Selection of the complex of microbiological tests for Bordetella bronchiseptica typing
Автор: Vasilyeva Yu.B.
Журнал: Вестник аграрной науки @vestnikogau
Статья в выпуске: 4 (43), 2013 года.
Бесплатный доступ
The article gives the results of the study of phenotypic signs of Bordetella bronchiseptica: morphological, tinctorial, biochemical and cultural ones. The selection of a complex of unique biological properties of bordetella was performed for the bacteriological identification of the agent.
Bordetella bronchiseptica, bordetellosis, microbiological tests, methods of typing
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/147124098
IDR: 147124098 | УДК: 619:578.832.1
Текст научной статьи Selection of the complex of microbiological tests for Bordetella bronchiseptica typing
The prophylactics and treating of any infectious disease can be considerably simplified by the early and precise identification of its agent. The main task of clinical microbiology lies in searching a minimal set of biological characteristics that can help to single out and type the wanted pathogen. In our country there are no standardized methods for identification of Bordetella bronchiseptica – the agent of bordetellosis of animals. The aim of the research is the study of biological properties of bordetella and the selection of a complex of unique diagnostic tests.
THE MATERIALS AND METHODS OF THE STUDY
The research was performed with the financial help of the government represented by the Ministry of Science and Education of the Russian Federation within the implementation of the Federal Target Project «Scientific and Scientific-Pedagogical Staff of the Innovative Russia» for the years 2009-2013 (agreement № 8267 from 10.08.2012). The study was performed at the laboratory of the department of Microbiology, Virology Epizootology and Veterinary-Sanitary Expertise FSBEI HPO «Ulyanovsk SAA n.a. P.A. Stolypin».The reference strains of B.bronchiseptica and the field strains singled out from the biomaterials of clinical patterns were used in the study.
47 strains of B.bronchiseptica were studied . The following biological properties of the bordetella were taken into consideration: the morphology, the characteristics of the colouring, specific peculiarities of the growth on different growth media and the biological signs of degrading of different substrates. The standard microbiological methods and their relevant media and reagents [1-4] were used.
THE RESULTS AND THE DISCUSSION
Within the colouring by Gram, Olt westated that all the strains of B.bronchiseptica are tiny gram-negative coccusbacilli located singularly, in pairs and occasionally in chains. Ovoid rods were 0,2-0,4 mcm wide and 0,5-1,5 mcm long, produced no spores. The morphological peculiarity of the agent was its phonotypical variability: the existence of avirulent (I), intermediate (II) and virulent (III) phases. The Bordetella are activein the avirulent phase because of the peritrichously located flagella (pict.1).The flagella provide moving of the bacteria along the respiratory passage to the rich in nutrient sparts of the organism. According to the data of Russian and foreign scientists the virulent phase of the bordetella does not produce flagella that is the consequence of flagellin synthesis negative regulation. The activity of the avirulent phase of B.bronchiseptica can beattributed to the number of potential factors of virulence since it provides the agent distribution along the mucous membrane of the respiratory passage at the moment of the contamination of the animal. Furthermore, positive correlation between the activity of bordetella and theirability for intracellular persistence was revealed [5, 6].
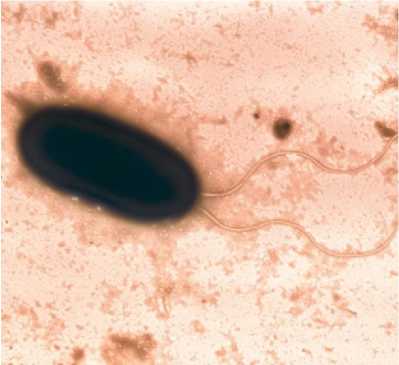
Picture 1 - Avirulent phase of B.bronchiseptica strain 8433 (35х103)
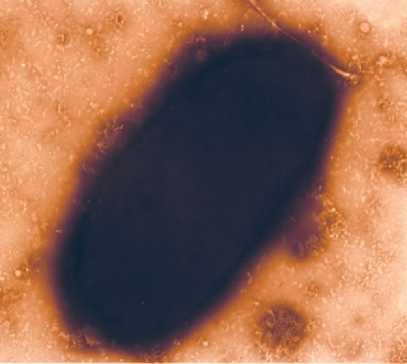
Picture 2 - Virulent phase of B.bronchiseptica 7 strain (50х103)
The virulent phase does not produce flagella. Within the process of transition into the virulent phase the bordetella covers itself with a tender microcapsule (pict. 2).
The analysis of the results of strain cultivation on liquid and solid growth media showed that bordetella are rigorous anaerobes with the optimal growth temperature of 35-37°С, at рН from 4 to 7,5. After 48 hours of incubation in beef-extract agar, bordetella caused even turbidity with subsequent forming of the deposit and parietal ring. B.bronchiseptica produced tiny colonies in the diameter up to 1-2 mm after 18-48 h. on average and selective media and bigger colonies in the diameter up to 3-4 mm when cultivated long (more than for 48 hours) and on agar media enriched with amino acids, vitamins and enzymes.
After 24-48 hours on beef-extract agar, bordetella produced several phenotypes corresponding to different phase condition of the bordetella. After 18-24 hours of incubation the appearance of tiny shining greyish and grey-white mildly salient damp colonies sized from 1 till 2 mm (pict.3) was registered.

Picture 3 - Growth of reference strain of B.bronchiseptica 22-067 on beef-extract agar after 24 hours
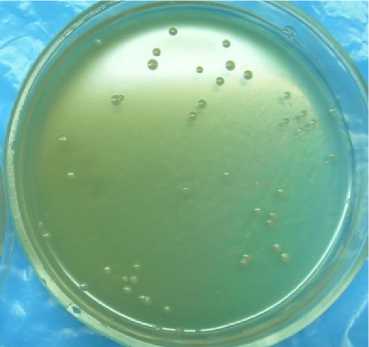
Picture 4 - Growth of reference strain of
B.bronchiseptica 22-067 on beef-extract agar after 48 hours
After 48 hours of incubation the size was from 2 to 3-4 mm, flat colonies with the raised center, oily and easy to remove from the surface appeared (pict. 4). When cultivated for a long time, the colonies of bordetella differed greatly out wardly both in size (some of them grew up to 13 mm), and in character: with even and rough edges, salient and flat, shining and dull, pearl white and grey with a bluish tinge. The types of the colonies corresponded to different phases of the microorganism contamination cycle. On the average the size of the colonies on beef-extract agar was 1,3±0,7 mm after 24 hours of cultivation; 2,5±1,2 mm after
48 hours of cultivation; 7,6±5,7 mm after 72 hours of cultivation. The existence of intermediate variants was also registered (phase II).
For the study of hemolytic activity we observed B.bronchiseptica strains in the field of vision of the microscope during 20-30 minutes. Erythrocytic suspension in dissolving of not more than 2×104 erythrocytes per ml was prepared for the microscopy. The preparation was made according to the «hanging drop» type with the erythrocytic suspension and 24-48 hours agar culture of B.bronchiseptica . The adsorption of bordetella cells on the erythrocytes’ surface and the decolouration of the latter (×1500 magnification) was observe. It was stated that the express method can be applied for the analysis of the strains that have even poor β -hemolysis, and takes up to 30 minutes, while the traditional method takes 48 hours.
The results of our investigation showed that 31,91% bordetella strains had hemolytic activity. 82,98% of the studied strains were active.
The study of the biochemical properties showed that B.bronchiseptica strains do not ferment carbohydrates and polyatomic alcohols. Within the glucose reaction some strains make a small amount of acid (4,26% of the studied strains). All the strains of B.bronchiseptica make indole. The tests of the evidence of cytochrome oxidase, urease, and catalase were positive within all the 47 strains of the agent. Within th edetection of the existence of nitrite reductase enzyme poor positive reaction was noticeable within every strain only after 2 days. Westated that all the studied strains do not have deoxyribonuclease activity, don’t need the X and V growth factors and do not produce gelatinase.
CONCLUSION
The studied strains of B.bronchiseptica had homogeneous morphological, tinctorial, cultural and biochemical properties. The data differed in the indication of the activity, the morphology of the colonies, the fermenting of glucoseand the hemolytic activity that is determined by the phage polymorphism of the agent. These signs can be used after singling out the pure culture for the study of the peculiarities of bordetellosis contamination cycle.
For the identification of B.bronchisеptica we recommend taking into consideration the following tests: anaerobic character, negative colouring by Gram, existence of cytochrome oxidase, catalase, urease, absence of carbohydrate fermentation, polyatomic alcohols, pigment formation of gelatinase, nitrate reduction, nitrate utilization. It should be taken into consideration that separate phenotypical signs have similar peculiarities within a great number of bacterial species, that is why the methodology of microbiological identification must be based on using a set of tests, the combination of which makes the tool of the identification.
According to the data derived, a complex of microbiological tests was selected for typing bacteria B.bronchisеptica that makes it possible to claim about the presence of the required agent with a great deal of certainty. The results of the study can be used for working out schemes of bacteriological identification of the agent of animal bordetellosis.
Список литературы Selection of the complex of microbiological tests for Bordetella bronchiseptica typing
- Labinsakya A.S. Mikrobiologiya s Techikoy Mikrobiologitcheskih Issledovanyi/A.S. Labinskaya, 1978, 394 pp
- Medytsynskiye Laboratornye Technologii/V.G. Vladymirov [at al] -S.Pb.: Intermedica, 2002. -V.2. P. 319 -384
- Metodytcheskye Ukazanya po Opredeleniyu Tchuvstvitelnosty k Antibiotikam Vozbudyteley Infektsionnyh Bolyezney Selskohozyaistvennyh Zhivotnyh. M., 1981
- Mikrobiologitcheskaya Diagnostyka Bakterialnyh Bolyezney Zhivotnyh/D.I. Skorodumov [at al]//M.: Izograph, 2005. -656 pp
- Shulyak B.F. Rukovodstvopo Bakterialnym Infektsyam Sobak. Gramotrytsatelnye Bakterii // B.F. Shulyak //M.: OLITA, 2003. – V.2. – 608 pp
- Bemis D.A. Bacteriological variation among B.bronchisеptica isolates from dogs and other species/D.A. Bemis, H.A. Greisen, M.J.G. Appel//J. Clin. Microbiol. -1977. -V.5. -P.471 -480


