Seed priming for better growth and yield of safflower (Carthamus tinctorius) under saline condition
Автор: Elouaer Mohamed Aymen, Kaouther Zhani, Ben Fredj Meriem, Cherif Hannachi
Журнал: Журнал стресс-физиологии и биохимии @jspb
Статья в выпуске: 3 т.8, 2012 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Salinity is considered as a major abiotic stress affecting crop production in arid and semi-arid region. In field condition, poor germination and decrease of seedling growth results in poor establishment and occasionally crop failure. Many research studies have shown that seed priming is an efficient method for increasing plant growth and improvement of yield in saline condition. That's why; this experiment was conducted to evaluate the effects of KCl priming on the growth traits and yield of Tunisian safflower under salinity conditions. Seeds were primed with KCl (5 g/l) for 24 h at 20°C. Primed (P) and un-primed (NP) seeds were directly sown in the field and followed during eight months of plant cycle. Experiments were conducted using various water irrigations concentrations induced by NaCl (0, 3, 6, 9 and 12 g/l). Results showed that plant height of primed seeds was greater than that of un-primed seeds. Numbers of branches per plant, fresh and dry weight, heads number per plant, petals and grains yield of plants derived from primed seeds were higher compared with un-primed seeds.
Growth, safflower, salinity, priming, yield
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/14323657
IDR: 14323657
Текст научной статьи Seed priming for better growth and yield of safflower (Carthamus tinctorius) under saline condition
The use of saline water especially in agriculture has become inevitable to compensate the rapid increase in demand and water competition between human needs and industry, specifically in arid and semi-arid regions (Katerji et al., 2000). Indeed, the supply of good water quality for agriculture will face in future decades a dramatic decline as most fresh water resources have already been mobilized (Hamdy, 2002).The use of saline water for irrigation threatens the sustainability of both agricultural land and crop productivity (Tester and Davenport, 2003; Ashraf and Foolad, 2007). Salinization of irrigated soils has become a major concern for global food production (Munns and Tester, 2008). Estimates have indicated that at least 20% of irrigated land was affected by salt (Ghassemi et al., 1995). In addition, statistics estimate that annually 10 million hectares of irrigated land was abandoned because of salinity problems (Hamdy, 1999). Salinity threatens the sustainability of high agricultural productivity (Flowers and Yeo, 1995). Consequently, the safe use of saline water for sustainable production of crops is a challenge that must be considered (Hamdy, 1995) which requires more complex preventive measures than when the water used is of good quality (Hamdy, 1993 and Hamdy, 1996). To reduce the impact of salinity on crop yields, several measures can be taken: the addition of organic matter (Walker and Bernal, 2008), the addition of calcium (Tuna et al., 2007) and potassium (Turkmen et al., 2000) or by genetic engineering methods to improve plant resistance to salt stress (Cushman and Bohnert, 2000). Another alternative is to use the technique of priming to increase tolerance and crop productivity under salt stress. Priming is a seed treatment before sowing to improve their germination, it consist in soaking seeds in an osmotic solution where the first two phases of germination (imbibition and activation phases) take place without emergence and growth of the radicle. This technique has proven its effectiveness for good crop establishment in saline soil (Ashraf and Rauf, 2001; Basra et al., 2005). Thus, this work attempts to apply priming technique on the culture of safflower under salt stress. Indeed, research studies can be found on the production of safflower in saline irrigation condition, but this plant is known to be moderately tolerant to salinity (Bassil and Kaffka, 2002), that’s why that this work tried to improve growth and productivity of safflower in saline irrigation regime using priming technique.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The experiment was carried in the field research of High Institute of Agriculture, Chott Mariem, Tunisia. Safflower seeds were primed with 5 g/l KCl solution for 24 hours, at 22 °C. After priming, primed and non primed seeds (control seeds) were sown directly in the soil at the month of November according to a plant density of 9 plants/m2. Throughout their vegetative cycles, plants from primed and control seeds were irrigated with saline water at five levels of NaCl concentrations (0, 3, 6, 9 and 12 g/l). The experiment was arranged factorial in a completely randomized design with two factors which are priming treatment (KCl primed seeds and control seed) and salinity levels (0, 3, 6, 9 and 12 g/l NaCl) with three replications and 20 plants per replicate.
Parameters measured in this study were: plant height, number of branches per plant and heads per plant and petals and seeds yields.
Growth and yield parameters of safflower were evaluated with analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Duncan multiple range test (p < 0.05) using the SPSS (13.0) System. Differences were considered significant at the 5% level (means followed by different letters).
RESULTS
Plant height
Salinity levels and seed priming had a significant ( p < 0.5) effect on plant height (Figure 1). Increasing salinity levels had significantly ( p < 0.05) reduced plant height. This reduction was more important in control seed when compared with primed seed exposed to different salinity levels. Similarly, the effect of seed priming was more profound on plant height at high salinity level (12 g/l). Seed priming had significantly ( p < 0.05) increased plant height of (9%) when exposed to 12 g/l salinity and compared with non-primed treatment.
Number of branches per plant
Increasing salinity levels negatively affected the number of branches per plant (Figure 2). Reduction in branches number due to salinity exposure was less important (11) in primed seed when compared with control seed (9) at the highest level of salinity (12 g/l NaCl). Seed priming had a significant (p > 0.05) effect on number of branches per plant.
Plant fresh and dry weight
Fresh weight of safflower plant significantly decreased due to an increase in NaCl salinity in both primed and control seed (Figure 3). Under saline conditions, plants of primed group had a higher fresh weight than non primed group. At 3 g/l NaCl, plant fresh weight of primed group is 23% higher than of control group.
As a general trend, increased NaCl salinity significantly decreased plant dry weight in both primed and control groups (Figure 4). However, dry weight in plant of primed group (KCl priming) was significantly higher in each salinity level than in the non primed group.
Number of heads per plant
The number of safflower head per plant was significantly (p < 0.05) affected by salinity levels and seed priming treatments (Figure 5). Increasing NaCl concentrations decreased heads number per safflower plant. The effect of seed priming in increasing the number of heads per plant was more profound in plant derived from KCl primed seeds than control group. Primed seeds have 30% more heads at 3 g/l when compared with non-primed treatment.
Petal yield
Priming seed treatments with KCl had a significant positive effect on petals yield compared with the control. Although salinity significantly decreased petals yield in all salinity levels, however, seed priming caused an increased in safflower petals yield. In fact, at 6 g/l NaCl, petals yield in primed group was 30% more than control group.
Grain yield
Grain yield of both cultivars was significantly ( p < 0.05) affected by increasing levels of salinity. The effect of salinity was more profound on plant derived from control seeds than plant derived from primed ones. Seed priming had significantly ( p < 0.05) increased grain yield of safflower (10 and 15% at 6 and 9 g/l NaCl) when compared with the nonprimed treatment at the same salinity levels.
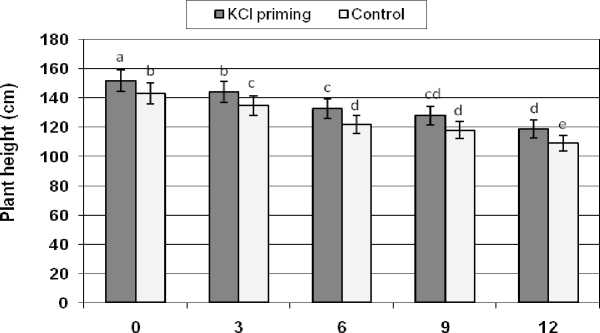
NaCI(g/l)
Figure 1: The effects of NaCl salinity on plant height of safflower plant derived from primed and control seeds
Means followed by the same letter are not significantly different at 5% level according to Duncan test.
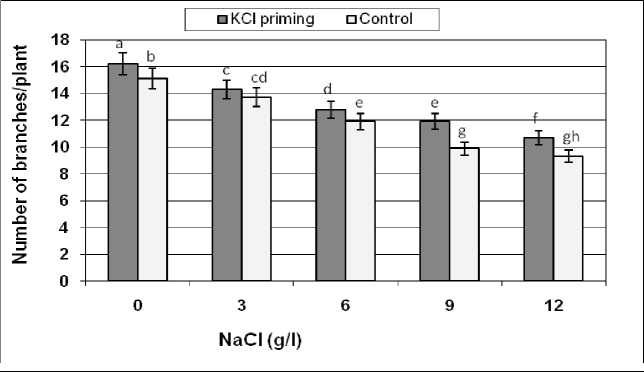
Figure 2: The effects of NaCl salinity on the number of branches of safflower plant derived from primed
and control seeds
Means followed by the same letter are not significantly different at 5% level according to Duncan test.
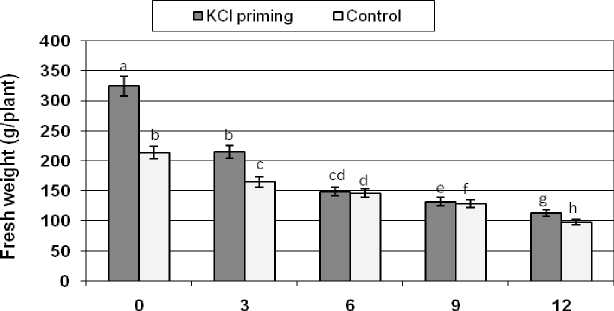
NaCI(g/l)
Figure 3: The effects of NaCl salinity on fresh weight of safflower plant derived from primed and control seeds
Means followed by the same letter are not significantly different at 5% level according to Duncan test.
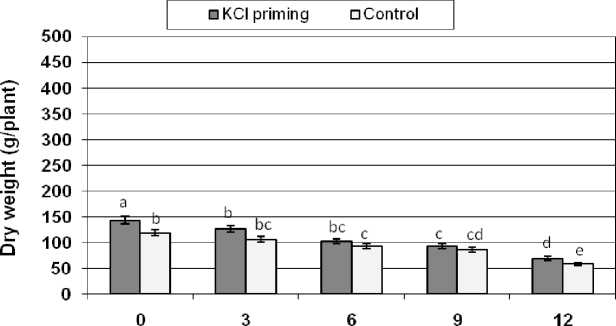
NaCI(g/l)
Figure 4: The effects of NaCl salinity on dry weight of safflower plant derived from primed and control seeds
Means followed by the same letter are not significantly different at 5% level according to Duncan test.
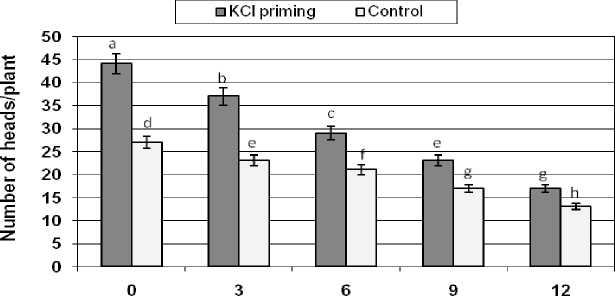
NaCI(g/l)
Figure 5: The effects of NaCl salinity on number of safflower heads from plant derived from primed and control seeds
Means followed by the same letter are not significantly different at 5% level according to Duncan test.
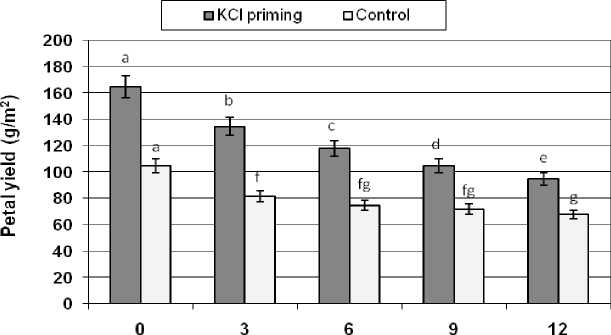
NaCI(g/l)
Figure 6: The effects of NaCl salinity on safflower petals yield of plant derived from primed and control seeds
Means followed by the same letter are not significantly different at 5% level according to Duncan test.
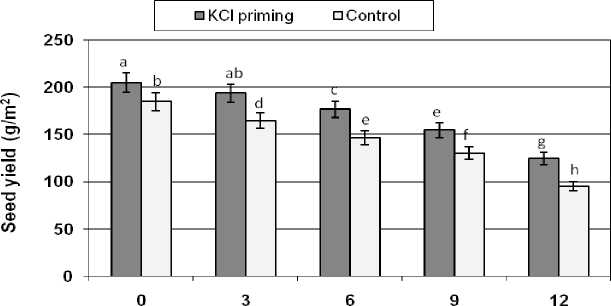
NaCI(g/l)
Figure 7: The effects of NaCl salinity on safflower seed yield of plant derived from primed and control seeds
Means followed by the same letter are not significantly different at 5% level according to Duncan test.
DISCUSSION
The present study investigated the effect of salinity and seed priming on the growth and yield of safflower. The data showed that salinity had significantly affected plant height under study. The present study also demonstrated that plant height recorded in plants derived from primed seeds were significantly different from plants derived from nonprimed treatments when exposed to different salinity levels. Similar results are also reported by Sivritepe et al., (2003) in melon. Growth parameters (plant height, number of branches per plant, plant fresh and dry weight) decreased with increasing salinity. Similar results were observed by Naseer (2001) and Shafi et al., (2010) working in barley; Kumar et al., (1981); Sharma and Grag (1985) working with wheat. It was observed that boosting levels of salinity has gradually decreased plant height which might be due to decreased physiological activities resulting from water and nutrients stress occurring under salinity stress. The adverse effect of salinity on plants may lead to disturbances in plant metabolism, which consequently led to reduction of plant growth and productivity (Sharma and Hall 1991; Shafi. et al ., 2009).
Seed priming and salinity levels have extensively affected shoot fresh and dry weight (g plant-1) of safflower. Shoot weight decreased progressively with the rise of stress level compared with control. Fortmeir and Swchuber (1995) also reported similar results in barley.
The increase in salinity levels resulted in the development of water and nutrient stresses. The toxic effect of sodium at high salt levels and physical damage to roots decreased their ability to absorb water and nutrient which caused marked reduction in photosynthesis, enzymatic process and protein synthesis (Tester and Davenport, 2003), which resulted in stunted growth and poor leaf area development. The decrease in the rate of photosynthesis due to leaf area might be responsible to decrease shoot fresh and in turn dry weight. It is evident from results that primed seeds in comparison with control seeds resulted in more crop growth rate (Basra et al., 2003). Therefore, it is concluded that seed priming could be more effective in improving safflower growth parameters. These results agree with the finding of Harris et al., (2001) and Basra et al., (2003). They reported greater plant weight following seed priming.
Salinity adversely affects almost all stages of plant growth and development, ultimately causing low economic yield and poor quality of yield production (Ashraf and Harris, 2004). Growth reduction due to salinity is mainly attributed to water deficit due to lowered water potential in root medium, nutritional imbalance and specific ion toxicity arising from higher concentration of Na+ and Cl- (Khan and Ashraf, 1988; Marschner, 1995).
Pre-sowing seed treatment with inorganic salt has been shown to improve plant establishment under saline conditions for different plants (Cayuela et al., 1996; Rehman et al., 1998 and Sivritepe et al., 2003). K+ and Ca2+ are well known to have an antagonistic effect on uptake of Na+ in plants subjected to NaCl stress and thus, mitigate the toxic effect of Na+ on plant metabolism (Greenway and Munns, 1980). There are several reports revealed that increasing the K+ and Ca2+ concentration in seeds of different crops significantly led to increase seed germination and enhancement of seedling growth under saline conditions (Cramer, 1990). The possible reason for improving growth and yield may be that salinity interacts with plant nutrients which become unavailability to seedlings however K or Ca2+ pre-treatments made the nutrients more available to seedlings under salt stress. It was also reported that potassium has a prevalent action in plants and is involved in maintenance of ionic balance in cell and bounds ironically to enzyme pyruvate kinase which is essential in respiration and carbohydrate metabolism (Aisha et al., 2007).
Список литературы Seed priming for better growth and yield of safflower (Carthamus tinctorius) under saline condition
- Aisha, A.H., Rizk, F.A., Shaheen, A.M., and Abdel-Mouty, M.M. (2007). Onion plant growth, bulb yield and its physical and chemical properties as affected by organic and natural fertilization. Res. J. Agric. Biol. Sci., 3(5), 380-388.
- Ashraf, M., and Rauf, H. (2001). Inducing salt tolerance in maize (Zea mays L.) through seed priming with chloride salts: Growth and ion transport at early growth stages. Acta Physiol. Planta., 23, 407-417.
- Ashraf, M., and Harris, P.I.C. (2004). Potential biochemical indicators of salinity tolerance in plant. Plant Sci., 166, 3-16.
- Basra, S.M.A., Ehsanullah, E., Warraich, A., Cheema, M.A., and Afzal, I. (2003). Effect of storage on growth and yield of primed canola seed. Int. J. Agric. Bio., 117-120.
- Basra, S.M.A., Afzal, I., Rashid, R.A., and Hameed, A. (2005). Inducing salt tolerance in wheat by seed vigor enhancement techniques. Intl. J. Biotechnol., 1, 173-179.
- Bassil, E.S., and Kaffka, S.R. (2002). Response of safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L.) to saline soils and irrigation II. Crop response to salinity. Agr. Water Manage., 54, 81-92.
- Cayuela, E., Alfocea, E.P., and Bolaryn, C.M. (1996). Priming of seeds with NaCl induces physiological changes in tomato plants growth under salt stress. Physiol. Plant, 96, 231-236.
- Cramer, G.R., Epstein, E., and Lauchli, A., (1990). Effects of sodium, potassium and calcium on salt-stressed barley. Physiol. Plant., 80, 83-88.
- Cushman, J.C., and Bohnert, H.J. (2000). Genomic approaches to plant stress tolerance. Curr Opin Plant Biol., 3, 117-124.
- Fortmeier, R. and Schubert, S. (1995). Salt tolerance of maize (Zea mays L.) The role of sodium exclusion. Plant cell and Environ., 18(9), 1041-1047.
- Greenway, H., and Munns, R. (1980). Mechanisms of salt tolerance in nonhalophytes. Annu. Rev. Plant. Physiol., 31, 149-190.
- Harris, D., Pathan, A.K., Gothkar, P., Joshi, A., Chivasa, W., and Nyamudeza, P. (2001). Onfarm seed priming: using participatory methods to revive and refine a key technology. Agric. Sys., 69(1-2), 151-164.
- Khan, A.H., and Ashraf, M.Y., (1988). Effect of sodium chloride on growth and mineral composition of sorghum. Acta Physiol. Plant., 10, 259-264.
- Kumar, D., Singh, C.P., and Sharma, N.N. (1981). Comparative studies of grain yield and nutrition in barley as affected by the application of saline water for irrigation. Indian J. Plant Physiol., 24, 229-236.
- Marschner, H. (1995). Mineral nutrition of higher plants. London, Orlando, San Diego, New York, Austin, Boston, Sydney, Tokyo, Toronto, Academic Press.
- Naseer, S., Nisar, A., and Ashraf, M. (2001). Effect of salt stress on germination and seedling growth of barley. Pak. J. Bio. Sci., 4(3), 359-360.
- Rehman, S., Harris, P.J.C., Bourne, W.F., and Wilkin, J. (1998). The effect of sodium chloride on germination and potassium and calcium contents of Acacia seeds. Seed Sci. Tech., 25, 45-57.
- Shafi, M., Bakht, J., Raziuddin, and Zhang, G. (2009). Effect of Cadmium and Salinity stresses on growth and antioxidant enzymes activity of wheat genotypes. Bull. Environ. Contaim. Toxicol., 82(6), 772-776.
- Shafi, M., Bakht, J., Khan, M.J., and Khan, M.A. (2010). Effect of salinity and ion accumulation of wheat genotypes. Pak J. Bot., 42(6), 4113-4121.
- Sharma, S.K., and Grag, O.P. (1985). Salinity induced changes in plant growth and activities of glutamate dehydrogenase, aspertate and alanine amino-transferases in wheat. Indian J. Plant Physiol., 28, 407-412.
- Sharma, P.K., and Hall, D.O. (1991). Interaction of salt stress and photo inhibition on photosynthesis in barley and sorghum. J. Plant Physiol., 138, 614-619.
- Sivritepe, N., Sivritepe, H.O., and Eris, A. (2003). The effects of NaCl priming on salt tolerance in melon seedling grown under saline conditions. Scientia Holti. 97, 229-237.
- Tester, M., and Davenport, R. (2003). Na+ tolerance and Na+ transport in higher plants. Ann. Bot., 9, 503-527.
- Tuna, A.L., Kaya, C., Ashraf, M., Altunlu, H., and Yokas Yagmur, B. (2007). The effects of calcium sulphate on growth, membrane stability nd nutrient uptake of tomato plants grown under salt stress. Environ. Exp. Bot., 59, 173-178.
- Türkmen, Ö., Sensoy, S., and Erdal, I. (2000). Effect of Potasium on Emergence and Seedling Growth of Cucumber Grown in Salty Conditions. Yuzuncu Yil University. J. Agric. Sci. 10, 113-117.
- Walker, D.J., and Bernal, M.P. (2008). The effects of olive mill waste compost and poultry manure on the availability and plant uptake of nutrients in a highly saline soil. Bioresour. Technol., 99, 396-403.


