Role of nitric oxide in regulation of H2O2 mediating tolerance of plants to abiotic stress: a synergistic signaling approach
Автор: Mohd Mazid, Taqi Ahmed Khan, Firoz Mohammad
Журнал: Журнал стресс-физиологии и биохимии @jspb
Статья в выпуске: 2 т.7, 2011 года.
Бесплатный доступ
The relationship between abiotic stress, nitric oxide (NO) and Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) is a challenging one. It is now clear that H2O2 and NO function as signaling molecules in plants. A wide range of abiotic stresses results in H2O2 generation, from a variety of sources and it has many essential roles in plant metabolism but at the same time, accumulation related to virtually any environmental stress is potentially damaging. NO is gaining increasing attention as a regulator of diverse pathophysiological processes in plant science, mainly due to its properties (free radicals, small size, no charge, short-lived, and highly diffusible across biological membranes) and multifunctional roles in plant growth, development and regulation of remarkably broad myriad of plant cellular mechanisms. Various abiotic stresses can induce NO synthesis, but its origin and mode of action in plants have not yet been completely resolved. Recent studies on NO production have tended to high light the questions that still remain unanswered rather than telling us more about NO metabolism. But regarding NO-H2O2 signaling and functions, new findings have given an impression of the intricacy of NO-H2O2 related signaling networks against abiotic stresses. Cellular responses to NO-H2O2 are complex, with considerable cross-talk between responses to several abiotic stresses. In last few years, the role of NO in H2O2 mediating tolerance in plants to abiotic stress has established much consideration.
Antioxidant, h2o2, no, oxidative stress, salinity, signaling molecules, uv-radiation
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/14323961
IDR: 14323961
Текст обзорной статьи Role of nitric oxide in regulation of H2O2 mediating tolerance of plants to abiotic stress: a synergistic signaling approach
There is now compelling evidence that H 2 O 2 and (Foyer et al., 1997; Neil et al., 1999; Bolwell, 1999;
NO function as signalling molecules in plants Durner and Klessing, 1999; Dat et al., 2000).
Previous studies also have shown that both NO and H 2 O 2 function as stress signals in plants, mediating a range of resistance mechanisms in plants under stress conditions (Neill et al., 2002a; Wendehenne et al., 2004; Delledonne, 2005). During the last few years, much attention has been paid to NO research since its discovery as a crucial signalling molecule in mammals that plays an number of diverse functions i.e. vasodilatation, neurotransmission, smooth muscle contraction and relaxation, innate immune response, egg fertilization, defence against pathogenic microorganisms and apoptosis (Schmidt and Walter, 1994; Jeffrey and Synder, 1995; Stamler, 1994; Lloyd-Jones and Bloch, 1996; Wink and Mitchell, 1998; Ignarro, 2000; Hess et al., 2005). It has been considered that NO also plays a vital role in diverse physiological functions in plants, induction of seed germination, reduction of seed dormancy (Beligni and Lamattina, 2000; Bethke et al., 2006, 2007; Libourel et al., 2006; Zheng et al., 2009) regulation of plant metabolism and senescence (Leshem et al., 1998; Guo and Cramford, 2005) induction in cell death (Pedroso and Durzan, 2000) regulation of stomatal movement (Garcia-Mata and Lamattina, 2001; Neill et al., 2003; Guo et al., 2003; Sakihama et al., 2003; Bright et al., 2006; Garcia-Mata and Lamattina, 2007) Photosynthesis regulation (Takahashi and Yamasaki, 2002) mitochondrial functionality (Zottini et al., 2002) and gravitopism (Hu et al., 2005) floral regulation (He et al., 2004). In spite of its potential role in a series of studies, NO proved to be capable of regulating the multiple plant responses towards a variety of biotic and abiotic stresses and alleviating some consequences provoked by oxidative stresses (Delledonne, 2005; Bligni and Lamatttima, 1999a; Crawford and Guo, 2005). In many research, high levels of NO has the capacity to damage membranes and DNA fragementation
(Pedroso et al., 2000; Yamasaki, 2000; Romero-Puertas et al., 2004) and to reduce photosynthesis in Oat and alfalfa (Hill and Bennet, 1970) and reproduction in carrot cell suspensions (Zottini et al., 2002) are inhibited by NO exposure.
Moreover, NO behaves as a plant hormone equivalent to ethylene (Fig. 1) that is, as a gaseous signal transmitter (Leshem, 2000; Guo et al., 2003; Yamasaki, 2005). There are several enzymatic systems that have been shown to produce NO, mainly nitrate reductase (NR) (Rockel et al., 2002) and L-Arg-dependent nitric oxide synthase (Corpas et al., 2004). However, the gene for the plant NOS has not been identified yet (Zemojtel et al., 2006; Neill et al., 2008). Interestingly, NO signalling is based on interactions with plant hormones. Furthermore, CTK stimulated more NO signal formation, probably mainly via a NR source under the conditions of drought stress in Zea mays . High NO signal intensity alleviated drought-induced Reactive oxygen species (ROS) damage to plants. Thus, the signal probably played a direct role in eliciting CTK regulation to energy absorption and excitation energy trapped in response to drought (Shao et al., 2010).
There are rapid increasing evidence that NO plays an important role in cyto-protection by regulating the level and toxicity of ROS (Lamattina et al., 2003) and by inducing transcriptional changes which permitted identification of genes involved in different functional processes such as signal transduction, defense and cell death, transport, biotic metabolism and ROS production and degradation (Palmieri et al., 2008). NO inhibits the plants from oxidative damage by the regulation of general mechanisms for cellular redox homeostasis and also promoting the transformation of O 2 to H 2 O 2 and O∙Ї and also by enhancing the H 2 O 2 -scavenging enzyme
Table 1. Electrochemical potential (mv) of heavy metals in aqueous media (pH 7, 25 °C, after Weast 1984)
|
Metal Cation |
Redox potential (mv) |
|
Zn2+ Cd2+ Ni 2+ Pb2+ Cu2+ Fe 2+ Hg2+ Ag2+ |
-1.18 -0.82 0.65 0.55 0.26 +0.35 +0.43 +0.1.57 |
Table 2. The inducible effect of heavy metal stress on the expression of some signalling molecules
(eg. H2O2) in plants
|
signalling molecule |
Heavy Metal |
References |
|
H 2 O 2 |
Cd Cd Cd Cu Cd, Cu Hg Mn |
Romero-Puertas et al.,1999 Cho and Seo (2005) Schutzendubel et al.(2001) Drazkiewicz et al.,(2004) Maksymice and Krupa (2006b) Cho and Park (2000) Demirerska-Kepova et al (2004) |
2004; Stohr and Ullrich, 2002; Beligni and lamattina, 2001; Yamasaki, 2005; Romero-Puertas et al., 2004; Wendehenne et al., 2004; Bolwell, 1999; Neill et al., 2003).
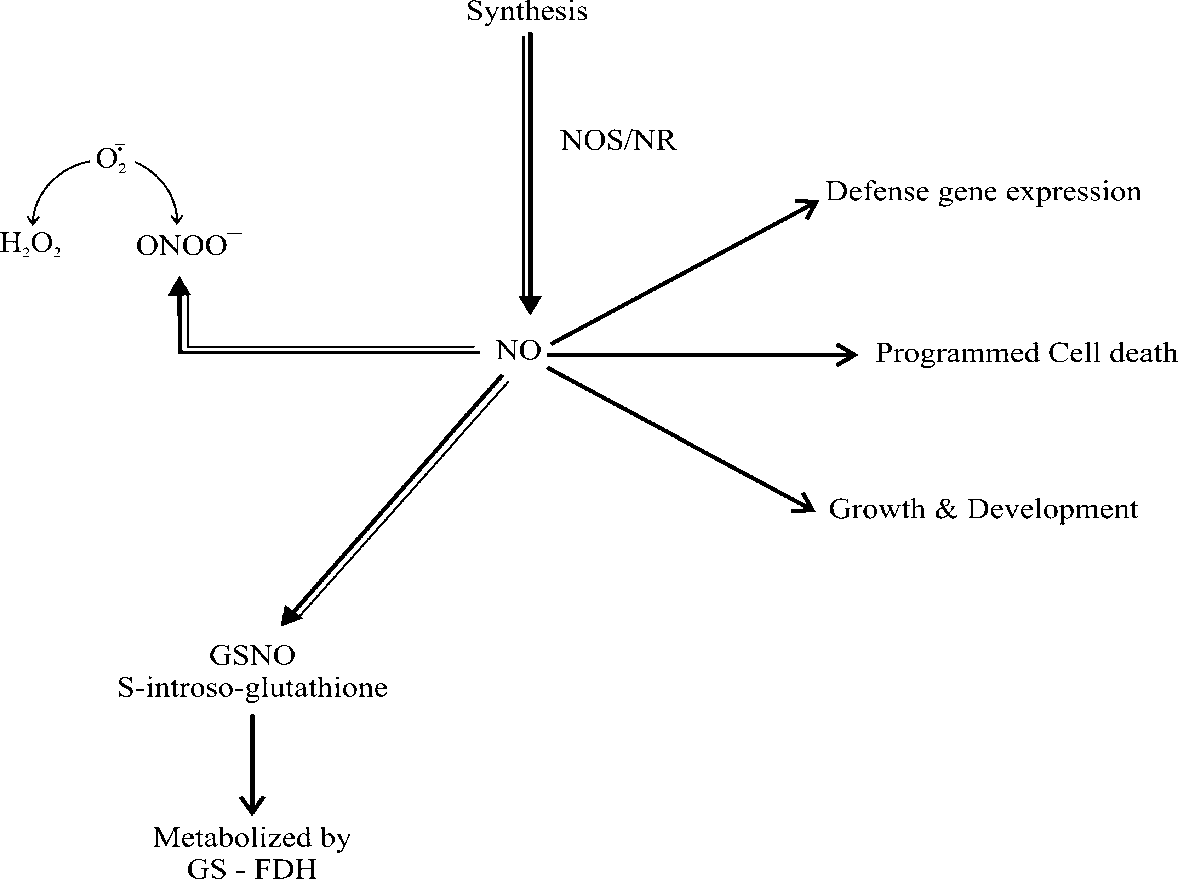
Fig. 1 NO signalling in plants. Double lined arrows represent potential synthesis and biochemical interactions while single lined arrows represent potential cellular effects and target sites for NO action
H 2 O 2 is potentially reactive oxygen (reduction product of O 2 ), but not a free radical (Halliwell et al., 2000), generated as a result of oxidative stress via superoxide (O 2 ∙-), presumably in a non-controlled manner during electron transport processes such as photosynthesis and mitochondrial respiration. Ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase oxygenase (RuBisCO), an enzyme best known for incorporating CO 2 into organic substrates in plants also has an ancient oxygenase function, which plays a key role in regulating peroxide balance in cells (Perry et al., 2010). Potential sources include
NADPH oxidase, cell wall peroxidases, amine oxidases, Oxalate oxidase, flavin-containing oxidases, Type III oxidases and misfires in the electron transport chains of chloroplasts and mitochondria (Mehler reaction) (Bolwell and Wojtaszek, 1997; Bolwell et al., 2002; Halliwell and Gutteridge, 1999). Broadly, these events are enhanced by stresses (Alscher et al., 1997; Bol-well, 1999) although they occur as an integral part of many facets of plant development. Whatever, the source of ROS, it is now apparent that H2O2 acts as a signal to induce a range of molecular, biochemical and physiological responses with in cells and plants (Fig. 2). Also, H2O2 participant in implication of ROS mediated control of the K+ channel resulting in mineral nutrient partitioning with in the plants by identifying a critical target Cys (168) to be essential for sensitivity of H2O2 (Garcia-Mata et al., 2010). H2O2 is produced in response to various stimuli and mediates cross-talk between signalling pathways and is an attractive signalling molecule contributing to the phenomenon of cross-tolerance in which exposure of plants to one stress offers protection towards another (Cheng and Song, 2006; Bowler and Fluhr, 2000). In addition, exposure to low levels of one stress can induce tolerance towards subsequent higher levels of exposure to the same stress, a phenomenon termed acclimation tolerance (Prasad et al., 1994; Bhattacharjee, 2005). Therefore, H2O2 is considered as a fundamental fact of life in anaerobic environment (Moller, 2001).
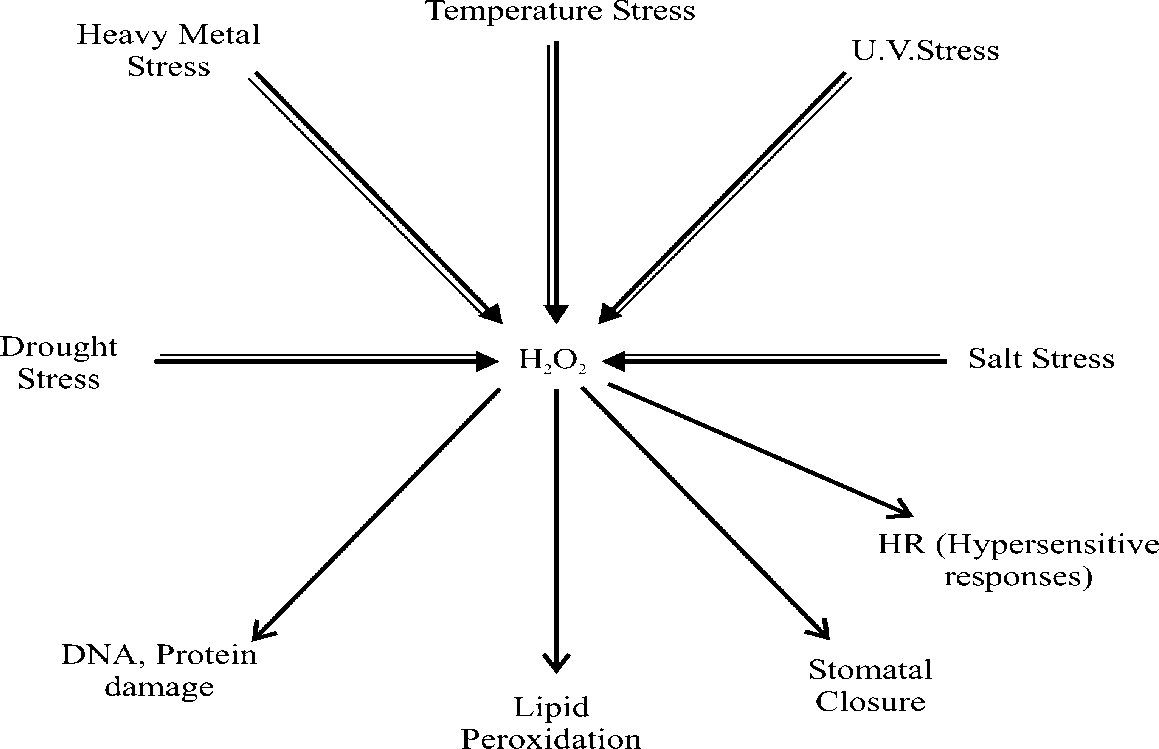
Fig. 2 H 2 O 2 signalling in plants. Double lined arrows represent potential synthesis and single lined arrows
represent major cellular effects of H 2 O 2
The cellular responses of H2O2 differ according to its site of synthesis or perception for example, whether the H2O2 is synthesized in plastids or at the plasma membrane. The genetically controlled production of H2O2 (e.g. by NADPH oxidases) is apparently used by plants to release an intracellular signal that, often together with NO, controls a variety of processes (Guo et al., 2003; Neil et al., 2002). H2O2 might induce a general stress response, but it does not have the required specificity to selectively regulate nuclear genes required for dealing with localized stress, e.g. in chloroplasts or mitochondria (Moller and sweetlove, 2010). During normal metabolism in a plant cell, H2O2 is generated in chloroplast, mitochondria and peroxisome and is kept in homeostasis by complicated and effective scavenging systems that have developed over the course of evolution (Zhao and Blumwald, 1998). In particular, H2O2 that is produced by cytosolic membrane-bound NADPH oxidases has been implicated as a signal in a wide range of biotic and abiotic stress responses. These responses include defense reactions against pathogens and herbivores (Mittler, 2002) the closure of stomata (Kwak et al., 2003) and the regulation of cell expansion and plant development (Kwak et al., 2003; Foreman et al., 2003). Its generation via electron transport is increased in response to environmental stresses such as excess excitation energy, drought and cold (Bartosz, 1997; Dat et al., 2000) and also induced in plants following exposure to a wide variety of abiotic and biotic stimuli.
It has a long lifespan, is able to cross biological membranes, and rapidly diffuses from cell to cell or can be transported long distances from its sites of origin in plants. Thus, H2O2 has all of the characteristic features of an intercellular signalling molecule and, for this reason, has received increasing attention in recent years (Levine et al., 1994; Alvarez et al., 1998; Neill et al., 2002).In addition, H2O2 is an evolutionarily ancient signalling molecule that not only played a key role in inducing evolution of oxygenic photosynthesis but also modulates many physiological events, such as stomatal movement, hypersensitive responses, and programmed cell death (Cheng and Song, 2006). As a response to oxidative stress and particularly H2O2 is involved in a variety of reactions against abiotic stresses and signalling cascades necessary for all aspects of plant growth and the integration of activity, ranging from the development of individual root hair to xylem differentiation, lignifications to wall loosening and wall cross-linking to root/shoot coordination and stomatal control. Understanding the role of H2O2 in plant growth or stress responses requires models that accommodate the large number of ways in which it can be formed and degraded at any given time, and that ROS produced by one source may be the drivers or substrates for a second (Allan and Fluhr, 1997).
Moreover, increasing evidence now indicates that H 2 O 2 acts as a local and systemic signal that directly regulates expression of numerous genes. Some of these are involved in plant pathogen defense responses, while others are invoked during adaptation of plants to abiotic stress (Desikan et al., 2001; Wang et al., 2006). Major abiotic stress includes extremes of temperatures, UV irradiation, O 3 exposure, heavy metal accumulation and drought (Prasad et al., 1994; Lamb and Dixon, 1997; Orozco-Cardenas and Ryan, 1993). Thus, while the involvement of H 2 O 2 in stress responses is of particular interest, it really must be considered in the context of and even as a special case of H 2 O 2 involvement in normal growth and metabolism. Several recent reviews have described the biological activities of ROS, placing special emphasis on the signalling role of H 2 O 2 (Mittler, 2002; Neil et al., 2002; Overmyer et al., 2003).
Abiotic stress
Because plants lack the capability of locomotion as a means of responding to change in their environment, they are exposed to various environmental stresses and must adapt to them in other ways. It is now well established that virtually all biotic and abiotic stresses induce or involve oxidative stress to some degree and the ability of plants to control oxidant levels is highly correlated with stress tolerance. For this purpose, they are equipped with complex processes such as perception, transduction and transmission of stress stimuli (Turner et al., 2002; Xiong et al., 2002; Kopyra and Gwozdz, 2004).
Abiotic stresses are major constraint to agricultural production worldwide. The plants have an inbuilt to respond to fluctuations in circadian and seasonal environmental conditions. Abiotic stresses disrupt the cellular redox homeostasis which leads to the oxidative stress or generation of ROS (Asada, 2006). The generation of ROS in different location of the plants cell (Mitochondria, Chloroplast, Peroxisome and Nucleus) causes injury and cell death (Mano, 2002). On the other hand, ROS play a vital role in intracellular redox signalling, activating antioxidant resistance mechanisms. Thus, it is a surviving response for plants to control the concentration of ROS. However, H 2 O 2 and NO both are important bioactive signalling molecules with multiple physiological functions in plants, synthesized in various plants under different environmental conditions (stresses).
NO is believed to be involve in two respiratory electron transport pathways in mitochondria (Yamasaki et al., 2001; Zottini et al., 2002) where it mediates the modulation of ROS and enhances anti oxidant defense systems in plants exposed to various abiotic stresses. The exogenous supply of NO protect plant from damage by eliminating the (O 2 ∙-) and lipid radical R, activates the antioxidant enzymes-activities especially superoxide dismutase (SOD) (Shi et al., 2007). However, in many studies, there have been increasing evidence that NO acts as a chain breaking antioxidant arresting lipid peroxidative reactions and activates gene expression of antioxidant enzymes (Nunoshiba et al., 1993; Ramamurthi and Lewis, 1997). Also, NO is an endogenous modulator of gibberellins-induced programme cell death in barley aleurone cells by inducing cytoprotective proteins and the synthesis of catalase (CAT), SOD, gluthione (GSH), S-transferase and alternative oxidase (Beligni et al.,
2002; Huang et al., 2002; Polverari et al., 2003). Furthermore, the properties of NO (Free radical, small size, no-charge, short-lived and highly diffusible across biological membranes) makes it is a very good agent to act as a signalling messenger in response of environmental stresses. NO generated at the same time as H 2 O 2 in response to abiotic stresses was found to mediate defense responses similar to those seen following H 2 O 2 generation. It is now clear that NO is a major signal molecule in plants (Durner and Klessing, 1999) and involve in signalling against abiotic stresses are discussed here because it seems likely that NO can be synthesized during stress responses at the same time as H 2 O 2 and may be that cellular effects reflects the responses to both H 2 O 2 and NO.
H2O2 is a form of ROS generated as a result of oxidative stress, arises from an imbalance in the generation and metabolism of ROS, with more ROS (such as H2O2) being produced than are metabolized. It is generated via O2∙-, presumably in a non– controlled manner, during electron transport processes such as photosynthesis and mitochondrial respiration in response to environmental stresses such as excess excitation energy, drought and cold (Bartosz, 1977; Dat et al., 2000). H2O2 is believed to mediate cross-tolerance and acclimation tolerance as well (Bowler and Fluhr, 2000; Prasad et al., 1994). Moreover, it may be that cellular responses to H2O2 differ according to its site of synthesis or perception, for example whether the H2O2 is synthesized in plastids or at the plasma membrane. Now it is apparent that H2O2 acts as a signal to induce a range of molecular, biochemical and physiological responses with in cells and plants. H2O2 can induce the expression of genes potentially involved in its synthesis such as NADPH oxidase (Desikan et al., 1998) and also of those encoding proteins involved in its degradation, implying a complex mechanism for cellular regulation of oxidative status. H2O2 induced the expression of genes encoding ascorbate peroxidase in germinating rice embryos (Morita et al., 1999) and in Arabidopsis leaves (Karpinski et al., 1999), and wounding induced the expression of gene encoding a CAT via H2O2 in embryos and leaves of maize (Guan and Scandalios, 2000). Systemic responses to excess excitation energy stress were found to be mediated by H2O2, indicating that it can also function as a signal during abiotic stresses (Mullineaux et al., 2000).
Recent work has shown that H2O2 induces the expression of genes encoding protein required for Peroxisome biogenesis (lopez-Huertas et al., 2000). Peroxisomes are important sources of ROS, as well as antioxidants and NO and are thus important regulator of the cellular redox state. Induction of peroxisome biogenesis genes by various abiotic stresses like temperature, UV and mechanical injury (also generates H2O2) and exogenous H2O2 (Lopez-Huertas et al., 2000), places H2O2 as a key signal molecule mediating various cellular responses to biotic and abiotic stresses. Plants pre-treated with low concentrations of H2O2 have shown significantly greater tolerance to abiotic stress than untreated control plants (Gechev et al., 2002). This acquisition of abiotic stress tolerance usually occurs concomitantly with enhanced antioxidative status, as reflected by higher activities and or protein levels of CAT. Results of (Asada, 1999; Kuzniak and Sklodouska, 1999; Nagalakshmi and Prasad, 2001; Wang et al., 2010) suggest that glutathione peroxidase (GPx) activites were significantly enhanced by H2O2 pre-treated from initiation to the end of chilling as found in Zoysia cultivars (Wang et al., 2010). In yeast, a GPx, GPx3, can function as a receptor for H2O2 and a transducer of redox signals, to activate gene expression (Delaunay et al., 2002). Further studies is needed to understand the actual function of GPx in chilling stress during H2O2 pretreated as observed during the chilling resistance. However, the fact that oxidative stress is a common facet of many cellular stress responses means that elucidating those intracellular signalling processes mediating H2O2 signalling is of potential significance to any programme aimed at improving crop tolerance of abiotic stresses in order to enhance crop productivity. It is probable that additional H2O2 responses will be characterized in the near future.
NO and interactions with H2O2 under abiotic stresses
It is commonly observed that NO and ROS such O 2 ∙- and H 2 O 2 are generated in response to similar abiotic stress stimuli and with similar kinetics. NO and ROS can interact in various ways under stress conditions. For example, they can interact chemically as in the formation of compounds such as peroxynitrite. NO may also affect the activities of enzymes that alter ROS levels and vice versa. Thus, they could both impact either negatively or positively on the same or related signalling pathways and thereby lead to additive and passively synergistic responses.
Lum et al., (2002) observed that exogenous H2O2 induced NO generation in the guard and other cells of Phaseolus aureus leaves. In a chemiluminescence-based assay, the H2O2 induced a substantial increase in an apparent NOS-like activity. This increase was reduced by using a potential NOS inhibitor. Interestingly, the H2O2-induced NO generation was inhibited by the calcium channel blocker verapamil. Thus, it is possible that Ca2+ ions may mediate this effect of H2O2. She et al., (2004) and He et al., (2005) also reported that H2O2 induced NO synthesis in vicia faba guard cells and that again this accumulation could be reduced by a NOS-inhibitor. Moreover, they found that both NO generation and stomatal closure stimulated by darkness or UV-B were dependent on guard cell synthesis of H2O2. Similarly, in Arabidopsis, H2O2 induces guard cells to synthesize NO, required if the induction of stomatal closure is to follow (Bright et al., 2006). Removal of the H2O2 with antioxidant or inhibition of its synthesis by inhibiting NADPH oxidase activity prevents NO generation and stomatal closure. However, H2O2 stimulates NO accumulation of guard cells in the At noa1 (At noa1) mutant was as in the wild type (Bright et al., 2006). Thus, the requirement of At NOS1 for NO synthesis must be epistatiscally upstream of H2O2 and its signalling effects.
Studies of Wi et al., (2010) suggest that H2O2 is important signalling molecule involves in response to biotic and abiotic stresses and in developmental and physiological processes and stress tolerance of H2O2 treated transgenic plants resulted from reduced ethylene biosynthesis, which decreased ROS accumulation via increased gene expression and activity of ROS-detoxifying enzymes, including MnSOD, CuZnSOD, and CAT. Regardless, the current evidence would suggest that H2O2 induces guard cell NO synthesis through the activity of NR. It also appears that the ABA-H2O2-NO cascade is not restricted to guard cells. Zhang et al., (2007) have now demonstrated that it also operates in the mesophyll cells of Zea mays leaves and that the effects of ABA and H2O2 on the induction of antioxidant defenses dependent on NO generation and could be reduced using cPTIO or L-NAME. While it is well established that H2O2 induces NO synthesis and accumulation, there has also been some suggestions that NO may modulate H2O2 levels. H2O2 accumulation can either to enhanced expression of antioxidant enzymes and increased expression of other defense proteins such as Glutathione S-transferase or it can initiate PCD depending on the intensity of the oxidative signal or oxidative load on the tissues. Both She et al., (2004) and He et al., (2005) have reported that this was the case in Vicia faba guard cells. However, Dong et al., (2005), also working with Vicia faba guard cells, did not observe this phenomenon. NO does not appear to induce H2O2 generation in Arabidopsis guard cells (Bright et al., 2006) or in maize mesophyll cells (Zhang et al., 2007). Thus, there is argument as to whether or not this occurs but feedback mechanisms and autocatalysis are part and parcel of signalling pathways, and it may be that such discrepancies simply reflect differences in the physiological states of the tissues examined.
Function of NO in H2O2 mediating tolerance to:Salinity stress
Soil salinity is one of the major abiotic stresses that adversely affect crop productivity and quality. About 20% of irrigated agricultural land is adversely affected by salinity (Flowers and Yeo, 1995). Salt tolerance is a complex trait involving the coordinated action of many gene families that perform a variety of functions such as control of water loss through stomata, ion sequestration, metabolic adjustment, osmotic adjustment and antioxidative defense (Abogadallah, 2010). In sodic soils, Na+ binds to negatively charged clay particles, causing swelling and dispersal, thus making the soil less unfit for crop growth (Chinnusamy et al., 2005). High salt concentration causes osmotic and ionic stress in plants (Zhu, 2002). It limits growth and development of plants by affecting several key metabolic processes (Hasegawa et al., 2000; Marschner, 2002; Siddiqui et al., 2008, 2009a ; Khan et al., 2010). Further, salinity alters the activities of many enzymes involve in nitrate and sulphate assimilation pathways in plants which lowers their energy status and increase the demand for nitrogen and sulphur (Siddiqui et al., 2009b). Much of the injury at cellular level caused by salinity stress is associated with oxidative damage due to ROS. Plants appear to possess wide arrays of defense strategies to protect from oxidative damage. However, less is known about NO involvement in tolerance of plants to salt stress. The exogenous sodium nitripruside (SNP), a NO donor significantly alleviated the oxidative damage of salinity to seedlings of rice (Uchida et al., 2002), lupin (Kopyra and Gwozdz, 2003) and cucumber (Fan et al., 2007; Yu-qing et al., 2007) enhanced seedlings growth (Song et al., 2009) and increased the dry weight of maize and Kodtetzkya virginica seedlings (Zhang et al., 2007; Guo et al., 2009) under salt stress. Pre-treatment of NO effectively contributed to better balance between C and N metabolism by increasing total soluble protein and by enhancing the activities of endopeptidase and carboxypeptidase in plant under salt stress (Zheng et al., 2010).
In previous studies, it was established that exogenous NO induced the expression of plasma membrane (PM) H+-ATPase in plants under salt stress. Zhao et al., (2004) in Phragmities communis and Zhang et al., (2007) in Populus euphratica reported that NO enhanced salt tolerance of calluses under salinity also by increasing K+/Na+ ratio , and this process was due to H2O2 dependent increase in the (PM) H+-ATPase activity. Exogenous H2O2 possibly functioned directly or may have induced intracellular H2O2 generation to act as a signalling molecule under stress. Pretreatment of wheat seeds with H2O2 has been shown to improve the subsequent salt tolerance of the seedlings (Wahid et al., 2007). The control of Na+ involvement across the PM and tonoplast to maintain a low Na+ concentration in adaptation to salt stress (Rausch et al., 1996). Liu et al., (2007) showed that glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase played an important role in NR-dependent NO production, and in establishing to tolerance of red kidney been root to salt stress.
In previous studies, NO decreases membrane permeability, rate of ROS production, malondialdehyde (MDA) and H2O2 and intracellular CO2 concentration under salt stress by inducing ROS scavenging enzymes activities CAT, peroxidises (POD), SOD, ascorbate peroxidise (APX) and proline accumulation (Kopyra and Gwozdz, 2003; Fan et al., 2007; Yu-quing et al., 2007; Shi et al., 2007; Sheokand et al., 2008; Lopez-Carrion et al., 2008; Guo et al., 2009). Moreover, NO induces not only ROS-scavenging enzymes activities, but also expression of transcripts for stress related genes encoding sucrose-phosphate synthase, ∆-pyroline-5-carboxylate synthase (Uchida et al., 2002). Furthermore, NO participate in enhancement of photosynthesis by inducing the photosynthetic pigments under salt stress (Ruan et al., 2002; Fan et al., 2007) and also in ATP synthesis and two respiratory electron transport pathways in mitochondria (Yamasaki et al., 2001; Zottini et al., 2002) where, it mediates the modulation of ROS and enhances the antioxidant defense system in plants subjected to salinity (Zheng et al., 2009). It has been initially hypothesized that H2O2 might be downstream signal molecules to regulate the activity of PM H+-ATPase. Avsian et al., (2004) have shown that salt stress induced oxidative stress in the form of H2O2, the production of which occurred in intracellular spaces. Further results indicated that H2O2 content increased greatly under salt stress. Since H2O2 might be the candidate downstream signal molecule, we tested PM H+-ATPase activity and K and Na ratio in calluses by adding H 2O2. The results suggested that H2O2 inducing an increased K to Na ratio. Therefore, it is clear from summing up this new assay that NO may be regulate the H2O2 generation. Since H2O2 is involved in downstream signal molecule of NO, PM-NADPH oxidase, the main source of H2O2 production might be the regulated target of NO. The results indicated that PM-NADPH oxidase is required for H2O2 accumulation and PM-NADPH oxidase activity could attribute to NO in calluses under salt stress (Fig. 3).
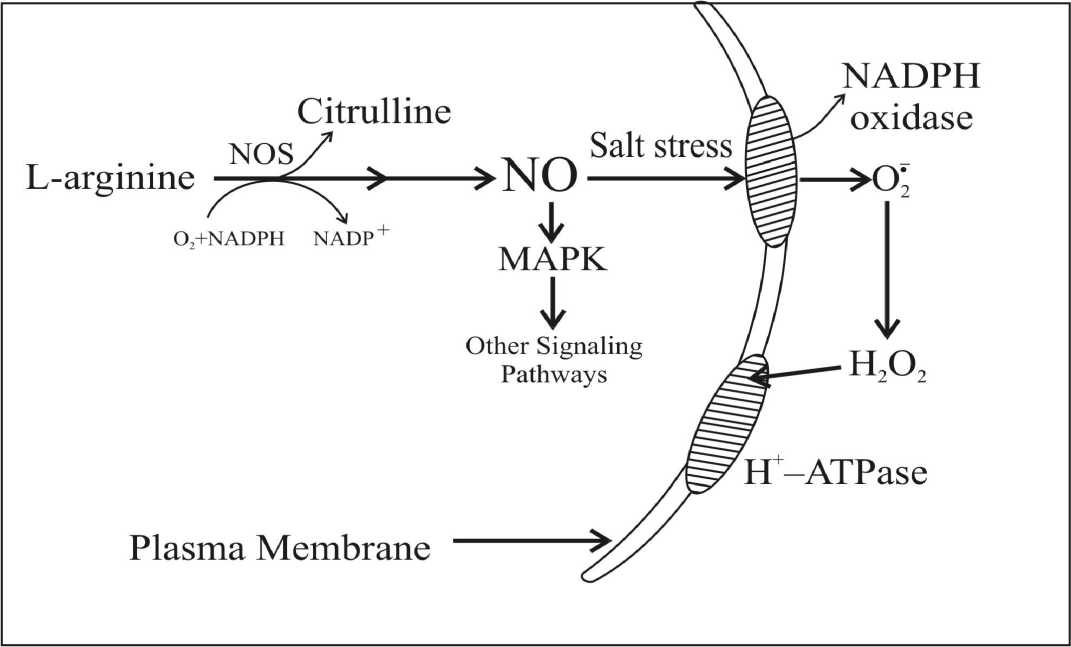
Fig. 3 A model for functioning of NO and H 2 O 2 as signalling molecules in inducing salt resistance.
In fig. 3, it clear that H 2 O 2 rather than NO is the major signalling molecule that mediate directly the activity of PM H+-ATPase under salt stress. Normally, NO generated from NOS, acts as a signal molecule to regulate other mechanisms. Under salt stress, accumulated NO activates PM-NADPH oxidase activity. Then, a number of H 2 O 2 produced from PM-NADPH oxidase. The PM H+-ATPase is activated greatly by the accumulated H 2 O 2 . Research on role of NO and H 2 O 2 under stress conditions in plant is advancing rapidly. Further research work is required to decipher the mechanisms through which NO and H 2 O 2 acts and how K and Na elements uptake might be connected with salt resistance.
Heavy metal stress
As we know that heavy metals contamination affects the biosphere in many places worldwide. Heavy metal toxicity is one of the major abiotic stresses leading to hazardous health effects in animals and plants. Because of their high reactivity they can directly influence growth, senescence and energy synthesizing processes (Maksymiec, 2007). Tolerance to heavy metals in plants may be defined as the ability to survive in a soil that is toxic to other plants, and is manifested by an interaction between a genotype and its environment (Macnair et al., 2000). Plants possess a range of potential cellular mechanisms that may be involved in the detoxification of heavy metals and thus tolerance to metal stress (Hall, 2002). The effects of their toxic influence on plants is largely a strong and fast inhibition of growth processes of the above and underground parts, as well as the activity decrease of the photosynthetic apparatus, often correlated with progressing senescence processes (Krupa et al., 1993; Maksymiec et al., 1994; Ouzounidou et al., 1995; Maksymiec and Baszynski, 1996b; Skorzynska-Polit and Baszynski, 1997; Weckx and clijsters, 1997; Molas, 2002; Sobkowiak and Dekert, 2003; Alaoui-Sosse et al., 2004; Lin et al., 2005). Growth inhibition and senescence stimulation caused by heavy metals in excess are intriguing effects, more so, as the knowledge of their mechanisms can have a great significance in ecophysiology and medicine.
Like other stresses, NO also plays the vital role in enhancement of antioxidant enzymes activities and alleviates the toxicity of heavy metals. Exogenous application of SNP reduced cupper (Cu) toxicity and NH4+ accumulation in rice leaves. Moreover, studies of Wang et al., (2010) also suggest that application of the NO donor SNP efficiently alleviated the copper toxicity effect, as shown by increases in chlorophyll content and the biomass of fresh/dry leaves in Lycopersicon esculentum. SNP treatment also induced the transcription and increased activities of antioxidant enzymes, including CAT, peroxidase, SOD and ascorbate peroxidase led to reduction in H2O2 accumulation in the leaves. Special inhibitors or scavengers of NO synthesis is diminished the ameliorating effect of NO on copper (Cu) toxicity (Wang et al., 2010). The protective effect of SNP on the toxicity and NH4+ accumulation can be reversed by PTIO, a NO scavenger, suggesting that the protective effect of SNP is attributable to NO released. These results also suggest that reduction of Cu induced toxicity and NH4+ accumulation by SNP is most likely mediated through its ability to scavenge active oxygen species (Yu et al., 2005). Kopyra and Gwozdz (2003) also found that SNP pretreatment significantly reduced O2∙- induced specific fluorescence in Lupinus luteus roots under heavy metals treatment. Results obtained in this study suggest that antioxidant function of NO may be traced by a scavenging O2-, resulting in a decrease of its intracellular concentration. The detoxification and antioxidative properties of NO also found in soyabean cell cultures under Cd and Cu (Singh et al., 2008). Moreover, NO decreased the Al3+ toxicity in root elongation of Hibiscus moschetuos (Tian et al., 2006). Application of SNP promoted ROS-scavenging enzymes reduced accumulation of H2O2 and induced the activity of H+-ATPase and H+-PPase in plasma membrane or tonoplast, also significantly alleviated the growth inhibition induced by CuCl2 in tomato plants. These results suggested that exogenous NO could effectively induced tomato seedlings to adjust physiological and biochemical mechanisms against Cu toxicity, and maintain fundamentally metabolic capacity and normal growth under heavy metal stress (Cui et al., 2009). Hu et al., (2007) also found that pre-treatment of NO improved wheat seeds germination and alleviated oxidative stress against Cu toxicity by enhancing the activity of SOD and CAT and by decreasing the lipoxygenase activity and malondialdehyde synthesis.
NO was reported to have the ability to reduce Cu-induced toxicity in tomato through antioxidant enzyme activity and metallothionein accumulation, and that metallothionein acts downstream of NO signalling (Wang et al., 2010). NO is most likely mediated through the modulation in the activities of antioxidant enzymes (CAT, POD and APX) involved in H2O2 detoxification and in the maintenance of cellular redox couples (GR), and contents of molecular antioxidants (Particularly non-protein thiol, ascorbate and its redox status) (Tewari et al., 2008). Zhang et al., (2008a) reported that pre-treatment with SNP increased the accumulation in Cu treated cells by about 1.5 fold, which this effect could be blocked by addition of cPTIO. Cu and NO were able to stimulate the ∆-pyroline-5-carboxylate synthetase (P5CS) activity, the key enzyme of proline biosynthesis and up regulate the expression of P5CS in the Cu treated algae. These results indicate that Cu-responsive proline biosynthesis is closely related to NO generation in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, suggesting the regulatory function of NO in proline metabolism under heavy metal stress. NO protected the plants against Al3+ induced oxidative stress and increased root elongation was correlated with a decreased in Al3+ accumulation in root apexes (Wang and Yang, 2005). SNP-exposed plants of Wheat showed enhanced activities of SOD, CAT, APX and protein content, whereas decreased H2O2 and Malondialdehyde under Al stress (Zhang et al., 2008b).
Furthermore, a recent study showed that SNP alleviated Cd-toxicity, atomic absorption spectrometry and fluorescence localization showed that treatment with SNP decreased Cd accumulation in both cell wall and soluble fraction of leaves; although SNP increased Cd accumulation in the rice roots obviously. SNP in nutrient solution had little effect on the transpiration rate of rice leaves, but this treatment increased pectin and hemicellulose content and decreased cellulose content significantly in the cell wall of rice roots. Based on these results, we conclude that decreased distribution of Cd in the soluble fraction of leaves and roots and increased distribution of Cd in the cell wall of roots are responsible for the NO induced increase of Cd tolerance in rice. It seems that exogenous application of NO enhances Cd tolerance of rice by increasing pectin and hemicelluloses content in the cell wall of roots, increasing Cd accumulation in root cell wall and decreasing Cd accumulation in soluble fraction of leaves (Xiong et al., 2009). The production of H2O2 in rice leaves enhanced under Cd treatment, in the case Cd alone, H2O2 content induced significantly with increase in the concentration of Cd (Fig. 4). Cd toxicity resulted in reduced length, biomass, protein content and activities of antioxidant enzymes (Sharma et al., 2010).
As a consequence of a general stress response, cytotoxic H 2 O 2 get accumulated in the cells (Levine et al., 1994) and can act as a secondary messenger (Dietz et al., 1999). High H 2 O 2 and O 2 ∙- had been reported earlier in the case of various other plants under Cr Zn Pb etc. (Dietz et al., 1999; Panda, 2003; Panda et al., 2003a, b; Choudhury and Panda, 2004). The increase in SOD activity indicated higher H 2 O 2 level seen by the increase in total peroxide content in leaves, which tallies with those observed in the case of Brassica juncea and Vigna radiata under Zn and Al treatment (Prasad et al., 1999; Panda et al., 2003b).
Moreover, H2O2 increase usually occurred after Cu, Cd (Drazkiewicz et al., 2004; Romero-Puertas et al., 2004; Maksymiec and Krupa, 2006b) and Hg (Cho and Park, 2000) treatment of Arabidopsis Thaliana and tomato plants, respectively. However, in barley plants only Mn increased the H2O2 content after 5 days but not Cu (Demirevska-Kepova et al., 2004). This difference may indicate that H2O2 accumulation developed differently during a larger stress action. After a long time of Cd action, SOD activity decrease was observed (Sandalio et al., 2001). However, this effect was connected with attenuation of the enzymic antioxidative system, and increased per oxidation of lipids may have not resulted in H2O2 level decrease.
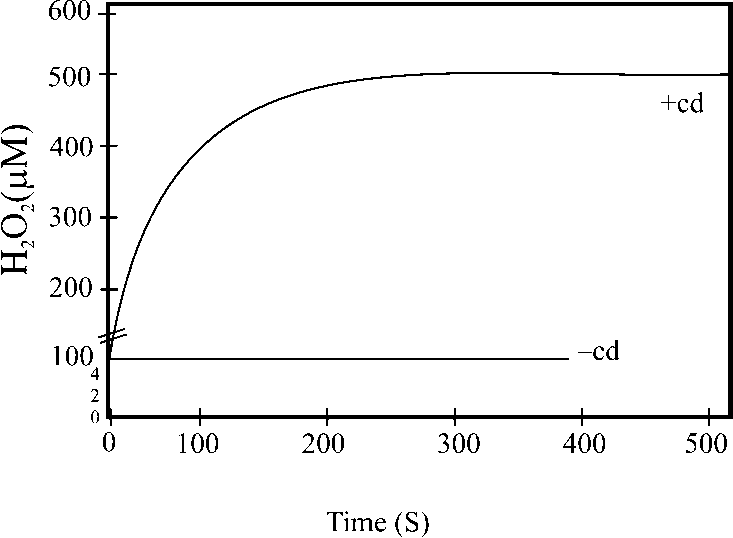
Fig. 4 Stimulated H 2 O 2 concentration in the absence and presence of 50 µM Cadmium
More recently, Lin et al., (2005) have shown that Cu can act through changes in H 2 O 2 -dependent peroxidase activity followed by cell wall stiffening due to the formation of cross-linking among the cell wall polymers. Also Cd (Non-reducing ions) enhances H 2 O 2 accumulation (Schutzendubel et al., 2001; Romero-Puertas et al., 2004; Cho and Seo, 2005; Maksymiec and Krupa, 2006b). NADPH oxidase (a source of H 2 O 2 production) is involved in plant growth (Papadakis and Roubelakis-Angelakis, 1999; Liszkay et al., 2003) and plant response to Cu (Lamb and Dixon, 1997; Orozco-Cardenas et al., 2001; Quartacci et al., 2001; Maksymiec and Krupa, 2006b). Increased accumulation of H 2 O 2 , usually connected with changes in the cellular redox status, alerts the plant cell against environmental stresses (Lamb and Dixon, 1997; Ghoshory et al., 1998; Orozco-Cardenas et al., 2001; Foyer and Noctor,
2003; Rentel and Knight, 2004) and may enhance the plants antioxidant response through calcium signalling in the expression of glutathione transeferase gene (Rentel and Knight, 2004).
In fact, accumulation of H2O2 has been observed in Cd-exposed roots (Schutzendubel et al., 2001) and in Cd exposed Nicotiana tabacum suspension cultures (Piqueras et al., 1999). It was suggested that Cd triggered an oxidant burst as in pathogenesis because they detected H2O2 in the culture medium (Piqueras et al., 1999). Taking all these observation together, a hypothetical framework may be suggested that Cd induces a transient loss in antioxidative capacity perhaps accompanied by a stimulation of oxidant producing enzymes, which results in intrinsic H2O2 accumulation. H2O2, then, would act as a signalling molecule triggering secondary defenses. These in turn, would cause an ultimately cell wall rigidification and lignifications, thereby, decreasing cellular viability and finally resulting in cell death (Fig. 5).
Drought stress
Drought stress induced free radicals cause lipid per oxidation and membrane deterioration in plants and it, also leads to an imbalance between antioxidant defenses and the amount of AOS resulting in oxidative stress (Van Breusegem et al., 2001). AOS are necessary for inter and intracellular signalling, but at high concentration can cause damage at various levels of organization including chloroplast (Smirnoff, 1993). Apart from morphological structures contributing to drought stress tolerance, plants have evolved a variety of physiological and biochemical processes, which act as components of drought tolerance (Ren et al., 2007; Wang et al., 2007). Plants have also developed enzymatic antioxidant system to cope with drought stress and to avoid oxidative damage (Shvaelva et al., 2006; Horvath et al., 2007).
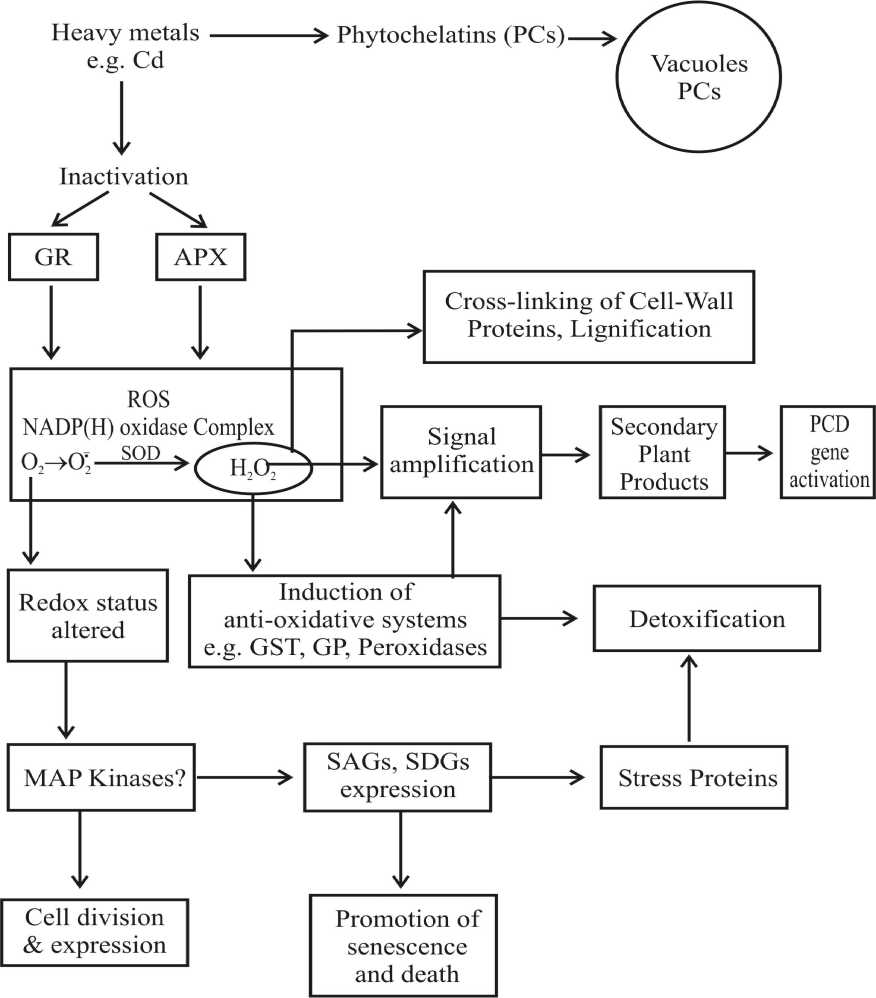
Fig. 5 Hypothetical view of heavy metal action on the cellular redox control and related for antioxidant signalling (SAGs, Senescence-associated genes; SDGs, Senescence-down-regulated genes)
Arasimowicz-Jelonek et al., (2009) reported in their study that roots subjected to mild (5 to10 h) water deficit showed slightly enhanced NO synthesis in cells of root tips and in the surrounding elongation zone as compared to severe (17 h) water stress resulted in an intensive NO production in cucumber roots. Also drought promoted NO production in pea, wheat and Nicotiana tabacum was reported by many researchers (Gould et al., 2003; Leshem and Haramaty, 1996; Kolbert et al., 2005).
Application of SNP enhanced plant tolerance to drought stress by reducing water stress, in leakage and transpiration rate, and inducing stomatal closure (Garcia-Lamattina, 2001). Exogenous SNP alleviated oxidative damage, accelerated protein synthesis and enhanced photosynthesis rate, and increased the activities of SOD and CAT and also maintained higher relative water content (RWC) and lower leaf water loss in leaves of wheat seedlings exposed to polyethylene glycol (PEG), termed was drought stress. Interestingly, such effects of SNP were reversed by the addition of carboxy-PTIO [2-(4-carboxyphenyl-4, 4, 5, 5-tetramethylimidazoline-1-oxyl-3-oxide], a specific NO scavenger (Tan et al., 2008). These results suggested that application of SNP might confer an enhanced resistance to drought stress in plants. Sang et al., (2008) demonstrated that water stress induced the synthesis of NO in the maize mesophyll cells and activity of NOS in cytosolic and microsomal fractions of maize leaves and this NO production was blocked by the pretreatment with inhibitors of NOS and NR, suggesting that NO is produced from NOS and NR in leaves of maize plants exposed to water stress. The pre-treatment of NOS and NR inhibitors inhibited activities of chloroplast and cytosolic antioxidant enzymes i.e. SOD, APX and GR and decreased activities of these enzymes were enhanced by the exogenous application of NOS, thereby, decreasing the accumulation of H2O2 induced by water stress. The potential ability of NO to scavenger H2O2 is at least in part due to the induction of sub-cellular antioxidant defense. Hao et al., (2008) reported that NO dependence on NOS-like activity in participated in the signalling of drought induced protective responses in maize seedlings. Both NOS activity and rate of NO release increased substantially under dehydration stress. The high NOS activity induced by c-PTIO as NO scavenger and NO accumulation blocked by NOS inhibitor- NG-nitro-L-arginine methyl-ester (L-NAME) in dehydration-treated maize seedlings indicated that most NO production under water deficit stress may be generated from NOS-like activity. After dehydration stress, detached maize leaves pre-treated with SNP maintained more water content by decreasing transpiration rate. Exogenous application of SNP alleviated the membrane permeability, a cell injury index when c-PTIO as a specific NO scavenger was applied, the effects of applied SNP was counteracted. Treatment L-NAME on leaves also led to higher membrane permeability, higher transpiration rate and lower SOD activity than those of control leaves indicating that NOS-like activity was involved in the antioxidative defense under water stress. These results suggested that NO dependence on NO-like activity serves as a signalling component in the induction of protective response and is associated with drought tolerance in maize seedlings. The protective effect of NO in osmotic stress was recently confirmed in two ecotypes of reed suspension cultures. The findings of Zhao et al., (2008) suggest that poly ethylene glycol (PEG-60000) induced NO release and activities of antioxidant enzymes in stress tolerant, but not sensitive, ecotype reed can effectively protect against oxidative damage and confers an increased tolerance to osmotic stress.
Moreover, studies of Li et al., (2010) suggest that the treatment with the ROS scavenger DMSO dramatically reduced the effects of localized root irradiation on the induction of HR and expression of the AtRAD54 gene in bystander tissues, suggesting that ROS play a critical role in mediating the bystander mutagenic effects in plants. Sergi et al., (2003) reported that accumulation of H2O2 in the walls of mesophyll cells of Cistus clusii and Cistus albidus plants increased at the onset of drought and also recently have shown that H2O2 accumulates in senescing leaves of drought-susceptible plants (Munne-Boch et al., 2001) and conclude that drought stress was the cause of H2O2 accumulation in test species. The accumulation of H2O2 observed at the onset of drought in the mesophyll cell walls of C .albidus and C.clusii may be associated with its function in cellular signalling at the first stage of drought or with drought-induced changes in cell wall structure (Scandalios et al., 1997) or both. Accumulation of H2O2 in mesophyll cell walls occurred at the first symptoms of drought in both species, indicating that H2O2 may play a role in inter or intracellular signalling or both (Doke, 1997; Foyer and Noctor, 1999). In addition, H2O2 is necessary for the peroxidase-mediated oxidative polymerization of cynnamil alcohols to form lignin (Potikha et al., 1999). Furthermore, diurnal variations in H2O2 suggest a particular role for this ROS in the response of plants to a combination of stresses. After a general introduction to the concept of drought and oxidative stress and its relationship, Jubany-Mari et al., (2010) describe the role of H2O2 in drought stress responses, emphasizing the importance of studies in H2O2 subcellular localization, needed for a better understanding of its role in plant responses to stress. Drought, oxidative stress and H2O2, in particular can enhance the expression of several genes (Bray, 1993; Dat et al., 2000; Desikan et al., 2000; Neale et al., 2000) and H2O2 can play a role in inter-and intracellular signalling (Doke, 1997; Foyer and Noctor, 1999). Thus, the possibility of an H2O2 -dependent regulation of stress response genes cannot be excluded, but further research is needed to conform it. Moreover, Sergi et al., (2003) reported also that the accumulation of H2O2 was associated with enhanced formation of lipophilic antioxidants indicating efficient scavenging of ROS in the chloroplasts of drought-stresssed C.clusii and C.albidus plants. The role of H2O2 in intracellular signalling in drought-stressed plants and in the putative regulation of antioxidant synthesis needs to be investigated (Fig. 6).
Temperature stress
Like other stresses, heat and cold stress have been a major limitation to crop productivity. Today, one of the biggest challenges for plant growth and productivity is to cope with the abrupt and often unpredictable temperature fluctuations. High temperature induces oxidative stress, lipid peroxidation, membrane injury, protein degradation, enzyme inactivation, pigment bleaching and DNA strands disruption in plants (Suzuki and Mitter, 2006).Similarly low temperature (cold stress) caused many changes in biochemical and physiological processes and ROS-homoeostasis in plants (Zhao et al., 2009; Xin and Browse, 1998; Suzuki and Mittler, 2006). The ability of plants to acquire tolerance to freezing temperature is a consequence of numerous changes in plant cells during a period called hardening (Browse and Xin, 2001). The initial perturbations in plant metabolism are followed by alteration in plant development and morphology with a final result achievement of maximum freezing tolerance (Huner et al., 1998). Potentially harmful to plant cells when in high levels, the ROS production during low temperature stress could have a role in stress perception and protection (Suzuki and Mittler, 2006). The tight control of ROS levels under optional growth conditions and especially during stress events is attained by a network of antioxidant enzymes and small molecules found in almost all cellular compartments (Mittler et al., 2004).
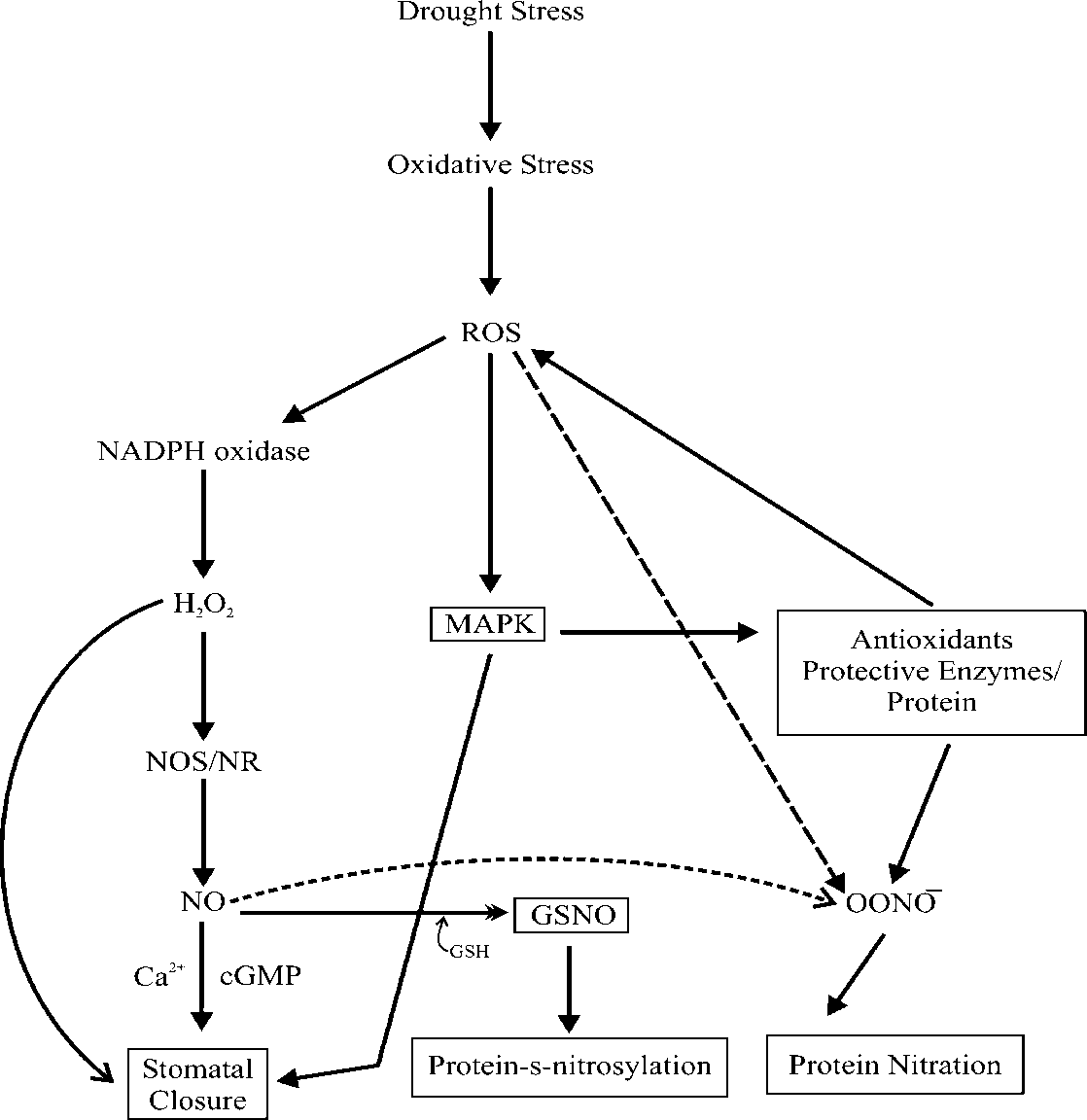
Fig. 6 Drought stress under signalling interaction between H 2 O 2 and NO in order to mediate plant survival under condition of water scarcity. H 2 O 2 induces NO generation by NR and NOS-like enzymes via as an yet to be fully characterized signalling pathway that may include the OX11 protein kinase and involve Ca2+. NO also enhances antioxidant gene and enzymes activity via MAPK and other signalling pathways. NO may also signal by inducing conformational changes in protein as a result of S-nitroslation/nitration
In many studies, researchers tried to find out the role of NO in alleviation of H 2 O 2 mediating heat and cold stress. However, high temperature treatment of lucerne cells resulted in an increase of NO synthesis, whereas, the application of exogenous NO induced cold tolerance in tomato, wheat and maize (Neil et al., 2003). NO production was increased by short time heat stress in alfalfa (Leshem, 2000). It is possible that this effect was related with antioxidative action of NO, which elevates adverse affects imposed by the intensification of peroxidative metabolism in heat and cold stress (Neil et al., 2002). Both heat and chilling caused reduction in membrane protein thiol level and increased accumulation of thiobarbituric acid reactive substances in 72 hr old germinating tissues (indicators of oxidative stress) and reduced germination and early growth performances (Bhattacharjee, 2009). Bouchard and Yamasaki (2008, 2009) reported that the increase in production of NO at high temperature and suggested that heat stress stimulated the NO production that could play a role in the induction of cell death in symbiodinium microadriaticum by mediating an increase in caspase like activity. Zhao et al., (2009) reported that cold acclimation induced an increase in endogenous NO production in wild type ( Arabidopsis thaliana ) and At noa1/rif1 (for nitric oxide associated1 resistant to inhibition by fosmidomycin1) leaves, while endogenous NO level in nia1 nia2 (NR-defective double mutant) leaves was lower than that is wild-type ones and it was little changed during acclimation. Cold acclimation stimulated NR activity and induced up-regulation of NIA1 gene expression.
In contrast, cold acclimation reduced quantity of NOA1/RIF1 protein, and inhibited NOS activity. These results indicate the up-regulation of NR dependent NO synthesis. Moreover, seedlings of nia1nia2 were less tolerant to freezing than wild type plants. Pharmacological studies using NR inhibitor, NO scavenger and NO donor showed that NR-dependent NO level was positively correlated with freezing tolerance. Further, cold acclimation up and down regulated expression of P5CS1 and ProDH genes, respectively, resulting in enhanced accumulation of Pro and wild-type plants. The stimulation of Pro accumulation by cold acclimation was reduced by NR inhibitor and NO scavenger, while pro accumulation by cold acclimation was not affected by NOS inhibitor. In contrast to wild type plants, cold acclimation up-regulated Pro DH gene expression in nia1nia2 plants than wild type plants. These findings demonstrate that NR-dependent NO production plays an important role in cold acclimation-induced increase in freezing tolerance by modulating Pro accumulation in Arabidopsis.
Furthermore, Uchida et al., (2002) reported that rice seedlings treated with low levels of H2O2 or NO allowed the survival of more green leaf tissue and resulted in higher quantum yield for photosynthesis ІІ than in non-treated controls under salinity and heat stress. Apostolova et al., (2008) reported that levels of endogenous peroxides were strongly increased in the spring wheat cultivar in response to cold hardening, and to a lesser extent in the winter wheat. However, H2O2 pre-treatment reduced production of H2O2 under further chilling stress, postponing oxidative damage. Results of Wang et al., (2010) showed that pre-treatment with H2O2 at appropriate concentration may improve the tolerance of warm-season Zoysia grasses to chilling stress and that manila grass had better tolerance to chilling, as evaluated by lower Malondialdehyde (MDA) and EL, and better turf grass quality, regardless of the pre-treatment applied. Pre-treatment with H2O2 has been shown to induce chilling tolerance in normally chill-sensitive maize seedlings (Neto et al., 2005). Similarly regenerated potato nodal explants treated with H2O2 became significantly more thermo tolerant compared with untreated control (Lopez-Delgodo et al., 1998). Apel and Hirt (2004) reported that H2O2 presumably provide an atmosphere in which peroxidases can act in two different catalytic modes. In the presence of H2O2 and phenolic substrates peroxidases operate in the peroxidatic cycle and are engaged in the synthesis of lignin and other phenolic polymers.
However, if the phenolic substrates are replaced by NADPH or related reduced compounds, a chain reaction starts that provides the basis for the H 2 O 2 producing NADPH-oxidase activity of peroxidases (Chen and Schopfer, 1999). Peroxidase H 2 O 2 production is distinguished from that by the phagocyte-type NADPH-oxidase by different Km values for oxygen, different requirements for NADH and NADPH, and different sensitivities of the two enzymes to inhibitors such as cyanide, azide and Diphenyleneiodnium (DPI). Because H 2 O 2 is a mild oxidant that can oxidize thiol residues, it has been speculated that H 2 O 2 is sensed via modification of thiol groups in certain proteins. So, therefore, H 2 O 2 activates several MAPK cascades have important functions in plant stress responses and development and are key players in ROS signalling and in innate immunity. In Arabidopsis, the transmission of ROS and pathogen signalling by MAPKs involves the coordinated activation of MPK6 and MPK3. Genetic analysis studies of Lumbreras et al., (2010) showing that MAPK phosphatase 2 (MKP2) regulates oxidative stress and pathogen defence responses and functionally interacts with MPK3 and MPK6 as well as MKP2 is a key regulator of MPK3 and MPK6
networks controlling both abiotic and specific pathogen responses in plants.
In Arabidopsis, H 2 O 2 activates the MAPKs, MAK3 and MAK6 via MAPKKKANP1 (Kovtun et al., 2000). Over-expression of ANP1 in transgenic plants resulted in increased tolerance to heat shock, freezing and oxidative stress (Kovtun et al., 2000). H 2 O 2 also increases expression of the Arabidopsis nucleotide diphosphate (NDP) kinase 2 (Moon et al., 2003). Over expression of AtNDPK2 reduced accumulation of H 2 O 2 and enhanced tolerance to multiple stresses including cold, salt and oxidative stress. The effect of NDPK2 might be mediated by the MAPKs, MAK3 and MPK6 because NDPK2 can interact and activate the MAPKs. These data suggest a scenario in which various stresses induce ROS generation that in turn activate MAPK signalling cascades.
It was also exhibited that pre-treatment of H 2 O 2 induces not only ROS-scavenging enzyme activities but also expression of transcripts for oxidative stress related gene encoding sucrose phosphate synthase, D-pyrroline-5-carboxylate synthase and small heat shock protein 26 (HSP26). These findings demonstrate that H 2 O 2 and NO plays an important role in tolerance of rice seedlings to both salt and heat stress by acting as signal molecules for the response. Song et al., (2006) found that application of SNP and S-nitrose-N-acetyl penicillamine (SNAP) (both are NO doner) dramatically alleviated heat stress induced ion leakage increase, growth suppression and cell viability decrease in callus of reed under heat stress and also elevated the activities of SOD, APX, CAT and POD. This result suggest that NO can effectively protect callus from oxidative stress induced by heat stress and that NO might act as a signal in activating active oxygen scavenging enzymes under heat stress (Fig. 7).
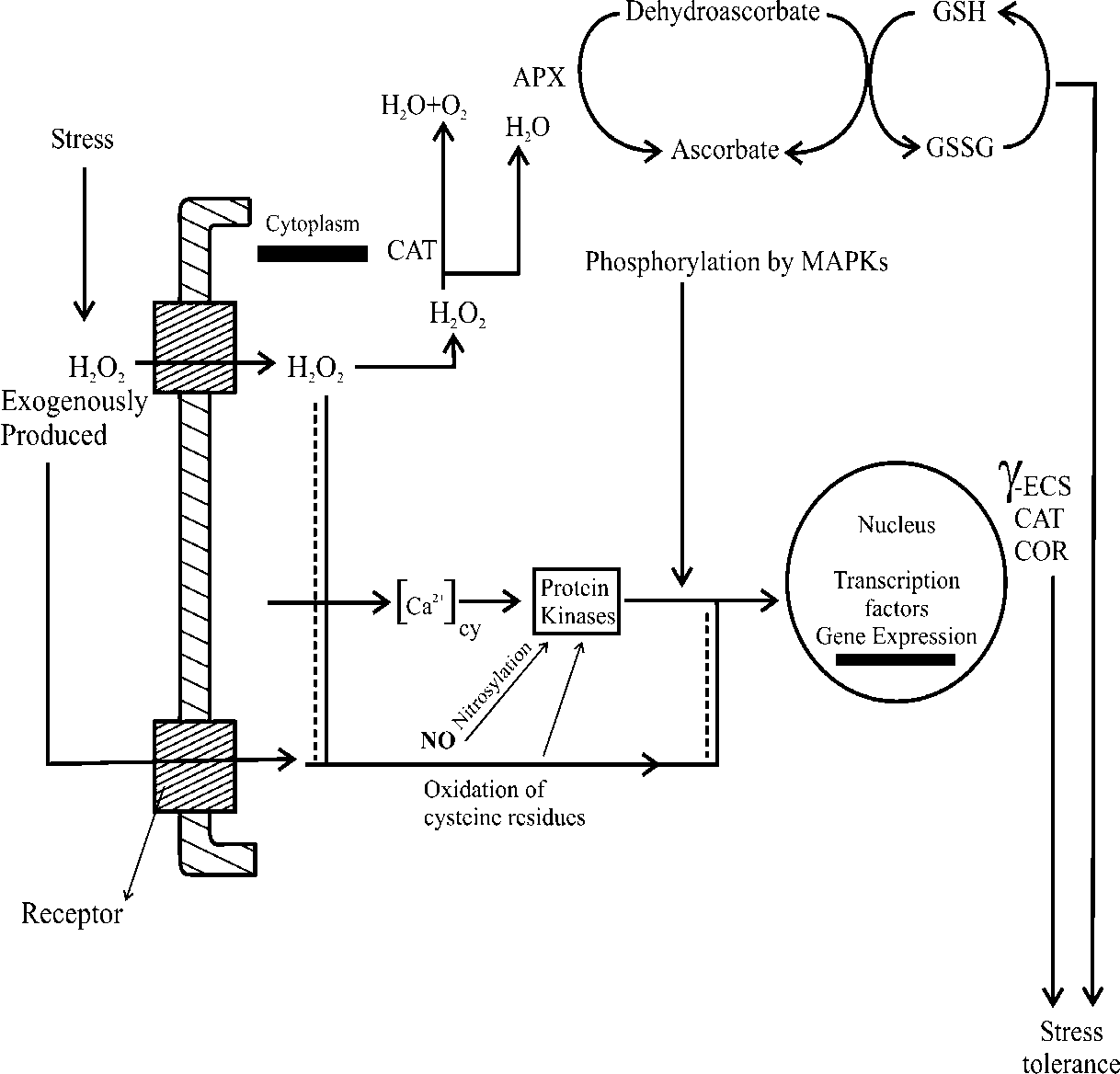
Fig. 7 H 2 O 2 , NO and gene expression. H 2 O 2 and NO might regulate the activity of transcriptional factor directly via nitrosylation/oxidation of cysteine residues. This can also via activation of a MAPK cascade
Microarray analysis of H2O2 induced gene expression in Arabidopsis indicates potential H2O2-responsive cis-elements in genes regulated by H2O2 (Desikan et al., 2001). One of these elements, the as-1 promoter element, also has high homology with redox-sensitive mammalian AP-1 cis–element (Karin et al., 1997). However, recent analysis of transgenic plants indicates that ROS other than H2O2 activates this as-1 element (Garreton et al., 2002). Further analysis will reveal whether similarity exists among plant, animal and fungal regulatory cis- elements of ROS-responsive genes. In contrast to O2∙-, H2O2 can diffuse in to cells and activate many of the plant defenses, including PCD (Dangl and Jones, 2001). The suppression of ROS detoxifying mechanisms is crucial for the onset of PCD. ROS production at the apoplast alone without suppression of ROS detoxification does not result in the induction in of PCD (Delledonne et al., 2001; Mittler et al., 1999). These data indicate an absolute requirement for the co-ordinated production of ROS and down-regulation of ROS scavenging mechanisms. The initial and very rapid accumulation of H2O2 is followed by a second and prolonged burst of H2O2 production. Recent work shows that H2O2 function as a second messenger mediating the systematic expression of various defense related genes in tomato plants (Orozco et al., 2001). Although oxidative stress is a primary response to any kind of stress (like temperature, drought and pathogen challenge) that leads to PCD (Bolwell, 1999) and H2O2 induces PCD in various system (Desikan et al., 1998; Levine et al., 1994; Solomon et al., 1999), in some cases H2O2 is not signal for PCD induction (Glazener et al., 1996; Ichinose et al., 2001). A study shows that a threshold exposure time of cells to H2O2 is required during which period transcription and translation are necessary (Desikan et al., 1998; Solomon et al.,1999). A transient increase in H2O2 was suggested to signal activation of protective mechanism for acclimation to chilling. Exogenous application of H2O2 can induce tolerance to chilling, high temperature and biotic stress, all of which cause elevated endogenous H2O2 production. A transient increase in H2O2 was suggested to signal activation of protective mechanisms for acclimation to chilling. These results suggests surprisingly that large number of genes that respond to an increase in H2O2 concentration would be in time with the proposed role of H2O2 as an ubiquitous signal for oxidative stress.
Ultra-violet Radiation stress
The decrease of stratospheric ozone layer from anthropogenic inputs of chlorinated fluorocarbons has resulted an increase of radiation of UV-B (280-315n.m) that leads to an increase of ion leakage, loss of chlorophyll, and decreases the maximum efficiency of PS-ІІ photochemistry (Fv/Fm) and the quantum yield of PS-ІІ electron transport (PS-ІІ)
and increase H 2 O 2 and thylakoid membrane protein oxidation. Protein oxidation is defined here as covalent modification of a protein induced by ROS or by-products of oxidative stress. Most types of protein oxidations are especially irreversible, whereas, a few involving sulphur containing amino acids are reversible (Ghezzi et al., 2003). Protein oxidation is wide spread and often used as a diagnostic marker for oxidative stress. Concerns about potential impacts of stratospheric ozone depletion contributed to spark-interest in studies of plant responses to enhanced UV-B levels during the last two decades (Caldwell et al., 2003). Ambient UV-B appears to have a measurable (generally modest) effect reducing plant growth, particularly in the case of herbaceous plants (Ballare et al., 1996; Krizek et al., 1998; Mazza et al., 1999a). However, its modification may have large impacts on the interactions between plants and phytophagous insects (Ballare et al., 2001; Paul and Gwynn-Jones, 2003). The most common effect of solar UV-B is increased plant resistance to insects, measured in terms of leaf area consumed and /or insect growth is standard feeding bioassays (Ballare et al., 1996; Rousseaux et al., 1998; Mazza et al., 1999b; Zavala et al., 2001).
Progress in the understanding of the mechanisms that mediate these effects of UV-B has been slow for various reasons. First, no specific UV-B receptors have yet been identified in plants, and no UV-B perception mutants are available for comparative studies. Second, most of the information on UV-B effects at the molecular level has been obtained in indoor-exposure experiments with heavily-unbalanced UV-B sources. Third, UV-B has the potential to damage key macro-molecules and cellular structures, particularly when high doses are used in laboratory studies, therefore specific
UV-B responses are difficult to separate from secondary consequences of generalized damage under these conditions.
UV-B radiation resulted in the increase in NO and ROS in Arabidopsis (Mackerness et al., 2001). The results of Wang et al., (2006) supported that NO generated from NOS-like activity appeared to act in the same direction or synergistically with ROS to induce ethylene synthesis in defence response under UV-B radiation in maize leaves. Zhang et al., (2003) and An et al., (2005) reported that UV-B induced increase of NOS activity in maize hypocotyls, indicating that NO may act as a second messenger and perform anti-oxidant responses to UV-B radiation, and SNP-exposed maize plants exhibited increase activity of glucosidase and protein synthesis. Moreover, UV-B induced stomatal closure, which was mediated by NO and H 2 O 2 and generation of NO was caused by a NOS-like activity (He et al., 2005). However, other authors reported that NO generated in guard cells were produced by NR activity (Bright et al., 2006). A study of SantaCruz et al., (2010) shows that NO protects against oxidative damage and that NOS-like activity is also required for HO-1 induction under UV-B radiation. Pre-treatments with SNP, a NO-donor, prevented chlorophyll loss, H 2 O 2 and O 2 ∙- accumulation and ion leakage in UV-B-treated plants. In addition, experiments carried out in the presence of L-NAME, well-known inhibitor of NOS and nitrate reductase, showed that NOS is the endogenous source of NO that mediates HO-1 (has antioxidant properties and is up-regulated by ROS in ultraviolet-B-irradiated soybean plants) expression.
Furthermore, Shi et al., (2005) reported that addition of SNP can partially alleviated UV-B induced decrease of chlorophyll content, Fv/Fm of ϕPS-І and oxidative damage to the thylakoid membrane in bean leaves. The potassium salt of cPTIO, arrested NO mediated protective effects against UV-B induced oxidative damage. Incubation of thylakoid membrane with increasing H2O2 concentration showed a progressive enhancement in carbonyl contents. H2O2 contents were suppressed in the presence of NO under UV-B radiation through increasing activities of CAT, SOD and APX and these results suggest that NO can effectively protect plants from UV-B destruction mostly mediated by enhanced activities of oxidative enzymes. As might be expected from previous work, some of H2O2-induced genes in Arabidopsis suspension cultures-encode anti-oxidant enzymes, defence and stress-related proteins. Interestingly, genes encoding signalling proteins such as transcription factors, protein kinases and protein phosphatases were also up-regulated by H2O2. These genes were similarly induced by other stresses such as wilting, UV-challenges. For example UV-B induced genes expression has been shown to occur via H2O2, as exposure of Arabidopsis plants to UV-B in the presence of antioxidants led to down-regulation of the UV-B induced gene (A-H-Mackerness et al., 1996). Moreover, activation of a NADPH oxidase by UV has been demonstrated in laboratory studies in Arabidopsis (Rao et al., 1996) and it is most interesting to note that the results of Casati and Walbot (2003) show clear up-regulation of a NADPH oxidase gene by solar UV-B in field grown plants. Moreover, UV-B may activate a variety of molecular sensitizers and give rise to enhanced H2O2 levels, which may lead to convergence with the wound induced cascade downstream of NADPH oxidase. Arabidopsis leaves pre-treated with H2O2 have been shown to develop increased tolerance to excess light (Karpinski et al., 1999). Finally, it has been concluded that consistent with a signalling role for this compound, some reports also have shown that endogenously synthesized H2O2 in response to abiotic stresses, can protect plants against UV-B stress and can induce stress response genes.
Conclusion and Future Prospects
From being molecules of somewhat novelty interest, in the last few years, H 2 O 2 and NO have emerged to be central players in the world of plant cell signalling, particularly under various stressful situations. The full range of biological functions for these two signalling molecules remain to be catalogued and determining the ways in which they interact, both together and with ever-increasing array of signals known to be recognized by plants, will need to be elucidated. Other research priorities must include full characterization of the enzymes through which the intracellular concentrations of H 2 O 2 and NO are regulated and where these enzymes are located in different cells and tissues. The intracellular signalling cascades that transduce H 2 O 2 and NO perception in to cellular responses have so far been characterized only superficially. Finally, they raise the question of how H 2 O 2 and NO are detected by cells. Such perception could conceivably involve direct interaction of H 2 O 2 and NO with cellular proteins, such as transcription factors, ion channels or enzymes.
Currently, research data show that H2O2 can play a dual role in the cells. During oxidative stress, H2O2 is a strong toxic oxidant causing cell damage or even cell death. At the same time it serves conversely as a signalling molecule to activate a defense system for restoring the redox homeostasis in plant cells. So far it is still under research whether H2O2 is situated at a common centre for the signalling pathways providing responses to various signals triggered by abiotic stresses like production of NO. The data available to date show that NO is a key factor involved in responses to a number of abiotic stimuli. They indicate that endogenous NO is a key factor in the tolerance of cells to the oxidative stress induced by a range of abiotic conditions, and that this probably involves the enhanced expression of genes encoding antioxidant enzymes. Of course, there are numerous unanswered questions and important areas for further research in future. The mechanisms by which NO is generated are still largely unresolved and elucidation of how it is made by different plant cells in different situations is clearly a research priority. No doubt, NO a ubiquitous bioactive molecule, plays an important role in a broad spectrum of multiple H2O2 mediating physiological processes in plants. However, most of the work has still to be done. In relevance of (1) NO functions as a signalling molecule in interaction with plant hormones, nutrients and metals, (2) NO mediated defense gene regulator in plants, (3) Functions of endogenous NO in different cells or organs of plants and (4) NO biosynthesis pathways in plant and its regulation to environmental stimulus and cellular redox homeostasis regulation. From above discussion, it is clear that both NO and H2O2 have now been shown to function as synergistic signals in plants mediating a range of responses to abiotic stresses. Given that such stresses impose considerable constraints on crop production, there is a real need for continued research in this field.
Acknowledgements
The authors are highly thankful for the facilities obtained at AMU Aligarh. Financial support from the Department of Science and Technology, New Delhi in the form of project (SR/FT/LS-087/2007) is gratefully acknowledged.
Список литературы Role of nitric oxide in regulation of H2O2 mediating tolerance of plants to abiotic stress: a synergistic signaling approach
- Abogadallah, G.M. (2010). Antioxidative defense under salt stress. Plant Signal. Behav., 5(4): 369-374.
- Agrawal, G.K., Iwahashi, H., Rakwal, R. (2003a). Rice MAPKs. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 302: 171-180.
- Agrawal, G.K., Jwa, N.S., Agrawal, S.K., Tamogami, S., Iwahashi, H., Rakwal, R. (2003b). Cloning of novel rice allene oxide cyclise (OsAOC): mRNA expression and comparative analysis with allene oxide synthase (OsAOS) gene provide insight into the transcriptional regulation of octadecanoid pathway biosynthetic genes in rice. Plant Sci., 164: 979-992.
- Agrawal, G.K., Tamogami, S., Iwahashi, H., Agrawal, V.P., Rakwal, R. (2003c). Transient regulation of jasmonic acid-inducible rice MAP kinase gene (OsBWMK1) by diverse biotic and abiotic stresses. Plant Physiol. Biochem., 41: 355-361.
- Alaoui-Sosse, B., Genet, P., Vinit-Dunand, F., Toussaint, M.L., Epron, D., Badot, P.M. (2004). Effect of copper on growth in cucumber plants (Cucumis sativus) and its relationships with carbohydrate accumulation and changes in ion contents. Plant Sci., 166: 1213-1218.
- Allan, A.C., Fluhr, R. (1997). Two distinct sources of elicited reactive oxygen species in tobacco epidermal cells. Plant Cell, 9: 1559-1572.
- Alscher, R., Donahue, J., Cramer, C.L. (1997). Reactive oxygen species and antioxidants: Relationships in green cells. Physiologia Plantarum, 100: 224-233.
- Alvarez, M.E., Pennell, R.I., Meijer, P.J., Ishkawa, A., Dixon, R.A., Lamb, C. (1998). Reactive oxygen species intermediates mediate a systemic signal network in the establishment of plant immunity. Cell, 92: 773-784
- An, L.Z., Liu, Y.H., Zhang, M.X. (2005). Effect of nitric oxide on growth of maize seedling leaves in the presence or absence of ultraviolet-B radiation. J. Plant Physiol., 162: 317-326.
- Apel, K., Hirt, H. (2004). Reactive oxygen species: Metabolism, oxidative stress, and signal transduction. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 55: 373-399.
- Apostolova, P., Yordanova, R., Popova, L. (2008). Response of antioxidative defence system to low temperature stress in two wheat cultivars. Gen. Appl. Plant Physiology, 34: 281-294.
- Arasimowicz, M., Floryszak-Wieczorek, J. (2007). Nitric oxide as a bioactive signalling molecule in plant stress responses. Plant Sci., 172: 876-887.
- Arasimowicz-Jelonek, M., Floryszak-Wieczorek, J., Kubis, J. (2009). Interaction between polyamine and nitric oxide signalling in adaptive responses to drought in cucumber. J. Plant Growth Regul., 28: 177-186.
- Asada, K. (1999). The water-water cycle in chloroplasts: scavenging of active oxygens and issipation of excess photons. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol., 50: 601-639.
- Asada, K. (2006). Production and scavenging of reactive oxygen species in chloroplasts and their functions. Plant Physiol., 141: 391-396.
- Avsian, K.O., Gueat, D.Y., Lev, Y.S., Gollop, R., Ben, H.G. (2004). The salt stress signal transduction pathway that activates the gpxl promoter is mediated hy intracellular H2O2, different from the pathway induced by extracellular H2O2. Plant Physiol., 135(3): 1685-1696.
- Ballare, C.L., Rousseaux, M.C., Searles, P.S., Zaller, J.G., Giordano, C.V., Robson, T.M., Caldwell, M.M., Sala, O.E., Scopel, A.L. (2001). Impacts of solar ultraviolet-B radiation on terrestrial ecosystems of Tierra del Fuego (southern Argentina). An overview of recent progress. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B: Biol., 62: 67-77.
- Ballare, C.L., Scopel, A.L., Stapleton, A.E., Yanovsky, M.J. (1996). Solar ultraviolet-B radiation affects seedling emergence, DNA integrity, plant morphology, growth rate, and attractiveness to herbivore insects in Datura ferox. Plant Physiol., 112: 161-170.
- Bartosz, G. (1997). Oxidative stress in plants. Acta Physiol. Plant, 19: 47-64.
- Beligni, M.V., Fath, A., Bethke, P.C., Lamattina, L., Jones, R.L. (2002). Nitric oxide acts as an antioxidant and delays programmed cell death in barley aleurone layers. Plant Physiol., 129: 1642-1650.
- Beligni, M.V., Lamattina, L. (1999a). Nitric oxide counteracts cytotoxic processes mediated by reactive oxygen species in plant tissues. Planta, 208: 337-344.
- Beligni, M.V., Lamattina, L. (1999b). Is nitric oxide toxic or protective? Trends Plant Sci., 4: 299-300.
- Beligni, M.V., Lamattina, L. (2000). Nitric oxide stimulates seed germination and de-etiolation, and inhibits hypocotyl elongation, three lightinducible responses in plants. Planta, 210: 215-221.
- Beligni, M.V., Lamattina, L. (2001). Nitric oxide in plants: the history is just beginning. Plant Cell Environ., 24: 267-278.
- Bethke, P.C., Badger, M.R., Jones, R.L. (2004). Apoplastic synthesis of nitric oxide by plant tissues. Plant Cell, 16: 332-341.
- Bethke, P.C., Libourel, I.G.L., Aoyama, N., Chung, Y., Still, D.W., Jones, R.L. (2007). The Arabidopsis thaliana aleurone layer responds to nitric oxide, gibberellin and abscisic acid and is sufficient and necessary for seed dormancy. Plant Physiol., 143: 1173-1188.
- Bethke, P.C., Libourel, I.G.L., Jones, R.L. (2006). Nitric oxide reduces seed dormancy in Arabidopsis. J. Exp. Bot., 57: 517-526.
- Bhattacharjee, S. (2005). Reactive oxygen species and oxidative burst: Roles in stress, senescence and signal transduction in plants. Current Sci., 89: 7-15.
- Bhattacharjee, S. (2009). Involvement of calcium and calmodulin in oxidative and temperature stress of Amaranthus lividus L. during early germination. J. Environ. Biol., 30(4): 557-562.
- Bolwell, G.P. (1999). Role of reactive oxygen species and NO in plant defence responses. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol., 2: 287-294.
- Bolwell, G.P., Bindschedler, L.V., Blee, K.A., Butt, V.S., Davies, D.R., Gardner, S.L., Gerrish, C., Minibayeva, F. (2002). The apoplastic oxidative burst in response to biotic stress in plants: a threecomponent system. Journal of Experimental Botany, 53: 1367-1376.
- Bolwell, G.P., Woftastek, P. (1997). Mechanism for the generation of reactive oxygen species in plant defense-Broad perspective. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol., 51: 347-349.
- Bouchard, J.N., Yamasaki, H. (2008). Heat stress stimulates nitric oxide production in symbiodinium microadriaticum: a possible linkage between nitric oxide and the coral bleaching phenomenon. Plant Cell Physiol., 49: 641-652.
- Bouchard, J.N., Yamasaki, H. (2009). Implication of nitric oxide in the heat-stress-induced cell death of the symbiotic alga Symbiodinium microadriaticum. Marine Biol., 156: 2209-2220.
- Bowler, C., Fluhr, R. (2000). The role of calcium and activated oxygen as signals for controlling cross-tolerance. Trends Plant Sci., 5: 241-246.
- Bray, E.A. (1993). Molecular responses to water deficit. Plant Physiol., 103: 1035-1040.
- Bright, J., Desikan, R., Hancock, J.T., Weir, I.S., Neill, S.J. (2006). ABA induced NO generation and stomatal closure in Arabidopsis are dependent on H2O2 synthesis. Plant J., 45: 113-122.
- Browse, J., Xin, Z.H. (2001). Temperature sensing and cold acclimation. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol., 4(3): 241-246.
- Caldwell, M.M., Ballare, C.L., Flint, S.D., Bjorn, L.O., Teramura, A.H., Kulandaivelu, G., Tevini, M. (2003). Terrestrial ecosystems, increased solar ultraviolet radiation and interactions with other climatic change factors. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2: 29-38.
- Casati, P., Walbot, V. (2003). Gene expression profiling in response to ultraviolet radiation in maize genotypes with varying flavonoid content. Plant Physiol., 132: 1739-175.
- Chaudhury, S., Panda, S.K. (2004). Induction of oxidative stress and ultrastructural changes in moss Taxithelium napalense (Schwaegr) Broth under lead (Pb) and arsenic (As) phytotoxicity. Current Sci.
- Chen, S.X., Schopfer, P. (1999). Hydroxylradical production in physiological reactions. A novel function of peroxidase. Eur. J. Biochem., 260: 726-735.
- Cheng, Y.L., Song, C.P. (2006). Hydrogen peroxide homeostasis and signalling in plant cells. Sci. China Ser. C Life Sci., 49(1): 1-11.
- Chinnusamy, V., Jagendorf, A., Jhu, J.K. (2005). Understanding and improving salt tolerance in plants. Crop Sci., 45: 437-448.
- Cho, U.H., Park, J.O. (2000). Mercury-induced oxidative stress in tomato seedlings. Plant Sci., 156: 1-9.
- Cho, U.H., Seo, N.H. (2005). Oxidative stress in Arabidopsis thaliana exposed to cadmium is due to hydrogen peroxide accumulation. Plant Sci., 168: 113-120.
- Corpas, F.J., Barroso, J.B., Carreras, A., Quiros, M., Leon, A., Romero-Puertas, M.C., Esteban, F.J., Valderrama, R., Palma, J.M., Sandalio, L.M., et al. (2004). Cellular and subcellular localization of endogenous nitric oxide in young and senescent pea plants. Plant Physiol., 136: 2722-2733.
- Crawford, N.M., Guo, F.Q. (2005). New insights into nitric oxide metabolism and regulatory functions. Trends Plant Sci., 10: 195-200.
- Cui, X., Zhang, Y., Chen, X., Jin, H., Wu, X. (2009). Effects of exogenous nitric oxide protects tomato plants under copper stress. Bioinformatics and Biomedical Engineering. 3rd International Conference, Beijing, pp. 1-7.
- Dangl, J.L., Jones, J.D.G. (2001). Plant pathogens and integrated defense responses to infection. Nature, 411: 826-833.
- Dat, J.F., Vandenabeele, S., Vranova, E., Van, M.M., Inze, D., VanBreusegem, F. (2000). Dual action of the active oxygen species during plant stress responses. Cell Mol. Life Sci., 57: 779-795.
- Delaunay, A., Pflieger, D., Barrault, M.B., Vinh, J., Toledano, M.B. (2002). A thiol peroxidase is an H2O2 receptor and redox-transducer in gene activation. Cell, 111: 471-481.
- Delledonne, M. (2005). NO news is good news for plants. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol., 8: 390-396.
- Delledonne, M., Zeier, J., Marocco, A., Lamb, C. (2001). Signal interactions between nitric nitric oxide and reactive oxygen intermediates in the plant hypersensitive disease resistance response. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA., 98: 13454-13459.
- Demirevska-Kepova, K., Simova-Stoilova, L., Stoyanova, Z., Holzer, R., Feller, U. (2004). Biochemical changes in barley plants after excessive supply of copper and manganese. Environ. Exp. Bot., 52: 253-266.
- Desikan, R., Mackerness, S., Hancock, J.T., Neill, S.J. (2001). Regulation of the Arabidopsis transcriptome by oxidative stress. Plant Physiol., 127: 159-172.
- Desikan, R., Neill, S.J., Hancock, J.T. (2000). Hydrogen peroxideinduced gene expression in Arabidopsis thaliana. Free Rad. Biol. Med., 5: 773-778.
- Desikan, R., Reynolds, A., Hancock, J.T., Neill, S.J. (1998). Harpin and hydrogen peroxide both initiate programmed cell death but have differential effects on gene expression in Arabidopsis suspension cultures. Biochem. J., 330: 115-120.
- Dietz, K.J., Baier, M., Kramer, U. (1999). Free radicals and reactive oxygen species as mediators of heavy metal toxicity in plants. In Prasad, M.N.V., Hagemeyer, J. (ed.), Heavy metal stress in plants from molecules to ecosystems. Berlin:Springer-Verlag, pp. 73-97.
- Doke, N. (1997). The oxidative burst: role in signal transduction and plant stress. In Scandalios, J.G. (ed.), Oxidative Stress and the Molecular Biology of Antioxidant Defenses, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York, pp. 785-813.
- Dong, Lu., Zhang, X., Jiang, J., An, G.Y., Zhang, L.R., Song, C.P. (2005). NO may function in the downstream of H2O2 in ABA-induced stomatal closure in Vicia faba L. Journal of Plant Physiology and Molecular Biology, 31: 62-70.
- Drazkiewicz, M., Skorzynska-Polit, E., Krupa, Z. (2004). Copper induced oxidative stress and antioxidant defence in Arabidopsis thaliana. BioMetals, 17: 379-387.
- Durner, J., Klessig, D.F. (1999). Nitric oxide as signal in plants. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol., 2: 369-374.
- Fan, H., Guo, S., Jiao, Y., Zhang, R., Li, J. (2007). Effects of exogenous nitric oxide on growth, active oxygen species metabolism, and photosynthetic characteristics in cucumber seedlings under NaCl stress. Front. Agri. China, 1: 308-314.
- Flowers, T.J., Yeo, A.R. (1995). Breeding for salinity resistance in crop plants-where next? Aust. J. Plant. Physiol., 22: 875-884.
- Foreman, J., Demidchik, V., Bothwell, J.H., Mylona, P., Miedema, H., Torres, M.A., Linstead, P., Costa, S., Brownlee, C., Jones, J.D. et al. (2003). Reactive oxygen species produced by NADPH oxidase regulate plant cell growth. Nature, 422: 442-446.
- Foyer, C.H., Lopez-Delgado, H., Dat, J.F., Scott, I.M. (1997). Hydrogen peroxide and glutathione-associated mechanisms of acclamatory stress tolerance and signalling. Physiol. Plant., 100: 241-254.
- Foyer, C.H., Noctor, G. (1999). Leaves in the dark see the light. Science, 284: 599-601.
- Foyer, C.H., Noctor, G. (2003). Redox sensing and signalling associated with reactive oxygen in chloroplasts, peroxisomes and mitochondria. Physiol. Plant., 119: 355-364.
- Garcia-Mata, C., Lamattina, L. (2001). Nitric oxide induces stomatal closure and enhances the adaptive plant responses against drought stress. Plant Physiol., 126: 1196-1204.
- Garcia-Mata, C., Lamattina, L. (2007). Abscisic acid (ABA) inhibits light-induced stomatal opening through calcium-and nitric oxide-mediated signalling pathways. Nitric Oxide, 17: 143-151.
- Garcia-Mata, C., Wang, J., Gajdanowicz, P., Gonzalez, W., Hills, A., Donald, N., Riedelsberger, J., Amtmann, A., Dreyer, I., Blatt, M.R. (2010). A minimal cysteine motif required to activate the SKOR K+ channel of Arabidopsis by the reactive oxygen species H2O2. J. Biol. Chem., 285(38): 29286-29294.
- Garreton, V., Carpinelli, J., Jordana, X., Holuigue, L. (2002). The as-1 promoter element is an oxidative stress-responsive element and salicylic acid activates it via oxidative species. Plant Physiol., 130: 1516-1526.
- Gechev, T., Gadjev, I., Van, B.F., Inze, D., Dukiandjiev, S., Toneva, V., Minkov, I. (2002). Hydrogen peroxide protects tobacco from oxidative stress by inducing a set of antioxidant enzymes. Cell Mol. Life Sci., 59(4): 708-714.
- Ghezzi, P., Bonetto, V. (2003). Redox proteomics: Identification of oxidatively, modified proteins. Proteomics, 3: 1145-1153.
- Ghoshroy, S., Freedman, K., Lartey, R., Citovsky, V. (1998). Inhibition of plant viral systemic infection by non-toxic concentration of cadmium. Plant J., 13: 591-602.
- Glazener, J.A., Orlandi, E.W., Baker, C.J. (1996). The active oxygen response of cell suspensions to incompatible bacteria is not sufficient to cause hypersensitive cell death. Plant Physiol., 110: 759-763.
- Gould, K.S., Lamotte, O., Klinguer, A., Pugin, A., Wendehenne, D. (2003). Nitric oxide production in tobacco leaf cells: a generalized stress response? Plant Cell Environ., 26: 1851-1862.
- Guan, L.M., Zhao, J., Scandalios, J.G. (2000). Ciselements and trans-factors that regulate expression of the maize Cat1 antioxidant gene in response to ABA and osmotic stress: H2O2 is the likely intermediary signalling molecule for the response. Plant J., 22: 87-95.
- Guo, F.Q., Crawford, N.M. (2005). Arabidopsis nitric oxide synthase1 is targeted to mitochondria and protects against oxidative damage and dark-induced senescence. Plant Cell, 17: 3436-3450.
- Guo, F.Q., Okamoto, M., Crawford, N.M. (2003). Identification of a plant nitric oxide synthase gene involved in hormonal signalling. Science, 302: 100-103.
- Guo, Y., Tian, Z., Yan, D., Zhang, J., Qin, P. (2009). Effects of nitric oxide on salt stress tolerance in Kosteletzkya virginica. Life Sciences J., 6: 67-75.
- Hall, J.L. (2002). Cellular mechanism for heavy metal detoxification and tolerance. Journal of Experimental Botany, 53(366): 1-11.
- Halliwell, B., Clement, M., Long, L. (2000). Hydrogen peroxide in the human body. FEBS Letters, 486: 10-13.
- Halliwell, B., Gutteridge, J. (1999). Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (3rd Edn), Oxford University Press, Oxford.
- Hao, G.P., Xing, Y., Zhang, J.H. (2008). Role of nitric oxide dependence on nitric oxide synthase-like activity in the water stress signalling of maize seedling. J. Integr. Plant Biol., 50: 435-442.
- Hasegawa, P.M., Bressan, R.A., Zhu, J.K., Bohnert, H.J. (2000). Plant cellular and molecular responses to high salinity. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol., Biol., 51: 463-499.
- He, J.M., Xu, H., She, X.P., Song, X.G., Zhao, W.M. (2005). The role and the interrelationship of hydrogen peroxide and nitric oxide in the UV-B-induced stomatal closure in broad bean. Funct. Plant Biol., 32: 237-247.
- Hess, D.T., Matsumoto, A., Kim, S.O., Marshall, H.E., Stamler, J.S. (2005). Protein S nitrosylation: purview and parameters. Nature Rev. Mol. Cell Biol., 6: 150-166.
- Hill, A.C., Bennett, J.H. (1970). Inhibition of apparent photosynthesis by nitrogen oxides. Atmos. Environ., 4: 341-348.
- Horvath, E., Pal, M., Szalai, G., Paldi, E., Janda, T. (2007). Exogenous 4-hydroxybenzoic acid and salicylic acid modulate the effect of short-term drought and freezing stress on wheat plants. Biol. Plant., 51: 480-487.
- Hu, K.D., Hu, L.Y., Li, Y.H., Zhang, F.Q., Zhang, H. (2007). Protective roles of nitric oxide on germination and antioxidant metabolism in wheat seeds under copper stress. Plant Growth Regul., 53: 173-183.
- Hu, X., Neill, S.J., Tang, Z., Cai, W. (2005). Nitric oxide mediates gravitropic bending in soybean roots. Plant Physiol., 137: 663-670.
- Huang, X., Von Rad, U., Durner, J. (2002). Nitric oxide induces transcriptional activation of the nitric oxide-tolerant alternative oxidase in Arabidopsis suspension cells. Planta, 215: 914-923.
- Huner, N.P.A., Oquist, G., Sarhan, F. (1998). Energy balance and acclimation to light and cold. Trends Plant Sci., 3(6): 224-230.
- Ichinose, Y., Andi, S., Doi, R., Tanaka, R., Taguchi, F., et al. (2001). Generation of hydrogen peroxide is not required for harpin-induced apoptotic cell death in tobacco BY-2 cell suspension cultures. Plant Physiol. Biochem., 39: 771-776.
- Ignarro, L.J. (2000). Nitric oxide, biology and pathobiology. Academic, San Diego.
- Jeffrey, S.R., Snyder, S.H. (1995). Nitric oxide: a neural messenger. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol., 11: 417-440.
- Jubany, M.T., Munne, B.S., Alegre, L. (2010). Redox regulation of water stress responses in field-grown plants. Role of hydrogen peroxide and ascorbate. Plant Physiol. Biochem., 48(5): 351-358.
- Karin, M., Liu, Z., Zandi, E. (1997). AP-1 function and regulation. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol., 9: 240-246.
- Karpinski, S., Reynolds, H., Karpinska, B., Wingsle, G., Creissen, G., Mullineaux, P. (1999). Systemic signalling and acclimation in response to excess excitation energy in Arabidopsis. Science, 284: 654-657.
- Karplus, P.A., Daniels, M.J., Herriot, J.R. (1991). Atomic structure of ferredoxin-NadpC reductase, prototype for a structurally novel flavoenzyme family. Sci., 251: 60-66.
- Khan, M.N., Siddiqui, M.H., Mohammad, F., Naeem, M., Khan, M.M.A. (2010). Calcium chloride and gibberellic acid protect Linseed (Linum usitatissimum L.) from NaCl stress by inducing antioxidative defence system and osmoprotectant accumulation. Acta Physiol. Plant., 32: 121-132.
- Kim, J.A., Agrawal, G.K., Rakwal, R., Han, K.S., Kim, K.N., Yun, Ch.H., Heu, S., Park, S.Y., Lee, Y.H., Jwa, N.S. (2003). Molecular cloning and mRNA expression analysis of a novel rice (Oryza sativa L.) MAPK kinase kinase, OsEDR1, an ortholog of Arabidopsis AtEDR1, reveal its role in defense/stress signalling pathways and development. Bioch. Biophys. Res. Commun., 300: 868-876.
- Kolbert, Z., Bartha, B., Erdei, L. (2005). Generation of nitric oxide in roots of Pisum sativum, Triticum aestivum and Petroselinum crispum plants under osmotic and drought stress. Acta Biol. Szegediensis, 49: 13-16.
- Kopyra, M., Gwozdz, E.A. (2003). Nitric oxide stimulates seed germination and counteracts the inhibitory effect of heavy metals and salinity on root growth of Lupinus luteus. Plant Physiol. Biochem., 41: 1011-1017.
- Kopyra, M., Gwozdz, E.A. (2004). The role of nitric oxide in plant growth regulation and responses to abiotic stresses. Acta Physiol. Plant, 26: 459-472.
- Kovtun, Y., Chiu, W.L., Tena, G., Sheen, J. (2000). Functional analysis of oxidative stress-activated mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade in plants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA., 97: 2940-2945.
- Krizek, D.T., Britz, S.J., Mirecki, R.M. (1998). Inhibitory effects of ambient levels of solar UV-A and UV-B radiation on growth of cv. New Red Fire lettuce. Physiol. Plant, 103: 1-7.
- Krupa, Z., Siedlecka, A., Maksymiec, W., Baszynski, T. (1993). In vivo response of photosynthetic apparatus of Phaseolus vulgaris L. to nickel toxicity. J. Plant Physiol., 142: 664-668.
- Kuzniak, E., Sklodowska, M. (1999). The effect of Botrytis cinerea infection on ascorbate glutathione cycle in tomato leaves. Plant Sci., 148: 69-76.
- Kwak, J.M., Mori, I.C., Pei, Z.M., Leonhardt, N., Torres, M.A., Dangl, J.L., Bloom, R.E., Bodde, S., Jones, J.D., Schroeder, J.I. (2003). NADPH oxidase AtrbohD and AtrbohF genes function in ROS-dependent ABA signalling in Arabidopsis. EMBO J., 22: 2623-2633.
- Lamattina, L., Garcia-Mata, C., Graziano, M., Pagnussat, G. (2003). Nitric oxide: the versatility of an extensive signal molecule. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol., 54: 109-136.
- Lamb, C., Dixon, R.A. (1997). The oxidative burst in plant disease resistance. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol., 48: 251-275.
- Leshem, Y. (2000). Nitric oxide in plants. Occurence, function and use. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Boston.
- Leshem, Y., Wills, R.B.H., Ku, V. (1998). Evidence for the function of the free radical gas-nitric oxide (NO) as an endogenous maturation and senescence regulating factor in higher plants. Plant Physiol. Biochem., 36: 825-833.
- Leshem, Y.Y., Haramaty, E. (1996). The characterization and contrasting effects of the nitric oxide free radical in vegetative stress and senescence of Pisum sativum Linn. foliage. J. Plant Physiol., 148: 258-263.
- Levine, A., Tenhaken, R., Dixon, R., Lamb, C. (1994). H2O2 from the oxidative burst orchestrates the plant hypersensitive disease resistance response. Cell, 79: 583-593.
- Li, F., Liu, P., Wang, T., Bian, P., Wu, Y., Wu, L., Yu, Z. (2010). The induction of bystander mutagenic effects in vivo by alpha-particle irradiation in whole Arabidopsis thaliana plants. Radiat. Res., 174(2): 228-237.
- Libourel, I.G.L., van Bodegom, P.M., Fricker, M.D., Ratcliffe, R.G. (2006). Nitrite reduces cytoplasmic acidosis under anoxia. Plant Physiol., 142: 1710-1717.
- Lin, C.H., Chen, L.M., Liu, Z.H. (2005). Rapid effect of copper on lignin biosynthesis in soybean roots. Plant Sci., 168: 855-861.
- Liszkay, A., Kenk, B., Schopfer, P. (2003). Evidence for the involvement of cell wall peroxidase in the generation of hydroxyl radicals mediating extension growth. Planta, 217: 658-667.
- Liu, Y., Wu, R., Wan, Q., Xie, G., Bi, Y. (2007). Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase plays a pivotal role in nitric oxide-involved defense against oxidative stress under salt stress in red kidney bean roots. Plant Cell Physiol., 48: 511-522.
- Lloyd-Jones, D.M., Bloch, K.D. (1996). The vascular biology of nitric oxide and its role in atherogenesis. Annu. Rev. Med., 47: 365-375
- Lopez-Carrion, A.I., Castellano, R., Rosales, M.A., Ruiz, J.M., Romero, L. (2008). Role of nitric oxide under saline stress: implications on proline metabolism. Biol. Plant, 52: 587-591.
- Lopez-delgado, H., Dat, J.F., Foyer, C.H., Scott, I.M. (1998). Induction of thermo tolerance in potato micro plants by acetylsalicylic acid and H2O2. J. Exp. Bot., 49: 713-720.
- Lopez-Huertas, E., Charlton, W.L., Johnson, B., Graham, I.A., Baker, A. (2000). Stress induces peroxisome biogenesis genes. EMBO Journal, 19: 6770-6777.
- Lum, H.K., Butt, Y.K.C., Lo, S.C.L. (2002). Hydrogen peroxide induces a rapid production of nitric oxide in mung bean (Phaseolus aureus). Nitric Oxide:Biology and Chemistry, 6: 205-213.
- Lumbreras, V., Vilela, B., Irar, S., Sole, M., Capellades, M., Valls, M., Coca, M., Pages, M. (2010). MAPK phosphatase MKP2 mediates disease responses in Arabidopsis and functionally interacts with MPK3 and MPK6. Plant J., DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2010.04297
- Mackerness, S., Butt, P.J., Jordan, B.R., Thomas, B.J. (1996). Amelioration of ultraviolet-Binduced down-regulation of mRNA levels for chloroplast proteins, by high irradiance, is mediated by photosynthesis. J. Plant Physiol., 148: 100-106.
- Mackerness, S.A.H., John, C.F., Jordan, B., Thomas, B. (2001). Early signalling components in ultraviolet-B responses: distinct roles for different reactive oxygen species and nitric oxide. FEBS Lett., 489: 237-242.
- Macnair, M.R., Tilstone, G.H., Smith, S.E. (2000). The genetics of metal tolerance and accumulation in higher plants In Terry, N., Banuelos, G. (ed.), Phytoremediation of contaminated soil and water. CRC Press LLC, pp. 235-250.
- Maksymiec, W., Baszynski, T. (1996). Chlorophyll fluorescence in primary leaves of excess Cutreated runner bean plants depends on their growth stages and the duration of Cuaction. J. Plant Physiol., 149: 196-200.
- Maksymiec, W. (2007). signalling responses in plants to heavy metal stress. Acta Physiol. Plant., 29: 177-187.
- Maksymiec, W., Krupa, Z. (2006b). The effects of short-term exposition to Cd, excess Cu ions and jasmonate on oxidative stress appearing in Arabidopsis thaliana. Environ. Exp. Bot., 57: 187-194.
- Maksymiec, W., Russa, R., Urbanik-Sypniewska, T., Baszynski, T. (1994). Effect of excess Cu on the photosynthetic apparatus of runner bean leaves treated at two different growth stages. Physiol. Plant., 91: 715-721.
- Mano, J. (2002). Early events in environmental stresses in plants. Induction mechanisms of oxidative stress (ed.), Oxidative stress in plants. London, Taylor and Francis, pp. 217-246.
- Marschner, H. (2002). Mineral nutrition of higher plants, 2nd edn. Academic, London.
- Mazza, C.A., Battista, D., Zima, A.M., Szwarcberg-Bracchitta, M., Giordano, C.V., Acevedo, A., Scopel, A.L., Ballare, C.L. (1999a). The effects of solar UV-B radiation on the growth and yield of barley are accompanied by increased DNA damage and antioxidant responses. Plant Cell Environ., 22: 61-70.
- Mazza, C.A., Zavala, J., Scopel, A.L., Ballare, C.L. (1999b). Perception of solar UVB radiation by phytophagous insects: behavioral responses and ecosystem implications. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA., 96: 980-985.
- Mittler, R. (2002). Oxidative stress, antioxidants and stress tolerance. Trends Plant Sci., 7: 405-410.
- Mittler, R., Herr, E.H., Orvar, B.L., Van Camp, W., Willekens, H., et al. (1999). Transgenic tobacco plants with reduced capability to detoxify reactive oxygen intermediates are hyperresponsive to pathogen infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA., 96: 14165-14170.
- Mittler, R., Vanderauwera, S., Gollery, M., Van Breusegem, F. (2004). Reactive oxygen gene network of plants. Trends Plant Sci., 9: 490-498.
- Molas, J. (2002). Changes of chloroplast ultrastructure and total chlorophyll concentration in cabbage leaves caused by excess of organic Ni (II) complexes. Environ. Exp. Bot., 47: 115-126.
- Moller, I.M. (2001). Plant mitochondria and oxidative stress: Electron transport, NADPH turnover and metabolism of reactive oxygen species. Annual Review of Plant Physiology and Plant Molecular Biology 52: 561-591.
- Moller, I.M., Sweetlove, L.J. (2010). ROS signalling-specificity is required. Trends Plant Sci., 7: 370-374.
- Moon, H., Lee, B., Choi, G., Shin, D., Prasad, T., et al. (2003). NDP kinase 2 interacts with two oxidative stress-activated MAPKs to regulate cellular redox state and enhances multiple stress tolerance in transgenic plants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA., 100: 358-363.
- Morita, S., Kaminaka, H., Masumura, T., Tanaka, K. (1999). Induction of rice cytosolic ascorbate peroxidase mRNA by oxidative stress; the involvement of hydrogen peroxide in oxidative stress signalling. Plant Cell Physiol., 40: 417-422.
- Mullineaux, P., Ball, L., Escobar, C., Karpinska, B., Creissen, G., Karpinski, S. (2000). Are diverse signalling pathways integrated in the regulation of aradopsis anti oxidant defence gene expression in response to excess excitation energy ? Philosophical Transation of Royal Society London 355: 1531-1540.
- Munne, B.S., Jubany, M., Alegre, L. (2001). Drought-induced senescence is characterized by a loss of antioxidant defences in chloroplasts. Plant Cell Environ., 24: 1319-1327.
- Nagalakshmi, N., Prasad, M.N.V. (2001). Responses of glutathione cycle enzymes and glutathione metabolism to copper stress in Scenedesmus bijugatus. Plant Sci., 160: 291-299.
- Neale, A.D., Blomstedt, C.K., Bronson, P., Le, T., Guthridge, K., Evans, J., Gaff, D.F., Hamill, J.D. (2000). The isolation of genes from the resurrection grass Sporolobus stapfianus which are induced during severe drought stress. Plant Cell Environ., 23: 265-277.
- Neill, S., Bright, J., Desikan, R., Hanckock, J., Harrison, J., Wilson, I. (2008). Nitric oxide evolution and perception. J. Exp. Bot., 59: 25-35.
- Neill, S., Desikan, R., Claarke, A., Hancock, J. (1999). H2O2 signalling in plant cells. In: Plant Responses to Environmental Stress (ed.) Bios Scientific Publishers, Oxford, pp. 59-64.
- Neill, S., Desikan, R., Hancock, J. (2002). Hydrogen peroxide signalling. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol., 5: 388-395.
- Neill, S., Desikan, R., Hancock, J.T. (2003). Nitric oxide signalling in plants. New Phytol., 159: 11-35.
- Neill, S.J., Desikan, D., Clarke, A., Hancock, J.T. (2002). Nitric oxide is a novel component of abscisic acid signalling in stomatal guard cells. Plant Physiology, 128: 13-16.
- Neill, S.J., Desikan, R., Clarke, A., Hurst, R.D., Hancock, J.T. (2002). Hydrogen peroxide and nitric oxide as signalling molecules in plants. J. Exp. Bot., 53: 1237-1247.
- Neto, A.D.A., Prisco, J.T., Eneas-Filho, J., Jand-Venes, R., Gomes-Filho, E. (2005). Hydrogen peroxide pre-treatment induces saltstress acclimation in maize plants. J. Plant Physiol., 162: 1114-1122.
- Nunoshiba, T., De Rojas-Walker, T., Wishnok, J.S., Tannenbaum, S.R., Demple, B. (1993). Activation by nitric oxide of an oxidativestress response that defends Escherichia coli against activated macrophages. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA., 90: 9993-9997.
- Orozco-Cardenas, M., McGurl, B., Ryan, C.A. (1993). Expression of an antisense prosystemin gene in tomato plants reduce the resistance towards Manduca sexta Larvae. Proc. NatI. Acad. Sci. USA., 90: 8273-8276.
- Orozco-Cardenas, M.L., Narvaez-Vasquez, J., Ryan, C.A. (2001). Hydrogen peroxide acts as a second messenger for the induction of defense genes in tomato plants in response to wounding, systemin, and methyl jasmonate. Plant Cell, 13: 179-191.
- Ouzounidou, G., Giamparova, M., Moustakas, M., Karataglis, S. (1995). Responses of maize (Zea mays L.) plants to copper stress. I. Growth Environ Exp. Bot., 35: 167-176.
- Overmyer, K., Brosche, M., Kangasjarvi, J. (2003). Reactive oxygen species and hormonal control of cell death. Trends Plant Sci., 8: 335-342.
- Palmieri, M.C., Sell, S., Huang, X., Scherf, M., Werner, T., Durner, J., Lindermayr, C. (2008). Nitric oxide-responsive genes and promoters in Arabidopsis thaliana: a bioinformatics approach. J. Exp. Bot., 59: 177-186.
- Panda, S.K. (2003). Heavy metal phytotoxicity induces oxidative stress moss Taxithelium sp. Curr. Sci., 84: 631-633.
- Panda, S.K., Chaudhury, I., khan, M.H. (2003a). Heavy metal induced lipid peroxidation and affects antioxidant in wheat leaves. Biol. Plant., 46: 289-294.
- Panda, S.K., Singa, L.B., Khan, M.H. (2003b). Does aluminium phytotoxicity induce oxidative stress in green gram (Vigna radiate)? Bulg. J. Plant Physiol., 29: 77-86.
- Papadakis, A.K., Roubelakis-Angelakis, K.A. (1999). The generation of active oxygen species differs in tobacco and grapevine mesophyll protoplasts. Plant Physiol., 121: 197-205.
- Paul, N.D., Gwynn-Jones, D. (2003). Ecological roles of solar UV radiation: towards an integrated approach. Trends Ecol. Evol., 18: 48-55.
- Pedroso, M.C., Durzan, D.J. (2000). Effect of different gravity environments on DNA fragmentation and cell death in Kalanchoe leaves. Annals Bot., 86: 983-994.
- Pedroso, M.C., Magalhaes, J.R., Durzan, D. (2000). Nitric oxide induces cell death in Taxus cells. Plant Sci., 157: 173-180.
- Perry, S.F., Spinelli O.E. (2010). Respiration in a changing environment. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol., 173: 20-25.
- Piqueras, A., Olmos, E., Martinez-Soalano, J.R., Hellin, E. (1999). Cd induced oxidative burst in tobacco BY2 cells: time-course subcellular location and antioxidant response. Free Radical Research, 31: 33-38.
- Polverari, A., Molesini, B., Pezzotti, M., Buonaurio, R., Marte, M., Delledonne, M. (2003). Nitric oxide-mediated transcriptional changes in Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact., 16: 1094-1105.
- Potikha, T.S., Collins, C.C., Johnson, D.I., Delmer, D.P., Levine, A. (1999). The involvement of hydrogen peroxide in the differentiation of secondary walls in cotton fibers. Plant Physiol., 119: 849-858.
- Prasad, K.V.S.K., Pardha Saradhi, P., Sharmila, P. (1999). Concerted action antioxidant enzyme and curtailed growth under Zinc toxicity in Brassica napus. Environ Exp. Bot., 42: 1-10.
- Prasad, T.K., Anderson, M.D., Martin, B.A., Stewart, C.R. (1994). Evidence for chilling induced oxidative stress in maize seedlings and a regulatory role of H2O2. Plant Cell, 6: 65-74.
- Przymusinski, R., Gwozdz, E.A. (1999). Heavy metal-induced polypeptides in lupin roots are similar to pathogenesisrelated proteins. J. Plant Physiol., 154: 703-708.
- Quartacci, M.F., Cosi, E., Navari-Izzo, F. (2001). Lipids and NADPH-dependent superoxide production in plasma membrane vesicles from roots of wheat grown under copper deficiency or excess. J. Exp. Bot., 52: 77-84.
- Ramamurthi, A., Lewis, R.S. (1997). Measurement and modeling of nitric oxide release rates for nitric oxide donors. Chem. Res. Toxicol., 10: 408-413.
- Rao, M.V., Paliyath, G., Ormrod, D.P. (1996). Ultraviolet-B-and ozone-induced biochemical changes in antioxidant enzymes of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Physiol., 110: 125-136.
- Rausch, T., Kirsch, M., Low, R., Lehr, A., Vierck, R., Zhigang, A. (1996). Salt stress response of higher plants: the role of proton pumps and Na+/H+antiporters. J. Plant Physiol., 148: 425-433.
- Ren, J., Dai, W., Xuan, Z., Yao, Y., Korpelainen, H., Li, C. (2007). The effect of drought and enhanced UV-B radiation on the growth and physiological traits of two contrasting poplar species. Forest Ecol. Manage., 239: 112-119.
- Rentel, M., Knight, M.R. (2004). Oxidative stressinduced calcium signalling in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol., 135: 1471-1479.
- Rockel, P., Strube, F., Rockel, A., Wildt, J., Kaiser, W.M. (2002). Regulation of nitric oxide (NO) production by plant nitrate reductase in vivo and in vitro. J. Exp. Bot., 53: 103-110.
- Romero-Puertas, M.C., McCarthy, I., sandalio, L.M., Palma, J.M., Corpas, F.J., Gomez, M., Del Rio, L.A. (1999). Cadmium toxicity and oxidative metabolism of pea leaves peroxisomes. Free Radical Research, 31: 25-31.
- Romero-Puertas, M.C., Perazzolli, M., Zago, E.D., Delledonne, M. (2004). Nitric oxide signalling functions in plant-pathogen interactions. Cellu. Microbiol., 6: 795-803.
- Rousseaux, M.C., Ballare, C.L., Scopel, A.L., Searles, P.S., Caldwell, M.M. (1998). Responses to solar ultraviolet-B radiation in a shrub-dominated natural ecosystem of Tierra del Fuego (southern Argentina). Oecologia, 116: 528-535.
- Ruan, H., Shen, W., Ye, M., Xu, L. (2002). Protective effects of nitric oxide on salt stressinduced oxidative damage to wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) leaves. Chin. Sci. Bull., 47: 677-681.
- Sakihama, Y., Murakami, S., Yamasaki, H. (2003). Involvement of nitric oxide in the mechanism for stomatal opening in Vicia faba leaves. Biol. Plant, 46: 117-119.
- Sandalio, L.M., Dalurzo, H.C., Gomez, M., Romero-Puertas, M.C., Del Rio, L.A. (2001). Cadmium-induced changes in the growth and oxidative metabolism of pea plants. J. Exp. Bot., 52: 2115-2126.
- Sang, J., Jiang, M., Lin, F., Xu, S., Zhang, A., Tan, M. (2008). Nitric oxide reduces hydrogen peroxide accumulation involved in water stressinduced subcellular anti-oxidant defense in maize plants. J. Integr. Plant Biol., 50: 231-243.
- Santa-Cruz, D.M., Pacienza, N.A., Polizio, A.H., Balestrasse, K.B., Tomaro, M.L., Yannarelli, G.G. (2010). Nitric oxide synthase-like dependent NO production enhances heme oxygenase up-regulation in ultraviolet-B-irradiated soybean plants. Phytochemistry, 71: 1700-1707.
- Scandalios, J.G., Guan, L., Polidoros, A.N. (1997). Catalases in plants: gene structure, properties, regulation, and expression. In: Scandalios, J.G. (ed.) Oxidative Stress and the Molecular Biology of Antioxidant Defenses, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York, pp. 343-398.
- Schmidt, H.W., Walter, U. (1994). NO at work. Cell, 78: 919-925.
- Schutzendubel, A., Schwanz, P., Teichmann, T., Gross, K., Langenfeld-Heyser, R., Goldbold, D.L., Polle, A. (2001). Cadmium induced changes in antioxidant systems, hydrogen peroxide content and differentiation in Scot pine roots. Plant Physiol., 127: 887-898.
- Sergi, M.B., Tana, J.M., Leonor, A. (2003). Enhanced photo and antioxidative protection and hydrogen peroxide accumulation in drought stresses cistus clusii and cistus albidus plants. Tree Physiology, 23: 1-12.
- Svo. FEBS Lett., 515: 75-78.


