Router-based Content-aware Data Redirection for Future CDN Systems
Автор: Janaka L. Wijekoon, Erwin H. Harahap, Shinichi Ishida, Rajitha L. Tennekoon, Hiroaki Nishi
Журнал: International Journal of Computer Network and Information Security(IJCNIS) @ijcnis
Статья в выпуске: 7 vol.6, 2014 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Delivery of data-enriched applications has become a top priority on the Internet, and Internet users are demanding faster and higher-quality services. Cater such requirements, Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) were introduced. However, the growth rate of information on the Internet requires infrastructural modifications to keep the consistency while maintaining quality of the Internet services. To this end, the Service-oriented Router is introduced to provide content based services by shifting the current Internet infrastructure to information-based open innovation platform. In this study, initially we provide implementation notes of a software-designed SoR. Then we propose a new method of CDN Request Redirection (RR) (SoR-based RR), which is designed to redirect packets based on the content of packets and the status of content servers using an SoR as an edge router of a CDN. Furthermore, we present the design and implementation of a prototype to realize the SoR-based RR in a testing network. By analyzing the result of the prototype implementation, we show that the SoR-based RR can enhance the both client experience and faster adaptations to the server changes in CDN environments.
Service-oriented Router, Network Simulation, Data Analysis, Content Delivery Networking, Request Redirection
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/15011316
IDR: 15011316
Текст научной статьи Router-based Content-aware Data Redirection for Future CDN Systems
Published Online June 2014 in MECS DOI: 10.5815/ijcnis.2014.07.01
Communication technologies have become significantly advanced in the past few decades, with new technologies being invented to achieve efficient communication. In addition, people are more interested in sharing knowledge and information for various purposes. Innovations in information sharing are continuously accelerated to cater user needs in such environments. These motives have encouraged the construction of sophisticated environments for effective communication and information delivery.
Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) are implemented to achieve low-latency content delivery such as; data streaming, on-line gaming and e-commerce web accesses by placing content servers near the customer [1]. RR techniques are used in CDNs to redirect client requests to the nearest surrogate server [1-7]. Therefore, it is important to maintain a better RR method that can find the nearest server for a particular user. Besides, a RR method can also achieve efficient server load balancing [6, 10]. DNS redirection and URL rewriting [1] are the most commonly used CDN redirection methods in the current CDNs.
Several studies have been conducted on the impact of content delivery on networks in the past few decades. Before the adoption of worldwide server caching, such as CDN, some early research on the effectiveness of interior web caching were performed by Gadde et al [8]. In addition, recent studies [9, 10] indicate the DNS-based method can significantly reduce the download latency. Top-level CDN providers, such as Akamai [3, 4] and CenturyLink [5], use DNS-based RR to redirect client requests to the nearest surrogate server, or sometimes known as a redirector or an edge server. However, all those studies use multi tire name servers in order to maintain the consistency of changes of surrogate servers [3, 6, 11].
The DNS-based redirection use small Time to Live (TTL) values at the clients in order to adapt the changes occurs on the CDN infrastructure [1, 3, 4]. Consequently, small TTL values lead the client to access the local name server frequently to get an up to date infrastructural changes [1, 11 - 13]. Furthermore, name server resolving process increases the client waiting time due to communication between local name server and authoritative name servers to find the CDN surrogate servers’ IP addresses. Poese et al. [6] proposed a content aware traffic engineering design that give some hints about the ISP collaborated method of redirecting packets based on both status of the servers and the network. But that study also was not able to provide a solution to the clients regarding the latency factors of connection initiation and lags of the connection due to the DNS resolving process and small TTL values. Therefore, we argue that the usage of multi tire name servers and small Time to Live (TTL) values on DNS-based RR considerably degrades the connection initiation process.
We argue that, if an edge router of the network can identify the server locations and redirects client request to the servers regardless of the IP address of the final destination, we can utilize data redirection process to achieve faster connection initiation and faster adaptation to the server changes in a CDN. To this end, this study proposes a redirection mechanism which is redirecting
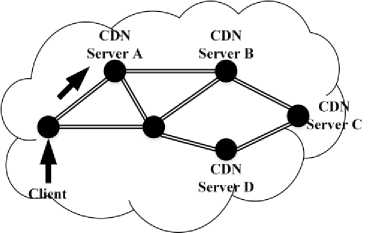
Fig. 1. SoR-based RR Overview packets based on the content of the packet by using an Service-oriented Router [14, 15, 16] as an edge router of a network. Furthermore, we confer that the basic functions of the SoR such as; DPI and content based data redirection, introduce the ideal test bed to implement a prototype for an edge router based date redirection. Fig. 1 illustrates the basic concept of SoR-based RR. The client sends the data stream to the SoR which is placed at the edge of network and SoR selects the proper surrogate; A, B, C or D, based on the content of the packet and the status of the server and, redirects the packet stream to the selected server. In addition, an SoR redirects packets by performing server load balancing if an SoR has routing records of more than one surrogate server.
The paper is arranged as follow. A review of the DNSbased RR is provided in the Section 2. Section 3 describes the motivation of this study. Section 4 describes the software implementation of the SoR followed by the detailed explanation of prototype implementation of the SoR-based RR in Section 5. Test cases designs, implementations and the test results are presented in the Section 6. Section 7 is used to discuss the effectiveness of the SoR for the CDN redirection process and how the SoR-based RR is able to overcome the limitations of existing methods. Section 8 concludes the paper with tentative future implementations.
-
II. background study
The Domain Name System (DNS) is a distributed database of records (name-to-address mapping) cached at intermediate name servers [17]. Each record has a time-to-live (TTL) value that indicates how long it will be cached. Generally TTL values are set to one day [17]. The original operation of the DNS is to resolve a Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) to its corresponding IP address [11, 17].
However, in CDN infrastructures, once the DNS is used to resolve the nearest surrogate server’s IP for a particular end-user, the DNS cache becomes a significant obstacle to providing real-time control of the CDN. The name resolution cache must be disabled by setting TTL values to zero in order to obtain real-time control in
CDNs [1]. Small TTL values allow fine-grained load balancing and rapid response to changes in the server or network load. Nonetheless, small TTL values force clients to contact the authoritative name server for every name resolution request. However, this phenomenon increases access latency for particular content.
To understand the behavior of the DNS in a real network, we captured and analyzed the traffic of a major Internet backbone network for academics in Japan. The most noticeable fact was that the occupation ratio of the DNS, which was occupied more than 25% of traffic during the captured time. Though we cannot conclude that the measured DNS traffic occupation was entirely from CDN networks, this clearly highlights that the DNS traffic is high in the Internet data exchange.
On the other hand, recent studies [6, 18, 19] have been done to research about the ISP involvement of the DNS redirection. Authors have theorized that the ISP-CDN and DNS collaboration make the ideal network infrastructure for faster data delivery on the Internet. Those studies suggested of placing low level name servers at the ISP. Then redirect clients to the nearest server based on the status of both ISP’s network the status of the content servers. However, this method also requires the clients to frequently contact local name server in order to get the status of the CDN upon the expiration of TTL values [1, 13, 19]. Besides, Anees et al. [1] confirmed that the DNSbased server redirection must be based on the name server’s location, not on the client’s location. Therefore, the response delay associated with connection initiations and request redirections depends on the number of hops to the authoritative name server. That study pointed out that aforementioned factors are significant factors in data redirection and client response time.
-
III. motivation
Список литературы Router-based Content-aware Data Redirection for Future CDN Systems
- Shaikh, A., Tewari, R., Agrawal, M.: On the effectiveness of dns-based server selection. In: INFOCOM 2001. Twentieth Annual Joint Conference of the IEEE Computer and Communications Societies, vol. 3, pp. 1801–1810.
- Stamos, K., Pallis, G., Vakali, A., Katsaros, D., Sidiropoulos, A., Manolopoulos, Y.: Cdnsim: A simulation tool for content distribution networks. In: ACM Trans. Model. Comput. Simul, vol. 20, p. 40 (2010).
- Nygren, E., Sitaraman, R.K., Sun, J.: The akamai network: a platform for high-performance internet applications. SIGOPS Oper 44(3), 2–19 (2010).
- Akamai Technologies: Fast Internet Content Delivery with FreeFlow. http://research.microsoft.com/en-us/um/people/ratul/akamai/freeflow.pdf.
- CenturyLink, I.: CenturyLink Technology Solutions. http://www.centurylinktechnology.com/
- Poese, I., Frank, B., Smaragdakis, G., Uhlig, S., Feldmann, A., Maggs, B.: Enabling content-aware traffic engineering. SIGCOMM Comput. Commun. Rev. 42(5) (2012).
- Cohen, E., Kaplan, H.: Proactive caching of dns records: Addressing a performance bottleneck. In: IEEE INFOCOM (2000).
- Gadde, S., Chase, J., Rabinovich, M.: Web caching and content distribution: A view from the interior. Computer Communication 24(2), 222–231 (2001).
- Koletsou, M., Voelker, G.: The medusa proxy: A tool for exploring user-perceived web performance. In: WCW, Boston, (2001).
- B. Frank, I. Poese, G. Smaragdakis, A. Feldmann, B. Maggs, S. Uhlig, V. Aggarwal, F. Schneider, "Collaboration Opportunities for Content Delivery and Network Infrastructures", in H. Haddadi, O. Bonaventure (Eds.), Recent Advances in Networking, (2013), pp. 305-377.
- Mao, Z., Cranor, C., Douglis, F., Rabinovich, M., Spatscheck, O., Wang, J.: A precise and efficient evaluation of the proximity between web clients and their local dns servers. In: USENIX Annu. Tech. Conf., Monterrey, pp. 229–242 (2002).
- Ager, B., M¨uhlbauer, W., Smaragdakis, G., Uhlig, S.: Comparing dns resolvers in the wild. In: Internet Measurement Conference, pp. 15–21 (2013).
- Kangasharju, J., Ross, K.W., Roberts, J.W.: Performance evaluation of redirection schemes in content distribution networks. Computer Communications 24(2), 207–214 (2001).
- Nishi, H: Service-oriented Backbone Router for Future Internet. http: //www.prime-pco.com/4thJEUsymposium/pdf/s1/s1_nishi.pdf.
- Inoue, K., Akashi, D., Koibuchi, M., Kawashima, H., Nish, H.: Semantic router using data stream to enrich services. In: International Conference on Future Internet Technologies (CFI08) (2008).
- Nishi, H., Kawashima, H., Koibuchi, M.: Information-based Open Innovation Platform. http://openinter.net/.
- Mockapetris, P.: RFC 1035, DOMAIN NAMES - IMPLEMENTATION AND SPECIFICATION. http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc1035.txt.
- Frank, B., Poese, I., an Georgios Smaragdakis, Y.L., an Bruce M. Maggs, A.F., Rake, J., Uhlig, S., Weber, R.: Pushing cdn-isp collaboration to the limit. Computer Communication Review 43(3), 34–44 (2013).
- Gummadi, K., Saroiu, S., Gribble, S.: A precise and efficient evaluation of the proximity between web clients and their local dns servers. In: USENIX Annu. Tech. Conf., Monterrey, pp. 229–242 (2002).
- Cohen, E., Kaplan, H.: Proactive caching of dns records: Addressing a performance bottleneck. In: IEEE INFOCOM (2000).
- Cohen, E., Kaplan, H.: Prefetching the means for document transfer: A new approach for reducing web latency. In: Symposium on Applications and the Internet (SAINT-2001) (2001).
- Gummadi, K., Saroiu, S., Gribble, S.: A precise and efficient evaluation of the proximity between web clients and their local dns servers. In: USENIX Annu. Tech. Conf., Monterrey, pp. 229–242 (2002).
- Nagatomi, Y., Koibuchi, M., Kawashima, H., Inoue, K., Nishi, H.: A regular expression processor embedded in service-friendly router for future internet. In: Parallel Processing Workshops (ICPPW), 2010 39th International Conference On, pp. 82–88 (2010).
- Takagiwa, K., Kubo, R., Ishida, S., Inoue, K., Nishi, H.: Feasibility study of service-oriented architecture for smart grid communications. In: Industrial Electronics (ISIE), 2013 IEEE International Symposium, pp. 1–7 (2013).
- Yamaki, H., Nishi, H.: An improved cache machanism for a cache-based network processor. In: The 2012 International Conference on Parallel and Distributed Processing Techniques and Applications (2012).
- Hogawa, D., Ishida, S., Nishi, H.: Hardware parallel decoder for of compressed http traffic on service-oriented routers. In: The 2013 International Conference on Engineering of Reconfigurable Systems and Algorithms RSA'13 in WORLDCOMP2013, pp. 3–9 (2013).
- Wijekoon, J., Harahap, E., Nishi, H.: Service-oriented router simulation module implementation in fNS2g simulator. The 4th International Conference on Ambient Systems, Networks and Technologies (ANT 2013), the 3rd International Conference on Sustainable Energy Information Technology (SEIT-2013), Procedia Computer Science 19, 478–485 (2013).
- Sanghi, D.: Unix Socket Programing Computer Networks. http://www.cse.iitk.ac.in/users/dheeraj/cs425/lec17.html/.
- Global Inter-cloud Technology Foruml (GICTF). http://www.gictf.jp/indexe.html.
- DongJin Lee, N.B. Brian E. Carpenter: Media streaming observations: Trends in udp to tcp ratio. International Journal on Advances in Systems and Measurements No 3 and 4, 147–162 (2010).
- Kuan-Ta Chen, Chun-Ying Huang, Polly Huang, and Chin-Laung Lei, "An Empirical Evaluation of TCP Performance in Online Games," In Proceedings of ACM SIGCHI ACE 06, Los Angeles USA, Jun (2006).


