Screening Barley Doubled Haploid Lines for Spot Blotch Resistance and Its Interrelationship with Common Root Rot Resistance
Автор: M. I. E. Arabi, E. Al-Shehadah, M. Jawhar
Журнал: Журнал стресс-физиологии и биохимии @jspb
Статья в выпуске: 3 т.17, 2021 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Spot blotch (SB) caused by the fungus Cochliobolus sativus, is a devastating disease of barley that causes significant yield losses worldwide. Development of resistant cultivars is generally considered difficult, therefore, in this work; doubled haploid (DH) lines derived from crossing common cultivars currently used in Europe and West Asia were tested for reaction to C. sativus. Following field experiments 40 lines were evaluated under artificial infection conditions during two consecutive seasons. Results demonstrated significant differences among barley lines with a broad spectrum of disease responses ranging from highly susceptible to highly resistant, which were consistent in both seasons. However, seven promising lines had slightly lower SB disease than the others. On the other hand, positive correlation (r=0.80, P=0.01) between SB and common root rot (CRR; caused also by C. sativus) was found when these highly resistant DH lines were inoculated by the same virulent pathotype Pt4, which could suggest that resistance to C. sativus in the sub-crown internodes and leaves might involve similar defence mechanisms. The newly identified DH resistance lines can be potential donors for ongoing SB and CRR resistance breeding program to generate high-yielding commercial barley cultivars.
Barley (Hordeum vulgare L.), doubled haploids, spot blotch, common root rot, resistance
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/143173900
IDR: 143173900
Текст научной статьи Screening Barley Doubled Haploid Lines for Spot Blotch Resistance and Its Interrelationship with Common Root Rot Resistance
Cochliobolus sativus (Ito and Kurib.) Drechsler ex Dastur (anamorph Bipolaris sorokiniana (Sacc.) Shoemaker), is one of the most destructive fungal diseases of barley and several small grains worldwide (Kumar et al. 2002 ). It can infect all the aboveground (spot blotch; SB) and the subterranean parts (common root rot; CRR) of the barley plant causing significant reduction in yield and quality of the crop (Fernandez and Holzgang 2009; Rehman et al. 2020). Barley breeding for C. sativus resistance is more economical and environment appropriate solution when compared by using fungicides (Sharma and Duveiller 2007 ; Anonymous 2011).
Development of stable forms of resistance to foliar diseases such SB depends on identification of resistances effective towards the prevalent fungal isolates in barley cultivation areas (Wilcoxson et al. 1990). However, the use of genetic resistance in breeding is hindered by several causes, especially the rapid breakdown under emerging new pathotypes pressure of fungal pathogens, but also partial effectiveness in elite cultivars due to linkage drag (Ghazvini and Tekauz 2007; Leng et al. 2016). Therefore, barley breeders need a continuous supply of new resistance sources to keep up with the pace imposed by the challenges of fungal pathogens and the demands of producers.
SB resistance is governed by both major and minor genes (Wang et al. 2019; Visioni et al. 2020). However, very little resistances combine all the desired characteristics for a perfect solution from a breeding point of view. Moreover, upon the successful incorporation and detection of resistance genes into barley lines, the fixing of these genes in a suitable genetic background and the subsequent producing inbred lines can still need a number of years before a new cultivar is ready for field trials. The doubled-haploid (DH) technique can reduce the time to introduce genetically stable progeny from a new cross (Park et al. 1976; Ohnoutkova et al. 2019).
In Syria, sources of complete resistance to SB have not been identified, and current barley cultivars are considered to be only moderately resistant toward SB. Therefore, new barley resistance sources to this disease are needed to provide efficient resistance due to the rapid change of pathotype patterns of C. sativus in fields. The aim of the present work was to screen barley breeding lines for resistance to SB disease through four crosses of barley cultivars presently grown in Europe and West Asia under Syrian field conditions which are typical of Mediterranean environments. The relationship for resistance to SB and CRR among resistant DH lines was also investigated.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Barley material
A total of 40 anther-culture-derived DH lines progenies produced according to Kasha and Kao (1970), were screened on the basis of agronomic characteristics and evaluated in this study (Table 1). These lines were produced through four resistant-by-susceptible barley crosses made between six parents possessing different SB reactions. Arabi Abiad is a Syrian local cultivar, Arrivate was received from USA, PK36-130 is a Pakistani cultivar, Igri from Germany, CI5791 from Ethiopia, and IC-9 is a new cultivar developed at ICARDA (International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas). Haploid plants were produced by crossing parents using the standard procedure (Kasha and Kao 1970). Briefly, spikes of barley were manually emasculated and each spike was pollinated with fresh pollen. Then, they were treated with 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D). Tillers from F1 plants were collected when the majority of microspores were at mid- to late-uninucleate stage of development. They were kept in the dark at 4 °C for 21 days in Hoagland’s salt solution. Then, tillers were sterilized with ethanol (96 %) under sterile conditions and the anthers were excised and transferred to modified FW culture medium. Seedling were vernalized for 8weeks and then treated with colchicine solution to induce chromosome doubling (Subrahmanyam and Kasha 1975).
Field trials
Experiments were performed in a location favorable for the development of SB disease, approximately 55 km south of Damascus for two years, under natural rainfed conditions (250 mm annual rainfall). Seeds were planted in three replicate plots (1 x 1 m) with 1-m wide borders. Each plot consisted of five rows 25 cm apart with 50 seeds sown per row.
SB inoculation
The most virulent Syrian pathotype C. sativus Pt4 (Arabi and Jawhar 2004) was used in the present study. The fungal mycelia were grown in Petri dishes containing potato dextrose agar (PDA, DIFCO, Detroit, MI, USA) and incubated for 10 days at 21 °C in darkness. Inoculation was performed at growth stage (GS) 12 (Zadoks et al. 1974) by spraying plants with conidial suspension of 2 ×104 conidia mL-1 in pure water. Tween 20 (polyoxyethylene-sorbitan monolaurate) was added as a surfactant (100 µL L-1) to the conidial suspension to facilitate dispersion of the inoculum over the leaf surface. Non-inoculated control plants were sprayed with distilled water and surfactant.
SB evaluation
Plant response to SB infection was scored 14 days post inoculation using a scale described previously by Arabi (2005), where response to infection 10-30% were deemed resistant, 40-50% moderate resistant, and 60 to 90% susceptible.
CRR inoculation
The field trials were conducted at the same location of SB experiments. Seed of the selected resistant DH lines was inoculated according to the method described by van Leur (1991), where, 30g seeds of each line were immersed in a plastic Petri dish (12-cm diameter) containing 10g sterile neutralized peat, 40 ml spore suspension (5 × 105 condia/ml) and 8 drops of natural Arabic gum. The components was mixed thoroughly and then planted at 6 cm depth to promote long subcrown internodes (Kokko et al. 1995) in a randomized complete block design, with three replicate plots (1 x1 m) separated with a 1-m wide border. Each plot consisted of five rows, 20 cm apart and with 50 seeds per row.
CRR evaluation
CRR was evaluated 8 weeks post-inoculation by measuring the percentage of subcrown internodes surface showing CRR symptoms using a 0-5 scale, as described by Kokko et al. (1995), where; 0 (resistant) and 5 (highly susceptible).
Data analysis
Data was subjected to analysis of variance using the STAT-ITCF statistical programme (2nd version ) . Differences between means were evaluated for significance by using Newman-Keuls test at 5% probability level, and the relationship between severity ratings for SB and CRR was examined using STAT-ITCF program (Anonymous 1988).
RESULTS
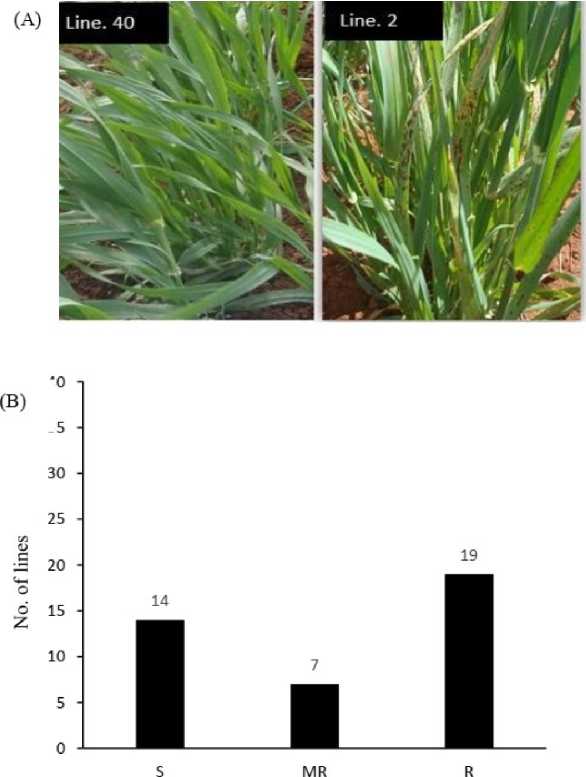
In this investigation, six barley parents currently used in Europe and West Asia with different resistance levels to SB infections were used (Table 1). Disease symptoms (presence of necrosis and/or chlorosis) were typically observed in infected plants with the severity values being consistently higher in the susceptible genotypes. As shown in Figure 1. SB caused more severe infection on the susceptible DH line 2 as compared with the resistant ones DH line 40. According to a scale described by Arabi (2005), the reactions of the 40 progeny lines to SB under field tests were classified into 19 lines as tolerant, 7 as moderate and 14 as severe groups (Fig. 1). However, significant differences ( P < 0.05) in mean severity values were detected among different lines, and a broad spectrum of reactions to the virulent C. sativus pathotype Pt4 from highly susceptible to highly resistant was observed (Table 2).
The data showed that seven lines (B08-AS-6, 9, 13, 31, 38, 39 and 40) were classified as highly resistant in both seasons, whereas lines B08-AS 15, 22, 25 and 33 were the most susceptible lines (Table 2). The other lines had SB ratings that ranged between moderately resistant and susceptible. Significant correlation coefficient ( r = 0.60, P = 0.001) was found between the two seasons for SB reaction, indicating that lines reacted similarly to C. sativus populations under field conditions. On the other hand, a positive correlation ( r =0.80, P =0.01) between SB and CRR was found when the highly seven resistant DH lines (B08-AS-6, 9, 13, 31, 38, 39 and 40) were inoculated by the same virulent pathotype Pt4 (Fig. 2).
Table 1. Barley parents reactions against spot blotch disease in this study.
|
Parents |
Origin |
Type |
Disease severity % |
Classification |
|
Arrivate |
USA |
6 |
77.5 a* |
S |
|
Arabi Abiad |
Syria |
2 |
57.5 c |
S |
|
PK30-136 |
Pakistan |
6 |
69.93 b |
S |
|
IC-9 |
ICARDA |
6 |
21.73.d |
R |
|
Igri |
Germany |
2 |
14.8 d |
R |
|
C15791 |
Ethiopia |
2 |
6.56 e |
R |
R=resistant, S: suspectible according to scail of Arabi (2005).
ICARDA: International Center for Agricultural Research in Dry Areas, Syria.
* Values within a column followed by different letters are significantly different at P<0.05 according to Mewman-Keuls test.
Disease reaction
Figure. 1. (A) Spot blotch symptoms on the barley resistant DH line 40 and the susceptible DH line 2 under field conditions. (B) Frequency distribution of spot blotch infection response of 40 DH barley line which were resistant (R), moderately resistant (MR) and susceptible (S) according to 1–3 scale described by Arabi (2005). Data were obtained from five crosses of barley parent.
Table 2. Mean disease of spot blotch (%) of 40 barley lines under field conditions.
|
Cross |
No |
Lines |
Disease Severity % |
Classification |
|
ArabiAbiad X IC-9 |
1 |
B08-AS-1 |
83.65 b |
S |
|
2 |
B08-AS-2 |
78.45 b |
S |
|
|
3 |
B08-AS-3 |
77.08 c |
S |
|
|
4 |
B08-AS-4 |
20.30 k |
R |
|
|
5 |
B08-AS-5 |
35.03 h |
MR |
|
|
6 |
B08-AS-6 |
5.99 m |
R |
|
|
7 |
B08-AS-7 |
41.08 g |
MR |
|
|
8 |
B08-AS-8 |
9.46 m |
R |
|
|
9 |
B08-AS-9 |
41.60 g |
MR |
|
|
10 |
B08-AS-10 |
50.80 f |
S |
|
|
11 |
B08-AS-11 |
24.50 k |
R |
|
|
12 |
B08-AS-12 |
13.63 l |
R |
|
|
13 |
B08-AS-13 |
18.18 l |
R |
|
|
14 |
B08-AS-14 |
61.99 d |
S |
|
|
15 |
B08-AS-15 |
93.16 a |
S |
|
|
Arrivate X PK30-136 |
16 |
B08-AS-16 |
41.20 g |
MR |
|
17 |
B08-AS-17 |
56.15 e |
S |
|
|
18 |
B08-AS-18 |
48.80 f |
MR |
|
|
19 |
B08-AS-19 |
17.85 l |
R |
|
|
20 |
B08-AS-20 |
25.90 k |
R |
|
|
21 |
B08-AS-21 |
16.60 l |
R |
|
|
22 |
B08-AS-22 |
86.70 a |
S |
|
|
23 |
B08-AS-23 |
37.00 h |
MR |
|
|
24 |
B08-AS-24 |
16.90 l |
R |
|
|
25 |
B08-AS-25 |
85.40 b |
S |
|
|
26 |
B08-AS-26 |
5.26 n |
R |
|
|
27 |
B08-AS-27 |
20.60 l |
R |
|
|
28 |
B08-AS-28 |
29.60 i |
R |
|
|
29 |
B08-AS-29 |
86.20 a |
S |
|
|
30 |
B08-AS-30 |
18.40 l |
R |
|
|
31 |
B08-AS-31 |
11.90 m |
R |
|
|
32 |
B08-AS-32 |
19.50 l |
R |
|
|
33 |
B08-AS-33 |
90.40 a |
S |
|
|
CI5791 X Igri |
34 |
B08-AS-34 |
43.10 g |
MR |
|
35 |
B08-AS-35 |
69.80 c |
S |
|
|
36 |
B08-AS-36 |
51.70 f |
S |
|
|
37 |
B08-AS-37 |
53.70 f |
S |
|
|
Arabi Abiad X Arrivate |
38 |
B08-AS-38 |
5.60 n |
R |
|
39 |
B08-AS-39 |
7.95 m |
R |
|
|
40 |
B08-AS-40 |
8.30 m |
R |
|
|
LSD |
7.1 |
R=resistant, S: suspectible according to scail of Arabi (2005).
* Values within a column followed by different letters are significantly different at P<0.05 according to Mewman-Keuls test.
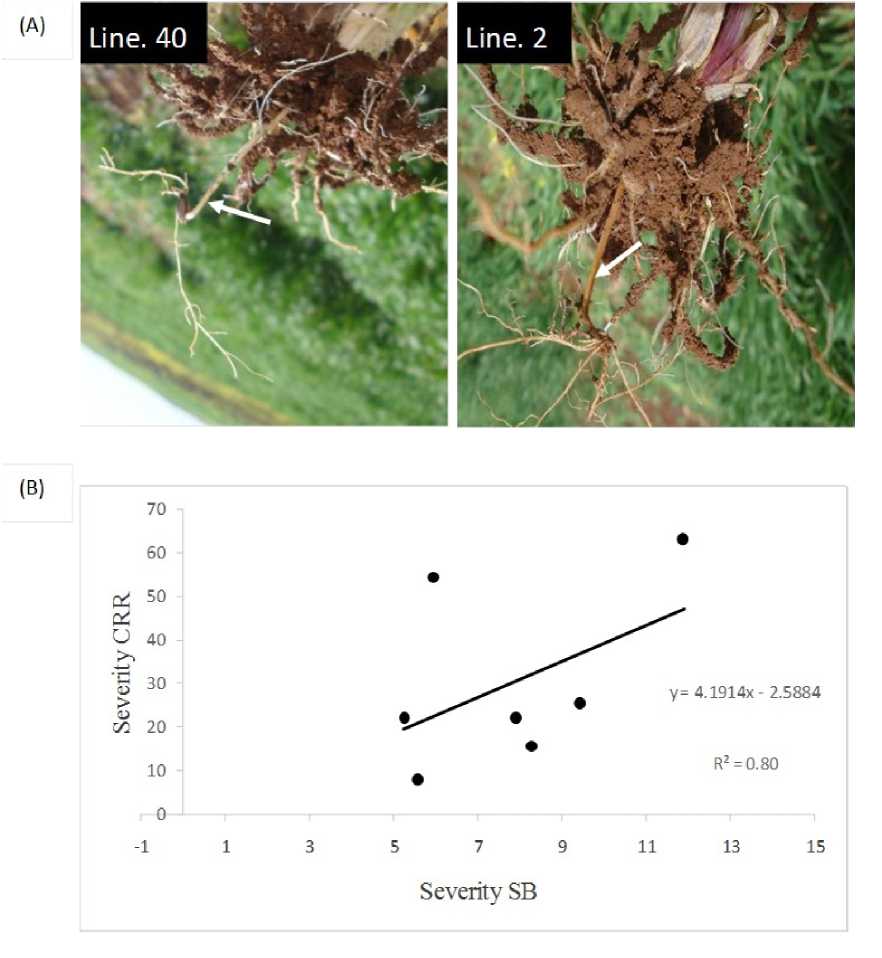
Figure. 2. (A) Common root rot symptoms on the barley resistant barley DH line 40 and susceptible DH line 2 line under field conditions. (B) Relationships between SB and CRR severity on 7 barley DH lines.
DISCUSSION
The genetic uniformity of SB resistance in barley two- and six-rowed cultivars and emerging and reemerging new C. sativus pathotypes (Zhou and Steffenson 2013), make barley vulnerable to SB epidemics. Therefore, identification of new sources of resistance is essential to combat the SB disease with barley plant resistance. In this work, we evaluated 40 barley DH lines for their reactions to the most Syrian virulent pathotype Pt4 under field conditions. The results showed that, all the seven resistant lines maintained their reaction during the two growing seasons, which reflects stability of their resistant levels. Moreover, the population of crosses Arabi Abiad/Arrivate and PK30-136/Arrivate will be used for mapping genes associated with SB resistance. Some lines from this cross were recovered with a high degree of resistance to SB (Table 2). These will be tested in multilocation experiments to be sure about their stability and adaptability.
On the other hand, several sources of SB resistance have been reported in winter barley in India (Kuldeep et al. 2008), and in spring barley in United States (Leng et al. 2016) and China (Guo et al. 2019). In the present study, the spring 40 DH lines had diversity for infection response against SB indicating the existence of genetic variability among them similar to the observations reported in winter and spring barley around the world. Therefore, inclusion of those diverse DH lines in the future barley breeding program may increase the dominance effect and epistatic variations controlling quantitative traits such as SB resistance (Bovill et al. 2010). These would also lead to extend segregation for different traits and in obtaining useful and new recombinants/transgressive segregants in the next generations.
In addition, a positive correlation (r=0.80, P=0.01) between SB and CRR was found when the seven resistant DH lines were inoculated by the same virulent pathotype Pt4, which might suggest that resistance to C. sativus in the sub-crown internodes and leaves involves similar defence mechanisms. This result would be of interest to plant breeders because testing for SB reaction needs less time than screening for CRR resistance. However, this relationship should be further examined with additional genotypes to determine whether screening for resistance to one disease indirectly selects for resistance to the other disease. Similar results were found by Conner (1990) on wheat, and by Arabi et al. (2006) on barley under controlled conditions.
CONCLUSION
This work has provided barley development programs with seven promising SB resistant DH derived lines that could be considered as possible donors in further breeding programs. It also aimed to identity greater diversity of resistance for breeders with the possibility of providing replacement cultivars in the near future. In addition, positive correlation between SB and CRR was found using the resistant DH lines inoculated by the same virulent pathotype Pt4, which suggest that similar defence mechanisms to C. sativus might involve in the barley sub-crown internodes and leaves. This would be useful in breeding programs since SB reaction needs less time than screening for CRR resistance.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors would like to thank the Director General of AECS and the Head of the Molecular Biology and Biotechnology Department for their continuous support throughout this work. Thanks are also extended to Dr. A. Al-Daoude for critical reading of the manuscript.
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
All authors have declared that they do not have any conflict of interest for publishing this research.
Список литературы Screening Barley Doubled Haploid Lines for Spot Blotch Resistance and Its Interrelationship with Common Root Rot Resistance
- Anonymous (1988) STAT-ITCF, Programme, MICROSTA, realized by ECOSOFT, 2nd Version. Institut Technique des cereals et des Fourrages, Paris, 55 p
- Anonymous (2011) Progress report of all India coordinated wheat and barley improvement project 2010-11, in Barley Networks, Vol. 6, eds R. P. S.
- Verma, A. S. Kharub, D. Kumar, B. Sarkar, R. Selva Kumar, R. Singh et al. (Karnal: Directorate of Wheat Research), 302.
- Arabi MIE (2005) Inheritance of partial resistance to spot blotch of barley. Plant Breed 124:605-607
- Arabi MIE, Jawhar M (2004) Identification of Cochliobolus sativus (spot blotch) isolates expressing differential virulence on barley genotypes in Syria. J Phytopathol 152:461-464
- Arabi MIE, Al-Daoude A, Jawhar M (2006) Interrelationship between spot blotch and common root rot in barley. Austral Plant Pathol 35:477-479
- Bovill J, Lehmensiek A, Sutherland MW, Platz GJ, Usher T, Franckowiak J, Mace E (2010) Mapping spot blotch resistance genes in four barley populations. Mol Breed 26:653–666
- Conner RL (1990) Interrelationship of cultivar reactions to common root rot, black point and spot blotch in spring wheat. Plant Dis 74:224-227
- Fernandez MR, Holzgang G (2009) Fungal populations in subcrown internodes and crowns of oat crops in Saskatchewan. Can J Plant Sci 89:549-557
- Ghazvini H, Tekauz A (2007) Virulence diversity in the population of Bipolaris sorokiniana. Plant Dis 91:814-821
- Guo H, Yao Q, Chen L, Wang F, Lang X, Pang Y, Feng J, Zhou JR, Xu S (2019) Virulence and molecular diversity in the Cochliobolus sativus population causing barley spot blotch in China. Plant Dis 103:2252-2262
- Kasha KJ, Kao KN (1970) High frequency haploid production in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Nature 225:874-876
- Kokko EG, Conner RL, Kozub GC, Lee B (1995) Effects of common root rot on discoloration and growth of spring wheat root system. Phytopathology 85:203-208
- Kuldeep T, Nandan R, Kumar U, Prasad LC, Ch R, Josh AK (2008) Inheritance and identification of molecular markers associated with spot blotch (Cochliobolus sativus) resistance through microsatellites analysis in barley. Genet Mol Biol 31:734-742
- Kumar J, Schäfer P, Hückelhoven R, Langen, G, Baltruschat H, Stein E, Kogel KH (2002) Bipolaris sorokiniana, a cereal pathogen of global concern: Cytological and molecular approaches towards better control. Mol Plant Pathol 3:185–195
- Leng Y, Wang R, Ali S, Zhao M, Zhong S (2016) Sources and genetics of spot blotch resistance to a new pathotype of Cochliobolus sativus in the USDA small grains collection. Plant Dis 100:1988-1993
- Ohnoutkova L, Vlcko T, Ayalew M (2019) Barley anther culture. In Barley: Methods and Protocols, W.A. Harwood, ed., 1900. Methods in Molecular Biology (New York: Humana Press), pp. 37–52
- Park SJ. Walsht EJ, Reinbergs E, Song LSP, Kasha KJ (1976) Field performance of doubled haploid barley lines in comparison with lines developed by the pedigree and single seed descent methods. Can J Plant Sci 56:467-474
- Rehman S, Gyawali S, Amri A, Verma RPS (2020) First report of spot blotch of barley caused by Cochliobolus sativus in Morocco. Plant Dis 104:3
- Sharma R, Duveiller E (2007) Advancement toward new spot blotch resistant wheats in South Asia. J Crop Sci 47:961–968
- Subrahmanyam NC, Kasha KJ (1975) Chomosome doubling of barley haploids by nitrous oxide and colchicines treatments. Can J Genet Cytol 17:573-583
- van Leur JG (1991) Testing barley for resistance to Cochliobolus sativus at ICARDA, Syria. In: RD.
- Tinline et al. (eds), Proceeding of the 1stInternational workshop on common root rot of cereals. Saskatoon, 128-134
- Visioni A, Rehman S, Viash SS, et al. (2020) Genome wide association mapping of spot blotch resistance t seedling and adult plant stages in barley. Front Plant Sci 11:642
- Wang R, Leng Y, Zhao M, Zhong S (2019) Fine mapping of a dominant gene conferring resistance to spot blotch caused by a new pathotype of Bipolaris sorokiniana in barley. Theor Appl Genet 132:41–51
- Wilcoxson RD, Rasmusson DC, Miles MR (1990) Development of barley resistant to spot blotch and genetics of resistance. Plant Dis 74:207–210
- Zadoks JC, Chang TT, Konzak CF (1974) A decimal code for the growth stages of cereals. Weed Res 14:415-421
- Zhou H, Steffenson B (2013) Genome-wide association mapping reveals genetic architecture of durable spot blotch resistance in US barley breeding germplasm. Mol Breed 32:139–154


