал воспроизводимого влияния на изучаемые параметры ПЖ. Наибольшее снижение медианной ПЖ на 6–21 % (р < 0.05) и возраста 90 % смертности на 9-19 % (р < 0.05) при применении эноксацина обнаружено у дрозофил с РНК-интерференцией гена AGO1.
В то же время у дрозофил без нокдауна генов Argonaute наблюдали снижение параметров ПЖ на 1–35 % (p < 0.05) во всех исследуемых концентрациях.
Эноксацин является индуктором факторов РНК-интерференции, который нацелен, в первую очередь, на механизм биогенеза микроРНК [21, 23]. В исследованиях на клеточных культурах продемонстрировано, что это вещество способно усиливать опосредованную микроРНК деградацию мРНК и способствует биогенезу микроРНК и эндогенных киРНК [23]. В частности, эноксацин улучшает процессинг микроРНК путем связывания с TAR РНК-свя-зывающим белком 2 (TRBP) [21, 27]. Также он вовлекает Dicer совместно с AGO2 в процессинг предшественников микроРНК и способствует последующей загрузке регуляторных молекул в РНК-индуцированный комплекс сайленсинга (RISC) [23].
Эноксацин является многообещающим средством для лечения некоторых заболеваний, в том числе связанных со старением. Он ингибирует рост многих типов раковых клеток in vitro и in vivo, включая остеосаркому [36], меланому [37], рак предстательной железы [26], поджелудочной железы [38], легкого [39], щитовидной железы [40], шейки матки [41]. Кроме того, это вещество останавливает прогрессирование аутоиммунного процесса в тканях желчевыводящих путей [42], а также уменьшает вызванное диетой (с высоким содержанием жиров 60 %) ожирение у мышей, нормализует уровень глюкозы в крови и снижает симптомы бокового амиотрофического склероза [43, 44]. Эноксацин имеет низкий уровень токсичности, поскольку избирательно блокирует рост раковых клеток, не затрагивая здоровые клетки [45], безопасен для людей и широко применяется для лечения бактериальных инфекций мочевыводящих путей. Тем не менее на мышах было показано, что эноксацин не влияет на микробиоту кишечника (на содержание бактерий и распределение типов бактерий в кале) [43]. Дополнительно он оказывает противовирусное действие через усиление РНК-интерференции некоторых патогенных молекул с помощью киРНК, вплоть до потенциальной активности против SARS-CoV-2 [46-48].
В исследовании на нематодах Caenorhabditis elegans было показано, что эноксацин в концентрации 100 мкг/мл способен увеличивать ПЖ [21, 49]. На особях Drosophila melanogaster линии дикого типа Canton-S мы также показали, что эноксацин в концентрациях 10-500 мкг/мл способен увеличивать медианную и максимальную ПЖ до 20 %. Тем не менее этот эффект не всегда воспроизводился между биологическими повторностями. Более того, мы изучили эффекты эноксацина на трансгенных дрозофилах (но без нокдауна генов Argonaute ), содержащих конструкции P{CaryP}attP2 и P{CaryP}attP40 вместе с драйвером da-GAL4 . У этих мух наблюдали снижение ПЖ на 1–35 %
Параметры продолжительности жизни особей Drosophila melanogaster с нокдауном генов Argonaute при обработке эноксацином
Table 3
Lifespan parameters of Drosophila melanogaster specimens with Argonaute gene knockdown upon enoxacin treatment
|
Генотип |
Повторность |
C m |
Самцы |
Самки |
||||
|
M |
90% |
N |
M |
90% |
N |
|||
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
|
GAL4-da>RNAi-AGO1 |
1 |
Контроль |
49 |
60 |
145 |
64 |
71 |
156 |
|
0,1 |
46 |
57 |
142 |
70*** |
74* |
154 |
||
|
0,5 |
52** |
63 |
148 |
67*** |
73 |
142 |
||
|
1 |
52 |
61 |
149 |
65** |
71 |
154 |
||
|
5 |
53** |
63 |
150 |
64 |
71 |
152 |
||
|
GAL4-da>RNAi-AGO2 |
1 |
Контроль |
35 |
46 |
143 |
64 |
73 |
154 |
|
0,1 |
35 |
49 |
153 |
63 |
72 |
150 |
||
|
0,5 |
35 |
49 |
154 |
65 |
72 |
151 |
||
|
1 |
35 |
46 |
152 |
63 |
72 |
152 |
||
|
5 |
35 |
44 |
155 |
63 |
73 |
162 |
||
|
GAL4-da>RNAi-AGO3 |
1 |
Контроль |
28 |
35 |
148 |
49 |
57 |
139 |
|
0,1 |
24*** |
35* |
151 |
43*** |
57 |
151 |
||
|
0,5 |
26 |
37** |
154 |
49 |
56 |
139 |
||
|
1 |
27 |
40*** |
121 |
45 |
56 |
145 |
||
|
5 |
29** |
40 |
112 |
47 |
51* |
148 |
||
|
GAL4-da>RNAi-Aub (1) |
1 |
Контроль |
49 |
60 |
150 |
63 |
73 |
153 |
|
0,1 |
52*** |
64** |
158 |
59 |
73 |
155 |
||
|
0,5 |
49 |
63 |
156 |
64** |
78* |
152 |
||
|
1 |
46 |
57 |
153 |
63 |
77 |
144 |
||
|
5 |
49 |
64 |
154 |
63 |
73 |
147 |
||
|
GAL4-da>RNAi-Aub (2) |
1 |
Контроль |
42 |
53 |
148 |
71 |
78 |
144 |
|
0,1 |
43 |
56 |
137 |
66*** |
74** |
155 |
||
|
0,5 |
49*** |
56 |
146 |
70 |
78 |
158 |
||
|
1 |
45* |
56 |
151 |
65*** |
74*** |
156 |
||
|
5 |
49** |
57 |
157 |
70 |
77* |
156 |
||
|
GAL4-da>RNAi-piwi |
1 |
Контроль |
42 |
52 |
92 |
52 |
63 |
147 |
|
0,1 |
48* |
58* |
92 |
52 |
64 |
112 |
||
|
0,5 |
50*** |
57 |
93 |
54 |
63 |
118 |
||
|
1 |
47* |
64*** |
108 |
55* |
66 |
117 |
||
|
5 |
47*** |
61** |
138 |
54 |
64 |
51 |
||
|
Gal4-da > P{CaryP} attP40 |
1 |
Контроль |
70 |
78 |
161 |
70 |
78 |
159 |
|
0,1 |
66** |
77* |
162 |
70* |
78 |
168 |
||
|
0,5 |
70 |
78 |
163 |
63 |
77 |
167 |
||
|
1 |
67* |
77 |
160 |
64 |
77 |
162 |
||
|
5 |
65* |
77* |
162 |
67 |
77 |
155 |
||
|
Gal4-da>P{CaryP}attP2 |
1 |
Контроль |
58 |
72 |
150 |
46 |
74 |
152 |
|
0,1 |
53** |
65* |
150 |
37* |
77 |
154 |
||
|
0,5 |
55 |
72* |
161 |
57 |
77 |
156 |
||
|
1 |
58 |
72 |
153 |
53 |
78** |
153 |
||
|
5 |
53*** |
65*** |
155 |
74*** |
81*** |
150 |
||
|
GAL4-da>RNAi-AGO1 |
2 |
Контроль |
52 |
64 |
158 |
71 |
78 |
163 |
|
0,1 |
54 |
64 |
154 |
65** |
78 |
156 |
||
|
0,5 |
51 |
64 |
155 |
64*** |
71** |
158 |
||
|
1 |
47*** |
60** |
159 |
57*** |
64** |
155 |
||
|
5 |
46*** |
60 |
156 |
56*** |
63** |
158 |
||
|
10 |
48*** |
60 |
156 |
57*** |
68* |
159 |
||
|
50 |
53 |
63 |
158 |
68 |
75 |
62 |
||
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
|
GAL4-da>RNAi-AGO2 |
2 |
Контроль |
35 |
44 |
151 |
73 |
78 |
140 |
|
0,1 |
36 |
49 |
151 |
72 |
79 |
159 |
||
|
0,5 |
36 |
44 |
154 |
70 |
78 |
154 |
||
|
1 |
38* |
48 |
150 |
70 |
77 |
155 |
||
|
5 |
35 |
47 |
145 |
68*** |
77 |
164 |
||
|
10 |
38 |
50* |
151 |
67*** |
74 |
156 |
||
|
50 |
37** |
50** |
153 |
71 |
79 |
156 |
||
|
GAL4-da>RNAi-AGO3 |
2 |
Контроль |
37 |
46 |
86 |
52 |
64 |
149 |
|
0,1 |
33*** |
42*** |
84 |
51** |
60* |
149 |
||
|
0,5 |
34* |
44 |
83 |
54 |
64 |
153 |
||
|
1 |
36* |
42* |
127 |
52 |
61 |
158 |
||
|
5 |
39 |
46 |
141 |
54 |
62*** |
164 |
||
|
10 |
36*** |
40*** |
136 |
53** |
60*** |
157 |
||
|
50 |
36 |
44 |
147 |
49*** |
60*** |
152 |
||
|
GAL4-da>RNAi-Aub (1) |
2 |
Контроль |
64 |
74 |
152 |
71 |
81 |
157 |
|
0,1 |
64 |
72 |
152 |
78*** |
86 |
155 |
||
|
0,5 |
64 |
72 |
162 |
79*** |
86 |
155 |
||
|
1 |
61 |
71 |
187 |
72 |
81 |
153 |
||
|
5 |
60** |
70*** |
159 |
71 |
82 |
144 |
||
|
10 |
60** |
69 |
148 |
71 |
82 |
157 |
||
|
50 |
60*** |
68** |
162 |
68 |
78 |
147 |
||
|
GAL4-da>RNAi-Aub (2) |
2 |
Контроль |
45 |
57 |
154 |
79 |
86 |
144 |
|
0,1 |
45 |
58 |
149 |
79 |
86* |
156 |
||
|
0,5 |
46 |
58 |
165 |
78 |
86*** |
154 |
||
|
1 |
49** |
57 |
151 |
78 |
85*** |
157 |
||
|
5 |
50*** |
61* |
155 |
71*** |
78*** |
157 |
||
|
10 |
47 |
60*** |
145 |
71*** |
82*** |
128 |
||
|
50 |
47 |
60* |
154 |
74*** |
82*** |
156 |
||
|
GAL4-da>RNAi-piwi |
2 |
Контроль |
47 |
61 |
73 |
63 |
72 |
116 |
|
0,1 |
57* |
65 |
80 |
61* |
69 |
106 |
||
|
0,5 |
53 |
62 |
76 |
60*** |
67*** |
81 |
||
|
1 |
58*** |
68 |
72 |
60** |
70* |
95 |
||
|
5 |
51 |
61 |
68 |
59** |
70 |
124 |
||
|
10 |
46 |
60 |
89 |
64 |
74 |
110 |
||
|
50 |
50 |
60 |
100 |
63 |
69 |
148 |
||
|
Gal4-da > P{CaryP} attP40 |
2 |
Контроль |
64 |
75 |
65 |
79 |
150 |
|
|
0,1 |
57*** |
68*** |
156 |
57** |
75* |
163 |
||
|
0,5 |
57*** |
70*** |
158 |
60 |
79 |
156 |
||
|
1 |
60** |
70 |
159 |
49*** |
77 |
142 |
||
|
5 |
51*** |
68 |
154 |
49*** |
68*** |
152 |
||
|
10 |
56*** |
67*** |
117 |
42*** |
67*** |
154 |
||
|
50 |
57*** |
67*** |
152 |
60*** |
68*** |
156 |
||
|
Gal4-da>P{CaryP}attP2 |
2 |
Контроль |
50 |
65 |
155 |
80 |
89 |
153 |
|
0,1 |
51 |
64 |
157 |
78* |
86* |
138 |
||
|
0,5 |
51 |
64 |
152 |
74*** |
86*** |
155 |
||
|
1 |
44** |
64 |
168 |
70*** |
83*** |
158 |
||
|
5 |
47 |
64 |
186 |
56*** |
79*** |
152 |
||
|
10 |
54 |
64 |
148 |
64*** |
76*** |
138 |
||
|
50 |
48 |
64 |
161 |
67*** |
82*** |
160 |
||
|
GAL4-da>RNAi-AGO1 |
3 |
Контроль |
49 |
60 |
157 |
67 |
78 |
142 |
|
10 |
50 |
58 |
161 |
63** |
74 |
153 |
||
|
50 |
51** |
63 |
164 |
66 |
74 |
160 |
||
|
GAL4-da>RNAi-AGO2 |
3 |
Контроль |
31 |
44 |
158 |
59 |
73 |
149 |
|
10 |
32 |
44 |
156 |
63 |
71 |
155 |
||
|
50 |
32 |
44 |
159 |
65*** |
78* |
159 |
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
|
GAL4-da>RNAi-AGO3 |
3 |
Контроль |
30 |
43 |
157 |
48 |
52 |
157 |
|
10 |
27*** |
41* |
157 |
43*** |
55 |
162 |
||
|
50 |
27*** |
41* |
161 |
49*** |
57* |
160 |
||
|
GAL4-da>RNAi-Aub (1) |
3 |
Контроль |
65 |
78 |
160 |
78 |
94 |
160 |
|
10 |
57*** |
69*** |
157 |
71*** |
85*** |
159 |
||
|
50 |
57*** |
65*** |
161 |
78 |
87 |
154 |
||
|
GAL4-da>RNAi-Aub (2) |
3 |
Контроль |
44 |
51 |
159 |
67 |
78 |
160 |
|
10 |
44* |
56 |
159 |
63*** |
73 |
159 |
||
|
50 |
44 |
53 |
157 |
70*** |
80** |
156 |
||
|
GAL4-da>RNAi-piwi |
3 |
Контроль |
48 |
62 |
147 |
55 |
63 |
145 |
|
10 |
50 |
60 |
160 |
55 |
63 |
154 |
||
|
50 |
47 |
60 |
155 |
56 |
68* |
167 |
||
|
Gal4-da > P{CaryP} attP40 |
3 |
Контроль |
63 |
71 |
155 |
56 |
78 |
153 |
|
10 |
56*** |
64*** |
157 |
51** |
70** |
153 |
||
|
50 |
57*** |
64* |
145 |
64 |
78 |
160 |
||
|
Gal4-da>P{CaryP}attP2 |
3 |
Контроль |
53 |
65 |
161 |
78 |
91 |
147 |
|
10 |
45*** |
57*** |
157 |
78*** |
81*** |
155 |
||
|
50 |
49*** |
63** |
160 |
80 |
88 |
160 |
Примечания. Cm – концентрация эноксацина, мкг/мл; М – медианная ПЖ (сут); 90 % – возраст 90 % смертности (сут). N – количество особей в выборке. Условные обозначения. * – различия с контролем статистически значимы при p < 0.05; ** – различия с контролем статистически значимы при p < 0.01, *** – различия с контролем статистически значимы при p < 0.001, достоверность различий для М указана по критерию Гехана-Бреслоу-Вилкоксона с поправкой Бонферрони, достоверность различий для 90 % указана по тесту Ванг-Аллисона с поправкой Бонферрони.
Note. Cm - concentration of enoxacin µg/mL; M - median lifespan (days); 90 % - age of 90 % mortality (days); N - number of individuals in the sample. Symbols. * - differences with control are statistically significant at p < 0.05; ** - differences with control are statistically significant at p < 0.01; *** -differences with control are statistically significant at p < 0.001, the significance of differences for M is indicated by the Gehan-Breslow Wilcoxon test with Bonferroni correction, the significance of differences for 90 % is indicated by the Wang-Allison test with Bonferroni correction.
Б
А
В
Г
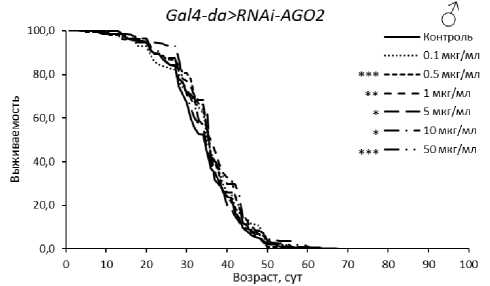
Рисунок 2. Кривые выживаемости особей Drosophila melanogaster с нокдауном генов подсемейства Argonaute при обработке эноксацином.
Условные обозначения. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001 – критерий Колмогорова-Смирнова с поправкой Бонферрони.
Figure 2. Survival curves of Drosophila melanogaster individuals with Argonaute subfamily gene knockdown treated with enoxacin.
Symbols. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001 – Kolmogorov-Smirnov test with Bonferroni correction.
Gal4-da>RNAi-piwi
■ - Контроль
0.1 мкг/мл 0.5 мкг/мл — — 1 мкг/мл — 5 мкг/мл • -10 мкг/мл - - 50 мкг/мл
" - Контроль
0.1 мкг/мл 0.5 мкг/мл 1 мкг/мл 5 мкг/мл 10 мкг/мл — ■ • 50 мкг/мл
Возраст, сут
Возраст, сут
Рисунок 3. Кривые выживаемости особей Drosophila melanogaster с нокдауном генов подсемейства PIWI при обработке эноксацином.
Условные обозначения. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001 – критерий Колмогорова-Смирнова с поправкой Бонферрони.
Figure 3. Survival curves of Drosophila melanogaster individuals with PIWI subfamily gene knockdown treated with enoxacin.
Symbols. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001 – Kolmogorov-Smirnov test with Bonferroni correction.
------ Контроль *++ ......... 0.1 мкг/мл
*** -----о.5мкг/мл ** — — — 1 мкг/мл *** — ^5 мкг/мл *** — . —10 мкг/мл *** — • • 50 мкг/мл
11 - Контроль
0.1 мкг/мл
0.5 мкг/мл
— — 1 мкг/мл — — 5 мкг/мл — ■ - 10 мкг/мл — ■ • 50 мкг/мл
Контроль 0.1 мкг/мл 0.5 мкг/мл 1 мкг/мл 5 мкг/мл 10 мкг/мл 50 мкг/мл
Контроль 0.1 мкг/мл 0.5 мкг/мл — 1 мкг/мл — 5 мкг/мл ■ -10 мкг/мл ■ • 50 мкг/мл
Контроль 0.1 мкг/мл 0.5 мкг/мл 1 мкг/мл 5 мкг/мл 10 мкг/мл 50 мкг/мл
■ Контроль
0.1 мкг/мл
0.5 мкг/мл 1 мкг/мл
— — 5 мкг/мл — - - 10 мкг/мл — - • 50 мкг/мл
при всех концентрациях индуктора РНК-интерференции. Это говорит о том, что действие эноксацина на старение и ПЖ организма может зависеть от комплекса внешних и внутренних факторов, и требуется детальное изучение лежащих в его основе механизмов.
Согласно результатам работы на нематоде, эноксацин действует на продолжительность жизни и старение через пути митогормезиса и SKN-1/Nrf2, снижая при этом уровень miR-34-5p [21,49]. Также в качестве мишени данного соединения у нематод описан РНК-специфическая аденозиндеаминаза (ADAR). При утрате функции ADAR у червей исчезал положительный эффект применения эноксацина [49]. Тем не менее, ввиду специфики организации аппарата биогенеза малых РНК у червей, до конца неясно, связан ли механизм действия эноксацина только с микроРНК, либо он также опосредован функционированием киРНК и пивиРНК.
У Drosophila melanogaster есть пять генов семейства Argonaute , относящиеся к двум подсемействам - Argonaute (AGO1, AGO2) и PIWI (AGO3, aub, piwi) , которые играют важную роль в регуляции экспрессии генов и транспозонов. Мы оценили вклад конкретных генов Argonaute , специфичных для разных типов малых РНК молекул, в эффект эноксацина на длительность жизни дрозофил. Ген AGO1 повсеместно экспрессируется в ходе развития, его белок обеспечивает активность связывания микроРНК, регулирует экспрессию генов, подавляя трансляцию [50]. AGO2 также повсеместно экспрессируется, а его белок выполняет функцию защиты от транспозонов и вирусов путем связывания с киРНК и участвует в формировании комплекса RISC [51]. Белки подсемейства PIWI (AGO3, Aub, piwi) необходимы для репрессии транспозонов зародышевой линии, однако ген piwi экспрессируется также в соматических клетках гонад дрозофилы [50–52].
В данном исследовании мы обнаружили, что у особей Drosophila melanogaster с нокдауном гена AGO1 эноксацин имел либо отрицательный, либо слабый положительный эффект на ПЖ. Полученный результат указывает на вклад механизма биогенеза микроРНК в спектр биологических активностей этого соединения, что согласуется с указанными выше литературными данными, полученными на клеточных культурах и нематодах.
Дрозофилы с РНК-интерференцией гена AGO2 реагировали на эноксацин схожим образом с линией дикого типа Canton-S . Эноксацин оказывал либо положительное действие, либо не вызывая статистически значимых изменений ПЖ. По-видимому, механизм биогенеза киРНК в меньшей степени определяет геропротекторную активность данного вещества, что согласуется с результатами анализа, проведенного на нематодах [49].
Особи с нокдауном генов подсемейства PIWI демонстрировали неожиданные эффекты эноксацина на ПЖ. В ряде случаев эноксацин вызывал снижение ПЖ у дрозофил с нокдауном AGO3, aub и piwi, что может указывать на вклад пивиРНК и генов PIWI в эффекты эноксацина и детерминирование жизнеспособности взрослого организма в целом. Этот вопрос требует детального изучения. В первую очередь, в связи с тем, что в настоящее время предполагается, что решающую роль пивиРНК имеет в за- родышевой линии и половых клетках [53, 54]. Тем не менее, в работе на раковых клетках человека было показано, что эноксацин может восстанавливать активность PIWIL3 (представитель подсемейства белков PIWI, обеспечивающих выработку пивиРНК) через микроРНК [28].
Список литературы Роль генов семейства Argonaute в эффектах активатора РНК-интерференции эноксацина на продолжительность жизни Drosophila melanogaster
- Yao, Q. The roles of microRNAs in epigenetic regulation / Q. Yao, Y. Chen, X. Zhou // Curr Opin Chem Biol. – 2019. – Vol. 51. – P. 11-17.
- Yang, J. H. Loss of epigenetic information as a cause of mammalian aging / J. H. Yang, M. Hayano, P. T. Griffin [et al.] // Cell. – 2023. – Vol. 186, № 2. – P. 305-326.e27.
- Sen, P. Epigenetic mechanisms of longevity and aging / P. Sen, P. P. Shah, R. Nativio [et al.] // Cell. – 2016. – Vol. 166, № 4. – P. 822-839.
- Huang, X. A. A major epigenetic programming mechanism guided by piRNAs / X. A. Huang, H. Yin, S. Sweeney [et al.] // Dev Cell. – 2013. – Vol. 24, № 5. – P. 502-516.
- Duempelmann, L. Small RNAs in the transgenerational inheritance of epigenetic information / L. Duempelmann, M. Skribbe, M. Bühler // Trends Genet. – 2020. – Vol. 36, № 3. – P. 203-214.
- Sankrityayan, H. Diabetic nephropathy: The regulatory interplay between epigenetics and microRNAs / H. Sankrityayan, Y. A. Kulkarni, A. B. Gaikwad // Pharmacol Res. – 2019. – Vol. 141. – P. 574-585.
- Iorio, M.V. Interplay between microRNAs and the epigenetic machinery: an intricate network / M. V. Iorio, C. Piovan, C. M. Croce // Biochim Biophys Acta. – 2010. – Vol. 1799, № 10-12. – P. 694-701.
- Moazed, D. Small RNAs in transcriptional gene silencing and genome defence / D. Moazed // Nature. – 2009. – Vol. 457, № 7228. – P. 413-420.
- Peters, L. Argonaute proteins: mediators of RNA silencing / L. Peters, G. Meister // Mol Cell. – 2007. – Vol. 26, № 5. – P. 611-623.
- Jia, D. D. The regulatory function of piRNA/PIWI complex in cancer and other human diseases: The role of DNA methylation / D. D. Jia, H. Jiang, Y. F. Zhang [et al.] // Int J Biol Sci. – 2022. – Vol. 18, № 8. – P. 3358-3373.
- Kim, V.N. Biogenesis of small RNAs in animals / V.N. Kim, J. Han, M.C. Siomi // Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. – 2009. – Vol. 10. – P. 126-139.
- Proshkina, E. N. Genome-Protecting Compounds as Potential Geroprotectors / E. N. Proshkina, M. V. Shaposhnikov, A. A. Moskalev // Int J Mol Sci. – 2020. – Vol. 21, № 12. – P. 4484.
- Memari, F. Epigenetics and Epi-miRNAs: Potential markers/ therapeutics in leukemia / F. Memari, Z. Joneidi, B. Taheri [et al.] // Biomed Pharmacother. – 2018. – Vol. 106. – P. 1668-1677.
- Cheng, Y. Targeting epigenetic regulators for cancer therapy: mechanisms and advances in clinical trials / Y. Cheng, C. He, M. Wang [et al.] // Signal Transduct Target Ther. – 2019. –Vol. 4. – P. 62.
- Audia, J. E. Histone modifications and cancer / J. E. Audia, R. M. Campbell // Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. – 2016. – Vol. 8, № 4. – P. a019521.
- Yang, X. Targeting DNA methylation for epigenetic therapy / X. Yang, F. Lay, H. Han [et al.] // Trends Pharmacol Sci. – 2010. – Vol. 31, № 11. – P. 536-546.
- Siklos, M. Therapeutic targeting of chromatin: status and opportunities / M. Siklos, S. Kubicek // FEBS J. – 2022. – Vol. 289, № 5. – P. 1276-1301.
- Morera, L. Targeting histone methyltransferases and demethylases in clinical trials for cancer therapy / L. Morera, M. Lübbert, M. Jung // Clin Epigenetics. – 2016. – Vol. 8. – P. 57.
- Dai, E. Epigenetic modulation of antitumor immunity for improved cancer immunotherapy / E. Dai, Z. Zhu, S. Wahed [et al.] // Mol Cancer. – 2021. – Vol. 20, № 1. – P. 171.
- Cao, J. Cancer epigenetics, tumor immunity, and immunotherapy / J. Cao, Q. Yan // Trends Cancer. – 2020. – Vol. 6, № 7. – P. 580-592.
- Felicetti, T. Modulating microRNA processing: enoxacin, the progenitor of a new class of drugs / T. Felicetti, V. Cecchetti, G. Manfroni // J Med Chem. – 2020. – Vol. 63, № 21. – P. 12275-12289.
- Zhang, S. Targeting microRNAs with small molecules: from dream to reality / S. Zhang, L. Chen, E. J. Jung [et al.] // Clin Pharmacol Ther. – 2010. – Vol. 87, № 6. – P. 754-758.
- Shan, G. A small molecule enhances RNA interference and promotes microRNA processing / G. Shan, Y. Li, J. Zhang [et al.] // Nat Biotechnol. – 2008. – Vol. 26, № 8. – P. 933-940.
- Zhao, R. Designing strategies of small-molecule compounds for modulating non-coding RNAs in cancer therapy / R. Zhao, J. Fu, L. Zhu [et al.] // J Hematol Oncol. – 2022. – Vol. 15, № 1. – P. 14.
- Wang, K. Epigenetic regulation of aging: implications for interventions of aging and diseases / K. Wang, H. Liu, Q. Hu [et al.] // Signal Transduct Target Ther. – 2022. – Vol. 7, № 1. – P. 374.
- Sousa, E. Enoxacin inhibits growth of prostate cancer cells and effectively restores microRNA processing / E. Sousa, I. Graca, T. Baptista [et al.] // Epigenetics. – 2013. – Vol. 8, № 5. – P. 548-558.
- Melo, S.A. Small molecule enoxacin is a cancer-specific growth inhibitor that acts by enhancing TAR RNA-binding protein 2-mediated microRNA processing / S. A. Melo, A. Villanueva, C. Moutinho [et al.] // Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. – 2011. – Vol. 108, № 11. – P. 4394-4399.
- Abell, N. S. Click quantitative mass spectrometry identifies PIWIL3 as a mechanistic target of RNA interference activator enoxacin in cancer cells / N. S. Abell, M. Mercado, T. Caneque [et al.] // J Am Chem Soc. – 2017. – Vol. 139, № 4. – P. 1400-1403.
- Marco, A. Regulatory RNAs in the light of Drosophila genomics / A. Marco // Brief Funct Genomics. – 2012. – Vol. 11, № 5. – P. 356-365.
- Xia, B. Transgenerational programming of longevity and reproduction by post-eclosion dietary manipulation in Drosophila / B. Xia, J.S. de Belle // Aging. – 2016. – Vol. 8, № 5. – P. 1115–1134.
- Hilton, J. F. An algorithm for conducting exact Smirnov tests / J. F. Hilton, C. R. Mehta, N. R. Patel // Computational Statistics & Data Analysis. – 1994. – Vol. 17, № 4. – P. 351–361.
- Martinez, R. L. A pretest for choosing between logrank and wilcoxon tests in the two-sample problem / R. L. M. C. Martinez, J. D. Naranjo // Metron. – 2012. – Vol. 68, № 2. – P. 111–125.
- Wang, C. Statistical methods for testing effects on «maximum lifespan» / C. Wang, Q. Li, D. T. Redden [et al.] // Mech Ageing Dev. – 2004. – Vol. 125, № 9. – P. 629-632.
- Armstrong, R.A. When to use the Bonferroni correction / R.A. Armstrong // Ophthalmic and Physiological Optics. – 2014. – Vol. 34, № 5. – P. 502–508.
- Han, S. K. OASIS 2: online application for survival analysis 2 with features for the analysis of maximal lifespan and healthspan in aging research / S. K. Han, D. Lee, H. Lee [et al.] // Oncotarget. – 2016. – Vol. 7, № 35. – P. 56147-56152.
- Luo, X. Enoxacin inhibits proliferation and invasion of human osteosarcoma cells and reduces bone tumour volume in a murine xenograft model / X. Luo, X. Liu, Q. Tao [et al.] // Oncol Lett. – 2020. – Vol. 20, № 2. – P. 1400-1408.
- Valianatos, G. A small molecule drug promoting miRNA processing induces alternative splicing of MdmX transcript and rescues p53 activity in human cancer cells overexpressing MdmX protein / G. Valianatos, B. Valcikova, K. Growkova [et al.] // PLoS One. – 2017. – Vol. 12, № 10. – P. e0185801.
- Nishi, K. Enoxacin with UVA irradiation induces apoptosis in the AsPC1 human pancreatic cancer cell line through ROS generation / K. Nishi, M. Kato, S. Sakurai [et al.] // Anticancer Res. – 2017. – Vol. 37, № 11. – P. 6211-6214.
- Cao, S. RNA helicase DHX9 may be a therapeutic target in lung cancer and inhibited by enoxacin / S. Cao, R. Sun, W. Wang [et al.] // Am J Transl Res. – 2017. – Vol. 9, № 2. – P. 674-682.
- Ramirez-Moya, J. Impaired microRNA processing by DICER1 downregulation endows thyroid cancer with increased aggressiveness / J. Ramirez-Moya, L. Wert-Lamas, G. Riesco-Eizaguirre [et al.] // Oncogene. – 2019. – Vol. 38, № 27. – P. 5486-5499.
- McDonnell, A. M. Enoxacin and epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) act synergistically to inhibit the growth of cervical cancer cells in culture / A. M. McDonnell, H. M. Pyles, E. S. Diaz-Cruz [et al.] // Molecules. – 2019. – Vol. 24, № 8. – P. 1580.
- Itoh, A. Enoxacin up-regulates microRNA biogenesis and down-regulates cytotoxic CD8 T-cell function in autoimmune cholangitis / A. Itoh, D. Adams, W. Huang [et al.] // Hepatology. – 2021. – Vol. 74, № 2. – P. 835-846.
- Rocha, A. L. Enoxacin induces oxidative metabolism and mitigates obesity by regulating adipose tissue miRNA expression / A. L. Rocha, T. I. de Lima, G. P. de Souza [et al.] // Sci Adv. – 2020. – Vol. 6, № 49. – P. eabc6250.
- Emde, A. Dysregulated miRNA biogenesis downstream of cellular stress and ALS-causing mutations: a new mechanism for ALS / A. Emde, C. Eitan, L. L. Liou [et al.] // EMBO J. – 2015. – Vol. 34, № 21. – P. :2633-2651.
- McDonnell, A. M. Enoxacin and epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) act synergistically to inhibit the growth of cervical cancer cells in culture / A. M. McDonnell, H. M. Pyles, E. S. Diaz-Cruz [et al.] // Molecules. – 2019. – Vol. 24, № 8. – P. 1580.
- Xu, Y.P. Zika virus infection induces RNAi-mediated antiviral immunity in human neural progenitors and brain organoids / Y.P. Xu, Y. Qiu, B. Zhang [et al.] // Cell Res. – 2019. – Vol. 29, № 4. – P. 265-273.
- Ahmadi, A. In silico analysis suggests the RNAi-enhancing antibiotic enoxacin as a potential inhibitor of SARSCoV-2 infection / A. Ahmadi, S. Moradi // Sci Rep. – 2021. – Vol. 11, №1. – P. 10271.
- Lyu, B. Enoxacin shows broad-spectrum antiviral activity against diverse viruses by enhancing antiviral RNA interference in insects / B. Lyu, C. Wang, Y. Bie [et al.] // J Virol. – 2022. – Vol. 96, № 4. – P. e0177821.
- Pinto, S. Enoxacin extends lifespan of C. elegans by inhibiting miR-34-5p and promoting mitohormesis / S. Pinto, V. N. Sato, E. A. De-Souza [et al.] // Redox Biol. – 2018. – Vol.18. – P. 84-92.
- Lewis, S.H. Duplication and diversification of Dipteran Argonaute genes, and the evolutionary divergence of piwi and Aubergine / S. H. Lewis, H. Salmela, D. J. Obbard // Genome Biol Evol. – 2016. – Vol. 8, №3. – P. 507-518.
- Malone, C.D. Specialized piRNA pathways act in germline and somatic tissues of the Drosophila ovary / C.D. Malone, J. Brennecke, M. Dus [et al.] // Cell. – 2009. – Vol. 137, № 3. – P. 522-535.
- Nishida, K.M. Gene silencing mechanisms mediated by Aubergine piRNA complexes in Drosophila male gonad / K. M. Nishida, K. Saito, T. Mori [et al.] // RNA. – 2007. – Vol. 13, № 11. – P. 1911-1922.
- Perera, B. P. U. Somatic expression of piRNA and associated machinery in the mouse identifies short, tissue-specific piRNA / B. P. U. Perera, Z. T. Tsai, M. L. Colwell [et al.] // Epigenetics. – 2019. – Vol. 14, № 5. – P. 504-521.
- Story, B. Defining the expression of piRNA and transposable elements in Drosophila ovarian germline stem cells and somatic support cells / B. Story, X. Ma, K. Ishihara [et al.] // Life Sci Alliance. – 2019. – Vol. 2, № 5. – P. e201800211.


