Шпунты из ультракомпозитных материалов в гидротехническом строительстве
Автор: Кокорева Ксения Александровна, Беляев Николай Дмитриевич, Ялышев Артем Илларионович
Журнал: Строительство уникальных зданий и сооружений @unistroy
Статья в выпуске: 4 (31), 2015 года.
Бесплатный доступ
В статье представлен сравнительный анализ металлических и композитных шпунтов с обзором их технических характеристик.Рассмотрены два одинаковых по конструктивной схеме, но различных по составу материалов способа реконструкции участка берегоукрепления. Конструктивная схема представляет собой возведение новой шпунтовой стенки и шапочного бруса в габаритах прилегающих участков существующего сооружения. В первом случае рассматривался вариант возведения новой металлической шпунтовой стенки с бетонным шапочным брусом, во втором - рассматривался вариант применения современного отечественного композитного шпунта ШК-150.В работе обосновывается возможность применения современных ультракомпозитных материалов, полученных с использованием пултрузионных технологий, в гидротехническом строительстве. Применение результатов, относящихся к расчетному обоснованию использования композитных материалов, позволит развить в дальнейшем методологию применения композита в гидротехническом строительстве.
Ультракомпозитные шпунты, металлические шпунты, коррозия, пултрузионные технологии, гидротехническое строительство
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/14322233
IDR: 14322233
Текст научной статьи Шпунты из ультракомпозитных материалов в гидротехническом строительстве
Corrosion of metal is one of the main reasons for the decrease in the reliability and safety of structures at marine and river berths [1-13]. Fight against its influence has primary value and can be considered as the independent task and the main source of saving resources. This means that you need to maintain the already constructed buildings, using modern methods of protection and, moreover, the construction of new structures using modern materials – a little corrosive or not subject to corrosion [14-18].
In actual use moorings are exposed not only to the different loads (static, dynamic, cyclic) and temperatures, but also aggressive environments. Besides, in case of the long use of constructions, the aging processes leading to the considerable change of mechanical properties of steel are activated. Frequently these factors may act together and in various combinations, significantly reducing the load carrying capacity and reducing the durability and safety of berths [1, 19, 20].
Causes of corrosion damage of metal in the construction of berthing facilities include [20, 21]:
-
- violation of the rules of production of works for the protection against corrosion;
-
- excessive long periods between manufacture and implementation of full protection after installation;
-
- non-compliance with the modes of operation of electrochemical protection systems;
-
- untimely recovery of protective coatings during operation of structures.
Metal sheet piling
In case of manufacture of sea and river moorings different alloys are applied, for the sheet pilling and anchor rods low-alloy steel is most often used. The sheet piling Larsen 4 according to the characteristics is one of the most high-quality sheet pilings, made in the Russian Federation, and also most often applied in domestic construction practice. Manufacture of sheet piling is carried out at the Nizhniy Tagil metallurgical plant [22].
The sheet piling presents in the form of a long (up to 22 m) and narrow (420 mm) metal profiles trough type. Manufacture of sheet piling is carried out by hot rolling according to TS 14-2-879-89 of steel grade STK.
The main advantage of metal sheet piling Larsen 4 is its high load-carrying capacity and the prevalence of the domestic market. The disadvantages include a high weight and the need for corrosion activities which entails more expensive construction. The cross section of the sheet piling is shown in Fig. 1.
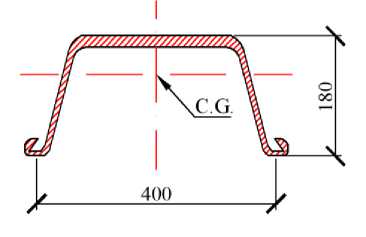
Figure 1. The cross section of the sheet piling Larsen 4
Technical characteristics of the sheet piling Larsen 4 are presented in table 1.
Table 1. Technical characteristics of the sheet piling Larsen 4 [22]
|
Name |
Measurement units |
One pile section |
1 linear meter of the wall |
|
Technical specification |
TS 14-2-879-89 |
||
|
Cross-sectional area ( F ) |
sm2 |
94.2 |
235.5 |
|
The weight of one meter ( G ) |
kg |
74.0 |
185.0 |
|
Moment of inertia ( J ) |
sm4 |
5234 |
39600 |
|
Moment of resistance ( W ) |
sm3 |
405 |
2200 |
|
Bending stiffness ( EJ ) |
kN∙м2 |
– |
83160 |
|
The calculated resistance of sheet piling ( R ) |
MPa |
230 |
230 |
|
The maximum bending moment ( M max ) |
kN∙м |
93 |
506 |
Ultra composite sheet piling
At the beginning of 2012 specialists of the Russian company JSC "Pultruded technology", based on the latest high-tech developments and the global composites industry, with the support of the "Skolkovo", developed and patented absolutely new series of sheet piles from the ultra composite material, called ShK-150 [23].
JSC "Pultruded technology" is one of the pioneers in the field of pultrusion glass composites – the industry which now is almost absent in the Russian Federation. Previously widespread use fibreglasses restrained mainly lack of industrial technology, which allows establish production of mass consumption. Creation of the pultrusion solved this problem: an issue glass composite profile of various configurations and sizes with the required accuracy was not only possible, but also economically expedient. Currently pultrusion is one of the fastest growing industries in the production of composite materials industry. The popularity of the technology is caused by its efficiency and high degree of automation. Now composite sheet pilings of ShK-150 are made in the Moscow region according to TS 2247-001-92530792-2012. It should be noted that this material has the necessary documentation to carry out its application: certified for compliance with normative documents; expert opinion on the compliance of the material common sanitary and epidemiological and hygienic requirements; certificate of technical qualification in construction; technical certificate GOSSTROY RF and test report. Sheet piles ShK-150 has several advantages over steel sheet pilings:
-
- less weight of the material;
-
- corrosion resistance;
-
- durability;
-
- lower cost (average market price of the sheet piling ShK-150 is approximately twice less than the cost of the metal sheet piling Larsen 4).
Composite sheet piling is created on the basis of polyester and composite resins, so that it has a carrying capacity that exceeds metallic analogs and the more PVC sheet pilings, which with all its advantages have low bearing capacity.
From the point of view of the geological situation, ultra composite sheet pilings can be used in noncohesive soils: consisting primarily of gravel, sand, sandy silt, as well as in cohesive: dense soil, consisting of clay and silt. At the end of the construction work we can see strong and reliable construction – an impressive ultra composite wall.
The sheet piling, which is made from ultra composite material has a high mechanical resistance to abrasion, cracking and scratching. It isn't subject to corrosion, rotting and influence of sea water and it doesn't require maintenance. It is flameproof, steady against seasonal difference of temperatures (bearing capacity of a wall makes 200 kNm/lm in case of temperature condition from minus 60ºC to plus 50ºC without causing permanent deformations). The ability of ultra composite material to withstand corrosive environments is significantly higher than that of steel and concrete. Warranty lifetime piles of this material are not limited.
Connections of the sheet piling take place on the side edge that protects the joint from the main loads experienced by the structure, as the area of the main load falls on the central part of pile section.
Technology of composite sheet pile-driving is quite simple and does not differ from working with steel sheet pilings. Piling of sheet piling ShK-150 can be carried out with the help of the vibratory pile driver, copra, as well as 165 Кокорева K.A., Беляев Н.Д., Ялышев А.И. Шпунты из ультракомпозитных материалов в гидротехническом строительстве. / Kokoreva K.A., Belyaev N.D., Yaleshev A.I. Sheet pilings from ultra composite in hydraulic engineering. © at a shallow depth of immersion, with the help of an excavator bucket, by forcing into the ground. You can also perform piling of sheet piling with specialized boats or pontoons.
Technical specifications of the composite sheet piling ShK-150 are presented in Tab. 2. Cross-section of the sheet piling ShK-150 is shown in Fig. 2.
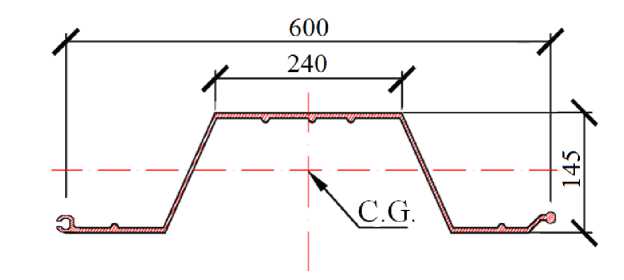
Figure 2. Cross-section of the composite sheet piling ShK-150
Table 2. Technical specifications of the sheet piling ShK-150 [24]
|
Name |
Measurement units |
One pile section |
1 linear meter of the wall |
|
Technical specification |
TS 2247-001-92530792-2012 |
||
|
Cross-sectional area ( F ) |
sm2 |
48.3 |
84.5 |
|
The weight of one meter ( G ) |
kg |
10.4 |
17.3 |
|
Moment of inertia ( J ) |
sm4 |
1684.1 |
2660.2 |
|
Moment of resistance ( W ) |
sm3 |
210.67 |
332.6 |
|
Bending stiffness ( EJ ) |
kN∙м2 |
4378.7 |
6919.6 |
|
The maximum bending moment ( M max ) |
kN∙м |
237.1 |
374.5 |
According to information provided by the manufacturer, to the present time composite sheet piling ShK-150 was used in a number of capital construction and reconstruction on the territory of the Russian Federation and CIS countries. As an example of the object, construction of a pier for mooring large motor yachts in Baku on the Caspian Sea are mentioned [24]. Length facilities – 800.0 m; driving depth – from 4.0 to 13.5 m; soil – sand / clay / shell rock; installation method – vibratory pile driver.
Results and discussion
In this work within the project of repair of bank protection in the form of anchored bulwark with an adjacent slope was estimated comparison of two options with the same design concept, but different range of materials. Constructive scheme implies the construction of a new sheet pile wall in front of the cordon line reconstructed section of coast protection, nodding to the construction of capping beam as construction type and in marks of an adjacent section (figure 3).
The first option involves the construction of shore protection reconstruction sheet pile wall of a metal sheet piling Larsen 4, the second – sheet pile wall from the composite sheet piling ShK-150.
Static analysis and calculation of stability on the circular cylindrical surfaces (CCS) are made to determine the minimum driving of the sheet piles for the two design concepts of the bulwark, which is not anchored.
The calculation is made in the CAD software package – "Hydraulic Engineering", developed by JSC "Lenmorniiproekt." The program complex has a certificate of conformity № ROSS RU. SP15.N00016.
Construction of Unique Buildings and Structures, 2015, №4 (31)
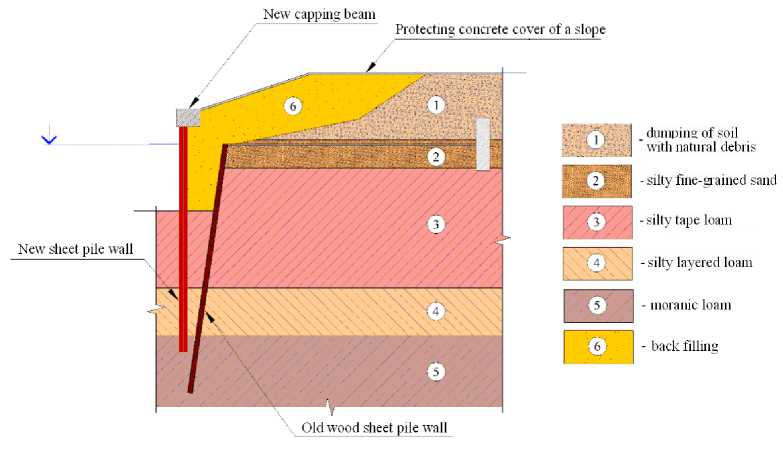
Figure 3. Constructive scheme of reconstructed site of bank protection
During the work in this program complex of two computational modules were used:
-
- the calculation module for CCS algorithm, which is built on the following guiding and reference documentation [25, 26];
Module static analysis algorithm, which is built on the following guiding and reference documentation [2729].
It is necessary to notice that the CAD software package – "Hydraulic Engineering" by the production of static analysis, unlike calculation of stability according to the CCS can not take into account the slope of the construction, that is why this part of the structure has been defined as equivalent to the load acting on the horizontal plane passing through the mark of the top of the cap piece at 1 meter length of the structure. Slope was replaced by an equivalent load in both calculations (static stability in the CCS) for uniformity of algorithm of calculation and results.
In conducting static calculations both options have shown good results in strength and stability. Results of the calculations have demonstrated that both types of sheet-pilings can be used for reconstruction of shore protection structures, but for composite sheet piling is required device anchor system, unlike metal, due to lower stiffness indicators. Taking into account the economic feasibility of the technology and production work for the reconstruction of the final version of the device was made of metal sheet piling, as the innovative anchoring system requires the dismantling of existing anchors that complicate the process of the construction work and will lead to significant financial losses.
Despite this, the work demonstrates the possibility of the use of modern ultra composite materials obtained with the use of pultrusion technologies in hydraulic engineering. Application of the results of current justification of the use of composite materials will develop the methodology for applying composite materials in hydraulic engineering. This sheet piling in comparison with the metal has many advantages such as lower cost (double superiority), less weight, good performance on the load-bearing capacity (comparable to metal analogs). Besides that, there is no difference in work between composite and metal sheet piling (the standard set of the equipment is required).
Resume
It is worth mentioning that the development of modern technologies in the production of building materials will help to solve many problems and first of all to reduce construction cost [30-34]. In Russia there are many structures similar to those considered in this work, in which according to the authors, it is possible to use composite sheet pilings. The Russian construction industry has to be changed significantly in the active expansion of composite materials application to the development of their use methods in hydrotechnical objects [35].
Список литературы Шпунты из ультракомпозитных материалов в гидротехническом строительстве
- Балашов Б.В., Беляев Н.Д., Михаленко Е.Б., Вилькевич В.В. Анализ проблем, связанных с обследованиями портовых ГТС (на примере глубоководной достроечной набережной)//Известия ВНИИГ им. Б.Е. Веденеева. 2013. Т. 269. № 1. С. 110-117.
- Беляев Н.Д. Причины аварий причальных сооружений. Сборник научных трудов: «Предотвращение аварий зданий и сооружений». Магнитогорск, 2003. С. 34-39.
- Беляев Н.Д., Вилькевич В.В. Экспертиза технического состояния морских гидротехнических сооружений//Гидротехническое строительство. 2007. № 5. С. 37-45.
- Беляев Н.Д., Михаленко Е.Б., Олехнович Я.А., Ялышев А.И. Анализ дефектов причальных и берегоукрепительных сооружений по результатам обследований 2013 г. Материалы НПК c международным участием «XLII Неделя науки СПбГПУ». НОЦ «Возобновляемые виды энергии и установки на их основе». СПб.: Изд-во Политехн. ун-та. 2014. С. 85-88.
- Вилькевич В.В., Вилькевич Е.В., Беляев Н.Д. Особенности оценки состояния причальных сооружений на свайном основании с передней шпунтовой стенкой//Известия ВНИИГ им. Б.Е. Веденеева. 2004. Т. 243. С. 123-130.
- Малеванов К.А., Беляев Н.Д. Характерные повреждения причалов типа «больверк» и мероприятия по их устранению. XXXII Неделя науки СПбГПУ. Ч. I. Материалы межвузовской конференции. СПб.: СПбГПУ, 2004. С. 17-19.
- Малеванов К.А., Шхинек К.Н., Беляев Н.Д. Сравнительный анализ технического состояния морских гидротехнических сооружений за пятилетний период эксплуатации. XXXIV Неделя науки СПбГПУ: Материалы Всероссийской межвузовской НТК. СПб.: Политехн., ун-т, 2006. Ч. I.
- Пучков А.Л., Беляев Н.Д. Основные виды повреждений глубоководной достроечной набережной ОАО «Адмиралтейские верфи». XL Неделя науки СПбГПУ: Материалы международной НПК. Ч. I. СПб.: Изд-во Политехн. ун-та. 2011. С. 16-17.
- Пучков А.Л., Беляев Н.Д. Сопоставление результатов двух обследований глубоководной достроечной набережной ОАО «Адмиралтейские верфи». XLI Неделя науки СПбГПУ: Материалы НПК с международным участием. Ч. I. СПб.: Изд-во Политехн. ун-та. 2012. С. 14-16.
- Wall H., Wadsö L. Corrosion rate measurements in steel sheet pile walls in a marine environment. Lund University Publications. Marine structures. V. 33, 2013. Pp. 21-32
- Osório1 P., Odenbreit C., Vrouwenvelder T. Structural reliability analysis of quay walls with steel sheet piles. PIANC MMX Congress, Liverpool, UK, 2010. 11 pp.
- Accelerated low water corrosion. Report of Working Group 44 of the Maritime navigation commission. International navigation association. 2005. 32 pp.
- Buslov V. Corrosion of Steel Sheet Piles in Port Structures. Journal of Waterway, Port, Coastal and Ocean Engineering, Vol. 109, No. 3, August 1983, pp. 273-295, ( )) DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-950X(1983)109:3(273
- Альхименко А.И., Беляев Н.Д., Фомин Ю.Н. Безопасность морских гидротехнических сооружений. СПб.: Изд-во «Лань», 2003. 288 с.
- Колгушкин А.В., Беляев Н.Д. Инженерные мероприятия по увеличению долговечности сквозных гидротехнических сооружений//Научно-технические ведомости СПбГПУ. 2007. № 49 (1). С. 185-193.
- Колгушкин А.В., Беляев Н.Д. Требования к выбору методов защиты ГТС от коррозии//Речной транспорт (XXI век). 2010. № 3 (45). С. 84-88.
- Bosch C., Billeke M. Improvement of Corrosion Resistance of Sheet Piling In Seawater. Document ID NACE-2014-3891. Corrosion 2014, 9-13 March, San Antonio, Texas, USA, 2014. 13 pp.
- Houyoux C., Alberts D., Heeling A., Benaissa B., De Cristofaro N. EUR 22433 -Steel products and applications for building, construction and industry. Design method for steel structures in marine environment including the corrosion behaviour. Technical steel research series. 2007, 298 pp. ISBN 92-79-03768-4, ISSN 1018-5593.
- Колгушкин А.В., Беляев Н.Д. Об учете коррозии при проектировании сквозных металлических ГТС. Сборник научных трудов «Предотвращение аварий зданий и сооружений». Магнитогорск, 2007. С. 159-168.
- Колгушкин А.В., Беляев Н.Д. Учет неравномерности коррозионного воздействия морской среды при проектировании и строительстве сквозных ГТС на металлическом основании//Гидротехническое строительство. 2008. № 10. С. 19-25.
- Колгушкин А.В., Беляев Н.Д. Влияние природных факторов на скорость коррозии морских ГТС. Сборник научных трудов «Предотвращение аварий зданий и сооружений». Москва, 2009. С. 216-227.
- Васильев А.Г. Пособие проектировщику ГТС. ГТС типа больверк/А. Г. Васильев -Москва 2003. -172 с.
- Илюхин Д.А. Сваи из ультракомпозитного материала -новая эра в строительстве/Д.А. Илюхин//Гидротехника 2(27). -2012. -с. 66 -67.
- Официальный интернет сайт ЗАО «Пултрузионные технологии»: http://www.pultrusion.ru/
- Проблемы проектирования, строительства и эксплуатации береговых сооружений морского транспорта: Сб. науч. тр./Ленморниипроект; . М.: ЦРИА «Морфлот», 1982. 117 с.
- СП 23.13330.2011. Основания гидротехнических сооружений
- РД 31.31.55-93. Руководство по проектированию морских причальных и берегоукрепительных сооружений
- РТМ 31.3016-78. Указания по проектированию больверков с учетом перемещений и деформаций элементов
- Будин А.Я. Тонкие подпорные стенки. Л.: Стройиздат (Ленинградское отделенние), 1974, 192 с.
- Connolly M., King J., Shidaker T., Duncan A. Characterization of Pultruded Polyurethane Composites: Environmental Exposure and Component Assembly Testing. Composites 2006. Convention and Trade Show American Composites Manufacturers Association. October 18-20, 2006. St. Louis, MO USA. Huntsman Polyurethanes, Auburn Hills, USA. MI. 10 pp.
- Connolly M., King J., Shidaker T., Duncan A. Technical Paper. Processing and Characterization of Pultruded Polyurethane Composites. Technical Paper. Huntsman International LLC. 2190 Executive Hills Boulevard, Auburn Hills, MI, USA. 2006, 16 pp.
- Makusheva N.Yu., Kolosova N.B. Comparative analysis of metal reinforcement and fibre-reinforced plastic rebar. Construction of Unique Buildings and Structures, 2014, №10 (25) ISSN 2304-6295. Pp. 60-72.
- Niroumand H. History of composite piles. The second official international conference of International instate for FRP in construction for Asia-Pacific Region. Seoul, Korea, 2009. Pp. 437-450.
- Pando M.A., Ealy C.D., Filz G.M., Lesko J.J., and Hoppe E.J. Laboratory and Field Study of Composite Piles for Bridge Substructures. Report No FHWA-HRT-04-043. Virginia Transportation Research Council. 530 Edgemont Road, Charlottesville, VA 22903. 686 pp.
- Ялышев А.И. Ремонт берегоукрепления на р. Неве с разработкой защиты от размыва. Магистерская диссертация. СПб.: СПбГПУ, 2014. 142 с.


