Salinity stress adaptation in finger millet - a mini review
Автор: Bevin Nishanth J., Premkumar A.
Журнал: Журнал стресс-физиологии и биохимии @jspb
Статья в выпуске: 4 т.19, 2023 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Abiotic stressors like salt and drought are two examples that may harm crop production. Therefore, increasing production and creating stress-tolerant cultivars requires crop innovation in response to these stresses. Whole genome sequence (WGS) data releases are used for crop trait development. Tolerance to abiotic stress cannot be induced through single-gene engineering transformation. Plants like finger millet can be mined for undiscovered genes because they already have the gene in their genomes, but it is dormant. Therefore, abiotic stress-tolerant genes can be expressed in the same plant by RNA sequencing and transcriptomics by creating abiotic stress for agricultural development. New genes can have their profiles refined with the aid of this transcriptome research.
Abiotic stress, finger millet, whole genome sequence, rna sequencing, transcriptomics, gene profiling
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/143180978
IDR: 143180978
Текст обзорной статьи Salinity stress adaptation in finger millet - a mini review
Abiotic stress is one of the biggest environmental risks to crop development and productivity which includes things like drought and salinity. Consequently, the introduction of stress-tolerant crop types and crop improvement in the face of these harsh conditions will increase productivity. Releases of genomic data, such as whole genome sequence (WGS), are used to enhance crop traits. The expression of tolerance to stress cannot be induced by engineering a single gene transformation for abiotic stress. Finger millet and other crops like it contain genes for fresh genomic data, but they are dormant until triggered to express them. Abiotic stress can be induced in the same plant by RNA sequencing and transcriptomics, allowing for the expression of abiotic stress-tolerant genes. This transcriptome study can aid in the profiling of uncharacterised genes.
SALINITY STRESS
One of the abiotic variables that hinders finger millet development is the soil's salinity. The crop quality and growth are severely impacted by this essential environmental stress (Hema et al. , 2014). Osmotic stress brought on by salinity causes physiological changes including membrane rupture, dietary imbalance, “impairment of the body's capacity to detoxify reactive oxygen species (ROS), reductions in photosynthetic activity and stomatal aperture, and changes in the antioxidant enzymes are just a few of the effects that may occur (Rahnama et al. , 2010; Shahzad et al. , 2021). Salinity stress has a considerable influence on the development of seeds and roots, ions and relative water content, photosynthetic pigments, proline content, membrane peroxidation, reducing sugars, and total protein levels (Kumar et al. , 2016; Sarabi et al. , 2017; Dugasa et al. , 2020; Mukami et al. , 2020)”. Due to its antioxidant, antidiabetic, antimicrobial, aldose reductase enzyme inhibitory, wound healing, antiulcerative, and anticancer properties, Predictions state that by 2050, More than half of the world's arable land may have been negatively impacted by salt. Because of its ability to respond to a variety of abiotic stress conditions, finger millet is considered a promising crop for the identification of genes and pathways involved in adaptation to extreme environmental settings. (Sood et al. , 2016).
Plant salinity tolerance mechanism
Plants are classified as halophytes (those that can survive in salt water) or glycophytes (those that can't) based on their specialized adaptations (which cannot endure salinity and finally die). Since glycophytes make up the vast majority of cultivated plants and are particularly vulnerable to salty conditions, this is one of the most significant negative pressures on worldwide crop output
(Munns and Tester, 2008). Ion toxicity caused by osmotic stress from salty soil is known to stunt plant growth ( ames et al. , 2011). There is an initial decrease in the roots' capacity to take in water and an increase in water loss through the leaves as a result of salinity stress. One of the most harmful impacts of salt stress is the buildup of Na+ and Cl- ions in plant tissues growing in media with high NaCl concentrations. When sodium levels are too high, plants cannot absorb potassium ions, which are essential for plant viability ( ames et al. , 2011). Hydrogen peroxide (H 2 O 2 ), hydroxyl radicals, and reactive oxygen species (ROS) are the plant responses to salinity stress (OH). Proteins, nucleic acids, membrane lipids, and chlorophyll are just a few of the biological elements that reactive oxygen species have the potential to oxidatively harm. Enzymatic and non-enzymatic defensive mechanisms are used by plants to protect themselves from oxidative stress. Plants adjust the pace at which various gene products are synthesized in response to environmental stresses like salt (RNA or protein). As a consequence of salt stress, several genes and transcription factors are upregulated in various plant species (Chakraborty et al. , 2012). Species and genotypes have a role in how well an organism can handle salt.
Biochemical response to salinity stress
Plants are split into two groups, the halophytes (which can tolerate salt) and the glycophytes (which cannot withstand salt and finally die). Since glycophytes, the most common type of cultivated plant, cannot withstand salinity stress, it has become one of the most significant negative pressures on crop production worldwide (Munns and Tester, 2008). Osmotic stress, which results in ion toxicity, is a known plant growth inhibitor, and so is soil salinity ( ames et al., 2011). “Increased salt buildup in soil and plants causes salinity stress, which first reduces the roots' ability to take in water and increases water loss through the leaves. The accumulation of Na+ and Cl- ions in plant tissues growing in a medium containing elevated NaCl concentrations is one of the most detrimental effects of salinity stress. The mortality of plants is caused by an excess of sodium because it stops them from taking in potassium, an essential nutrient ( ames et al., 2011). Hydroxyl radicals, hydrogen peroxide, and reactive oxygen species are all produced by plants in response to salinity stress (OH). Reactive oxygen species via oxidative stress cause harm to membrane lipids, proteins, nucleic acids, and chlorophyll, among other biological components. Both enzymatic and non-enzymatic defences against oxidative damage are present in plants. In response to salt stress, plants use several strategies to regulate gene expression, including or down-regulation of the synthesis of certain gene products (RNA or protein). Many plant species upregulate a huge number of genes and transcription factors in response to salt stress, each of which has a somewhat different function (Chakraborty et al., 2012). There are genetic variations in salt tolerance in addition to species- and genotype-specific variances.
Genetic improvement for abiotic stress tolerance
Plants are divided into halophytes (which may survive in salty environments) and glycophytes (which require a high level of moisture to survive) (which cannot endure salinity and finally die). Because most cultivated plants are glycophytes and are sensitive to salt, salinity stress has emerged as one of the most important factors lowering agricultural yield globally (Munns and Tester, 2008). Inhibiting plant growth via osmotic stress and subsequently ion toxicity, soil salinity has been widely documented ( ames et al., 2011). Salt accumulates in the soil and on the plants, reducing the plants' ability to take in water, and increasing the rate at which they lose water via their leaves. One of the most harmful impacts of salt stress is the buildup of Na+ and Cl- ions in plant tissues growing in media with high NaCl concentrations. An excessive amount of Na+ prevents the absorption of the crucial nutrient K+, which results in plant death ( ames et al., 2011). Reactive oxygen species (ROS), hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), and hydroxyl radicals are all produced by plants as a defense mechanism against salinity stress (OH). Lipids in cell membranes, proteins, nucleic acids, and chlorophyll can all be damaged by oxidation when exposed to reactive oxygen species. Plants use both non-enzymatic and enzymatic defensive mechanisms to combat oxidative stress”. It is known as gene expression monitoring (RNA or protein) when plants use a variety of strategies to either boost or reduce the synthesis of certain gene products when exposed to high levels of salt. In response to salt stress, several plant species upregulate numerous genes and transcription factors, each of which plays a distinct function (Chakraborty et al., 2012). The rate at which organisms can adapt to settings with high salt content varies according to the genotype and species.
Phytohormones' role in stress resistance
Plants are divided into halophytes (which can survive salinity) and glycophytes (which can't) based on their morphological and physiological adaptations (which cannot withstand salt and finally die). Since the bulk of farmed plants are glycophytes and cannot withstand saline stress, it has become one of the most severe negative pressures on agricultural output worldwide (Munns and Tester, 2008). “It is well recognized that salt in the soil inhibits plant development due to osmotic stress and consequent ion toxicity ( ames et al. , 2011). Early on, salt accumulation in the soil and plants reduces plants' capacity to absorb water via their roots, while water loss through the leaves rises. The accumulation of Na+ and Cl-ions in plant tissues growing in a medium with high NaCl concentrations is one of the most detrimental effects of salt stress. Potassium ions, which are essential for plant vitality, can't be absorbed by plants when there are high salt concentrations ( ames et al. , 2011). Plants also release hydroxyl radicals (OH), reactive oxygen species
(ROS), and hydrogen peroxide (H 2 O 2 ) in response to salt stress (OH). Proteins, nucleic acids, lipids, and chlorophyll in membranes may all be ruined by reactive oxygen species (ROS). To stop oxidative damage, plants contain both enzymatic and non-enzymatic defense mechanisms”. In response to environmental challenges like salt (RNA or protein), plants use a variety of methods to regulate the pace of gene synthesis. Numerous plant species experience increases in gene expression and transcription factors in response to salt stress, and these responses have a range of functions (Chakraborty et al. , 2012). The pace at which organisms can adapt to high salt concentrations varies depending on the species and genotype.
ANNOTATION
To functionally annotate the transcript sequences, It is crucial to compare the unknown transcript readings to a reference genome that is quite similar to them to demonstrate the molecular processes changed during the stress (Ward et al. 2012). Comparative transcriptome mapping of finger millet, rice, and foxtail millet (all members of the Poaceae family). The data in Figure 2 for finger millet were analyzed using this reference genome.
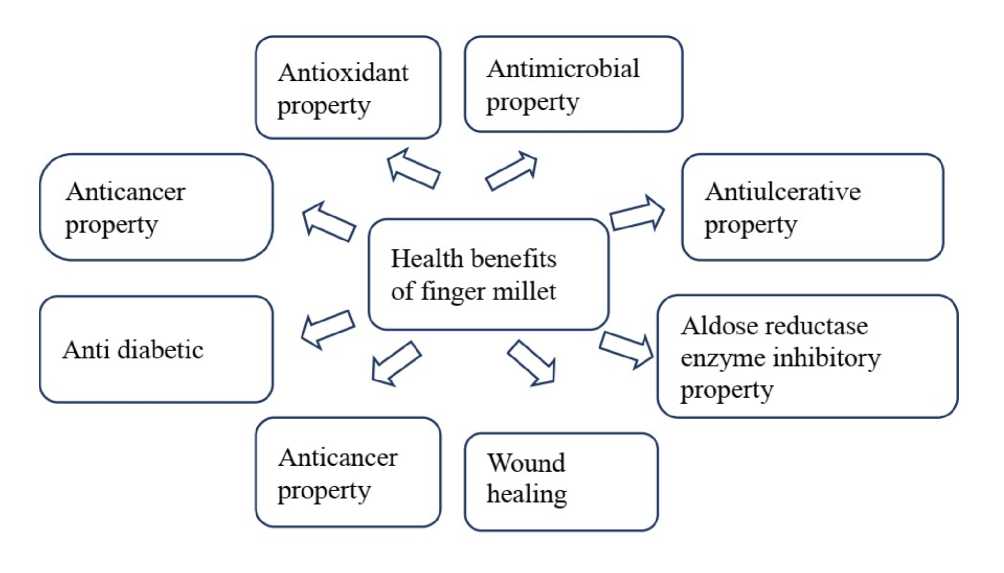
Figure. 1. Health benefits of finger millet (Adopted from Dinesh et al. , 2016)
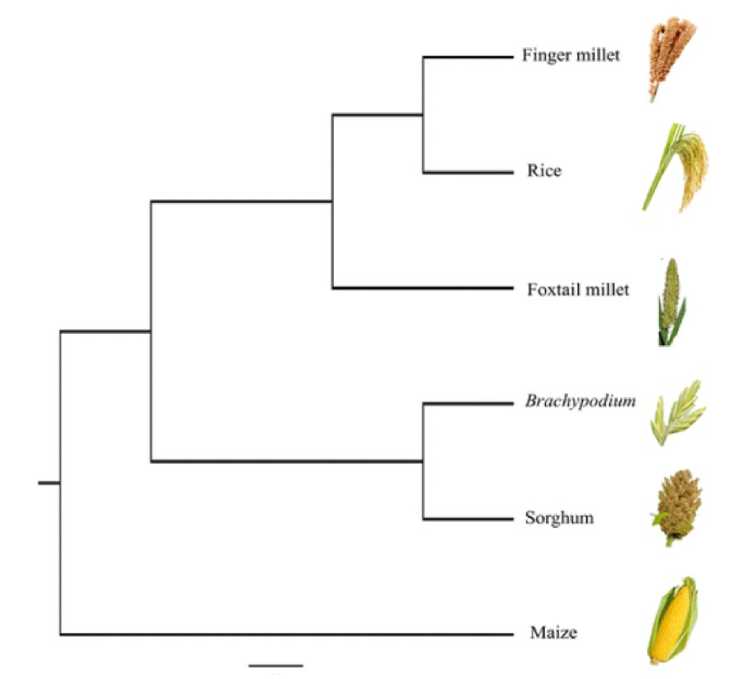
Figure 3. Six species of Poaceae have their phylogenetic relationships revealed using single copy ortholog genes. (Adopted from Hittalmani et al. , 2017)
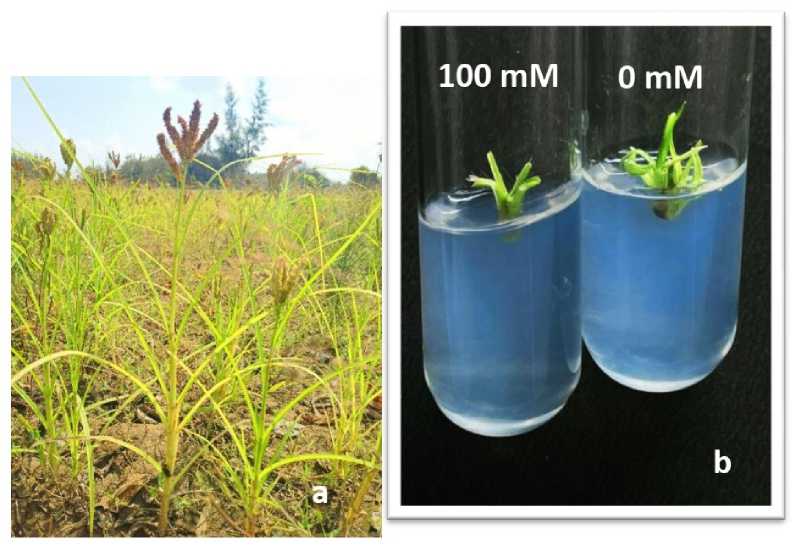

Figure. 4. (a) Finger millet grown in agricultural field, Villupuram, Tamil Nadu.
(b) Multiple shoot formation observed at 0 mM and 100 mM concentration of NaCl supplemented with BAP
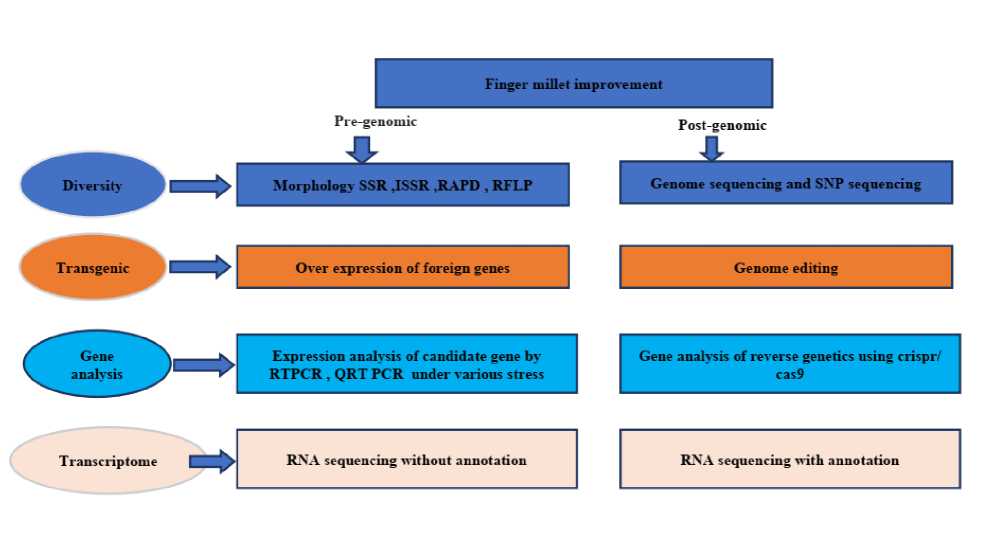
Figure. 5. Finger millet improvement in the pre-genomic and post genomic eras
IN VITRO REGENERATION UNDERSALINITY STRESS
We have also generated salinity stress at 0 and 100 millimoles of sodium chloride, respectively. The seedlings' shoots have emerged after germination. “This investigation has been carried out by the Department of Plant Biology and Biotechnology at Loyola College in Chennai, India. We are grateful that this research used finger millet from the Tamil Nadu Agricultural University (TNAU) in Coimbatore, India, shown in Figure 3. VL 400 and KM 252 were shown to be particularly prone to NaCl, but GPU 28, GPU 67, ML 365, Udurumallige, PYR1, and GPU 48 were found to be less susceptible were found to be less susceptible were unaffected by salt accumulation at 150 Mm or 200 Mm (Divya et al. , 2022).
WHOLE GENOME SEQUENCE
The long-awaited whole genome sequence (WGS) of the finger millet genotype ML-365 has been successfully acquired by researchers using Illumina and Sequencing by Oligonucleotide Ligation and Detection (SOLID) sequencing technology” (a genotype with good properties that is drought tolerant and resistant to blast disease). This work resulted in the generation of 21 GB of mate-pair data and approximately 45 GB of paired-end data. The N50 length of the assembled genome was 23.73 Kb, and the average scaffold length was 2275 bp. In total, there were 525,759 scaffolds (200 bp) in the assembly. Transcriptomes were successfully sequenced and constructed from both In this research, genotype ML-365 plants were well-watered (WW) (53,300 unigenes) and low moisture stressed (LMS). Using protein-protein homology modeling, researchers were able to identify 11,125 genes in plants that were likely to share homology with TFs from 56 different families. Involvement in calcium transport and accumulation was shown to be mediated by 330 genes, whereas roughly 1766 genes were found to be R-genes for different illnesses. In comparison to other Poaceae species, there was more co-linearity between the finger millet WGS and foxtail millet and rice. “This study also shows how closely linked the genome sizes of the coracana and African subspecies of E. coracana are. The availability of WGSs of ML-365 and PR-202 allows for the development of finger millet. These WGSs may be used for many different types of research, including marker-assisted breeding projects, next-generation sequencingbased allele discovery, building linkage and association maps, identifying candidate genes for agronomically important characteristics, and characterizing candidate genes' functional properties”.
TRANSCRIPTOME ANALYSIS
Examining how plant gene expression varies in response to abiotic stress has been done using transcriptomics or during any developmental changes to find genes that affect plant growth, development, and tolerance to external stress. A deeper comprehension of these factors may help in plant breeding and culture as well as targeted selection of superior varieties. To gather plant genomic information rapidly, with great coverage, efficiency, and throughput. Overexpression of foreign genes, Genome editing, Expression study of candidate gene by RT-PCR and QRT-PCR under different stress conditions; CRISPR/cas9-based study of reversed-genes (Clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats) Pre-genomic RNA sequencing, RNA sequencing with annotation, and RNA sequencing without annotation. It has been used in a variety of post-genomic contexts (figure 4), including the identification of plant developmental pathways, the manufacture of secondary metabolites, and the mining of novel functional genes (Huang et al. , 2014), Understanding the intricate mechanisms that control gene expression throughout development and under stress requires transcriptome analysis. For genome-wide transcriptome studies, microarrays and RNA-seq have emerged as the de facto standard methods of choice (Kogenaru et al. 2012). In crops for which there is no genomic sequence data, RNA-seq has lately emerged as a prominent approach to transcriptome study.
CONCLUSION AND FUTUREPERSPECTIVES
Recent studies have demonstrated that finger millet is vulnerable to salinity stress while being a nutrient-rich and drought-resistant crop. Some genotypes can independently express the abiotic stress-tolerant genes, but it is still important to reevaluate the germplasm resources to find the most promising alleles. Allele mining refers to the process of searching through several genotypes for evidence of allelic variation in a known gene. This overview explains how finger millet's biochemical and molecular pathways can shift as a result of salt stress. Characterizing the genes, proteins, metabolites, and the mechanisms that finger millet uses to tolerate salt will shed light on how this trait is expressed. These expressions may be increased or downregulated depending on the trait. The crop can respond to numerous environmental elements thanks to ongoing research into the systems. CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing, high-throughput phenotyping, genomic selection, and speed breeding are all approaches to crop development that can help with the trait prediction required for salt management.
CONFLICT OF INTERESTS
The authors declare that they have no potential conflicts of interest.
Список литературы Salinity stress adaptation in finger millet - a mini review
- Ahmed, F., Baloch, D. M., Hassan, M. J., & Ahmed, N. (2013). Role of plant growth regulators in improving oil quantity and quality of sunflower hybrids in drought stress. Biologia, 59(2), 315-322.
- Antony Ceasar, S., & Ignacimuthu, S. (2011). Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of finger millet (Eleusine coracana (L.) Gaertn.) using shoot apex explants. Plant Cell Reports, 30, 1759-1770.
- Athar, H. R., & Ashraf, M. (2009). Strategies for crop improvement against salinity and drought stress: An overview. Salinity and water stress: improving crop efficiency, 1-16.
- Ceasar, S. A., & Ignacimuthu, S. (2009). Genetic engineering of millets: current status and prospects. Biotechnology Letters, 31, 779-788
- Ceasar, S. A., Rajan, V., Prykhozhij, S. V., Berman, J. N., & Ignacimuthu, S. (2016). Insert, remove, or replace: A highly advanced genome editing system using CRISPR/Cas9. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Molecular Cell Research, 1863(9), 2333-2344.
- Chakraborty, K., Sairam, R. K., & Bhattacharya, R. C. (2012). Differential expression of salt overly sensitive pathway genes determines salinity stress tolerance in Brassica genotypes. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 51, 90-101.
- Chen, K., Li, G. J., Bressan, R. A., Song, C. P., Zhu, J. K., & Zhao, Y. (2020). Abscisic acid dynamics, signaling, and functions in plants. Journal of integrative plant biology, 62(1), 25-54.
- Dida, M. M., Wanyera, N., Harrison Dunn, M. L., Bennetzen, J. L., & Devos, K. M. (2008). Population structure and diversity in finger millet (Eleusine coracana) germplasm. Tropical Plant Biology, 1, 131141.
- Divya, S., Geetha, K., Kumar, R. S., Prabu, P. C., Parasuraman, P., Kumari, A. N., & Sharavanan, P. T. (2022). Early identification of salt-tolerant genotypes in finger millet (Eleusine coracana L.) at germination stage by observing the morphological characters. Indian Journal of Agricultural Research, 56(6), 631-637.
- Guo, J., Huang, Z., Sun, J., Cui, X., & Liu, Y. (2021). Research progress and future development trends in medicinal plant transcriptomics. Frontiers in plant science, 12, 6918.
- Gupta, N., Kumar Gupta, A., Singh, N. K., & Kumar, A. (2011). Differential expression of PBF Dof transcription factor in different tissues of three finger color. Plant molecular biology reporter, 29, 69-76.
- Gupta, P., Raghuvanshi, S., & Tyagi, A. K. (2001). Assessment of the efficiency of various gene promoters via biolistics in leaf and regenerating seed callus of millets, Eleusine coracana and Echinochloa crusgalli. Plant Biotechnology, 18(4), 275-282.
- Puranik, S..... & Kumar, A. (2017). Finger millet: a certain crop for an uncertain future and a solution to food insecurity and hidden hunger under stressful environments. Frontiers in plant science, 8, 643.
- Gupta, S., Gupta, S. M., Gupta, A. K., Gaur, V. S., & Kumar, A. (2014). Fluctuation of Dof1/Dof2 expression ratio under the influence of varying nitrogen and light conditions: involvement in differential regulation of nitrogen metabolism in two genotypes of finger millet (Eleusine coracana L.). Gene, 546(2), 327-335.
- Hatakeyama, M., Aluri, S., Balachadran, M. T., Sivarajan, S. R., Patrignani, A., Gruter, S.....& Shimizu, K. K. (2018). Multiple hybrid de novo genome assembly of finger millet, an orphan allotetraploid crop. DNA Research, 25(1), 39-47.
- Hema, R., Vemanna, R. S., Sreeramulu, S., Reddy, C. P., Senthil-Kumar, M., & Udayakumar, M. (2014). Stable expression of mtlD gene imparts multiple stress tolerance in finger millet. PLoS One, 9(6), e99110.
- Hittalmani, S., Mahesh, H. B., Shirke, M. D., Biradar, H., Uday, G., Aruna, Y. R..... & Mohanrao, A. (2017). Genome and transcriptome sequence of finger millet (Eleusine coracana (L.) Gaertn.) provides insights into drought tolerance and nutraceutical properties. BMC genomics, 18, 1-16.
- Huang, X. H., Xu, F., Cheng, H., Li, L. L., & Cheng, S. Y. (2014). Advances in transcriptome sequencing in higher plants. J. Huanggang Norm. Univ, 34, 28-35.
- Major genes for Na+ exclusion, Nax1 and Nax2 (wheat HKT1; 4 and HKT1; 5), decrease Na+ accumulation in bread wheat leaves under saline and waterlogged conditions. Journal of experimental botany, 62(8), 2939-2947.
- Jayaprakash, T. L., Ramamohan, G., Krishnaprasad, B. T., Prasad, T. G., Mathew, M. K., & Udayakumar, M. (1998). Genotypic Variability in Differential Expression of lea2 and lea3 Genes and Proteins in Response to Salinity Stress in Fingermillet (Eleusine coracana Gaertn) and Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Seedlings. Annals of Botany, 82(4), 513-522.
- Kanakachari, M., Solanke, A. U., Prabhakaran, N., Ahmad, I., Dhandapani, G., Jayabalan, N., & Kumar, P. A. (2016). Evaluation of suitable reference genes for normalization of qPCR gene expression studies in brinjal (Solanum melongena L.) during fruit
- Cramer, G. R., & Quarrie, S. A. (2002). Abscisic acid is millet genotypes differing in seed protein content and James, R. A., Blake, C., Byrt, C. S., & Munns, R. (2011).
- Gupta, R., Verma, K., Joshi, D. C., Yadav, D., & Singh, M. Gupta, S. M., Arora, S., Mirza, N., Pande, A., Lata, C., developmental stages. Applied biochemistry and biotechnology, 178, 433-450.
- Kaya, C., Tuna, A. L., & Yoka§, I. (2009). The role of plant hormones in plants under salinity stress. Salinity and water stress: improving crop efficiency, 45-50.
- Singh, S.....& Yadav, R. (2016). Nutraceutical value of finger millet [Eleusine coracana (L.) Gaertn.], and their improvement using omics approaches. Frontiers in plant science, 7, 934.
- N., Balachandran, S. M., Rani, N. S. & Madhav, M. S. (2010). Allele mining in crops: prospects and potentials. Biotechnology advances, 28(4), 451-461.
- Production of transgenic plants resistant to leaf blast Gaertn.). Plant Science, 169(4), 657-667. Mgonja, M. A., Lenne, J. M., Manyasa, E., & Sreenivasaprasad, S. E. (2007). Finger millet blast management in East Africa Creating opportunities for improving production and utilization of finger millet.
- Transcriptional expression analysis of genes involved in regulation of calcium translocation and storage in finger millet (Eleusine coracana L. Gartn.). Gene, 550(2), 171-179.
- J. (1998). Relative importance of osmotic-stress and ion-specific effects on ABA-mediated inhibition of leaf expansion growth in Phaseolus vulgaris. Plant, Cell & Environment, 21(1), 54-62.
- Suprasanna, P., & Nikam, T. D. (2016). Plant salt stress: adaptive responses, tolerance mechanism and bioengineering for salt tolerance. The Botanical Review, 82, 371-406.
- Mukami, A., Ng'etich, A., Syombua, E., Oduor, R., & Mbinda, W. (2020). Varietal differences in physiological and biochemical responses to salinity stress in six finger millet plants. Physiology and Molecular Biology of Plants, 26, 1569-1582.
- Mushtaq, N. U., Alghamdi, K. M., Saleem, S., Shajar, F., Tahir, I., Bahieldin, A..... & Hakeem, K. R. (2022). Selenate and selenite transporters in proso millet: Genome extensive detection and expression studies under salt stress and selenium. Frontiers in Plant Science, 13.
- Parvathi, M. S., & Nataraja, K. N. (2017). Discovery of stress responsive TATA-box binding protein associated Factor6 (TAF6) from finger millet (Eleusine coracana (L.) Gaertn). Journal of Plant Biology, 60, 335-342.
- Parvathi, M. S., Nataraja, K. N., Yashoda, B. K., Ramegowda, H. V., Mamrutha, H. M., & Rama, N. (2013). Expression analysis of stress responsive pathway genes linked to drought hardiness in an adapted crop, finger millet (Eleusine coracana). Journal of plant biochemistry and biotechnology, 22, 193-201.
- Pedranzani, H., Racagni, G., Alemano, S., Miersch, O., Ramírez, I., Peña-Cortés, H.....& Abdala, G. (2003). Salt tolerant tomato plants show increased levels of jasmonic acid. Plant Growth Regulation, 41, 149-158.
- Pedranzani, H., Racagni, G., Alemano, S., Miersch, O., Ramírez, I., Peña-Cortés, H.....& Abdala, G. (2003). Salt tolerant tomato plants show increased levels of jasmonic acid. Plant Growth Regulation, 41, 149-158.
- Pu, F., Chen, N., & Xue, S. (2016). Calcium intake, calcium homeostasis and health. Food Science and Human Wellness, 5(1), 8-16.
- Sachin, B., Sasikala, R., Senthil, N.& Muthurajan, R. (2014). Transcriptome analysis of salinity responsiveness in contrasting genotypes of finger millet (Eleusine coracana L.) through RNA-sequencing. Plant molecular biology, 85, 485-503.
- Rahman, H., Ramanathan, V., Nallathambi, J., Duraialagaraja, S., & Muthurajan, R. (2016). Overexpression of a NAC 67 transcription factor from finger millet (Eleusine coracana L.) confers tolerance against salinity and drought stress in rice. BMC biotechnology, 16, 7-20.
- Kogenaru, S., Yan, Q., Guo, Y., S Wang, N. (2012). RNA-Kumar, A., Metwal, M., Kaur, S., Gupta, A. K., Puranik, S., Kumar, G. R., Sakthivel, K., Sundaram, R. M., Neeraja, C. Latha, A. M., Rao, K. V., S Reddy, V. D. (2005). disease in finger millet (Eleusine coracana (L.)
- Mirza, N., Taj, G., Arora, S., S Kumar, A. (2014). Montero, E., Cabot, C., Poschenrieder, C. H., S Barcelo, Rahman, H., Jagadeeshselvam, N., Valarmathi, R., Muchate, N. S., Nikalje, G. C., Rajurkar, N. S., Rahnama, A., James, R. A., Poustini, K., & Munns, R. (2010). Stomatal conductance as a screen for osmotic stress tolerance in durum wheat growing in saline soil. Functional Plant Biology, 37(3), 255-263.
- Ramakrishna, C., Singh, S., Raghavendrarao, S., Padaria, J. C., Mohanty, S., Sharma, T. R., & Solanke, A. U. (2018). The membrane tethered transcription factor EcbZIP17 from finger millet promotes plant growth and enhances tolerance to abiotic stresses. Scientific Reports, 8(1), 2148.
- Gupta, C., Govind, G.....& Senthil-Kumar, M. (2017). GBF3 transcription factor imparts drought tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Scientific Reports, 7(1), 9148.
- Ramegowda, V., Senthil-Kumar, M., Nataraja, K. N., Reddy, M. K., Mysore, K. S., and Udayakumar, M. (2012). Expression of a finger millet transcription factor. EcNAC1, in tobacco confers abiotic stress-tolerance. PLoS One 7:e40397.
- Rana, M. M., Takamatsu, T., Baslam, M., Kaneko, K., Itoh, K., Harada, N..... & Mitsui, T. (2019). Salt tolerance improvement in rice through efficient SNP marker-assisted selection coupled with speed-breeding. International journal of molecular sciences, 20(10), 2585.
- Sarabi, B., Bolandnazar, S., Ghaderi, N., & Ghashghaie, J. (2017). Genotypic differences in physiological and biochemical responses to salinity stress in melon (Cucumis melo L.) plants: Prospects for selection of salt tolerant landraces. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 119, 294-311.
- Schmittgen, T. D., & Livak, K. J. (2008). Analyzing realtime PCR data by the comparative CT method. Nature protocols, 3(6), 1101-1108.
- Shah, Z. H., Rehman, H. M., Akhtar, T., Daur, I., Nawaz, M. A., Ahmad, M. Q.....& Chung, G. (2017). Redox and ionic homeostasis regulations against oxidative, salinity and drought stress in wheat (a systems biology approach). Frontiers in genetics, 8, 141.
- Shahzad, B., Rehman, A., Tanveer, M., Wang, L., Park, S. K., & Ali, A. (2021). Salt stress in brassica: effects, tolerance mechanisms, and management. Journal of Plant Growth Regulation, 1-15.
- Shan, Q., Wang, Y., Li, J., Zhang, Y., Chen, K., Liang, Z. & Gao, C. (2013). Targeted genome modification of crop plants using a CRISPR-Cas system. Nature biotechnology, 31(8), 686-688.
- Shukla, A., Lalit, A., Sharma, V., Vats, S., & Alam, A. (2015). Pearl and finger millets: the hope of food security. Applied Research Journal, 1(2), 59-66.
- Singh, M., Kumar, J., Singh, S., Singh, V. P., & Prasad, S. M. (2015). Roles of osmoprotectants in improving salinity and drought tolerance in plants: a review. Reviews in Environmental Science and Bio/Technology, 14, 407-426.
- Yoshida, T., Mogami, J., & Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K. (2014). ABA-dependent and ABA-independent signaling in response to osmotic stress in plants. Current opinion in plant biology, 21, 133-13


