Role of serum lactoferrin and calprotectin in the inflammatory response in patients with bone fractures
Автор: Amshawee A. M., Hussain M. A., Khafel M. A. L., Alhusseini N. B., Al-fahham A. A.
Журнал: Гений ортопедии @geniy-ortopedii
Рубрика: Оригинальные статьи
Статья в выпуске: 1 т.31, 2025 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Introduction Elevated concentrations of serum calprotectin and lactoferrin were observed to make prediction about microvascular changes in patients with bone fractures.The aim of the present study was to assess the diagnostic value of serum calprotectin and lactoferrin in the development of inflammatory response in patients with bone fractures.Material and Methods Seventy patients were included in the study between October 2021 and January 2022; of these, 40 had bone fractures and 30 were healthy participants (control group). Calprotectin and lactoferrin were measured by immunosorbent assay.Results 12 patients (30 %) had open bone fractures while 28 (70 %) had closed bone fractures. The study revealed that levels of serum calprotectin significantly increased in patients with bone fractures as compared to healthy subjects, while lactoferrin exhibited a borderline but not significant increase (P = 0.06). Patients with open bone fractures had higher levels of serum calprotectin compared to those with closed fractures (P = 0.05). The correlation matrix exhibited that there was a strong positive correlation between calprotectin and lactoferrin in patients with bone fractures.Discussion Calprotectin is classified as a potent pro-inflammatory marker that has been noted to be elevated in chronic inflammation such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), atherosclerotic lesions, different types of arthritis, and immunological rejection. The present study may only confirm an increase in calprotectin in patients with bone fractures. Recently published studies indicate the potential new role of calprotectin in bone healing and fracture risk.Conclusion High serum calprotectin and lactoferrin indicate a strong inflammatory status in bone fracture patients, especially in those with open fractures.
Total knee replacement, personalized alignment, kinematic alignment, mechanical alignment, knee joint arthrosis
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/142243881
IDR: 142243881 | УДК: 616.71-001.5-002-072.5:612.398.12 | DOI: 10.18019/1028-4427-2025-31-1-6-11
Текст научной статьи Role of serum lactoferrin and calprotectin in the inflammatory response in patients with bone fractures
Bone fractures are of both clinical and public health major concern. The complexity entails a dependence of a variety and an array of etiologies. Bone fractures manifest as a range in types that are classified either as open or closed fractures. An open fracture is the one in which there is an open wound or break through to the skin near the site of a broken bone; it has higher risk potential for infection while a closed fracture does not break through to the skin.
Healing of bone fractures is biological and can be influenced by several complexities, one of which is the presence of an adaptive immune system. D. Toben et al. stated that without an adaptive immune system the healing of a fracture would be accelerated in an enormous manner, thus providing a potential role for immune modulation in clinical treatments for fractures [1]. Consistent with the finding above, more evidence was also reported that though the inflammatory response is essential to the initial stages of bone healing, too much inflammation inhibits recovery [2]. Dendritic cells and macrophages are immune effector cells expressing a variety of membrane-bound receptors for self-molecules such as calprotectin. In this context, calprotectin is hypothesized to act as an endogenous differentiation biomarker for phagocytes as well as an extrinsic protein complex, hence classified as a DAMP (danger-associated molecular pattern). Serum levels of calprotectin have been shown to be elevated in patients with skeletal damage that reflects vascular damage as well. Bone fractures do indeed elevate serum calprotectin. The serum calprotectin level is dramatically elevated in early OA stages, with a reverse relationship with disease severity [3]. It may thus be proposed as a promising blood-based marker for early knee osteoarthritis (OA).
More recent studies show the potential role that calprotectin might play in bone healing and fracture risk. Special attention is drawn to the modulation of the inflammatory response during bone healing, thereby indicating possible key players expressed during the process of healing, notably discussed being inflammatory cytokines and proteins, like calprotectin [4]. Lactoferrin (Lf) is found in highest concentration in human and mammalian milk, and in smaller amounts in other exocrine fluids (i.e. salivary secretions, semen, tears, gastrointestinal secretions, vaginal secretions) as well. Lf is also synthesized by the hematopoietic tissue of the bone marrow and is present within neutrophil granules [5–6]. It contributes to a variety of physiological processes in vivo . Consequently, lactoferrin was capable of decreasing oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis processes, which are the basic pathways involved in the bone inflammatory disorders of different etiologies [6].
The purpose of the present study was to assess the diagnostic value of serum calprotectin and lactoferrin in the development of inflammatory response in patients with bone fracture.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The total number of participants in this research was seventy subjects, forty individuals with bone fractures and thirty apparently healthy control group subjects. It was conducted at the Endocrine Center in Al-Sadr Medical City in Al-Najaf province, Iraq, from June 2023 to February 2024. It was prepared through a questionnaire tool for recording demographic information (age, gender) and type of fracture (open or closed fracture). A 10-ml blood sampling after fasting for 12 hours was done and kept in deep freeze (–20 °C) till laboratory measurements were applied and then assayed for calprotectin and lactoferrin by immunosorbent assay kits after separation of serum. Blood samples were taken within 24–28 hours after fracture. Strictly according to manufacturers’ instructions (Calprotectin test, Nova Tec, Germany), this is a monoclonal antibody test coated with calibrator directed against polyclonal antibody against calprotectin. Optical density mean value was read in duplicates at 450 nm. The control curve was constructed at different concentrations of calprotectin. Data were analyzed using Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS) software, version 25. Analysis was done by descriptive statistics (percentage and frequency) and inferential statistics (t-test and Chi-squared test). Pearson Correlation Coefficient (r) is appropriate for measuring the relationship between quantitative variables.
RESULTS
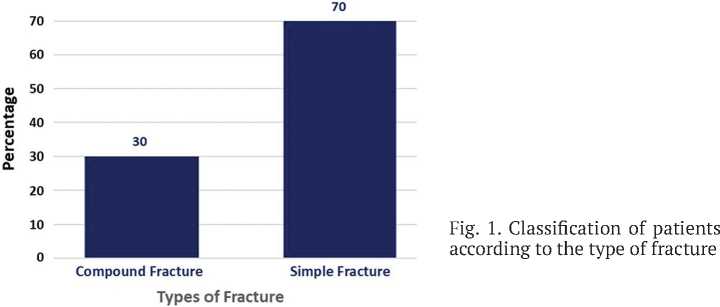
The current study assessed the demographic characteristics of both patients and control groups. There was no significant variation ( P > 0.05) in age and gender between patients and healthy groups (Table 1). On the other hand, 12 patients (30 %) had open fractures while 28 (70 %) had closed bone fractures (Fig. 1).
Table 1
Demographic characteristics of patients and control groups
|
Indicators |
Patients ( No = 40) |
Control ( No = 30) |
Chi Square |
P value (Sig.) |
|||
|
Freq. |
Percent |
Freq. |
Percent |
||||
|
Age/Years |
20–24 |
13 |
32.5 |
7 |
35.0 |
0.05 |
0.97 (NS) |
|
25–29 |
10 |
25.0 |
5 |
25.0 |
|||
|
30–34 |
17 |
42.5 |
8 |
40.0 |
|||
|
Gender |
Male |
23 |
57.5 |
8 |
40.0 |
1.64 |
0.20 (NS) |
|
Female |
17 |
42.5 |
12 |
60.0 |
|||
Notes : NS — Non-significant at P value > 0.05
Serum levels of calprotectin and lactoferrin were evaluated in patients and control groups. The results exhibited a significant increase ( P < 0.05 in calprotectin (µg/dl) in the patients compared to the healthy group (Table 2). The same table shows that there was no significant difference ( P < 0.06) in lactoferrin (µg/dl) in the patients compared to the control group.
Table 2
Differences in calprotectin and lactoferrin between patients and healthy groups
|
Indicators |
Patients ( No = 40) |
Control ( No = 30) |
Independent T Test |
P value (Sig.) |
||
|
Mean |
SD |
Mean |
SD |
|||
|
Calprotectin, µg/dl |
68.22 |
22.37 |
35.88 |
10.22 |
8.09 |
0.000 (HS) |
|
Lactoferrin, µg/dl |
10 |
25.0 |
5 |
25.0 |
1.93 |
0.06 (NS) |
Notes : SD — Standard Deviation; HS — High Significant at P value < 0.01; NS — No-Significant at P value > 0.05.
The inflammatory response in terms of calprotectin and lactoferrin between the patients with open and those with closed fractures was assessed. The results exhibited a significant increase ( P < 0.05)in calprotectin (µg/dl) in patients with open fractures compared to those with closed fractures (Table 3). The same table revealed that there was no significant difference ( P < 0.06) in lactoferrin (µg/dl) in patients with open and closed fractures. The correlation test was achieved with the Pearson correlation coefficient (r) after assessing the normality of data. There was a high positive significant correlation ( P < 0.01) between serum lactoferrin and calprotectin (r = 0.522), as shown in Figure 2.
Table 3
Differences in calprotectin and lactoferrin between patients with compound and simple fractures
|
Indicators |
Compound Fracture ( No = 12) |
Simple Fracture ( No = 28) |
Independent T Test |
P value (Sig.) |
||
|
Mean |
SD |
Mean |
SD |
|||
|
Calprotectin, µg/dl |
70.41 |
6.33 |
66.03 |
5.13 |
2.05 |
0.05 (S) |
|
Lactoferrin, µg/dl |
9.78 |
4.55 |
8.01 |
1.29 |
1.32 |
0.21 (NS) |
Notes : SD — Standard Deviation; NS — No-Significant at P value; S — Significant at P value < 0.05.
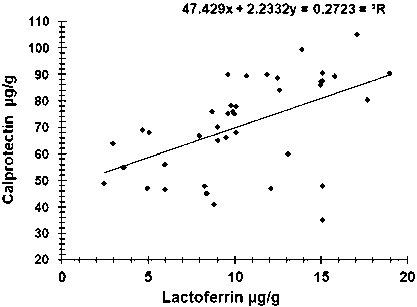
Fig. 2. Scatter plot and regression equation between calprotectin and lactoferrin
DISCUSSION
Recently published studies indicate the potential new role of calprotectin in bone healing and fracture risk. It was noted that during modulation of the inflammatory response in bone healing process, the indicators of inflammatory cytokines and proteins are critical and the role played by calprotectin seems fundamental [4]. The same view is shared by a recent study that went even further to explain how aging and inflammation change behavior of stem cells and herefore impact bone healing hence the high levels of calprotectin could also be a reason for retarded bone repair [7]. It was recommended that inflammatory biomarkers, such as calprotectin, may be used as predictors for complications in the healing process in long bone fracture non-union, delayed union, mal-union. It can have an impact on making clinical decisions. In other words, this relationship therefore infers that monitoring the levels of calprotectin would show how the status of fracture healing is going on [8].
The particular mechanisms through which calprotectin may influence bone health are still under study, along with the studies on how mechanical loading and biological factors regulate bone remodeling [9]. In this sense, inflammatory biomarkers like calprotectin might modulate bone remodeling as indicated by the relatedness to some biochemical bone turnover markers [10]. One integration into the future may be the results from studies on genetic and clinical determinants of fracture risk. It is emphasized that fracture risk assessment is complex and may one day include inflammatory biomarkers, such as calprotectin. Integration such as this would enhance the model’s precision in calculating an individual’s probability of fracturing, which is of particular value in high prevalence populations with systemic inflammation [10].
In the present study, the levels of lactoferrin were not significantly different compared to the controls, though the p -value in question was at the borderline level (< 0.06). This may be because lactoferrin has been found to influence several cellular processes in relation to bone healing. Thus, it is underlined that coupling angiogenesis with osteogenesis during repair of bone fractures is crucial. This is an important step toward supplying the healing tissue with blood; where lactoferrin may have a role through effects on inflammatory processes and cellular differentiation. First of all, lactoferrin potentially affects this linkage because of the promotion of new types of floras or blood vessel growth shapes and bone [11]. Secondly, where one of the contributing factors is better understood, lactoferrin is set to play a role as well since macrophages are understood to contribute to bone healing by enhancing osteoblastic differentiation and playing a critical role in endochondral ossification. Such immunomodulatory effects by lactoferrin would reasonably enhance activity by macrophages to allow more effective bone regeneration. Indeed, lactoferrin may not act alone but may interact with other bio-molecules during bone healing [12–13]. For instance, materials that promote bone regeneration could be developed to work in synergy with the properties of lactoferrin for better healing [14].
A study on cell therapy of delayed unions leaves open the possibility that appropriate combination of lactoferrin with cellular therapies may also allow improvement to be obtained where nonunion fractures are found [15].
The other is bone healing under hypoxic conditions. Results from previous studies proved that hypoxic mesenchymal stem cell exosomes could drive the healing of fractures. There might be possible complicated interactions between lactoferrin and exosomal miR-126 transfer in future studies, especially to explicate how lactoferrin may enhance efficacy of stem cell therapies during fracture healing. Lactoferrin acts not only in antimicrobial protection but in provision of homeostasis related to intractable inflammation and iron metabolism — two pathways directly pertinent to situations of bone healing [16]. An informative review paper clearly described the structure and functions of lactoferrin that determine its important role in control over inflammation and maintenance of iron homeostasis, essential preconditions for optimal healing of fractures [17].
Previous studies indicated that patients suffering from conditions such as infections have high elastase levels, which degrade lactoferrin; hence the doses for individuals with severe conditions could be heightened. The present study revealed that there was a significant positive correlation between lactoferrin and calprotectin, several researchers have noted the positivity between lactoferrin and calprotectin in different inflammatory conditions. Thus, both markers showed a significant positive relationship with endoscopic scores among Crohn’s patients (calprotectin, p = 0.0001; lactoferrin, p = 0.038), indicating their importance in evaluating disease activity [18].
Another study reported a high correlation between fecal levels of lactoferrin and calprotectin, with r² = 0.74; thus, the two biomarkers may act as complementary indicators of inflammation [19]. Lactoferrin and calprotectin were also valid to differentiate various disease states for mucosal healing independent of clinical symptoms in patients with ulcerative colitis by using fecal biomarkers [20]. This means these two biomarkers both have perspective as noninvasive indices in monitoring inflammatory activity.
CONCLUSION
It was concluded that high serum calprotectin and lactoferrin indicated a strong inflammatory status in patients with bone fractures. Patients with open fractures exhibited higher inflammatory response in terms of calprotectin compared to patients with closed fractures.
Conflict of interests None.
Funding None.
Ethical approval This case-control study was approved by the medical ethics committee at the Faculty of Medicine/Kufa University (Reference#: MEC-16 on June 21, 2022).
Список литературы Role of serum lactoferrin and calprotectin in the inflammatory response in patients with bone fractures
- Toben D, Schroeder I, El Khassawna T, et al. Fracture healing is accelerated in the absence of the adaptive immune system. J Bone Miner Res. 2011;26(1):113-124. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.185.
- Rupp M, Biehl C, Budak M, et al. Diaphyseal long bone nonunions - types, aetiology, economics, and treatment recommendations. Int Orthop. 2018;42(2):247-258. doi: 10.1007/s00264-017-3734-5.
- Safa A, Bagherifard A, Hadi Al-Baseesee H, et al. Serum Calprotectin as a Blood-Based Biomarker for Monitoring Knee Osteoarthritis at Early but Not Late Stages. Cartilage. 2021;13(1_suppl):1566S-1571S. doi: 10.1177/1947603520961161.
- Maruyama M, Rhee C, Utsunomiya T, et al. Modulation of the Inflammatory Response and Bone Healing. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020;11:386. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2020.00386.
- Cao X, Ren Y, Lu Q, et al. Lactoferrin: A glycoprotein that plays an active role in human health. Front Nutr. 2023;9:1018336. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.1018336.
- Kell DB, Heyden EL, Pretorius E. The Biology of Lactoferrin, an Iron-Binding Protein That Can Help Defend Against Viruses and Bacteria. Front Immunol. 2020;11:1221. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01221.
- Gibon E, Lu L, Goodman SB. Aging, inflammation, stem cells, and bone healing. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2016;7:44. doi: 10.1186/s13287-016-0300-9.
- Ekegren CL, Edwards ER, de Steiger R, Gabbe BJ. Incidence, Costs and Predictors of Non-Union, Delayed Union and Mal-Union Following Long Bone Fracture. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2018;15(12):2845. doi: 10.3390/ijerph15122845.
- Wang L, You X, Zhang L, et al. Mechanical regulation of bone remodeling. Bone Res. 2022;10(1):16. doi: 10.1038/s41413-022-00190-4.
- Trajanoska K, Morris JA, Oei L, et al. Assessment of the genetic and clinical determinants of fracture risk: genome wide association and mendelian randomisation study. BMJ. 2018;362:k3225. doi: 10.1136/bmj.k3225.
- Kusumbe AP, Ramasamy SK, Adams RH. Coupling of angiogenesis and osteogenesis by a specific vessel subtype in bone. Nature. 2014;507(7492):323-328. doi: 10.1038/nature13145.
- Schlundt C, El Khassawna T, Serra A, et al. Macrophages in bone fracture healing: Their essential role in endochondral ossification. Bone. 2018;106:78-89. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2015.10.019.
- Vi L, Baht GS, Whetstone H, et al. Macrophages promote osteoblastic differentiation in-vivo: implications in fracture repair and bone homeostasis. J Bone Miner Res. 2015;30(6):1090-1102. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.2422.
- Jeong J, Kim JH, Shim JH, et al. Bioactive calcium phosphate materials and applications in bone regeneration. Biomater Res. 2019;23:4. doi: 10.1186/s40824-018-0149-3.
- Gomez-Barrena E, Rosset P, Lozano D, et al. Bone fracture healing: cell therapy in delayed unions and nonunions. Bone. 2015;70:93-101. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2014.07.033.
- Liu W, Li L, Rong Y, et al. Hypoxic mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes promote bone fracture healing by the transfer of miR-126. Acta Biomater. 2020;103:196-212. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2019.12.020.
- Wang B, Timilsena YP, Blanch E, Adhikari B. Lactoferrin: Structure, function, denaturation and digestion. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2019;59(4):580-596. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2017.1381583.
- Novak G, Parker C, Pai R, et al. Histologic scoring indices for evaluation of disease activity in Crohn's disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017;7(7):CD012351. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012351.pub2.
- Yamamoto T, Shiraki M, Bamba T, et al. Fecal calprotectin and lactoferrin as predictors of relapse in patients with quiescent ulcerative colitis during maintenance therapy. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2014;29(4):485-491. doi: 10.1007/s00384-013-1817-3.
- Yamamoto T, Shiraki M, Bamba T, et al. Faecal calprotectin and lactoferrin as markers for monitoring disease activity and predicting clinical recurrence in patients with Crohn's disease after ileocolonic resection: A prospective pilot study. United European Gastroenterol J. 2013;1(5):368-374. doi: 10.1177/2050640613501818.


