Salt tolerance evaluation in cotton ( Gossypium hirsutum L.) using RAPD marker
Автор: Saleh B.
Журнал: Журнал стресс-физиологии и биохимии @jspb
Статья в выпуске: 4 т.11, 2015 года.
Бесплатный доступ
The aim of this study was to evaluate four upland cotton ( Gossypium hirsutum L.) [Niab78 (N78), Deir-Ezzor22 (DE22), Deltapine50 (DP50) and Aleppo118 (A118)] varieties towards salt stress (0 and 200 mM NaCl) for 7 weeks based on RAPD marker. Our data showed that the highest total polymorphic bands identified by the 26 RAPD tested primers were 150 bands generated by N78 variety, while the lowest ones were recorded for DP50 (29 bands). Otherwise, unique (negative and positive) markers characterized the two tolerant varieties (N78 and DE22) were 22 and 29 markers, respectively. Our data indicated that the highest polymorphism level was detected in N78 variety (68.5%) followed by DE22 (60.9%), whereas, the lowest one was recorded for DP50 (21.3%). Our data obtained herein indicates that RAPD marker provided molecular markers for salinity tolerance screening in early stage in genetic improvement programs.
Cotton, dna changes, rapd marker, salt stress
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/14323932
IDR: 14323932
Текст научной статьи Salt tolerance evaluation in cotton ( Gossypium hirsutum L.) using RAPD marker
Cotton is an economically important plant grown world-wide as a principal source of staple fiber and vegetable oil. A great deal of effort has been made to improve cotton cultivation and characteristics by breeders. Cotton is one of the major fiber crops in Syria, with a cultivated area amount to 125,000 hectares, and a production of 470,000 tons of seed cotton and lint production is estimated at 160,000 tons. Yarn spinning capacity is estimated at 180,000 tons (USDA 2011). Salinity tolerance is a complex trait that involves physiological, biochemical, cellular and genetic strategies. At present, out of 1.5 billion hectares of cultivated land around the world, about 77 million hectares (5%) is affected by excess salt content (Moradi et al ., 2011). The effect of high salt concentration on plant physiology has been mentioned in many reports e.g. in cotton (Dojan et al ., 2012; Saleh 2011, 2013). Random Amplified Polymorphic DNA (RAPD) technique previously developed (Williams et al. , 1990) is a sensitive, fast and simple method to indicate wide range of DNA damage types. Many investigations detected variations in gain or loss of DNA bands following salt exposure, these losses or gains can be considered as an indicator for DNA changes (Kurup et al ., 2009; Daffalla et al ., 2011; Dojan et al ., 2012, Khan et al ., 2013; Abdel-Hamid 2014). Different PCR-based marker systems are currently available for monitoring DNA damages induced by an abiotic stress such as salt stress e.g. QTL marker in rice (Hu et al ., 2012), RAPD technique in rice (Mansuri et al ., 2012), RAPD in wheat ( Triticum aestivum L.) (El-Amin et al ., 2011), SSR in wheat (Shahzad et al ., 2012), and ITS and
ETS markers in Acacia sp. (Joseph et al ., 2013). Moreover, SDS-PAGE, isozymes and RAPD markers were employed to detect DNA damages induced by heat stress in cotton (Mohamed and Abdel-Hamid 2013).
In the current study, RAPD marker system was employed to provide genetic diversity information for 4 cotton varieties cultivated in Syria. These varieties were selected based on their differences in the level of salinity tolerance (Saleh 2011). The data gained from this investigation may provide useful information for selecting appropriate varieties in breeding program for improving salt tolerance of elite varieties based on genetic variations in salt tolerance levels.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Plant materials and growth conditions
Two local varieties have been selected on the basis of their wide range of tolerance towards salinity; Deir-Ezzor22 (DE22) as salt-tolerant and Aleppo118 (A118) as salt-sensitive variety (Saleh 2011). These two varieties were examined compared with two introduced cotton varieties, Niab78 (N78) (known as salt-tolerant) and Deltapine50 (DP50) (known as saltsensitive) under 0 and 200 mM NaCl for 7 weeks. Seeds of upland cotton (G. hirsutum L.) N78, DE22, DP50 and A118 varieties were provided by the General Commission for Scientific Agricultural Research of Syria (GCSAR), Damascus-Syria. Seeds were soaked in distilled H2O for 24 h and then planted in pots filled with a 1/3:2/3 (v/v) mixture of perlite:peat mosse. Germination was carried out in a greenhouse at temperature of 18°C, 12 h photoperiod and relative humidity of 80%. Seedlings were allowed to grow in a greenhouse under controlled conditions (temperature of 25°C, 12 h photoperiod and relative humidity of 80 %). Seedlings were irrigated with tap water for one week before the initiation of NaCl treatment. Salt stress application was carried out by adding NaCl (200 mM) to the water. Plants were irrigated twice a week by water with or without salt. All solutions were changed twice a week. The same environmental conditions were maintained during the experiment. The experiment (five replicates by treatment) was carried out in the greenhouse for 7 weeks.
DNA isolation
Plant genomic DNA was extracted from (bulk of 5 plants/ variety) young leaves including the control and stressed plants (200 mM NaCl) for the four tested cotton varieties by a CTAB (cetyltrimethylammonium bromide) protocol as described by Doyle and Doyle (1987) with minor modifications. Leaves tissue (150 mg) were ground in liquid nitrogen, the powder was transferred to a 2 mL Eppendorf tube, mixed with 900 μL of extraction buffer (100 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.0, 1.4 M NaCl, 20 mM EDTA, 0.0018 ml β-mercaptoethanol, 2% CTAB), and incubated at 65 °C for 20 min. DNA was extracted with one volume of a chloroform:isoamyl alcohol mix (24:1, v/v) and centrifuged at 12,000 g for 10 min at 4 °C. The aqueous phase was transferred to a fresh tube, and the DNA was precipitated with an equal volume of cold isopropanol and kept at -20 °C for 10 min. Then centrifuged at 12,000 g for 10 min at 4 °C, the supernatant was discarded, DNA was then spooled out and washed with 1 M ammonium acetate and
100% ethanol. The cleaned DNA pellet was air dried and dissolved in 100 μL of 0.1x TE buffer (1 mM Tris-HCl, 0.1 mM EDTA, pH 8.0). After addition of 5 μL of RNase (10 mg/ mL), and incubation for 30 min at 37 °C. DNA concentration was quantified by DNA Fluorimeter at 260/280 nm and adjusted to final concentration of 10 ng/ μL. DNA was stored at -80 °C until needed.
RAPD assay
Twenty-three RAPD primers belonging to Operon Technologies Inc. USA and three primers from UBC (University of British Columbia) were tested for detection DNA changes in stressed plants and their respective control for 4 cotton varieties. RAPD marker was performed as described by Williams et al . (1990) with a minor modification. PCR amplification reaction was carried out in 25 μL reaction volume containing 1xPCR buffer, 2 mM MgCl 2 , 0.25 mM dNTPs (Fermentas, USA), 25 pmol primer, 1.5 U of Taq DNA polymerase and 30 ng template DNA. PCR amplification was performed in a T-gradient thermal cycler (Bio-Rad, Hercules, USA). It was programmed to 42 cycles after an initial denaturation cycle for 4 min at 94 °C. Each cycle consisted of a denaturation step 1 min at 94 °C, an annealing step for 2 min at 35 °C, and an extension step at 72 °C for to 2 min, followed by extension cycle for 7 min at 72 °C in the final cycle. The PCR products were separated on a 1.5% ethidium bromide- stained agarose gel (Bio-Rad, USA) in 0.5xTBE buffer. Electrophoresis was performed for 3 h at 85V and visualized with a UV transilluminator. Band sizes were determined by comparison with a 1 kb DNA Ladder Mix, ready to use
(Fermentas, USA).
RESULTS
A set of 26 random10-mer primers was used for detecting the DNA changes among four cotton varieties under salt stress application compared to their respective control. RAPD fragment sizes ranged from 200-3000 bp. The generated variant bands characteristics for each variety for the four varieties were summarized in Table 1. Otherwise, unique
(negative and positive) markers characterized the two tolerant varieties were summarized in Table 2. Moreover, total number of bands amplified, number of polymorphic bands and proportion of polymorphic bands (P%) were presented in Table 3. Fig. 1 shows the amplification products using OPQ01 and OPR12 RAPD primers with template DNA from the four varieties under control and saline conditions (200 mM NaCl).
Table 1. Number of variant bands identified by 26 RAPD primers for the four tested cotton varieties under 200 mM NaCl compared to their respective control
|
Primer name |
Sequence (5' - 3') |
N78 |
DE22 |
DP50 |
A118 |
Total |
|
OPA02 |
TGCCGAGCTG |
6 |
6 |
2 |
2 |
16 |
|
OPA04 |
AATCGGGCTG |
3 |
2 |
0 |
0 |
5 |
|
OPB05 |
TGCGCCCTTC |
7 |
5 |
1 |
1 |
14 |
|
OPB17 |
AGGGAACGAG |
7 |
6 |
0 |
7 |
20 |
|
OPC08 |
TGGACCGGTG |
4 |
3 |
1 |
2 |
10 |
|
OPC13 |
AAGCCTCGTC |
6 |
6 |
0 |
0 |
12 |
|
OPD08 |
GTGTGCCCCA |
4 |
6 |
2 |
3 |
15 |
|
OPD20 |
GGTCTACACC |
5 |
4 |
2 |
2 |
13 |
|
OPE07 |
AGATGCAGCC |
6 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
7 |
|
OPE15 |
ACGCACAACC |
5 |
3 |
0 |
0 |
8 |
|
OPG11 |
TGCCCGTCGT |
1 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
2 |
|
OPJ01 |
CCCGGCATAA |
9 |
7 |
0 |
4 |
20 |
|
OPJ07 |
CCTCTCGACA |
6 |
7 |
4 |
4 |
21 |
|
OPK12 |
TGGCCCTCAC |
6 |
5 |
0 |
0 |
11 |
|
OPK13 |
GGTTGTACCC |
6 |
6 |
4 |
4 |
20 |
|
OPK17 |
CCCAGCTGTG |
7 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
19 |
|
OPQ01 |
GGGACGATGG |
8 |
2 |
0 |
0 |
10 |
|
OPQ18 |
AGGCTGGGTG |
6 |
2 |
0 |
1 |
9 |
|
OPR09 |
TGAGCACGAG |
6 |
2 |
0 |
1 |
9 |
|
OPR12 |
ACAGGTGCGT |
10 |
10 |
3 |
5 |
28 |
|
OPT18 |
GATGCCAGAC |
5 |
3 |
0 |
1 |
9 |
|
OPW17 |
GTCCTGGGTT |
7 |
7 |
0 |
3 |
17 |
|
OPY10 |
CAAACGTGGG |
4 |
4 |
1 |
3 |
12 |
|
UBC132 |
AGGGATCTCC |
7 |
6 |
1 |
3 |
17 |
|
UBC159 |
GAGCCCGTAG |
6 |
5 |
4 |
4 |
19 |
|
UBC702 |
GGGAGAAGGG |
3 |
3 |
0 |
1 |
7 |
|
Total |
150 |
115 |
29 |
55 |
350 |
Table 2. Unique (negative and positive) markers identified by 26 RAPD primers in salt-tolerant (N78 and D22) varieties under 200 mM NaCl
|
Primer name |
Sequence (5' - 3') |
Unique negative marker (number and size) |
Unique positive marker (number and size) |
|
OPA02 |
TGCCGAGCTG |
(2) 650 & 2500 |
(1) 600 |
|
OPA04 |
AATCGGGCTG |
0 |
(2) 400 & 500 |
|
OPB05 |
TGCGCCCTTC |
(2) 450 & 2000 |
(2) 500 & 1100 |
|
OPB17 |
AGGGAACGAG |
(1) 1800 |
0 |
|
OPC08 |
TGGACCGGTG |
0 |
0 |
|
OPC13 |
AAGCCTCGTC |
(1) 1000 |
(3) 300, 1100 & 1350 |
|
OPD08 |
GTGTGCCCCA |
(1) 450 |
(1) 1350 |
|
OPD20 |
GGTCTACACC |
0 |
0 |
|
OPE07 |
AGATGCAGCC |
(1) 1800 |
0 |
|
OPE15 |
ACGCACAACC |
0 |
(1) 1500 |
|
OPG11 |
TGCCCGTCGT |
0 |
(1) 600 |
|
OPJ01 |
CCCGGCATAA |
(3) 400, 600 & 850 |
(4) 350, 500, 950 & 1800 |
|
OPJ07 |
CCTCTCGACA |
(2) 500 & 1600 |
(1) 1200 |
|
OPK12 |
TGGCCCTCAC |
(2) 900 & 1350 |
0 |
|
OPK13 |
GGTTGTACCC |
(1) 1100 |
(4) 450, 750, 1200 & 1350 |
|
OPK17 |
CCCAGCTGTG |
(1) 1850 |
0 |
|
OPQ01 |
GGGACGATGG |
(1) 1100 |
0 |
|
OPQ18 |
AGGCTGGGTG |
0 |
(1) 1600 |
|
OPR09 |
TGAGCACGAG |
0 |
0 |
|
OPR12 |
ACAGGTGCGT |
(1) 2250 |
(1) 1800 |
|
OPT18 |
GATGCCAGAC |
0 |
0 |
|
OPW17 |
GTCCTGGGTT |
0 |
(3) 450, 500 & 800 |
|
OPY10 |
CAAACGTGGG |
(1) 3000 |
(2) 400 & 2500 |
|
UBC132 |
AGGGATCTCC |
(1) 3000 |
0 |
|
UBC159 |
GAGCCCGTAG |
0 |
(1) 700 |
|
UBC702 |
GGGAGAAGGG |
(1) 800 |
(1) 2500 |
|
Total |
22 |
29 |
Table 3. Total number of bands amplified, number of polymorphic bands and proportion of polymorphic bands (P%)
|
Variety |
Total bands |
Polymorphic bands |
P (%) |
|
N78 |
219 |
150 |
68.5 |
|
DE22 |
189 |
115 |
60.9 |
|
DP50 |
136 |
29 |
21.3 |
|
A118 |
151 |
55 |
36.4 |
0PQO1 0PR12
N78 DE22 DP50 А118 N78 DE22 DP50 А118
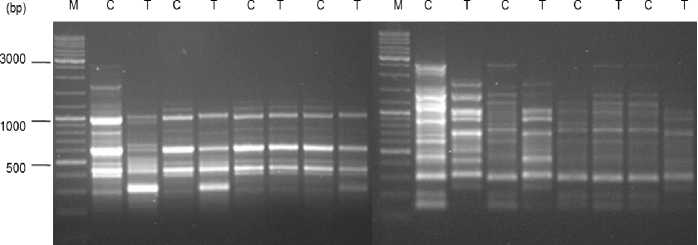
Figure 1 . RAPD profiles generated by OPQ01 and OPR12 primers into the four tested cotton varieties showing DNA changes induced by NaCl application, C: Control, T: Treated plants. M: 1 kb DNA Ladder Mix, ready to use
DISCUSSION
OPT18, OPW17 and UBC59) and 2 (OPA02, OPB05, OPJ07 and OPK12). Whereas, the highest number (3) was yielded by OPJ01 (Table 2). While, in the case of unique positive markers, bands were ranged between 0 (OPB17, OPC08, OPD20, OPE7, OPK12, OPK17, OPQ01, OPR09, OPT18 and UBC132) and 3 (OPC13 and OPW17). Whereas, the highest number (4) was yielded by OPJ01 and OPK13 (Table 2). It was noticed that, N78 variety was identified as having the highest polymorphic bands (150) among the tested varieties while, the lowest one was recorded for DP50 (29).
Recently, Abdel-Hamid (2014) tested 6 RAPD primers for screening markers linked to salinity tolerance in two barley ( Hordeum vulgaris L.) cultivars salt-tolerant and two salt-sensitive cultivars. Where, salt stress application was performed by plants exposure to 9000 ppm NaCl for 40 days after planting. The later study revealed unique positive markers in the two salt-tolerant with 970 bp (OPA10), 420 bp (OPB14), 2100 bp (OPD20) and 640 bp (OPZ11).
In the current investigation, the highest total number of bands and polymorphism level identified by RAPD marker (219 bands and P% of 68.5%) was recorded for N78 variety, while the lowest one was recorded for DP50 (136 bands) with P% of 21.3% (Table 3).
Abdel-Hamid (2014) applied 6 RAPD primers for screening salinity tolerance in 4 barley ( H. vulgaris L.) cultivars differed in their salinity tolerance level; exposed to 9000 ppm NaCl for 40 days after planting. The later study mentioned that total number of bands varied between 5 (OPB08 and OPB14) and 13 (OPD20) with a total of 48 bands. Whereas, P% values ranged between 37.5 (OPA10) and 100% (OPB08) with an average of 59%.
Different physiological indices ( e.g. fresh and dry weight, leaf K+/Na+ ratio and protein pattern expression) as selection criteria, have been previously investigated in cotton under salt stress (Saleh 2011, 2013). Our data presented herein are in agreement with the physiological characteristics previously exhibited by the examined varieties (N78, DE22, DP50 and A118) where the former two varieties were superior to the latter (Saleh 2011, 2013). The amplified fragments which proved to be specific for the relatively high salinity tolerant N78 and DE22 varieties, may serve as markers for early evaluation/screening for salinity tolerance in cotton. Dojan et al . (2012) reported the potential of RAPD marker for detection DNA damages induced by NaCl in cotton. The previous investigation stated that RAPD analysis could be considered as useful biomarker assay for observing environmental stresses such as high salinity in cotton. Whereas, Mohamed and Abdel-
Hamid (2013) reported the effect of heat stress (40 °C) on four cotton genotypes at molecular and biochemical levels. The later investigation indicated that, heat treatment caused variation in number, intensity of protein SDS-PAGE and isozymes activities bands. Moreover, variation in RAPD profile has been also detected in all cotton tested genotypes using five RAPD primers. Whereas, Shahzad et al. (2012) reported the response of wheat landrace genotypes towards salt tolerance at vegetative stage based upon morphological and molecular markers. The later study mentioned that different selected criteria including the number of tillers / plant, root length, root fresh and dry weights, and shoot fresh and dry weights were associated with salt tolerance. Moreover, SSR technique showed high genetic variability among tested wheat genotypes. Where, 12 SSR markers were found to be associated with salt tolerance. Moreover, Hu et al. (2012) investigate rice salt tolerance based on genetics and molecular approaches. This study allowed identifying more than 70 QTLs controlling the salt related traits of Na+/K+ contents. While, Joseph et al. (2013) applied two DNA markers (ITS and ETS) for evaluate 4 species of Acacia sp towards salinity tolerance and thereby, the salt tolerant genotypes could be used in the future for reclamation of saline affected regions. Whereas, Kurup et al. (2009) used RAPD marker to identify salinity tolerant in four date palms (Phoenix dactylifera L.) varieties based on analysis of morphological and physiological parameters. While, El-Zaeem (2012) used RAPD technique to identify three genotypes of fish full-sib Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus), Blue tilapia (O. aureus) and their diallel interspecific hybridization for their salinity tolerance. Likewise, RAPD marker has the potential to be applied in environmental pollution detection’s; e.g. Gupta and Sarin (2009) applied same marker to detect pollution by cadmium (Cd) in aquatic plants Hydrilla verticillata and Ceratophyllum demersum. Zhou et al. (2011) also used RAPD bands for indicating DNA damage in Euplotes vannus (Protozoa, Ciliophora) induced by nitrofurazone in marine ciliates. Moreover, Aly (2012) used the same marker for genotoxic effects detection of Cd stress on Egyptian clover and Sudan grass plants. Indeed, Saleh (2013) reported that salt application induced changes in protein pattern including decrease, increase or induction of some polypeptides bands. The later investigation indicated also that the estimated total dry weight (TDW), membrane stability index (MSI) and salt tolerance index (STI) were higher in N78 and DE22 compared to other tested varieties (DP50 and A118). In addition, according to GCSAR, DE22 exhibited good technological traits. It was considered as the highest local variety in gin turnout percentage and the most temperature tolerant at vegetative stage compared to the other cotton varieties. El-Amin et al. (2011) reported the impact of salt stress on agronomical and molecular traits in six wheat (T. aestivum L.) cultivars. The later study revealed the RAPD potential with high variation among the six cultivars using six RAPD primers. Indeed, the closer cultivars genetically grouped in the same cluster had the same trend in their response to salt stress. Whereas, Mansuri et al. (2012), reported the rice tolerant genotyping of 21
genotypes at different growth stages using RAPD marker and some physiological parameters as a useful tool for rice salinity tolerance screening. The previous study showed that Na+ and Na+/K+ ratio were lower in salt-tolerant genotypes than the sensitive ones in young seedling stage. Moreover, UBC251 and UBC244 RAPD primers showed genetic variation in the RAPD pattern among the tested genotypes. Where, about 1100 pb and 800 bp RAPD bands size yielded by UBC251 and UBC244, respectively, allowed to somewhat to discriminate the 21 rice genotypes tested. According to our results, N78 and DE22 varieties showed a better protection mechanism against salinity damage than the other two tested varieties. All over, the highest polymorphic bands identified into N78 and DE22 varieties could be attributed to the fact that genome was much changed and getting recombinant, translated new proteins. These protein could be play a major role in protection mechanism against salt stress damages. Accumulation of these proteins is a common response to salt stress (Kong-ngern et al ., 2005; Metwali et al ., 2011; Saleh 2013).
The present study showed the capability of RAPD technique as a useful tool for assessment of DNA alterations in cotton varieties under saline conditions. Furthermore, it allows somewhat to differentiate between cotton salt-tolerant and salt-sensitive varieties. Overall, RAPD technique has proven an important approach for detecting of DNA changes under salt stress. Consequently, the identified unique makers observed in N78 and DE22 (salt-tolerant varieties) could be associated with salinity tolerance.
Similar findings were recently reported by AbdelHamid (2014) in barley who stated that observed induced DNA changes by salt stress could be associated with some genes involved in barley salinity tolerance. Thereby, N78 and DE22 varieties could be considered as appreciated and promised selected varieties that may be introduced in breeding program for enhancing salinity tolerance in cotton.
Список литературы Salt tolerance evaluation in cotton ( Gossypium hirsutum L.) using RAPD marker
- Abdel-Hamid, A.M.E. (2014) Physiological and molecular markers for salinity tolerance in four barley cultivars. Euro. Sci. J., 10: 252-272
- Aly, A.A. (2012) Application of DNA (RAPD) and ultrastructure to detect the effect of cadmium stress in Egyptian clover and Sudan grass plantlets. J. Stress. Physiol. Biochem., 8: 241-257
- Daffalla, H.M., Habeballa, R.S., Elhadi, E.A. and Khalafalla, M.M. (2011) Random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) marker associated with salt tolerance during seeds germination and growth of gelected Acacia senegal provenances. Afr. J. Biotechnol., 10: 5820-5830
- Dojan, I., Kekec, G., Ozyigit, I.I., Sackali, M.M. (2012) Salinity induced changes in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Pak. J. Bot., 44: 21-25
- Doyle, J.J. and Doyle, J.L. (1987) A rapid DNA isolation procedure for small quantities of fresh leaf tissue. Phytochem. Bull., 19: 11-15
- El-Amin, H.K.A, Hamza, N.A. and Abuali, A.I. (2011) Molecular and agronomical assessment of six wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) cultivars under salt-stress conditions. Int. J. Agric. Res., 6: 163-171
- El-Ezaeem, S.Y. (2012) Identification of different selected genotypes of salinity resistance of each of full-sib Nile tilapia, Blue tilapia and their diallel interspecific hybridization using random amplified polymorphic DNA fingerprinting. Afr. J. Biotechnol., 11: 8645-8652
- Gupta, M. and Sarin, N.B. (2009) Heavy metal induced DNA changes in aquatic macrophytes: Random amplified polymorphic DNA analysis and identification of sequence characterized amplified region marker. J. Environ. Sci., 21: 686-690
- Hu, S., Tao, H., Qian, Q. and Guo, L. (2012) Genetics and molecular breeding for salt-tolerance in rice. Rice. Gen. Genet., 3: 39-49
- Joseph, S., Murphy, D.J., Miller, J.T. and Bhave, M. (2013) Application of molecular markers for identification of potential salt tolerant plant species for use in agroforestry and saline land reclamation. APCBEE Procedia., 5: 514 -519
- Khan, F., Hakeem, K.R., Siddiqi, T.O. and Ahmad, A. (2013) RAPD markers associated with salt tolerance in soybean genotypes under salt stress. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol., 170: 257-272
- Kong-ngern, K., Daduang, S., Wongham, C., Bunnag, S., Kosittrakun, M. and Theerakulpisut, P. (2005) Protein profiles in response to salt stress in leaf sheaths of rice seedlings. ScienceAsia., 31: 403-408
- Kurup, S.S., Hedar, Y.S., Al-Dhaheri, M.A., El-Heawiety, A.Y., Aly, M.A.M. and Alhadrami, G. (2009) Morpho-physiological evaluation and RAPD markers-assisted characterization of date palm (Phoenix dactylifera L.) varieties for salinity tolerance. J. Food. Agr. Environ., 7: 503-507
- Mansuri, S.M., Jelodar, N.B. and Bagheri, N. (2012) Evaluation of rice genotypes to salt stress in different growth stages via phenotypic and random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) marker assisted selection. Afr. J. Biotechnol., 11: 9362-9372
- Metwali, E.M.R., Eid, M.H. and Bayoumi, T.Y. (2011) Agronomical traits and biochemical genetic markers associated with salt tolerance in wheat cultivars (Triticum aestivum L.). Aust. J. Basic. Appl. Sci., 5: 174-183
- Mohamed, H.I. and Abdel-Hamid, A.M.E. (2013) Molecular and biochemical studies for heat tolerance on four cotton genotypes. Rom. Biotech. Lett., 18: 8823-8831
- Moradi, A, Tahmourespour, A., Hoodaji, M. and Khorsandi, F. (2011) Effect of salinity on free living -diazotroph and total bacterial populations of two saline soils. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res., 5:144-148
- Saleh, B. (2011) Effect of salt stress (NaCl) on biomass and K+/Na+ ratio in cotton. J. Stress. Physiol. Biochem., 7: 05-14
- Saleh, B. (2013) Water status and protein pattern changes towards salt stress in cotton. J. Stress. Physiol. Biochem., 9: 113-123
- Shahzad, A., Ahmad, M., Iqbal, M., Ahmed, I. and Ali, G.M. (2012) Evaluation of wheat landrace genotypes for salinity tolerance at vegetative stage by using morphological and molecular markers. Gen. Mol. Res., 11: 679-692
- USDA (2011) Syria cotton and products annual cotton report, GAIN Report, (www.fas.usda.gov)
- Williams, J.G.K., Kubelik, A.R., Livak, K.J., Rafalski, A.J. and Tingey, S.V. (1990) DNA polymorphisms amplified by arbitrary primers are useful as genetic markers. Nucleic. Acids. Res., 18: 6531-6535
- Zhou, L., Li, J., Lin, X. and Al-Rasheid, K.A.S. (2011) Use of RAPD to detect DNA damage induced by nitrofurazone in marine ciliate Euplotes vannus (Protozoa, Ciliophora). Aquat. Toxicol., 103: 225-232


