Семафорин SEMA4D в иммунной системе
Автор: Куклина Е.М., Валиева Ю.В.
Журнал: Вестник Пермского университета. Серия: Биология @vestnik-psu-bio
Рубрика: Медико-биологические науки
Статья в выпуске: 3, 2018 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Семафорин IV класса Sema4D, подобно другим членам семейства семафоринов, играет ключевую роль в процессах аксонального наведения в ходе роста нейронов. Однако его эффекты в организме не ограничиваются регуляцией нейрогенеза - Sema4D широко представлен также в иммунной системе и контролирует различные формы иммунного ответа. В настоящей работе представлен детальный анализ иммунорегуляторных эффектов Sema4D in vitro и in vivo, с особым акцентом на рецепторах для семафорина в иммунной системе и механизмах реализации Sema4D-зависимых эффектов в иммунных клетках. Актуальность работы диктуется тем, что данный семафорин рассматривается в настоящее время как перспективная терапевтическая мишень в лечении целого ряда заболеваний, и применение такой терапии требует четкого понимания роли Sema4D в контроле иммунитета.
Лимфоциты, моноциты, дендритные клетки, иммунный ответ
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/147227037
IDR: 147227037 | УДК: 612.018
Текст научной статьи Семафорин SEMA4D в иммунной системе
Семафорины – это семейство мембранных и секретируемых белков, которые первоначально были идентифицированы в нервной системе как сигнальные молекулы, участвующие в процессах аксонального наведения в ходе роста нейронов [Kolodkin, Matthes, Goodman, 1993; Semaphorin …, 1999]. Будучи преимущественно репульсивными факторами, эти молекулы по системе сигнализации подобны семафору, что и определило название семейства.
В отличие от других семафоринов, Sema4D впервые был описан в иммунной системе – как трансмембранная молекула, экспрессируемая Т-лимфоцитами [Bougeret et al., 1992]. Именно с лимфоцитарным «происхождением» связано его первоначальное обозначение – CD100 (CD (clasters of differentiation) – мембранные маркеры лейкоцитов). В 1999 г., после клонирования гена CD100, этот белок был отнесен к семейству семафоринов
IV класса и переименован в Sema4D [Semaphorin …, 1999].
Эффекты данного семафорина в иммунной системе наиболее активно изучались в начале 2010-х гг. и показали, что Sema4D участвует в ключевых событиях адаптивного иммунного ответа – в антигенной активации В-лимфоцитов [Kumanogoh et al., 2000, 2005], в созревании дендритных клеток и в процессах примирования Т-лимфоцитов [Kumanogoh et al., 2002], реализуя свои эффекты через специфический рецептор – CD72 [Ku-manogoh, Kikutani, 2001]. При этом, согласно принятым представлениям, основным источником Sema4D в иммунной системе являются Т-лимфоциты, основными мишенями для семафори-на служат клетки, экспрессирующие CD72, в первую очередь, В-лимфоциты, моноциты и дендритные клетки, а основным механизмом реализации иммунорегуляторных эффектов семафорина является Sema4D/CD72-сигнализация. Однако в настоящее время имеются серьезные причины вер-
нуться к этому вопросу на новом уровне: ряд данных, как новых, так и давно известных, но остававшихся за рамками имеющихся обзоров, указывает на необходимость пересмотра роли Sema4D в иммунорегуляции: выявлены новые рецепторы для Sema4D в иммунной системе [Granziero et al., 2003; Chabbert-de Ponnat et al., 2005], а также способность самого Sema4D выступать в качестве не только лиганда, но и рецептора, проводя сигнал в клетку, на которой экспрессирован [Witherden et al., 2012; Zhang et al., 2013], что поднимает вопрос о новых механизмах реализации Sema4D-зависимых эффектов. Именно на этих аспектах сделан акцент в настоящем обзоре. Особая актуальность его диктуется перспективой использования терапевтических подходов, основанных на регуляции Sema4D в организме [He et al., 2014; Evans et al., 2015]: применение такой терапии требует как можно более полного представления о возможных проявлениях активности семафорина.
Характеристика Sema4D и Sema4D-специфичных рецепторов
Sema4D (CD100) – трансмембранный белок размером 150 kDa, принадлежащий IV классу се-мафоринов. Подобно другим семафоринам, он имеет в своем экстраклеточном регионе Sema-домен, представляющий собой 7-лопастную β-пропеллерную структуру [Love et al., 2003]. У мышей и у человека Sema4D может находиться как в мембран-связанной, так и в растворимой форме. Растворимый Sema4D (soluble Sema4D, sSema4D) имеет размер 120 kDa и образуется за счет протеолитического отщепления, сохраняя при этом функции своего мембранного аналога [Wang et al., 2001; Elhabazi et al., 2001]. Отщепление Sema4D от мембраны происходит в виде димера размером 240 kDa и осуществляется матриксными металлопротеиназами [Elhabazi et al., 2001].
Эффекты Sema4D, согласно традиционным представлениям, реализуются в различных тканях через разные типы рецепторов: в неиммунных тканях – через высокоаффинный плексин В1 ( K d = ~1x10-9 M), а в иммунных – через низкоаффинный CD72 ( K d = 3x10-7 M) [Tamagnone et al., 1999; Kumanogoh et al., 2000; Kumanogoh, Kikutani, 2001]. Кроме того, ряд данных свидетельствует о том, что Sema4D способен связываться не только с плексином В1, но и с двумя другими плексинами В-класса, В2 и В3 [Masuda et al., 2004; Witherden et al., 2012].
Плексин В1 представляет собой большую трансмембранную молекулу, которая, как и сема-форин, имеет в своем экстраклеточном регионе Sema-домен, причем взаимодействие плексина с семафорином предполагает связывание их Sema-доменов [Janssen et al., 2010]. Основная роль се- мафорин/плексин-зависимой сигнализации в различных клетках – реорганизация цитоскелета, которая реализуется главным образом за счет регуляции активности малых ГТФаз семейств Ras и Rho. Второй рецептор для Sema4D, CD72 является членом семейства лектинов и экспрессируется преимущественно в иммунной системе [Tutt Landolfi, Scollay, Parnes, 1997; Kumanogoh et al., 2000, 2002]. Цитоплазматический домен CD72 содержит два иммунорецепторных тирозиносновных ингибиторных мотива (immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motifs, ITIM), ассоциированных с фосфатазой SHP1 [Adachi et al., 1998], что определяет преимущественно негативную роль CD72-зависимого сигнала в активации клеток [Kumanogoh et al., 2000].
Кроме того, цитоплазматический домен самого Sema4D содержит консенсусные сайты для серинового фосфорилирования [Elhabazi et al., 1997], что определяет способность данного семафорина выступать не только в качестве лиганда, но и как рецептор, проводя сигнал в клетку, на которой экспрессирован. К тому же, Sema4D ассоциирован с тирозиновой фосфатазой CD45, которая в иммунных клетках также может участвовать в передаче Sema4D-зависимого сигнала в клетку [Herold et al., 1996].
Важно отметить, что некоторые данные указывают на экспрессию плексиновых рецепторов иммунными клетками [Granziero et al., 2003; Chabbert-de Ponnat et al., 2005], что свидетельствует о необходимости пересмотра принятых на сегодняшний день представлений об опосредовании эффектов семафорина в иммунных и неиммунных клетках разными рецепторами, CD72 и плексином В1, соответственно.
Экспрессия Sema4D в иммунной системе
Sema4D широко представлен в иммунной системе (рисунок). Он конститутивно экспрессируется Т-лимфоцитами [Kumanogoh et al., 2000] и, в меньшей степени, В-клетками [Granziero et al., 2003], естественными киллерами (Natural Killer cells, NK) [Mizrahi et al., 2007] и эозинофилами [Hiraguchi et al., 2015]. В незначительных количествах Sema4D присутствует также на мембране дендритных клеток [Kumanogoh et al., 2002]. Активация лимфоцитов сопровождается повышением уровня экспрессии Sema4D на клеточной мембране [Bougeret et al., 1992; Witherden et al., 2012], а также его протеолитическим отщеплением, с образованием растворимой формы, sSema4D [Elhabazi et al., 2001; Wang et al., 2001]. Данный эффект регистрируется как in vitro, в культуральных супернатантах активированных лимфоцитов, так и in vivo, в сыворотке животных, иммунизированных Т- зависимыми антигенами [Wang et al., 2001]. При этом растворимый Sema4D сохраняет функции мембранного аналога [Wang et al., 2001].
Эффекты Sema4D в иммунной системе
Sema4D непосредственно вовлечен в иммунные реакции организма. У животных, дефицитных по Sema4D (Sema4D(CD100)-/--), снижен В-клеточный ответ на стимуляцию антителами к CD40 и липополисахаридом in vitro , а также гуморальный иммунный ответ на Т-зависимые антигены in vivo [Shi et al., 2000]. И, напротив, клетки, трансфеци-рованные Sema4D и стабильно экспрессирующие его на мембране, или растворимый рекомбинантный Sema4D, индуцируют агрегацию и выживание В-лимфоцитов [Hall et al., 1996], а также усиливают CD40-индуцированную пролиферацию В-клеток и продукцию иммуноглобулинов [Kumanogoh et al., 2000; Wang et al., 2001; Ishida et al., 2003].
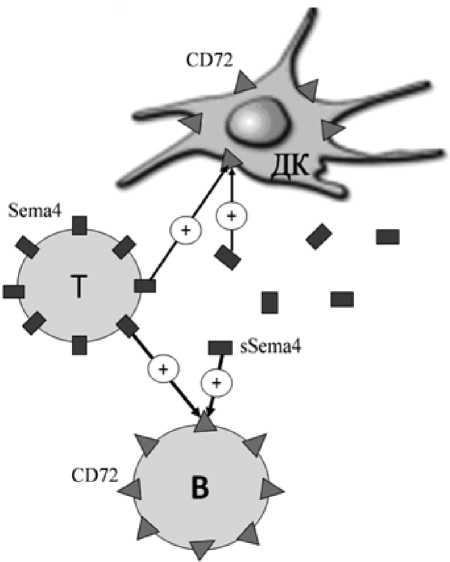
Потенциальные механизмы Sema4D-зависимой регуляции функций иммунных клеток:
Т – Т-лимфоцит, В – В-лимфоцит, ДК – дендритная клетка
Наряду с этим, Sema4D участвует в созревании и функционировании дендритных клеток: растворимый рекомбинантный Sema4D усиливает СD40-зависимую активацию этих клеток in vitro, что регистрируется по повышению экспрессии на мембране костимулирующих CD40 и CD80, а также продукции IL-12 [Kumanogoh et al., 2002; Ishida et al., 2003]. А в экспериментах in vivo показано, что у Sema4D-/--мышей существенно подавлены про- цессы примирования Т-лимфоцитов, которые напрямую зависят от активности дендритных клеток [Shi et al., 2000; Kumanogoh et al., 2002]. Кроме того, семафорин усиливает цитотоксическую активность NK-клеток [Mizrahi et al., 2007].
Механизмы реализации эффектовSema4D в иммунной системе
Основной рецептор для Sema4D, описанный в иммунной системе, – CD72, экспрессируемый преимущественно В-лимфоцитами [Kumanogoh et al., 2000, 2005]. Он ассоциирован с CD79a, компонентом В-клеточного рецепторного комплекса, и является негативным регулятором В-лимфоцитов: у мышей, дефицитных по СD72, В-клетки демонстрируют повышенную пролиферацию в ответ на различные стимулы [Pan, Baumgarth, Parnes, 1999]. Негативная роль CD72-зависимого сигнала в В-клеточной активации связана с наличием в его цитоплазматическом домене двух иммунорецеп-торных тирозин-основных ингибиторных мотивов, ITIM, ассоциированных с фосфатазой SHP1 [Adachi et al., 1998; Kumanogoh et al., 2000]. Связывание Sema4D с СD72 блокирует ассоциацию последнего с В-клеточным рецептором (B cell receptor, BCR), вызывает дефосфорилирование его по тирозину и диссоциацию SHP1 от цитоплазматического региона CD72, давая возможность В-клетке активироваться в ответ на антиген [Kumanogoh et al., 2000, 2005; Ishida et al., 2003]. Таким образом, связывание Sema4D «выключает» ингибиторный сигнал с СD72. Помимо В-лимфоцитов, СD72 экспрессируется «профессиональными» антигенпрезентирующими клетками, такими как макрофаги и дендритные клетки [Tutt Landolfi, Scollay, Parnes, 1997; Kumanogoh et al., 2002], и участвует в регуляции функций этих клеток. Так, агонисты CD72 имитируют эффекты sSema4D в отношении экспрессии дендритными клетками костимулирующих молекул CD40 и CD80, а также продукции IL-12, указывая на CD72-зависимые механизмы реализации этих эффектов [Ishida et al., 2003]. Синтез моноцитами провоспалительных цитокинов IL-6, IL-8 и TNFα, индуцируемый sSema4D, также воспроизводится агонистами CD72 [Ishida et al., 2003].
Что касается высокоаффинного рецептора для Sema4D, плексина В1, которому традиционно приписывается реализация эффектов семафорина в неиммунных тканях, есть целый ряд работ, демонстрирующих его присутствие и в иммунной системе. Экспрессия плексина В1 выявлена на фолликулярных дендритных клетках [Granziero et al., 2003], на незрелых дендритных клетках моноцитарного происхождения [Chabbert-de Ponnat et al., 2005], а также на части активированных Т-лимфоцитов [Granziero et al., 2003]. Наряду с плексином В1, в иммунной системе выявлена экспрессия и плексина В2 – на макрофагах и дендритных клетках [Roney et al., 2011].
Важной особенностью Sema4D является тот факт, что он не только использует специфические рецепторы для реализации своих эффектов, но и сам может выступать в качестве рецептора, проводя сигнал в клетку, на которой экспрессирован [Granziero et al., 2003; Witherden et al., 2012; Zhang et al., 2013]. Обеспечивается такая способность как минимум двумя факторами: во-первых, цитоплазматический домен семафорина содержит консенсусные сайты для серинового фосфорилирования [Elhabazi et al., 1997]; во-вторых, у Т-лимфоцитов Sema4D ассоциирован с тирозиновой фосфатазой CD45, которая также может участвовать в передаче семафорин-зависимого сигнала в клетку [Herold et al., 1996].
Механизмы сигнальной трансдукции, инициируемые Sema4D в иммунных клетках, изучены слабо и фрагментарно. Показано, что в В-лимфоцитах семафорин-зависимые сигналы участвуют в фосфорилировании по тирозину целого ряда факторов – CD79b, Syk, BLNK, FcRIIB и ERK-2: у Sema4D-/--мышей уровень фосфорилирования этих молекул в ответ на стимуляцию через В-клеточный антигенный рецептор существенно снижен, как и мобилизация внутриклеточного Са2+ [Kumanogoh et al., 2005], однако какими рецепторами опосредуются эти эффекты Sema4D, CD72 или плексином В1, точно сказать нельзя.
Заключение
В целом, эффекты Sema4D в иммунной системе отличаются высоким разнообразием, и определяется это, по-видимому, целым рядом причин. Во-первых, Sema4D экспрессируется практически всеми основными эффекторами как адаптивного, так и врожденного иммунитета. Во-вторых, многие клетки иммунной системы одновременно экспрессируют два рецептора для семафорина с разной аффинностью, CD72 и плексин В1, а также могут использовать сам Sema4D, представленный на мембране, в качестве рецептора. Как следствие, эффекты Sema4D в таких клетках будут напрямую зависеть от концентрации семафорина. В-третьих, мембранный Sema4D и основной семафориновый рецептор в иммунной системе, CD72, ассоциированы с молекулами, участвующими в антиген-зависимой активации лимфоцитов, и непосредственно контролируют активационные сигналы. Следует отметить, что, несмотря на интенсивное изучение роли Sema4D в иммунной системе, внутриклеточные механизмы реализации действия се-мафорина в иммуноцитах на сегодняшний день почти не изучены, и многие эффекты Sema4D в этих клетках сложно объяснить и, тем более, спрогнозировать.
Работа выполнена в рамках государственного задания, номер госрегистрации темы: 01201353248.
Список литературы Семафорин SEMA4D в иммунной системе
- Adachi T. et al. The B cell surface protein CD72 recruits the tyrosine phosphatase SHP-1 upon tyro-sine phosphorylation // Journal of Immunology. 1998. Vol. 160. P. 4662-4665.
- Bougeret C. et al. Increased surface expression of a newly identified 150-kDa dimer early after human T lymphocyte activation // Journal of Immunology. 1992. Vol. 148. P. 318-323.
- Chabbert-de Ponnat I. et al. Soluble CD100 functions on human monocytes and immature dendritic cells require plexin C1 and plexin B1, respectively // International Immunology. 2005. Vol. 17. P. 439-447.
- Elhabazi A. et al. The human semaphorin-like leukocyte cell surface molecule CD100 associates with a serine kinase activity // Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1997. Vol. 272. P. 23515-23520.
- Elhabazi A. et al. Biological activity of soluble CD100. I. The extracellular region of CD100 is released from the surface of T lymphocytes by regulated proteolysis // Journal of Immunology. 2001. Vol. 16. P. 4341-4347.
- Evans E. et al. Antibody Blockade of Semaphorin 4D Promotes Immune Infiltration into Tumor and Enhances Response to Other Immunomodulatory Therapies // Cancer Immunology. 2015. Vol. 3. P. 689-701.
- Granziero L. et al. CD100/Plexin-B1 interactions sustain proliferation and survival of normal and leu-kemic CD5 B lymphocytes // Blood. 2003. Vol. 101 (5). P. 1962-1969.
- Hall K.T. et al. Human CD100, a novel leukocyte semaphorin that promotes B-cell aggregation and differentiation // Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 1996. Vol. 93 (21). P. 11780-11785.
- He Y. et al. CD100 up-regulation induced by inter-feron-a on B cells is related to hepatitis C virus infection // PLoS One. 2014. Vol. 9. P. 1-15.
- Herold C. et al. CD100 is associated with CD45 at the surface of human T lymphocytes. Role in T cell homotypic adhesion // Journal of Immunology. 1996. Vol. 157. P. 5262-5268.
- Hiraguchi Y. et al. Semaphorin 4D is expressed con-stitutively by human eosinophils // Allergology International. 2015. Vol. 64. P. S77eS79.
- Janssen B.J. et al. Structural basis of semaphorin-plexin signaling // Nature. 2010. Vol. 467. P. 1118-1122.
- Ishida I. et al. Involvement of CD100, a lymphocyte semaphorin, in the activation of the human immune system via CD72: implications for the regulation of immune and inflammatory responses // International Immunology. 2003. Vol. 15. P. 1027-1034.
- Kolodkin A.L., Matthes D.J., Goodman C.S. The semaphorin genes encode a family of transmem-brane and secreted growth cone guidance molecules // Cell. 1993. Vol. 75. P. 1389-1399.
- Kumanogoh A. et al. Identification of CD72 as a lymphocyte receptor for the class IV semaphorin CD100: a novel mechanism for regulating B cell signaling // Immunity. 2000. Vol. 13. P. 621-631.
- Kumanogoh A., Kikutani H. The CD100-CD72 interaction: a novel mechanism of immune regulation // Trends in Immunology. 2001. Vol. 22 (12). P. 670-676.
- Kumanogoh A. et al. Requirement for the lymphocyte semaphorin, CD100, in the induction of antigen-specific T cells and the maturation of dendritic cells // Journal of Immunology. 2002. Vol. 169. P. 1175-1181.
- Kumanogoh A. et al. Requirement for CD100-CD72 interactions in fine-tuning of B-cell antigen receptor signaling and homeostatic maintenance of the B-cell compartment // International Immunology. 2005. Vol. 17. P. 1277-1282.
- Love C.A. et al. The ligand-binding face of the sema-phorins revealed by the high-resolution crystal structure of SEMA4D // Nature Structural Biology. 2003. Vol. 10. P. 843-848.
- Masuda K. et al. Sema4D stimulates axonal outgrowth of embryonic DRG sensory neurons // Cenes to Cells. 2004. Vol. 9. P. 321-829.
- Mizrahi S. et al. CD100 on NK cells enhance IFNgamma secretion and killing of target cells expressing CD72 //PLoS One. 2007. Vol. 2 (9). P. e818.
- Pan C., Baumgarth N., Parnes J. R. CD72-deficient mice reveal nonredundant roles of CD72 in B cell development and activation // Immunity. 1999. Vol. 11. P. 495-506.
- Semaphorin Nomenclature Committee. Unified nomenclature for the semaphorins/collapsins // Cell. 1999. Vol. 97. P. 551-552.
- Roney K.E. et al. Plexin-B2 negatively regulates macrophage motility, Rac, and Cdc42 activation // PLoS One. 2011. Vol. 6 (9). P. e24795.
- Shi W. et al. The class IV semaphorin CD100 plays nonredundant roles in the immune system: defective B and T cell activation in CD100-deficient mice // Immunity. 2000. Vol. 13. P. 633-642.
- Tamagnone L. et al. Plexins are a large family of receptors for transmembrane, secreted, and GPI-anchored semaphorins in vertebrates // Cell. 1999. Vol. 99. P. 71-80.
- Tutt Landolfi M., Scollay R., Parnes R. Specific de-methylation of the CD4 gene during CD4 T lymphocyte differentiation // Molecular Immunology. 1997. Vol. 34. P. 53-61.
- Wang X. et al. Functional soluble CD100/Sema4D released from activated lymphocytes: possible role in normal and pathologic immune responses // Blood. 2001. Vol. 97. P. 3498-3504.
- Witherden A. et al. The CD100 receptor interacts with its plexin B2 ligand to regulate epidermal y5 T cell function // Immunity. 2012. Vol. 37 (2). P. 314-325.
- Zhang Y. et al. Sema 4D/CD100-plexin B is a multifunctional counter-receptor // Cellular & Molecular Immunology. 2013. Vol. 10 (2). P. 97-98.


